5 LSMS Reports
This chapter contains procedures for generating, viewing, and printing LSMS reports in a predefined format. It also contains information about the Report Generator, which enables you to create customized LSMS reports.
Introduction
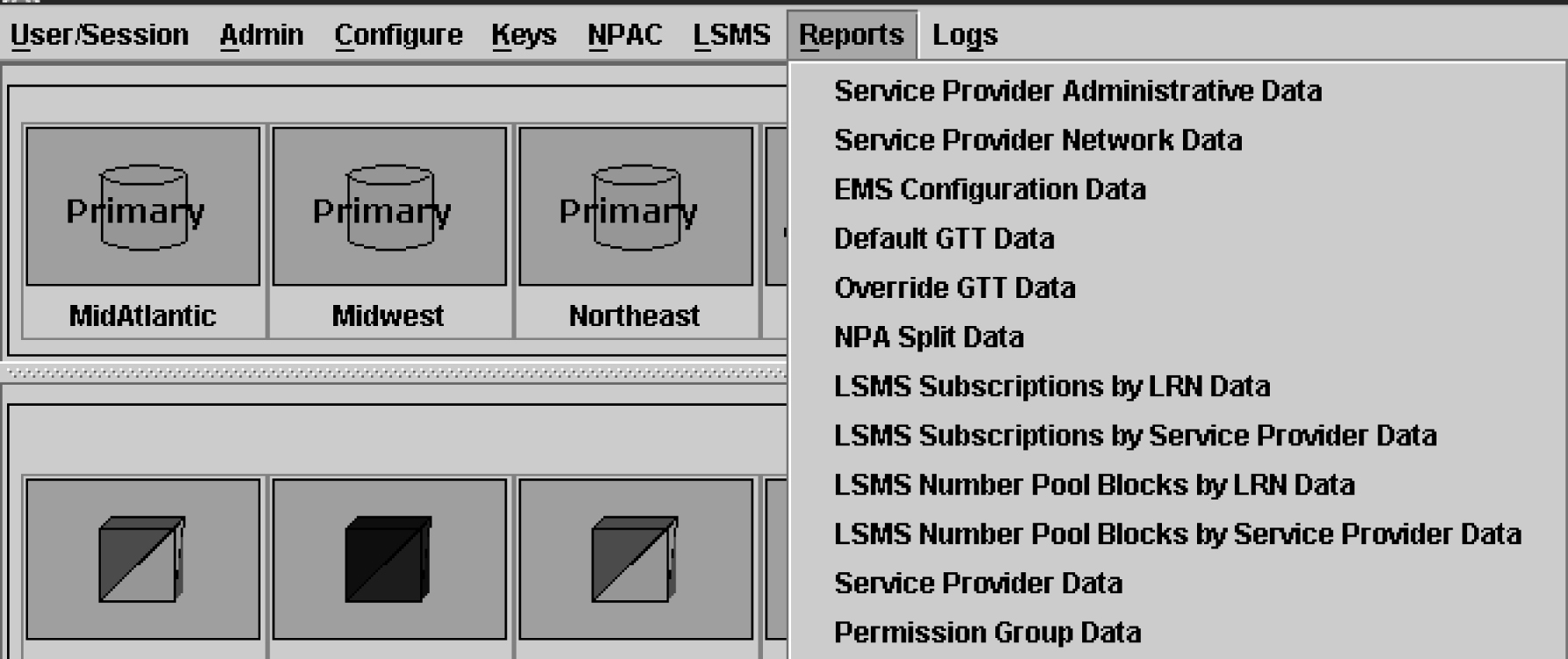
This chapter provides general information about viewing reports in a browser window. It also provides specific, step-by-step procedures for creating, viewing, and deleting the following types of pre-formatted LSMS reports.
Note:
You can generate up to ten reports at a time using the Reports menu item.
-
Service Provider Administrative Data
-
Service Provider Network Data
-
EMS Configuration Data
-
Default GTT Data
-
Override GTT Data
-
NPA Split Data
-
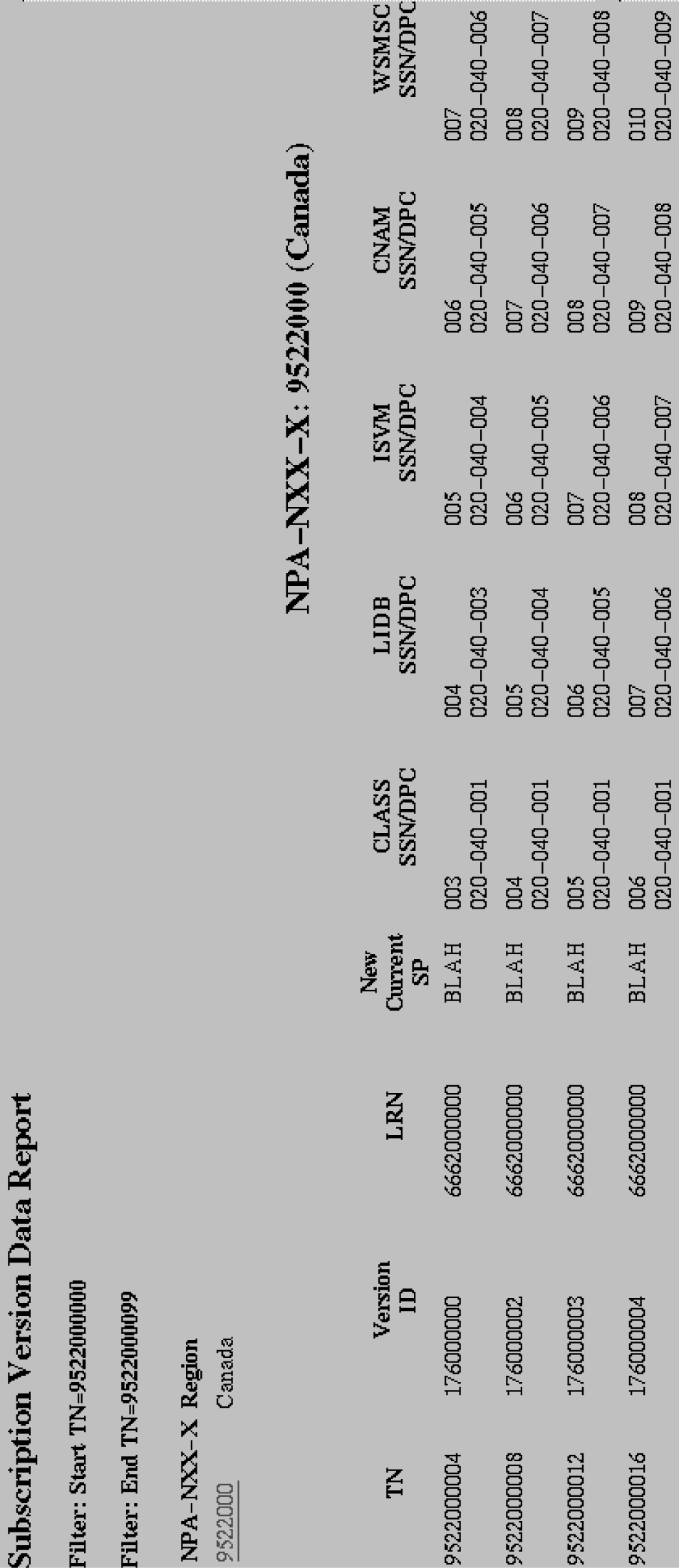
LSMS Subscriptions by LRN Data
-
LSMS Subscriptions by Service Provider Data
-
LSMS Number Pool Blocks by LRN Data
-
LSMS Number Pool Blocks by Service Provider Data
-
Service Provider Data
-
Permission Group Data
Procedures to help you create, view, and delete each type of report follow this introductory section, beginning with “Service Provider Administrative Data Reports”.
This chapter also provides information about the Report Generator, which enables you to customize your own reports.
Viewing Reports
The browser from which you launched the GUI is used to display the reports.
A new browser window opens for the first report that you view, and is reused for viewing all subsequent reports.
Use the browser file functions to perform desired tasks, such as printing, searching, and exiting.
Service Provider Administrative Data Reports
The following procedures explain how to create, view, and delete Service Provider Administrative Data reports.
Creating a Service Provider Administrative Data Report
To create a Service Provider Administrative Data report:
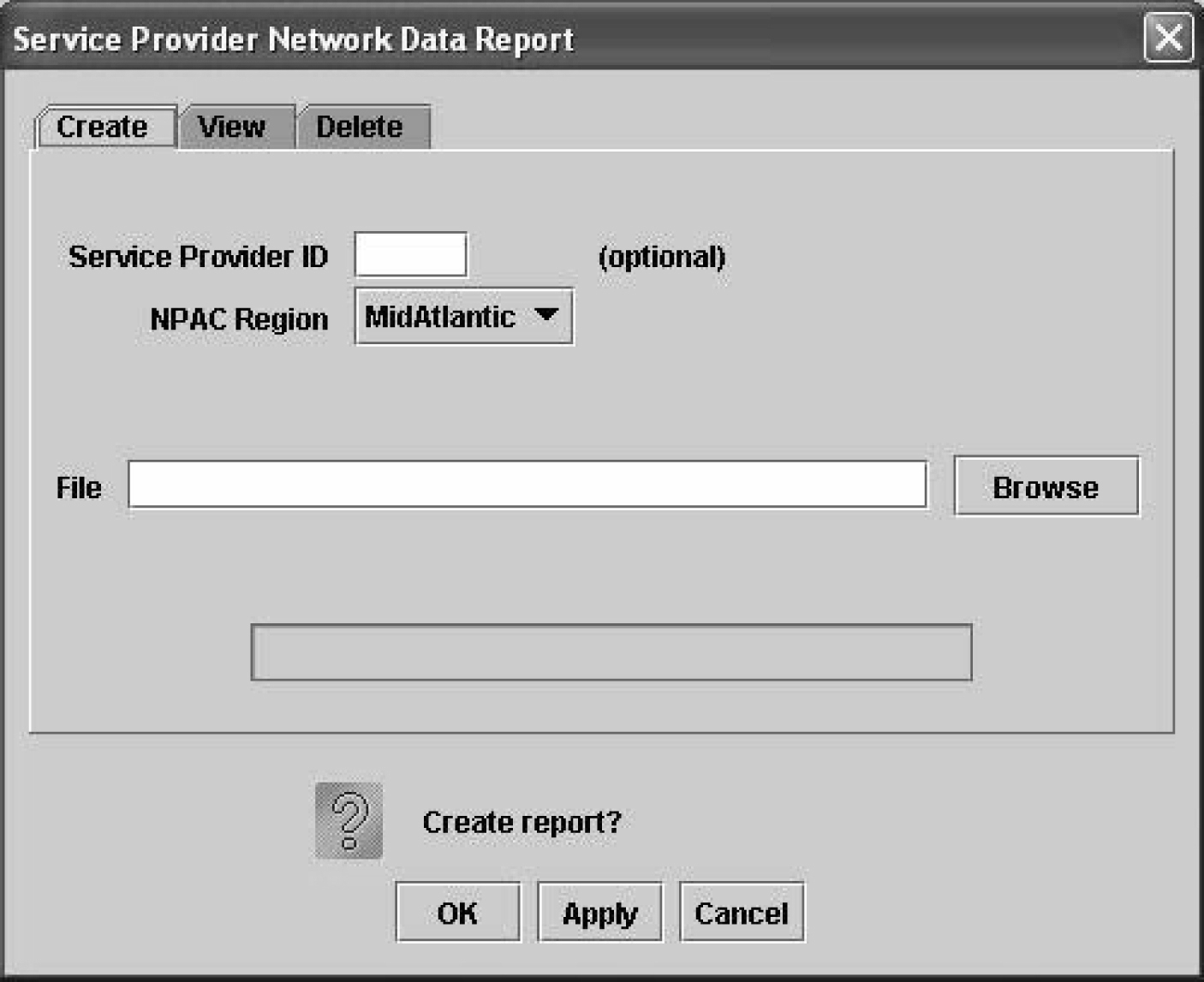
Service Provider Network Data Reports
The following procedures explain how to create, view, and delete Service Provider Network Data reports.
