2 Oracle Internal Imports and Exports
Oracle Retail Collect and Receive Enterprise Returns Integration
Order Administration is now integrated into the Oracle Retail Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service. When configured, Order Administration allows a Courier (that is, Uber) to be scheduled to pick up a customer’s return package and drop it off at a retailer’s store location.
A courier can be scheduled for a return authorization that has not been received or credited. The following features allow scheduling a courier:
-
Modern View Order Returns/Refunds tab
-
Create Return Authorization Service where alreadyScheduled is set to ‘false’
-
Update Return Authorization Service where alreadyScheduled is set to ‘false’
Setup Requirements
Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service Setup:
Required properties: The following new properties are available to configure the integration with Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service:
-
oms.car.service.url (PROP):The prefix URL for Oracle Retail Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service. Provided by your Oracle representative. Defaults to http://hostname:port/. OACS only supports version 2 of the Delivery API.
-
oms.car.scope (CPRP): The scope used for the Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service services. Provided by your Oracle representative. Defaults to domain:scope.
Note:
When calling Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service Services, Order Administration builds the URL using the oms.car.service.url value, version and a hard coded suffix.
The Order Administration Client ID and Client Secret will be used to authenticate and access Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service services.
Required system control value settings: Use the following new system control values to enable the use of Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service:
-
Use CaR Returns (M81): Select this system control value to enable the scheduling of a courier pickup for returns through Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service.
-
Courier Pickup Message (M82): Defines a company-specific message to be displayed within the body of an information banner on the Courier Pickup for Return Authorization screen in Modern View when scheduling a courier pickup.
OOCS Setup:
For Order Administration to confirm a pick up location is eligible for a courier to pickup the return, a location eligible for drop-off must also be selected. This information is retrieved using Order Orchestration: Eligible Returns Locations REST/JSON Service.
Required properties: The following new properties are available to configure the integration with OOCS Return Locations:
-
oocs.return.locations.service (PROP): The prefix URL for the OOCS Eligible Return Location service. Provided by your Oracle representative. Defaults to https://server:port/Locate/rest/api/org/v1/returns/..
Required system control value settings: Use the following new system control values to set filters for locations returned:
-
Maximum Number of Eligible Return Drop-Off Locations (M83): Defines the maximum number of locations to return within the OOCS Eligible Return Drop-Off Location Service response message, when a customer initiates a courier pickup for a Return Authorization. If not populated, it uses the "Maximum No. Responses" Preference for the Organization associated to the system in OOCS.
-
Search Distance for Eligible Return Drop-Off Locations (M84): Defines the maximum distance to search for an eligible return drop-off location when a customer initiates a courier pickup for a Return Authorization. If not populated, it uses the "Maximum Turn-by-Turn Distance" Preference for the Organization associated to the system and in OOCS.
Schedule Courier Pickup in Modern View Order
A new Schedule Courier Pickup button is now available on the Returns/Refunds tab of an Order in Modern View when:
-
Use CaR Returns (M81) system control value is set to Yes.
-
All lines and units on the Return Authorization are not received, credited, or canceled.
-
A courier pickup is not already scheduled.
Check Eligibility
Within the Courier Pickup Return Authorization screen, the system will immediately check eligibility for a courier pickup using the Customer’s Ship-To Address from the originating order and select the nearest drop-off location to the customer’s address.
-
Calls OOCS Eligible Return Locations service and selects the nearest location
-
Calls Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service Build Quote service with Customer Pickup Address and Dropoff Location Address
If the eligibility check is successful, the screen will now display additional sections to Select Time Zone, Select Pickup Window and enter Package Details. If unsuccessful, an error will display the user can Edit the pickup address and Check Eligibility again.
Select Time Zone
A time zone must be selected to continue. The time zone selected will be used to provide a list of dates and times available to select a pickup window where the customer’s package will be picked up.
Only time zones in North America will be available.
Select Pickup Window
A customer can select a single 2-hour window between 8:00AM and 6:00PM that falls within the available store hours which will be provided to the courier for the pickup time range. If the local time is 10:05 AM (based on the time zone selected), the list of pickup window options will start at 12:00PM - 2:00PM.
Drop-off Location Details and Store Hours can be defined within the Order Orchestration Location screen and will be returned in the Eligible Return Locations service for display.
Package Details
The size and number of packages being returned must be entered which will be provided to the courier for pickup through the CaR integration.
Select +Add Package for Pickup to open a drawer and set the number of packages for pickup. A package size must be selected for the number of packages entered. Options are:
-
Small (Can be carried with one hand)
-
Medium (Can be carried in a shopping bag)
-
Large (Needs two hands to carry)
-
X-Large (Heavy or odd size, requires two hands)
Notes for the courier can be added about the pickup location.
Submit to Courier
Once all Pickup and Package details are entered, click Submit to Courier button and the pickup will be scheduled.
-
Calls Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service Build Delivery service with Customer Pickup Address, Drop-off Location Address, Pickup Window, Package Details and Courier Notes.
If scheduling is successful, the following will occur:
-
A confirmation will be displayed, and the Courier Pickup screen will close.
-
An Order Activity message will be written.
-
A CWEmailOut Courier Pickup Notification (CP) will be sent if configured.
If unsuccessful, an error will display the user can Edit the details and Submit to Courier again.
Courier Pickup Details in Modern View Order
A new Courier Pickup Details drop-down list is now available on the Returns/Refunds tab of an Order in Modern View when:
-
Use CaR Returns (M81) system control value is set to Yes.
-
A courier pickup is already scheduled.
Select the Courier Pickup Details drop down list to select a specific Delivery ID to advance to the Courier Pickup Details screen where you can review the Pickup Location, Dropoff Location, Current Status and History, Pickup Window, Package Details and Canceled Reason.
Immediately upon loading the screen, Order Administration calls the Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service getStatus service for the current status.
Cancel Courier Pickup in Modern View Order
Within the Courier Pickup Details screen, you can select Cancel Courier Pickup only when the status is either ‘Pending’ or ‘Enroute Pickup’. Additionally, the Delivery ID must have received a successful response from CaR when retrieving the latest status.
If cancelation is successful, the following will occur:
-
A confirmation will be displayed, and the Courier Pickup screen will close.
-
An Order Activity messages will be written.
-
A CWEmailOut Courier Pickup Notification (CP) will be sent if configured.
Schedule Courier Pickup through OACS Web Services
An external merchant application can call Order Administration to schedule or cancel a courier pickup or schedule a courier pickup for a return authorization directly and then pass details about the courier pickup to OACS.
If an external merchant application schedules the courier directly and is providing information to OACS, the Unique Delivery ID used to schedule the pickup in CaR must also be passed in the OACS services so display and additional processing can be tracked and displayed through Modern View.
If OACS is scheduling the courier, the pickup address, drop-off address, pickup window, and package details must all be passed in the service.
The following services can be used with the alreadyScheduled flag set to ‘true’ for including data about an already scheduled pickup and set to ‘false’ for Order Administration to perform the scheduling.
-
Create a Return Authorization Service
-
Update Return Authorization Service
If scheduling is successful, the following will occur:
-
An Order Activity message will be written.
-
A CWEmailOut Courier Pickup Notification (CP) will be sent if configured.
If unsuccessful, an error will be returned in the response. However, the Return Authorization will be created or updated.
Courier or Provider Cancels the Pickup
The courier or provider can cancel a trip if for example the customer is not home, or the store location is closed. If this occurs, OACS will receive a status of Canceled or Returned from Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service during a Collect and Receive Foundation Cloud Service getStatus request.
-
Canceled occurs when a scheduled courier service is canceled successfully before packages get picked up from the customer's address.
-
Returned occurs when a scheduled courier service is canceled successfully after packages get picked up by a courier but are not delivered to the retailer and instead need to be returned back to the customer's address.
OACS calls the CaR getStatus request when:
-
A user displays the Courier Pickup Details screen in the Modern View Order, Returns/Refunds tab.
-
An external system calls the Get Return Authorization service for a return authorization with an associated courier pickup in open status.
If the status is updated to Canceled or Returned, the following will occur:
-
An Order Activity message will be written.
-
A CWEmailOut Courier Pickup Notification (CP) will be sent if configured.
Address Validation Integration
Order Administration supports the latest API formats with Experian Data Quality and has introduced Type-Ahead Address Lookup.
Order Administration supports the following integrations for address validation:
-
Experian Data Quality (EDQ) Address Validate API using the RESTful format. This is also referred to as QAS.
-
Generic RESTful Address Validation API that can be leveraged to integrate to an external address verification provider.
Order Administration supports the following integrations for type-ahead address lookup:
-
Experian Data Quality (EDQ) Address Search API
-
Generic RESTful Address Search API that can be leveraged to integrate to an external address search provider.
Setup Requirements
The following will need to be configured to enable Address Validation and/or Address Lookup unless indicated that it’s only used for one of the integrations:
-
Populate the 3-digit ISO Country Code in Work with Countries (WCTY)
-
Only countries where the region (or state code) is either empty or has a 2-character code are supported. For example: Canada (CAN), United Kingdom (GBR), United States (USA) and Australia (AUS) are all supported.
-
-
Address Service Authorization Token (B66) system control value
-
Address Validation Service Endpoint URL (B67) system control value. This URL is only used for Address Validation.
-
Address Type-Ahead Service Endpoint URL (B68) system control value. This URL is only used for Address Lookup.
-
Address Interface (I67) system control value. This setting is only used for Address Validation.
-
Must select QAS (Experian) or GENERIC to indicate the type of Address Service Interface.
-
Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration
Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration allows you to send customer, sales, and return information from Order Administration to Customer Engagement. Sending this information to Customer Engagement provides a centralized view of the customer’s value across your enterprise. You can use this information to perform data analysis, or segmentation, in Customer Engagement.
Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration Process Flow
Send sales and return Information to Customer Engagement: On a nightly basis, run the Customer Engagement Sales Feed to send sales and return information to Customer Engagement.
-
Order Administration generates the: Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message for invoices that are not excluded from the Customer Engagement Sales feed.
-
Customer Engagement processes the messages from Order Administration and updates Customer Engagement with the sales and return information.
See Customer Engagement Sales Feed for processing details.
Viewing sales and return information in Customer Engagement: You can review the information sent to Customer Engagement in Customer Lookup / Edit. The Customers section of the Customer Engagement User Guide provides information on reviewing and updating a customer in Customer Engagement.
-
The Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message creates or updates a customer in Customer Engagement on a periodic basis. Customer information displays on the Customer Lookup / Edit screen. You can also review a summary of the customer on the Customer Dashboard screen.
Note: See the Customer Engagement Customer Integration for information on communicating customer information interactively between Customer Engagement and Order Administration.
-
The Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message creates sale and return transactions in Customer Engagement. Sale and return information displays on the Transaction History screen for a selected customer. You can also review a summary of the transactions associated with a customer in the Purchase Activity section of the Customer Dashboard screen.
See each message layout in the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for more information on how Order Administration populates each message, how the information updates the Customer Engagement database, and where you can view the information on the Customer Engagement screens.
Viewing sales and return information from Customer Engagement in Order Administration: You can use the Display Purchase History Screen to review a customer’s purchase history from Customer Engagement. See Customer Engagement Purchase History Integration for an overview, required setup, and detailed information about the Display Purchase History screen.
In this topic:
-
Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration Process Flow
-
Setup in Customer Engagement for the Sales and Customer Integration
For more information: This section provides information on the Order Administration sales and item integration with Customer Engagement. See:
-
The Customer Engagement Implementation Guide (Installer Version) for more information on the procedures and instructions required to install and configure the Customer Engagement application and database.
-
The Customer Engagement Implementation Guide for information on working with system configuration settings in Customer Engagement.
-
The Customer Engagement Batch Processing & Web Services Guide for more information on the Customer Engagement messaging interface, including how Customer Engagement processes XML messages and the details of each message.
-
The Customer Engagement Database Dictionary for more information on the tables in the Customer Engagement database.
-
The Customer Engagement User Guide for more information on using the Customer Engagement application.
-
Customer Engagement Customer Integration for information on interactively synchronizing customer information between Customer Engagement and Order Administration.
-
Customer Engagement Purchase History Integration for information on reviewing a customer’s purchase history from Customer Engagement in Order Administration.
-
Customer Engagement Customer Wish List Integration for more information on how to review and modify a customer’s wish list from Customer Engagement using the Display Wish List Screen in Order Administration.
-
Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration for information on using the Customer Engagement Loyalty integration with Order Administration.
-
The Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for details on messages.
Customer Engagement Integration Setup (Sales and Customer)
The setup required to use the Customer Engagement Sales Feed and Customer Engagement Customer Integration is described below.
Required versions: To use the Order Administration sales or customer integrations with Customer Engagement, you must be on these versions:
-
Order Management System version 4.5 or higher, or Order Administration.
-
Customer Engagement version 10.5 or higher, or Order Administration.
In addition, the Customer Engagement Customer Integration, Customer Engagement Purchase History Integration, and Customer Engagement Customer Wish List Integration uses version 2.3 of the Customer Engagement Customer API.
Setup is required in both Order Administration and Customer Engagement.
-
Setup in Order Administration for the Customer Engagement Sales and Customer Integration
-
Setup in Customer Engagement for the Sales and Customer Integration
Also, see Customer Engagement File Transfer Service (FTS) for additional setup requirements related to the file transfer service.
Setup in Order Administration for the Customer Engagement Sales and Customer Integration
The setup required in Order Administration to use the Customer Engagement Sales Feed and Customer Engagement Customer Integration is described below.
Also, see Customer Engagement File Transfer Service (FTS) for additional setup requirements related to the file transfer service.
System Control Values
| System Control Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Defines whether you assign a long SKU class or retail class to an item. Deselect this field to assign a long SKU class to an item. In this situation, select the following system control values: Select this field to assign a retail class to an item. A retail class is a long SKU class that is linked to a long SKU department. Also, the system requires you to enter long SKU values for an item: long SKU department, long SKU class (retail class), long SKU style, and long SKU subclass. Note: Not related to the Customer Engagement Customer Integration. |
|
|
Use the ORCE Integration Values (L52) umbrella screen to set the following values: |
|
|
Defines the store ID associated with customers sent to Customer Engagement in the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message, provided the customer does not already have a RELATE_ID assigned. Note: The location cannot be greater than 8 positions and should not be greater than the length specified in the Retail Transaction Location ID Length specified in Customer Engagement, typically 5 positions. Also, the location code must be numeric to prevent any possible issues displaying a customer’s purchase history in Xstore. The system also includes the store ID you define here in the name of the XML batch file that is sent to Customer Engagement. Example: MESSAGE_CO#_STORE_ID_DATETIME.xml, where:
An example of the XML batch file name that contains the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message is: cw-customer_007_12301974_101123092141.xml. If the store ID does not exist in Customer Engagement, Customer Engagement automatically creates it when it processes the Customer message. Note: Not related to the Customer Engagement Customer Integration. |
|
|
Enter INTERACT to send information on new and updated customers to Customer Engagement interactively if Customer Engagement is the system of record for customer information. See Customer Engagement Customer Integration for more information. |
|
|
Defines the item code to include in the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message to represent all non-merchandise amounts for an invoice, such as freight, additional freight, handling and additional charges. Required if the Merchandise Only in Sales Feed (L36) system control value is unselected. Note: Not related to the Customer Engagement Customer Integration. |
|
|
Defines the types of sales (debit) invoices Order Administration excludes from the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message. Note: Not related to the Customer Engagement Customer Integration. |
|
|
Defines the return disposition code assigned to return (credit) invoices that Order Administration excludes from the Customer Engagement Sales Feed when the Suppress refund field in the Order Payment Method table is Y. In this situation, Order Administration does not generate a return confirmation for these returns. Note: Not related to the Customer Engagement Customer Integration. |
|
|
Select this field to include merchandise and tax amounts only in the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message. Deselect this field to include full invoice totals, including merchandise, freight, and additional charges, in the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message. Use the Item for Non-Merchandise Amounts (L39) system control value to define the item code to include in the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message to represent all non-merchandise amounts for an invoice, such as freight, additional freight, handling and additional charges. Note: Not related to the Customer Engagement Customer Integration. |
|
|
Use this field to identify the Customer Engagement organization that maps to your Order Administration company. Note: For integration with Customer Engagement 20.0+, this field now controls the web service messages structure rather than the organization descriptor, and must be set to ws. |
|
|
Select this field to include demographic profile data in the customer integration with Customer Engagement. Deselect this field to omit demographic profile date from the customer integration with Customer Engagement. See Order Management System Customer Profile > Customer Engagement Attribute Definition for details on how to configure and map attribute data. |
|
|
Use this field to define the URL to use when sending customer, sales, or item information XML files to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement through the file transfer service (FTS). This field is required for transfers to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement 20.0 or higher; otherwise, leave this field blank. See Customer Engagement File Transfer Service (FTS) for more information. |
|
|
Use this field to define the folder path where the file transfer service (FTS) should place zip files containing customer, sales, or item information XML files for import into Oracle Retail Customer Engagement. This field is required for transfers to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement 20.0 or higher; otherwise, leave this field blank. See Customer Engagement File Transfer Service (FTS) for more information. |
|
|
Additional system control value |
|
|
Defines whether to send the ORCE customer ID or the Order Administration customer number as the customer_id in the Narvar Order Request Message. |
|
Store Cross Reference
Use Work with Store Cross Reference (WSCR) to set up cross reference information between a store location and Order Administration.
-
The Store # must match the store ID defined in the Default Location for ORCE Integration (K69) system control value. .
Note:
If the store ID does not exist in Customer Engagement, Customer Engagement automatically creates it when it processes the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message.Note:
Not related to the Customer Engagement Customer Integration.
Store Tender
In Working with Pay Types (WPAY), define a store tender for each pay type that you send to Customer Engagement in the Customer Engagement Sales Feed. This code can be used in Customer Engagement as a loyalty qualifier.
Note:
If the store tender does not exist in Customer Engagement, Customer Engagement automatically creates it in the DTV_TENDER_TYPES table when it processes the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message.
Note:
Not related to the Customer Engagement Customer Integration.
ISO Currency Codes
Order Administration sends the currency code for the offer associated with the source code on the order header in the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message. Create ISO currency codes in Working with Currency (WCUR) and assign the ISO currency codes to your offers in Working with Offers (WOFR).
Example: USD is the ISO currency code for the US Dollar.
The code passed is:
-
The currency code from the Order Header Extended table, if any. The currency for the order is defined here if the Multi Currency by Offer (E03) system control value is selected when the order is created. Otherwise,
-
The currency code defined in the Local Currency Code (A55) system control value, if any. Otherwise,
-
No currency code is passed.
Note:
Not related to the Customer Engagement Customer Integration.
Web Service Authentication for Customer Engagement
If the web services used to process inbound messages to Customer Engagement require web service authentication, you must provide a valid web service authentication user and password in Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA), or client ID and client ID if using OAuth. In this situation, when Order Administration generates a message to send to Customer Engagement it includes the web service authentication information in the HTTP header of the message. See Web Service Authentication Process for Customer Engagement for more information.
Customer Engagement Properties
Working with Customer Properties (PROP) contains settings required for integration with Customer Engagement.
| Setting | Description | Setting |
|---|---|---|
|
ORCE_DIRECTORY_PATH |
Defines the location where Order Administration places the batch files to send to Customer Engagement. See Working with Admin Properties (CPRP). Note: Not related to the Customer Engagement Customer Integration. |
This property is defined by Oracle and cannot be changed. |
|
ORCE_CUSTOMER_ ID_DIRECTORY_PATH |
Defines the location on the Order Administration application server where the RLTCSID Update Customer with Relate ID periodic function (program name PFRCIU) looks for the Customer Engagement query results comma separated value file (CSV) to process. See Customer Engagement Update Customer with Relate ID Process. |
This property is defined by Oracle and cannot be changed. |
|
ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX |
The system uses this property to build the URL for communication with Customer Engagement. |
https://server:8447/ where: server = the name of your Customer Engagement server 8447 = the port to use on the Customer Engagement server |
|
ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_SUFFIX |
The system uses this property, along with the ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX and the value in the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) to build the URL for communication with Customer Engagement using the Customer Services API. |
/OrceWebServices/v2_3/CustomerServicesApiService?wsdl where 2_3 is the version of the Customer Services API |
|
ORCE_SECURITY_ USER_ID |
The Customer Engagement user ID with Security Group permission included in the Customer Engagement API messages. |
Must be a valid user ID in Customer Engagement that has Security Group permission |
|
ORCE_DAY_PHONE_LABEL |
Indicates the Telephone Type in Customer Engagement that maps to the daytime phone number in Order Administration. Should be set to BUSINESS. How to define in Customer Engagement? You can create a telephone type of BUSINESS in Customer Engagement by:
|
ORCE_DAY_PHONE_LABEL=BUSINESS |
|
ORCE_EVE_PHONE_LABEL |
Indicates the Telephone Type in Customer Engagement that maps to the evening phone number in Order Administration. How to define in Customer Engagement? You can create a telephone type of HOME in Customer Engagement by:
|
ORCE_EVE_PHONE_LABEL=HOME |
|
ORCE_FAX_PHONE_LABEL |
Indicates the Telephone Type in Customer Engagement that maps to the third phone number in Order Administration. The Third Phone Number Type (L53) system control value controls whether the third phone number is labeled as the mobile or fax number in Order Administration. Note: Match the name entered in the Third Phone Number Type (L53) system control value to the value defined for the ORCE_FAX_PHONE_LABEL. How to define in Customer Engagement? You can create a telephone type of FAX or MOBILE in Customer Engagement by:
|
ORCE_FAX_PHONE_LABEL=MOBILE |
|
ORCE_ALT_ID_OROMS |
Indicates the Alt Key Type of the alternate key in Customer Engagement that maps to the Order Administration customer number. Customer Engagement automatically creates this entry for a customer when you send the customer to Customer Engagement if it does not already exist. Also, Customer Engagement adds a row to the CST_ALT_KEY_TYPCODE table in the Customer Engagement database if it does not already exist. Note: If you use the Customer Engagement Customer Integration and also generate the POSlog file for the Sales Integration with Customer Engagement, you need to leave this property set to SERENADE_ID. |
ORCE_ALT_ID_OROMS=SERENADE_ID |
|
ORCE_ALT_ID_POS |
Not currently implemented. |
N/A |
|
ORCE_ALT_ID_WEB |
Indicates the Alt Key Type of the alternate key in Customer Engagement that maps to the ecommerce site’s customer number. How to define in Customer Engagement? You can create a alternate key type such as OCP_CUST_ID in Customer Engagement by:
Note: See the Customer Engagement Customer Integration for information on how the ecommerce customer ID is used to identify the customer in the order API. |
ORCE_ALT_ID_WEB=OCP_CUST_ID |
Periodic Functions
Customer Engagement Sales Feed: Use the RLTSLSF Customer Engagement Sales Feed periodic function (program name PFR0102) to send the Customer Engagement Sales Feed and Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message to Customer Engagement during the Customer Engagement Sales Feed. Assign this periodic function to a daily periodic process. See How to Schedule a Job. Note that the ORCE File Service URL (M62) and ORCE Import Folder Path (M63) system control values must be specified for the company for this function to run.
