3 Defining Your PSR Models
Use PSR (Product-Service-Resource) Models in Solution Designer to model end-to-end solutions. A PSR Model includes products, services, resources, and their relationships.
About PSR Models
PSR models in Solution Designer define end-to-end solutions tailored to customer services. The key principle of PSR models is to decouple commercial offers from technical implementations using customer-facing service (CFS) and resource-facing service (RFS) specifications. When new products or services are introduced, the underlying PSR model isolates itself from frequent commercial changes. PSR models provide a CFS layer with technology-agnostic, reusable specifications, and an RFS layer with technology-specific specifications. There are three main types of PSR models:
-
Service Models: Created by service specialists, service models define the complete design of customer services.
-
Technology Models: Created by network specialists, technology models define the design of technology-specific RFSs.
-
Product Fulfillment Models: Created by product specialists, fulfillment models define an end-to-end design of commercial products.
About Service Models
Service models establish relationships between the services represented by products and the resources necessary for their implementation. A service model typically includes CFSs, RFSs, resources, locations, components, and configuration attributes such as design parameters, characteristics, parameter mappings, design policies, and delivery policies.
Service models describe how the customer services (CFSs) are designed and delivered. Solution Designer provides a guided user interface to the service specialists to holistically define an end-to-end configuration of customer services. The key steps in defining a service model are:
-
Select an initiative.
-
Select or create a service domain.
-
Build a service model that includes CFSs, RFSs, resources, locations and their components.
-
Configure attributes for each of the specifications, including:
-
The service design parameters required to fulfill the customer service.
-
The list of characteristics to support the inventory system requirements.
-
The design parameters mapping to the inventory characteristics to provision the services.
-
The standard and advanced design policies to assign appropriate resources in the inventory system.
-
The delivery policies to ensure the complete delivery of the service.
-
About Technology Models
Technology models define how commercial products and technical services are linked, allowing you to associate sold products with the technical services and resources needed to fulfill orders. A technology model includes RFSs and their components, as well as resources and locations.
Technology models describe how technology specific RFSs are implemented and provisioned in the network. Solution Designer provides a guided user interface to the network specialists to holistically define an end-to-end configuration of network technologies. The key steps to define a technology model:
-
Select an initiative.
-
Select or create a technology domain.
-
Build a technology model that includes RFSs, resources, location and their components.
-
Configure attributes for each of the specifications. You can configure the following for the specifications:
-
The service design parameters required to fulfill the customer service.
-
The list of characteristics that must be defined in the inventory systems.
-
The design parameters mapping to the inventory characteristics to provision the services.
-
The standard and advanced design policies to assign resources in inventory system.
-
The delivery policies to ensure the complete delivery of the service.
-
About Product Fulfillment Models
Product fulfillment models define relationships between commercial products and their services. The model connects product specifications to customer-facing service specifications, enabling association between products sold and required services. Product fulfillment models include product specifications, CFSs, fulfillment patterns, routing rules, and fulfillment functions.
Solution Designer guides product specialists in defining the commercial product configuration. The key steps to define a product fulfillment model include:
-
Select an initiative.
-
Select or create a commercial domain.
-
Build a fulfillment model that includes product specifications and its primary and auxiliary services.
-
Configure parameters for each of the specifications. You can configure the following for the specifications:
-
The commercial parameters that are required from the commercial product.
-
The design parameters required to fulfill the customer service.
-
The commercial parameters mapping to the design parameters to fulfill the service.
-
The product specification association to the fulfillment pattern.
-
The routing rules to define the fulfillment functions that is implemented by the fulfillment systems and by granularity.
-
About Guided Process
PSR models can be created in Solution Designer using a guided process, which provides an intuitive, user-friendly interface and a streamlined workflow. The guided process provides a series of sequential steps by dividing the modeling process.
-
A process overview panel on the right side lists the steps involved.
-
The top-of-page indicator shows the current step in the process.
-
Click the steps indicator at the top to expand or collapse it.
-
Click Save to save your progress in any step.
-
Click Cancel to discard any of the changes made.
Creating PSR Models using Guided Process
You can create PSR models, including service models, technology models, and fulfillment models, using a top-down or bottom-up approach:
-
Top-down: A product specialist creates a fulfillment model; a service specialist creates a service model including CFSs, RFSs, resources, and locations.
-
Bottom-up: A network specialist creates a technology model with RFSs, resources, and locations; a service specialist creates a service model with CFSs and uses the technology model to complete the service model. Product specialists create fulfillment models using existing CFSs.
See "About Service Models", "About Technology Models", "About Product Fulfillment Models" for more details on PSR models.
Creating Service Models using Guided Process
-
Click the PSR Models application in the Solution Designer landing page.
-
In the PSR Models application, click Create Service Model.