EMS Configuration Data Reports
The following procedures explain how to create, view, and delete EMS Configuration Data reports.
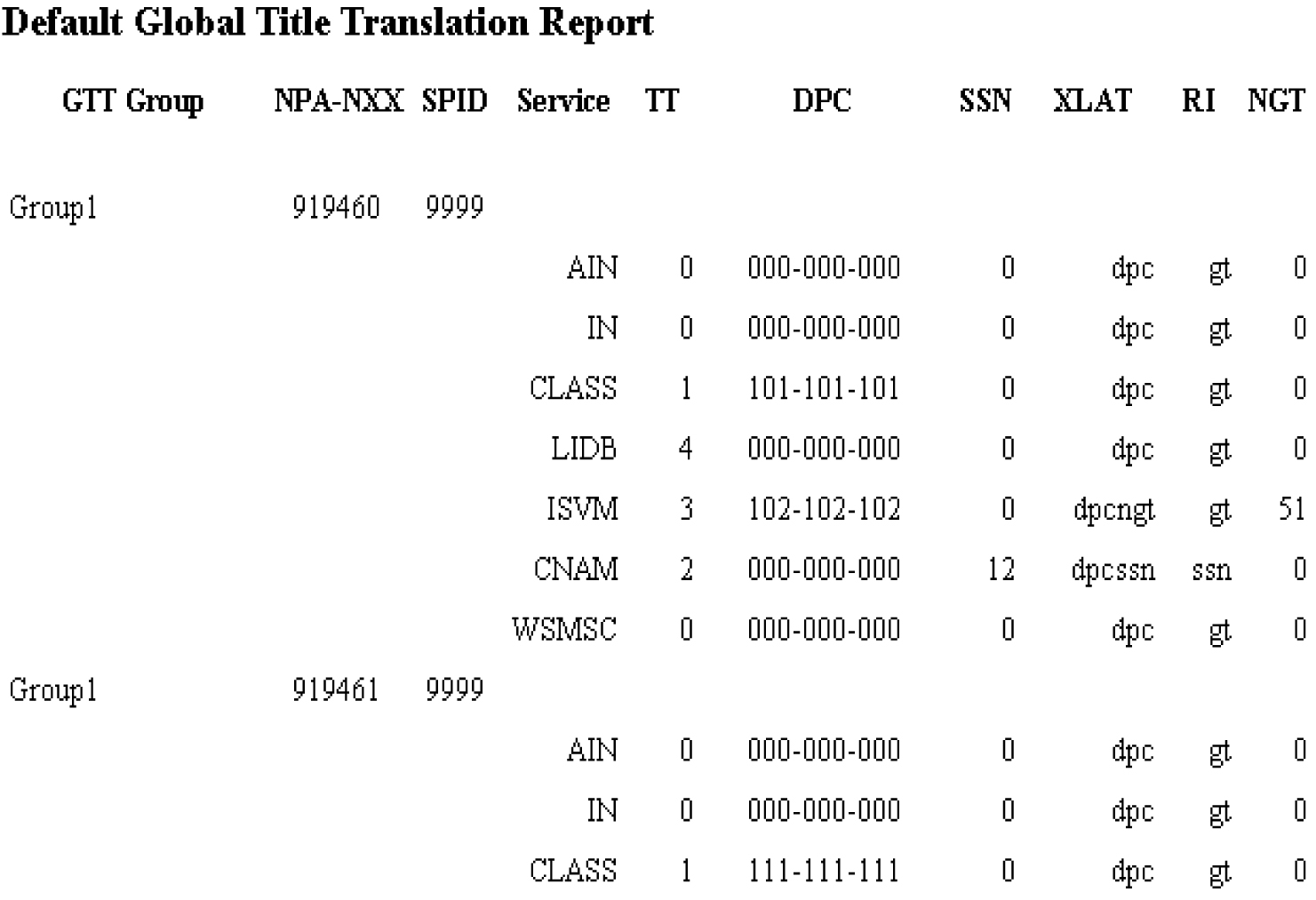
Default GTT Data Reports
This section contains information about Query GTT by DPC, which enables you to retrieve certain global title translation (GTT) information for a specific destination point code (DPC). This section also includes procedures that explain how to create, view, and delete Default GTT Data reports.
Query GTT by DPC
Query GTT by DPC enables you to retrieve the following global title translation (GTT) information for a specific destination point code (DPC).
-
Numbering Plan Area-Number Exchange (NPA-NXX) default data
-
Location Routing Number (LRN) override data
The report contains all the fields included in reports generated by prior releases of LSMS, but includes only those entries for NPA-NXX translations associated with the specified DPC.
You can use this information to verify the accuracy of locally provisioned global title data and to determine impacted translations for various network changes.
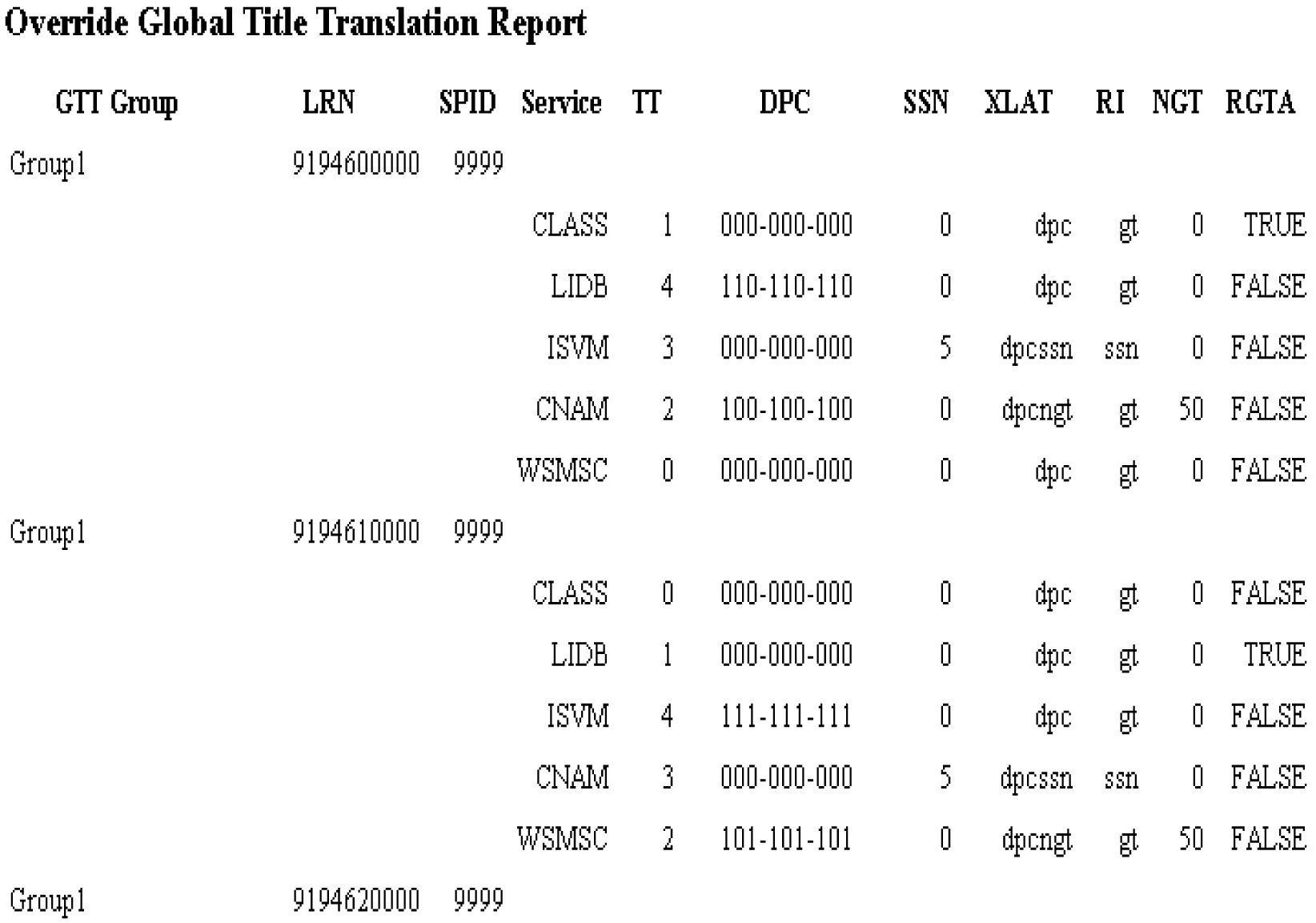
Override GTT Data Reports
This section contains information about Query GTT by DPC, which enables you to retrieve certain global title translation (GTT) information for a specific destination point code (DPC). This section also includes procedures that explain how to create, view, and delete Override GTT Data reports.