Customer Engagement Customer Integration Synchronization: Use the SYNCRDB periodic function (program name PFR0105) to send customer information to Customer Engagement, either as part of an initial export of customer records to Customer Engagement, or when there is a communication failure during interactive processing. See Synchronizing Customer Information through a Periodic Function for more information.
Customer Upload to Customer Engagement: Use the RLTCSUP Customer Upload to Customer Engagement periodic function (program name PFRBCC) to send all Order Administration sold to customers to Customer Engagement; see Customer Engagement Batch Customer Conversion. Note that the ORCE File Service URL (M62) and ORCE Import Folder Path (M63) system control values must be specified for the company for this function to run.
Update Customer with Relate ID: Use the RLTCSID Update Customer with Relate ID periodic function (program name PFRCIU) to update the Relate ID in the Customer Sold To table with the Customer ID from Customer Engagement; see Customer Engagement Batch Customer Conversion.
Customer Engagement Batch Customer Conversion
This process may be useful when you first integrate Order Administration with Customer Engagement and want to begin using the Customer Engagement Customer Integration.
The Customer Engagement Batch Customer Conversion process consists of the following steps:
-
Running the RLTCSUP Customer Upload to Customer Engagement periodic function (program name PFRBCC) to send all Order Administration sold to customers, excluding any sold to customers whose Ghost field in the Customer Sold To table is Y or that already have a Relate ID, to Customer Engagement using the batch Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message.
-
Running the RLTCSID Update Customer with Relate ID periodic function (program name PFRCIU) to update the Relate ID in the Customer Sold To table with the Customer ID from Customer Engagement.
Customer Engagement Batch Customer Upload to Customer Engagement Process
This process generates a batch customer conversion XML batch file, containing all sold to customers minus any flagged as a ghost or that already have a Relate ID, to send to Customer Engagement for processing.
Before you begin: Before you send all sold to customers to Customer Engagement, you should:
-
Run Customer Sold To Merge/Purge to eliminate duplicate records.
-
Make sure you have completed the Customer Engagement Integration Setup (Sales and Customer).
-
Optionally, run the CTYCONV Country Code Conversion periodic function (program name PFCCC32) to update the country code in Order Administration tables from a 3-digit country code to a 2-digit ISO country code. If you run this periodic function, once it is done, you should also run the CTY3DEL Delete 3 Character Country Code periodic function (program name PFCCCD3) to delete the 3 position country code from the Order Administration tables since it is no longer used.
Note:
Before you run these programs, you should end any running jobs and have the following tables cleared:
-
Catalog Request Interface
-
Customer API
-
EC Tables: Country, SCF State, Ship Exclusion, State
-
Marketing Download Tables: Customer Address Chg, Customer Inquiry, Customer Status Chg, Order Header, Vendor Download
-
MBS Tables: Changed Customers, Work File
-
Promotion Upload
-
RI Item Upload
-
Vendor Interface Download
-
Vendor Upload
Also, the ORCE File Service URL (M62) and ORCE Import Folder Path (M63) system control values must be specified for the company.
| # | Step |
|---|---|
|
1. |
Run the RLTCSUP Customer Upload to Customer Engagement periodic function (program name PFRBCC) to submit the RLTCUSTUP job. Note: When you submit the RLTCSUP periodic function, the system creates an Active Procedure to keep track of the updates made so that the process can be stopped and restarted at a later time. |
|
2. |
Order Administration writes any messages related to the Customer Engagement batch customer conversion, including any errors that may occur during processing, to the Application Log. |
|
3. |
Order Administration generates the following message using customer information from the Order Administration database: Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message: Contains customer information for all sold to customers in the Order Administration company for which the Customer Engagement batch customer conversion was run. Order Administration creates an XML batch file that contains all of the Customer messages generated and names the file cw-customer_conversion_CO#_STORE_ID_DATETIME.xml where:
Example file name: cw-customer_conversion_007_12301974_101123092141.xml |
|
4. |
Order Administration places the customer conversion XML batch file in the directory defined in the ORCE_DIRECTORY_PATH property. Order Administration also creates an empty text file named OTHER.done to notify Customer Engagement that the XML batch file is ready to be picked up and processed by Customer Engagement. |
|
5. |
Unless you are using the Customer Engagement File Transfer Service (FTS), Customer Engagement retrieves the customer conversion XML batch files from the ORCE_DIRECTORY_PATH and process the messages. |
|
7. |
For each XML message that is processed successfully, Customer Engagement updates the appropriate tables in the Customer Engagement database. You can view the results in the Customer Engagement application. See the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message in the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for more information on how Order Administration populates the message, the tables in the Customer Engagement database that are updated and where you can view the information in Customer Engagement. |
Customer Engagement Multiple Organizations
Each company in Order Administration can now be configured to communicate with a specific organization in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement (ORCE) and Order Retail Promotion Engine (ORPE). This allows a retailer to support multiple organizations to keep customer data separated within one instance of ORCE.
There are no changes required within Order Administration to support a single organization setup configure or continue to communicate to the default organization in ORCE and ORPE.
Order Administration will not store or pass the ORCE Organization ID in any communication. OMS communicates with a specific ORCE organization based on Application Client id. When there is more than the default organization in ORCE, each Application Client is assigned to Primary organization in the User screen within ORCE.
Once more than one organization is created within ORCE, the organization must be assigned to each Application Client ID within the User screens. If more than one organization is assigned to the Client, the primary organization will be used by Order Administration.
The Application Client ID (and Secret) that the ORCE Organization has access to, will be defined in the Work with Outbound Web Services (WWSA) in Classic View for each company. That Client ID for the company is what ORCE will use for selecting the organization to work with.
-
Update the Client ID and Secret for each of the Web Services within Work with Outbound Web Services (WWSA) to ensure all communication is pointing to the correct ORCE Organization:
-
-
ORCE Coupon Service
-
ORCE Customer
-
ORCE File Service
-
ORCE Loyalty
-
ORCE Purchase History
-
ORCE Registry
-
ORCE Stored Value Card
-
ORPE Promotion
-
Additionally, once ORCE is configured for multiple organizations and you are sending the ORCE POSLog, the ORCE Import Folder Path (M63) system control value must be updated to include the ORCE Organization ID.
-
For a single organization the path is ‘imports/fileset/’
-
For multiple organization the path is ‘imports/fileset/#/’ where # is the ORCE Organization ID available through the ORCE Organization UI.
Customer Engagement Update Customer with Relate ID Process
This process updates the Relate ID in the Customer Sold To table with the correct customer ID from Customer Engagement.
| # | Step |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Runs a query over the Customer Engagement database to produce a list of Customer Engagement customers that have a Order Administration customer ID defined in the alternate key SERENADE_ID. Example: 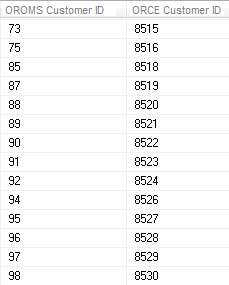 |
|
2 |
Saves the query results as a comma separated value file (CSV) in the directory specified in the ORCE_CUSTOMER_ ID_DIRECTORY_PATH property. |
|
3 |
Runs the RLTCSID Update Customer with Relate ID periodic function (program name PFRCIU) to submit the RLTCUSTID job. This job uses the Order Administration Customer number and Customer Engagement Customer ID in the saved query file to update the Relate ID for the sold to customer in the Customer Sold To table. For each record in the Customer Sold To table that is updated, the system also updates the Synchronize with Remote DB field to N. Note: This periodic function updates the Relate ID for the sold to customer in the Customer Sold To table based on the query results file, regardless of whether a Relate ID was already defined for the sold to customer. |
|
4 |
Order Administration writes any messages related to the Relate ID update, including any errors that may occur during processing, to the Application Log. |
|
5 |
Once the job is complete, the system deletes the query results file saved in the ORCE_CUSTOMER_ ID_DIRECTORY_PATH. |
Setup in Customer Engagement for the Sales and Customer Integration
The setup required in Customer Engagement to use the Customer Engagement Sales Feed and Customer Engagement Customer Integration is described below.
Order Management System Company > Customer Engagement Organization
An organization in Customer Engagement corresponds to a company in Order Administration. You associate a Customer Engagement organization with an Order Administration company through the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) system control value.
Use the System Configuration screens to define configuration settings for the Customer Engagement organization that integrates with Order Administration. See the Customer Engagement Implementation Guide for information on working with system configuration settings in Customer Engagement.
Configuration Settings Required for the Order Administration Customer and Sales Integrations with Customer Engagement
Select System > Configuration in Customer Engagement to define these settings for the organization that integrates with Order Administration.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
|
Organization Descriptor |
The organization descriptor must match the setting in the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) system control value. This setting identifies the Customer Engagement organization that maps to your Order Administration company. |
|
Default Location ID |
Enter a default location ID of up to 12 positions. |
|
Customer Classes All Types |
Enter NONE, NONE. |
|
Customer Classes Default Type |
Enter NONE. |
|
Enable Xstore Alt Key Creation |
Select this field if the integration to Customer Engagement includes Order Administration and Oracle Retail Xstore Point-of-Service. Selecting this field will assign an XSTORE_ID to the customer if one does not already exist. |
|
Use Customer Validation |
Select this option to validate customer input and strip invalid character data. Customer validation is performed using the Customer Engagement customer-validation.xml file. Customer information is checked for extra spaces, special characters, numbers in inappropriate places, and other similar configurable checks. |
|
Retail Transaction Register ID Length |
Set to 8. |
|
Retail Transaction Store ID Length |
The store ID sent to Customer Engagement from Order Administration is defined in the Default Location for ORCE Integration (K69) system control value and cannot be greater than 8 positions and should not be greater than the length specified in the Retail Transaction Location ID Length specified in Customer Engagement, typically 5 positions. |
Note:
Whenever you make changes to an organization’s configuration settings, you must stop Customer Engagement, deploy the configuration settings to Customer Engagement, and restart Customer Engagement. See:
-
Shut Down Services in the Add New Organization section of the Customer Engagement Implementation Guide (Installer Version) for more information on how to stop Customer Engagement.
-
the Customer Engagement Implementation Guide for more information on deploying configuration settings to Customer Engagement.
-
Restart Services in the Add New Organization section of the Customer Engagement Implementation Guide (Installer Version) for more information on how to restart Customer Engagement.
Order Management System Customer Profile > Customer Engagement Attribute Definition
In Customer Engagement, use the Attribute Definition screen to create an attribute definition for each Order Administration profile code that may be associated with a customer exported to Customer Engagement. See the Attribute Definition section of the Customer Engagement User Guide for detailed instructions.
Requirement: This setup is required whenever you send profile data to Customer Engagement, regardless of whether you use the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message or the interactive Customer Engagement Customer Integration. The Send Profile Data to ORCE (L51) system control value controls whether to include demographic profile data.
Required settings: When creating the attribute definition, define the fields as follows:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Intended Use |
Select Customer. |
|
Attribute Name |
Enter the Profile Description as defined in Order Administration. |
|
Unique |
Select this checkbox. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the attribute definition. Example: If the Order Administration profile is MARITAL STATUS, enter MARITAL STATUS. |
|
Data Type |
Select Character. |
If a customer profile > attribute definition cross reference does not exist:
-
Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration: If you send a profile code in the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message to Customer Engagement that does not exist as an attribute definition in Customer Engagement, Customer Engagement will not process the message and instead places the message in an error status.
Example:
XML Line Number: 3
Response: UNKNOWN_ATTRIBUTE_TYPE: attributeType=CALL ANYTIME
Exception(s) :
com.dtv.csx.services.customer.attributes.AttributeException: UNKNOWN_ATTRIBUTE_TYPE: attributeType=CALL ANYTIME
-
Customer Engagement Customer Integration: If Customer Engagement sends an attribute value for an attribute that you have not created as a profile category in Setting Up Customer Profiles (WPFL), Order Administration ignores the profile data when creating or updating the customer. Also, if Customer Engagement sends an attribute value for an attribute that exists as a profile category in Order Administration, but you have not set up a corresponding profile data option, Order Administration ignores the profile data. See Profile data under Customer Data Mapping between Order Administration and Customer Engagement for more information.
Customer Engagement attributes required if you also use Oracle Retail Xstore Point-of-Service: use the Attribute Definition screen in Customer Engagement to create an attribute definition for the following attributes.
| Name | Use | Description | Unique | Data Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ACTIVE_FLAG |
Customer |
Xstore Active Flag |
Y |
Logical |
|
EMAIL_RCPT_FLAG |
Customer |
Xstore Email Receipt Flag |
Y |
Logical |
|
CUSTOMER_GROUPS |
Customer |
Xstore groups |
Y |
Character |
|
PROMPT_TO_JOIN_LOYALTY |
Customer |
TRUE=Prompt Customer to Join Loyalty |
N |
Character |
|
PARTY_TYPE_CODE |
Customer |
Xstore Party Type |
N |
Character |
Creating Customer Type Codes
Purpose: If you use the Customer Engagement Customer Integration and have not sent customer information to Customer Engagement through the Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration, you need to confirm that all the required type codes are set up in Customer Engagement to support the mapping in the customer integration. If necessary, you need to create the type codes by adding rows to the corresponding tables in the Customer Engagement database.
Created dynamically? If you have previously used the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message to send customer information to Customer Engagement, then the type codes were dynamically created in the Customer Engagement database tables listed below.
Properties file entries: If a type code is one of the properties defined in the Customer Engagement Properties, the property is indicated in the table below. Normally, you should use the setting indicated in the table unless your representative indicates otherwise.
Displayed where?
-
The customer address type is displayed on the Customer Addresses screen in Customer Engagement.
-
The alternate key type is displayed on the Customer Alternate Keys screen in Customer Engagement.
-
The email type is displayed on the Customer Email Addresses screen in Customer Engagement.
-
The phone type is displayed on the Customer Telephone Numbers screen in Customer Engagement.
| Type Code | ORCE Table | Setting | Property |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Address |
CST_ADDR_TYPCODE |
HOME |
none |
|
Alternate key |
CST_ALT_KEY_TYPCODE |
Example: SERENADE_ID |
ORCE_ALT_ID_ OROMS |
|
|
CST_EMAIL_TYPCODE |
HOME |
none |
|
Phone |
CST_PHONE_TYPCODE |
daytime phone: BUSINESS evening phone: HOME fax or mobile phone: MOBILE |
ORCE_DAY_PHONE_LABEL ORCE_EVE_PHONE_LABEL ORCE_FAX_PHONE_LABEL |
Customer Engagement Sales Feed
The Customer Engagement Sales Feed allows you to send sales and return information from Order Administration to Customer Engagement.
Customer Engagement Sales Feed Setup: See Customer Engagement Integration Setup (Sales and Customer).
Customer Engagement Sales Feed Process
-
Run the RLTSLSF Customer Engagement Sales Feed periodic function (program name PFR0102) to submit the RLTSLSF job.
The ORCE File Service URL (M62) and ORCE Import Folder Path (M63) system control values must be specified for the company.
-
Order Administration writes any messages related to the Sales feed, including any errors that may occur during processing, to the Application Log.
-
Order Administration generates the following messages using item and invoice information from the Order Administration database:
Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message: Contains sales and credit invoice information for invoices whose Extracted to Store field in the Invoice Header table is blank.
Excluded sales (debit) invoices: The system excludes sales (debit) invoices from the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction message whose OST OBR Delivery Type in the Order Ship To table matches the setting of the Cross Channel Orders to Exclude in Sales Feed (L35) system control value.
Excluded return (credit) invoices: The system excludes return (credit) invoices from the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction message whose return disposition code matches the setting of the Return Disposition Code to Exclude in ORCE Sales Feed (M22) system control value when the Suppress refund field in the Order Payment Method table is Y.
Merchandise amounts only? The setting of the Merchandise Only in Sales Feed (L36) system control value determines whether Order Administration includes full invoice totals or only merchandise and tax amounts in the message.
ItemID setting: The setting of the ORCE Integration Item ID (L38) system control value determines how Order Administration populates the ItemID in the message.
Non-merchandise amounts: If the Merchandise Only in Sales Feed (L36) system control value is unselected, the Item for Non-Merchandise Amounts (L39) system control value defines the item code that represents all non-merchandise amounts for an invoice, such as freight, additional freight, handling and additional charges in the message.
Order Administration creates an XML batch file that contains all of the POS messages generated and names the file cw-poslog_CO#_STORE_ID_DATETIME.xml where:-
CO# is the Order Administration company number
-
STORE_ID is the value defined in the Default Location for ORCE Integration (K69) system control value
-
DATETIME is the date and time the file was created in YYMMDDHHMMSS format; for example if the file was created on November 23, 2023 at 9:21:41, the DATETIME displays as 231123092141.
Example file name: cw-poslog_007_12301974_231123092141.xml
-
-
Order Administration creates an XML batch file that contains all of the POS messages generated and names the file cw-poslog_CO#_STORE_ID_DATETIME.xml where:
-
SKU Relate Extracted field in the SKU table for the items/SKUs included in the Customer Engagement Feed to Y.
-
Extracted to Store field in the Invoice Header table to Y.
-
-
Order Administration places the XML batch files in the directory defined in the ORCE_DIRECTORY_PATH property. If the XML batch file contains the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message or the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message, Order Administration also creates an empty text file named OTHER.done to notify Customer Engagement that the XML batch files are ready to be picked up and processed by Customer Engagement.
-
Unless you are using the Customer Engagement File Transfer Service (FTS), Customer Engagement retrieves the XML batch files from the ORCE_DIRECTORY_PATH and processes the messages.
-
For each XML message that is processed successfully, Customer Engagement updates the appropriate tables in the Customer Engagement database. You can view the results in the Customer Engagement application. For more information on how Order Administration populates each message, the tables in the Customer Engagement database that are updated and where you can view the information in Customer Engagement, see the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1).
Customer Engagement File Transfer Service (FTS)
Overview: The Oracle Retail Customer Engagement file transfer service enables you to transfer customer, sales, and item information to Customer Engagement through a RESTful API.
Note:
Use of the file transfer service is required for integration with Oracle Retail Customer Engagement 20.0 or higher; however, it is not supported in earlier releases of Customer Engagement.
If the file transfer service is enabled, it transfers data generated through the following Periodic Functions:
-
Customer Engagement Sales Feed (RLTSLSF)
Process overview:
-
When each of the above periodic functions runs, it creates the xml files that are stored temporarily at the ORCE_DIRECTORY_PATH, as described above under Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration Process Flow and Customer Engagement Sales Feed.
-
If the ORCE File Service URL (M62) and ORCE Import Folder Path (M63) system control values are specified, the system creates a zip file that contains the generated xml files for the company. The zip file is named OMS_123_ws_210503092141.zip where:
-
OMS is hard-coded
-
123 is the company code
-
ws is the value defined in the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) system control value
-
210503092141 is the date and time in YYMMDDHHMMSS format
-
-
The system posts a request to the Customer Engagement file transfer service using the ORCE File Service authentication, as described below. The request includes the objectName tag, set to the ORCE Import Folder Path setting plus the zip file name. For example, if the ORCE Import Folder Path is set to imports/fileset/, and the zip file name is OMS_123_ws_210503092141.zip, then the objectName tag is set to imports/fileset/OMS_123_ws_210503092141.zip.
-
If the request is successful, the file transfer service returns:
-
A pre-authorization request (PAR) in the response message. This pre-authorization is valid for a limited time.
-
The accessUri indicating where to place the file.
-
-
The system then posts a PUT request to put the file in the specified accessUri.
-
If the PUT succeeds, the system then removes the files from the ORCE_DIRECTORY_PATH.
Customer Engagement scans the storage folder path on a regular basis (based on the Batch File Processing Schedule property defined in Customer Engagement) for new files to process, based on the Batch File Processing Schedule configuration setting.
Errors and troubleshooting:
-
If the request fails, the system removes the generated zip file, but the xml files remain in the ORCE_DIRECTORY_PATH so that they can be included the next time you run one of the periodic functions listed above for the company.
-
If the ORCE Import Folder Path is not populated but not valid, the file transfer service does not return an error, but Customer Engagement does not process the transferred file. Unprocessed files are automatically purged after seven days. See the ORCE Import Folder Path (M63) for more information.
-
If the client ID specified for the ORCE File Service is not assigned the FileReview role in Customer Engagement, the request will fail.
Required configuration: In addition to the requirements described under Customer Engagement Integration Setup (Sales and Customer), the following setup is required for the file transfer service:
-
System control values:
-
Web service authentication: Use the Work with Outbound Web Service Authentication Screen to set up authentication for the ORCE File Service.
Note:
OAuth authentication is required for the ORCE File Service. Also, the client ID specified must be assigned the FileReview role in Customer Engagement.
Customer Engagement Customer Integration
Purpose: Use the Customer Engagement customer integration to keep customer information in Order Administration in sync with Customer Engagement when Customer Engagement is the system of record for customer information. This integration also keeps Order Administration in sync with an additional system, such as your e-commerce site or your point-of-sale application, if that system also integrates with Customer Engagement as its system of record for customers.
When does Order Administration communicate with Customer Engagement?
- Searching for a customer: When you search for an existing customer in an Order Administration menu option, Customer Engagement returns a list of customers matching the search criteria. See Notes on Searching for a Customer on Order Administration Screens for more information.
- Synchronizing customer information (add/update customer): Synchronization occurs when:
-
You create a new customer in Order Administration Classic View or Contact Center Order Entry. Order Administration sends a message indicating to create the new customer in Customer Engagement.
-
You retrieve an existing customer record from Customer Engagement. When Customer Engagement sends the current customer information to Order Administration, Order Administration creates or updates its customer record based on the information received from Customer Engagement. The creation or update occurs through both Classic View and Modern View.
-
You update an existing customer at an Order Administration Classic View or Modern View screen. Order Administration sends an update message to Customer Engagement.
-
You update an existing customer through the order API, in certain cases. See Customer Synchronization through the Order API for a discussion.
-
You use a periodic function to synchronize Order Administration customer records with Customer Engagement. Order Administration sends its current customer information to Customer Engagement and stores the Relate ID in the Customer Sold To table. See Synchronizing Customer Information through a Periodic Function for more information.
