19 Replenishment Parameters
This chapter describes the functionality that allows you to set up and review the replenishment and inventory parameters that are used within the Allocation & Replenishment calculations. The Replenishment Parameters Workspace is where you can set up the replenishment parameters, change parameters, constraint parameters and inventory planning parameters. Once they are defined you can configure rules and conditions to specify where they should be applied. In a similar way to the Network workspace, the rule engine does the heavy work for you and calculates the right parameters at the product and location level using the available assortment and lifecycle information.
You can further specify the priority and the period where the rule should apply (start and end date if applicable). Based on the set up, the rules engine determines the most appropriate rule and then distributes the parameter to each item and location.
Figure 19-1 Rules Engine Process
Replenishment Parameters Workspace, Steps, and Views
The following table lists the workspaces, steps, and views of the Replenishment Parameters task.
Table 19-1 Replenishment Parameters Workspace, Steps, and Views
| Workspace | Step | Tab | Views |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Overview |
|||
|
Scope |
|||
|
Replenishment Parameters |
|||
|
Inventory Plan Parameters |
|||
|
Constraint Parameters |
|||
|
Setup |
|||
|
Review |
|||
|
Filter |
Replenishment Parameters Workspace
The Replenishment Parameters workspace allows you to access all the views listed in the Replenishment Parameters Workspace, Steps, and Views. To build the Replenishment Parameters workspace, perform these steps:
-
From the left sidebar menu, click the Task Module to view the available tasks.
Figure 19-2 Task Module
-
Click the Business Rule Setup activity to access the available workspaces.
-
Click Replenishment Parameters.
-
The Replenishment Parameters wizard opens. You can open an existing workspace, but to create a new workspace, click Create New Workspace.
Figure 19-3 Replenishment Parameters Wizard
-
Enter a name for your new workspace in the label text box and click OK.
Figure 19-4 Enter Workspace Label
-
Select the rule groups you want to work with and click Finish.
Figure 19-5 Workspace Wizard: Rule Groups
Note:
Only the rule groups that are from the Replenishment rule group type are available for selection. The rule group type value is managed in the Manage Rule Groups workspace.
-
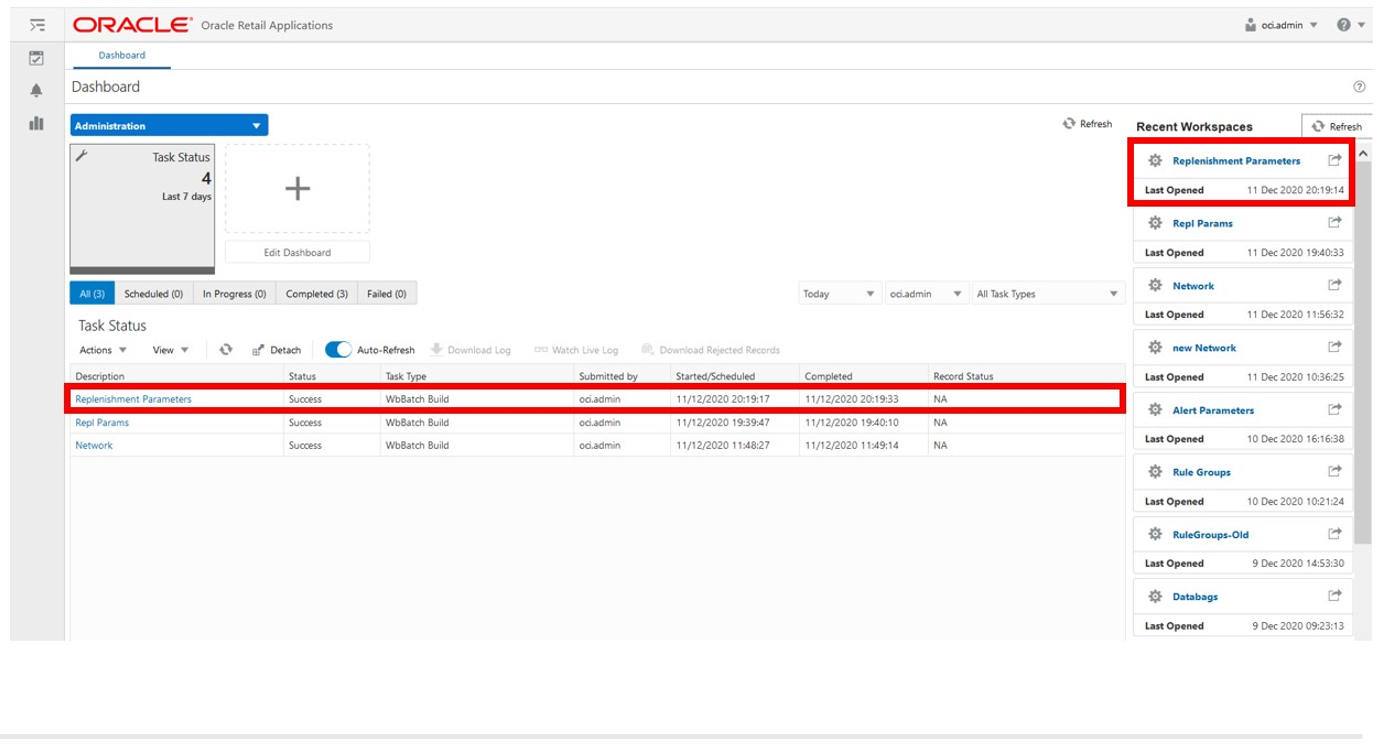
The wizard notifies you that your workspace is being prepared. Successful workspaces are available from the Dashboard.
Figure 19-6 Successful Workspace Build
Note:
The workspace is built using the selected rule group scope. The products, locations, source locations and attributes available in the workspace are the ones in the rule group scope that is managed in the Manage Rule Groups workspace.
Overview Step
This step contains these views:
Statistics View
The Statistics View, under the Overview tab, allows you to review the statistics of the Replenishment Parameters. The view has statistical information regarding the number of valid counts for each set up (for example, Replenishment Parameters, Change Parameters) and rules. It also provides the number of product and location combinations within the workspace.
Figure 19-7 Statistics View
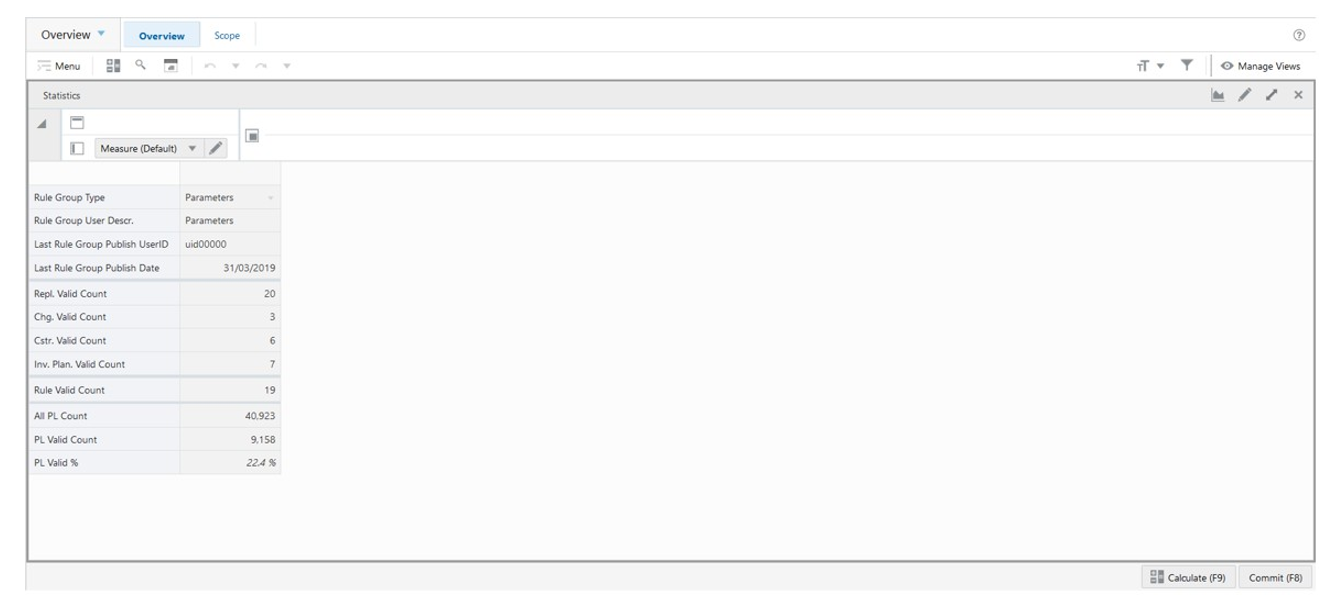
Statistics View - Default Profile Measures
The Statistics view contains the following measures.
Rule Group Type
Rule Group Type is a loaded read-only measure used to display the rule group type that was set up for the rule group in the Manage Rule Group workspace.
Rule Group User Descr.
Rule Group User Description is a loaded read-only measure used to display the user-description that was set up for the rule group in the Manage Rule Group workspace.
Last Rule Group Publish User ID
Last Rule Group Publish User ID is a loaded read-only measure used to display the user-identifier that performed the last rule group’s change in the Manage Rule Group workspace.
Last Rule Group Publish Date
Last Rule Group Publish Date is a loaded read-only measure used to display the date and time when the last rule group’s change was performed in the Manage Rule Group workspace.
Repl. Valid Count
Replenishment Valid Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of valid replenishment parameters that are set up for the rule group.
Chg. Valid Count
Change Valid Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of valid change parameters that are set up for the rule group.
Cstr. Valid Count
Constraint Valid Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of valid constraint parameters that are set up for the rule group.
Inv. Plan. Valid Count
Inventory Plan Valid Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of valid inventory plan parameters that are set up for the rule group.
Rule Valid Count
Rule Valid Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of valid rules that are set up for the rule group.
All PL Count
All Product and Location Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that have a lifecycle phase value.
PL Valid Count
Product and Location Valid Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that have a valid rule assigned.
PL Valid %
Product and Location Valid Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate, in percentage, how much the product and location combinations with a valid rule assigned represent in the total of product and location combinations with a lifecycle phase value. The measure is calculated as:
Figure 19-8 Calculation
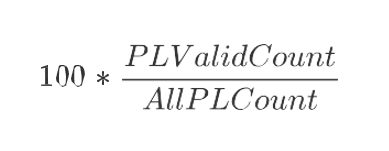
Location Scope View
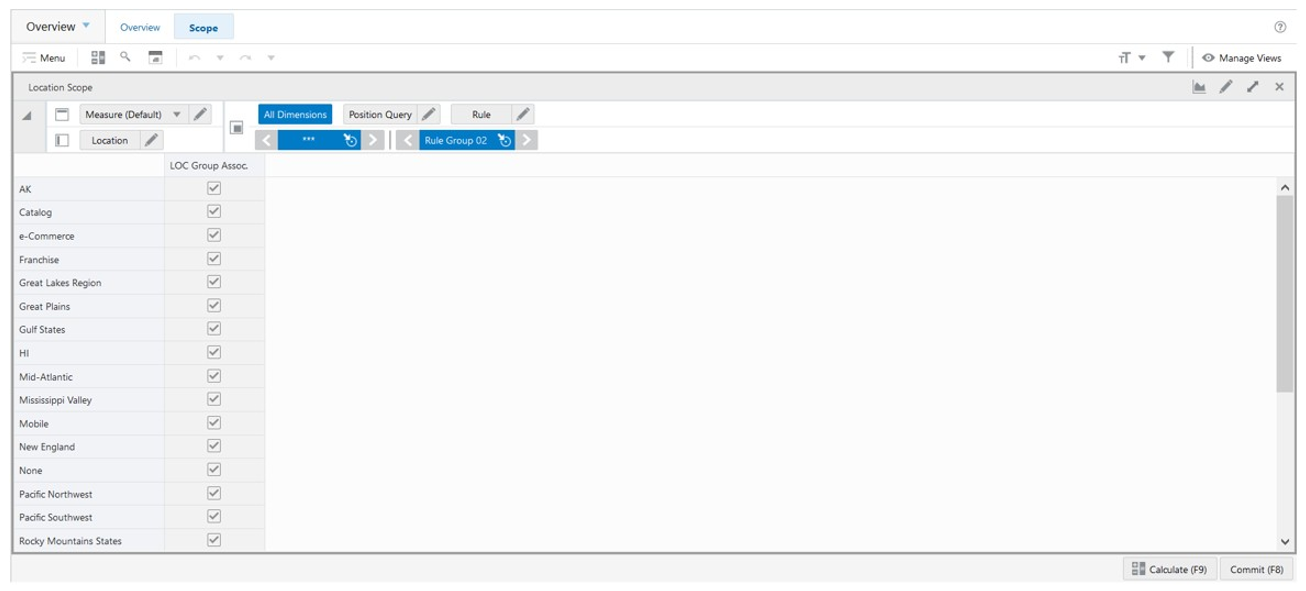
The Location Scope View, under the Scope tab, allows you to review what specific locations are in the scope of a rule group and loaded into the workspace.
Figure 19-9 Location Scope View
Location Scope View - Default Profile Measures
The Location Scope view contains the following measure.
LOC Group Assoc.
Location Group Associated is a loaded read-only measure used to indicate the location groups that are associated with the rule group. This measure is managed in the Manage Rule Groups workspace.
Product Scope View
The Product Scope View, under the Scope tab, allows you to review what specific products are in the scope of a rule group and loaded into the workspace.
Figure 19-10 Product Scope View
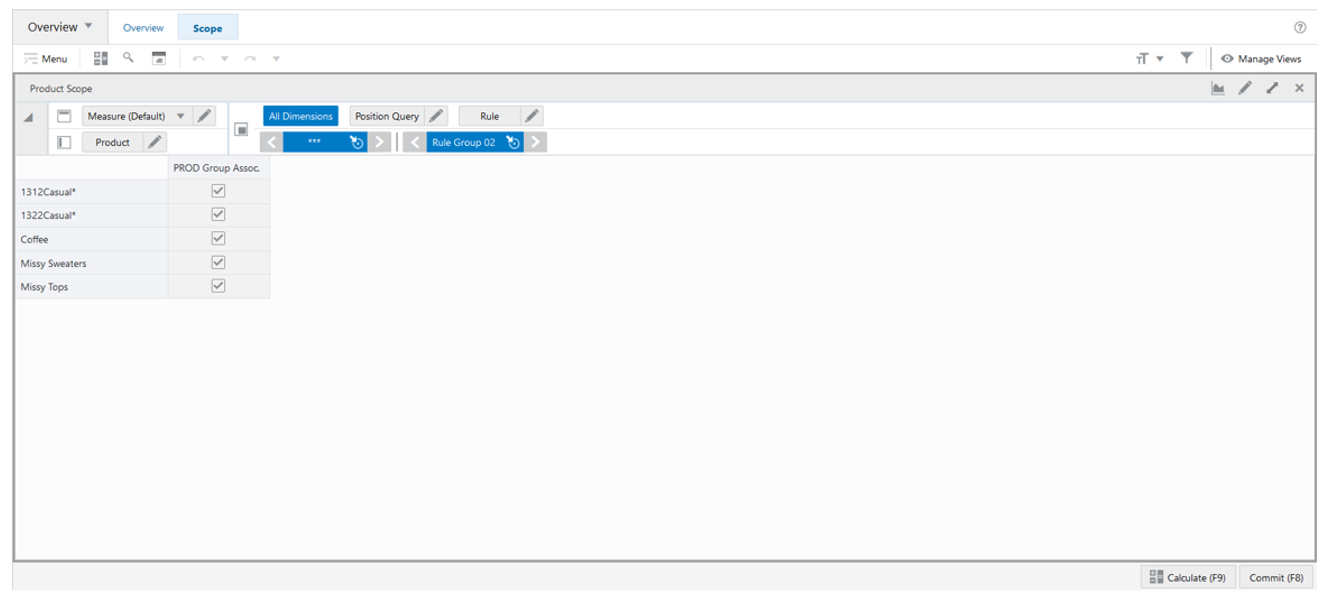
Product Scope View - Default Profile Measures
The Product Scope view contains the following measure.