Query GTT by DPC
Query GTT by DPC enables you to retrieve the following global title translation (GTT) information for a specific destination point code (DPC).
-
Numbering Plan Area-Number Exchange (NPA-NXX) default data
-
Location Routing Number (LRN) override data
The report contains all the fields included in reports generated by prior releases of LSMS, but includes only those entries for NPA-NXX translations associated with the specified DPC.
You can use this information to verify the accuracy of locally provisioned global title data and to determine impacted translations for various network changes.
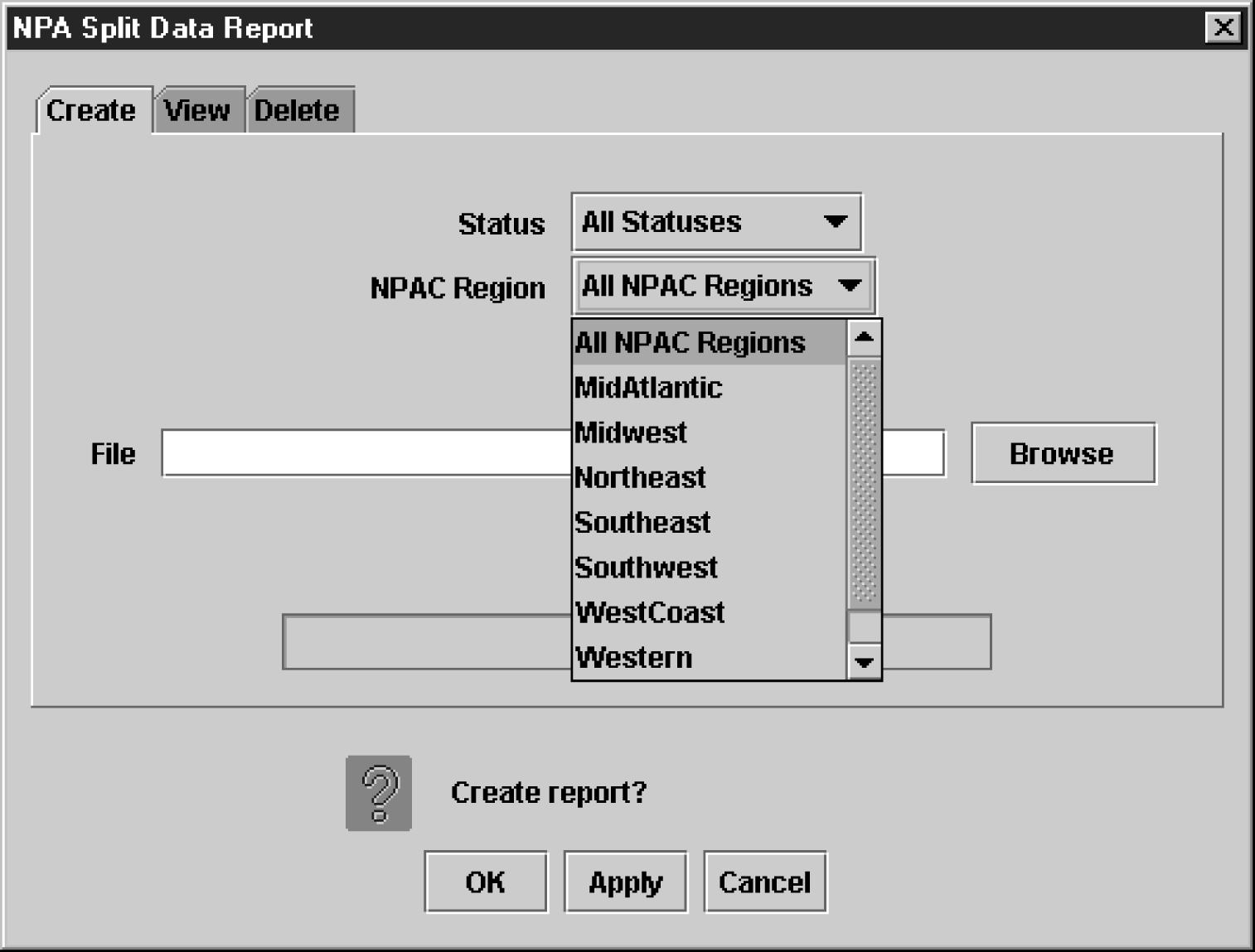
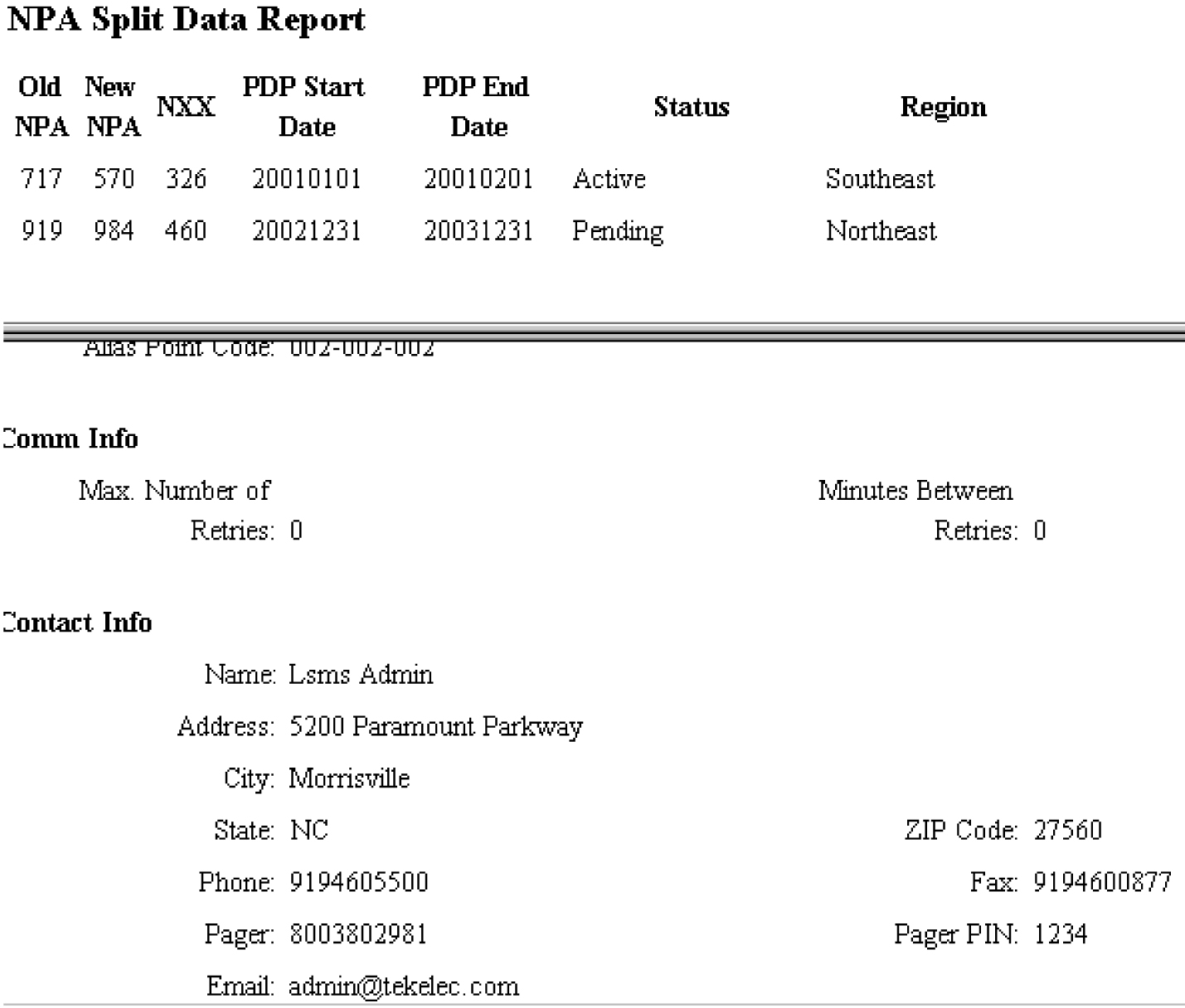
NPA Split Data Reports
The following procedures explain how to create, view, and delete NPA Split Data reports.
NPAC Audit Report
The iconectiv NPAC configuration options/features for each region include:
$ lsmsdb -c features | grep ICONECTIV
N CANADA_ICONECTIV
N MIDATLANTIC_ICONECTIV
N MIDWEST_ICONECTIV
N NORTHEAST_ICONECTIV
N SOUTHEAST_ICONECTIV
N SOUTHWEST_ICONECTIV
N WESTCOAST_ICONECTIV
N WESTERN_ICONECTIV
The value of these features can be changed using the
dbcfginternal utility.
The audit script identifies the enabled NPAC regions and the corresponding NPAC and logs them:
$ auditnpac
Audit is started
Audit complete. Check /var/TKLC/lsms/logs/trace/npacAudit.log.1001 for results
$ cat /var/TKLC/lsms/logs/trace/npacAudit.log.1001
********** NPAC Audit Started **********
Total number of NPAC regions connected : 7
Npacagent MidAtlantic is running
Npacagent MidAtlantic is connected to Neustar
Npacagent Northeast is running
Npacagent Northeast is connected to iconectiv
Npacagent Southeast is running
Npacagent Southeast is connected to Neustar
Npacagent Southwest is running
Npacagent Southwest is connected to Neustar
Npacagent Western is running
Npacagent Western is connected to Neustar
Npacagent WestCoast is running
Npacagent WestCoast is connected to Neustar
Npacagent Midwest is running
Npacagent Midwest is connected to iconectiv
Total 2 regions are connected to iconectiv and 5 are connected to Neustar.