-
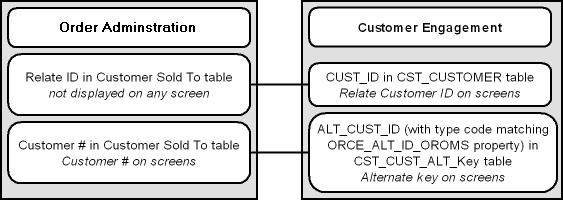
How are synchronized customers linked? A pair of synchronized Order Administration and Customer Engagement customer records are linked by matching customer numbers:
- Order Administration: the Relate Id in the Customer Sold To table identifies the customer ID in Customer Engagement
- Customer Engagement: the Alternate key in Customer Engagement identifies the customer number in Order Administration. The ORCE_ALT_ID_OROMS setting in Working with Customer Properties (PROP) defines the alternate key type for the Order Administration customer number in Customer Engagement.
E-Commerce site: If your e-commerce site also uses Customer Engagement as the system of record for customers, then the e-commerce customer ID is also stored in Customer Engagement as an alternate key. In this situation, the e-commerce site might pass its customer ID in the CWOrderIn message to help Order Administration identify the correct record when synchronizing customer information with Customer Engagement if the e-commerce site does not have the Order Administration customer number. The e-commerce site does not pass the Relate ID to Order Administration in the order API. See Customer Synchronization through the Order API for a discussion.
Setup for the Customer Engagement customer integration: Customer synchronization takes place if the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT. See Customer Engagement Integration Setup (Sales and Customer) for more information on required setup.
Order Administration initiates contact: In the Customer Engagement customer integration, Order Administration initiates all customer searches and add/update messages by sending these requests to Customer Engagement.
Customer Engagement version compatibility: The Customer Engagement customer integration in Order Administration, as described below, is compatible with version 10.5 or higher of Customer Engagement.
In this topic:
- Customer Engagement Customer Integration: Typical Information Flows
- Notes on Searching for a Customer on Order Administration Screens
- Customer Data Mapping between Order Administration and Customer Engagement
- Updating an Existing Customer
- Synchronizing Customer Information through a Periodic Function
- Customer Engagement Customer Integration: Notes and Troubleshooting
For more information: See:
- Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration for more information on sending merchandise hierarchy, item, customer, sales and return information from Order Administration to Customer Engagement using a batch process. This section also includes Customer Engagement Integration Setup (Sales and Customer).
- Customer Engagement Purchase History Integration for more information on reviewing completed sales and return transactions from Customer Engagement on the Display Purchase History Screen in Order Administration.
- Customer Engagement Customer Wish List Integration for more information on how to review and modify a customer’s wish list from Customer Engagement using the Display Wish List Screen in Order Administration.
- Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration for more information on using the Customer Engagement Loyalty integration with Order Administration.
- The Customer Engagement Implementation Guide for more information on configuration settings for Customer Engagement.
- The Customer Engagement Batch Processing and Web Services Guide for more information on the Customer Engagement API interface.
- The Customer Engagement Database Dictionary for more information on the tables in the Customer Engagement database.
- The Customer Engagement User Guide and JET UI User Guide for more information on using the Customer Engagement application.
Customer Engagement Customer Integration: Typical Information Flows
Overview: Through the customer integration with Customer Engagement, information about the customer flows between the e-commerce site, the point-of-sale (POS) system, Customer Engagement, and Order Administration, so that the customer’s current name, address, and email address are synchronized across systems. Customer Engagement stores both the Order Administration customer number and the Xstore or e-commerce customer number as alternate keys. The ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value must be set to INTERACT.
Orders also flow between systems, such as between the POS system and Order Orchestration, and the customer information included in an order can trigger customer creation or update across systems.
Customer Synchronization through the Order API
Communication between Customer Engagement, the e-commerce site, and Order Administration through the Generic Order Interface (Order API) varies, depending on whether the customer registers and is logged in at the e-commerce site.
- Registered: If the customer registers or logs in at the e-commerce site, then the e-commerce site and Customer Engagement synchronize customer information in Customer Engagement before the e-commerce site sends the order to Order Administration. In this situation, Order Administration does not need to notify Customer Engagement to create the customer record, since the communication between the e-commerce site and Customer Engagement has already taken place; however, if the customer did not previously exist in all of the integrated systems or the customer information was not previously synchronized, Order Administration might need to update Customer Engagement with its customer number, and record the Relate ID in the Customer Sold To table. The most likely scenarios are described below.
| Scenario | Can Occur When: | More Information: |
|---|---|---|
|
Site has received OACS customer and Relate ID number from ORCE: The e-commerce site synchronizes customer information with Customer Engagement, where at that time there was a Order Administration customer number as an alternate key. |
The customer has previously placed an order in Order Administration, either through the order API or through the call center, and Order Administration has already synchronized the customer information with Customer Engagement. In this scenario, Customer Engagement optionally provides the Order Administration customer number as well as the Relate ID to the e-commerce site, and the e-commerce site provides these numbers to Order Administration in the CWOrderIn message. In this case, Order Administration updates its own customer record with current name and address information, but does not need to communicate with Customer Engagement, since the e-commerce site has already done so. The relate_cust_sync_success flag is set to Y. |
When the Customer Registers or Logs in at the E-Commerce Site |
|
Site does not have OACS customer number: The e-commerce site synchronizes customer information with Customer Engagement, and at that time there is no Order Administration customer number in Customer Engagement as an alternate key. |
A new customer registers on the e-commerce site and creates an order, and no previous communication has occurred between Order Administration and Customer Engagement. In this case, the e-commerce site providesthe ORCE customer ID in the CWOrderIn message, and Order Administration needs to synchronize its customer information with the current information that is already in Customer Engagement and the e-commerce site, including assignment of the current ORCE customer ID to the Order Administration customer record. The relate_cust_sync_success flag is set to Y. |
When the Customer Registers or Logs in at the E-Commerce Site |
|
E-Commerce site does not communicate with ORCE |
The customer checks out as a guest or the e-commerce site is unable to communicate with Customer Engagement for any reason before submitting the order to Order Administration, even if the customer might already exist in either Customer Engagement or Order Administration, or both. In this situation, an ecommerce customer number is passed, rather than the Order Administration or the ORCE customer ID. Order Administration notifies Customer Engagement to create or update the customer. The relate_cust_sync_success flag is set to Y. |
After Order Administration ships the order, it uses the Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration to communicate sales information to Customer Engagement.
The communication flows described below are:
- When the Customer Registers or Logs in at the E-Commerce Site
- When the Customer Checks Out as a Guest at the E-Commerce Site or the E-Commerce Site Cannot Communicate with Customer Engagement
- When Order Administration Cannot Communicate with Customer Engagement
When the Customer Registers or Logs in at the E-Commerce Site
Registration (new account) or login (existing account): The registration or account login process involves communication between Customer Engagement and the e-commerce site. For example:
- When the customer logs into the e-commerce site or creates a new
account, the e-commerce site:
-
searches Customer Engagement for the customer
-
if the customer does not exist in Customer Engagement, sends an add/update message to create the customer in Customer Engagement
-
if the customer does exist in Customer Engagement, sends an add/update message to update the customer in Customer Engagement with any changes to the customer’s name or address
-
- Customer Engagement:
-
creates the customer record if it does not exist, using the e-commerce site’s customer number as an alternate key; otherwise,
-
updates the customer record if it already exists, including adding the e-commerce site’s customer number as an alternate key, and updating the current name and address if necessary
-
acknowledges the e-commerce site’s request, including the e-commerce ID, the ORCE customer ID, and the Order Administration customer number if it already exists as an alternate key
-
Submitting the order for an existing Order Administration customer: The e-commerce site should include the Order Administration customer number and/or the ORCE customer ID, if they are available, in the CWOrderIn message. This could occur if:
- the customer has previously registered at the e-commerce site and used it to place an order; or,
- the customer has previously placed an order through the call center as well as registering through the e-commerce site, and Order Administration and Customer Engagement have synchronized the customer records independently of the e-commerce site.
In this scenario:
- the customer record in Customer Engagement includes:
-
the ORCE customer ID
-
the Order Administration customer number as an alternate key, with the type of key specified in the ORCE_ALT_ID_OROMS property.
-
the e-commerce ID as an alternate key
-
-
the customer record in Order Administration includes:
-
the Order Administration customer number
-
the ORCE Customer ID
Note:
The e-commerce ID is used to synchronize the customer record with Customer Engagement. Once the records are synchronized , the e-commerce ID is not retained.
-
- the CWOrderIn message from the e-commerce site should include:
-
the current customer name and address
-
the Order Administration customer_number and/or the Relate ID, passed as the orce_customer_ID
-
the relate_cust_sync_success flag set to Y, indicating that the e-commerce site and Customer Engagement have been synchronized with current customer information
-
the sold_to_address_update flag set to Y, indicating that Order Administration should update the customer information from the message in the Order Administration database
-
- Order Administration updates the customer name and address using the information from the CWOrderIn message and does not communicate with Customer Engagement, since the e-commerce site has already communicated with Customer Engagement and the ORCE customer ID is already stored in the customer record.
Exceptions:
- If the customer record with the specified number does not currently exist in Order Administration (for example, as a result of a merge/purge), Order Administration uses its standard matchcode search logic (see Customer Creation, Matching and Update Logic in the Order API) to attempt to find the customer in the Customer Sold To table, creates or updates the customer as needed, and sends the current customer information, including the Order Administration customer number, to Customer Engagement.
- When the customer record exists in Order Administration and the relate_cust_sync_success flag is set to N, but no orce_customer_id is passed, Order Administration uses the customer’s email address to obtain the ORCE customer ID and update the existing customer record if the record did not previously have a ORCE customer ID and the CWOrderIn message does not include the name and address, but does include:
-
A valid customer number and an email address, if the customer record did not previously have an email address specified, or
-
A valid customer number, if the customer record did previously have an email address specified.
If the CWOrderIn message includes just a valid customer number, and the customer’s email address is not known, Order Administration does not update the customer record with the ORCE customer ID.
When it creates the order, Order Administration sends the CWORDEROUT message, including the Order Administration customer number, to the e-commerce site.
Note:
-
If the e-commerce system submits multiple CWOrderIn messages for the same order (for example, if the payment information is sent after the initial message), it should include the Order Administration customer number or the ORCE customer ID each time.
-
The sold_to_address_update flag should be set to Y when the CWOrderIn message includes customer name and address information.
When it creates the order, Order Administration sends the CWORDEROUT message, including the Order Administration customer number and the ORCE customer ID, if known, to the e-commerce site.
When the Customer Checks out as a Guest at the E-Commerce Site or the E-Commerce Site Cannot Communicate with Customer Engagement
Unknown customer? If the e-commerce site has not synchronized the customer information with Customer Engagement, the CWOrderIn message does not include either the Order Administration customer number or the e-commerce ID. This situation could occur if:
- the customer has opted to check out as a guest, or
- communication is down between the e-commerce site and Customer Engagement.
In either case, the e-commerce site cannot determine whether the customer record exists in either Customer Engagement or Order Administration.
In this scenario:
- the CWOrderIn message from the e-commerce site should include:
-
the current customer name, address, and email address
-
the relate_cust_sync_success flag set to N, indicating that the e-commerce site and Customer Engagement have not been synchronized with current customer information
-
the sold_to_address_update flag set to Y, indicating that Order Administration should update the customer information from the message in the Order Administration database
-
Note:
In this scenario, the CWOrderIn message does not include either the Order Administration customer number or the e-commerce ID.- To synchronize the customer records across the systems, Order
Administration:
-
searches for the customer in Order Administration using its standard matchcode search logic; see Customer Creation, Matching and Update Logic in the Order API
-
if it finds a matching customer and that customer does not currently have an ORCE Customer ID:
-
updates the customer name and address with the information from the CWOrderIn message
-
sends an update to Customer Engagement including the Order Administration customer number to add as an alternate key and the current name and address information from the CWOrderIn message, and updates the Order Administration customer with the ORCE Customer ID
-
-
if it finds a matching customer and that customer already has a ORCE Customer ID
-
updates the customer with the information from the CWOrderIn message
-
sends an update to Customer Engagement, including the Order Administration customer number and the current name and address information
-
-
if there is no matching customer in Order Administration:
-
creates a new customer in Order Administration using the information from the CWOrderIn message
-
sends a message to search Customer Engagement based on the customer’s email address
-
if Customer Engagement returns any matching customers, selects the first customer in the response that does not currently have a Order Administration alternate key; sends an update to Customer Engagement, including the Order Administration customer number to add as an alternate key and the current name and address information from the CWOrderIn message; and updates the Order Administration customer with the Relate ID
-
if Customer Engagement does not return any matching customers, creates a new customer in Customer Engagement and synchronizes the current customer name and address, Order Administration customer number, and Relate ID between Order Administration and Customer Engagement
-
-
Note:
Order Administration searches Customer Engagement for a customer using email address only if the relate_cust_sync_success flag is set to N.Exception: If Order Administration creates a new customer or selects an existing customer without a Relate ID, but Customer Engagement returns only customers that already have Order Administration alternate keys in the search response, Order Administration selects the first customer record returned in the search response and updates it with the current name and address information and the Relate ID.
Note:
Set the sold_to_address_update flag to Y when the CWOrderIn message includes customer name and address information.When it creates the order, Order Administration sends the CWORDEROUT message, including the Order Administration customer number, as well as the ORCE customer ID, to the e-commerce site.
When Order Administration Cannot Communicate with Customer Engagement
If Order Administration cannot communicate with Customer Engagement during order API processing, it selects the Synchronize with remote DB flag for the customer sold to record. The next time you run the SYNCRDB periodic function, it attempts to synchronize the Order Administration customer record with Customer Engagement.
If an e-commerce ID was passed in the CWOrderIn message, this ID is stored in the Customer Sold To table until the record is synchronized.
See Synchronizing Customer Information through a Periodic Function for more information on the SYNCRDB periodic function.
What Does the relate_cust_sync_success flag Control?
The relate_cust_sync_success flag in the CWOrderIn message indicates whether the e-commerce site has successfully synchronized information about the customer with Customer Engagement when the ORCE customer ID is not passed.
If this flag is set to Y:
- When the system searches Order Administration for a customer using standard customer selection rules, if the selected customer already has an ORCE customer ID, the system creates a new customer for the order, since the existing Order Administration customer record is not consistent with the Customer Engagement customer record. The system then synchronizes the customer record with Customer Engagement, updating the ORCE_ALT_ID_OROMS in Customer Engagement as an alternate customer number as well as the ORCE_ALT_ID_WEB, if available, but not updating other fields such as the signup store or home store.
- When creating a new customer for the order, the system does not search Customer Engagement for a customer record based on email address; it only sends an update, as described above.
- The system does not send an update to Customer Engagement if the CWOrderIn message specifies a valid Order Administration customer by customer number or alternate customer number, and the customer already has an ORCE customer ID.
Otherwise, if this flag is set to N:
- When the system searches Order Administration for a customer using standard customer selection rules, if the selected customer already has an ORCE_ALT_ID_OROMS in Customer Engagement, the system uses this customer instead of creating a new customer for the order, and sends a name and address update to Customer Engagement if the information is different; however, it does not update the home store or signup store.
- The system searches Customer Engagement for a customer record based on the email address for the customer on the order when it creates a new customer because a customer does not match the name and address in the CWOrderIn message, or when it selects an existing customer that does not have a ORCE customer ID or e-commerce ID. In this case, if there is a match found in Customer Engagement, the customer record in Order Administration is updated with the alternate keys from Customer Engagement.
- The system always sends a create/update request to Customer Engagement that includes the customer’s name, address, and customer number. The request does not include other fields, such as the signup store or home store, if the customer is already assigned an ORCE customer ID.
-
If the customer exists in Order Administration but does not already have an ORCE customer ID, Order Administration obtains the ORCE customer ID when the CWOrderIn message does not include the name and address, but does include:
-
A valid customer number and an email address, if the customer record did not previously have an email address specified, or
-
A valid customer number, if the customer record did previously have an email address specified.
-
Otherwise, if the CWOrderIn message includes just a valid customer number, and the customer’s email address is not known, Order Administration does not update the customer record with the Customer Engagement customer ID.
When the Customer Contacts the Call Center
Overview: A customer can also create an order by contacting the call center. When the customer contacts the call center to place an order, request a catalog, create a customer membership outside of order entry, or update name and address information, the CSR needs to first search for the customer in order to keep the Customer Engagement and Order Administration customer records in sync and prevent creating duplicate records. The process when a customer contacts the call center is:
- Search Customer Engagement first: When the CSR performs a search, Order Administration first checks in Customer Engagement for any matches. Unlike the process used for the order API, the customer search can send various criteria to Customer Engagement. If the CSR selects a customer from the search results and enters any updates, Order Administration syncs these updates with the Customer Engagement customer record.
- Search Order Administration second: If the CSR’s search does not find any matches in the Customer Engagement database, Order Administration checks for any matches in its Customer Sold To table. When the CSR selects and works with a Order Administration record, Order Administration sends the current information to Customer Engagement, creating the customer record there and stores the returned ORCE customer ID with the customer record.
- Create customer if no match: If there are no matches in either database, then the CSR can create a new customer, and Order Administration sends the new customer record to Customer Engagement, then stores the returned ORCE customer ID with the new customer record.
Examples of these processes are provided below.
Searching Customer Engagement for the Customer
When the customer contacts the call center to place an order, request a catalog, create a customer membership outside of order entry, or update name and address or other information:
Searching:
- The CSR enters the search criteria at the Customer Scan Screen.
- There is at least one customer record in Customer Engagement that matches the search criteria.
- The Results tab at the Customer Scan screen displays the names, home addresses, email addresses, and primary phone numbers of any customers in the Customer Engagement database matching the search criteria. The Results tab displays the error message Maximum search results exceeded, please refine your search if the number of matching records exceeds the Customer Lookup Limit system configuration setting in Customer Engagement. In this situation, you need to make your search criteria more specific to make sure that you can find the customer record you are looking for.
Selecting a customer from the Customer Engagement search results:
- If the CSR selects a record from the Results tab:
-
Order Administration requests information on the complete customer record from Customer Engagement
-
Customer Engagement sends the customer information, including the alternate key, if any, that maps to the Order Administration customer number.
-
If the alternate key identifies an existing customer in the Customer Sold To table, Order Administration updates the customer record with the current information from Customer Engagement. Also:
-
If more than one record in Customer Engagement is assigned the same alternate key mapping to the Order Administration customer number, Order Administration uses the information from the first matching record to update the customer record in the Customer Sold To table.
-
If the alternate key that identifies an existing customer in the Customer Sold To table has a different ORCE customer ID, Order Administration updates the ORCE customer ID for the customer record.
-
-
If there is not an alternate key that identifies an existing customer in Order Administration, Order Administration creates a new customer record.
-
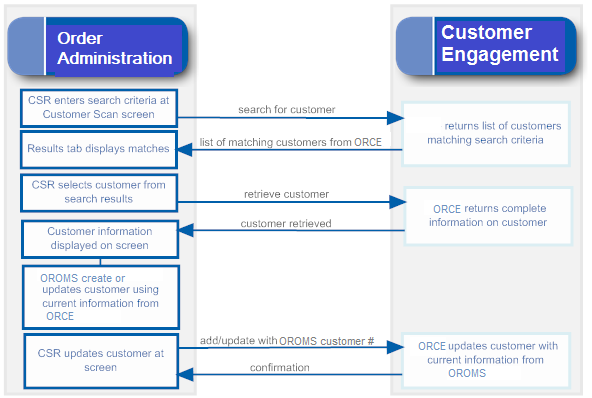
Searching Order Administration for the Customer in Classic View
Searching:
- The CSR enters the search criteria at the Customer Scan Screen.
- There are no records in Customer Engagement that match the search criteria, but there is at least one match in the Order Administration Customer Sold To table.
- The Results tab at the Customer Scan screen displays the names, home addresses, email addresses, and primary phone numbers of any customers in Order Administration’s Customer Sold To table that match the search criteria.
Selecting a customer from the Order Administration search results:
- If the CSR selects a record from the search results:
-
Order Administration retrieves the current information from its Customer Sold To table.
-
When the CSR updates or accepts the customer information, Order Administration sends an add/update message to Customer Engagement.
-
Customer Engagement creates the customer record, assigning the Order Administration customer number as an alternate key, and sends the Customer Engagement customer number to Order Administration.
-
Order Administration updates the Customer Sold To record with the Relate Id.
-
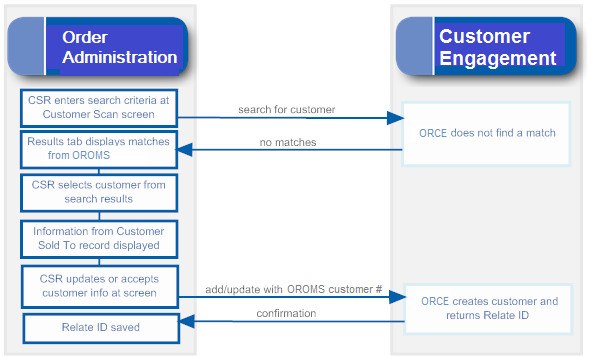
Creating a New Customer
Searching:
- The CSR enters the search criteria at the Customer Scan Screen.
- There are no records matching the search criteria in either Customer Engagement or Order Administration.
- The results do not include any records.
Creating the customer:
- When the CSR enters the information on the new customer:
-
Order Administration creates the customer record in its Customer Sold To table.
-
Order Administration sends an add/update message to Customer Engagement.
-
Customer Engagement creates the customer record, assigning the Order Administration customer number as an alternate key, and sends the Customer Engagement customer number to Order Administration.
-
Order Administration updates the Customer Sold To record with the Relate Id.
-
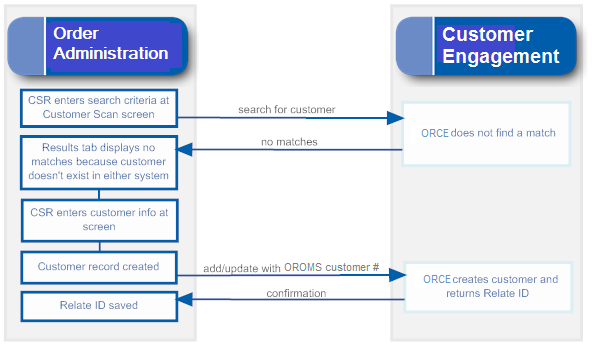
Notes on Searching for a Customer on Order Administration Screens
Since the Customer Engagement customer integration is based on Customer Engagement acting as the system of record for customer information, searching on Order Administration screens always looks to Customer Engagement first for the customer unless the menu option is related to existing orders.
Customer Scan screen availability: Order Administration provides the Customer Scan Screen to search for a customer in order entry, customer maintenance, and customer membership creation if the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT. When you search using this screen, the system first calls Customer Engagement when searching for customers, and checks the Order Administration Customer Sold To table only if Customer Engagement does not return any records that match your search criteria.
You cannot use the Customer Scan Screen when searching for a customer in regular or streamlined order inquiry, order maintenance, or return authorizations, because these options are related to existing orders for the customer in Order Administration. In these options, if you scan on a field related to customer name or address, you advance to a subsequent scan screen that displays customer records from the Order Administration database.