The Create Service Model overview page opens that lists the steps involved in creating a service model.
-
Click Start to start the guided process and to move to Add general information step.
The Add general information page opens.
The key steps to create service models in the guided process:
-
Adding General Information: Add the general information such as Model name, Model Id, and so on.
-
Selecting Domain: Select service domain.
-
Building Model: Build the model graphically in a canvas and define relationships between CFSs and the specifications.
- Configuring Model: Configure characteristics, design parameters, parameter mappings, design policies, and delivery policies.
Creating Technology Models using Guided Process
Creating technology models follows the same four-step guided process as service models, with technology domains and RFSs.
-
Click the PSR Models application in the Solution Designer landing page.
In the PSR Models application, Click More Actions and select Create Technology Model.
The Create Technology Model overview page opens and lists the steps involved in creating a technology model.
-
Click Start to start the guided process and to move to Add general information step.
The Add general information page opens.
You can create technology models in the guided process by using the following four steps:
-
Adding General Information: Add the general information such as Model name, Model Id, and so on.
-
Selecting Domain: Select the technology domain.
-
Building Model: Build the model graphically in a canvas and create relationships between RFSs and the specifications.
-
Configuring Model: Configure characteristics, design parameters, parameter mappings, design policies, and delivery policies.
Creating Product Fulfillment Models using Guided Process
-
Click the PSR Models application in the Solution Designer landing page.
-
In the PSR Models application, click More Actions and then click Create Product Fulfillment Model.
The Create Fulfillment Model overview page opens that lists the steps involved in creating a fulfillment model.
-
Click Start to start the guided process and to move to Add general information step.
The Add general information page opens.
You can create fulfillment models in the guided process using the following steps:
-
Adding General Information: Add the general information such as model name, model Id, and so on.
-
Selecting Domain: Select commercial domain.
-
Building Model: Build the model graphically in a canvas and create relationships between product specifications and CFSs.
-
Configuring Parameters for Product Fulfillment Model: Configure commercial parameters, design parameters, and parameter mappings.
-
Defining Fulfillment in Product Fulfillment Model: Assign and preview fulfillment pattern flow ( functions and systems).
-
Configuring Routing Rules in Product Fulfillment Model: Configure routing rules to associate fulfillment functions that are implemented by the fulfillment systems or granularity.
Steps for PSR Models in the Guided Mode
This section describes the steps required to create PSR models, including service models, technology models, and product fulfillment models.
Adding General Information
-
In the Add general information page, enter Model name, Model ID, Description, and Initiative. For product fulfillment model, select Capabilities cartridge. You can change the capabilities cartridge only after saving the product fulfillment model. The model ID must follow the naming rules. See "About Naming Rules" for more information on naming rules.
Note:
You cannot modify the model ID and the initiative after the model is saved for the first time. -
Click Continue to progress to the select domain step.
-
For service model, the Select service domain page opens.
-
For technology model, the Select technology domain page opens.
-
For fulfillment model, the Select commercial domain page opens.
-
Selecting Domain
- Do one of the following:
-
For service model, select an existing service domain or create a new service domain.
-
For technology model, select an existing technology domain or create a new technology domain.
-
For product fulfillment model, select an existing commercial domain or create a new commercial domain.
See "Creating Domains" for more information on how to create a service, technology, or commercial domain.
Note:
-
For service model and technology models, you cannot modify the domain after you add the first entity in the Build Model step.
-
You can select only one domain in the service model and technology model, whereas multiple commercial domains can be selected in the product fulfillment model.
-
-
Click Continue to progress to the Build model step.
The Build model page opens.
Building Model
You start building a service model using CFSs, a technology model using RFSs, and a product fulfillment model using product specifications. You can create the following relationships while building the PSR models:
-
Product specification to CFSs. This is applicable for product fulfillment models only.
-
CFS to location, resource, RFS, or another CFS. This is applicable for service models only.
-
RFS to location, resource, or another RFS. This is applicable to service and technology models only.
-
Resource to location, another resource, or RFS. This is applicable to service and technology models only.
-
In the Build model page, click Create to build the model for the first time. If you already have any configuration defined, click Edit which opens the diagram in the edit mode in full screen.
The Edit Configuration page opens.
-
Click + symbol on the canvas to add a specification to the model.
-
For service model, the Customer Facing Services dialog opens.
-
For technology model, the Resource Facing Services dialog opens.
-
For product fulfillment model, click Associate Product Specification and the Products dialog opens.
The specifications ( Products, CFSs, RFSs, resources, and location) dialog lists all the specifications that meet the following criteria:-
Specifications that have the primary domain that match the selected domain.
-
Specifications that have the secondary domains that match the selected domain.
-
Specifications from the released initiatives that match the selected domain.