********** NPAC Audit Is Complete **********
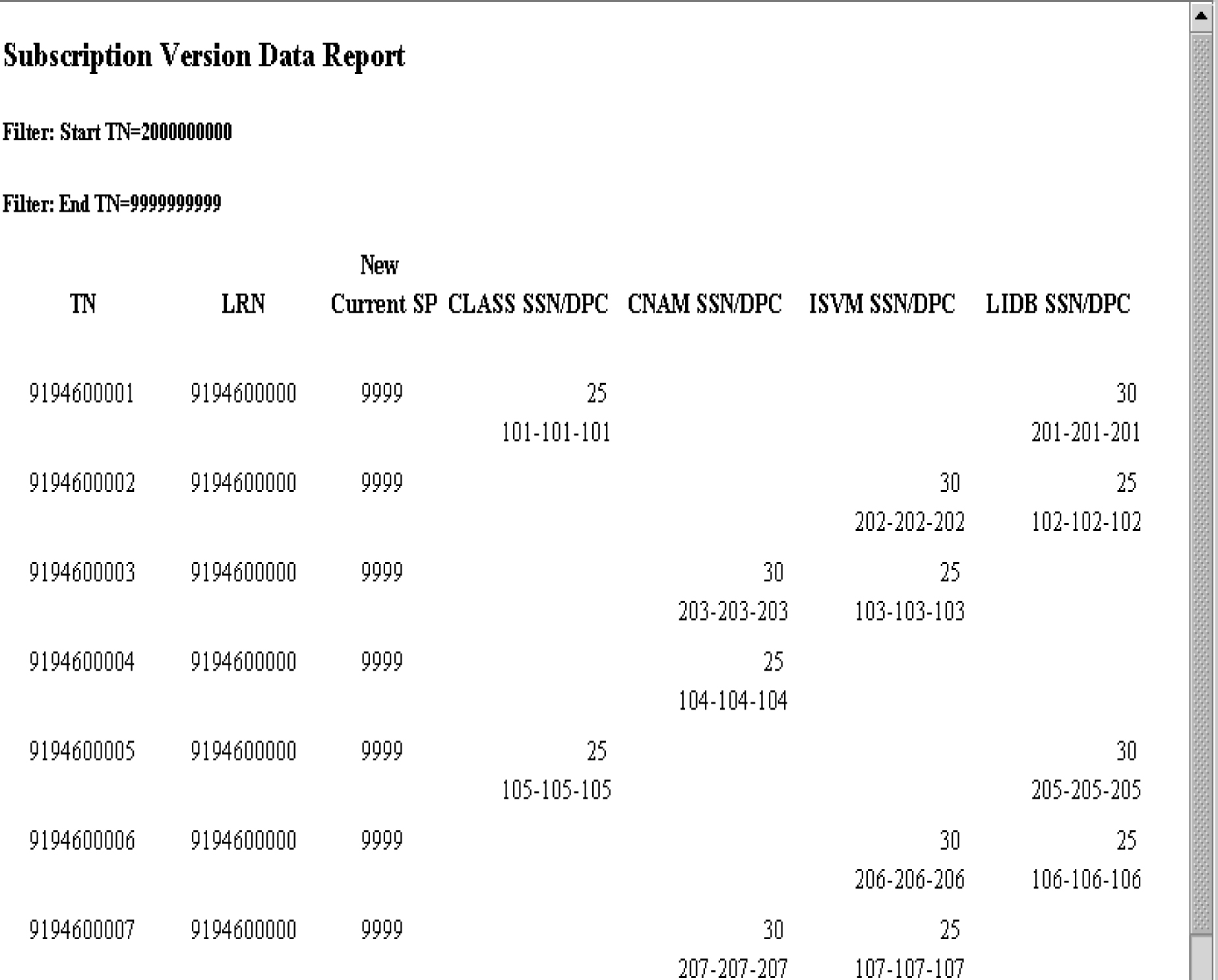
LSMS Subscriptions by LRN Reports
The following procedures explain how to create, view, and delete LSMS Subscriptions by LRN reports.
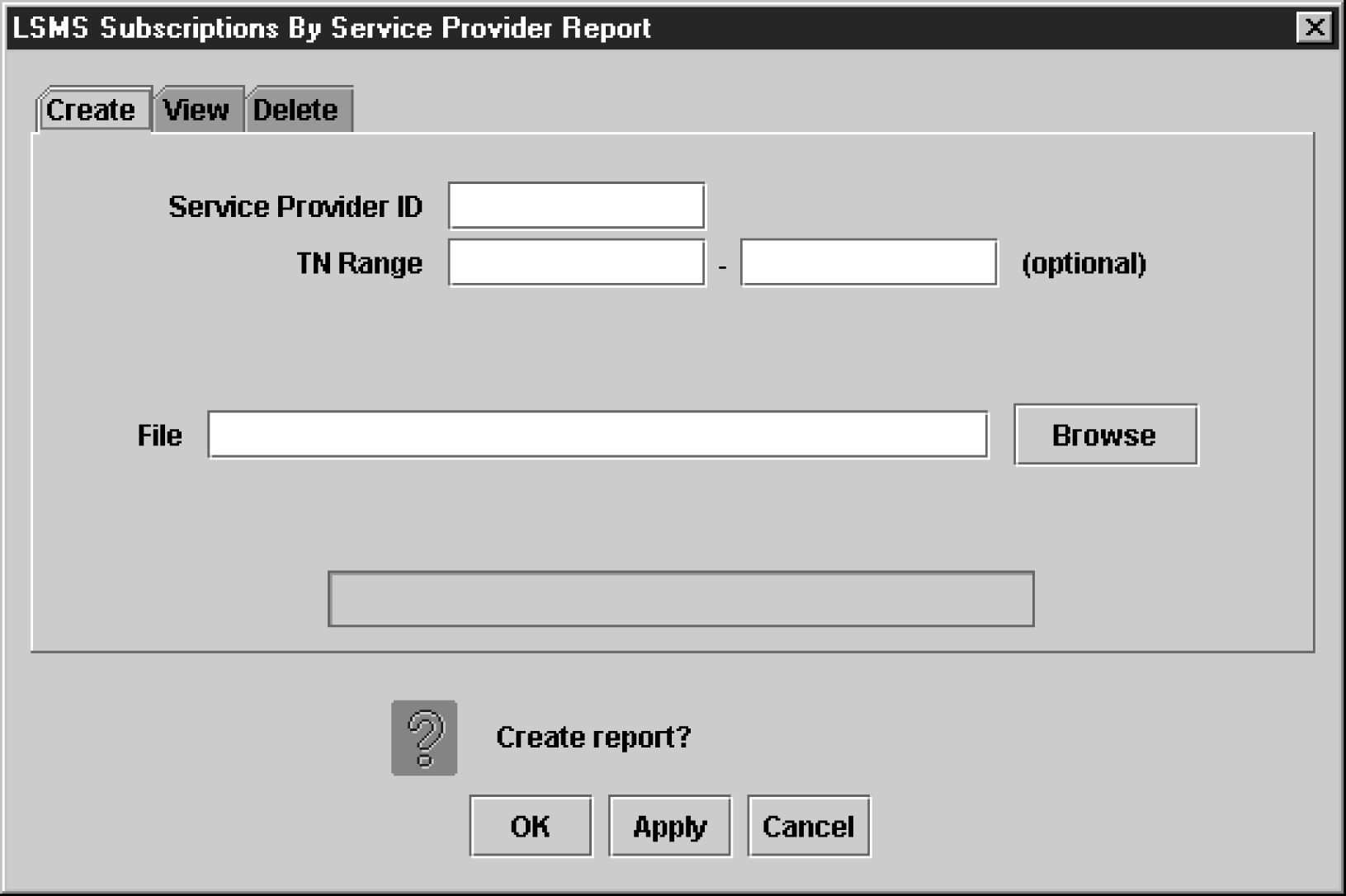
LSMS Subscriptions by Service Provider Data Reports
The following procedures explain how to create, view, and delete LSMS Subscriptions by Service Provider Data reports.