PROD Group Assoc.
Product Group Associated is a loaded read-only measure used to indicate the products groups that are associated with the rule group. This measure is managed in the Manage Rule Groups workspace.
Replenishment Parameters Step
This step contains these views:
Replenishment Key Concepts
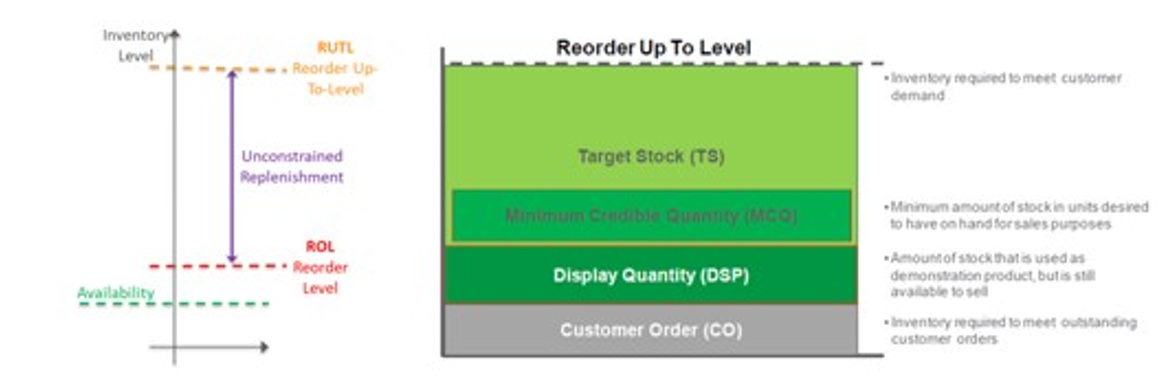
Replenishment parameters are used to specify the Reorder Level (ROL) and the Reorder Up to Level (RUTL) methods along with the associated parameters that is used in generating point in time planned orders.
Reorder Level (ROL) is the inventory level that determines whether an order for replenishment should be placed at the time of review or not. At the time of review, if the stock levels are less than the ROL, then an order for replenishment is placed, otherwise it is ignored until the next cycle.
Reorder Up to Level (RUTL) is level that must be maintained to meet expected service levels for demand fulfilment.
Figure 19-11 ROL and RUTL
The replenishment is a point in time replenishment. In another words, it calculates the replenishment units, for a particular product and location combination, to fulfil the demand from the system date until the next planning day in the planning calendar plus the lead time.
Figure 19-12 Point in Time Replenishment
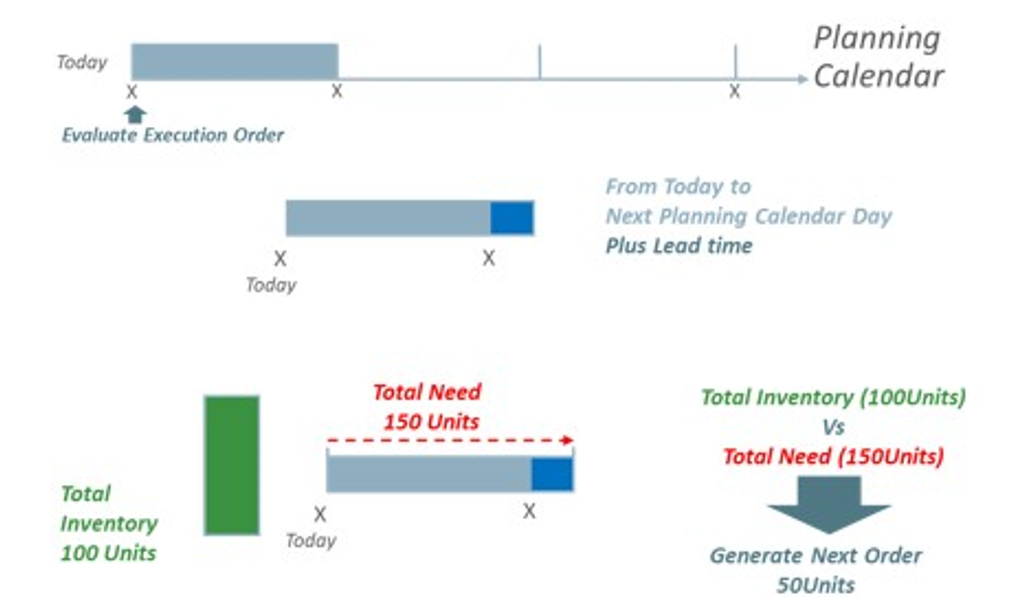
Point in Time Replenishment Methods
Lifecycle Inventory Planning has the following replenishment methods for the ROL and RUTL calculations.
ROL Methods
-
Statistical SS (Statistical Safety Stock): This replenishment method calculates the ROL taking into account the cumulated demand forecast from current date up to the number of days set as Lead Time plus Next Review Time. It considers the Target Service Level (Tgt SL %) and Volatility (Volatility %) in the calculation too
-
Min Time Supply (Minimum Time Supply): This replenishment method calculates the ROL taking into account the cumulated demand forecast from current date up to the number of days defined as minimum time to supply (in days).
-
Min Quantity (Minimum Quantity): This replenishment method calculates the ROL taking into account the value defined as the minimum quantity units.
-
Min Safety Time (Minimum Safety Time): This replenishment method calculates the ROL to the cumulated demand forecast from the first forecast date up to the number of days set to Lead Time plus Next Review Time plus the number of days to shift set in Min Safety Time (days).
-
Min (Minimum): This replenishment method calculates the ROL to the minimum of the active ROL methods.
-
Max (Maximum): This replenishment method calculates the ROL to the maximum of the active ROL methods.
-
Sum (Sum): This replenishment method calculates the ROL to the sum of the active ROL methods.
RUTL Methods
-
Max Quantity (Maximum Quantity): This replenishment method calculates the RUTL taking into account the value defined as the maximum quantity units.
-
Max Time Supply (Minimum Time Supply) : This replenishment method calculates the RUTL taking into account the cumulated demand forecast from current date up to the number of days defined as maximum time to supply (in days).
-
Target DOS (Days Of Supply):This replenishment method calculates the RUTL taking into account the cumulated demand forecast from current date up to the number of days defined as days of supply or up to the number of days of Lead Time plus Next Review Time. The application picks the highest number of days between the two options.
-
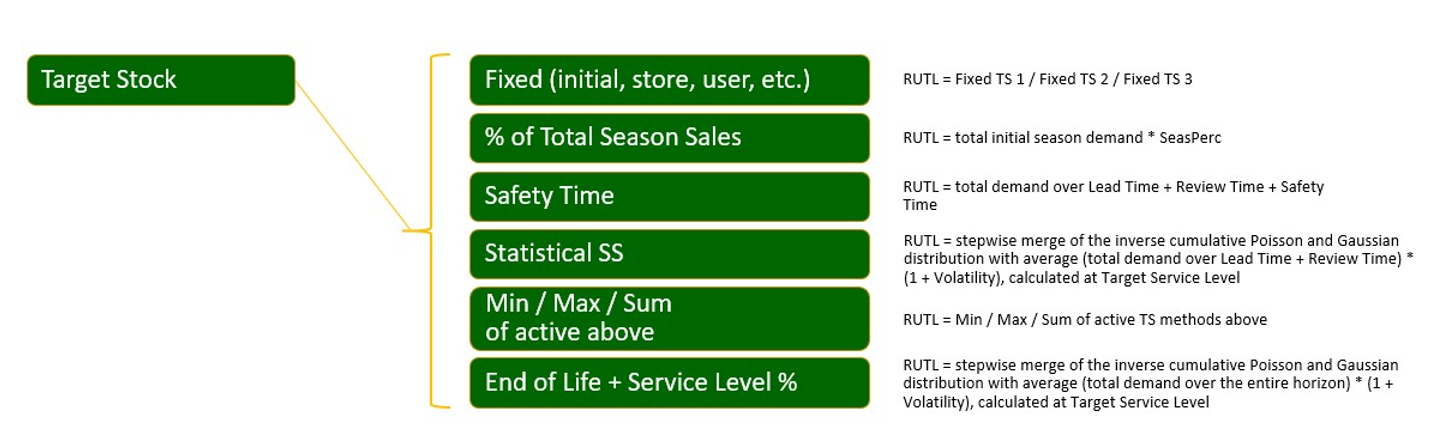
Target Stock: This replenishment method more suitable to the short lifecycle products. The replenishment engine calculates the RUTL based on a target stock quantity. The target stock quantity can be calculated using the following options.
-
Fixed 1: This method sets the target stock to the initial allocation quantity (loaded from external sources).
-
Fixed 2: This method sets the target stock to an user-entered allocation quantity (managed within IPOCS-Lifecycle Allocation and Replenishment).
-
Fixed 3: This method sets the target stock to any other potential source for the initial allocation (this is a placeholder than can be used by customers).
-
Ssn Perc: This method sets the target stock a percentage of the total season sales. Used to define percentage to calculate the value from the total initial forecast for the season.
-
Sft. Time: This method sets the target stock to the cumulated demand forecast from the first forecast date in the future up to the number of days set to Lead Time plus Next Review Time plus the number of days to shift.
-
Stat SS (Statistical Safety Stock): This method sets the target stock to the cumulated demand forecast from current date up to the number of days set as Lead Time plus Next Review Time. It considers the Target Service Level (Tgt SL %) and Volatility (Volatility %) in the calculation too.
-
EOL (End of Life): This method sets the target stock to the cumulated demand forecast from current date up to the end of life date. It considers the Target Service Level (Tgt SL %) and Volatility (Volatility %) in the calculation too.
-
-
Min (Minimum): This method sets the target stock to the minimum of the active Target Stock methods (excluding End of Life).
-
Max (Maximum): This method sets the target stock to the maximum of the active Target Stock methods (excluding End of Life).
-
Sum (Sum): This method sets the target stock to the sum of the active Target Stock methods (excluding End of Life).
-
Min (Minimum): This replenishment method calculates the RUTL to the minimum of the active RUTL methods.
-
Max (Maximum): This replenishment method calculates the RUTL to the maximum of the active RUTL methods.
-
Sum (Sum): This replenishment method calculates the RUTL to the sum of the active RUTL methods.
Figure 19-13 Point in Time Replenishment Methods
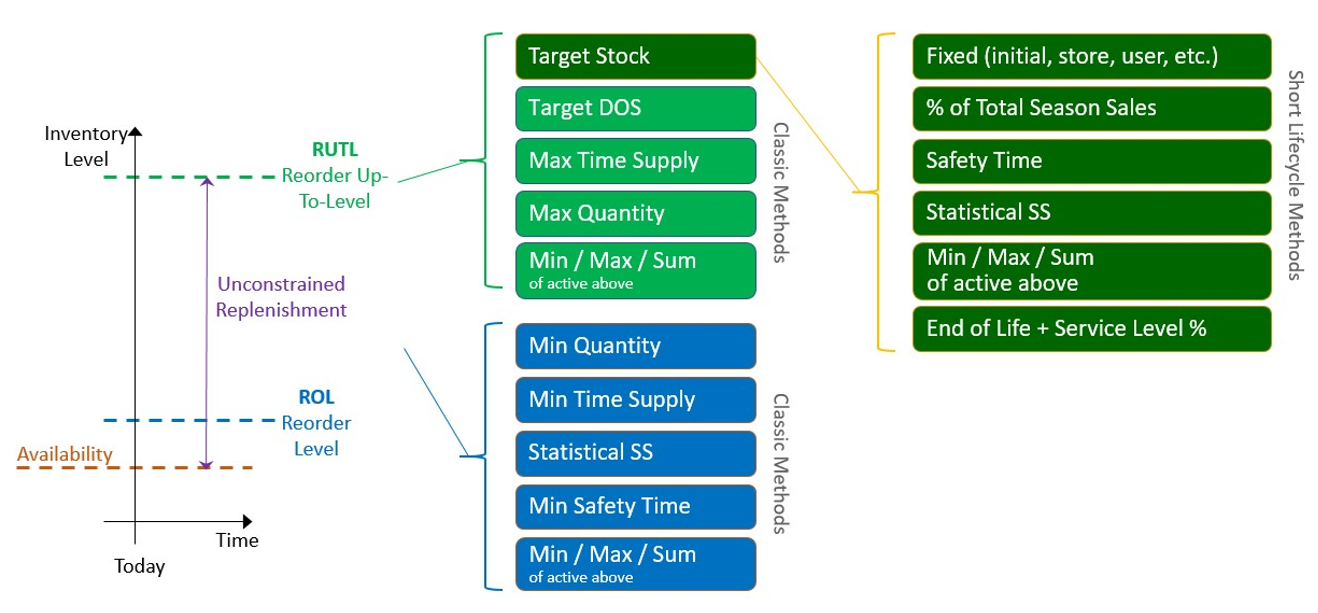
Figure 19-14 ROL and RUTL Method Details
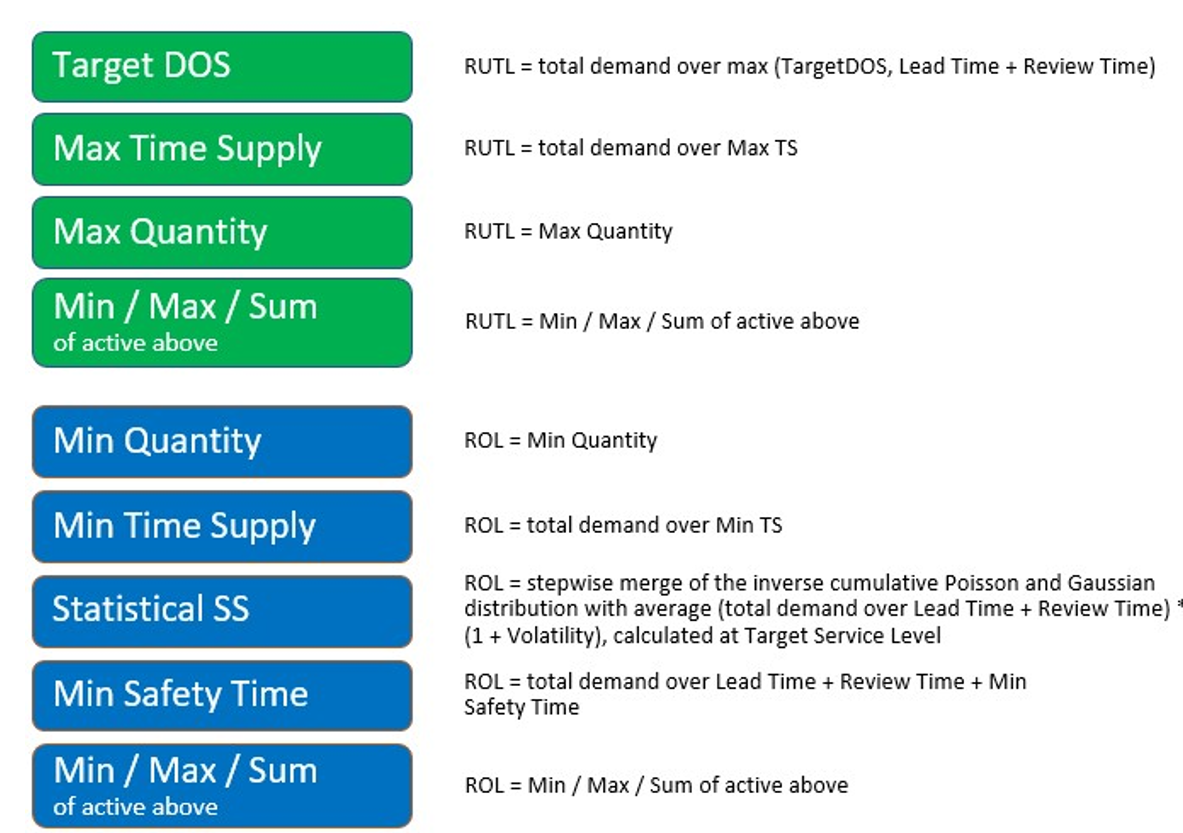
Figure 19-15 ROL and RUTL Method: Target Stock Details
Replenishment Parameters View
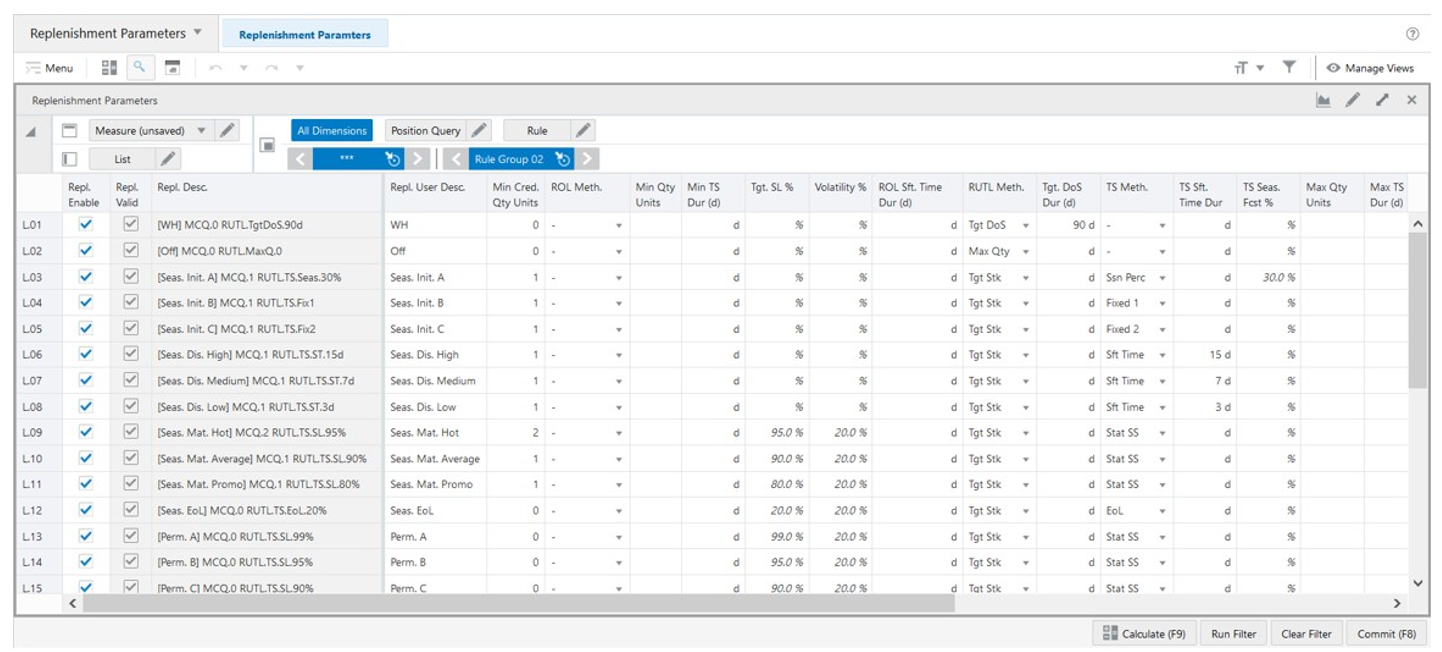
The Replenishment Parameters View, under the Replenishment Parameters tab, allows you to set up of all possible Replenishment Parameters that can be used by the replenishment parameters rules to be applied on products and locations for the Replenishment (Point-In-Time) calculation. Each list (row) in the view represents a different replenishment parameter set up.