-
- Do one of the following based on the relationships that you want to
create between Product specifications, CFSs, RFSs, resources, and locations:
-
Add Product specifications to the model: This step is applicable only for product fulfillment models.
In the Product fulfillment mode, select an existing product specification from the list or create a new product specification. You can select primary and auxiliary CFSs for each product specifications. See "Creating New Product Specifications in the Model" for information on how to create product specifications in the Product fulfillment model.
-
Add CFSs to the model: This step is applicable only for service models and product fulfillment models.
Service Model: You can select an existing CFS from the list or create a new CFS. In the service model, when you add a CFS for the first time, you need not add a CFS component. When you add a child CFS to the canvas, you must add a CFS component to relate a CFS.
Product Fulfillment Model: click + in the product specification and click Associate CFS Specification to associate an existing CFS specification or create a new CFS specification.
See "Creating New CFS in the Model" for creating a new CFS in the Edit Configuration page.
- Add Components to the Model:
This step is applicable only to service models and technology models. Click the + symbol on the specification to add a component to the model. To add a child specification to a parent specification, you must create a new component. For example, create a RFS component as a child of the selected CFS. See "About Components" for more details on components.
See "Creating New Components in the Model" for details on creating new components.
After you add the appropriate component to the canvas, click the + symbol on the newly created component to add the child specification.
-
Add RFS to the model: In the technology model, when you add a RFS for the first time, you need not add a RFS component. When you add a child RFS to the canvas, you must add a RFS component to the related parent specification. After you add the RFS component, click the + symbol on the RFS component. In the Resource Facing Service dialog, select an existing RFS specification from the list or create a new RFS specification. See "Creating New RFS in the Model" for information on how to create RFS in the PSR model.
- Add Resource to the model: After you add a resource component in the canvas, click the + symbol on the resource component. In the Resources dialog, select an existing resources specification from the list or create a new resource specification. See "Creating New Resources in the Model" for information on how to create resources in the model.
-
Adding Location to the model: After you add a location component in the canvas, click the + symbol on the location component. In the Locations dialog, select an existing location specification from the list or create a new location. The Locations dialog lists all the locations within the same initiative or the released initiatives. See "Creating Locations in the Model" for information on creating locations in the model.
-
- After building the model, click Continue to progress to the next step.
Creating New Product Specifications in the Model
-
Click New product in the Products dialog.
The New product dialog opens.
-
Enter name, ID, Primary Domain, and description. The ID must be unique and follow the entity naming rules. See "About Naming Rules" for more information.
Note:
The commercial domains selected in the Select Commercial Domain step are displayed in the Primary Domain drop-down list. -
Click Create.
The product specification is created and added to the canvas. The newly created product specifiation utilizes the model's initiative.
Creating New CFS in the Model
-
Click New customer facing service in the Customer Facing Services dialog.
The New customer facing service dialog opens.
-
Enter name, ID, and description. The ID must be unique and follow the entity naming rules. See "About Naming Rules" for more information.
-
Click Create.
The CFS is created and added to the canvas. The newly created CFS utilizes the model's initiative and the domain.
Creating New Components in the Model
-
Click New component.
The New component dialog opens.
-
Enter Name, Type, Minimum Cardinality, Maximum Cardinality, Relationship Type, and Description. Select Relationship type as Config hierarchy for adding a Other Resource resource specification. When you add Other Resource resource specification, it creates a configuration in the UIM run-time.
-
Click Create.
The component is added as a child of the selected specification. You can add multiple components to a selected specification.Note:
You must create components to add a child specification such as CFS, RFS, resource, and locations based on your business requirements.
Creating New RFS in the Model
-
Click New resource facing service in the Resource Facing Services dialog.
The New resource facing service dialog opens.
-
Enter name, ID, and description. The ID must be unique and follow entity naming rules. See "About Naming Rules" for more information.
-
Click Create.
The RFS is created and added to the canvas. The newly created RFS utilizes the model's initiative and the model's domain or the primary domain of its parent specification.
Creating New Resources in the Model
-
Click New resource in the Resources dialog.
The New resource dialog opens.
-
Enter name, ID, and optional description. The ID must be unique and follow entity naming rules. See "About Naming Rules" for more information.
Select the type that matches the UIM's resources. For example, Connectivity Specification, Flow Identifier Specification. Select the Delivery action target check box to mark the resource to be the delivery action target for the delivery policies. Only those resources that have delivery action target selected are available for delivery policies.
-
Click Create.
The resource is created and added to the canvas. The newly created resource utilizes the service model's initiative and the primary domain of the parent specification.
For resource components with Relationship Type as Exclusive, you must add only the resources with the following resource types:-
Custom Object Specification
-
Custom Network Address Specification
-
Device Interface Specification
-
Flow Identifier Specification
-
IPv4Address Resource Extension
-
IPv6Address Resource Extension
-
Telephone Number Specification
-
Creating Locations in the Model
-
Click New location in the Locations dialog.