Note:
If the CSR creates a new customer without first searching, this indicates to create the customer in Customer Engagement regardless of whether any duplicate customers exist there. To avoid creating duplicate customers in Customer Engagement, it is important to search first.For more information: See the Customer Scan Screen for more information on searching for customers at Order Administration screens.
Customer Synchronization through Modern View
Searching for a Customer at the Home Page
If the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT, when you search for a customer in Modern View, Order Administration submits the search to Customer Engagement.
Customer(s) found in Customer Engagement? If Customer Engagement returns any customer records, they are displayed in the customer search results:
-
If a customer returned in the response is selected, but did not previously exist in Order Administration, the customer record is created, and an Order Administration customer number is assigned.
-
If a customer returned in the response is selected and did previously exist in Order Administration, but was not assigned a Customer Engagement ID, the customer record in Order Administration is updated with the ID passed from Customer Engagement, as well as the name and address information from Customer Engagement
-
If a customer returned in the response is selected and previously existed in Order Administration with a Customer Engagement ID assignment, the customer’s name and address information are updated with the information from Customer Engagement.
Customer not found in Customer Engagement? If there are no matches returned from Customer Engagement, any matching records in the Order Administration Customer Sold To table are displayed. If there is only one matching record, Order Administration sends the customer information to Customer Engagement. Customer Engagement creates a record for the customer and sends the new Customer Engagement ID to Order Administration, and Order Administration updates the customer record with the ID.
The page indicates whether the search results were found in Customer Engagement or in Order Administration.
Search based on Customer Engagement ID? The Use Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Customer Number on Search flag in Work with Contact Center controls whether to submit your entry in the customer number search field as the Order Administration customer number or the ORCE Customer ID. If you enter a customer number, any other search criteria you enter are ignored. If this flag is selected and the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT, Modern View screens display the Customer Engagement customer ID rather than the Order Administration customer number.
Contact Center Order Entry
If the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT, you can create or update a customer in Customer Engagement through Contact Center Order Entry in Modern View.
In Contact Center Order Entry, if the customer is:
-
New in both Order Administration and Customer Engagement: If you enter the name and address for a new customer, or update the information for an existing customer, the customer information is created or updated in Customer Engagement after you complete this step and advance to the Items step.
-
New in Order Administration but exists in Customer Engagement: If the information you enter to create a new customer in Order Administration matches an existing customer in Customer Engagement, the customer record in Customer Engagement is updated, including assigning the Order Administration customer number.
-
Exists in Order Administration but new in Customer Engagement: If the information you enter to create a new customer matches an existing customer in Order Administration and you select that customer at the Duplicate Customer Found window, but the customer is not already assigned a Customer Engagement ID, the customer record in Customer Engagement is created, and the new Customer Engagement ID is assigned to the customer in Order Administration.
-
Exists in both Order Administration and Customer Engagement: If the information you enter to create a new customer matches an existing customer in Order Administration and you select that customer at the Duplicate Customer Found window, and the customer is already assigned a Customer Engagement ID, the update applies to both the Order Administration and the Customer Engagement customer records.
-
If communication fails between Order Administration and Customer Engagement, the customer information is synchronized the next time you run the SYNCRDB periodic function. See Synchronizing Customer Information through a Periodic Function for more information.
Additional Customer Updates through Modern View
You can also update a customer in Modern View through the Edit Customer Information panel when searching for an order or customer, and the Edit Sold-To panel from the Order Summary page. In this case:
-
Exists in Order Administration but new in Customer Engagement: If you update a customer that is not already assigned a Customer Engagement ID, the customer record in Customer Engagement is created, and the new Customer Engagement ID is assigned to the customer in Order Administration.
-
Exists in both Order Administration and Customer Engagement: If you update a customer that is already assigned a Customer Engagement ID, the update applies to both the Order Administration and the Customer Engagement customer records.
-
If communication fails between Order Administration and Customer Engagement, the customer information is synchronized the next time you run the SYNCRDB periodic function. See Synchronizing Customer Information through a Periodic Function for more information.
Additional Ways to Create or Update a Customer in Order Administration and Customer Engagement
In addition to order entry, you can search for, create, or update a customer through the additional options listed below. If the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT:
| Option | Description | For more information, see: |
|---|---|---|
| Catalog request interface (WCRU) |
When you create a customer through the catalog request interface, the new customer information is also created in Customer Engagement. |
|
| Customer maintenance (WCST) |
When you select the Work with Customers option, you advance to the Customer Scan Screen. When you:
|
|
| Work with Customer Memberships (WWCM) |
When you prompt on the Customer # field at the Create Customer Membership Window, you advance to the Customer Scan Screen. If you:
|
|
| Customer API |
When you receive the Inbound Customer Message (CWCustomerIn) to create a new customer or update customer name, address, email, phone, or preferences, the customer information is sent to Customer Engagement so that the records are synchronized. For more information see the Order Administration Web Services Guide on https://support.oracle.com My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1). Note: Resubmitting a customer API request through Working with Customer API (WCAI) is not currently implemented. |
Generic Customer API For more information see the Order Administration Web Services Guide on https://support.oracle.com My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1). |
| Order Orchestration Integration |
When submitting a new order to Order Orchestration, the ORCE customer ID is sent as the customer_no in the SubmitOrder request if:
Receiving from Order Orchestration: When creating new orders based on the fulfillments response message, if:
The customer_no passed in the fulfillments response maps to the ORCE customer ID rather than the Order Administration customer number. When updating an existing customer through a retail pickup or delivery order, the updated customer information is sent to Customer Engagement for synchronization if the Sold to Email Update for Orders Brokered to OROMS (K96) or Sold to Address Update for Orders Brokered to OROMS (K97) system control values are selected. |
Retail Pickup (including Ship-for-Pickup) or Delivery Orders |
| Creating or selecting an order recipient |
When you:
Note: Only sold-to and recipient customers are synchronized with Customer Engagement. Order ship-tos and permanent ship-tos are not included in the integration with Customer Engagement. |
|
| Order maintenance |
When you: update the customer name, address, email, phone, or preferences for the customer placing or receiving the order (recipient customer but not a permanent ship-to or order ship-to), the updated customer information is sent to Customer Engagement. This update occurs regardless of whether the customer was previously synchronized with Customer Engagement. |
Customer Data Mapping between Order Administration and Customer Engagement
Overview: The table below lists the fields that are mapped between Order Administration and Customer Engagement in the customer integration.
Note:
- When Order Administration creates or updates a customer, it puts alphanumeric information in all uppercase. If the customer name and address in Customer Engagement is not all uppercase, this indicates that Order Administration has not created or updated the customer. The exception is the email address, which can be upper and lower case in both Customer Engagement and Order Administration.
- Not all mapped fields are the same length in both systems. When Order Administration imports information from Customer Engagement, it truncates certain fields as indicated in the table below, and updates the corresponding fields in Customer Engagement with the truncated information.
Reviewing the customer in Customer Engagement: Use the Customer Lookup / Edit option in Customer Engagement to search for, review, or update a customer.
Which tables? Customer records are stored in:
- Order Administration: the Customer Sold To table, except where noted below.
- Customer Engagement: the CST_CUSTOMER table.
For more information: See the Information that is not mapped for a listing of some of the fields that are not mapped as part of the Customer Engagement customer integration.
| OACS Field | ORCE Field | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Customer numbers | ||
|
Displaying in Customer Engagement: |
|
 |
|
Customer number |
Alternate key OROMS_ID |
Indicates the Alt Key Type of the alternate key in Customer Engagement that maps to the Order Administration customer number. This field is available for display in Customer Engagement by selecting Alternate Key in the Customer Lookup /Edit option. Customer Engagement automatically creates this entry for a customer when you send the customer to Customer Engagement interactively or through the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message if it does not already exist based on the ORCE_ALT_ID_OROMS setting in the Customer Engagement Properties file. In this situation, Customer Engagement also adds a row to the CST_ALT_KEY_TYPCODE table in the Customer Engagement database if it does not already exist. |
|
Relate id |
Customer ID |
Note: The Relate id:
|
| Name |
Displaying in Customer Engagement: Under Customer. |
 |
|
Prefix |
Prefix |
Truncated in Order Administration to 3 positions. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
First name |
First name |
Truncated in Order Administration to 15 positions. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
Middle initial |
Middle name |
Truncated in Order Administration to 1 position. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
Last name |
Last name |
Truncated in Order Administration to 25 positions. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
Suffix |
Suffix |
Truncated in Order Administration to 3 positions. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
Company |
Business Name |
Truncated in Order Administration to 30 positions. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
| Customer-level information and permissions |
The customer-level permissions in Customer Engagement are informational only. |
Displaying in Customer Engagement: Included under the Customer option. See above. |
|
Retail Store ID |
Signup Store Home Store |
The value defined in the Default Location for ORCE Integration (K69) system control value is passed if the relate_cust_sync_success flag is set to N in the CWOrderIn message, indicating that the e-commerce site has not yet successfully synchronized information about the customer with Customer Engagement. Otherwise, if the relate_cust_sync_success flag is set to Y, the location ID is not passed, in order to prevent updating the existing store locations in Customer Engagement. |
|
N/A |
Source |
Contact Center defaults when a new customer is sent to Customer Engagement. |
|
Mail flag |
Mail contact permission flag |
Order Administration to Customer Engagement: Y defaults if the Mail flag is selected Customer Engagement; otherwise leave blank. Order Administration does not automatically update the setting sent from Customer Engagement. |
|
Opt in/out setting for primary email address |
Email contact permission flag |
Order Administration does not automatically update the setting sent from Customer Engagement. |
|
Day or Evening phone number |
Phone contact permission flag |
Order Administration does not automatically update the setting sent from Customer Engagement. |
|
Do not fax |
Fax contact permission flag |
Order Administration to Customer Engagement: Y defaults if the Third Phone Number Type (L53) system control value is set to FAX and the Do Not Fax field for the customer in Order Administration is unselected; otherwise leave blank. Customer Engagement does not send this setting to Order Administration. |
|
Rent |
Rent contact permission flag |
Order Administration does not automatically update the setting sent from Customer Engagement. |
|
Birth Month and Birth Date |
Birth date |
Order Administration to Customer Engagement: The month and date defined in the Birth month and Birth date fields for the customer. The year passed to Customer Engagement defaults to 1900; however this year is not used if a birth year has already been defined in Customer Engagement. Note: If you remove the Birth month and Birth date from the customer in Order Administration, the Birth date defined in Customer Engagement is retained. Customer Engagement to Order Administration: The date defined in the Birth date field, including the actual month, day, and year defined. |
| Address Note: Only the customer’s HOME address in Customer Engagement is mapped to Order Administration. If more than one HOME address exists in Customer Engagement, the system uses the primary HOME address. This information is required in order for Order Administration to create the customer record correctly.Customer Engagement automatically creates an Address type of HOME when it receives a customer from Order Administration interactively or through the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message. In this situation, Customer Engagement also adds a row to the CST_ADDR_TYPCODE table for ADDRESS_TYPECODE HOME in the Customer Engagement database if it does not already exist. |
No address validation in Customer Engagement: Unlike Order Administration, Customer Engagement does not require an address for a customer, and does not validate that the address includes certain required components; for example, no address lines are required. To prevent problems in Order Administration, it is important that any other means you use to create customers in Customer Engagement, such as through your e-commerce site, always creates a home address when you use the Customer Engagement customer integration. If a home address does not exist in Customer Engagement, Customer Engagement displays the customer in Order Administration without an address. Also, if certain fields for the home address are not defined in Customer Engagement, these fields will be blank when you display the customer in Order Administration. However, when you update the customer’s address in Order Administration so that is passes validation, the system will also update the customer’s home address in Customer Engagement |
Displaying in Customer Engagement: Select Address.  |
|
N/A |
Primary |
Set to Yes in Customer Engagement. |
|
Street |
Address line 1 |
Truncated in Order Administration to 32 positions. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
Apt/Suite |
Apartment |
Truncated in Order Administration to 32 positions. If deleted in Order Administration, also deleted in Customer Engagement. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
Address (lines 2-4) |
Address lines 2-4 |
Truncated in Order Administration to 32 positions. Stored in the Customer Sold To Extended table. If deleted in Order Administration, also deleted in Customer Engagement. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
City |
City |
Truncated in Order Administration to 25 positions. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
State |
State |
Truncated in Order Administration to 2 positions and validated against the states in the Country table. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
Postal code |
Postal code |
Truncated in Order Administration to 10 positions and validated against the SCF table. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
Country |
Country |
Must be a 2-position country code; validated in Order Administration against the Country table. Note: Use the two-position ISO country code; for example, use US instead of USA.Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
|
Contact permission/opt in setting (address level) |
Order Administration to Customer Engagement updates:
Customer Engagement to Order Administration updates:
Note: The mail permission setting in Customer Engagement must consist of or start with the letters Y or N; otherwise, synchronizing the customer with Order Administration results in an error when validating the customer in Order Administration because the only valid settings in Order Administration are Y and N. |
| Phone numbers The phone numbers in Order Administration map to the soft-coded Telephone types based on the Customer Engagement Properties. Customer Engagement automatically creates the Telephone type codes of HOME, BUSINESS, and FAX or MOBILE when it receives a customer from Order Administration interactively or through the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message. In this situation, Customer Engagement also adds rows to the CST_PHONE_TYPCODE table for types of WORK, HOME, and FAX or MOBILE in the Customer Engagement database if they do not already exist. Note: Phone number extensions are not mapped between Customer Engagement and Order Administration. |
Phone numbers in Order Administration are stored in the Customer Sold To Phone # table. Any formatting is removed from the phone number before sending to Customer Engagement. Removing a phone number: If you delete a phone number in either Customer Engagement or Order Administration, the system deletes the associated phone number in the other system. |
Displaying in Customer Engagement: Select Phone. Optionally, highlight a phone number to open the Phone Detail window. 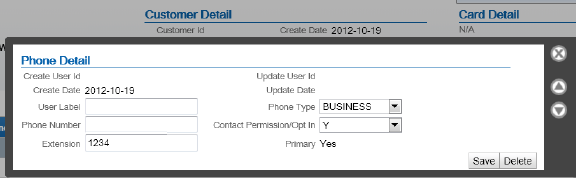 |
|
Day |
varies |
The ORCE_DAY_PHONE_LABEL setting in the Customer Engagement Properties file indicates the Telephone Type in Customer Engagement that maps to the daytime phone number in Order Administration; this setting should be set to BUSINESS. Any trailing spaces are removed from the phone number. Primary? If there is a daytime phone number, this phone number in Customer Engagement is flagged as Primary by default after synchronizing customer information with Order Administration. |
|
Eve |
varies |
The ORCE_EVE_PHONE_LABEL setting in the Customer Engagement Properties file indicates the Telephone Type in Customer Engagement that maps to the evening phone number in Order Administration; this setting should be set to HOME. Any trailing spaces are removed from the phone number. Primary? If there is no daytime phone number, then the evening phone number in Customer Engagement is flagged as Primary by default after synchronizing customer information with Order Administration. Also, if you delete the daytime phone number in Order Administration, then the evening phone number is flagged as Primary in Customer Engagement. |
|
Mbl or Fax |
varies |
The ORCE_FAX_PHONE_LABEL setting in the Customer Engagement Properties file indicates the Telephone Type in Customer Engagement that maps to the third phone number in Order Administration; this setting should be set to FAX or MOBILE. Any trailing spaces are removed from the phone number. Note: The Third Phone Number Type (L53) system control value controls whether the third phone number is labeled as the mobile or fax number in Order Administration.Primary? If there is no daytime or evening phone number, then the fax/mobile phone number in Customer Engagement is flagged as Primary by default after synchronizing customer information with Order Administration. Also, if you delete the daytime and evening phone number in Order Administration, then the fax/mobile phone number is flagged as Primary in Customer Engagement. |
|
N/A |
Contact permission/opt in setting (phone-level) |
For the day and evening phone numbers: Y defaults if a corresponding phone number is defined; otherwise N defaults. If the Third Phone Number Type (L53) system control value is set to FAX:
If the Third Phone Number Type (L53) system control value is set to MOBILE: Y defaults if a mobile phone number is defined; otherwise, N defaults. |
| Email address In Order Administration, the primary email address is stored in both the Customer Sold To table and the Customer Sold To Email table. Additional, non-primary email addresses are stored only in the Customer Sold To Email table. Only the HOME email address that is flagged as primary in Customer Engagement is eligible to be included in the integration. |
Customer Engagement automatically creates an Email type of HOME when it receives a customer from Order Administration interactively or through the Customer Engagement Add or Update Customer Message. In this situation, Customer Engagement also adds a row to the CST_EMAIL_TYPCODE table for EMAIL_TYPECODE HOME in the Customer Engagement database if it does not already exist. |
Displaying in Customer Engagement: Select Email. Optionally, highlight the email address to open the Email Detail window. 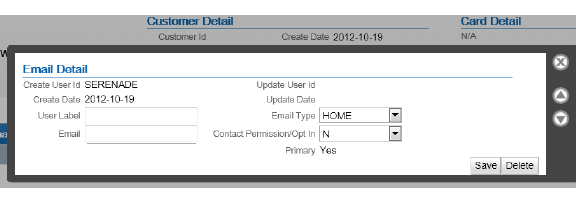 |
|
N/A |
Primary |
Set to Yes in Customer Engagement. |
|
Email address |
Email type: HOME |
Only the HOME email address that is flagged a primary is eligible to be included in the integration. If the customer has any other email type in Customer Engagement, but not a HOME email type, the email address(es) are not passed to Order Administration. Any trailing spaces are removed. |
|
Opt in/opt out |
Contact permission/opt in setting (email level) |
Order Administration to Customer Engagement updates:
Customer Engagement to Order Administration updates:
|
|
Format |
Format preference |
|
| Profile data In Order Administration, profile data is stored in the Customer Profile table. |
Included in the integration? The Send Profile Data to ORCE (L51) system control value controls whether to include demographic profile data when synchronizing customer information. Required setup: You need to complete the setup described under Order Management System Customer Profile > Customer Engagement Attribute Definition in order to synchronize the information between the systems. Examples are provided below. |
Displaying in Customer Engagement: Select Attributes.  |
|
Profile description |
Attribute name |
Use the Setting Up Customer Profiles (WPFL) option in Order Administration to set up the type of demographic information you are capturing, and also use the Attribute Definition screen in Customer Engagement to create a corresponding attribute definition for each Order Administration profile code. Example: To capture marital status, you can set up:
|
|
Profile data description |
Attribute value |
Use the Setting Up Customer Profiles (WPFL) option in Order Administration to set up each valid profile data value that you can capture. It is not necessary to set up valid data in Customer Engagement; Customer Engagement stores the data as a text string. Example: In the Setting Up Customer Profiles (WPFL) option in Order Administration, set up profile data options such as:
Customer Engagement stores an attribute value of MARRIED. |
| Additional information |  |
|
|
user ID |
Create user |
For new customers, set to OROMS-USERID, where USERID is the user ID of the person who performed the customer create, if the customer record originated in Order Administration. |
|
user ID |
Update user |
Set to OROMS-USERID, where USERID is the user ID of the person who performed the customer update, if the customer record was most recently updated by Order Administration. |
|
N/A |
Create date |
The date when the customer record was created in Customer Engagement. |
|
N/A |
Update date |
The most recent date when the customer record was changed. Activities in Order Administration that change the Update date include:
The above activities change the Update date in Customer Engagement, even if there is no change to the information about the customer or if you reject the order in order entry. Note: Creating an order for the customer through the order API changes the Update date in Customer Engagement if the sold_to_address_update flag in the CWOrderIn message is selected and no customer_number is passed, even if there is no change to the customer’s name and address information. |
|
ORCE_SECURITY_USER_ID |
Security ID |
The Customer Engagement user ID with security group permission defined in the ORCE_SECURITY_ USER_ID setting in the Customer Engagement Properties file. Note: This value does not display on any screen in Customer Engagement. |
Information that is not mapped
- From Order Administration:
-
PO Box
-
Delivery code: From the Default Delivery Code for New Order Entry Customers (D13), but you can override this default. Not related to the Address type in Customer Engagement, although only addresses with a type of HOME are used as part of the integration.
-
Class: From the Default Customer Class in Order Entry (D63), but you can override this default.
-
Alternate customer number: However, if a third system, such as the e-commerce site, synchronizes with Customer Engagement, then its customer number might also be stored in Customer Engagement as an additional alternate key. Also, select the Enable Xstore Alt Key Creation system configuration setting in Customer Engagement if the integration to Customer Engagement includes Order Administration and XStore. Selecting this field will assign an XSTORE_ID to the customer if one does not already exist.
-
- From Customer Engagement:
-
County: If the county is populated in Customer Engagement, this information is cleared when the customer record is synched with Order Administration.
-
Address type: Only the address with a type of HOME is used as part of the integration. If the customer record in Customer Engagement does not have a HOME address, then the address you enter for the customer in Order Administration is created as the HOME address in Customer Engagement.
-
Email address: Only the email address with a type of HOME is used as part of the integration.
-
Class: The Default Customer Class in Order Entry (D63) defaults in Order Administration
-
Updating an Existing Customer
Overview: In general, the integration keeps existing Order Administration and Customer Engagement customer records synchronized when you update customer information through either system. A few things to note are listed below.
Deleting customer information through screens in Order Administration:
- If you delete address lines 2-4 or apartment in Order Administration, these address lines are also deleted in Customer Engagement.
- Deleting other data in Order Administration does not delete the corresponding fields in Customer Engagement; as a result, this data is repopulated when the customer information is resynchronized. This occurs if you delete the customer’s prefix, middle initial, suffix, company name, phone numbers, and primary email address in Order Administration.
Deleting customer information through Customer Engagement: Deleting prefix, first name, middle initial, suffix, last name or business name, address lines 2-4, apartment, phone number extensions, or email address in Customer Engagement deletes the corresponding fields in Order Administration. However, deleting phone numbers in Customer Engagement does not delete the phone numbers in Order Administration; as a result, the phone numbers are repopulated in Customer Engagement when the customer information is resynchronized.
Phone number extensions: If you add an extension to an existing phone number:
- if you add the extension in Order Administration, the extension is not added to Customer Engagement.
- if you add the extension in Customer Engagement, the extension is not added to Order Administration and is removed when the customer information is resynchronized.
For more information: See Customer Synchronization through the Order API.
