3 Installing ATS for Different Network Analytics Suite Products
This section describes how to install ATS for different Network Analytics Suite products.
3.1 Installing ATS for OCNADD
The Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director (OCNADD) can be installed with or without TLS (Transport Layer Security) Support feature. To enable TLS feature support, see Enabling TLS Support on ATS and Enable TLS Support on OCNADD ATS before proceeding with ATS installation.
Installing ATS for OCNADD
3.1.1 Resource Requirements
This section describes the ATS resource requirements for OCNADD.
Overview - Total Number of Resources
- OCNADD SUT
- ATS
Table 3-1 OCNADD - Total Number of Resources
| Resource Name | CPU | Memory (GB) |
|---|---|---|
| OCNADD SUT Totals | 7 | 360 |
| ATS Totals | 14 | 22 |
| Grand Total OCNADD ATS | 84 | 382 |
OCNADD Pods Resource Requirement Details
This section describes the resource requirements, which are needed to deploy OCNADD ATS successfully.
Table 3-2 OCNADD Pods Resource Requirement Details
| OCNADD Service | CPUs Required per Pod | Memory Required per Pod (GB) | # Replicas (regular deployment) | # Replicas (ATS deployment) | CPUs Required - Total | Memory Required - Total (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ocnaddconfiguration | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ocnaddalarm | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ocnaddadmin | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ocnaddhealthmonitoring | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ocnadduirouter | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| ocnaddscpaggregation | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| ocnaddnrfaggregation | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| ocnaddseppaggregation | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| ocnaddadapter | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 8 |
| ocnaddkafka | 6 | 64 | 4 | 4 | 24 | 256 |
| zookeeper | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| kraftcontroller | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| ocnaddgui | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| ocnaddfilter | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| ocnaddcorrelation | 3 | 24 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 24 |
| ocnaddredundancyagent | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
| ocnaddstorageadapter | 3 | 24 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 24 |
| ocnaddexport | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
| ocnaddingressadapter | 3 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| ocnaddnonoracleaggregation | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| ocnaddpcfaggregation | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| ocnaddbsfaggregation | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| OCNADD SUT Totals | 70 CPU | 360 GB | ||||
For more information about OCNADD Pods Resource Requirements, see the "Resource Requirements" section in Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
ATS Resource Requirement details for OCNADD
This section describes the ATS resource requirements, which are needed to deploy OCNADD ATS successfully.
Table 3-3 ATS Resource Requirement Details
| Microservice | CPUs Required per Pod | Memory Required per Pod (GB) | # Replicas (regular deployment) | # Replicas (ATS deployment) | CPUs Required - Total | Memory Required - Total (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ATS Behave | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| OCNADD Producer Stub (SCP, NRF, SEPP,PCF,BSF) | 10 | 20 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 20 |
| OCNADD Consumer Stub | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| ATS Totals | 14 | 22 | ||||
3.1.2 Downloading the ATS Package
Locating and Downloading ATS Images
To locate and download the ATS Image from MOS:
- Log in to My Oracle Support using the appropriate credentials.
- Select the Patches & Updates tab.
- In the Patch Search window, click Product or Family (Advanced).
- Enter Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director in the Product field.
- Select Oracle Communications Network Analytics Data Director <release_number> from the Release drop-down.
- Click Search. The Patch Advanced Search Results list appears.
- Select the required ATS patch from the list. The Patch Details window appears.
- Click Download. The File Download window appears.
- Click the <p********_<release_number>_Tekelec>.zip file to download the OCNADD ATS package file.