Figure 19-16 Replenishment Parameters View
Replenishment Parameters View - Default Profile Measures
The Replenishment Parameters view contains the following measures.
Repl. Enable
Replenishment Enable is an editable measure used to enable or disable a replenishment parameter. Each row (or list) represents a different replenishment parameter.
Repl. Valid
Replenishment Valid is a calculated measure used to indicate if the set up of the replenishment parameter is valid or not. For example, if the ROL and RUTL methods are missing then the replenishment parameter is not valid for the rule engine.
Repl. Desc.
Replenishment Description is a calculated measure used to indicate the replenishment parameter description. The description is calculated based on the replenishment parameter user-defined description and the replenishment parameter set up selected by you.
Repl. User Desc.
Replenishment User Description is an editable measure used to enter a user-defined replenishment parameter description. The final replenishment parameter description takes the user-defined description into consideration. The entered value must not contain a colon punctuation mark (:).
Min Cred. Qty Units
Minimum Credit Quantity Units is an editable measure used to define the minimum amount of stock desired to have on hand for sales purposes.
ROL Meth.
Reorder Level Method is an editable measure to select the method to be used by the replenishment engine to calculate the ROL. Valid values are:
-
-
Option to clear the ROL Method.
-
Min Qty
Option to set up the ROL Method as the Minimum Quantity method. When selected the ROL is calculated to the value set in the measure Min Qty Units.
-
Min TS
Option to set up the ROL Method as the Minimum Time Supply method. When selected the ROL is calculated value of the cumulated demand forecast from current date up to the number of days set in the measure Min TS Dur (d).
-
Stat SS
Option to set up the ROL Method as the Statistical Safety Stock method. When selected the ROL calculation uses the lead time, the next review time in the planning calendar, the service level set in the measure Tgt. SL % and the volatility set in the measure Volatility %.
Note:
When the RUTL method is set to Tgt Stk the RUTL and ROL will have the same value. No need to select the ROL method in this case.
Min Qty Units
Minimum Quantity Units is an editable measure used to fix the minimum amount of stock desired when the ROL method is set to Min Qty.
Min TS Dur (day)
Minimum Time Supply Duration (d) is an editable measure used to fix the number of days to use to calculate the ROL value from the cumulative demand forecast. This measure is used when the ROL method is set to Min TS.
Tgt. SL %
Target Service Level Percentage is an editable measure used to define the service level. This value is used in the ROL and RUTL calculation when the statistical safety stock method is used.
Volatility %
Volatility Percentage is an editable measure used to define the volatility. This value is used in the ROL and RUTL calculation when the statistical safety stock method is used.
ROL Sft. Time Dur (d) RUTL Meth.
Reorder Level Sft. Time Duration (day) Reorder Up to Level Method is an editable measure to select the method to be used by the replenishment engine to calculate the RUTL. The valid values are:
-
-
Option to clear the RUTL Method.
-
Max Qty
Option to set up the RUTL Method as the Maximum Quantity method. When selected the RUTL is calculated to the value set in the measure Max Qty Units.
-
Max TS
Option to set up the RUTL Method as the Maximum Time Supply method. When selected the RUTL is calculated to the value of the cumulated demand forecast from current date up to the number of days set in the measure Max TS Dur (d).
-
Tgt. DoS
Option to set up the RUTL Method as the Target Days of Supply method. When selected the RUTL is calculated to the value of the cumulated demand forecast from current date up to the highest number of days from the following options.
-
Number of days fixed in the measure Tgt. DoS Dur (d)
-
Number of days of lead time plus number of days to the next review time
-
-
Tgt Stk
Option to set up the RUTL Method as the Target Stock method. When selected the RUTL is calculated using the method selected in the measure TS Meth.
Note:
When the RUTL method is set to Tgt Stk the RUTL and ROL will have the same value. No need to select the ROL method in this case.
Tgt. DoS Dur (d)
Target Days of Supply Duration (day) is an editable measure used to fix the number of days to use to calculate the RUTL value from the cumulative demand forecast. This measure is used when the RUTL method is set to Tgt DoS.
TS Meth.
Target Stock Method is an editable measure to select the target stock method to be used by the replenishment engine when the RUTL method is Tgt Stk. The valid values are:
-
-
Option to clear the target stock Method.
-
Fixed 1
When selected the target stock is calculated to the value set in the measure TS Fixed 1 (initial allocation).
-
Fixed 2
When selected the target stock is calculated to the value set in the measure TS Fixed 2 (manual allocation).
-
Fixed 3
When selected the target stock is calculated to the value set in the measure TS Fixed 3 (placeholder for other source of allocation).
-
Ssn Perc
When selected the target stock is calculated as a percentage of the total forecast sales for the season. The percentage used in the calculation is the one set in the measure TS Seas. Fcst %.
-
Sft Time
When selected the target stock is calculated to the value of the cumulated demand forecast from current date up to the number of days of the lead time plus the number of days to the next review time plus the number of days for the Target Stock Safety Time Duration (measure TS Sft. Time Dur (d)).
-
Stat SS
When selected the target stock is calculated to the value of the cumulated demand forecast plus the safety stock from current date up to the number of days of the Lead Time plus the number of days for the next review time plus the number of days for the Target Stock Safety Time Duration (measure TS Sft. Time Dur (d)). It also considers the service level set in the measure Tgt. SL % and the volatility set in the measure Volatility % when calculating the target stock.
-
EOL
When selected the target stock is calculated to the value of the cumulated demand forecast plus the safety stock from current date up to the number of days to reach the end-of-life date. It also considers the service level set in the measure Tgt. SL % and the volatility set in the measure Volatility % when calculating the target stock.
-
Min
When selected the target stock is the minimum value from the methods of Fixed, % of Total Season Sales, Safety Time and Statistical SS.
-
Max
When selected the target stock is the maximum value from the methods of Fixed, % of Total Season Sales, Safety Time and Statistical SS.
TS Sft. Time Dur (d)
Target Stock Sft. Time Duration (day) is an editable measure used to set the number of days for the stock safety. This value is used in the target stock calculations when the RUTL method (RUTL Meth.) is set to Tgt Stk and the target stock method (TS Meth.) is set either to Sft Time or to Stat SS.
TS Seas. Fcst %
Target Stock Seasonal Forecast Percentage is an editable measure used to set the percentage of the Seasonal Forecast that should be used to calculate the target stock. This value is used when the RUTL method (RUTL Meth.) is set to Tgt Stk and the target stock method (TS Meth.) is set Ssn Perc.
Max Qty Units
Max Quantity Units is an editable measure used to fix the maximum amount of stock desired when the RUTL method is set to Max Qty.
Max TS Dur (d)
Max Target Stock Duration (day) is an editable measure used to fix the number of days to use to calculate the RUTL value from the cumulative demand forecast. This measure is used when the RUTL method is set to Max TS.
Order Round
Order Round is an editable measure used to set the percentage on when to round up the orders if the pack size is greater than 1.
Rule Rpl. Count
Rule Replenishment Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of rules that are using the replenishment parameter.
PL Rpl. Count
Product and Location Replenishment Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that associated with the replenishment parameter.
PL Rpl. %
Product and Location Replenishment Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate, in percentage, how much the product and location combinations associated with the replenishment parameter represents in the total of product and location combinations with a lifecycle phase value. The measure is calculated as:
Figure 19-17 Calculation
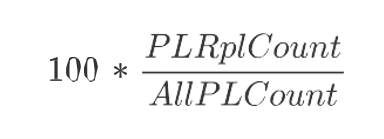
Rpl. User Filter
Rpl. User Filter is an editable measure used to select the replenishment parameter to filter the views by the selected replenishment parameter. This measure is used by the Run Filter action button responsible to calculate the filters applied to the views within the Replenishment Parameters workspace.
Replenishment Change Parameters Concept
Replenishment change parameters allows you to set up parameters to override the system calculated Re-Order Level (ROL) and the Re-Order Up to Level (RUTL) values (calculated from the replenishment parameters set up).
The change replenishment parameters provide the following capabilities. You can:
-
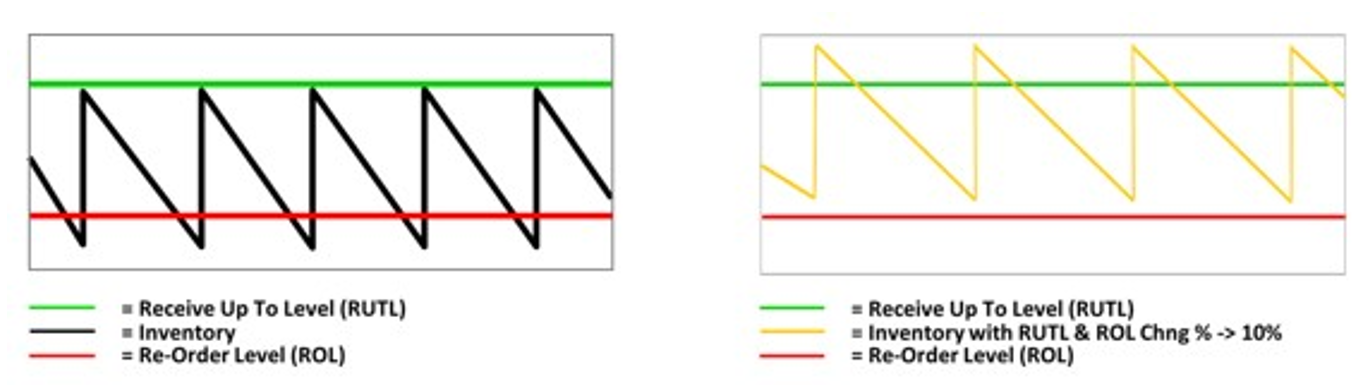
Define a percentage to increase or decrease the system calculated ROL and RUTL.
-
Override the replenishment parameters status. When a replenishment parameter status is enabled, the change parameter can force the replenishment parameter status to disable and the other way around.
As an example, the replenishment change parameters can be leveraged to prepare for an upcoming event by incising the RUTL providing the adequate stock to cover the upcoming demand.
Following are some examples of a set up for the change parameters:
-
ON – Overrides replenishment parameters status to Enable OFF – Overrides replenishment parameters status to Disable
-
RUTL +10% – Overrides the system calculated receipt up to level to increase it by 10%
-
RUTL +25 % – Overrides the system calculated receipt up to level to increase it by 25%
-
RUTL -10 % – Overrides the system calculated receipt up to level to decrease it by 10%
-
RUTL -25 % – Overrides the system calculated receipt up to level to decrease it by 25%
Figure 19-18 Replenishment Change Parameters RUTL +10%
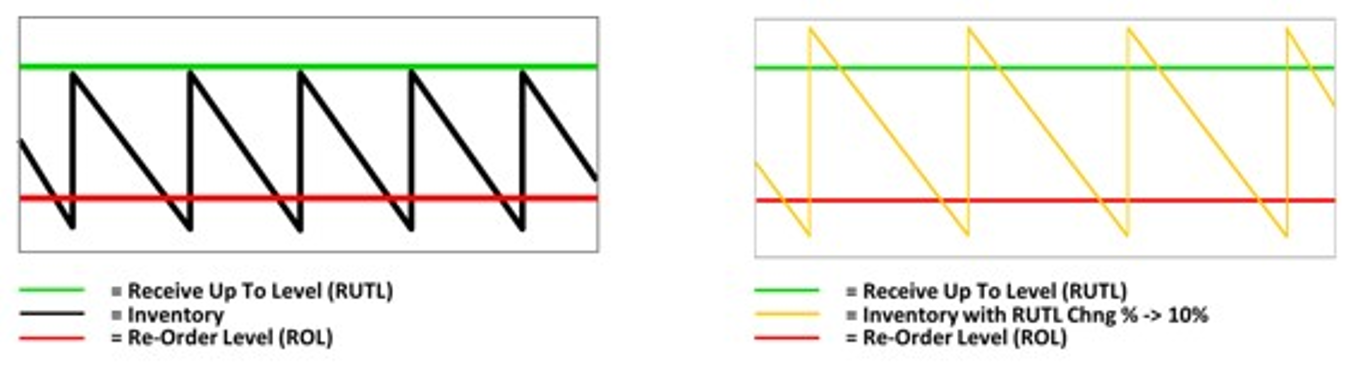
Figure 19-19 Replenishment Change Parameters RUTL +10% & ROL +10%
Replenishment Change Parameters View
The Replenishment Change Parameters View, under the Replenishment Parameters tab, allows you to set up changes to the existing replenishment set up. The change parameters allows you to increase or decrease the calculated RUTL and ROL values and also allows you to override the replenishment status by enabling or disabling it.
Figure 19-20 Replenishment Change Parameters View
Replenishment Change Parameters View - Default Profile Measures
The Replenishment Change Parameters view contains the following measures.