Creating an LSMS Subscription by Service Provider Data Report
To create an LSMS Subscription by Service Provider Data report:
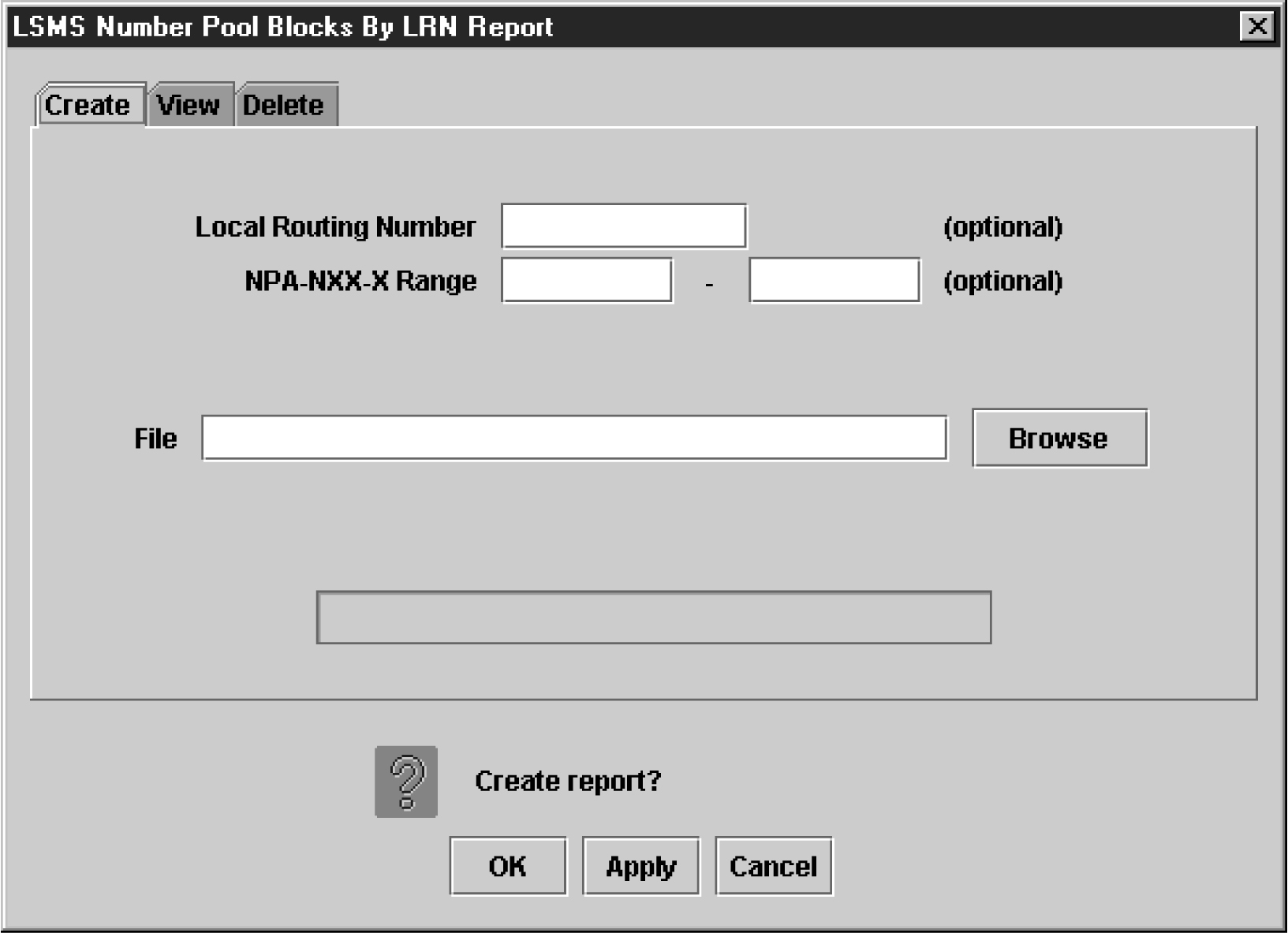
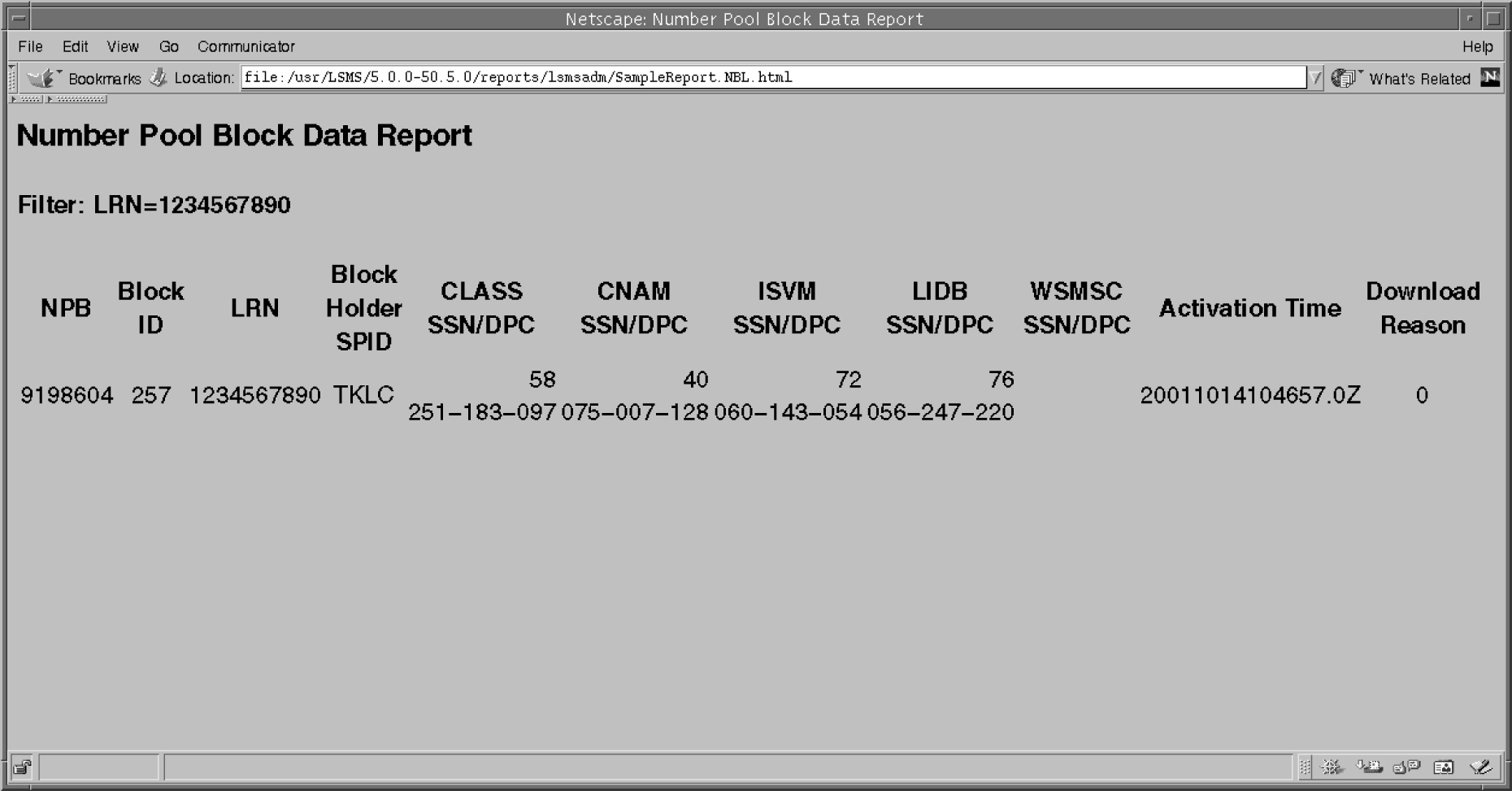
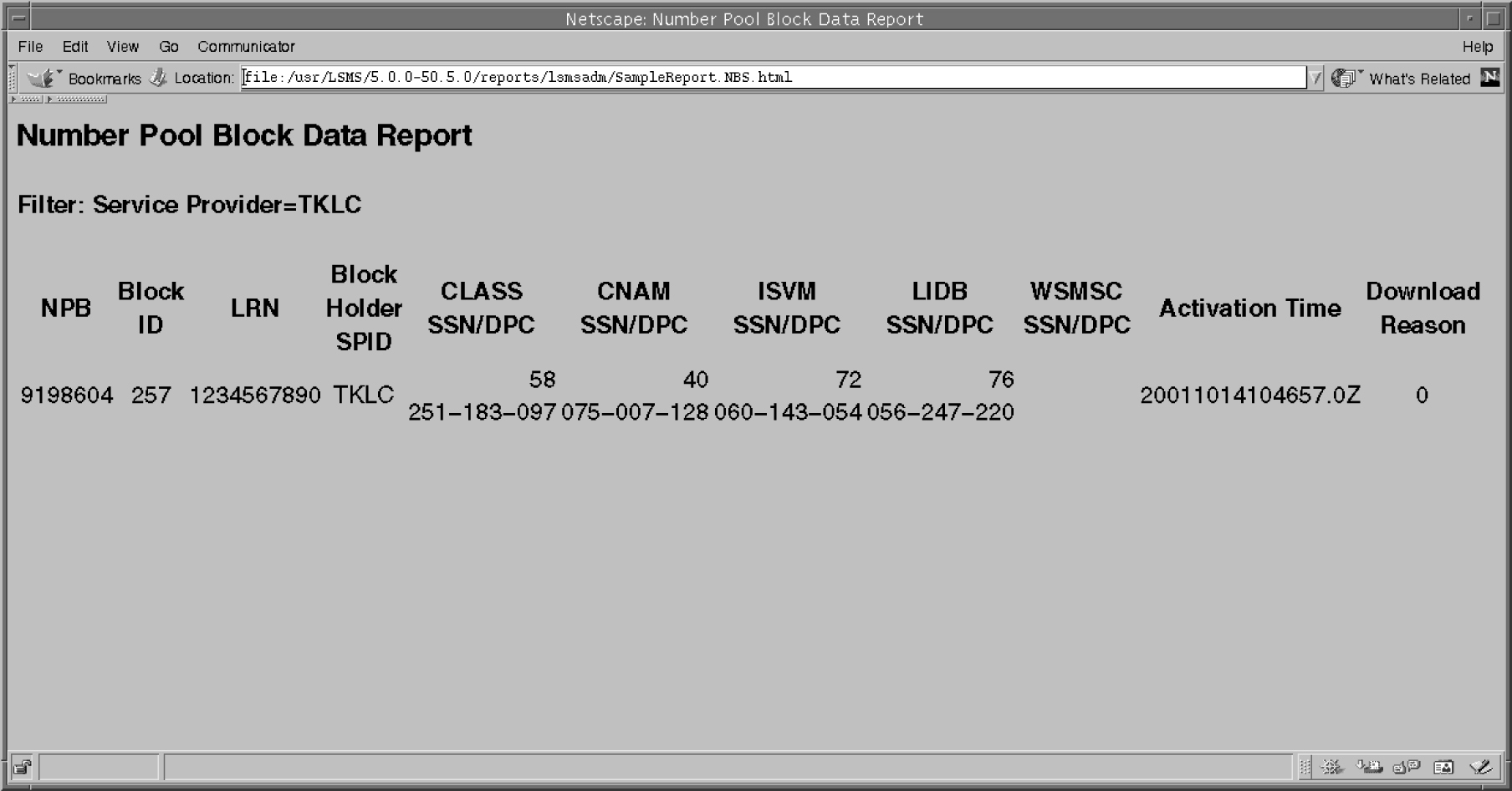
LSMS Number Pool Blocks by LRN Data Reports
The following procedures explain how to create, view, and delete LSMS Number Pool Blocks by LRN Data reports.