- Untar the zip file to access all the ATS Images. The
<p********_<release_number>_Tekelec>.zip directory has
following files:
ocats-ocnadd-tools-pkg-25.1.202.tgz ocats-ocnadd-tools-pkg-25.1.202-README.txt ocats-ocnadd-tools-pkg-25.1.202.tgz.sha256 ocats-ocnadd-custom-configtemplates-25.1.202.zip ocats-ocnadd-custom-configtemplates-25.1.202-README.txtTheocats-ocnadd-tools-pkg-25.1.202-README.txtfile has all the information required for the package. Theocats-ocnadd-tools-pkg-25.1.202.tgzfile has the following images and charts packaged as tar files:ocats-ocnadd-tools-pkg-25.1.202.tgz | |_ _ _ocats-ocnadd-pkg-25.1.202.tgz | |_ _ _ _ _ _ ocats-ocnadd-25.1.202.tgz (Helm Charts) | |_ _ _ _ _ _ ocats-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar (Docker Images) | |_ _ _ _ _ _ OCATS-ocnadd-Readme.txt | |_ _ _ _ _ _ ocats-ocnadd-25.1.202.tgz.sha256 | |_ _ _ _ _ _ ocats-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar.sha256 | |_ _ _ _ _ _ ocats-ocnadd-data-25.1.202.tgz (ATS test scripts and Jenkins data) | |_ _ _ _ _ _ ocats-ocnadd-data-25.1.202.tgz.sha256 | | |_ _ _ocstub-ocnadd-pkg-25.1.202.tgz |_ _ _ _ _ _ ocstub-ocnadd-25.1.202.tgz (Helm Charts) |_ _ _ _ _ _ ocstub-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar (Docker Images) |_ _ _ _ _ _ OCSTUB-ocnadd-Readme.txt |_ _ _ _ _ _ ocstub-ocnadd-25.1.202.tgz.sha256 |_ _ _ _ _ _ ocstub-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar.sha256In addition to the above images and charts, there is anocats-ocnadd-custom-configtemplates-25.1.100.zipfile in the package file.ocats-ocnadd-custom-configtemplates-25.1.202.zip | |_ _ _ocats-ocnadd-custom-values_25.1.202.yaml (Custom values file for installation) | |_ _ _ocats_ocnadd_custom_serviceaccount_25.1.202.yaml (Template to create custom service account) - Copy the tar file to the CNE, OCI, or Kubernetes cluster where you want to deploy ATS.
3.1.3 Pushing the Images to Customer Docker Registry
Preparing to deploy ATS and Stub Pod in Kubernetes Cluster
To deploy ATS and Stub Pod in Kubernetes Cluster:
- Run the following command to extract tar file content.
tar -xvf ocats-ocnadd-tools-pkg-25.1.202.tgzThe output of this command is:
ocats-ocnadd-pkg-25.1.202.tgz ocstub-ocnadd-pkg-25.1.202.tgz ocats-ocnadd-custom-configtemplates-25.1.202.zip - Run the following command to extract the helm charts and docker images of ATS.
tar -xvf ocats-ocnadd-pkg-25.1.202.tgzThe output of this command is:
ocats-ocnadd-25.1.202.tgz ocats-ocnadd-25.1.202.tgz.sha256 ocats-ocnadd-data-25.1.202.tgz ocats-ocnadd-data-25.1.202.tgz.sha256 ocats-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar ocats-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar.sha256 OCATS-ocnadd-Readme.txtNote:
Theocats-ocnadd-Readme.txtfile has all the information required for the package. - Run the following command to untar the ocstub package.