Chg. Enable
Change Enable is an editable measure used to enable or disable a replenishment change parameter. Each row (or list) represents a different replenishment change parameter.
Chg. Valid
Change Valid is a calculated measure used to indicate if the set up of the replenishment change parameter is valid or not. For example, if the replenishment status is kept as default and no ROL and/or RUTL change percentage are indicated then the replenishment change parameter is not valid for the engine.
Chg. Desc.
Change Description is a calculated measure used to indicate the replenishment change parameter description. The description is calculated based on the replenishment change parameter user-defined description and the replenishment change parameter set up selected by you.
Chg. User Desc.
Change User Description is an editable measure used to enter a user-defined replenishment change parameter description. The final replenishment change parameter description takes the user-defined description into consideration. The entered value must not contain a colon punctuation mark (:).
Repl. Status
Replenishment Status is an editable measure that allows you to override the replenishment status. The valid values are: Default : Option to not change the replenishment status and keep the system generated replenishment status.
-
On — Option to force the replenishment to turn on the replenishment
-
Off— Option to force the replenishment to turn off the replenishment
ROL Chng %
Reorder Level Change Percentage is an editable measure used that allows you to increase or decrease the system generated ROL value by the percentage value set in this measure. When the ROL should be increase then enter a positive value. When the ROL should be decreased then enter a negative value.
RUTL Chng %
Reorder Up to Level Change Percentage is an editable measure used that allows you to increase or decrease the system generated RUTL value by the percentage value set in this measure. When the RUTL should be increase then enter a positive value. When the RUTL should be decreased then enter a negative value.
Rule Chg. Count
Rule Change Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of rules that are using the replenishment change parameter.
PL Change Count
Product and Location Change Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that associated with the replenishment change parameter.
PL Change %
Product and Location Change Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate, in percentage, how much the product and location combinations associated with the replenishment change parameter represents in the total of product and location combinations with a lifecycle phase value. The measure is calculated as:
Figure 19-21 Calculation
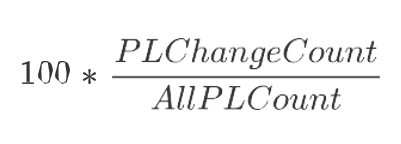
Chg. User Filter
Change User Filter is an editable measure used to select the replenishment change parameter to filter the views by the selected replenishment change parameter. This measure is used by the Run Filter action button responsible to calculate the filters applied to the views within the Replenishment Parameters Rules workspace.
Default Replenishment Parameters View
The Default Replenishment Parameters view allows you to set up the default replenishment strategies.
Figure 19-22 Default Replenishment Parameters View
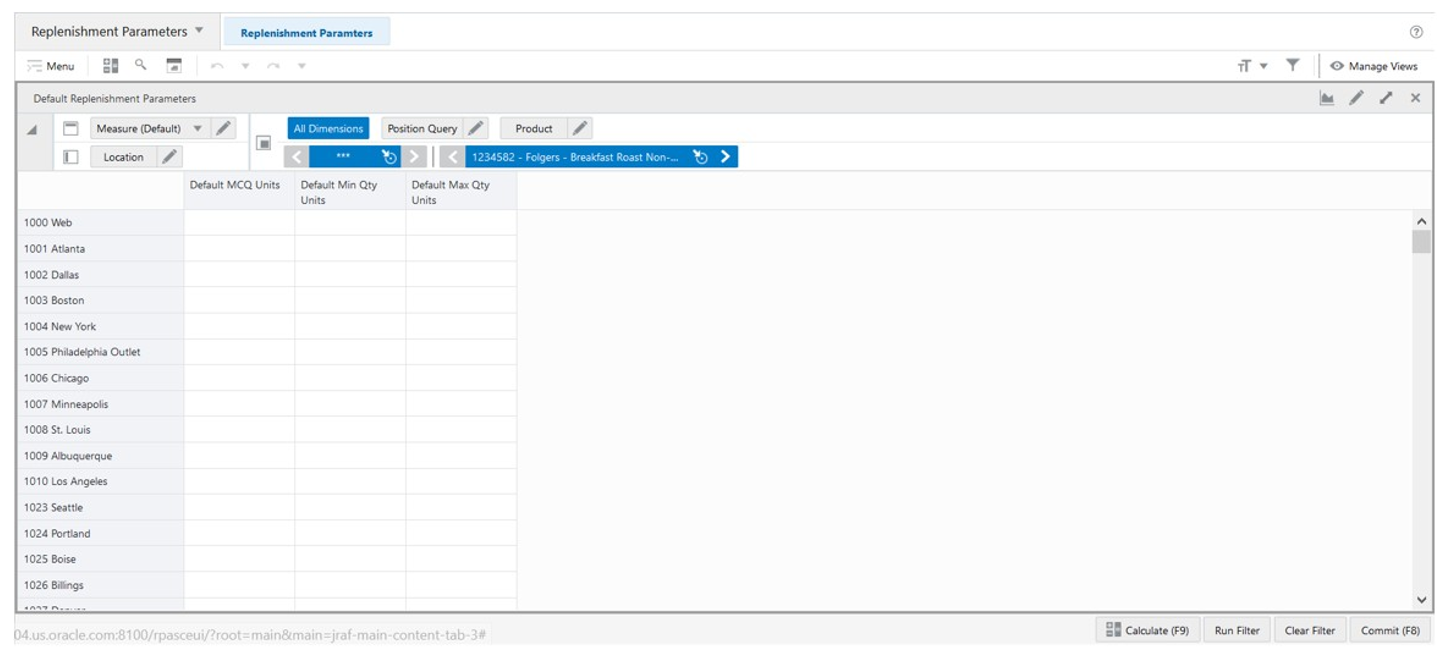
Default Replenishment Parameters View - Default Profile Measures
The Default Replenishment Parameters view contains the following measures.
Default MCQ Units
Default Minimum Credible Quantity Units an editable measure used to define the default Minimum Credible Quantity for the product and location combination.
Default Min Qty Units
Default Minimum Quantity Units is an editable measure used to define the default the minimum amount of stock desired when the ROL method is set to Min Qty.
Default Max Qty Units
Default Max Quantity Units is an editable measure used to define the default maximum amount of stock desired when the RUTL method is set to Max Qty.
Inventory Plan Parameters Step
This step contains this view, Inventory Plan Parameters View.
Inventory Planning Parameters Key Concept
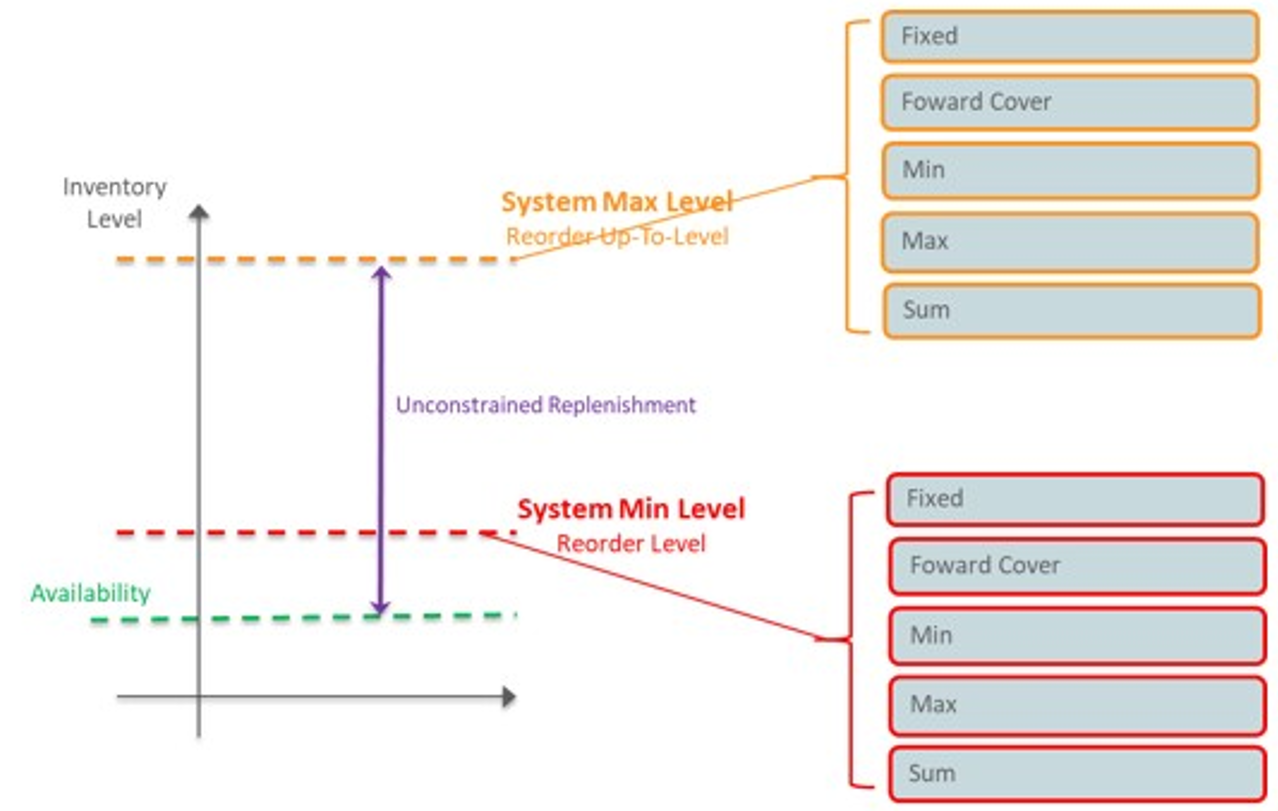
Use Inventory planning parameters to generate the time-phased inventory planning. Inventory parameters specify the System Minimum (which is the reorder level) and the System Maximum (which is the reorder up to level) methods along with the associated parameters is used in generating the time phased plans.
-
System Minimum (ROL) is the inventory level that determines whether an order for replenishment should be placed at point of receipting week. At the point of receipting week, if the stock levels are less than the System Minimum, then an order for replenishment is placed, otherwise it is ignored until the next cycle.
-
System Maximum (RUTL) is the target inventory level. While the replenishment point in time generates the orders at the system date. The time-phased inventory planning provides you with a weekly view on the inventory and the orders to be placed (the inventory plan is a projection based on current point in time network and product lifecycle status).
Time-Phased Replenishment Methods
IPOCS-Lifecycle Allocation and Replenishment has the following replenishment methods for the System Minimum (ROL) and System Maximum (RUTL) calculations.
System Minimum (ROL)
-
Fixed
This method uses the point-in-time replenishment values and does not calculate at every receipt opportunity. Either the ROL or RUTL values can be chosen from the point in time replenishment.
-
Forward Cover
This method calculates the value to cover the demand for the minimum number of days that should set by you in this method.
-
Min
This method uses the calculated value from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods and results is the lowest value between the two.
-
Max
This method uses the calculated value from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods and the result is the highest value between the two.
-
Sum
This method uses the calculated value from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods and the result is the sum both values.
System Maximum (RUTL)
-
Fixed
This method sets the value to a fixed user-defined value.
-
Forward Cover
This method calculates the value to cover the demand for the maximum number of days that should set by you in this method.
-
Min
This method uses the calculated value from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods and results is the lowest value between the two.
-
Max
This method uses the calculated value from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods and the result is the highest value between the two.
-
Sum
This method uses the calculated value from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods and the result is the sum both values.
Figure 19-23 Time-Phased Replenishment Methods
Inventory Plan Parameters View
The Inventory Plan Parameters View, under the Inventory Plan Parameters tab, allows you to set up all the possible Minimum and Maximum Level Methods for the Inventory Plan that can be used to set up the replenishment rules that will then be used by the engine to generate the time-phased replenishment.
Figure 19-24 Inventory Plan Parameters View
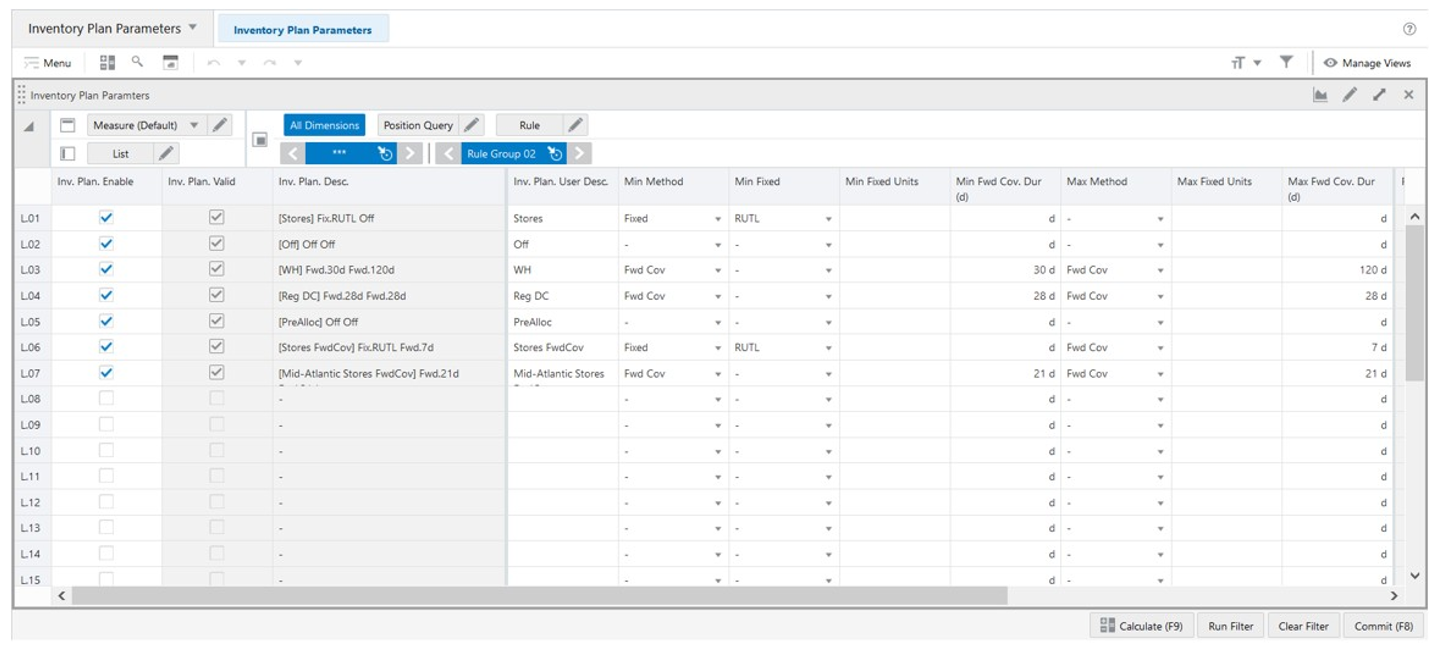
Inventory Plan Parameters View - Default Profile Measures
The Inventory Plan Parameters view contains the following measures.
Inv. Plan. Enable
Inventory Planning Enable is an editable measure used to enable or disable an inventory planning parameter. Each row (or list) represents a different inventory planning parameter.
Inv. Plan. Valid
Inventory Planning Valid is a calculated measure used to indicate if the set up of the inventory planning parameter is valid or not. An inventory planning parameter is considered valid if it is enabled.
Inv. Plan. Desc.
Inventory Planning Description is a calculated measure used to indicate the inventory planning parameter description. The description is calculated based on the inventory planning parameter user-defined description and the inventory planning parameter set up selected by you.
Inv. Plan. User Desc.
Inventory Planning User Description is an editable measure used to enter a user-defined inventory planning parameter description. The final inventory planning parameter description takes the user-defined description into consideration. The entered value must not contain a colon punctuation mark (:).
Min Method
Minimum Method is an editable measure used to select the method to calculate the System Minimum (which is the reorder level) value. The valid values are:
-
Fixed
When this option is selected, then the point-in-time replenishment is used for the calculation and in the measure Min Fixed.
-
Forward Cover
When this option is selected, then the calculation calculates the demand to cover the amount of stock required for the number of days indicated in the measure Min Fwd Cov. Dur (d).
-
Min
When this option is selected, then the calculation sets the value to the minimum value resulted from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods.