The New location dialog opens.
-
Enter Name, ID, Type, Place Type and optional Description. The ID must be unique and follow entity naming rules. See "About Naming Rules" for more information.
You can select Site, Address, Address Range, and Location as the Place Type. See "About Locations" for more information on location specification.
-
Click Create.
The location is created and added to the canvas. The newly created location utilizes the service model's initiative.
Configuring Model
To configure a service or technology model:
-
In the Configure model step, in Specification Configuration, you can configure the following:
-
Design Parameters: See "Defining Design Parameters" for details on how to configure design parameters.
-
Characteristics: See "Defining Characteristics" for details on how to configure entity characteristics.
-
Parameter Mapping: See "Mapping Design Parameters" for details on how to configure parameter mappings.
-
Design Policies: See "Defining Design Policies" for details on how to configure design policies.
-
Delivery Policies: See "Defining Delivery Policies" for details on how to configure delivery policies.
-
-
Click Finish to complete the model.
Configuring Parameters for Product Fulfillment Model
-
In the Configure model step, in Specification Configuration, you can configure the following:
-
Commercial Parameters: Add commercial parameters to the product specifications. See "Defining Commercial Parameters" for information on how to add commercial parameters.
-
Design Parameters: Add design parameters to the CFSs. See "Defining Design Parameters" for information on how to add design parameters.
-
Parameter Mapping: Map the commercial parameters of the product specification to the design parameters of the CFS. See "Mapping Commercial Parameters" for information on how to map the commercial parameters to the design parameters.
-
-
Click Continue to proceed to the Define fulfillment step.
Mapping Commercial Parameters in the Model
You map commercial parameters from product specifications to the design parameters of the associated CFS specification. When mapping parameters, the data elements and feature groups must be of the same type. For example, you must map a commercial parameter of boolean type to a design parameter of boolean type only.
You can map the commercial parameters manually, automatically, or through both the methods. You can map the parameters automatically and also choose to map few of them manually.
-
In the PSR Models application, in the product fulfillment model, in the Configure parameters step, expand Parameter mapping and select a CFS specification.
The Parameter Mapping page opens, displaying the CFS with its design parameters and the product specifications with their commercial parameters. -
Map the parameters manually, automatically, or through both the methods.
-
Click the + sign on the commercial parameter and then drag and drop to the target design parameter to manually map the parameters.
-
Click the three dots in the design parameter and click Auto select to automatically map the design parameter to the commercial parameter with the same name and referenced data element type.
-
Click Automap to map all the source commercial parameters with the matching destination design parameters at once. Clicking Automap maps the parameters with the same name and data elements type of that source entity.
You can map a source design parameter to multiple destination parameters.
-
-
After you complete the parameter mapping, click Save.
The parameter mappings are saved and the application returns to the Specification Configuration page.
Defining Fulfillment in Product Fulfillment Model
In the Define Fulfillment step, map each product specification to an available fulfillment pattern. Each product specification can be linked to only one fulfillment pattern, but multiple product specifications can map to the same fulfillment pattern. To remove the link between a product specification and a fulfillment pattern, click the three dots on the product specification and select Remove link to fulfillment pattern.
-
In the product fulfillment model, select the Define fulfillment step in the guided process.
-
Click Edit to map the product specification to a fulfillment pattern.
The Fulfillment canvas appears, showing the product specifications associated with the fulfillment model from the Build Model step. -
Hover over the product specification and select the + sign.
The Fulfillment Patterns drawer opens, listing all fulfillment patterns available for the selected capabilities cartridge.
-
Select a fulfillment pattern to map to the chosen product specification.
-
Click Add.
The fulfillment pattern is mapped to the product specification and appears in the fulfillment canvas.
-
After you complete the mapping, click Done.
The Define fulfillment page appears.
-
Click Continue to proceed to the Configure routing rules step.
Configuring Routing Rules in Product Fulfillment Model
You can define and manage routing rules to determine the destination and processing path of orders based on specific criteria. Routing rules specify how order items are allocated to each order component during decomposition. OSM evaluates each order item in the source component against the conditions defined in the routing rule. If an order item meets all specified conditions, OSM includes it in the target order component.
Use routing rules when the orchestration fulfillment pattern associated with the order item is not sufficient to determine if additional order components are needed.
-
On the Configure Routing Rules page, click Add routing rule.
The Rule builder page opens and displays a template for building a rule for order items.
-
Enter the basic details.
To enter the basic details:-
In the rule builder canvas, click the Basics node.
The Basics drawer opens.