tar -xvf ocstub-ocnadd-pkg-25.1.202.tgzThe output of this command is:
ocstub-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar ocstub-ocnadd-25.1.202.tgz.sha256 ocstub-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar.sha256 ocstub-ocnadd-25.1.202.tgz OCSTUB-ocnadd-Readme.txt OCSTUB_OCNADD_Installation_Readme.txt - Run the following command to extract the content of the custom configuration templates:
unzip ocats-ocnadd-custom-configtemplates-25.1.202.zipThe output of this command is:
ocats-ocnadd-custom-values_25.1.202.yaml (Custom yaml file for deployment of OCATS-OCNADD) ocats_ocnadd_custom_serviceaccount_25.1.202.yaml (Custom yaml file for service account creation to help the customer if required) - Run the following commands in your
cluster to load the ATS docker image, '
ocats-ocnadd-image-25.1.100.tar:$ podman load -i ocats-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar - Run the following commands to tag the imported image and push it to the local registry:
$ podman tag docker.io/<image-tag> <local_registry>/<image-name>:<image-tag> $ podman push <local_registry>/<image-name>:<image-tag> - Run the following commands in your cluster to load the Stub docker images
ocstub-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar:$ podman load -i ocstub-ocnadd-image-25.1.202.tar - Run the following commands to tag each imported image and push it to the local registry:
$ podman tag docker.io/<image-tag> <local_registry>/<image-name>:<image-tag> $ podman push <local_registry>/<image-name>:<image-tag> - Update the image name and tag in the
ocats-ocnadd-custom-values.yamlandocnaddsimulator/values.yamlfiles of simulator Helm as required. Forocats-ocnadd-custom-values.yamlupdate the 'image.repository' with respectivelocal_registry.For
ocnaddsimulator/values.yamlupdate the 'repo.REPO_HOST_PORT' and 'initContainers.repo.REPO_HOST_PORT' with respectivelocal_registry.
3.1.4 Configuring ATS
3.1.4.1 Enabling Static Port
- To enable static port:
- In the ocats-ocnadd-custom-values.yaml file under service section, set the
staticNodePortEnabled parameter value to 'true' and staticNodePort
parameter value with valid
nodePort.
service: customExtension: labels: {} annotations: {} type: LoadBalancer ports: https: port: "8443" staticNodePortEnabled: false staticNodePort: "" http: port: "8080" staticNodePortEnabled: false staticNodePort: "" staticLoadBalancerIPEnabled: false staticLoadBalancerIP: ""
Note:
ATS supports static port. By default, this feature is not enabled.Note:
To enablestaticLoadBalancerIP, set thestaticLoadBalancerIPEnabledparameter value to 'true' andstaticLoadBalancerIPparameter value with validLoadBalancer IPvalue. By default, this is set to false. - In the ocats-ocnadd-custom-values.yaml file under service section, set the
staticNodePortEnabled parameter value to 'true' and staticNodePort
parameter value with valid
nodePort.
3.1.4.2 Enabling TLS Support on ATS
If user wish to enable TLS support on ATS deployment (this is irrespective of OCNADD
deployment), update the following parameters to "true" in the
ocats-ocnadd-custom-values.yaml file. Else, this step can be
skipped.
atsGuiTLSEnabledatsCommunicationTLSEnabled
For example:
atsGuiTLSEnabled: false ## --> updated it with 'true'
atsCommunicationTLSEnabled: false ## --> updated it with 'true' 3.1.5 Deploying ATS and Stub in Kubernetes Cluster
Note:
It is important to ensure that the ATS and Stub are deployed as follows:- In Centralized Deployment mode (fresh deployments), the ATS and Stub must be deployed in the Worker Group namespace.
- In Non-Centralized Deployment mode (when the OCNADD is upgraded from any older release), the ATS and Stub should be deployed in the default OCNADD namespace.
- When OCNADD is deployed as a two-site georedundant deployment, ATS and Stub should be deployed on both Primary and Secondary sites.
- OCNADD-ATS suite supports mTLS. To use this feature, ensure that mTLS is set to "true" during OCNADD deployment.
For the test cases to run successfully, ensure the intraTLSEnalbled parameter value in the Jenkins pipeline script is identical to the value in the OCNADD deployment. The Alert Manager does not support HTTPS connections. When intraTLSEnalbled is set to true, the following Alert Manager test cases may fail:
- Verify the OCNADD_CONSUMER_ADAPTER_SVC_DOWN alert, this alert is raised when deployments of OCNADD are broken.
- Verify the OCNADD_ADMIN_SVC_DOWN alert, this alert is raised when deployments of OCNADD are broken.
- Verify the OCNADD_NRF_AGGREGATION_SVC_DOWN alert, this alert is raised when deployments of OCNADD are broken.
- Verify the OCNADD_SCP_AGGREGATION_SVC_DOWN alert, this alert is raised when deployments of OCNADD are broken.