-
Max
When this option is selected, then the calculation sets the value to the maximum value resulted from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods.
-
Sum
When this option is selected, then the calculation sets the value to the sum of the values resulted from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods.
Min Fixed
Minimum Fixed is an editable measure used to select how the Fixed method calculates the System Minimum (which is the reorder level) value. The valid values are:
-
-
When this option is selected the result is set to the value in the measure Min Fixed Units.
-
ROL
When this option is selected the result is set to the ROL value from the point-in-time replenishment.
-
RUTL
When this option is selected the result is set to the RUTL value from the point-in-time replenishment.
Min Fixed Units
Minimum Fixed Units is an editable measure used to define the minimum fixed quantity to be used when the Min Method is Fixed and the Min Fixed is -.
Min Fwd Cov. Dur (d)
Minimum Fwd Cover Duration (day) is an editable measure used to define the minimum number of days of cover to be used when the Min Method is Forward Cover.
Max Method
Maximum Method is an editable measure used to select the method to calculate the System Maximum (which is the reorder up-to level) value. The valid values are:
-
Fixed
When this option is selected the calculation sets it to the value in the measure Max Fixed Units.
-
Forward Cover
When this option is selected, then the calculation calculates the demand to cover the amount of stock required for the number of days indicated in the measure Max Fwd Cov. Dur (d).
-
Min
When this option is selected, then the calculation sets the value to the minimum value resulted from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods.
-
Max
When this option is selected, then the calculation sets the value to the maximum value resulted from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods.
-
Sum
When this option is selected, then the calculation sets the value to the sum of the values resulted from the Fixed and Forward Cover methods.
Max Fixed Units
Maximum Fixed Units is an editable measure used to define the maximum fixed quantity to be used when the Max Method is Fixed.
Max Fwd Cov. Dur (d)
Maximum Fwd Cover Duration (day) is an editable measure used to define the maximum number of days of cover to be used when the Max Method is Forward Cover.
Rule Ivp. Count
Rule Inventory Planning Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of rules that are using the inventory planning parameter.
PL Ivp. Count
Product and Location Inventory Planning Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that associated with the inventory planning parameter.
PL Ivp. %
Product and Location Inventory Planning Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate, in percentage, how much the product and location combinations associated with the inventory planning parameter represents in the total of product and location combinations with a lifecycle phase value. The measure is calculated as:
Figure 19-25 Calculation
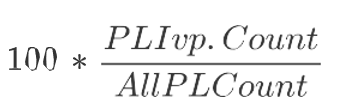
Ivp. User Filter
Inventory Planning User Filter is an editable measure used to select the inventory planning parameter to filter the views by the selected inventory planning parameter. This measure is used by the Run Filteraction button responsible to calculate the filters applied to the views within the Replenishment Parameters workspace.
Constraint Parameters Step
This step contains these views:
Replenishment Constraint Parameters Concept
Replenishment Constraint Parameters allows you to set up parameters to indicate to the replenishment engine how to ration the stock when there is a stock constraint (for example, shortage). When facing stock shortages, the engine needs to adapt and fulfil the remaining stock to the stores in a way that ensures that the highest probability of sales is covered.
Figure 19-26 Example of a Replenishment Constraint
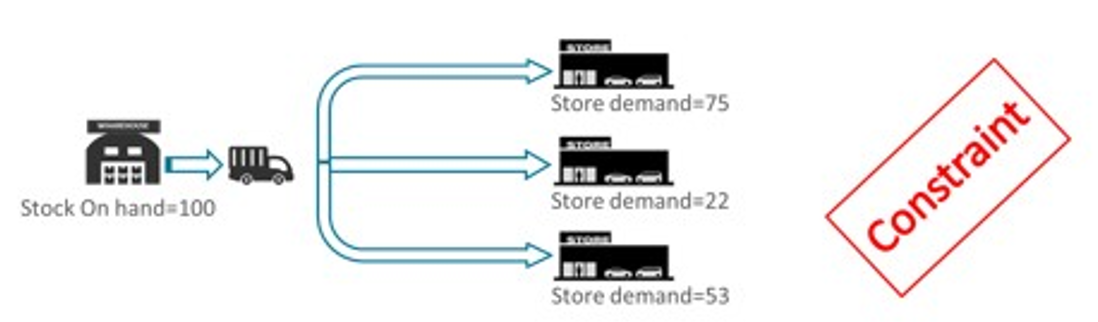
The rationing within the engine is not based on store priority only as that will most likely allocate all the stock to the biggest (or most important) stores and might end up in missing sales opportunities. The replenishment engine approaches rationing is based on the concept of layers. It will try to fulfil the most important layers on all the stores requiring stock (using the store priority) before more to the next layer. This way the replenishment engine maximizes the service level and thus the provability to sell.
The following available layers within IPOCS-Lifecycle Allocation and Replenishment are listed from the highest priority to the lowest priority:
-
Costumer Orders
-
Display Quantity
-
Minimum Credible Quantity
-
Target Stock - Reorder Level (ROL)
-
Target Stock - Reorder Up-To Level (RUTL)
-
Target Stock - Pack
-
Target Stock - Push
Figure 19-27 Example of Rationing based on Layers
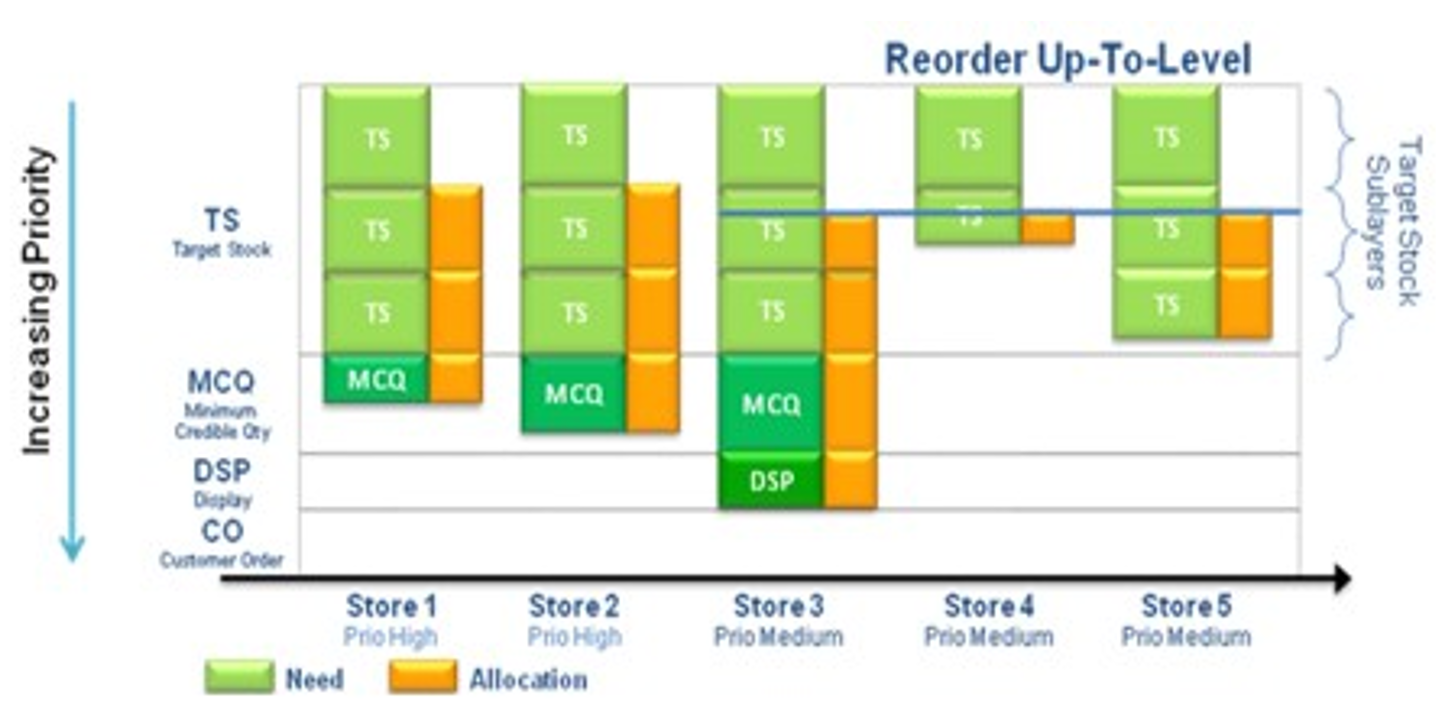
As illustrated in the previous image the engine prioritizes the Store 3 despite the fact it is not the store with the higher priority. However, the Store 3 is where the layer with the higher priority needs to be fulfilled first. Once that layer is fulfilled, the engine moves to the stores the next layer with more priority needs to be fulfilled and so on until the available stock is distributed. Note that if there are two stores for the same layer priority to be fulfilled then the store priority is used.
Constraint Parameter View
The Constraint Parameters View, under the Constraint Parameters tab, allows you to set up the constraints for the engine to manage the stock rationing. The constraints parameters define how the allocation of stock behaves in the engine by changing the priorities of the destination location and/or changing up to what layer of allocation the engine must fulfil. You can also set if the destination location is active or not and set the source location if it is constrained or unconstrained.
Figure 19-28 Constraint Parameters View
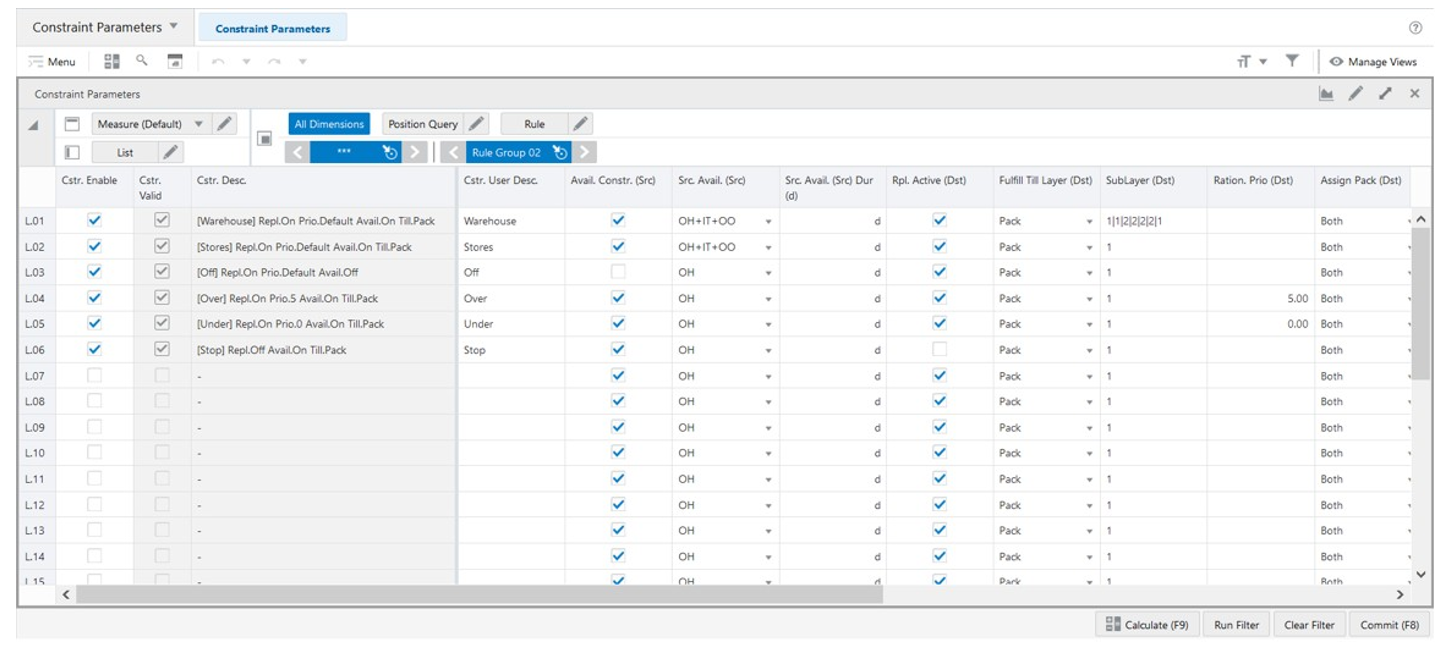
Constraint Parameters View - Default Profile Measures
The Constraint Parameters view contains the following measures.
Cstr. Enable
Constraint Enable is an editable measure used to enable or disable a replenishment constraint parameter. Each row (or list) represents a different replenishment constraint parameter.
Cstr. Valid
Constraint Valid is a calculated measure used to indicate if the set up of the replenishment constraint parameter is valid or not. A replenishment constraint parameter is considered valid if it is enabled.
Cstr. Desc.
Constraint Description is a calculated measure used to indicate the replenishment constraint parameter description. The description is calculated based on the replenishment constraint parameter user-defined description and the replenishment constraint parameter set up selected by you.
Cstr. User Desc.
Constraint User Description is an editable measure used to enter a user-defined replenishment constraint parameter description. The final replenishment constraint parameter description takes the user-defined description into consideration. The entered value must not contain a colon punctuation mark (:).
Avail. Constr. (Src)
Avail. Constraint (Source) is an editable measure used to enable or disable the constraint for the source location.
Src. Avail. (Src)
Source Avail. (Source) is an editable measure to select which stock units are used from the source locations. The valid values are:
-
OH
Option to use stock on hand as the available stock.
-
OH+IT
Option to use stock on hand plus the stock in transit as the available stock. OH+IT+OO : Option to use stock on hand plus the stock in transit plus the stock on-order as the available stock.
Src. Avail. (Src) Dur (d)
Source Avail. (Source) Duration (day) is an editable measure used to define the number of days to get the in-transit and on-order stock. This number of days is used to calculate the available stock at the source location, measure Src. Avail. (Src), when the in-transit and/or on-order option is selected.
Rpl. Active (Dst)
Replenishment Active (Distribute) is an editable measure used to enable or disable the replenishment for the destination location.
Fulfill Till Layer (Dst)
Fulfill Till Layer (Distribute) is an editable measure used to select the layer until which the engine should fulfill the demand at the destination location. You should select one of the following options:
-
1st layer = Customer Order
-
2nd layer = Display Qty
-
3rd layer = Min Credible Qty
-
4th layer = Reorder Level
-
5th layer = Reorder Up to Level
-
6th layer = Pack
-
7th layer = Push
SubLayer (Dst)
SubLayer (Distribute) is an editable measure used to define the sublayer at the destination location for each of the layers until the selected layer in the measure FulFill Till Layer (Dst). Use the | character to separate the number of sublayers between layers. For example, if the layer selected in the measure FulFill Till Layer (Dst) is the 5th layer = Reorder Up-To Level and the sublayers are as follows:
-
Costumer Order has one layer
-
Display Qty has two layers
-
Min Cred Qty has two layers
-
ROL has two layers
-
RUTL has two layers
Then the value for this measure is: 1|2|2|2|2
Ration. Prio (Dst)
Ration Priority (Distribute) is an editable measure used to define a rationing priority for the destination locations.
Assign Pack (Dst)
Assign Pack (Distribute) is an editable measure to define pack types assigned for the destination locations. The valid values are:
-
Complex
Option to select pack which type is complex
-
Simple
Option to select pack which type is complex
-
Both
Option to select all pack types – simple and complex
Min Pack Fill Rate 1 (Dst) %
Minimum Pack Fill Rate 1 (Distribute) Percentage is an editable measure used to define the minimum pack fill rate percentage for 1st round of complex pack assignment.
Min Pack Fill Rate 2 (Dst) %
Minimum Pack Fill Rate 2 (Distribute) Percentage is an editable measure used to define the minimum pack fill rate percentage for 2nd round of complex pack assignment.
Rule Cst. Count
Rule Constraint Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of rules that are using the replenishment constraint parameter.
PL Cst. Count
Product and Location Constraint Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that associated with the replenishment constraint parameter.