Creating an LSMS Number Pool Block by LRN Data Report
To create an LSMS Number Pool Block by LRN Data report:
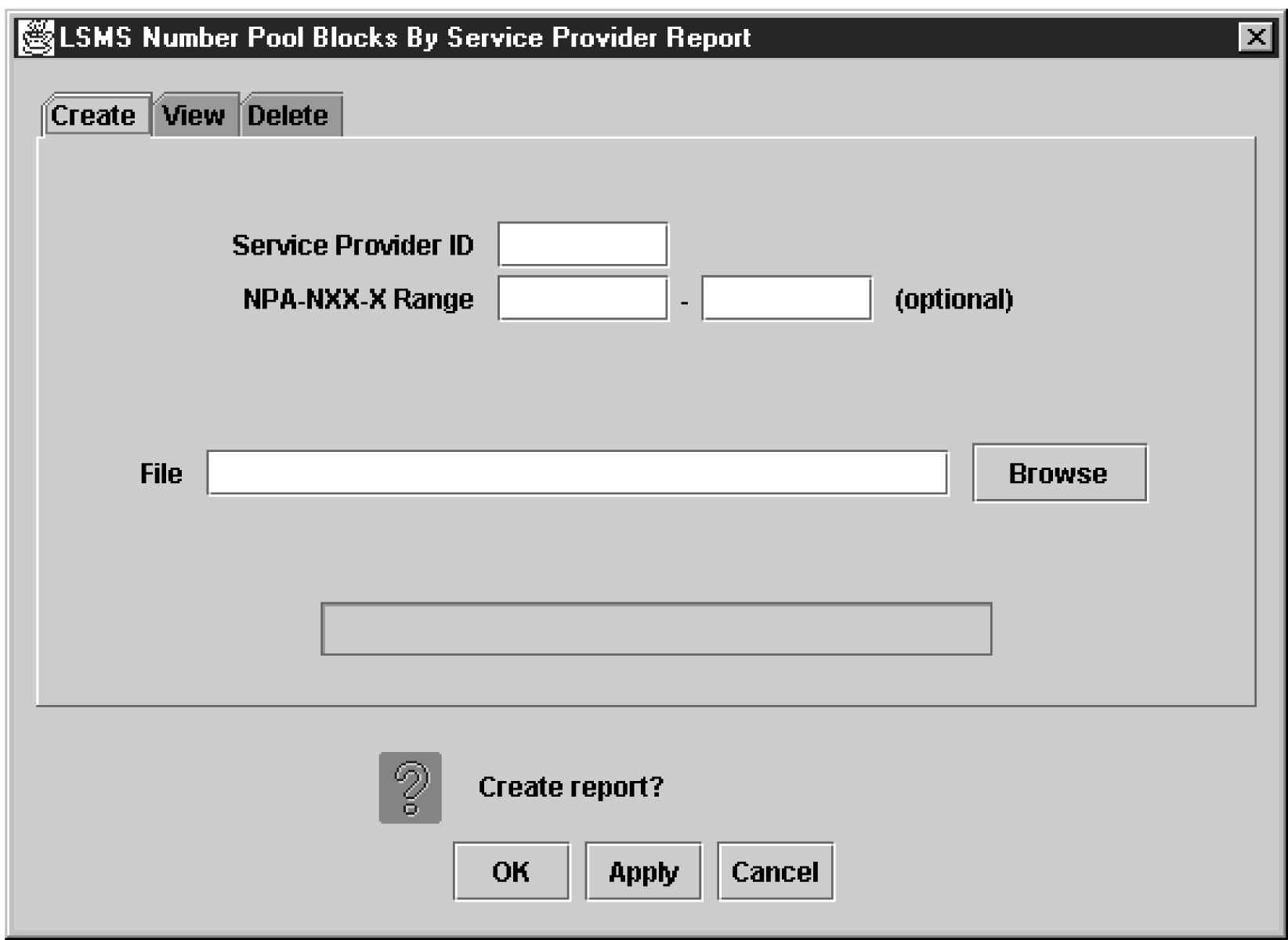
LSMS Number Pool Blocks by Service Provider Data Reports
The following procedures explain how to create, view, and delete LSMS Number Pool Blocks by Service Provider Data reports.
Creating an LSMS Number Pool Block by Service Provider Data Report
To create an LSMS Number Pool Block by Service Provider Data report:
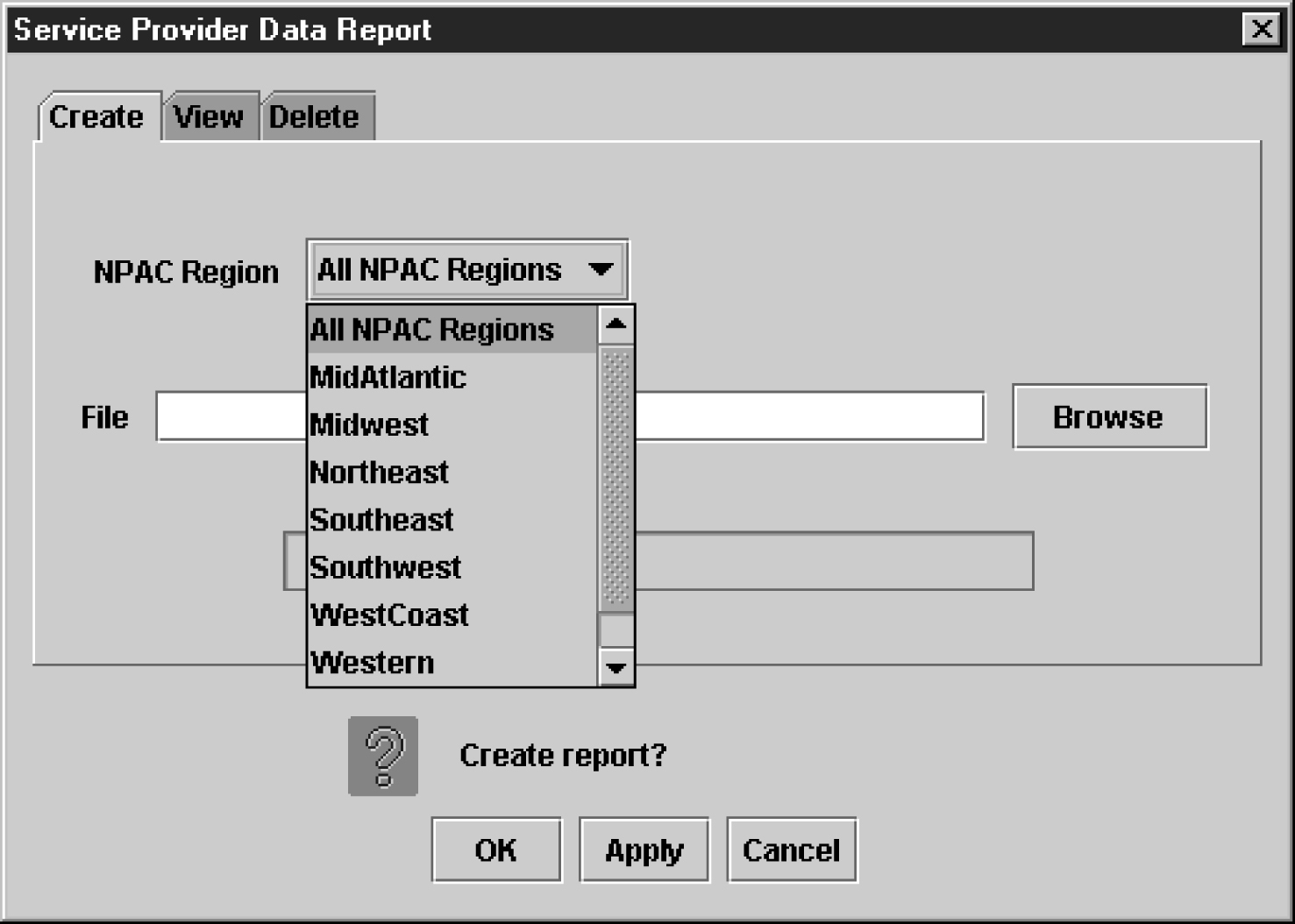
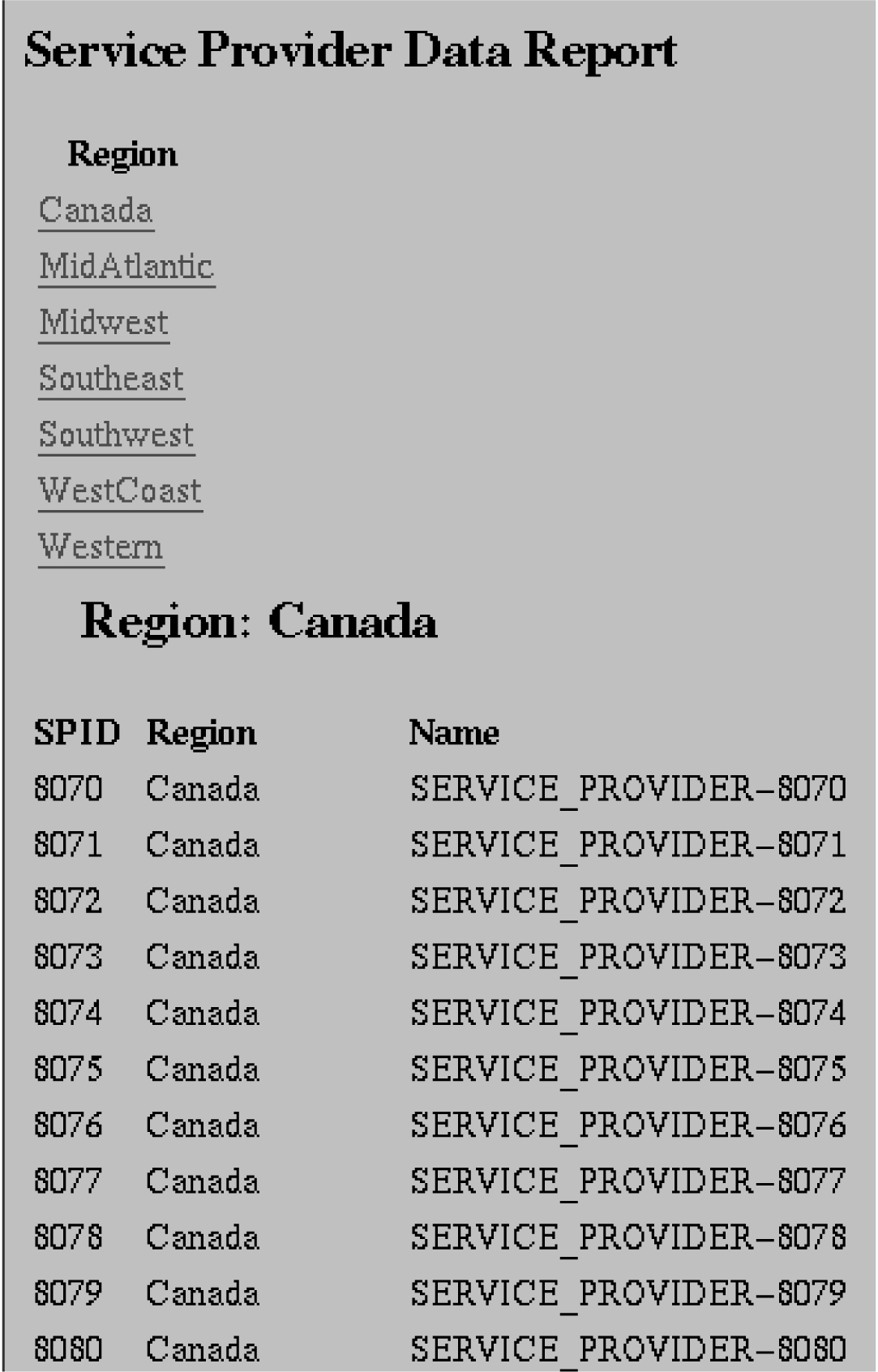
Service Provider Data Reports
The following procedures explain how to create, view, and delete Service Provider Data reports.