- Verify the OCNADD_ALARM_SVC_DOWN alert, this alert is raised when deployments of OCNADD are broken.
- Verify the OCNADD_HEALTH_MONITORING_SVC_DOWN alert, this alert is raised when deployments of OCNADD are broken.
ATS and Stub Support Helm Deployment
Choose the namespace to deploy the ATS and Stub based on the OCNADD deployment mode, see Note.
kubectl create namespace <namespace_name>Note:
- It is recommended to use the
<release_name>asocnadd-simwhile installing stubs. - The ATS deployment with OCNADD does not support the Persistent Volume (PV) feature. Therefore, the default value of the deployment.PVEnabled parameter in
ocats-ocnadd-custom-values.yamlmust not be changed. By default, the parameter value is set to false.
Deploying ATS:
Run the following command:
helm install -name <release_name> ocats-ocnadd-25.1.202.tgz --namespace <namespace_name> -f <values-yaml-file>
helm install -name ocats ocats-ocnadd-25.1.202.tgz --namespace ocnadd-deploy -f ocats-ocnadd-custom-values.yamlNote:
Before you deploy stubs, update the parameter oraclenfproducer.REST_BASED_TRAFFIC to true in the ocnaddsimulator/values.yaml file. The default value of the parameter is false.helm install -name <release_name> <ocstub-ocnadd-chart> --namespace <namespace_name> Note:
For more details about installing the stub, refer to theOCSTUB_OCNADD_Installation_Readme.txt file.
Example:
helm install -name ocnadd-sim ocnaddsimulator --namespace ocnadd-deploy
3.1.6 Verifying ATS Deployment
Run the following command to verify ATS deployment.
helm status <release_name> -n <namespace>Once ATS and Stub are deployed, run the following commands to check the pod and service deployment:
To check pod deployment:
kubectl get pod -n ocnadd-deployTo check service deployment:
kubectl get service -n ocnadd-deploy3.1.7 Enable TLS Support on OCNADD ATS
If user has enabled TLS support on ATS deployment as mentioned in Enabling TLS Support on ATS section, follow the steps listed below:
- Generate .jks File for the Jenkins Server
- Enable the ATS GUI with HTTPS during Installation
- Installing ATS for OCNADD
Generate .jks File for the Jenkins Server
For Jenkins to support GUI access through HTTPS, a .jks file has to be created. Follow the steps below to create the .jks file:
-
Generate the Root Certificate (caroot.cer)
If you have CA signed root certificate and key or your own root certificates, use the same certificates.
If the root certificate (caroot.cer) is not there, follow the steps below to create the certificate to create self-signed certificates. The root certificate is added to the Trust Store (of the browser). However, this step is not required for CA signed certificates.
- Follow any browser's documentation, for example:
-
Mozilla Firefox
- Navigate to the Settings and search for Certificate.
- Click View Certificates in the search results.
- The Certificate Manager window appears on the screen.
- Navigate to the Authorities section and click Import. Upload the caroot certificate.
- A new window appears on the screen, click Trust Options and then click OK.
- Save the changes and restart the browser.
-
Google Chrome
- Navigate to the Settings and search for Security.
- Click Security in the search results.
- Locate Manage Device Certificates and click to select the option.
- The Certificates window appears on the screen. Click Trusted Root Certification Authorities bar.
- Import the caroot certificate.
- Save the changes and restart the browser.
-
- Use the Root Certificate to sign the Application or ATS certificate.