Synchronizing Customer Information through a Periodic Function
Overview: The SYNCRDB periodic function (Program Name = PFR0105) sends current customer information to Customer Engagement. You can use this periodic function:
- if communication has failed for any reason during normal operations, so that customer information was not synchronized interactively
- to initially export customer information from Order Administration to Customer Engagement
Synchronization trigger: If the Synchronize with remote DB flag in the Customer Sold To table is set to Y, the SYNCRDB periodic function attempts to synchronize the customer record with Customer Engagement. Order Administration sets this flag to Y automatically when communication with Customer Engagement fails. To initially export existing customer information to Customer Engagement, you can use a SQL statement to set this flag to Y for all customer records if you do not use the conversion periodic function.
Synchronization updates: The SYNCRDB periodic function:
- sends current customer information from Order Administration to Customer Engagement, including creating an alternate key in Customer Engagement using the Order Administration customer number; see Customer Data Mapping between Order Administration and Customer Engagement for details
- populates the Relate Id field in the Customer Sold To table if the field is currently blank
- clears the Synchronize with remote DB flag for the Customer Sold To record
- clears the E-commerce ID for the Customer Sold To record if the order API has saved this information to use when synchronizing the customer; see Customer Engagement Customer Integration: Typical Information Flows for more information
The periodic function does not retrieve information from the Customer Engagement customer record to update the Order Administration customer record, with the exception of populating the Relate Id.
Note:
The periodic function synchronizes customer records only if the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT.Information used for matching: The SYNCRDB periodic function uses the following information to match customer records between Order Administration and Customer Engagement:
- Relate Id: Customer Engagement customer number = Relate Id in the Order Administration Customer Sold To table
- Customer number: Customer Engagement alternate key record whose Alt Key Type matches the ORCE_ALT_ID_OROMS setting in Working with Customer Properties (PROP) = the Order Administration customer number
- E-commerce ID: Customer Engagement alternate key record whose Alt Key Type matches the ORCE_ALT_ID_WEB setting in Working with Customer Properties (PROP) = the e-commerce site’s customer number. From the ecommerce_id passed in the CWOrderIn message, and saved as the E-commerce ID in the Customer Sold To table only if the order API was unable to synchronize the Order Administration and Customer Engagement customer records
- Primary email address: an email address for the customer in Customer Engagement = the customer’s primary email address in Order Administration
Matching rules: The SYNCRDB periodic function uses the following rules:
- If a Relate Id or an e-commerce ID is specified in the Customer Sold To table and the Synchronize with remote DB flag is set to Y, Order Administration sends the current Order Administration customer number, e-commerce ID (if any), and customer name and address, including phone numbers and the primary email address.
Customer Engagement returns its Customer Engagement customer number; if this number is different from the current Relate Id in the Customer Sold To table, Order Administration updates the Relate Id. The current Relate Id might be different if, for example, a merge/purge took place in Customer Engagement.
- If no Relate Id or e-commerce ID is specified in the
Customer Sold To table, and the Synchronize with remote DB flag is set to Y, Order Administration first searches Customer
Engagement based on primary email address. If Customer Engagement
returns:
-
any matching customers, Order Administration synchronizes the customer with the first customer returned that is not already assigned a Order Administration alternate key; if all matching customers already have Order Administration alternate keys, it selects the first customer returned in the response
-
no matching customers, Order Administration sends an add/update message to create a new customer in Customer Engagement
-
Troubleshooting: The SYNCRDB function always creates a new customer in Customer Engagement if the Order Administration customer does not have an email address, e-commerce ID, or valid Relate Id. The function does not match customers based on name, address, or phone number.
Customer Engagement Customer Integration: Notes and Troubleshooting
Things to note:
- Must search before creating a customer at Order Administration screens: Because the Customer Engagement customer integration is based on using Customer Engagement as the system of record for customers, you need to use the Customer Scan Screen to search for a customer and make sure that the record does not already exist before creating a new record to avoid the possibility of creating a duplicate. Creating the customer without searching first indicates that you want the customer created, regardless of any existing duplicates.
- Customer Engagement customer ID: The Customer Engagement customer ID is stored in the Order Administration Customer Sold To table, and may be included in web service requests or used for customer matching as described above, but is not displayed on any screens in Order Administration.
- Logging: The information passed between Order Administration and Customer Engagement is written to the Trace Log if its logging level is set to DEBUG or ALL.
- If customer information returned from Customer Engagement is masked: If the customer information returned from Customer Engagement displays as asterisks instead of the actual data, there may be an authority problem with the ORCE_Security_User in Customer Engagement. In this situation, verify that the Default View Where No Security Group is Assigned property is set to Read/Write. If the default view cannot be changed, assign the ORCE_Security_User to the system admin role.
- If communication fails: If for any reason the communication fails between Order Administration and Customer Engagement and the synchronization cannot be completed, the Synchronize with remote DB flag in the Customer Sold To table is set to Y. You can use the SYNCRDB periodic function to synchronize the customer records; see Synchronizing Customer Information through a Periodic Function for more information.
- Customer Lookup Limit: The Results tab at the Customer Scan Screen displays the error message Maximum search results exceeded, please refine your search if the number of matching records exceeds the Customer Lookup Limit system setting in Customer Engagement. In this situation, you need to make your search criteria more specific to make sure that you can find the customer record you are looking for.
-
Narvar integration: If the Send ORCE Customer ID to Narvar (M70) system control value is selected, the ORCE customer ID, if assigned to the customer, is sent in the Narvar Order Request message.
-
Web services using the ORCE customer ID: See the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT, the ORCE customer ID is included in various web service messages rather than the Order Administration customer number. See that system control value for more information
-
Order Orchestration: The Send ORCE Customer ID to OROB (M71) system control value controls whether to send the ORCE customer ID in the SubmitOrder request, and the ORCE Customer ID in OROB Fulfillment (M72) controls whether the customer_no passed in the fulfillments response maps to the ORCE customer ID rather than the Order Administration customer number. See these system control values for more information.
Additional data from Customer Engagement not passed to Order Administration: Not all customer information in Customer Engagement is sent to Order Administration. See the Customer Data Mapping between Order Administration and Customer Engagement for details on the information that is mapped.
Additional data in Order Administration not passed to Customer Engagement: Not all customer information in Order Administration is passed to Customer Engagement. For example, permanent ship-to addresses, bill-to accounts, and contract pricing information are not passed. See the Customer Data Mapping between Order Administration and Customer Engagement for details on the information that is mapped.
Email addresses never deleted from Customer Engagement: Even if you change or delete a customer’s email address, this information is not visible on the screen but is retained in the Customer Engagement database. For this reason, searching on the deleted or overwritten email address still finds the customer, and customer matching logic described under Customer Synchronization through the Order API uses the deleted or overwritten email address as it would use a current email address.
Phone number extension: Phone number extensions are not passed between Customer Engagement and Order Administration.
Customer Engagement customer changed to uppercase by synchronization: When a Customer Engagement customer record is updated from the corresponding Order Administration customer record, the alphanumeric characters in Customer Engagement change to all uppercase. This occurs because Order Administration stores customer information in all uppercase. The exception is the email address, which is stored in upper and lowercase in both systems.
Company/business name: When you use the Customer Engagement customer integration, you cannot search for customer by name if the customer has a company/business name but not a last name.
No address validation in Customer Engagement: Unlike Order Administration, Customer Engagement does not require an address for a customer, and does not validate that the address includes certain required components; for example, no address lines are required.
Setup information: See Customer Engagement Integration Setup (Sales and Customer) for information on the required setup for integration with Customer Engagement.
Activities that do not Trigger Communication with Customer Engagement
Functions that do not request or update customer information from Customer Engagement include:
- generating backorder cards
- generating soldout notifications
- generating return or shipment confirmations
- pick slip generation
- membership order generation
- reviewing an order in order inquiry, including displaying the customer
- maintaining an order, unless you change information about the customer
- billing an order
- creating an order for the customer through the ChannelAdvisor integration
Deleting Certain Information for an Existing Customer
Certain information deleted in Order Administration is not deleted in Customer Engagement, and becomes repopulated in Order Administration after resynchronization. The information that persists in this process is:
- name fields, including the company/business name
- email address
Example: You delete the customer’s middle initial in Order Administration, but this does not delete this field in Customer Engagement. The next time the Customer Engagement and Order Administration customer records are resynchronized, the middle initial is repopulated in Order Administration.
Address fields: If you delete additional address fields in Order Administration, such as the second through fourth address lines and the apartment/suite, this information is also deleted in Customer Engagement and does not reappear after resynchronization.
Email and phone: If you change the email address and phone numbers in Order Administration, the previous information persists in the Customer Engagement database, although it is no longer displayed on the screen and does not repopulate the Order Administration customer record at resynchronization. However, if you search for a customer using the previous email address or phone number as a search criterion, the customer is eligible to be included in the search results.
Functions that are Inconsistent with the Customer Engagement Customer Integration
Customer search API: The generic customer inquiry (search) API does not support searching Customer Engagement for customers. This API searches across Order Administration customer records only.
Mass customer updates: Updates using NCOA or similar options in Order Administration are not recommended if you use the Customer Engagement customer integration.
Cannot delete a customer if using the Customer Engagement customer integration: If the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT, you cannot delete a customer in Order Administration customer maintenance.
Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration allows you to register customers in the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement loyalty program. Once a customer is registered in the loyalty program, you can retrieve the customer’s loyalty points and awards balances, accrue points from completed purchases, and redeem awards as a pro-rated merchandise discount on an order.
About loyalty programs: Loyalty programs define the rules used for tracking the purchases of customers belonging to store loyalty programs, usually through a system of points. The loyalty points can then be redeemed for discounts of a fixed amount (though the points alone have no intrinsic value). The discounts can be distributed through the mail as paper coupons, or made available to customers as an award coupon created by the award program associated with the customer’s loyalty card.
The Customer Engagement Loyalty integration retrieves a customer’s loyalty information from Customer Engagement at specific points in Order Administration so users can view a customer’s loyalty card information, current loyalty points, and current award coupons. Communication with Customer Engagement uses the Customer Engagement API Interface; the loyalty information is not stored in Order Administration. Certain activities in Order Administration update the customer’s loyalty account information in Customer Engagement:
- Modern View
-
the Customer Order List pages can display a prompt for the customer to join loyalty a loyalty program if not already a member.
-
a Loyalty tab is available at the Customer Order List pages to display the customer’s current loyalty and award programs. Optionally, you can issue points for a loyalty program, or issue an award coupon for an award program.
-
in Contact Center Order Entry, you can prompt for the customer to join a loyalty program if not already a member. If the customer is already a member of more than one program, you can select a card so that an award from the card can be applied to the order. At the Review step, you can specify the award amount to apply.
-
- Classic View
-
at Customer Loyalty Registration Window, you can ask a customer to join the loyalty program; when a customer joins, Customer Engagement generates a card for the customer and creates the customer’s loyalty account.
-
at the Issue Loyalty Points Window, you can issue points to the customer’s loyalty account; Customer Engagement increases the points in the customer’s loyalty program.
-
at the Issue Loyalty Coupon Window, you can issue an award coupon to the customer’s loyalty account; Customer Engagement creates the award coupon in the customer’s awards program.l
-
during order entry (interactive and using the generic order interface), you can apply an award amount to an order. When you accept the order, Customer Engagement subtracts the award amount from the customer’s awards program.
-
- the Customer Engagement Sales Feed sends sales and return information to Customer Engagement in the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message; Customer Engagement increases or decreases the loyalty points from the customer’s loyalty program based on the program rules defined for the customer’s loyalty card in Customer Engagement.
Entitlement Programs are not supported.
Note:
Other applications, such as XStore and the web storefront, communicate with Customer Engagement to retrieve and update loyalty account information for the customer. This section explains the Customer Engagement Loyalty integration between Customer Engagement and Order Administration only.In this topic:
- Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration Setup
- Setup in Order Administration for the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
- Setup in Customer Engagement for the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
- Registering a Customer in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Program
- Reviewing Customer Engagement Loyalty Account Information
- Applying Points to a Customer’s Loyalty Card
- Applying Coupons to a Customer’s Loyalty Card
- Accruing Loyalty Points during Order Processing
- Applying and Redeeming Customer Engagement Awards during Order Processing
- Oracle Retail Customer Engagement APIs used in the Loyalty Integration
For more information: See:
- Customer Engagement Customer Integration for more information on interactively communicating with Customer Engagement to keep customer information in Order Administration in sync with Customer Engagement when Customer Engagement is the system of record for customer information.
- Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration for more information on sending merchandise hierarchy, item, customer, sales and return information from Order Administration to Customer Engagement using a batch process. This section also includes Customer Engagement Integration Setup (Sales and Customer).
- Customer Engagement Purchase History Integration for more information on reviewing a customer’s purchase history from Customer Engagement on the Display Purchase History Screen in Order Administration.
- Customer Engagement Customer Wish List Integration for more information on how to review and modify a customer’s wish list from Customer Engagement using the Display Wish List Screen in Order Administration.
- The Customer Engagement Implementation Guide for more information on system configuration properties for Customer Engagement.
- The Customer Engagement Batch Processing and Web Services Guide for more information on the Customer Engagement API interface.
- The Customer Engagement Database Dictionary for more information on the tables in the Customer Engagement database.
- The Customer Engagement User Guide and the JET UI User Guide for more information on using the Customer Engagement application.
Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration Setup
Before you can use the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration, you must complete the required setup.
Required versions: To use the Loyalty Integration with Customer Engagement, you must be on these versions:
- Order Management System version 4.5 or higher, or Order Administration.
- Customer Engagement version 10.5 or higher.
In addition:
- the Customer Engagement Customer Integration and Customer Engagement Purchase History Integration uses version 2.3 of the Customer Services API.
- generating a new loyalty card and assigning it to a customer uses
version 3.1 of the Stored Value Card Transaction Services API.
Note:
In order for transactions to process correctly, the Franchisee feature must be disabled in Customer Engagement. - retrieving loyalty and award summary information for all accounts attached to a specified loyalty card uses version 2.1 of the Card Services API.
- issuing loyalty points to a specified loyalty card and retrieving all of the loyalty points account activity for a specified loyalty account uses version 1.2 of the Loyalty Account Services API.
- issuing an award coupon to a specified loyalty card, retrieving all of the award account activity for a specified loyalty account, and automatically redeeming an award coupon for a specified amount uses version 1.2 of the Award Account Services API.
Setup is required in both Order Administration and Customer Engagement.
- Setup in Order Administration for the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
- Setup in Customer Engagement for the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
For more information: See Customer Engagement Integration Setup (Sales and Customer) for more information on the setup required to use the Customer Engagement Sales Feed, and Customer Engagement Customer Integration.
Setup in Order Administration for the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
- System Control Values for the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
- Secured Feature for the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
- Web Service Authentication for Customer Engagement
- Customer Engagement Property Settings
- Menu Options Related to the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
System Control Values for the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
| System Control Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Select this system control value to automatically display the Enter Loyalty Award Discount Window when you select the Reprice option in order entry. |
|
|
Use this field to identify the Customer Engagement organization that maps to your Order Administration company. |
|
|
Use this field to define the Customer Engagement location to associate with the Customer Engagement loyalty program. Note: The location code must be numeric to prevent any possible issues displaying a customer’s purchase history in Xstore. |
|
|
Select this system control value if you want to use the Customer Engagement Loyalty integration. Important: If you select this system control value:
|
|
|
Select this system control value if you want the system to automatically display the Customer Loyalty Registration Window during order entry and Work with Customers when the sold to customer is not already registered in the Loyalty program. Note: If you select this system control value, the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value must be set to INTERACT, indicating you communicate with Customer Engagement interactively. |
|
|
Defines the 5 digit prefix assigned to the Card Definition in Customer Engagement that is used to assign new loyalty cards to sold to customers that join the loyalty program. Note: This setting must match the setting in Customer Engagement; for example, if the card prefix in Customer Engagement is00905, you must enter 00905 in this system control value.
|
|
|
Defines the 2 digit card series number assigned to the Card Definition in Customer Engagement that is used to assign new loyalty cards to sold to customers that join the loyalty program. Note: This setting must match the setting in Customer Engagement; for example, if the card series sequence number in Customer Engagement is02, you must enter 02 in this system control value.
|
|
|
Defines the program used to generate a Loyalty Registration Notification email when a sold to customer joins the loyalty program and is assigned a loyalty card in Customer Engagement. LoyRegNotf is the base program that generates the Loyalty Registration Notification email in HTML format. In this situation, the XML Only flag for the Loyalty Registration Notification email template must be unselected. |
Secured Feature for the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
| Secured Feature | Description |
|---|---|
|
This feature controls whether the Issue Points and Issue Awards options display on the Display Loyalty Account Screen.
|
Web Service Authentication for Customer Engagement
If the web services used to process inbound messages to Customer Engagement require web service authentication, you must provide a valid web service authentication user and password in Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA), or a client ID and client secret if using OAuth. In this situation, when Oracle Retail Order Administration generates a message to send to Customer Engagement it includes the web service authentication information in the HTTP header of the message. See Oracle Retail Omnichannel Web Service Authentication Configuration Guide on My Oracle Support (2728265.1) for more information.
Customer Engagement Property Settings
Working with Customer Properties (PROP) contains settings required for integration with Customer Engagement.
| Setting | Description | Example Setting |
|---|---|---|
|
ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX |
The system uses this property to build the URL for communication with Customer Engagement using the Customer Servics API. |
https://server:8447/ where: server = the name of your Customer Engagement server 8447 = the port to use on the Customer Engagement server |
|
ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_SUFFIX |
The system uses this property, along with
the |
/OrceWebServices/v2_3/CustomerServicesApiService?wsdl where 2_3 is the version of the Customer Services API |
|
ORCE_SVC_SERVICE_SUFFIX |
The system uses this property, along with
the |
/OrceWebServices/v3_1/SvcTransactionServicesApiService?wsdl where 3_1 is the version of the Stored Value Card Transaction Services API |
|
ORCE_CARD_SERVICE_SUFFIX |
The system uses this property, along with
the |
/OrceWebServices/v2_1/CardServicesApiService?wsdl where 2_1 is the version of the Card Services API |
|
ORCE_LOYALTY_SERVICE_SUFFIX |
The system uses this property, along with
the |
/OrceWebServices/v1_2/LoyaltyAccountServicesApiService?wsdl where 1_2 is the version of the Loyalty Account Services API |
|
ORCE_LOYALTY_AWARD_SERVICE_SUFFIX |
The system uses this property, along with
the |
/OrceWebServices/v1_2/AwardAccountServicesApiService?wsdl where 1_2 is the version of the Award Account Services API |
|
ORCE_LOYALTY_PROMPT_ATTRIBUTE |
Defines the corresponding Customer Engagement custom attribute to identify whether Order Administration should automatically display the Customer Loyalty Registration Window for a customer that is not already assigned to a loyalty card. See Customer Engagement PROMPT_TO_JOIN_LOYALTY Attribute Definition for setup instructions. |
PROMPT_TO_JOIN_LOYALTY |
|
ORCE_SECURITY_ USER_ID |
The Customer Engagement user ID with Security Group permission included in the Customer Engagement API messages. |
Must be a valid user ID in Customer Engagement that has Security Group permission |
|
ORCE_LOYALTY_REG_MESSAGE |
The text to display on the Customer Loyalty Registration Window, up to 55 positions. |
Does the customer want to join the loyalty program? |
Menu Options Related to the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
| Menu Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
Define default text to include in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Loyalty Registration Notifications. |
|
|
Create the RL (Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Communication Failure) order hold reason code. |
Setup in Customer Engagement for the Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration
- Order Management System Company > Customer Engagement Organization
- Customer Engagement PROMPT_TO_JOIN_LOYALTY Attribute Definition
- Card Definition
Order Management System Company > Customer Engagement Organization
An organization in Customer Engagement corresponds to a company in Order Administration. You associate an Customer Engagement organization with an Order Administration company through the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) system control value.
Use the System Configuration option in Customer Engagement to define settings for the Customer Engagement organization that integrates with Order Administration. See the Customer Engagement Implementation Guide for more information on how to define configuration settings for Customer Engagement.
Configuration Settings Required for the Loyalty Integration with Customer Engagement
Select System Configuration in Customer Engagement to define these settings for the organization that integrates with Order Administration.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
|
Default Location ID |
Enter a default location ID of up to 12 positions. |
|
Account Activity Lookup Limit |
Enter the maximum number of account activity records that can be returned when making any type of account activity lookup request to the Customer Engagement Services server. The default value is 400. If the number of loyalty account transactions
returned to Order Administration exceeds this setting, Order Administration
does not display any activity on the Display Loyalty Account History Screen and instead
displays an error message: |
|
Card Number Length |
Controls the number of digits in a card number. Must be between 10 and 16. |
|
Process Loyalty Returns |
Select Yes to process returns to a loyalty account. |
Note:
Whenever you makes changes to an organization’s configuration settings, you must use the Deploy option, available at the Customer Engagement System Configuration screen, to deploy the configuration settings.Customer Engagement PROMPT_TO_JOIN_LOYALTY Attribute Definition
In Customer Engagement, use the Attribute Definition screen to create an attribute definition that identifies whether Order Administration should automatically display the Customer Loyalty Registration Window for a customer that is not already assigned to a loyalty card.
Note:
The attribute you create must match the entry for the ORCE_LOYALTY_PROMPT_ATTRIBUTE setting in the Customer Engagement Property Settings.See the Attribute Definition section of the Customer Engagement User Guide for detailed instructions.
Required settings: When creating the attribute definition, define the fields as follows:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Intended Use |
Select Customer. |
|
Attribute Name |
Enter the value defined for the ORCE_LOYALTY_PROMPT_ATTRIBUTE setting in the Customer Engagement Property Settings, such as |
|
Unique |
Leave this check box unselected. |
|
Description |
Enter a description for the attribute definition. Example: |
|
Data Type |
Select Character. |
Card Definition
Create a card definition in Customer Engagement to use when assigning new loyalty cards to customers that join the loyalty program.
When creating the card definition:
- the 5 digit card prefix you define must also be entered in the Order Administration ORCE Loyalty Card Prefix (M08) system control value.
- the 2 digit sequence number you define must also be entered in the Order Administration ORCE Loyalty Card Series Sequence Number (M09) system control value.
- make sure you assign the Customer Engagement organization that integrates with Order Administration to the card definition.
For more information: See Card Definitions in the Customer Engagement User Guide for instructions on creating and updating a card definition in Customer Engagement.
Card Series Distribution for Card Definition
Create a card series distribution for the card definition you created. The card series distribution contains one or more batches of cards to be generated and then distributed to customers.
For more information: See Card Series Distribution under Card Definitions in the Customer Engagement User Guide for instructions on creating and updating a card series distribution in Customer Engagement.
Generate and Activate Cards for Card Definition
Generate and activate a set of cards within the card definition.
For more information: See Generate Cards and Activate Cards under Card Definitions in the Customer Engagement User Guide for instructions on generating and activating a set of cards within a card definition.
Programs for Card Definition
Create the following programs for the card definition you created:
- Loyalty program: The loyalty program defines the rules used to track the purchases of customers belonging to the program through a system of points that can then be redeemed for discounts on an order. Example: Create a rule to earn 1 point for each purchase dollar.