Permission Group Data Report
The "Permission Group Data" report provides a listing of all permission groups, commands authorized for each permission group, and users assigned to each permission group.
Report Generator
This optional feature is activated by Oracle customer service using secure activation procedures.
Beginning with LSMS Release 5.0, LSMS offered as an optional feature a report generator that uses a new LSMS Query Language (LQL) to enable the user to create reports that are not already available through the Reports menu item on the LSMS GUI. This feature supports queries against the following data types:
-
Subscription versions (SVs)
-
Number pool blocks (NPBs)
-
Default Global Title Translation (GTT)
-
Override GTT
-
Numbering Plan Area (NPA) splits
LQL can be run only on the command line on the active server.
Note:
This feature is intended for specific queries on indexed fields that return small result sets (less than 10,000 records). Queries of non-indexed fields or overly general queries use extensive memory resources, result in extremely long response times, and may impact LSMS system performance. For information about indexed fields, see SV Table, NPB Table, DGTT Table, OGTT Table, and SPLIT Table. For more information about avoiding poor performance, see Avoiding Overly General Queries.Invoking LQL
After the feature has been activated, the user can invoke LQL in either of the following ways:
-
Interactively by entering the command
lqlwithout a filename. The command-line prompt changes to LQL> and the user can enter any of the supported commands (see LQL Commands). -
In batch mode by entering the command
lqlwith a file name. LQL processes each line in the file as an LQL command (see LQL Commands). Batch processing is terminated when any invalid command or an EXIT command is encountered in the file The batch file can contain comment lines, which must begin with the # character.
Multiple LQL processes can be active, but only one LQL process at a time can perform a query (issue the SELECT command). For more information, see SELECT <column> FROM <table> WHERE <expression>;.
LQL Commands
The LQL command set is a restricted subset of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Structured Query Language-92 (SQL-92) and uses the SQL syntax, except where noted. For more information about SQL, refer to:
http://www.w3schools.com/sql/default.asp
Each LQL command is terminated with a semicolon. Therefore, in interactive mode, a command can span multiple lines. However, in batch mode, each command must appear all on one line of the file.
USING REGION <database>;
-
ALL_REGIONS
-
CANADA
-
MIDATLANTIC
-
MIDWEST
-
NORTHEAST
-
SOUTHEAST
-
WOUTHWEST
-
WESTCOAST
-
WESTERN
The regional database specified is the one queried for all subsequent queries for SVs and NPBs until this command is issued again with another value for <database>. For examples of this command, see LQL Examples.
Note:
This command is not part of the SQL standard.SELECT <column> FROM <table> WHERE <expression>;
- <table> has one of the values shown in LQL Table Names .
- <column> is a comma-separated list of column names (as shown in NPB Table, SV Table, DGTT Table, OGTT Table, and SPLIT Table) within the relevant table; in addition, service names can be used to select multiple column names, as described above each table
- WHERE <expression> is described in WHERE Expressions.
- In interactive mode, an error message is displayed and the command fails
- In batch mode, the entire batch file is aborted
For examples of this command, see LQL Examples.
LQL Table Names
Specify one of the values shown in the first column of this table for the <table> parameter in the SELECT command.
Table 5-6 LQL Table Names
| LQL Table Name (<table>) | Data Type | For Column Names, See: |
|---|---|---|
|
SV |
Subscription version |
|
|
NPB |
Number pool block |
|
|
DGTT |
Default GTT |
|
|
OGTT |
Override GTT |
|
|
SPLIT |
NPA split |
WHERE Expressions
- <column> is a column name within the relevant table as shown in SV Table, NPB Table, DGTT Table, OGTT Table, and SPLIT Table.
- <operator> is one of the following:
WHERE Operator (<operator>) Means +
Plus
-
Minus
>
Greater than
<
Less than
>=
Greater than or equal to
<=
Less than or equal to
=
Equal to
!=
Not equal to
LIKE
Pattern match (Note)
NOT LIKE
Inverse pattern match (Note)
Note:
For possible performance impact of using this operator, see “Avoiding Overly General Queries”. - <value> is a valid value for the field that appears in the type of column specified by <column name>; for more information about the fields and syntax rules that apply to them, refer to the Alarms and Maintenance Guide
- NOT negates the expression
- AND requires that both of two expressions must be true for the statement to be true
- OR requires that only one of two expressions must be true for the statement to be true
SQL Data Types
- SV (Subscription Version)
- NPB (Number Pool Block)
- DGTT (Default GTT)
- OGTT (Override GTT)
- Split (NPA Split)
Table 5-7 SQL Data Types and Descriptions
SQL Data Type Description CHAR[n]
A fixed length character array. A column of type CHAR will always have a value n characters long. As part of a WHERE clause, a CHAR field must be compared against a character string (e.g. TN = '9194600000', not TN=9194600000).
VARCHAR[n]
A variable length character array. A column of type VARCHAR will have a value between 0 and n characters long. As part of a WHERE clause, a VARCHAR field must be compared against a character string (e.g. TN = '9194600000', not TN=9194600000).
BYTE
An 8-bit integer field. As part of a WHERE clause, a BYTE field must be compared against a number (e.g. CLASS_SSN > 0, not CLASS_SSN > '0').
SHORT
A 32-bit integer field. As part of a WHERE clause, a BYTE field must be compared against a number (e.g. VERSION_ID > 0, not VERSION_ID > '0').
SV Table
- CLASS
- CNAM
- LIDB
- ISVM
- WSMSC
- ALL_SERVICES
Note:
These values cannot be used in a WHERE expression. For more information about these values, refer to the Alarms and Maintenance Guide.This table describes the values that can be specified for any <column> parameter (including in a WHERE expression) in a SELECT command where the value of <table> is SV. This table also describes which columns are indexed, as well as the width of each output column. For descriptions of the data types, see SQL Data Types .
Table 5-8 SV Table Column Names
| Column Name | Indexed? | Output Width | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
|
VERSION_ID |
YES |
10 |
SHORT |
|
TN |
YES |
10 |
CHAR[10] |
|
LRN |
NO |
10 |
CHAR[10] |
|
NEW_CURRENT_SP |
NO |
10 |
CHAR[4] |
|
ACTIVATION_TIME |
NO |
14 |
CHAR[24] |
|
EUL_VALUE |
NO |
5 |
CHAR[4] |
|
EUL_TYPE |
NO |
4 |
CHAR[4] |
|
BILLING_ID |
NO |
7 |
CHAR[4] |
|
LNP_TYPE |
NO |
4 |
CHAR[1] |
|
DOWNLOAD_REASON |
NO |
8 |
CHAR[1] |
|
CLASS_SSN |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_DPC |
NO |
5 |
CHAR[11] |
|
CNAM_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_DPC |
NO |
4 |
CHAR[11] |
|
LIDB_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_DPC |
NO |
4 |
CHAR[11] |
|
ISVM_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_DPC |
NO |
4 |
CHAR[11] |
|
WSMSC_SSN |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_DPC |
NO |
5 |
CHAR[11] |
|
Maximum possible output width |
126 |
||
NPB Table
- CLASS
- CNAM
- LIDB
- ISVM
- WSMSC
- ALL_SERVICES
This table displays the values that can be specified for any <column> parameter (including in a WHERE expression) in a SELECT command where the value of <table> is NPB. It also displays which columns are indexed and shows the width of each output column. For descriptions of the data types, see SQL Data Types.
Table 5-9 NPB Table Column Names Used in WHERE Expressions
| Column Name | Indexed? | Output Width | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
|
BLOCK_ID |
YES |
10 |
SHORT |
|
NPA_NXX_X |
YES |
6 |
CHAR[7] |
|
LRN |
NO |
10 |
CHAR[10] |
|
BLOCK_HOLDER_SPID |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[4] |
|
ACTIVATION_TIME |
NO |
14 |
CHAR[24] |
|
DOWNLOAD_REASON |
NO |
8 |
CHAR[1] |
|
CLASS_SSN |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_DPC |
NO |
5 |
CHAR[11] |
|
CNAM_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_DPC |
NO |
4 |
CHAR[11] |
|
LIDB_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_DPC |
NO |
4 |
CHAR[11] |
|
ISVM_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_DPC |
NO |
4 |
CHAR[11] |
|
WSMSC_SSN |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_DPC |
NO |
5 |
CHAR[11] |
|
Maximum possible output width |
103 |
||
DGTT Table
- CLASS
- CNAM
- LIDB
- ISVM
- WSMSC
- ALL_SERVICES
This table displays the values that can be specified for any <column> parameter (including in a WHERE expression) in a SELECT command where the value of <table> is DGTT. It also displays which columns are indexed and shows the width of each output column. For descriptions of the data types, see SQL Data Types.
Table 5-10 DGTT Table Column Names Used in WHERE Expressions
| Column Name | Indexed? | Output Width | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
|
GTT_GROUP |
NO |
40 |
VARCHAR[40] |
|
NPA_NXX |
NO |
6 |
CHAR[6] |
|
SPID |
NO |
4 |
CHAR[4] |
|
AIN_ENABLED |
NO |
7 |
BYTE |
|
IN_ENABLED |
NO |
7 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_TT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_DPC |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[11] |
|
CLASS_SSN |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_XLAT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_RI |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_NGT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_TT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_DPC |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[11] |
|
CNAM_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_XLAT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_RI |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_NGT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_TT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_DPC |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[11] |
|
LIDB_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_XLAT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_RI |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_NGT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_TT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_DPC |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[11] |
|
ISVM_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_XLAT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_RI |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_NGT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_TT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_DPC |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[11] |
|
WSMSC_SSN |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_XLAT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_RI |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_NGT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
Maximum possible output width |
223 |
||
OGTT Table
-
CLASS
-
CNAM
-
LIDB
-
ISVM
-
WSMSC
-
ALL_SERVICES
This table displays the values that can be specified for any <column> parameter (including in a WHERE expression) in a SELECT command where the value of <table> is OGTT. It also displays which columns are indexed and shows the width of each output column. For descriptions of the data types, see SQL Data Types.