- To generate the key caroot.key, run the command
openssl genrsa 2048 > caroot.key. - Generate the caroot certificate, for example:
[cloud-user@star23-bastion-1 edo]$ openssl req -new -x509 -nodes -days 1000 -key caroot.key > caroot.cer You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:IN State or Province Name (full name) []:KA Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:BLR Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:ORACLE Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:CGBU Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:ocats Email Address []: [cloud-user@star23-bastion-1 edo]$
- Follow any browser's documentation, for example:
-
Generate Application or Client Certificate
Follow the steps below to generate an application or client certificate:
- Create and edit the ssl.conf file as below:
In the
[alt_names]section, list the IPs through which the ATS GUI is opened. User can add multiple IPs such as IP.1, IP.2, and so on.[ req ] default_bits = 4096 distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name req_extensions = req_ext [ req_distinguished_name ] countryName = Country Name (2 letter code) countryName_default = IN stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name) stateOrProvinceName_default = KN localityName = Locality Name (eg, city) localityName_default = BLR organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company) organizationName_default = ORACLE commonName = Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) commonName_max = 64 commonName_default = ocats.scpsvc.svc.cluster.local [ req_ext ] keyUsage = critical, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth, clientAuth basicConstraints = critical, CA:FALSE subjectAltName = critical, @alt_names [alt_names] IP.1 = 127.0.0.1 IP.2 = 10.75.217.5 IP.3 = 10.75.217.76 DNS.1 = localhost DNS.2 = ocats.scpsvc.svc.cluster.localTo access the GUI with DNS ensure that the
commonName_defaultvalue is the same as the configured DNS name and the format is<service_name>.<namespace>.svc.cluster.local. User can add multiple DNS'es like DNS.1,DNS.2, and so on.To support ATS API's, add
127.0.0.1asIP.1. - Create a Certificate Signing Request or CSR file, as follows:
[cloud-user@star23-bastion-1 ocats]$ openssl req -config ssl.conf -newkey rsa:2048 -days 1000 -nodes -keyout rsa_private_key_pkcs1.key > ssl_rsa_certificate.csr Ignoring -days; not generating a certificate Generating a RSA private key ...+++++ ........+++++ writing new private key to 'rsa_private_key_pkcs1.key' ----- You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated into your certificate request. What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN. There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank For some fields there will be a default value, If you enter '.', the field will be left blank. ----- Country Name (2 letter code) [IN]: State or Province Name (full name) [KA]: Locality Name (eg, city) [BLR]: Organization Name (eg, company) [ORACLE]: Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) [ocats]: [cloud-user@star23-bastion-1 ocats]$ - To view all the components of the file, run the command
openssl req -text -noout -verify -in ssl_rsa_certificate.csr. Verify all the configurations in the file. - Sign the .csr file with the root certificate, as below:
[cloud-user@star23-bastion-1 ocats]$ openssl x509 -extfile ssl.conf -extensions req_ext -req -in ssl_rsa_certificate.csr -days 1000 -CA ../caroot.cer -CAkey ../caroot.key -set_serial 04 > ssl_rsa_certificate.crt Signature ok subject=C = IN, ST = KA, L = BLR, O = ORACLE, CN = ocats Getting CA Private Key [cloud-user@star23-bastion-1 ocats]$ - Verify if the certificate is correctly signed by root certificate, as below:
[cloud-user@star23-bastion-1 ocats]$ openssl verify -CAfile caroot.cer ssl_rsa_certificate.crt ssl_rsa_certificate.crt: OK
- Create and edit the ssl.conf file as below:
- Save the application certificate and the root certificates for future use.
- Add the caroot.cer certificate as a trusted author in the browser.
- The generated application or client certificates cannot be provided directly to the Jenkins server. Follow the steps below:
- Generate the .p12 keystore file, run the following command:
[cloud-user@star23-bastion-1 ocats]$ openssl pkcs12 -inkey rsa_private_key_pkcs1.key -in ssl_rsa_certificate.crt -export -out certificate.p12 Enter Export Password: Verifying - Enter Export Password:You will receive a password prompt, note the password provided for future use.
- Convert .p12 file to .jks file, run the following command:
[cloud-user@star23-bastion-1 ocats]$ keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore ./certificate.p12 -srcstoretype pkcs12 -destkeystore jenkinsserver.jks -deststoretype JKS Importing keystore ./certificate.p12 to jenkinsserver.jks... Enter destination keystore password: Re-enter new password: Enter source keystore password: Entry for alias 1 successfully imported. Import command completed: 1 entries successfully imported, 0 entries failed or cancelledYou will receive a password prompt, provide the same password used for creating .p12 file.