PL Cst. %
Product and Location Constraint Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate, in percentage, how much the product and location combinations associated with the replenishment constraint parameter represents in the total of product and location combinations with a lifecycle phase value. The measure is calculated as:
Figure 19-29 Calculation
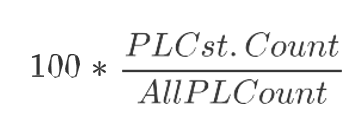
Cst. User Filter
Constraint User Filter is an editable measure used to select the replenishment constraint parameter to filter the views by the selected replenishment constraint parameter. This measure is used by the Run Filter action button responsible to calculate the filters applied to the views within the Replenishment Parameters workspace.
Default Store Priority View
The Default Store Priority View, under the Constraint Parameters tab, allows you to set up the locations priority by product partition to be used by the rationing process.
Figure 19-30 Default Store Priority View
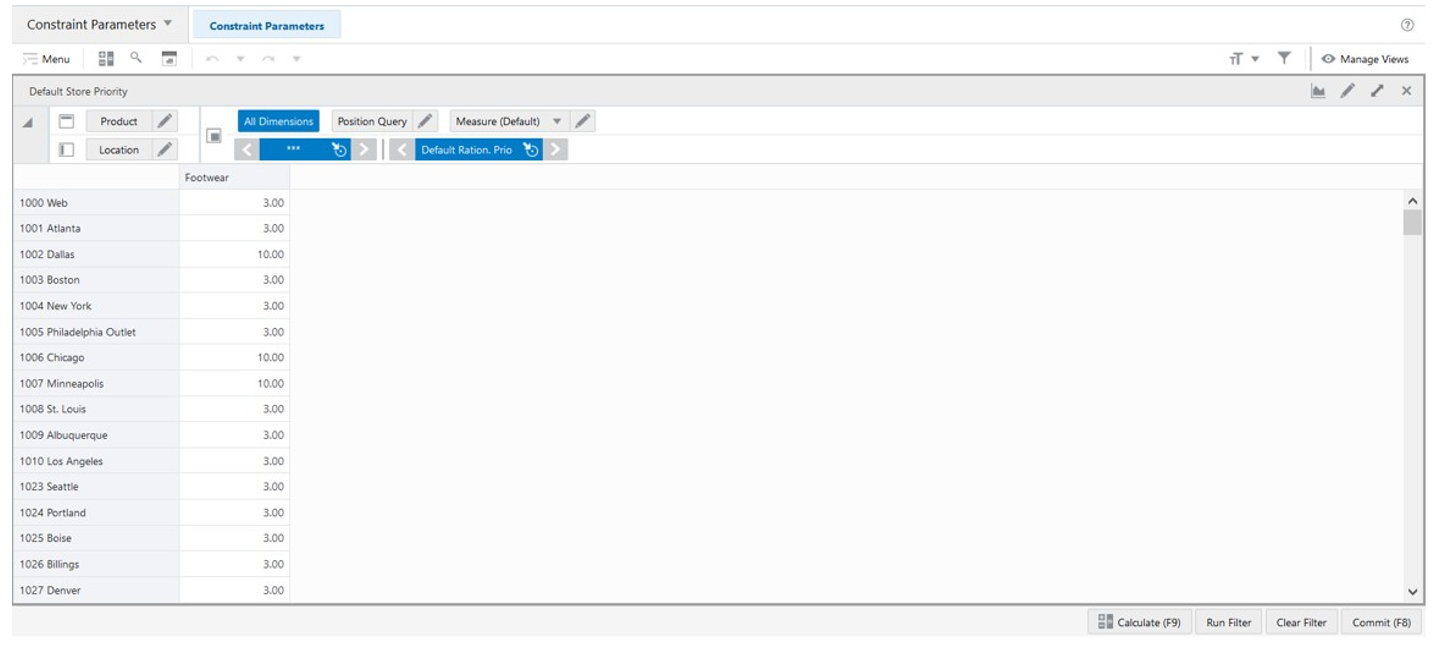
Default Store Priority View - Default Profile Measures
The Default Store Priority view contains the following measure.
Default Ration. Prio
Default Rationing Priority is an editable measure used to define the location’s priority, for the selected product partition, to be used by the engine for the rationing.
Rules Step
This step contains these views:
Rules Concept for the Replenishment Parameters Task
In a similar way to the Network workspace, IPOCS-Lifecycle Allocation and Replenishment provides a powerful engine that enables you to create a set of rules to apply all the set up completed, within the Replenishment Parameters Task (replenishment parameters, replenishment change parameters, replenishment constraint parameters and inventory planning parameters), down to the item and location levels. You can define multiple rules at a higher-level using product, location and product-location attributes and then let the rule engine to calculate at the lowest level, product and location combinations, what is the correct set up to be applied.
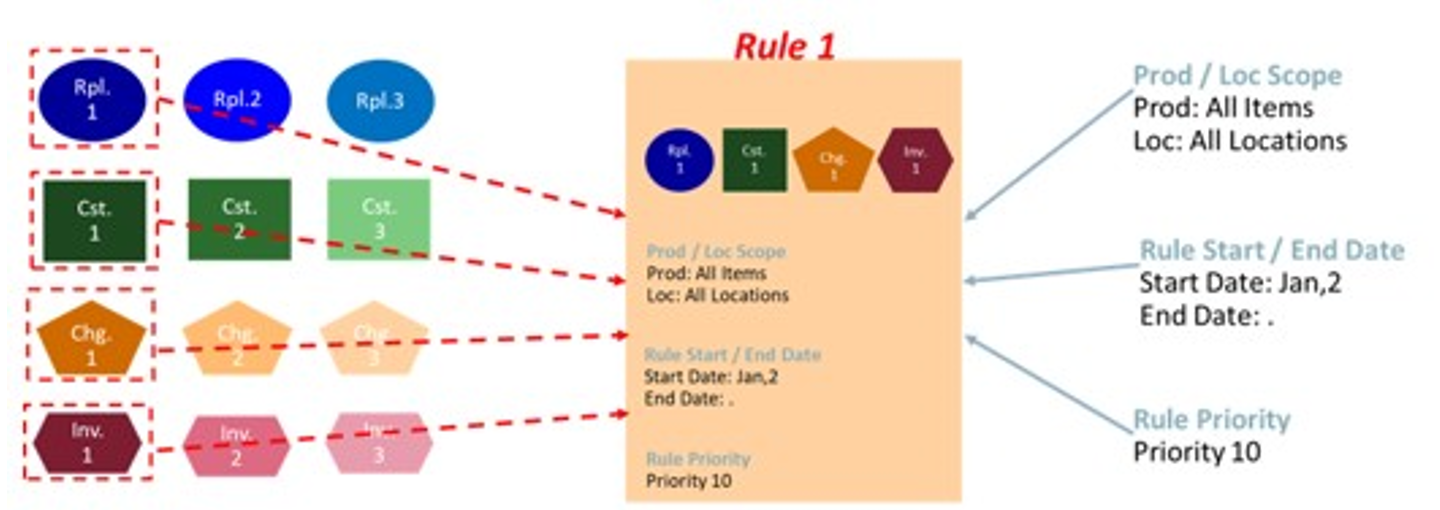
Rules allow to specify the period when the rule should be applied (if applicable) and the rules’ priority. The rule priority will allow the rule engine to choose the correct rule to be applied if a product and location combination fits in more than one replenishment parameter rule (higher the number, higher the priority). The rule start and end date are used by the engine to know if the rule should be considered or discarded. If the system date falls in the start date and end date (or rule dates are empty) then it is considered. Otherwise, it is discarded.
Following are two examples and illustrations of rules for the Replenishment Parameters task.
-
Rule 1
Should be configured to apply the Repl. Param 1, Change Param 1, Constraint Param 1, and Inv. Plan Param 1.
-
The scope of the rule is the scope of the rule group where it is being configured (for example, Sport Bag products and the country France).
-
The condition where the rule applies is for all locations and products in the scope where the product-location lifecycle phase attribute is Discovery.
-
-
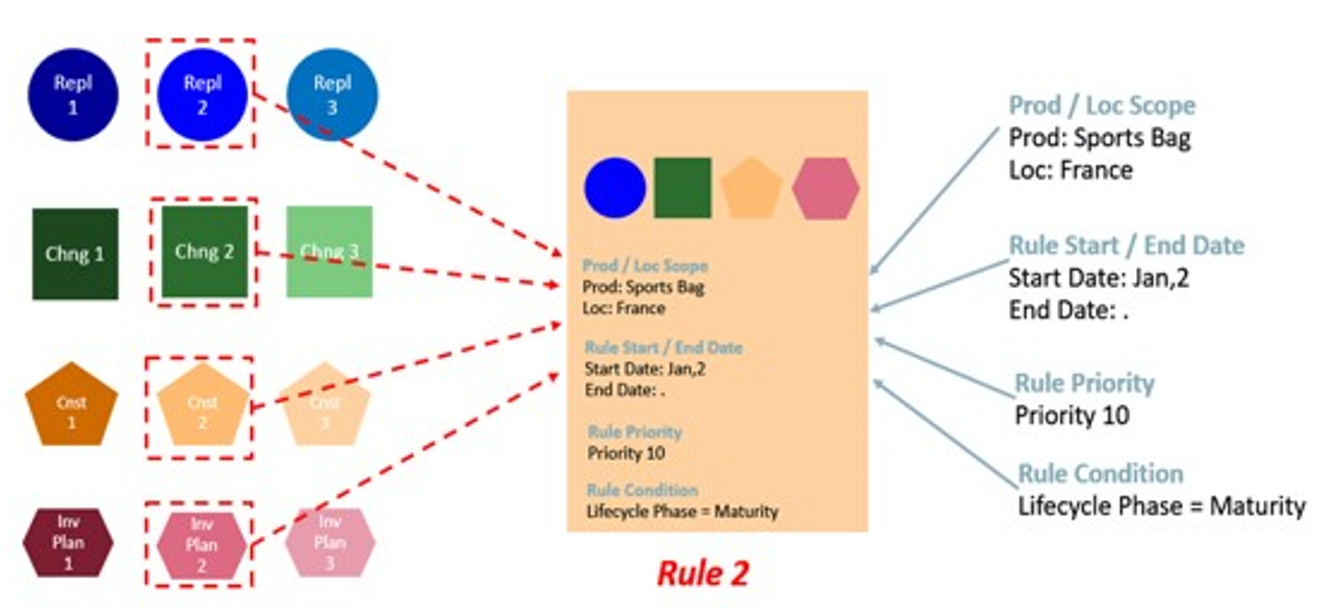
Rule 2
Should be configured to apply the Repl. Param 2, Change Param 2, Constraint Param 2, and Inv. Plan Param 2.
-
The scope of the rule is the scope of the rule group where it is being configured (for example, Sport Bag products and the country France).
-
The condition where the rule applies is for all locations and products in the scope where the product-location lifecycle phase attribute is Maturity.
-
Note:
The condition is used by the rule engine to apply the set up to the product and location combinations that match the condition within the rule scope. The rule scope is defined by the Product Groups and Location Groups associated with the rule’s rule group.
Figure 19-31 Illustration for a Rule 1
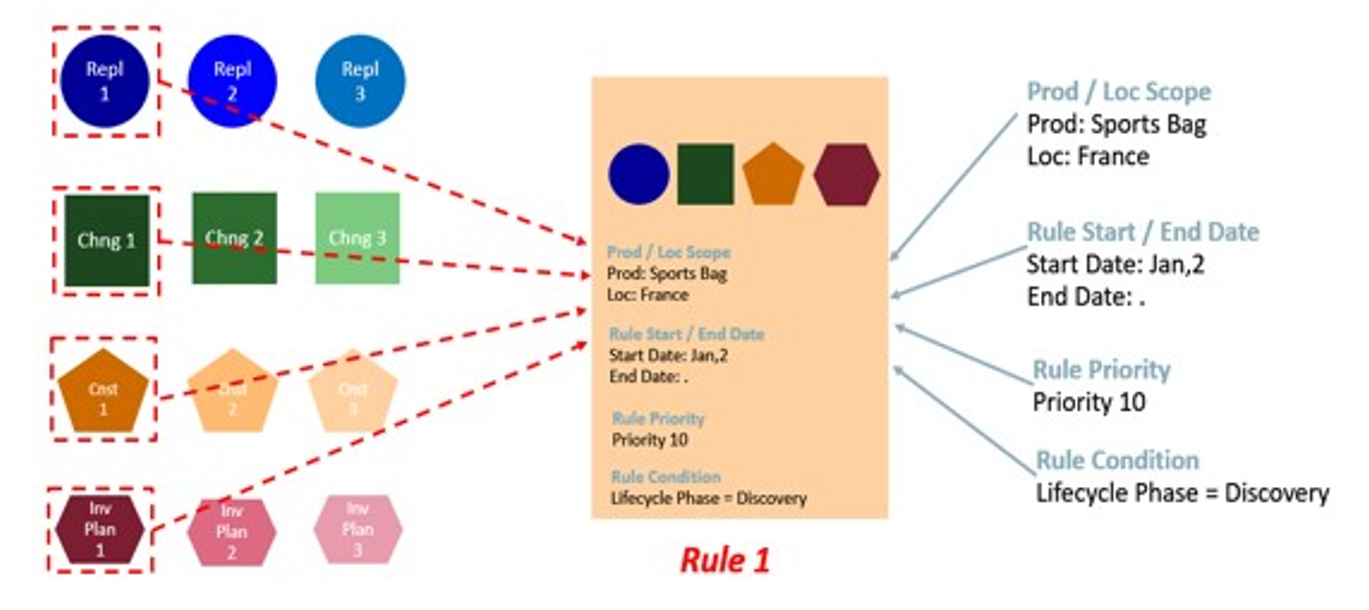
Figure 19-32 Illustration for a Rule 2
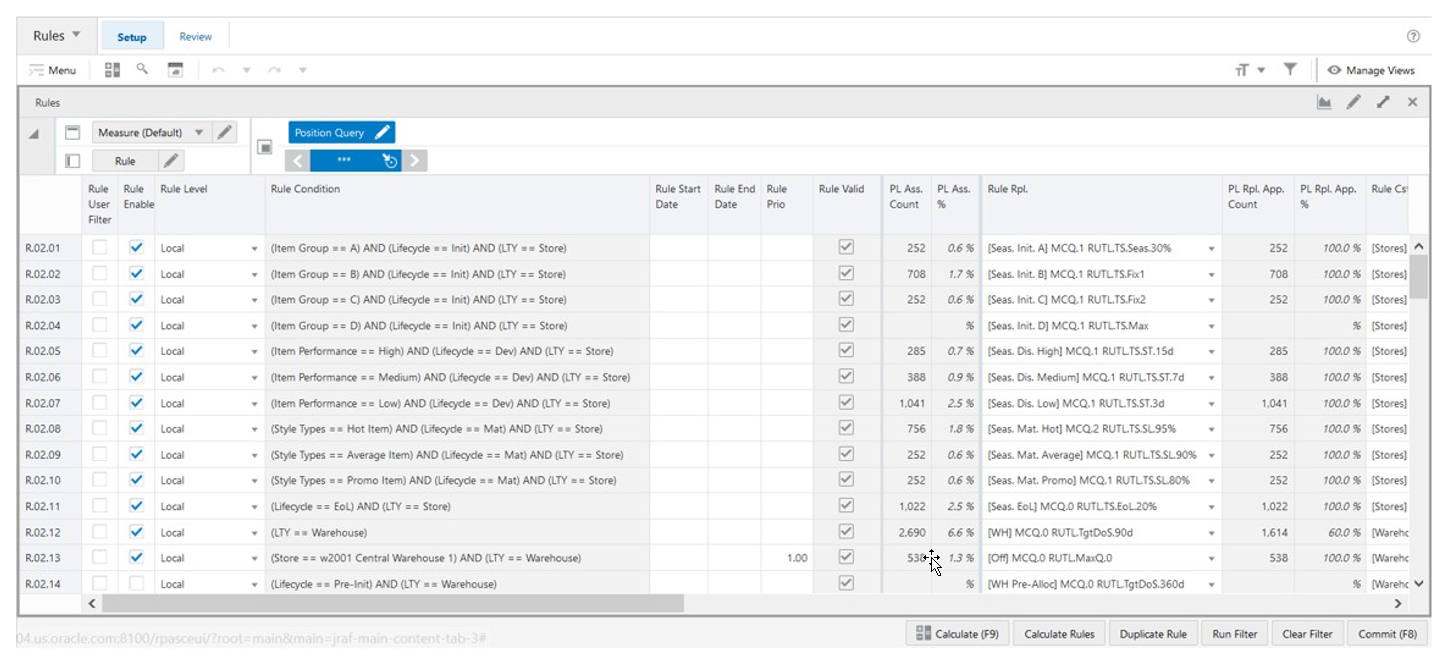
Rules View
The Rules View, under the Setup tab, allows you to configure the rules by enabling them and define the rule start date, end date and priority for each one. Once configured you can set up the rule by selecting the replenishment parameters, replenishment change parameters, replenishment constraint parameters and inventory planning parameters that the rule uses. The product and locations that applies the rule set up is based on the scope of the rule’s rule group (Product Scope and Location Scope views) and the rule’s condition that is set up and managed in the Conditions view.