-
Enter the name and objective of the rule. Select Product Centric to include commercial parameters from the product specifications when defining conditions in the Conditions node.
-
Click Add. The details appear in the rule builder canvas.
-
-
Select a fulfillment function to which the rule applies at OSM runtime.
To select a fulfillment function:-
Click the Applies to node.
The Applies to drawer opens.
-
Select a fulfillment function from the available list, which is loaded from the selected capabilities cartridge, then click Add.
The selected function is added to the canvas in the Applies to node.
-
-
Add conditions as needed.
To add conditions to the rule:-
Click the Case 1 node to add a condition.
The Case 1 drawer opens.
-
Choose the If clause:
-
All: The action is applied only when all the conditions are met.
-
Any: The action is applied when any one condition is met.
-
-
Select a parameter from the available list. The list includes order item properties from the capabilities cartridge and commercial parameters from the product specifications (if Product Centric is selected).
-
Select an operator from the list. The available operators are Equals, Not equals, Contains, Equals ignore case, Contains ignore case, Not equals ignore case.
-
Enter a value that the parameter to be validated against.
-
Click Add filter to add more conditions.
Note:
Click Delete to remove a condition. Click Copy to duplicate a condition; a new row with the same details is created.
-
Click Add.
The conditions are added and the number of conditions is shown in the Case 1 node in the rule builder canvas.
-
-
To add more condition cases, click the + sign on the rule builder canvas.
To remove a condition case, click the three dots on the case node and select Delete case.
If the conditions are met, the True path is selected, otherwise the false path is selected.
-
Add an action for each case.
To add an action:-
Click the Action node.
The Action drawer opens.
-
Select the routing option:
-
Route to: Select this if the order item should be routed to a fulfillment system.
-
Ignore routing: Select this to not send a fulfillment request to any fulfillment system.
-
-
Choose a fulfillment system in Which system would you like this item to be routed to?. The fulfillment systems are listed from the selected capabilities cartridge.
-
Select the level of granularity in the How would you like to send this? field. The available options are derived from the capabilities cartridge. Examples include:
- CommercialBundleGranularity
- OrderItemGranularity
- PackageGranularity
- ServiceBundleGranularity
- WholeGranularity or OrderGranularity
-
Click Add.
The details are added to the Action node in the rule builder canvas.
-
-
When you have finished adding actions for all cases, click Done.
The rule is added to the Configure Routing Rules page.
-
View Errors appears if there are any errors in the routing rules.
To edit a routing rule, click the rule name and then click Edit.
To delete a routing rule, click the rule name and then click Delete.
Features in the Configuration Canvas
You can perform the following actions in the Edit Configuration canvas page:
-
When you hover over the entities in the model, Solution Designer highlights the complete relationship hierarchy for that entity.
-
To expand all the entities in the model, click Expand All on the top left. To collapse all the entities in the model, click Collapse All on the top left.
-
To collapse the descendants for a selected entity, click the three dots on the entity and click Collapse. To expand the immediate children for a selected entity, click the three dots on the entity and click Expand. To expand all the descendants for a selected entity, click the three dots on the entity and click Expand All.
-
To remove an entity from the model, click the entity and click Remove in the entity details pop-up. Removing an entity removes it from the canvas but doesn't delete it permanently from Service Specifications and Resource Specifications.
-
To delete a component, click the component and click Delete in the component details pop-up. Deleting a component deletes the component permanently.
-
To delete a relationship between a component and specification, click the three dots on the component and select Remove link to child specifications where child specifications are the specifications that are related to the selected component.
-
You can search for any entity in the PSR model including components by clicking Search using the sticky tool bar. Clicking Search in the sticky tool bar expands the search panel. Type the name of the entity that you want to search in the model. The searched entity is expanded in the model tree and when you click the entity in the search panel, the entity along with its children is shown in the model canvas. When you search for an entity that is referenced by two or more parent entities, the search returns all the instances of that entity. When you search for entities that has the same name, the search returns all the entities that matches the search criteria.
-
You can set the display settings for the PSR model canvas. Click Diagram settings in the sticky tool bar to expand the diagram settings panel. The panel includes display settings to hide and show Entity icon and Entity type to fine-tune the diagram. You can choose the orientation to display the model horizontally or vertically. When you have collapsed some of the entities in the canvas and then modify Diagram settings, the complete PSR model including all the collapsed entities is displayed.