- Award program: The award program defines the coupons, or e-wards, that are distributed to the customers belonging to the program. These awards are typically distributed as part of promotions such as birthday or anniversary awards, or they can be made available to customers who have accumulated a certain number of points as part of the loyalty program. Example: Create a rule to issue a $25.00 award coupon each time the customer spends $100.00.
For more information: See Programs in the Customer Engagement User Guide for more information on creating and updating programs for a card definition in Customer Engagement.
Registering a Customer in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Program
Includes:
Enrolling a Customer in Loyalty: Classic View
The system registers a sold to customer in the Customer Engagement loyalty program when you select Yes on the Customer Loyalty Registration Window.
When you select to register the customer in the Customer Engagement loyalty program:
- Order Administration sends a Customer Engagement Loyalty Generate Card Request to Customer Engagement.
- Customer Engagement uses the information in the Loyalty Generate Card Request to associate and activate a new loyalty card for the customer.
- Customer Engagement returns the Customer Engagement Loyalty Generate Card Response to Order Administration, containing the customer’s loyalty card number.
- Order Administration:
- generates a Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Loyalty Registration Notifications email to send to the customer. This email contains the loyalty card number assigned to the customer; see Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Loyalty Registration Notifications for the setup required to generate the notice and see Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Loyalty Registration Notification Sample and Contents for a sample email.
- creates a record in the Customer Note table indicating a Customer
Engagement Loyalty Registration Notice has been sent to the customer:
Loyalty Reg Notice to sflye@EXAMPLE.com. You can review customer notes on the Edit Customer Notes Screen. The note is written even if the system generates the Inbound Order XML Message (CWORDERIN) rather than an actual email, or if the email cannot be relayed if, for example, there is a problem with the destination email address.
- Order Administration sends a Customer Engagement Update Customer
Request to:
- update the ORCE_LOYALTY_PROMPT_ATTRIBUTE setting for the customer to FALSE so that Order Administration will not prompt the customer again to join the Loyalty program.
- update the customer’s birth month and day if it was entered on the Customer Loyalty Registration Window.
- Customer Engagement returns the Update Customer Response indicating whether the update was successful.
- If you advanced to the Customer Loyalty Registration window from
the Customer Selection Screen:
- Order Administration sends a Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Request to Customer Engagement, requesting the details of the loyalty card.
- Customer Engagement returns the details of the loyalty card in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response.
- Order Administration uses the information in the Loyalty Card Response to display the loyalty card number and its associated points and awards on the Customer Selection screen.
Communication failure:
- If you select Yes on the Customer Loyalty Registration
window and a connection could not be made to Customer Engagement,
the system displays an error message similar to the following:
No response from ORCE-card not generated. - If the value in the ORCE Loyalty Card Prefix (M08) or ORCE Loyalty Card Series Sequence Number (M09) system control
value is not valid in Customer Engagement, the system displays an
error message similar to the following:
No response from ORCE-card not generated.
Customer Loyalty Registration Window
Use this window to ask a sold to customer to join the Customer Engagement loyalty program.
How to display this screen: This window is available when the Use ORCE Loyalty (M06) system control value is selected, the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT, and you:
- Select Loyalty from the Action drop-down menu on the Customer Scan Screen in Work with Customers (WCST) or Order Entry (OEOM).
- Select Loyalty on the Customer Selection Screen after selecting a sold to customer.
- Select Loyalty Account on the Display More Options Screen.
- Select Loyalty Account on the More Customer Sold To Options Screen.
When you select the Loyalty option, the system retrieves the sold to customer’s information from Customer Engagement. If Customer Engagement does not find a loyalty card for the customer, the system advances you to the Customer Loyalty Registration Window, where you can select to enroll the customer in the Customer Engagement Loyalty program.
Note:
- If Customer Engagement finds a loyalty card assigned to the customer, the system advances you to the Display Loyalty Account Screen. If Customer Engagement finds more than one loyalty card assigned to the customer, the loyalty account information for the first card displays on the screen.
- If a Relate ID is not defined for the customer in the Customer
Sold To table, the system displays an error message similar to the
following:
This customer does not have a Relate ID. - If a connection could not be made to Customer Engagement, the
system displays an error message similar to the following:
Unable to connect to ORCE.
When this window displays automatically: If the Prompt to Join Loyalty (M07) system control value is selected, this window displays automatically when you:
- Select a sold to customer on the CTI Customer Selection Screen if Customer Engagement does not find a loyalty card for the customer and the customer’s ORCE_LOYALTY_PROMPT_ATTRIBUTE setting in Customer Engagement is TRUE or blank.
- Change a sold to customer in Creating and Updating Sold-to Customers (WCST) if Customer Engagement does not find a loyalty card for the customer and the customer’s ORCE_LOYALTY_PROMPT_ATTRIBUTE setting in Customer Engagement is TRUE or blank.
- Create a sold to customer in Creating and Updating Sold-to Customers (WCST) or Order Entry (OEOM) after the customer is created in Customer
Engagement.
- In Work with Customers, this window automatically displays after the final Accept to create the customer.
- In Order Entry, this window automatically displays after the system validates the customer information and source code on the order and you click Accept.
- Create an order in Order Entry (OEOM) if you do not use the CTI Customer Selection Screen and Customer Engagement does not find a loyalty card for the customer and the customer’s ORCE_LOYALTY_PROMPT_ATTRIBUTE setting in Customer Engagement is TRUE or blank. This window automatically displays after the system validates the customer information and source code on the order and you click Accept.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Loyalty Registration Message (unlabeled field above customer) |
The text defined for the ORCE_LOYALTY_REG_MESSAGE setting in Working with Customer Properties (PROP). |
|
Customer |
The number, company name, last name, and first name of the sold to customer being asked to join the Customer Engagement loyalty program. |
|
Birth month/day |
The sold to customer’s birth month and birth day. Valid birth months are: Valid birth days are Note: If you enter a birth month and day on this window, regardless of whether the customer joins the Customer Engagement loyalty program or not, the system updates the birth month and day in the Customer Sold To table. The birth year does not display on the screen; however, it defaults to1900 in the Customer Sold To table unless it has been updated through
the Customer Engagement Customer Integration.
Birth Month: Numeric, 2 positions (01-12 in table); required if you define a birth day. Birth Day: Numeric, 2 positions; required if you define a birth month. Birth Year (in table only): Numeric, 4 positions; optional. |
| Screen Option | Procedure |
|---|---|
|
Register the customer in the Customer Engagement loyalty program |
Select Yes. See Registering a Customer in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Program. |
|
Do not register the customer in the Customer Engagement loyalty program, but ask the customer again at a later time |
Select Not Now. |
|
Do not register the customer in the Customer Engagement loyalty program and do not ask the customer again |
Select Never. The system sends an Add or Update Customer Request to Customer Engagement to update the ORCE_LOYALTY_PROMPT_ATTRIBUTE setting in Customer Engagement to FALSE. |
Enrolling a Customer in Loyalty: Modern View
Prompts are displayed in Modern View at the Customer Order List, Customer Item List and Customer Purchase History List pages, as well as the Review step in Contact Center Order Entry, if:
-
the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT, and
-
the Use ORCE Loyalty (M06) and Prompt to Join Loyalty (M07) system control values are selected, and
-
the customer has an ORCE customer ID and is not already a loyalty member, and has not previously requested to stop prompting for loyalty membership, such as by selecting the Never option at the prompt.
Loyalty prompt options: A prompt to join loyalty is displayed below the customer’s name and customer number, providing the following options:
-
Never: Do not ask the customer again about joining loyalty. In this case, Order Administration sends a Customer Engagement Update Customer Request to update the ORCE_LOYALTY_PROMPT_ATTRIBUTE setting for the customer to FALSE so that Order Administration will not prompt the customer again to join the Loyalty program.
-
Not Now: The customer is not joining loyalty now, but can be prompted again in the future. Order Administration does not send an update to Customer Engagement.
-
Enroll: Enroll the customer in loyalty.
Prompt wording: The ORCE_LOYALTY_REG_MESSAGE property from Working with Customer Properties (PROP) defines the wording of the prompt message. Defaults to Does the customer want to join the loyalty program?
There is also an option to enroll the customer in loyalty at the Customer Loyalty List page in Modern View if the above conditions are met and if the customer is not already enrolled.
When enrollment of the customer is confirmed, the communication with Customer Engagement and updates described above under Enrolling a Customer in Loyalty: Classic View take place
Reviewing Customer Engagement Loyalty Account Information
Classic View: Use the following screens to review loyalty account information for a customer that is registered in the Customer Engagement Loyalty program:
- Display Loyalty Account Screen: allows you to review the current points accrued and the awards available to the customer.
- Display Loyalty Account History Screen: allows you to review the points activity and award activity associated with the customer’s loyalty card.
- Customer Selection Screen: allows you to review the loyalty card number, current earned points, and current awards balance assigned to the customer’s loyalty account.
Important:
If the customer is assigned to more than one loyalty card in Customer Engagement, Order Administration Classic View displays loyalty card information for the first card returned from Customer Engagement.Modern View: The Customer Loyalty List page in Modern View displays the customer’s cards, loyalty and awards programs, account numbers, levels, and balances. This page is available by selecting the Loyalty tab at the Customer Order List page. From this page, you can also open the Account Details panel to review details of each account and optionally issue loyalty points or award coupons, with proper authority. See the Modern View online help for more information.
Customer Engagement: You can also review the loyalty account information in Customer Engagement; see Reviewing the Customer’s Loyalty Card in Customer Engagement.
Display Loyalty Account Screen
Use this Classic View screen to review the current points accrued and the awards available for the loyalty program and award program associated with the customer’s loyalty card.
When you advance to the Display Loyalty Account screen:
- Order Administration sends a Get Customer Request to Customer Engagement containing the customer’s Relate ID from the Customer Sold To table.
- Customer Engagement uses the Relate ID in the Get Customer Request to find the customer and returns the Get Customer Response containing the customer’s information, including the customer’s cards.
- Order Administration sends a Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Request to Customer Engagement containing the customer’s card number.
- Customer Engagement uses the customer’s card number in the Loyalty Card Request to retrieve the loyalty points and awards for the loyalty program and award program associated with the customer’s loyalty card.
- Customer Engagement returns the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response to Order Administration, containing the customer’s loyalty account information.
- Order Administration displays the loyalty account information returned from Customer Engagement on the Display Loyalty Account screen.
How to display this screen: This screen is available when the Use ORCE Loyalty (M06) system control value is selected and you:
- Select Loyalty from the Action drop-down menu on the Customer Scan Screen in Work with Customers (WCST) or Order Entry (OEOM).
- Select Loyalty on the Customer Selection Screen after selecting a sold to customer.
- Select Loyalty Account on the Display More Options Screen.
- Select Loyalty Account on the More Customer Sold To Options Screen.
When you select the Loyalty option, the system retrieves the sold to customer’s information from Customer Engagement. If Customer Engagement finds a loyalty card assigned to the customer, the system advances you to the Display Loyalty Account Screen. If Customer Engagement finds more than one loyalty card assigned to the customer, the loyalty account information for the first card returned displays on the screen.
Note:
- If Customer Engagement does not find a loyalty card for the customer, the system advances you to the Customer Loyalty Registration Window, where you can select to enroll the customer in the Customer Engagement Loyalty program.
- If a Relate ID is not defined for the customer in the Customer
Sold To table, the system displays an error message similar to the
following:
This customer does not have a Relate ID. - If a connection could not be made to Customer Engagement, the
system displays an error message similar to the following:
Unable to connect to ORCE.
Column sort: You can sort on the Coupon ID, Coupon Amount, and Expiration Date columns on this screen by clicking on the column name. An arrow pointing up displays next to the field when the values for the field display in ascending sequence; an arrow pointing down displays next to the field when the values for the field display in descending sequence.
The information that displays on this screen is from Customer Engagement and is not stored in Order Administration.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Customer # |
The number, company name, last name, and first name of the sold to customer registered in the Customer Engagement Loyalty program. Customer number: Numeric, 9 positions; display-only. Customer name: Alphanumeric, 40 positions; display-only. |
|
Loyalty Card # |
The loyalty card number assigned to the customer in Customer Engagement. The points and awards associated with this card display on the screen. From cardNumber in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response. |
|
Loyalty Points The loyalty points for the loyalty program associated with the customer’s loyalty card. Only loyalty points from Customer Engagement display on this screen; escrow and bonus points from Customer Engagement do not display. |
|
|
Current Points |
The total current earned points balance for the customer loyalty account. From EARNED points value in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response. |
|
Points Earned This Year |
The total earned points balance for the current year for the customer’s loyalty account. From YTD points value in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response. |
|
Total Points Earned |
The total lifetime earned points balance for the customer’s loyalty account. From LTD points value in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response. |
|
Program Level |
A description of the current level of the loyalty program to which the customer’s loyalty account is assigned. From loyaltyProgramLevel value in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response. |
|
Current Awards |
|
|
Coupon ID |
The ID number for the coupon created or redeemed by the award activity. From coupon id in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response. |
|
Amount |
The amount of the coupon applied to the customer’s award account by the activity. From coupon amount in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response. |
|
Expiration Date |
The date when the coupon expires.
From coupon ExpirationDate in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response. |
| Screen Option | Procedure |
|---|---|
|
Review loyalty account history |
Select Loyalty History to advance to the Display Loyalty Account History Screen. |
|
Issue points |
Select Issue Points to advance to the Issue Loyalty Points Window. Note: This option is available only if you have authority to the ORCE Issue Awards/Points (J07) secured feature. |
|
Issue awards |
Select Issue Awards to advance to the Issue Loyalty Coupon Window. Note: This option is available only if you have authority to the ORCE Issue Awards/Points (J07) secured feature. |
Display Loyalty Account History Screen
Use this screen to review points activity and award activity for the loyalty program and award program associated with the customer’s loyalty card.
When you advance to the Display Loyalty Account History screen:
- Order Administration sends a Customer Engagement Get Customer Request to Customer Engagement containing the customer’s Relate ID from the Customer Sold To table.
- Customer Engagement uses the Relate ID in the Get Customer Request to find the customer.
- Customer Engagement returns the Customer Engagement Get Customer Response to Order Administration, containing the customer’s information, along with the customer’s loyalty card information.
- Order Administration sends a Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Request to Customer Engagement containing the customer’s card number.
- Customer Engagement uses the customer’s card number in the Loyalty Card Request to retrieve the loyalty account and award account associated with the customer’s loyalty card.
- Customer Engagement returns the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response to Order Administration, containing the customer’s loyalty account and award account information.
- Order Administration sends a Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Request and Customer Engagement Award Account History Request to Customer Engagement.
- Customer Engagement uses the information in the Loyalty Account History Request and Award Account History Request to retrieve the customer’s loyalty account and award account activity.
- Customer Engagement returns the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response and Customer Engagement Award Account History Response to Order Administration, containing the customer’s loyalty account and award account activity.
- Order Administration displays the loyalty account and award account activity returned from Customer Engagement on the Display Loyalty Account History screen.
Note:
- If Customer Engagement finds more than one loyalty card assigned to the customer, the loyalty account information for the first card returned displays on the screen.
- Order Administration does not display
Inquirytype transactions on the screen. - If the number of loyalty account transactions returned exceeds
the Account Activity Lookup Limit setting in Customer
Engagement, the system does not display any activity on the Display
Loyalty Account History screen and instead displays an error message:
Max results value defined in ORCE has been exceeded.
How to display this screen: Select Loyalty History on the Display Loyalty Account Screen.
Column sort: You can sort on the Coupon ID, Coupon Amount, and Expiration Date columns on this screen by clicking on the column name. An arrow pointing up displays next to the field when the values for the field display in ascending sequence; an arrow pointing down displays next to the field when the values for the field display in descending sequence.
The information that displays on this screen in from Customer Engagement. Activity transactions display in descending activity date sequence.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Customer # |
The number, company name, last name, and first name of the sold to customer registered in the Customer Engagement Loyalty program. Customer number: Numeric, 9 positions; display-only. Customer name: Alphanumeric, 40 positions; display-only. |
|
Loyalty Card # |
The loyalty card number assigned to the customer in Customer Engagement. The points and awards associated with this card display on the screen. From cardNumber in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response. |
|
Loyalty Account History |
|
|
Activity Date |
The date and time when the loyalty points or award coupon activity occurred. Note: The time for loyalty points activity always displays as 12:00:00.Loyalty account: From businessDate in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response. Award account: From activityDateTime in the Customer Engagement Award Account History Response. |
|
Activity |
The type of activity that occurred against the card. Points Activity
Awards Activity
Loyalty account: From transactionType in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response. Award account: From transactionType in the Customer Engagement Award Account History Response. |
|
Award Effect |
The effect of the awards activity. Positive Awards Activity A positive amount displays if the awards activity increased the awards amount on the loyalty card.
Negative Awards Activity Automatic Redeem A negative amount displays if the awards activity decreased the awards amount on the loyalty card.
No Effect (Positive or Negative) Awards Activity
Note: This field is blank for loyalty account activity.From activityAmount in the Customer Engagement Award Account History Response. |
|
Point Effect |
The effect of the points activity. Activities that Add Points to the Loyalty Card
Activities that Subtract Points from the Loyalty Card
Activities that have No Effect on Loyalty Points
Note: This field is blank for award account activity.From numPoints in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response. |
|
Pending |
Yes displays if the points are pending being issued; otherwise this field is blank. Note: This field is blank for award account activity.From pendingFlag in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response. |
|
Location ID |
The location ID associated with the transaction. Loyalty account: From locationId in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response. Award account: From locationId in the Customer Engagement Award Account History Response. |
|
Activity ID |
The activity transaction ID assigned to the transaction in Customer Engagement. You can use this value as a reference for voiding a transaction in Customer Engagement or when writing a customer or order note. Loyalty account: From accountActivityId in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response. Award account: From awardTranId in the Customer Engagement Award Account History Response. |
Reviewing the Customer’s Loyalty Card in Customer Engagement
Use the following screens in Customer Engagement to review the loyalty card assigned to the customer.
Customer Dashboard: The Card / Accounts section of the Customer Dashboard displays the card number generated for the customer and information about the loyalty program and award program associated with the customer’s card.
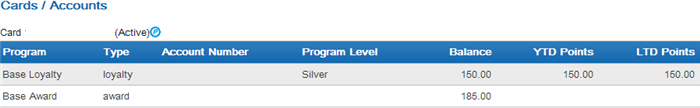
Card / Account Administration Screen: The Card / Account Association screen displays information about the card assigned to the customer.
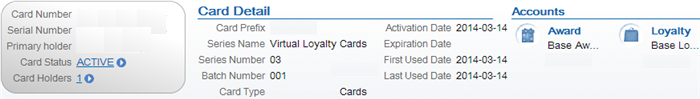
- Selecting the Award account on the Card / Account Association screen displays basic information and activity for the award program associated with the card. You can click on a transaction to display additional information about the activity.
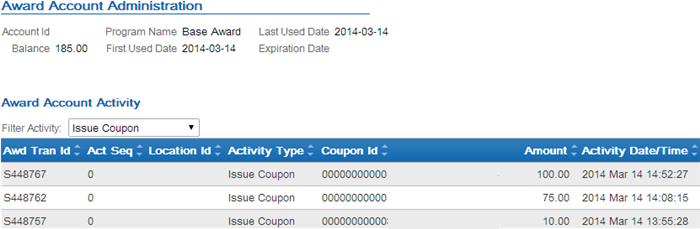
- Selecting the Loyalty account on the Card / Account Association screen displays basic information and activity for the loyalty program associated with the card. You can click on a transaction to display additional information about the activity.
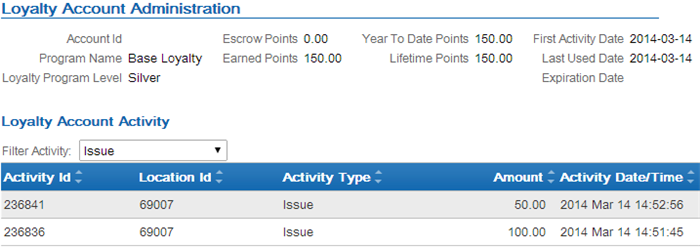
Applying Points to a Customer’s Loyalty Card
Use the Issue Loyalty Points window to issue points to the loyalty program assigned to the customer’s card.
Modern View: The option to issue points is also available in Modern View at the Account Details panel from the customer order list page, requiring authority to the same secured feature as Classic View.
Issue Loyalty Points Window
How to display this screen: Select Issue Points on the Display Loyalty Account Screen. You must have authority to the ORCE Issue Awards/Points (J07) secured feature to advance to this window.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Loyalty Card # |
The loyalty card number assigned to the customer in Customer Engagement to which you wish to issue points. This is the card number that displays on the Display Loyalty Account Screen. Display-only. |
|
Points Amount |
The number of points to issue. Updates the earned points balance for the customer’s loyalty account in Customer Engagement. Numeric, 7 positions with a 2-place decimal; Required. |
|
Comments |
An informational field to describe the points being issued. Alphanumeric, 1000 positions; Required. |
To issue points:
- Enter a Points Amount and Comments.
- Click OK.
When you click OK:
- Order Administration generates a Customer Engagement Issue Points Request to Customer Engagement containing the loyalty card information and the loyalty points to issue.
- Customer Engagement receives the request and adds the loyalty points to the customer’s loyalty account.
- Customer Engagement generates a Customer Engagement Issue Points Response to Order Administration.
- Order Administration generates a Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Request containing the customer’s card number.
- Customer Engagement receives the Loyalty Card Request and returns a Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response containing information on the customer’s card, current points balances and current award coupons.
- Order Administration returns you to the Display Loyalty Account Screen. The Current Points, Points Earned This Year, and Total Points Earned fields will include the new points issued.
Note:
If a connection could not be made to Customer Engagement, the system displays an error message:Unable to connect to ORCE.
Reviewing the issue points transaction in Customer Engagement: You can review the issue points transaction in Customer Engagement by selecting the Loyalty account on the Card / Account Association screen; activity for the loyalty program associated with the card displays at the bottom of the screen.

Click on the issue points transaction to advance to the Activity Detail window where you can review the details of the transaction.