Figure 19-33 Rules View
Rules View - Measure Profiles
The Rules View contains the following profiles to change the measures that are visible in the view:
-
Default
This profile is used as default by the view. All the available or visible measures are listed and described in the section Measure: Default Profile.
-
Change
This profile displays a subset of measures from the default profile. It focuses on the rule and in the replenishment change parameters measures only. All other parameter related measures are left out of the visible measures.
-
Constraint
This profile displays a subset of measures from the default profile. It focuses on the rule and in the replenishment constraint parameters measures only. All other parameter related measures are left out of the visible measures.
-
Inventory Plan
This profile displays a subset of measures from the default profile. It focuses on the rule and in the inventory planning parameters measures only. All other parameter related measures are left out of the visible measures.
-
Replenishment
This profile displays a subset of measures from the default profile. It focuses on the rule and in the replenishment parameters measures only. All other parameter related measures are left out of the visible measures.
Rules View - Default Profile Measures
The Rules View contains the following measures.
Rule User Filter
Rule User Filter is an editable measure used to select the rule to filter the views by the selected rule. This measure is used by the Run Filter action button responsible to calculate the filters applied to the views within the Replenishment Parameters workspace.
Rule Enable
Rule Enable is an editable measure used to enable or disable a rule. Each row (or list) represents a different rule.
Rule Level
Rule Level an editable measure used to select the level at what the engine will run the rule. The valid options are:
-
Global
In this option the rule engine will fully override the rule group scope that was set up in the Manage Rule Groups workspace and applies the rule to all valid product and location combinations.
-
All Prod
In this option the rule engine will partially override the rule group scope that was set up in the Manage Rule Groups workspace. The rule engine applies the rule to all valid product but for the locations in the rule group location’s scope only.
-
All Loc
The rule engine applies the rule only to the products in the rule group product’s scope and all valid locations. Local : In this option the rule engine applies the rule to products and locations in the rule group scope defined in the Manage Rule Groups workspace.
Rule Condition
Rule Condition is a calculated measure used to indicate the condition for which the rule is valid. The condition is the result of the set up completed in the Conditions view.
Rule Start Date
Rule Start Date is an editable measure used to define a start date for the rule (when the rule should become active). When the rule is valid, and the start date is empty then the rule engine applies it. When the rule is valid, and the start date is populated the rule engine will start to apply it only when the start date is reached.
Rule End Date
Rule End Date is an editable measure used to define an end date for the rule (when the rule should become inactive). When empty, the rule engine assumes that the rule has no end date and if it is valid, then the rule engine applies it. When the rule is valid, and the end date is populated, the rule engine stops applying it starting from the defined date.
Rule Prio
Rule Priority is an editable measure used to define the rule’s priority. The higher the number the higher the priority of the rule is. This rule priority is important to the rule engine as it is used when rules overlap each other. The rule engine uses the rule priority to select which one to apply.
Rule Valid
Rule Valid is a calculated measure used to indicate if the set up of the rule is valid or not. For example, if all replenishment parameters are missing then the rule is not valid for the rule engine. The engine needs at least one of them to be assigned for the rule to be considered as valid.
PL Ass. Count
Product and Location Associated Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that are associated with the rule based on the rule’s condition.
PL Ass. %
Product and Location Associated Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate, in percentage, how much the product and location combinations, where the rule is applicable, represent in the total of product and location combinations within the rule group scope. The measure is calculated as:
Figure 19-34 Calculation

Rule Rpl.
Rule Replenishment is an editable measure for the you to select the replenishment parameter to be applied by the rule. This measure is a picklist populated with all valid replenishment parameters that were set up in the Replenishment Parameters view.
PL Rpl. App. Count
Product and Location Replenishment Applied Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that applies this rule’s replenishment parameter. The calculation takes into account all the valid rules where the product and location combinations fall into and based on the priority calculates the count of product and location that applies the selected replenishment parameter.
PL Rpl. App. %
Product and Location Replenishment Applied Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate, in percentage, how much the product and location combinations, where the rule’s replenishment parameter is applicable, represent in the total of product and location combinations within the rule group scope. The measure is calculated as:
Figure 19-35 Calculation
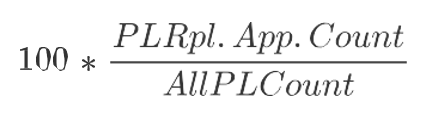
Rule Cst.
Rule Constraint is an editable measure used to select the replenishment constraint parameter to be applied by the rule. This measure is a picklist populated with all valid replenishment constraint parameters that were set up in the Constraint Parameters view.
PL Cst. App. Count
Product and Location Constraint Applied Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that applies this rule’s replenishment constraint parameter. The calculation takes into account all the valid rules where the product and location combinations fall into and based on the priority calculates the count of product and location that applies the selected replenishment constraint parameter.
PL Cst. App. %
Product and Location Constraint Applied Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate, in percentage, how much the product and location combinations, where the rule’s replenishment constraint parameter is applicable, represent in the total of product and location combinations within the rule group scope. The measure is calculated as:
Figure 19-36 Calculation
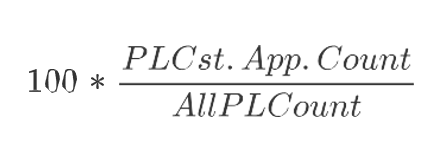
Rule Chg.
Rule Change is an editable measure used to select the replenishment change parameter to be applied by the rule. This measure is a picklist populated with all valid replenishment change parameters that were set up in the Replenishment Change Parameters.
PL Chg App. Count
Product and Location Change Applied Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that applies this rule’s replenishment change parameter. The calculation takes into account all the valid rules where the product and location combinations fall into and based on the priority calculates the count of product and location that applies the selected replenishment change parameter.
PL Chg App. %
Product and Location Change Applied Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate, in percentage, how much the product and location combinations, where the rule’s replenishment change parameter is applicable, represent in the total of product and location combinations within the rule group scope. The measure is calculated as:
Figure 19-37 Calculation
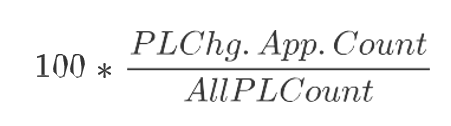
Rule Ivp.
Rule Inventory Planning is an editable measure used to select the inventory planning parameter to be applied by the rule. This measure is a picklist populated with all valid inventory planning parameters that were set up in the Inventory Plan Parameters view.
PL Ivp. App. Count
Product and Location Inventory Planning Applied Count is a calculated measure used to display the total number of product and location combinations that applies this rule’s inventory planning parameter. The calculation takes into account all the valid rules where the product and location combinations fall into and based on the priority calculates the count of product and location that applies the selected inventory planning parameter.
PL Ivp. App. %
Product and Location Inventory Planning Applied Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate, in percentage, how much the product and location combinations, where the rule’s inventory planning parameter is applicable, represent in the total of product and location combinations within the rule group scope. The measure is calculated as:
Figure 19-38 Calculation
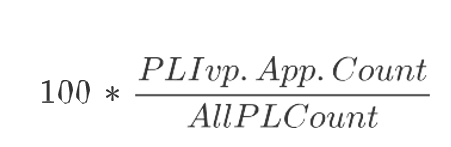
Copy & Paste
Copy and Paste is an editable measure to select whether the rule is the source or destination for the copy paste rules functionality (Copy-Paste Rules). Valid values are:
-
Copy
Option to select in the rule to be used as the source of the copy.
-
Paste
Option to select in the rule to be used as destination of the copy.
-
-
Option selected to clear the measure.
Note:
Only one rule should be selected as a source, Copy but multiple rules can be selected as a destination, Paste.
Conditions View
This view allows you to define the conditions for the rules based in product, location, and product-location attributes. A rule condition is what allows the engine to find the product and location combinations where the rule is applicable.
Figure 19-39 Conditions View
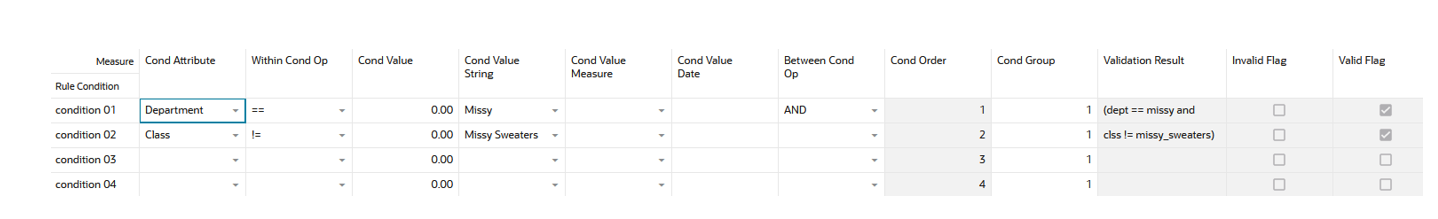
Conditions View - Default Profile Measures
The Conditions view contains the following measures.
Condition Attribute
The Condition Attribute measure allows you to select the attribute for the condition, The attributes for the rules are assigned in the Attribute Review workspace.
Within Cond Op
The Within Cond Op measure allows you to specify the operator to be used inside the condition.
Table 19-2 Within Cond Op Measure Available Operators
| Available Operators | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
|
= = |
Checks if the attribute value is equal with the Condition Value |
brand == Private Label |
|
!= |
Checks if the attribute value is different from the Condition Value |
Average sales !=0 |
|
> |
Checks if the attribute value is larger than the Condition Value |
Average sales >5 |
|
< |
Checks if the attribute value is less than the Condition Value |
Standard deviation of sales <6 |
|
>= |
Checks if the attribute value is larger or equal than the Condition Value |
|
|
<= |
Checks if the attribute value is less or equal than the Condition Value |
|
|
contain |
||
|
Not contain |
||
|
Match |
||
|
Not match |
Cond Value
The Cond Value measure is used when the type of the attribute is numeric. Example: average sales > 10
Cond Value String
The Cond Value String measure is used when the type of the attribute is a string. Example: brand == Private Label
Cond Value Measure
The value of the Cond Value measure is a measure name, which is populated by an expression that let’s you refine the condition value. For instance private label versus non-private label.
This measure is used when you want to refine the condition value.
For instance, for the coffee items, except Private Label, you want to assign items to the rule that sell more than 50 per week. For Private Label items you may want the value to be 100. You need to populate your Condition measure with a value of 100 for all Private Label items, and the rest of the coffee items with 50.
Cond Value Date
The Cond Value Date measure is used when the type of the attribute is a date. Example: today >= 02/30/2024"
Between Cond Op
Within a rule there can be multiple conditions and also multiple condition groups. This is specified in the Cond Group measure. Conditions with the same Cond Group value belong to the same group.
For example, if a rule has 4 conditions, Conditions 1 and 2 can belong to condition group 1, and conditions 3 and 4 can belong to the condition group 2. Also, the Cond Order measure gives the ranking of the conditions inside the group.
The following table is an assumed use case:
Table 19-3 Between Cond Op Assumed Use Case
| Condition | Between Con Op | Cond Order | Cond Group |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Condition 1 |
AND |
1 |
1 |
|
Condition 2 |
OR |
2 |
1 |
|
Condition 3 |
OR |
3 |
2 |
|
Condition 4 |
4 |
2 |
The value for the Between Cond Op can be the logical operators AND or OR.
The conditions are evaluated first inside a condition group and then between groups. In the previous case, the resulting condition is:
(Condition 1 AND Condition 2) OR (Condition 3 OR Condition 4)
Here is an example where all conditions belong to the same condition group:
Table 19-4 Example: All Conditions Belong to the Same Condition Group
| Condition | Between Con Op | Cond Order | Cond Group |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Condition 1 |
AND |
1 |
1 |
|
Condition 2 |
OR |
2 |
1 |
|
Condition 3 |
OR |
3 |
1 |
|
Condition 4 |
4 |
1 |
The resulting condition for the rule is given by:
Condition 1 AND Condition 2 OR Condition 3 OR Condition 4
Note that the conditions are evaluated in the order given by the values in the Cond Order measure.
Cond Order
The Cond Order measure displays the order in which conditions are evaluated, wither independently or inside a condition group.
Cond Group
The Cond Group measure allows you to group conditions. This is useful when you want to evaluate conditions in a two-step process. First, the conditions are evaluated inside groups. In the second step, the group results are evaluated .
Validation Result
The Validation Result measure displays the condition expressions that are validated.
Invalid Flag
The Invalid Flag measure indicates if a condition is invalid.
Valid Flag
The Valid Flag measure indicates if a condition is valid.
SKU-LOC View
The SKU-LOC View, under the Review tab, allows you to review the results of running the rule engine calculation based on the rules set up in the workspace. In this view you can review to the results at the lowest level, item and location levels, and can also create exceptions, at the item-location level, to overwrite the replenishment set up calculated by the rule engine (for example, a particular item and location that should apply a different replenishment parameter from all the other item locations in the same rule).
Figure 19-40 SKU-LOC View
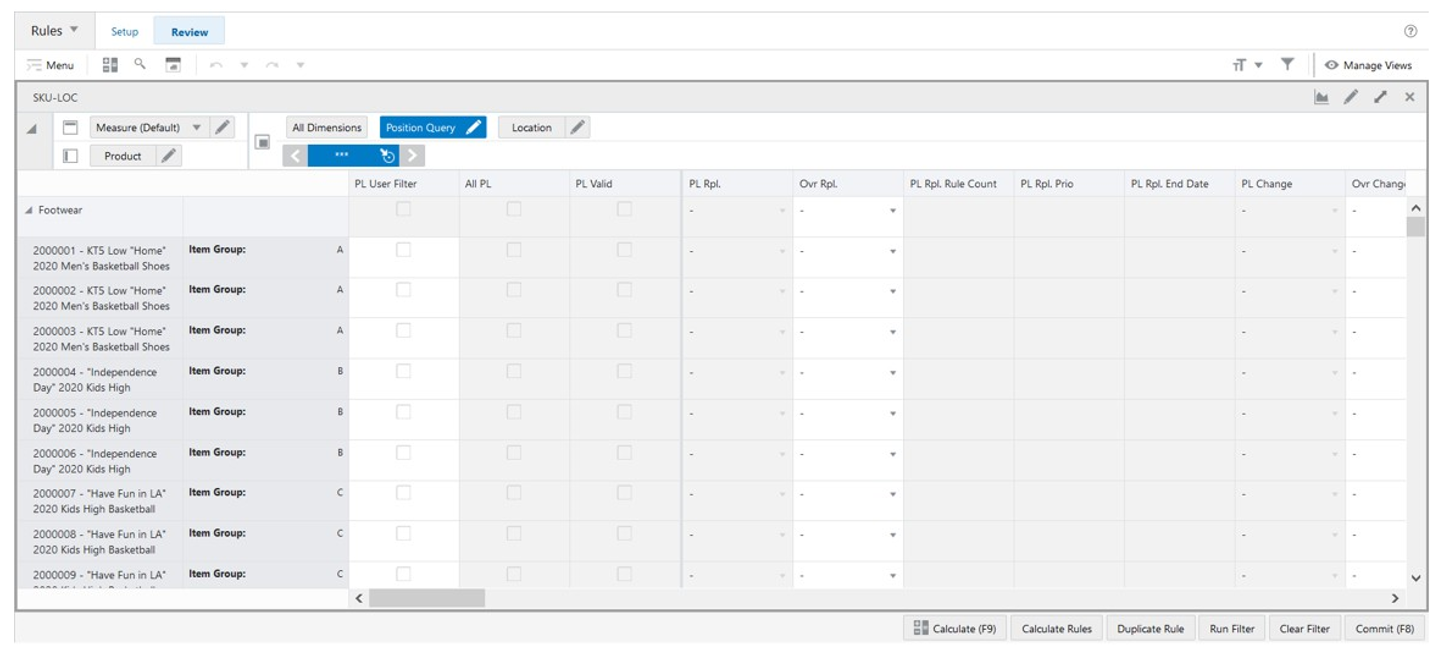
SKU-LOC View - Measure Profiles
The SKU-LOC View contains the following profiles to change the measures that are visible in the view:
-
Default
This profile is used as default by the view. All the available/visible measures are listed and described in the section Measure: Default Profile.