Mobile Service Example of Service Models
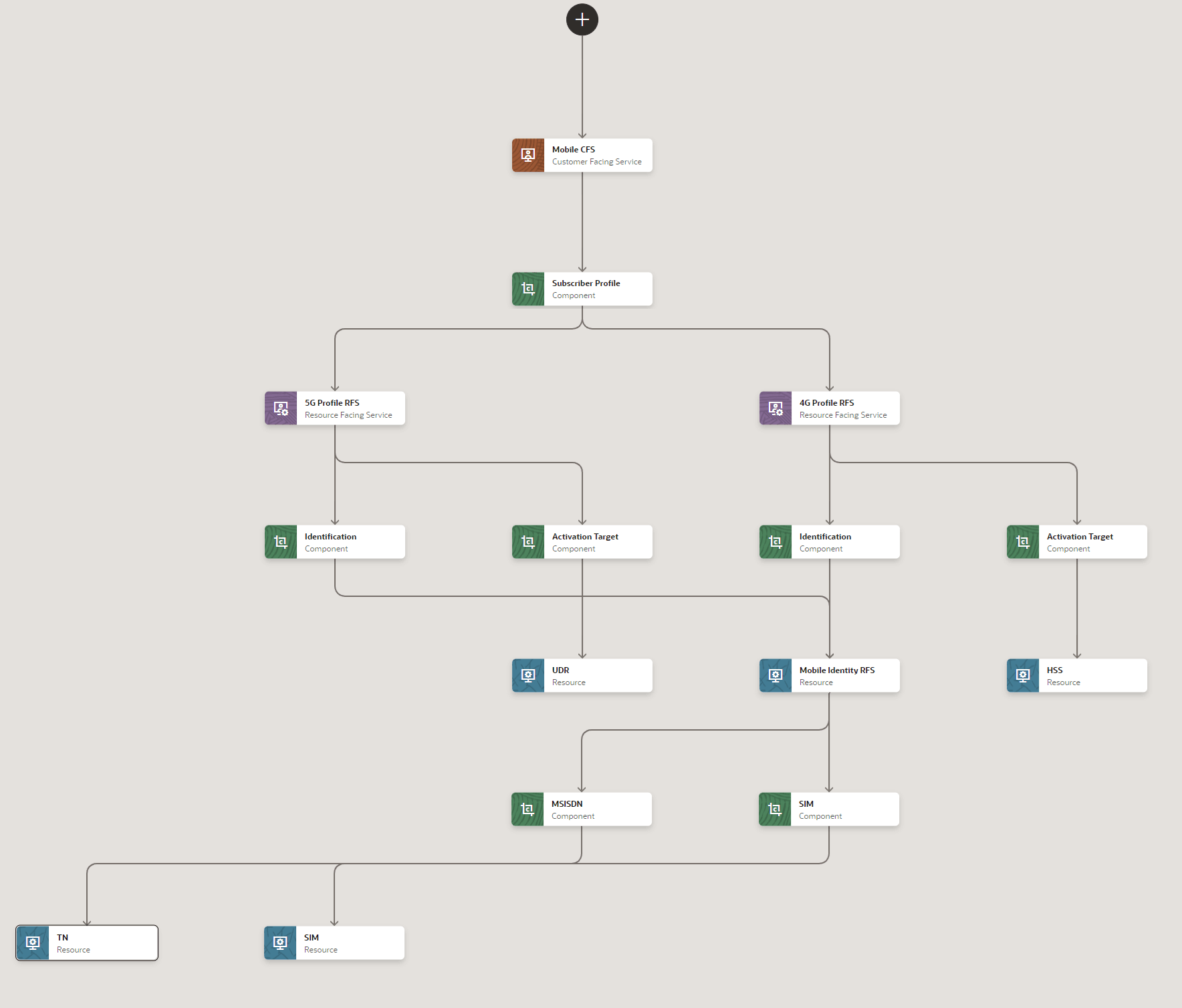
The example is to create a service model for new mobile service. Figure 3-1 is a completed service model showing a design for a Mobile Service. The service model shows the component links for the CFSs, RFSs, and resources.
Figure 3-1 Mobil Service Example of a Service Model
Releasing a New Mobile Service
-
Service catalog administrator creates a new initiative, for example, Mobile.
-
Service specialist creates the service domain such as Mobile. The relative path of the helper class and libraries are added to the service domain.
-
Service specialist creates the Mobile Service service model and builds the service model in the diagram Figure 3-1. See "Creating Service Models using Guided Process" for more information on defining service models.
-
Service specialist creates the design parameters such as Call waiting, Call barring, Call Conferencing, and Service Address for the Mobile CFS. The Service Address design parameter is a feature group which has State and City data elements.
-
Service specialist creates design policies using standard and advanced policies for the Mobile CFS. For example:
-
Standard policy: Select the technology 5G or 4G based on the State design parameter.
-
Advanced policy: Select UDR in the same State as the 5G Profile RFS. See "Defining Design Policies" for more information on defining design policies.
-
-
Service specialist creates the delivery policies to activate the Call waiting, Call barring, and Call conferencing services in the activation system such as ASAP.