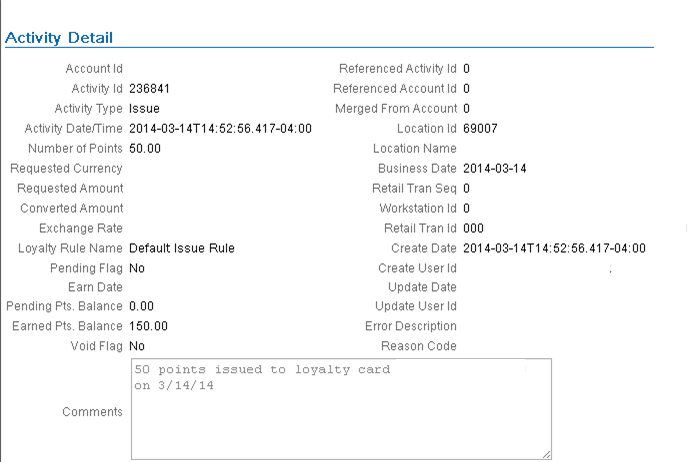
Applying Coupons to a Customer’s Loyalty Card
Use the Issue Loyalty Coupon window to issue an award coupon to the award program assigned to the customer’s card.
Modern View: The option to issue an award coupon is also available in Modern View at the Account Details panel from the customer order list page, requiring authority to the same secured feature as Classic View.
Issue Loyalty Coupon Window
How to display this screen: Select Issue Awards on the Display Loyalty Account Screen. You must have authority to the ORCE Issue Awards/Points (J07) secured feature to advance to this window.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Loyalty Card # |
The loyalty card number assigned to the customer in Customer Engagement. This is the card number that displays on the Display Loyalty Account Screen. Display-only. |
|
Award Amount |
The amount to assign to the award coupon. Updates the award balance for the customer’s award account in Customer Engagement. Numeric, 7 positions with a 2-place decimal; Required. |
|
Expiration Date |
The date when the award coupon expires. The expiration date you enter must be greater than the current date. If you do not define an expiration date, the award coupon uses the award program rules defined in Customer Engagement. Optional. |
|
Comments |
An informational field to describe the award coupon being issued. Alphanumeric, 1000 positions; Required. |
To issue an award coupon:
- Enter an Award Amount and Comments.
- Optionally, enter an Expiration Date.
- Click OK.
When you click OK:
- Order Administration generates a Customer Engagement Issue Coupon Request to Customer Engagement containing the loyalty card information and the award coupon amount to issue.
- Customer Engagement receives the request and adds the award coupon for the specified amount to the customer’s award account.
- Customer Engagement generates a Customer Engagement Issue Coupon Response to Order Administration.
- Order Administration generates a Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Request containing the customer’s card number.
- Customer Engagement receives the Loyalty Card Request and returns a Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response containing information on the customer’s card, current points balances and current award coupons.
- Order Administration returns you to the Display Loyalty Account Screen. The Current Awards section of the screen will include the new award coupon issued.
Note:
If a connection could not be made to Customer Engagement, the system displays an error message:Unable to connect to ORCE.
Reviewing the issue coupon transaction in Customer Engagement: You can review the issue coupon transaction in Customer Engagement by selecting the Award account on the Card / Account Association screen; activity for the award program associated with the card displays at the bottom of the screen.

Click on the issue coupon transaction to advance to the Activity Detail window where you can review the details of the transaction.
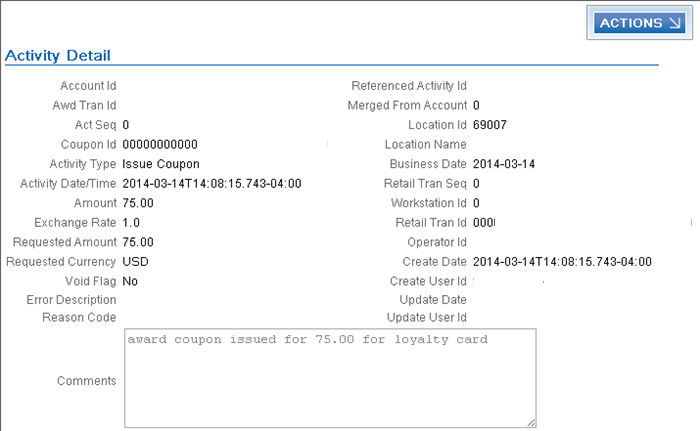
Accruing Loyalty Points during Order Processing
Customers enrolled in the Customer Engagement loyalty program accrue points from completed purchases based on the program rules defined for the loyalty account in Customer Engagement.
When you send sales and return information to Customer Engagement in the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message during the Customer Engagement Sales Feed, Customer Engagement:
- determines the loyalty account to accrue points against based on the customer passed in the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction message.
- for sales transactions, increases the loyalty points on the customer’s loyalty account based on the program rules defined for the loyalty account in Customer Engagement.
- for return transactions, decreases the loyalty points on the customer’s loyalty account based on the program rules defined for the loyalty account in Customer Engagement.
Example: The issue rule defined for the customer’s loyalty program in Customer Engagement is to issue 1 point for each purchase dollar.
The customer has 155 earned points in Customer Engagement.
The customer places an order for $80.00.
When you run the Customer Engagement Sales Feed to update Customer Engagement with the sales and return information in the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message, Customer Engagement increases the customer’s earned loyalty points to $235.00 (155 earned points + 80 points associated with sales).
The customer returns an item for $30.00.
When you run the Customer Engagement Sales Feed to update Customer Engagement with the sales and return information in the Customer Engagement Post POSlog Transaction Message, Customer Engagement decreases the customer’s earned loyalty points to $205.00 (235 earned points - 30 points associated with returns).
For more information: See Issue Rule in the Customer Engagement User Guide for more information on defining rules for a loyalty program.
Applying and Redeeming Customer Engagement Awards during Order Processing
You can apply an award amount to an order as a pro-rated merchandise discount and redeem the award amount applied to the order in Customer Engagement.
- Applying Awards during Interactive Order Entry (Classic View)
- Applying Awards during the Generic Order Interface (Order API)
- Combining the Loyalty Award Amount with Other Discounts
- Loyalty Award Discount Calculations
- Redeeming Awards during Order Processing
- If Communication Fails during Coupon Redemption
Note:
- You can apply an award amount to an order during order creation only; you cannot apply an award amount to an order in order maintenance.
- You can apply an award amount to a pre-order quote; however, the award amount is not redeemed until you convert the quote to an order. When you convert the quote to an order, the system allows you to change the award amount for the order before you accept the order and redeem the award amount. See Entering Pre-Order Quotes and Converting Quotes to Orders for more information about quote processing.
- Canceling an order or order line associated with a redeemed award amount does not increase a customer’s award balance. You must issue points or awards to the customer’s loyalty card manually; see Applying Points to a Customer’s Loyalty Card and Applying Coupons to a Customer’s Loyalty Card.
Applying Awards during Contact Center Order Entry (Modern View)
The option to apply an award amount to an order is available in Contact Center Order Entry at the Review step, through the Apply Awards window. You can specify an awards amount to apply for each displayed awards program. The Order Summary panel on the right displays the total value of awards that are available to apply to the order.
If the customer has more than one loyalty card, the Select Card window opens automatically when you advance to the Items step so you can select the card to use when applying any awards to the order. Optionally, you can change your loyalty card selection at the Items, Shipping, or Review step.
Applying Awards during Interactive Order Entry (Classic View)
Use the following steps to apply an award amount to an order during interactive Order Entry.
To apply an award amount to the order: On the Enter Loyalty Award Discount Window, enter the award amount to apply to the order and click OK. The system applies the award amount as a pro-rated merchandise discount. The discount is applied to all discountable order lines, including order lines that contain a price override reason code.
Note:
- The award amount does not apply to order lines that contain a non-discountable item or to sale items if the Exclude Sale Item When Prorating Discounts (I65) system control value is selected.
- If the entered award amount is greater than the discountable merchandise
amount on the order, the system displays a message similar to the
following:
Award amount cannot exceed discountable merchandise. - If the entered award amount is greater than the current awards
balance for the loyalty card, the system displays a message similar
to the following:
Award amount cannot exceed remaining balance. - If more than one order ship to exists on the order, the system applies the award amount to the selected order ship to only.
- The system updates the Customer Engagement Award Amount in the Order Ship To table with the award amount applied to the order.
- The system includes the award amount in the Discount field on the order.
Enter Loyalty Award Discount Window
Use this window to apply a coupon award amount as a pro-rated merchandise discount during order repricing.
Note:
This window is available during order entry only; this window is not available during order maintenance.How to display this screen: Select Reprice during order entry. The system displays the Enter Loyalty Award Discount Window if:
- the Use ORCE Loyalty (M06) system control value is selected, and
- the Prorate Dollar Discounts and Coupons (D90) system control value is selected, and
- the Price Method for the source code on the order header is set to Reg Plus Reprice, and
- the sold to customer on the order is assigned to a loyalty card in Customer Engagement, and
- there are current awards associated with the customer’s loyalty account that are available for redemption.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Loyalty Card # |
The loyalty card number assigned to the customer that is associated with the awards balance. Note: If the customer is assigned to more than one loyalty card in Customer Engagement, Order Administration displays loyalty card information for the first card returned from Customer Engagement.Display-only. |
|
Available awards balance |
The total current awards balance for the loyalty card. Display-only. |
|
Max award amount allowed |
The maximum award amount that can be applied
to the order. Display-only. |
|
Enter award amount to apply |
The award amount to apply to the order as a pro-rated merchandise discount. A message similar to the
following displays if you enter an award amount that is greater than
the Available awards balance: A message similar
to the following displays if you enter an award amount that is greater
than the merchandise amount: Numeric, 7 positions with a 2-place decimal; Optional. |
For more information: See Combining the Loyalty Award Amount with Other Discounts and Loyalty Award Discount Calculations for more information on how the award amount is applied to the order.
Applying Awards during the Generic Order Interface (Order API)
Use the following steps to apply a coupon award amount to a web order.
To apply an award amount to the order: Enter the award amount to apply to the order in the relate_award_amount tag included in the ShipTo element of the Inbound Order XML Message (CWORDERIN).
For more information see the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1).
When Order Administration processes the CWOrderIn message, the system determines if the order is eligible for the relate award amount.
Does the sold to customer have a loyalty card? The system verifies that the customer in Customer Engagement has a loyalty card.
-
If the Customer Engagement customer does not have a loyalty card, the system does not apply the award amount to the order and creates a record in the Order Transaction History table for the order indicating the award amount was not redeemed on the order. For example:
| Date | Type | Transaction Note | Amount | User |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
3/06 |
SYSTEM UPDATE |
Award amt not redeemed-card# not found |
10.00 |
your default user |
Is prorating dollar discounts and coupons enabled? The system applies the award amount defined in the relate_award_amount tag to the order only if the Prorate Dollar Discounts and Coupons (D90) system control value is selected.
Does the customer’s award balance cover the relate_award_amount? If the Customer Engagement customer has a loyalty card, the system determines if the award balance for the loyalty card is equal to or greater than the relate_award_amount entered on the order.
- If the award balance is 0.00 or less, the system does not apply the award amount to the order and creates a record in the Order Transaction History table for the order indicating the award amount was not redeemed on the order. For example:
| Date | Type | Transaction Note | Amount | User |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
3/06 |
SYSTEM UPDATE |
Award amt not redeemed-award balance=0 |
25.00 |
your default user |
- If the award balance is less than the relate_award_amount, the system applies the available award balance to the order as a pro-rated merchandise discount. For example, if the relate_award_amount on the order is 25.00, but the award balance is $5.00, the system applies 5.00 to the order. The system creates a record in the Order Transaction History table for the order indicating the award amount that was redeemed on the order. For example:
| Date | Type | Transaction Note | Amount | User |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
3/06 |
UPSELL PROMO |
Total Prorated Order Level Discount |
5.00 |
SFLYE |
|
3/06 |
UPSELL PROMO |
Award Redeemed-ID: S444399 |
5.00 |
SFLYE |
- If the award balance is equal to or greater than the relate_award_amount, the system applies the entire award amount to the order as a pro-rated merchandise discount. The system creates a record in the Order Transaction History table for the order indicating the award amount that was redeemed on the order. For example:
| Date | Type | Transaction Note | Amount | User |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
3/06 |
UPSELL PROMO |
Total Prorated Order Level Discount |
25.00 |
SFLYE |
|
3/06 |
UPSELL PROMO |
Award Redeemed-ID: S444399 |
25.00 |
SFLYE |
The award amount is applied as a pro-rated merchandise discount to all discountable order lines, including order lines that contain a price override reason code.
The system updates the Customer Engagement Award Amount in the Order Ship To table with the award amount applied to the order.
Note:
- The award discount does not apply to order lines that contain a non-discountable item or to sale items if the Exclude Sale Item When Prorating Discounts (I65) system control value is selected.
- If the discountable merchandise amount is less than the entered award amount, the system decreases the Customer Engagement Award Amount in the Order Ship To table to match the discountable merchandise amount. If the discountable merchandise amount is 0.00 or a negative amount, the system updates the Customer Engagement Award Amount in the Order Ship To table to 0.00.
- If more than one order ship to exists on the order, the system applies the award amount to the selected order ship to only.
- If you send a subsequent Inbound Order XML Message (CWORDERIN) to complete a web order with payment information or update an order with errors, in order to apply the relate_award_amount to the order, the payment_only flag for the subsequent message must be set to N so that the Order API program deletes the existing order and recreates it using the information provided in the inbound message. It is important that the subsequent message include all information required to complete the order, or the information that was not included in the subsequent message will be lost.
For more information see the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1).
For more information: See Combining the Loyalty Award Amount with Other Discounts and Loyalty Award Discount Calculations for more information on how the award amount is applied to the order.
Combining the Loyalty Award Amount with Other Discounts
The loyalty award amount is applied as a pro-rated merchandise discount AFTER order detail coupons and any line level promotions have been applied to the lines on the order.
If the merchandise amount after applying discounts is less than the loyalty award amount to apply to the order, the system automatically adjusts the loyalty award amount so that the amount is equal to the discounted merchandise amount.
Loyalty Award Discount Calculations
The system uses the following calculations to determine the award discount amount to apply to each order line.
The system calculates the Discount Percentage for each order line:
Order line extended amount after applying order detail
coupons and line level promotions / order merchandise total = discount
percentage
The system calculates the Unit Selling Price for each order line:
order line post-discount unit price - [(total award amount
X discount % from above calculation) / line unit quantity] = unit
selling price
Example 1: Award Amount Only
An order has the following order lines:
- line 1: 1 unit for 50.00
- line 2: 1 unit for 10.00 (non-discountable)
- line 3: 1 unit for 10.00
The merchandise total is 70.00, 60.00 of which is discountable.
The system applies a 10.00 loyalty award amount to the order.
The system calculates the discount percentage for each eligible order line:
line 1: 50.00 / 60.00 = .833 x 100 = 83.33% discount percentage
line 3: 10.00 / 60.00 = .166 x 100 = 16.66% discount percentage
The system calculates the unit selling price for each order line:
line 1: 10.00 loyalty award amount x 83.33% discount percentage
= 8.33
8.33 / 1 line unit quantity = 8.33
50.00 unit price - 8.33 = 41.67 unit selling price
line 3: 10.00 loyalty award amount x 16.66% discount percentage
= 1.666
1.666 / 1 line unit quantity = 1.666
10.00 unit price - 1.66 = 8.33 unit selling price
The merchandise total after applying the loyalty award amount is 60.00 (line 1 41.67 + line 2 10.00 + line 3 8.33).
Example 2: Award Amount with Line Level Promotion
An order has the following order lines:
- line 1: 1 unit for 50.00
- line 2: 1 unit for 10.00 (non-discountable)
- line 3: 1 unit for 10.00
The merchandise total is 70.00, 60.00 of which is discountable.
The system applies a 5.00 line level promotion and 10.00 loyalty award amount to the order.
The system calculates the discount percentage for each eligible order line:
line 1: 50.00 / 60.00 = .833 x 100 = 83.33% discount percentage
line 3: 10.00 / 60.00 = .166 x 100 = 16.66% discount percentage
The system calculates the unit selling price for each order line:
line 1: 15.00 (line level promotion + loyalty award amount)
x 83.33% discount percentage = 12.50
12.50 / 1 line unit quantity = 12.50
50.00 unit price - 12.50 = 37.50 unit selling price
line 3: 15.00 line level promotion + loyalty award amount
x 16.66% discount percentage = 2.50
2.50 / 1 line unit quantity = 2.50
10.00 unit price - 2.50 = 7.50 unit selling price
The merchandise total after applying the line level promotion and loyalty award amount is 55.00 (line 1 37.50 + line 2 10.00 + line 3 7.50).
Example 3: Award Amount with Order Level Coupon
An order has the following order lines:
- line 1: 1 unit for 50.00
- line 2: 1 unit for 10.00 (non-discountable)
- line 3: 1 unit for 10.00
The merchandise total is 70.00, 60.00 of which is discountable.
The system applies a 50.00 loyalty award amount and 20.00 order level coupon to the order.
The system calculates the discount percentage for each eligible order line:
line 1: 50.00 / 60.00 = .833 x 100 = 83.33% discount percentage
line 3: 10.00 / 60.00 = .166 x 100 = 16.66% discount percentage
The system calculates the unit selling price for each order line:
line 1: 70.00 (loyalty award amount + 20.00 order level
coupon) x 83.33% discount percentage = 58.33
58.33 / 1 line unit quantity = 58.33
50.00 unit price - 58.33 = -8.33 unit selling price (the
system updates the price of the line to .00)
line 3: 70.00 (loyalty award amount + 20.00 order level
coupon) x 16.66% discount percentage = 11.66
11.66 / 1 line unit quantity = 11.66
10.00 unit price - 11.66 = -1.66 unit selling price (the
system updates the price of the line to .00)
The merchandise total after applying the order level coupon and loyalty award amount is 10.00 (line 1 .00 + line 2 10.00 + line 3 .00).
Since the merchandise amount after applying discounts is less than the loyalty award amount to apply to the order, the system automatically adjusts the loyalty award amount so that the amount is equal to the discounted merchandise amount; in this example, the system adjusts the loyalty award amount to 40.00 (20.00 coupon amount + 40.00 loyalty award amount = 60.00 total discount, which matches the merchandise amount that is eligible for discount).
Redeeming Awards during Order Processing
To redeem the award amount applied to the order: During the final order accept process, if an award amount is defined on the order, the system:
- sends a Customer Engagement Automatic Redeem Request to Customer Engagement for the award amount applied to the order.
- Customer Engagement redeems award coupons associated with the
customer’s loyalty account until the award amount applied to the order
has been reached.
- Customer Engagement redeems coupons whose expiration date is closest to expiring first.
- If the award coupon amount is greater than the amount to redeem, Customer Engagement subtracts the redeemed amount from the coupon; for example, if the award coupon amount is $100.00 and the amount to redeem is $15.00, Customer Engagement updates the award coupon amount to $85.00.
- Customer Engagement subtracts the amount to redeem from the customer’s award balance.
- Customer Engagement sends a Customer Engagement Automatic Redeem Response to Order Administration.
- Order Administration creates a record in the Order Transaction History table for the order indicating the award amount that was redeemed. For example:
| Date | Type | Transaction Note | Amount | User |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
3/06 |
UPSELL PROMO |
Total Prorated Order Level Discount |
10.00 |
SFLYE |
|
3/06 |
UPSELL PROMO |
Award Redeemed-ID: S444399 |
10.00 |
SFLYE |
You can display order history by selecting Order History in standard order inquiry or at the Work with Order Lines screen in Order Maintenance, or by selecting History in streamlined order inquiry. See the Display Order Line History Screen for more information.
- updates the Award Amount in the Order Ship To table with the award amount applied to the order.
If communication fails: See If Communication Fails during Coupon Redemption.
Reviewing the automatic redeem transaction in Customer Engagement: You can review the automatic redeem transaction in Customer Engagement by selecting the Award account on the Card / Account Association screen; activity for the award program associated with the card displays at the bottom of the screen.
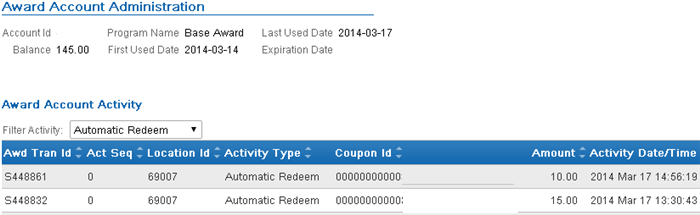
Click on the automatic redeem transaction to advance to the Activity Detail window where you can review the details of the transaction.
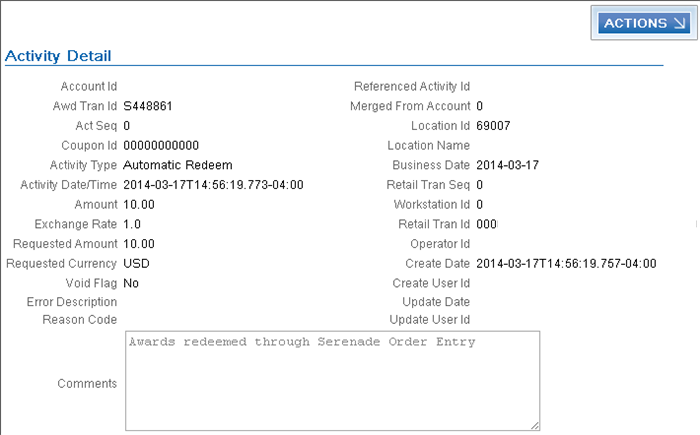
If Communication Fails during Coupon Redemption
If Order Administration cannot connect with Customer Engagement
to redeem the award amount applied to an order, the system places
the order on RL ORCE Communication Failure hold and writes an order
transaction history message indicating the award amount was not automatically
redeemed: SYSTEM UPDATE ORCE Loyalty Award Redemption Failed
20.00, where 20.00 is the award amount applied
to the order.
In this situation, you can either:
- log in to Customer Engagement and void coupons until the award amount applied to the order is covered. If the amount voided is greater than the amount needed for redemption (for example, the amount applied to the order was $20.00 and you voided a $25.00 award coupon), you can issue a new award coupon for the difference (in this example, $5.00).
- cancel the order and create a new order with the award amount, making sure communication with Customer Engagement during the redemption process is successful.
Oracle Retail Customer Engagement APIs used in the Loyalty Integration
The following Customer Engagement APIs are used to communicate with Customer Engagement during the Customer Engagement Loyalty integration:
- Customer Engagement Customer Services API v2.3: used to interactively create and update customer information between Customer Engagement and Order Administration; see the Customer Engagement Customer Integration for more information.
- Customer Engagement Stored Value Card Transaction Services
API v3.1: used to generate a new loyalty card and assigns it
to a customer.
Note:
In order for transactions to process correctly, the Franchisee feature must be disabled in Customer Engagement. - Customer Engagement Card Services v2.1 API: used to retrieve loyalty and award summary information for all accounts attached to the specified loyalty card number.
- Customer Engagement Loyalty Account Services v1.2 API: used to:
- issue points to the loyalty account specified.
- retrieve all of the loyalty points account activity for the loyalty account specified.
- Customer Engagement Award Account Services v1.2 API: used to:
- issue an award coupon to the loyalty account specified.