-
Change
This profile displays a subset of measures from the default profile. It focuses on the replenishment change parameters measures only. All other parameter related measures are left out of the visible measures.
-
Constraint
This profile displays a subset of measures from the default profile. It focuses on the replenishment constraint parameters measures only. All other parameter related measures are left out of the visible measures.
-
Inv Plan
This profile displays a subset of measures from the default profile. It focuses on the inventory planning parameters measures only. All other parameter related measures are left out of the visible measures. Replenishment: This profile displays a subset of measures from the default profile. It focuses on the replenishment parameters measures only. All other parameter related measures are left out of the visible measures.
SKU-LOC View - Default Profile Measures
The SKU-LOC View contains the following measures.
PL User Filter
Product and Location User Filter is an editable measure used to select the product and location combinations to filter the views by the selected the product and location combinations. This measure is used by the Run Filter action button is responsible to calculate the filters applied to the views within the Setup Rules workspace.
All PL
All Product and Location is a calculated measure used to indicate if a product and location combination is valid or not. If the measure is selected, the combination is valid, if it has a lifecycle phase value. If the measure is clear, the combination is invalid.
PL Valid
Product and Location Valid is a calculated measure used to indicate if a product and location combination has a valid rule from where the rule engine calculates the replenishment parameters. If the measure is selected, the item and location combinations have at least one valid rule that applies. If the measure is clear, the item and location combinations do not have at least one valid rule that applies.
PL Rpl.
Product and Location Replenishment is a calculated measure used to indicate the replenishment parameter applied to the product and location combination. The replenishment parameter displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Ovr Rpl.
Over Replenishment is an editable measure that allows you to create exceptions at the item-location level. You can select the replenishment parameter to override the assigned replenishment parameter (measure PL Rpl.). This measure is a picklist populated with all valid replenishment parameter that were set up in the Replenishment Parameters view.
PL Rpl. Rule Count
Product and Location Replenishment Rule Count is a calculated measure used to indicate the total number of replenishment parameters that are assigned to the product and location combination based on the Rules set up. Note that a product and location combination can only have one replenishment parameter active. The one that is active is the one from the rule with the highest priority or the user-exception override.
PL Rpl. Prio
Product and Location Replenishment Priority is a calculated measure used to indicate the priority of the rule from where the replenishment parameter was calculated for the product and location combination.
PL Rpl. End Date
Product and Location Replenishment End Date is a calculated measure used to indicate the end date of the rule from where the replenishment parameter was calculated for the product and location combination.
PL Change
Product and Location Change is a calculated measure used to indicate the replenishment change parameter applied to the product and location combination. The replenishment change parameter displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Ovr Change
Over Change is an editable measure used that allows you to create exceptions at the item-location level. You can select the replenishment change parameter to override the assigned replenishment change parameter (measure PL Change). This measure is a picklist populated with all valid replenishment change parameters that were set up in the Replenishment Change Parameters view.
PL Chg. Rule Count
Product and Location Change Rule Count is a calculated measure used to indicate the total number of Replenishment change parameters that are assigned to the product and location combination based on the Rules set up. Note that a product and location combination can only have one replenishment change parameter active. The active Replenishment change parameter is either the one from the rule with the highest priority or the user-exception override.
PL Chg. Prio
Product and Location Change Priority is a calculated measure used to indicate the priority of the rule from where the replenishment change parameter was calculated for the product and location combination.
PL Chg. End Date
Product and Location Change End Date is a calculated measure used to indicate the end date of the rule from where the replenishment change parameter was calculated for the product and location combination.
PL Cst.
Product and Location Constraint is a calculated measure used to indicate the replenishment constraint parameter applied to the product and location combination. The replenishment change parameter displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Ovr Cst.
Over Constraint is an editable measure used that allows you to create exceptions at the item-location level. You can select the replenishment constraint parameter to override the assigned replenishment constraint parameter (measure PL Cst.). This measure is a picklist populated with all valid replenishment constraint parameters that were set up in the Constraint Parameters view.
PL Cst. Rule Count
Product and Location Constraint Rule Count is a calculated measure used to indicate the total number of replenishment constraint parameters that are assigned to the product and location combination based on the Rules set up. Note that a product and location combination can only have one replenishment constraint parameter active. The active Replenishment constraint parameter is either the one from the rule with the highest priority or the user-exception override.
PL Cst. Prio
Product and Location Constraint Priority is a calculated measure used to indicate the priority of the rule from where the replenishment constraint parameter was calculated for the product and location combination.
PL Cst. End Date
Product and Location Constraint End Date is a calculated measure used to indicate the end date of the rule from where the replenishment constraint parameter was calculated for the product and location combination.
PL Ivp.
Product and Location Inventory Planning is a calculated measure used to indicate the inventory planning parameter applied to the product and location combination. The inventory planning parameter displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Ovr Ivp.
Over Inventory Planning is an editable measure used that allows you to create exceptions at the item-location level. You can select the inventory planning parameter to override the assigned inventory planning parameter (measure PL Ivp.). This measure is a picklist populated with all valid inventory planning parameters that were set up in the Inventory Plan Parameters view.
PL Ivp. Rule Count
Product and Location Inventory Planning Rule Count is a calculated measure used to indicate the total number of inventory planning parameters that are assigned to the product and location combination based on the Rules set up. Note that a product and location combination can only have one inventory planning parameter active. The active inventory planning parameter is either the one from the rule with the highest priority or the user-exception override.
PL Ivp. Prio
Product and Location Inventory Planning Priority is a calculated measure used to indicate the priority of the rule from where the inventory planning parameter was calculated for the product and location combination.
PL Ivp. End Date
Product and Location Inventory Planning End Date is a calculated measure used to indicate the end date of the rule from where the inventory planning parameter was calculated for the product and location combination.
Default MCQ Units
Default Minimum Credible Quantity Units is an editable measure used to define the default Minimum Credible Quantity for the product and location combination.
Min Cred. Qty @ Today Units
Minimum Credible Quantity at Today Units is a calculated measure used to indicate the Minimum Credible Quantity applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The Minimum Credible Quantity displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up. In case there is no Minimum Credible Quantity from the replenishment rule set up the value from the measure Default MCQ Units is used instead.
ROL Meth. @ Today
Reorder Level Method at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate the ROL method applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The ROL method displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Default Min Qty Units
Default Minimum Quantity Units is an editable measure used to define the default the minimum amount of stock desired when the ROL method is set to Min Qty.
Min Qty @ Today Units
Minimum Quantity at Today Units is a calculated measure used to indicate the ROL minimum quantity units applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The minimum quantity units displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Min TS @ Today Dur (d)
Minimum Target Stock at Today Duration (day) is a calculated measure used to indicate the ROL minimum time supply (in days) applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The minimum time supply displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Volatility @ Today %
Volatility at Today Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate the Volatility % applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The Volatility % displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Tgt. SL @ Today %
Target Service Level at Today Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate the Target Service Level % applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The Target Service Level % displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
ROL Sft. Time @ Today Dur (d)
Reorder Level Safety Time at Today Duration (day) details the Reorder level safety time duration applicable today based on rules association and used in replenishment calculations where RUTL method is not Target Stock. The ROL level is determined as lead time + review time + ROL Sft Time @ Today Dur (d).
RUTL Meth. @ Today
Reorder Up to Level Method at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate the RUTL method applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The RUTL method displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Default Max Qty Units
Default Maximum Quantity Units is an editable measure used to define the default maximum amount of stock desired when the RUTL method is set to Max Qty.
Max Qty @ Today Units
Maximum Quantity at Today Units is a calculated measure used to indicate the RUTL maximum quantity units applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The maximum quantity units displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Max TS @ Today Dur (d)
Maximum Target Stock at Today Duration (day) is a calculated measure used to indicate the RUTL maximum time supply (in days) applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The maximum time supply displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Tgt. DoS @ Today Dur (d)
Tgt. DoS at Today Duration (day) is a calculated measure used to indicate the Target Days of Supply (in days) applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The Target Days of Supply displayed (and used by the Tgt DoS RUTL method) is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
TS Meth. @ Today
Target Stock Method at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate the target stock method applied to the product and location combination at the system date (when the RUTL method is target stock). The target stock method displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
TS Sft. Time @ Today Dur (d)
Target Stock Safety Time at Today Duration (day) is a calculated measure used to indicate the number of days for the stock safety applied to the product and location combination at the system date (to be used when the RUTL method is target stock). The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
TS Seas. Fcst @ Today %
Target Stock Seasonal Forecast at Today Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate the percentage of the Seasonal Forecast applied to the product and location combination at the system date (to be used when the RUTL method is target stock). The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Order Rounding Threshold @ Today %
Order Rounding Threshold at Today Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate the percentage to round up the orders applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Repl. Status @ Today
Replenishment Status at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate whether product and location combination at the system date is replenished or not. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
ROL Chng @ Today %
Reorder Level Change at Today Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate the percentage to increase or decrease the system generated ROL value applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
RUTL Chng @ Today %
Reorder Up to Level Change at Today Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate the percentage to increase or decrease the system generated RUTL value applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Avail. Constr. (Src) @ Today
Available Constraint (Source) at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate whether a constraint is enable or disable (at the source location) for the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Src. Avail. (Src) @ Today
Source Available (Source) at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate which stock units to be used from the source locations is applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Src. Avail. (Src) @ Today Dur (d)
Source Available (Source) at Today Duration (day) is a calculated measure used to indicate the number of days to get the in-transit and on-order stock is applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Rpl. Active (Dst) @ Today
Replenishment Active (Distribution) at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate for the product and location combination at the system date if the location has the replenishment active or not. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Fulfill Till Layer (Dst) @ Today
Fulfill Till Layer (Distribution) at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate the layer applied to the product and location combination at the system date (layer until which the engine should fulfill the demand). The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
SubLayer (Dst) @ Today
SubLayer (Distribution) at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate the sublayers applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Default Ration. Prio
Default Rationing Priority is an editable measure used to define the default rationing priority for the product and location combination.
Ration. Prio (Dst) @ Today
Rationing Priority (Distribution) at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate the rationing priority applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up. In case there is no rationing priority from the replenishment rule set up the value from the measure Default Ration Prio. is used instead.
Assign Pack (Dst) @ Today
Assign Pack (Distribution) at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate the pack types’ assignment applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Min Pack Fill Rate 1 (Dst) @ Today %
Minimum Pack Fill Rate 1 (Distribution) at Today Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate the minimum pack fill rate percentage for 1st round of complex pack assignment applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Min Pack Fill Rate 2 (Dst) @ Today %
Minimum Pack Fill Rate 2 (Distribution) at Today Percentage is a calculated measure used to indicate the minimum pack fill rate percentage for 2nd round of complex pack assignment applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Min Method @ Today
Minimum Method at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate the inventory planning method, to calculate the System Minimum value, applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The inventory planning method displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Min Fixed @ Today
Minimum Fixed at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate how the Fixed inventory planning method calculates the System Minimum value for the product and location combination at the system date. The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Min Fixed @ Today Units
Minimum Fixed at Today Units is a calculated measure used to indicate the minimum fixed quantity applied to the product and location combination at the system date (used when the Min Method @ Today is Fixed and the Min Fixed @ Today is -). The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Min Fwd Cov. @ Today Dur (d)
Minimum Forward Cover at Today Duration (day) is a calculated measure used to indicate the minimum number of days of cover applied to the product and location combination at the system date (used when the Min Method @ Today is Forward cover). The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Max Method @ Today
Maximum Method at Today is a calculated measure used to indicate the inventory planning method, to calculate the System Maximum value, applied to the product and location combination at the system date. The inventory planning method displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Max Fixed @ Today Units
Maximum Fixed at Today Units is a calculated measure used to indicate the maximum fixed quantity applied to the product and location combination at the system date (used when the Max Method @ Today is Max). The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Max Fwd Cov. @ Today Dur (d)
Maximum Forward Cover at Today Duration (day) is a calculated measure used to indicate the maximum number of days of cover applied to the product and location combination at the system date (used when the Max Method @ Today is Forward cover). The value displayed is the one calculated by the rule engine using the replenishment rules set up.
Filter Step
This step contains this view, Filter Parameters View.
Filter Parameters View
The Filter Parameters View, under the Filter tab, allows you to set up the filter that can change the scope of the products and locations displayed in all relevant views under the Rules Step within the Repl. Param. Rules Workspace.
Figure 19-41 Filter Parameters View
Filter Parameters View - Default Profile Measures
The Filter Parameters view contains the following measures.
Filter Not Valid
Filter Not Valid is an editable measure to change the scope of the products and locations displayed in all relevant views under the Rules Step. If the measure is selected, the Run Filter action button is responsible to calculate the filters that only display non-valid product and location combinations. When clear the filter only displays valid product and location combinations. By default, the measure is clear. The measure PL Valid identifies whether or not a product and location combination is valid.
Rule -> PL Filter
Rule -> PL Filter is an editable measure to select how the filter should work in the SKU- LOC view. Valid values are:
-
Associated
The view is filtered to display the product and location combinations that are associated with the rules selected in the Rules view (measure Rule User Filter). Note that a product and location combination can fit in more than one rule. When they fit in a rule they are associated regardless, if that rule is the actual one to be applied.
-
Applied
The view is filtered to display the product and location combinations that apply the rules selected in the Rules view (measure Rule User Filter). The rule is consider as applied when the LIP CS Rule Engine sets the replenishment set up for the product and location combination based on the rule (for example, BOD, PLC, and so on).
PL -> Rule Filter
Product and Location -> Rule Filter is an editable measure to select how the filter should work in the Rules view. Valid values are:
-
Associated
The view is filtered to display rules that are associated with the product and location combinations selected in the SKU-LOC view (measure PL User Filter). Note that a product and location combinations can fit in more than one rule. When they fit in a rule they are associated regardless, if that rule is the actual one to be applied.
-
Applied
The view is filtered to display rules that are associated with the product and location combinations selected in the SKU-LOC view (measure PL User Filter). The rule is consider as applied when the LIP CS Rule Engine sets the replenishment set up for the product and location combination based on the rule (for example, BOD, PLC, and so on).
Note:
In the same way as in the Network workspace, the measure in this view is used by the Replenishment Parameters Run Filter action button to filter the relevant views within the Replenishment Parameters workspace.
Replenishment Parameters Action Buttons
The Replenishment Parameters workspace has the following action buttons available:
-
Run Filter
Use the Run Filter action button for applying the filters in the Rules views based on the filter set up completed within the workspace. For example, filter based on the User Filter measures.
-
Clear Filter
Use the Copy-Paste Exceptions action button for removing all filters applied in the Rules views and clears all the User Filter measures within the workspace.
-
Calculate Rules
Use the Calculate Rules action button for running the rules engine to calculate which rule’s replenishment and inventory planning parameters set up would be applied to the product and location combination level and applying the rule’s replenishment and inventory planning parameters set up down to the product and location combination level.
-
Duplicate Rule
Use the Duplicate Rule action button to copy all the rules information from the rule selected as the source of the copy and paste it into all the rules selected as the destination of the copy. This action copies all the information in the Rules view and Conditions view.