-
Service specialist completes defining the Mobile Service service model by transitioning the initiative to the Advanced Configuration status.
-
In the advanced configuration status, publish the initiative to the Test workspace. See "Publishing Initiatives to Generate Design Studio Workspaces" for more information.
The requested Design Studio workspace is generated.
-
You can download the workspace and a developer can write the implementation code in the extended designer class for the advanced policy in Design Studio. See "Extending Solution Designer" in the Developer's Guide for details on the extended designer class.
The developer can upload the extended designer class with its helper classes and third party libraries to object store and then update the relative path in Solution Designer automatically using Object Store Utility or manually by placing them in the S3-compatible object store and updating the relative path in Solution Designer. See "Working with Object Store Utility" in the Developer's Guide for details on the Object Store Utility.
-
After you complete advanced configuration phase, you can transition the initiative through the lifecycle till acceptance testing. You can publish the initiative to Test workspace and the requested cartridges are generated. See "Publishing Initiatives to Generate Test Cartridges" for more information.
-
You can download and deploy the generated cartridge in the UIM run-time for testing purposes.
-
After the initiative is approved for rollout, service catalog administrator publishes it to the production workspace. The production cartridges are generated that can be deployed in UIM run-time environment. The initiative transitions to Released status after the production cartridges are generated. See "Lifecycle of Initiatives" and "Publishing Initiatives to Generate Production Cartridges" for more information.
Upgrading the Mobile Service
After the Mobile initiative is released, the product manager decides to add new Closed User Group (CUG) calling product.
The steps for upgrading the Mobile Service are as follows:
-
Service catalog administrator creates a new initiative Mobile Upgrade.
-
Service specialist revises the Mobile Service service model and revises the Mobile CFS and 5G Profile RFS. See "Revising PSR Models" for more information.
-
Service specialist adds the new CUG parameter to Mobile CFS and 5G Profile RFS.
-
Service specialist creates the design policy to enable the CUG service only for enterprise customers using the standard policy.
-
Service specialist creates the delivery policy to pass the CUG parameter to UDR for 5G Profile RFS.
-
Service catalog administrator publishes the initiative to the Test workspace. The generated cartridges are then deployed in UIM for testing purposes. See "Publishing Initiatives to Generate Design Studio Workspaces" for more information.
-
After the Mobile Upgrade initiative is approved for rollout, service catalog administrator publishes the initiative to the production workspace. The Mobile Upgrade initiative transitions to the Released status after the Mobile Upgrade cartridge is generated. See "Lifecycle of Initiatives" and "Publishing Initiatives to Generate Production Cartridges" for more information.
Importing PSR Models
You can import service or technology models from other environments or download and import sample PSR models from Oracle Software Delivery Cloud. You can export the model that you created in your test environment and import it into your production environment.
As a prerequisite, you must have an initiative that is in Definition status.
To import a model:
-
In the Solution Designer landing page, click the PSR Models application.
-
In the PSR Models application, click More Actions and then click Import.
The Import dialog box opens.
-
You can drag and drop the source file or click the file picker and select a file from your local computer.
-
Select an initiative to which the model should be associated.
-
Click Import.
-
Click Done.
The imported model is listed in the PSR Models page.
Exporting PSR Models
You can export the released service and technology models. The model will be downloaded as a JSON file.
-
In the Solution Designer landing page, click the PSR Models application.
-
In the PSR Models application, search for the PSR model that you want to export.
The PSR Models page opens.
Note:
The PSR model must be in Released status to export it. - Click the three-dot menu on the PSR model and click
Export.
The PSR model is downloaded in the JSON format with the file name same as the PSR model name. You can access the exported model file from the web browser's Downloads folder.
Viewing PSR Models
-
On the Solution Designer landing page, click the application that you want to work with.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the PSR models application, search for a service or a technology model. You can filter the list by:
-
Model Name: Name of the model.
-
Domain: The domain of the model. It can be a service domain, a technology domain, or a commercial domain.
-
Type: The type of the model (Service Models, Technology Models, Fulfillment Models).
-
Status: The current status of the initiative.
-
Initiative: The initiative of the model.
-
Last Updated: The last updated date of the initiatives.
-
-
In the Initiatives application, search for an initiative and click the Initiative Items tab in the initiatives editor page.
-
-
Select a model to view it.
The model details page opens when the model is in the Functional Testing, Acceptance Testing, Approval, or Released status.
The model details page has two tabs:
-
PSR Model: Displays the complete service or technology model in the canvas. Click Explore to view the PSR model in the Edit Configuration page. You can search for an entity in the Edit Configuration page.
-
General Information: Displays the general information of the service or technology model.
The Edit Service Model or Edit Technology Model page opens based on the model type when the model is in the Definition status. The Build model page in the guided process opens which lets you view or edit the model. The default view is to show only CFS or RFS, without the descendants. You can expand and collapse all the child entities using Expand All and Collapse All.