- Ensure that both p12 and jks files have the same password.
- Provide the generate jenkinserver.jks file to the Jenkins Server.
- Convert .p12 file to .jks file, run the following command:
- Generate the .p12 keystore file, run the following command:
Enable the ATS GUI with HTTPS during Installation
Follow the procedure below to enable the ATS GUI with HTTPS during installation:
-
To create the .jks file, see Generate .jks File for the Jenkins Server. You can choose to use the either a CA signed certificate or a self signed certificate.
- Create a Kubernetes secret by using the files created in the Generate .jks File for the Jenkins Server procedure, run the following command:
kubectl create secret generic ocats-tls-secret --from-file=jenkinsserver.jks --from-file=ssl_rsa_certificate.crt --from-file=rsa_private_key_pkcs1.key --from-file=caroot.cer -n scpsvcView the K8s secret, for example:
[cloud-user@star23-bastion-1 ~]$ kubectl describe secret ocats-tls-secret -n scpsvc Name: ocats-tls-secret Namespace: scpsvc Labels: <none> Annotations: <none> Type: Opaque Data ==== caroot.cer: 1147 bytes ssl_rsa_certificate.crt: 1424 bytes jenkinsserver.jks: 2357 bytes rsa_private_key_pkcs1.key: 1675 bytes - After creating the secret, follow the Installing ATS for OCNADD procedure to install the ATS. Once the installation is successfully completed, proceed to the next step.
- The ATS GUI opens with HTTPS protocol. The link to open the GUI appears as https://<IP>:<port>.
For example:
Figure 3-1 HTTPS Address

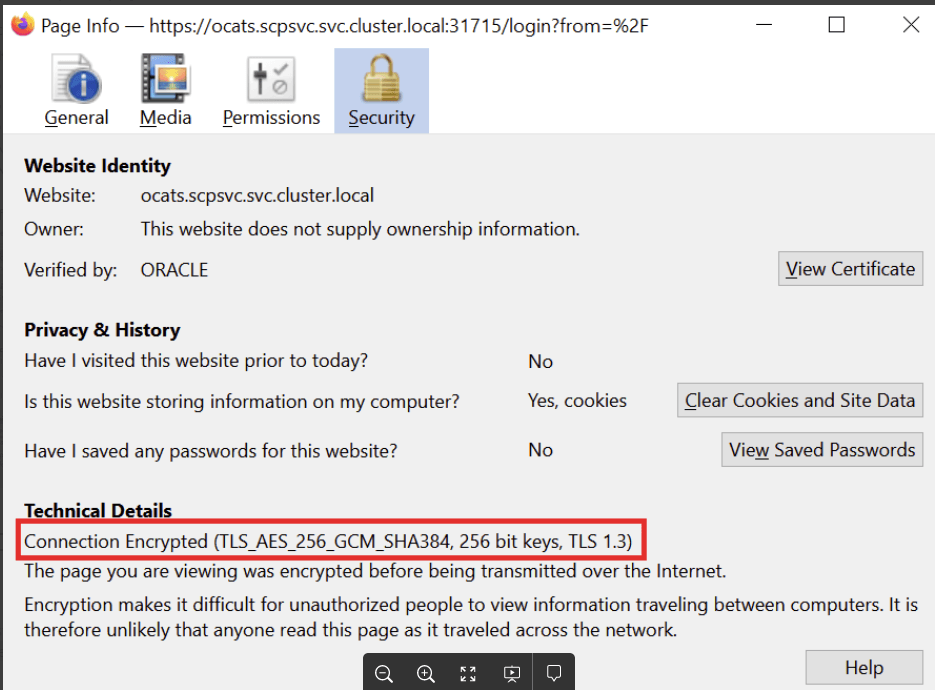
- In Mozilla Firefox browser, click the Lock symbol in the address bar, the page information is displayed as below:
Figure 3-2 Page Information