Table 5-11 OGTT Table Column Names Used in WHERE Expressions
| Column Name | Indexed? | Output Width | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
|
GTT_GROUP |
NO |
40 |
VARCHAR[40] |
|
LRN |
NO |
10 |
CHAR[10] |
|
SPID |
NO |
4 |
CHAR[4] |
|
CLASS_TT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_DPC |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[11] |
|
CLASS_SSN |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_XLAT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_RI |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_NGT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CLASS_RGTA |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_TT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_DPC |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[11] |
|
CNAM_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_XLAT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_RI |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_NGT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
CNAM_RGTA |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_TT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_DPC |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[11] |
|
LIDB_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_XLAT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_RI |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_NGT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
LIDB_RGTA |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_TT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_DPC |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[11] |
|
ISVM_SSN |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_XLAT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_RI |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_NGT |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
ISVM_RGTA |
NO |
4 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_TT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_DPC |
NO |
11 |
CHAR[11] |
|
WSMSC_SSN |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_XLAT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_RI |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_NGT |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
WSMSC_RGTA |
NO |
5 |
BYTE |
|
Maximum possible output width |
249 |
||
SPLIT Table
This table displays the values that can be specified for any <column> parameter (including in a WHERE expression) in a SELECT command where the value of <table> is SPLIT. It also displays which columns are indexed and shows the width of each output column. For descriptions of the data types, see SQL Data Types.
Table 5-12 SPLIT Table Column Names Used in WHERE Expressions
| Column Name | Indexed? | Output Width | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|
|
OLD_NPA |
YES |
3 |
CHAR[3] |
|
NEW_NPA |
YES |
3 |
CHAR[3] |
|
NXX |
YES |
3 |
CHAR[3] |
|
REGION |
YES |
8 |
BYTE |
|
PDP_START |
YES |
8 |
SHORT |
|
PDP_END |
YES |
6 |
SHORT |
|
STATUS |
YES |
6 |
BYTE |
|
Maximum possible output width |
37 |
||
Avoiding Overly General Queries
Queries should not be made against columns that are not indexed (as indicated in SV Table, NPB Table, DGTT Table, OGTT Table, and SPLIT Table ). In addition, avoid overly general queries which can result from using:
-
The * wildcard character with the LIKE operator anywhere except at the end of the search value For example:
-
SELECT * FROM SV WHERE TN LIKE ‘919*’ uses the TN index and completes quickly
-
SELECT * FROM SV WHERE TN LIKE ‘*919’ does not use the TN index and exhibits the same poor performance as a query on a non-indexed column
-
-
The NOT_LIKE operator for indexed columns. For example:
-
SELECT * FROM SV WHERE TN NOT_LIKE ‘919*’ does not use the TN index and exhibits the same poor performance as a query on a non-indexed column
-
Table 5-13 provides some example performance times, assuming an SV table that contains 1,000,005 records.
Table 5-13 Query Performance Examples
| Query | Search Using Index? | Number of Records Searched | Number of Records Matched | Time to Complete Query |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
SELECT TN FROM SV; |
YES |
1,000,005 |
1,000,005 |
75 seconds |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN >= '2191209000' AND TN < '2191210000'; |
YES |
1,000,005 |
1,000 |
< 1 second |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN >= '2191200000' AND TN < '2191210000'; |
YES |
1,000,005 |
10,000 |
1 second |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN >= '2191200000' AND TN < '2191300000'; |
YES |
1,000,005 |
100,000 |
8 seconds |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN >= '2190000000' AND TN < '2200000000'; |
YES |
1,000,005 |
1,000,005 |
75 seconds |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN >= '9190000000' AND TN < '9200000000'; |
YES |
1,000,005 |
0 |
< 1 second |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN LIKE '219*'; |
YES |
1,000,005 |
1,000,005 |
90 seconds |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN LIKE '919*'; |
YES |
1,000,005 |
0 |
< 1 second |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN NOT_LIKE '919*'; |
YES |
1,000,005 |
0 |
< 1 second |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN NOT_LIKE '219*'; |
NO |
1,000,005 |
1,000,005 |
75 seconds |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE CLASS_SSN = 30; |
NO |
1,000,005 |
0 |
25 seconds |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE CLASS_SSN = 1; |
NO |
1,000,005 |
1,000,005 |
75 seconds |
|
SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN >= ’2191209000’ AND TN < ‘2191210000’ |
NO |
1,000,005 |
0 |
25 seconds |
Relationship to SQL
The following keywords, which are part of the SQL standard, are not supported by LQL:
-
BETWEEN operator
-
ORDER BY
-
DISTINCT
-
All SQL Functions
-
GROUP BY
-
HAVING
-
ALIAS
-
All multiple-table SELECTs
-
All JOINs
-
AGGREGATE
-
UNION
-
INTERSECTION
DISPLAY <RECORDS|COUNTS>;
Use this command to specify how output is to be displayed:
-
To display the full query results, use DISPLAY RECORDS
-
To display only the number of records resulting from the query, use DISPLAY COUNTS
The setting remains in effect until another DISPLAY command is entered. For examples of this command, see LQL Examples.
Relationship to SQL
This command is not part of the SQL standard.
SAVE <COMMANDS|RESULTS> <IN <filename>|OFF>;
Use this command to specify that either all commands issued or all results of a query are to be stored in the indicated file, or to stop saving commands or results. If a filename is provided, the filename is given an extension of .lql and is saved in the user’s reports directory.
To save both commands and results, enter the command twice. If the same filename is used for both SAVE commands, the commands and results are interleaved in the output file. For examples of this command, see Using the SAVE Command.
Relationship to SQL
This command is not part of the SQL standard.
STATUS;
Use this command to display the current settings as set by the following commands:
-
USING REGION
-
DISPLAY
-
SAVE
For examples of this command, see Using the STATUS Command.
Relationship to SQL
This command is part of the SQL standard.
HELP;
Use this command to display the list of supported commands.
Relationship to SQL
This command is not part of the SQL standard.
EXIT;
Use this command to exit the LQL executable. For examples of this command, see “LQL Examples”.
Relationship to SQL
This command is not part of the SQL standard.
LQL Output
LQL displays its results as a set of space-padded values. Before writing the first record, LQL writes a header line that contains the name of each column; if the column name contains an underscore, the name LQL writes the column name on two lines.
LQL writes each row returned from the query as one line of output. An empty or missing column appears as only spaces.
LQL Errors
All LQL errors are written to stderr. LQL generates the following types of errors:
-
Errors generated by the LQL software—Most errors will be of this type. These errors are plain text messages that indicate the user’s error and often indicate a corrective course of action.
-
Errors generated by the underlying database—This type of error generally occurs for an incorrect SELECT statement, which cannot be detected until the command is submitted to the database for execution. These errors usually generate a database error message, such as:
E4343:OM_PSR_SYNTAX_ERROR: VQL PARSE ERR: parse error: on/near token...
LQL Examples
Simple SELECT
Here is an example of a simple SELECT operation:
# lql
LQL> USING REGION SOUTHEAST;
LQL> DISPLAY RECORDS;
LQL> SELECT LRN FROM SV WHERE TN = '9194605500';
LRN
9194600000
LQL> EXIT;Using AND in a WHERE Expression
Here is an example of using AND in a WHERE expression:
# lql
LQL> DISPLAY RECORDS;
LQL> SELECT CLASS,CNAM FROM OGTT WHERE GTT_GROUP = 'Group1' AND AIN_ENABLED != 0;
CLASS CLASS CLASS CLASS CLASS CLASS CLASS CNAM CNAM
CNAM CNAM CNAM CNAM CNAM
TT DPC SSN XLAT RI NGT RGTA TT DPC
SSN XLAT RI NGT RGTA
1 100-200-100 0 0 0 0 0
LQL> EXIT;
In this example, only the CLASS service is defined for the GTT in this example; therefore, no entries display for the CNAM columns.
Using OR in a WHERE Expression
Here is an example of using OR in a WHERE expression:
# lql
LQL> DISPLAY RECORDS;
LQL> SELECT SPID, NPA_NXX FROM DGTT WHERE CLASS_SSN = 121 OR CNAM_SSN = 121;
SPID NPA
NXX
1234 717323
1234 717326
LQL> EXIT
Using NOT in a WHERE Expression
Here is an example of using NOT in a WHERE expression:
# lql
LQL> DISPLAY RECORDS;
LQL> SELECT * FROM SPLIT WHERE NOT (REGION = 3);
OLD NEW NXX START END REGION STATUS
NPA NPA PDP PDP
919 864 227 20010801 20020301 4 2
LQL> EXIT
Using LIKE in a WHERE Expression
Here is an example of using LIKE in a WHERE expression (the first query in this example does not follow the guidelines recommended in “Avoiding Overly General Queries”):
# lql
LQL> USING REGION SOUTHEAST;
LQL>DISPLAY COUNTS;
LQL>SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN LIKE ‘*0000’;
Query returned 0 rows.
LQL> DISPLAY COUNTS;LQL>SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN LIKE ‘919460*’;
Query returned 936 rows.
LQL> EXIT
Using NOT_LIKE in a WHERE Expression
Here is an example of using NOT_LIKE in a WHERE expression (this example does not follow the guidelines recommended in “Avoiding Overly General Queries”):
# lql
LQL> USING REGION CANADA;
LQL>DISPLAY COUNTS;
LQL>SELECT TN FROM SV WHERE TN NOT_LIKE ‘1*’;
Query returned 945 rows.
LQL> EXIT
Using the SAVE Command
Here is an example of using the SAVE command to save results to a file:
# lql
LQL> USING REGION CANADA;
LQL> DISPLAY COUNTS;
LQL> SELECT * FROM SV WHERE LRN = '9194600000' OR LRN = '9194610000';
Query returned 215 rows.
LQL> DISPLAY RECORDS; LQL>SAVE RESULTS IN NpaNxx919460; LQL> SELECT * FROM SV WHERE LRN = '9194600000' OR LRN = '9194610000'; LQL> SELECT * FROM SV WHERE TN LIKE '919460*' ;LQL> SAVE RESULTS OFF; LQL> EXIT
The results will be stored in the file /var/TKLC/lsms/free/data/reports/lsmsadm/.
Using the STATUS Command
Here is an example of using the STATUS command:
# lql
LQL> USING REGION CANADA;
LQL>DISPLAY COUNTS;
LQL STATUS;
Queries will use region: SOUTHEAST
Query results will show the number of rows found.
Commands will not be saved.
Query results will not be saved.
LQL> EXIT