-
-
Do one of the following:
-
Click Cancel in the Create Service Model page or the Create Technology Model page to return to the PSR Models page.
-
Click Go to PSR Models to return to the PSR Models page or Go to Initiatives to return to the Initiatives Items tab in the initiative editor page.
-
Updating PSR Models
Note:
-
You cannot update the initiative or ID after the model is saved for first time.
-
You cannot update the domain after you add the first entity in the Build Model step.
-
In the Solution Designer landing page, click the application that you want to work with.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the PSR models application, search for a service model or technology model that is in the status Definition.
-
In the Initiatives application, search for an initiative and click the Initiative Items tab in the initiatives editor page.
-
-
Select a model to update it.
The Edit Service Model page, Edit Technology Model, or Edit Fulfillment Model page opens. If the PSR model has a domain, the Build model page opens. If the PSR model does not have a domain, the Select domain page opens.
-
You can update the general information, domain, model relationships, and configuration. See "Configuring Service and Resource Specifications" for more information on configuring the specifications. See "Configuring Product Relationships" for information on how to configure product to CFS relationship.
Note:
You cannot update a domain after you add the first entity in the Build model step. -
After you finish updating the details in all the steps, click Finish in the Configure model step.
Clicking Finish returns to the PSR Models page or the Initiative Items tab in the initiatives editor page.
Cloning PSR Models
You can clone the existing service or technology models to create a copy and update the details as necessary. See "About Cloning Entities" for information on the cloning process.
-
In the Solution Designer landing page, click the application that you want to work with.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the PSR Models application, search for a model.
In the PSR models result list page, click Clone.
-
In the PSR Models application, select a PSR model by searching for it.
In the PSR model details page, click Clone.
The Clone Service Model or Clone Technology Model pop-up appears.
-
In the Initiatives application, search and select an initiative. Click the model in the Initiative Items tab in the initiatives editor page.
In the respective models page, click Clone.
The Clone Service Model or Clone Technology Model pop-up appears.
-
-
Enter the ID and update the name, and description as necessary. You must follow entity naming rules. See "About Naming Rules" for more information.
Note:
- You can't select a new initiative when you clone a PSR model in the Definition and the Advanced Configuration status.
- You must select a new initiative that is in Definition status when you clone a PSR model in the Released status.
-
Click Continue.
The respective models page opens with all the details in the guided process pages.
You can update general information, domain, model, and configuration including design parameters, entity characteristics, parameter mapping, design policies, and delivery policies.
Revising PSR Models
You can revise a PSR model that is in Released status. See "About Revising Entities" for information on revising an entity.
-
In the Solution Designer landing page, click the application that you want to work with.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the PSR Models application, search for a model.
The model is listed in the results section in the PSR Models page.
-
In the PSR Models application, select a model by searching for it.
The respective model details page opens.
-
In the Initiatives application, search for an initiative and click the Initiative Items tab in the initiatives editor page.
-
-
Click Revise.
The Revise Service Model or Revise Technology Model or Revise Product Fulfillment Model dialog box opens.
-
Select a different initiative in Definition status and click Continue.
The Create Service Model or Create Technology Model or Create Product Fulfillment Model page opens.
- Update the details as necessary in the revised model. You can add
new product specifications, service specifications (CFSs and RFSs) and resource
specifications (resources, and locations) to the model.
Note:
-
If you want to update any specification that includes design parameters and characteristics in the model, you must first revise that specification in the Service Specifications or Resource Specifications application. See "Revising Service Specifications" and "Revising Resource Specifications" for details on revising specifications.
-
You can update the selected capabilities cartridge to a new version when you revise the product fulfillment model. However, you cannot switch to a different capabilities cartridge.
-
-
After you update the necessary details, click Finish in the Configure Model step.
The application returns to the PSR Models page or the Initiative Items tab in the initiative editor page.
Deleting PSR Models
You can delete PSR models from the PSR Models application or from the Initiative Items tab in the Initiatives application.
To delete a model:
-
In the Solution Designer landing page, click the application that you want to work with.
-
Do one of the following:
-
In the PSR Models application, search for a service model or a technology model.
The model is listed in the results section in the PSR Models page.
-
In the PSR Models application, select a PSR model by searching for it.
The respective model details page opens.
-
In the Initiatives application, search for an initiative and click the Initiative Items tab in the Initiatives details page.
-
-
Click Delete.
A confirmation dialog box appears.
-
Click Delete in the confirmation dialog box.
The PSR model is deleted. If you are deleting a revised model, only the current revision is deleted and the model is reverted to the previously released version.
Note:
You can't delete a model after you complete the Advanced Configuration phase of the associated initiative.