- automatically redeem award coupons for the specified amount.
- retrieve all of the award coupon account activity for the loyalty account specified.
ORCE log: Order Administration logs the loyalty transactions passed between Order Administration and Customer Engagement in the ORCE (Oracle Retail Customer Engagement) Log.
Web service authentication? If the web services used to process inbound messages to Customer Engagement require web service authentication, you must provide a valid web service authentication user and password in Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA), or client ID and secret if using OAuth. In this situation, when Oracle Retail Order Administration generates a message to send to Customer Engagement it includes the web service authentication information in the HTTP header of the message. See Oracle Retail Omnichannel Web Service Authentication Configuration Guide on My Oracle Support (2728265.1) for more information.
For more information: See the Customer Engagement Batch Processing and Web Services Guide for more information on the Customer Engagement API interface.
Customer Engagement Stored Value Card Transaction Services API v3.1
Order Administration calls the Customer Engagement Stored Value Card Transaction Services API version 3.1 to generate the Customer Engagement generateCard Method.
The system uses the value in the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) along with the ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX and ORCE_SVC_SERVICE_SUFFIX settings in Working with Customer Properties (PROP) to build the URL for communication with Customer Engagement.
Note:
In order for transactions to process correctly, the Franchisee feature must be disabled in Customer Engagement.Customer Engagement generateCard Method
The generateCard method generates a new loyalty card and assigns it to a customer.
When called? The system calls this method when you select Yes on the Customer Loyalty Registration Window, or when you enroll a customer in loyalty in Modern View.
Customer Engagement Loyalty Generate Card Request
Order Administration sends the following information to Customer Engagement.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
|
card Prefix |
The card prefix associated with the Loyalty Card Definition in Customer Engagement; this is the card prefix defined in the ORCE Loyalty Card Prefix (M08) system control value. |
|
card Series Sequence |
The card series sequence number associated with the Loyalty Card Definition in Customer Engagement; this is the card series sequence number defined in the ORCE Loyalty Card Series Sequence Number (M09) system control value. |
|
location Id |
The location ID associated with the loyalty program; this is the location defined in the Default Location for ORCE Integration (K69) system control value. If you do not define a location in the Default Location for Sales Download (K69) system control value, Customer Engagement uses the location defined in the Default Location ID system configuration setting. |
|
currency Id |
The currency code defined in the Local Currency Code (A55) system control value. This system control value must be set to a valid currency code. This system control value must be set to a valid currency code. |
|
customer ID |
The Customer Engagement customer ID to assign to the loyalty card; this is the Relate ID defined for the customer in the Customer Sold To table. |
|
security User ID |
The user ID defined in the ORCE_SECURITY_USER_ID property |
Customer Engagement Loyalty Generate Card Response
The generateCard method returns a GenCardResponseContainerType element. Customer Engagement sends the following information to Order Administration.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
|
dateTime |
The date and time when the response was generated. |
|
cardSeries |
|
|
CardPrefix |
The card prefix associated with the Loyalty Card Definition in Customer Engagement. |
|
CardSeriesSequence |
The card series sequence number associated with the Loyalty Card Definition in Customer Engagement. |
|
Instrument |
|
|
CardName |
The name of the Loyalty Card Definition in Customer Engagement. |
|
CardNumber |
The loyalty card number assigned to the customer in Customer Engagement. |
|
BatchNumber |
The batch number associated with the loyalty card in Customer Engagement. |
|
Customer |
|
|
CustomerID |
The Customer Engagement customer ID assigned to the loyalty card. |
Customer Engagement Card Services
Order Administration calls the Customer Engagement Card Services to generate the Customer Engagement getCardInquiryData Method.
The system uses the value in the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) along with the ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX and ORCE_CARD_SERVICE_SUFFIX settings in Working with Customer Properties (PROP) to build the URL for communication with Customer Engagement.
Customer Engagement getCardInquiryData Method
The getCardInquiryData method retrieves loyalty and award summary information for all accounts attached to the specified loyalty card number.
When called? The system calls this method when you:
- advance to the Display Loyalty Account Screen to review the customer’s loyalty points and award coupons.
- advance to the Customer Selection Screen; this screen displays the customer’s loyalty card number, current earned points, and current awards balance.
-
Open the Account Details panel at the Customer Loyalty List page in Modern View; this page displays the customer’s cards and the programs for each, as well as the program types, account numbers, levels, and current balances for each program.
-
View loyalty cards and awards in Contact Center Order Entry, and redeem awards in Contact Center Order Entry.
Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Request
The information that Order Administration sends to Customer Engagement includes the following:
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
|
cardNumber |
The loyalty card number assigned to the customer whose loyalty and award information is retrieved from Customer Engagement. |
|
currencyCode |
The default currency defined in the Local Currency Code (A55) system control value. This system control value must be set to a valid currency code.. |
|
transactionStoreId |
The store ID associated with the loyalty program; this is the location defined in the Default Location for ORCE Integration (K69) system control value. If you do not define a location in the Default Location for Sales Download (K69) system control value, Customer Engagement uses the location defined in the Default Location ID system configuration setting. |
Customer Engagement Loyalty Card Response
The getCardInquiry method returns a CardInquiryResponse class object. Customer Engagement sends the following information to Order Administration.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
ResponseStatus |
|
|
date/time |
The date and time of the inquiry. |
|
Instrument The Instrument element contains card information. |
|
|
card number |
The loyalty card number assigned to the customer whose loyalty and award information you wish to review. |
|
card serial number |
The serial number assigned to the loyalty card in Customer Engagement. |
|
card expiration date |
The date the card expires, if any. |
|
Loyalty Account The LoyaltyAccount element contains the loyalty accounts associated with the card. |
|
|
loyalty account ID |
The ID for the loyalty account in Customer Engagement. |
|
loyalty program |
The ID and name of the loyalty program associated with the account in Customer Engagement. |
|
loyalty program level |
The ID and name of the current level of the loyalty program to which the loyalty account belongs. |
|
points balance |
The current points balance for the loyalty account. |
|
card inquiry points entry |
The current points for the loyalty card for the following types of points:
|
|
AwardAccount The AwardAccount element contains the award accounts associated with the card. |
|
|
award account ID |
The award account ID associated with the loyalty card in Customer Engagement. |
|
award program |
The ID and name of the award program in Customer Engagement. |
|
coupon list |
The award coupons associated with the loyalty card in Customer Engagement. For each coupon:
|
|
Customer |
|
|
customer ID |
The Customer Engagement customer ID associated with the loyalty card. |
Customer Engagement Loyalty Account Services v3.4 API
Order Administration calls the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account Services version 3.4 API to generate the following methods:
The system uses the value in the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) along with the ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX and ORCE_LOYALTY_SERVICE_SUFFIX settings in Working with Customer Properties (PROP) to build the URL for communication with Customer Engagement.
Customer Engagement issuePoints Method
The issuePoints method issues points to the loyalty account specified and creates a retail transaction ID for the transaction.
When called? The system calls this method when you click OK on the Issue Loyalty Points Window.
Customer Engagement Issue Points Request
Order Administration sends the following information to Customer Engagement.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
|
loyalty account Id |
The loyalty account ID associated with the issued points. |
|
transaction store Id |
The store ID where the transaction was performed; this is the location defined in the Default Location for ORCE Integration (K69) system control value. If you do not define a location in the Default Location for Sales Download (K69) system control value, Customer Engagement uses the location defined in the Default Location ID system configuration setting. |
|
points amount |
The number of points being issued. |
|
client comments |
Informational comments associated with the issue points transaction. |
Customer Engagement Issue Points Response
The issuePoints method returns a loyaltyActivity class object. Customer Engagement sends the following information to Order Administration.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
account activity Id |
The Customer Engagement activity transaction number for issuing points to the loyalty card. |
|
account Id |
The loyalty account ID associated with the issued points. |
|
activity date/time |
The date and time when the activity occurred. |
|
activity typecode |
|
|
bonus points balance |
The bonus points balance at the time of the issue points transaction. |
|
earned points balance |
The earned points balance at the time of the issue points transaction. |
|
escrow points balance |
The escrow points balance at the time of the issue points transaction. |
|
escrow transferred flag |
Indicates whether escrow points were transferred as part of the issue points transaction. |
|
loyalty rule Id |
The ID for the loyalty rule used in the issue points transaction. |
|
LTD points balance |
The current life to date points balance for the account at the time of the issue points transaction. |
|
points amount |
The confirmed points amount issued to the loyalty card. |
|
points method typecode |
The code indicating the method uses for points calculations. |
|
points originally requested |
The number of points that were defined in the issue points transaction. |
|
retail transaction business date |
The business date when the issue points transaction occurred. |
|
YTD points balance |
The current year to date points balance for the account at the time of the issue points transaction. |
Customer Engagement getLoyaltyAccountHistory Method
The getLoyaltyAccountHistory method retrieves all of the loyalty points account activity for the loyalty account specified. This method is specific to the loyalty points transactions associated with the loyalty card and does not include award coupons.
When called? The system calls this method
when you select Loyalty History on the Display Loyalty Account panel for a program in Modern
View. All loyalty points activity returned in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response except Inquiry activity displays on the Display Loyalty Account History Screen.
Note:
If the number of records available in the Customer Engagement Award Account Services v3.1 API exceeds the maximum setting in Customer Engagement, a relateExceptionCode will be in the response with a value ofMAXIMUM_LOOKUP_RESULTS_ERROR and the response will not include any history. If this occurs, Order
Administration displays a message similar to the following, where 400 is the maximum setting defined in Customer Engagement: Max results exceeded of: 400.
Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Request
Order Administration sends the following information to Customer Engagement.
| Variable | Description |
|---|---|
|
card number |
The loyalty card number whose loyalty points account activity you wish to review. |
|
currency code |
The default currency defined in the Local Currency Code (A55) system control value. This system control value must be set to a valid currency code. |
|
history start date |
The start date of the loyalty points account activity to return in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response. The start date defaults to the current date minus 2 years in order to get 2 year’s worth of loyalty points account activity; for example, if the current date is 3/4/2024, the start date will be 3/4/2022. |
|
history end date |
The end date of the loyalty points account activity to return in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response. The end date defaults to the current date. |
Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response
The getLoyaltyAccountHistory method returns a CardInquiryResponse class object. Customer Engagement sends the following information to Order Administration.
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
|
CardInqResponseStatus The status of the inquiry response. |
|
|
date/time |
The date and time of the inquiry. |
|
status |
|
|
CardInqInstrument Card information. |
|
|
card number |
The loyalty card number associated with the loyalty points account activity. |
|
card serial number |
The serial number assigned to the loyalty card in Customer Engagement. |
|
card expiration date |
The date the card expires, if any. |
|
CardInqLoyaltyAccount |
|
|
loyalty account ID |
The ID for the loyalty account in Customer Engagement. |
|
loyalty program |
The ID and name of the loyalty program associated with the account. |
|
loyalty program level |
The ID and name of the current level of the loyalty program to which the loyalty account belongs. |
|
points balance |
The current points balance for the account. |
|
card inquiry points entry |
The current points for the loyalty card for the following types of points:
|
|
LoyaltyActivityList A list of loyalty account activities performed. |
|
|
transaction type |
The type of transaction activity performed.
The Display Loyalty Account History Screen displays all types
of activity except |
|
number of points |
The amount of points that were applied as a negative or positive to the loyalty card. |
|
pending flag |
|
|
account activity ID |
The Customer Engagement assigned activity transaction number for the record. |
|
location ID |
The location ID where the transaction was performed. |
|
create user |
The ID of the user who performed the activity. |
|
update user |
The ID of the user who updated the activity. |
|
void flag |
|
|
escrow points balance |
Escrow points balance for the account at the time of the activity. |
|
earned points balance |
Earned points balance for the account at the time of the activity. |
|
bonus points balance |
Bonus points balance for the account at the time of the activity. |
|
comments |
Informational comments associated with the activity. |
|
business date |
The business date on which the activity occurred. |
|
rule name |
The rule that governed the points in the activity. |
|
reference transaction ID |
The ID for the transaction referred to by the activity. |
|
retail transaction ID |
The retail transaction ID associated with the activity. |
|
CardInqCustomer The customer associated with the card. |
|
|
customer ID |
The Customer Engagement customer ID associated with the loyalty card. |
Customer Engagement Award Account Services v3.1 API
Order Administration calls the Customer Engagement Award Account Services version 1.2 API to generate the following methods:
- Customer Engagement issueCoupon Method
- Customer Engagement automaticRedeem Method
- Customer Engagement getAwardAccountHistory Method
The system uses the value in the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) along with the ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX and ORCE_LOYALTY_AWARD_SERVICE_SUFFIX settings in Working with Customer Properties (PROP) to build the URL for communication with Customer Engagement.
Customer Engagement issueCoupon Method
The issueCoupon method issues an award coupon to the loyalty account specified and creates a retail transaction ID for the transaction.
When called? The system calls this method when you click OK on the Issue Loyalty Coupon Window or when you issue an award coupon in Modern View.
Customer Engagement Issue Coupon Request
Order Administration sends the following information to Customer Engagement.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
|
award account ID |
The award account ID associated with the loyalty card. |
|
store ID |
The store ID where the transaction was performed; this is the location defined in the Default Location for ORCE Integration (K69) system control value. If you do not define a location in the Default Location for Sales Download (K69) system control value, Customer Engagement uses the location defined in the Default Location ID system configuration setting. |
|
user ID |
|
|
card number |
The loyalty card number associated with the award coupon. |
|
currency ID |
The default currency defined in the A55 system control value. This system control value must be set to a valid currency code. |
|
amount |
The amount of the award coupon to issue to the loyalty card. |
|
expiration date |
The date the award coupon expires. |
|
comments |
Informational comments about the issued award coupon. |
Customer Engagement Issue Coupon Response
The issueCoupon method returns an awardTransactionResult class object. Customer Engagement sends the following information to Order Administration.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
|
award transaction ID |
The Customer Engagement activity transaction number for issuing an award coupon to the loyalty card. |
|
account ID |
The award account ID associated with the award coupon. |
|
amount |
The confirmed award coupon amount issued to the loyalty card. |
|
coupon ID |
The award coupon ID generated by Customer Engagement for the issued award coupon. |
|
expiration date |
The date when the award coupon expires. |
Customer Engagement automaticRedeem Method
The automaticRedeem method automatically redeems award coupons for the specified amount and creates a retail transaction ID for the transaction. Award coupons with the closet expiration date are redeemed first.
When called? The system calls this method during the final order accept for an order that contains a loyalty award coupon discount in Classic View Order Entry or in Contact Center Order Entry; see Applying and Redeeming Customer Engagement Awards during Order Processing.
Customer Engagement Automatic Redeem Request
Order Administration sends the following information to Customer Engagement.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
|
award account ID |
The award account ID associated with the loyalty card. |
|
store ID |
The store ID where the transaction was performed; this is the location defined in the Default Location for ORCE Integration (K69) system control value. If you do not define a location in the Default Location for Sales Download (K69) system control value, Customer Engagement uses the location defined in the Default Location ID system configuration setting. |
|
user ID |
|
|
card number |
The loyalty card number to redeem the award coupon against. |
|
currency ID |
The default currency defined in the A55 system control value. This system control value must be set to a valid currency code. |
|
amount |
The amount of the award coupon to redeem against the loyalty card. |
|
comments |
Informational comments about the redeemed
award coupon. A message similar to the following defaults if the award
coupon was redeemed through the Order API: |
Customer Engagement Automatic Redeem Response
The automaticRedeem method returns a CardInquiryResponse class object. Customer Engagement sends the following information to Order Administration.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
|
card number |
The loyalty card number redeemed against. |
|
card serial number |
The serial number assigned to the loyalty card in Customer Engagement. |
|
loyalty account ID |
The ID for the loyalty account in Customer Engagement. |
|
loyalty program |
The ID and name of the loyalty program associated with the account in Customer Engagement. |
|
loyalty program level |
The ID and name of the current level of the loyalty program to which the loyalty account belongs. |
|
points balance |
The current points balance for the account. |
|
card inquiry points entry |
The current points for the loyalty card for the following types of points:
|
|
award account ID |
The ID for the award account in Customer Engagement. |
|
award program |
The ID and name of the award program associated with the account in Customer Engagement. |
|
coupon amount |
The amount of awards that were applied as a negative or positive to the loyalty card. |
|
coupon ID |
The ID of the coupon associated with the award coupon activity. |
|
customerID |
The Customer Engagement customer ID associated with the loyalty card. |
Customer Engagement getAwardAccountHistory Method
The getAwardAccountHistory method retrieves all of the award coupon account activity for the loyalty account specified. This method is specific to the award coupon transactions associated with the loyalty card and does not include loyalty points.
When called? The system calls this method when you;
-
Select Loyalty History on the Display Loyalty Account Screen.
-
Open the Account Details panel at the Customer Loyalty List page in Modern View; this page displays the customer’s cards and the programs for each, as well as the program types, account numbers, levels, and current balances for each program.
Note:
If the number of records available in the Customer Engagement Award Account History Response exceeds the maximum setting in Customer Engagement, a relateExceptionCode will be in the response with a value ofMAXIMUM_LOOKUP_RESULTS_ERROR and the response will not include any history. If this occurs, Order
Administration displays a message similar to the following, where 400 is the maximum setting defined in Customer Engagement: Max results exceeded of: 400.
Customer Engagement Award Account History Request
Order Administration sends the following information to Customer Engagement.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
|
card number |
The loyalty card number whose loyalty award coupon account activity you wish to review. |
|
currency code |
The default currency defined in the Local Currency Code (A55) system control value. This system control value must be set to a valid currency code. |
|
history start date |
The start date of the loyalty award coupon account activity to return in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response. The start date defaults to the current date minus 2 years in order to get 2 year’s worth of loyalty points account activity; for example, if the current date is 3/4/2014, the start date will be 3/4/2012. |
|
history end date |
The end date of the loyalty award coupon account activity to return in the Customer Engagement Loyalty Account History Response. The end date defaults to the current date. |
Customer Engagement Award Account History Response
The getAwardAccountHistory method returns a CardInquiryResponse. Customer Engagement sends the following information to Order Administration.
| Information | Description |
|---|---|
|
status |
|
|
card number |
The loyalty card number associated with the loyalty award coupon account activity. |
|
card serial number |
The serial number assigned to the loyalty card in Customer Engagement. |
|
award account ID |
The ID for the award account in Customer Engagement. |
|
award program |
The ID and name of the award program associated with the account in Customer Engagement. |
|
coupon amount |
The amount of awards that were applied as a negative or positive to the loyalty card. |
|
ID |
The ID of the coupon associated with the award coupon activity. |
|
transaction type |
The type of transaction activity performed.
The Display Loyalty Account History Screen displays all
types of activity except |
|
award transaction ID |
The Customer Engagement assigned activity transaction number for the record. |
|
location ID |
The location ID where the transaction was performed. |
|
create user |
The ID of the user that performed the activity. |
|
void flag |
|
|
retail transaction ID |
The retail transaction ID associated with the activity. |
|
activity date/time |
The date when the activity occurred. |
|
activity amount |
The amount of awards that were applied as a negative or positive to the loyalty card. |
|
requested amount |
The amount of awards that were applied as a negative or positive to the loyalty card. |
Customer Engagement Purchase History Integration
Purpose: The Customer Engagement Purchase History integration allows you to review a customer’s completed sales and return transactions across multiple channels, such as retail, call center, and e-commerce using the Display Purchase History Screen in Order Administration. When you advance to this screen, the system retrieves the sold to customer’s purchase history information from Oracle Retail Customer Engagement to display on the screen.
In this topic:
For more information: See:
-
the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for details on web service messages.
- Customer Engagement Customer Integration for more information on interactively communicating with Oracle Retail Customer Engagement to keep customer information in Order Administration in sync with Oracle Retail Customer Engagement when Oracle Retail Customer Engagement is the system of record for customer information.
- Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration for more information on sending merchandise hierarchy, item, customer, sales and return information from Order Administration to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement using a batch process. This section also includes Customer Engagement Integration Setup (Sales and Customer).
- The Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Implementation Guide (Installer Version) for more information on the procedures and instructions required to install and configure the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement application and database.
- The Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Implementation Guide for more information on configuration settings for Oracle Retail Customer Engagement that are defined using in system configuration properties.
- The Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Batch Processing and Web Services Guide for more information on the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement API interface.
- The Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Database Dictionary for more information on the tables in the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement database.
- The Oracle Retail Customer Engagement User Guide for more information on using the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement application.
- The Oracle Retail Omnichannel Web Service Authentication Configuration Guide on My Oracle Support (2728265.1).
Customer Engagement Purchase History Integration Setup
Before you can review purchase history from Oracle Retail Customer Engagement, you must complete the required setup.
Required versions: To review purchase history from Oracle Retail Customer Engagement, you must be on these versions:
- Order Management System version 5.0 or higher, or Order Administration.
- Oracle Retail Customer Engagement version 10.5 or higher.
In addition retrieving purchase history from Oracle Retail Customer Engagement uses version 2.3 of the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Customer API.
Setup is required in both Order Administration and Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
For more information: See:
- Customer Engagement Batch Customer and Sales Integration for more information on the setup required to use the Customer Engagement Sales Feed, , and Customer Engagement Customer Integration.
- Customer Engagement Loyalty Integration for more information on the setup required to use the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement loyalty program.
Setup in Order Administration for Customer Engagement Purchase History
System Control Values for Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Purchase History
| System Control Value | Description |
|---|---|
|
Use the ORCE Integration Values (L52) umbrella screen to set the following values. |
|
|
Enter INTERACT to send information on new and updated customers to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement interactively. See Customer Engagement Customer Integration for more information. |
|
|
Defines the store ID associated with a sale or return transaction in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement. This value is used to determine the channel where the sales or return transaction took place. Note: The location cannot be greater than 8 positions, and should not be greater than the length specified in the Retail Transaction Location ID Length specified in Customer Engagement. Also, the location code must be numeric to prevent any possible issues displaying a customer’s purchase history in Xstore.
|
|
|
Defines how Order Administration identifies items/SKUs returned in the Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Response. ITEM = Order Administration uses the Item code and SKU code. XREF = Order Administration uses the Retail reference number. Order Administration determines the item and SKU using the itemID with ItemType Stock for a sale, customer order for delivery, customer order for pickup, sale for delivery, or return line type transaction:
|
Web Service Authentication for Oracle Retail Customer Engagement
If the web services used to process inbound messages to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement require web service authentication, you must provide a valid web service authentication user and password or client ID and client secret in Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA). In this situation, when Oracle Retail Order Administration generates a message to send to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement it includes the web service authentication user and password or client ID and token in the HTTP header of the message. See the Oracle Retail Omnichannel Web Service Authentication Configuration Guide on My Oracle Support (2728265.1).
Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Property Settings for Purchase History
The Working with Customer Properties (PROP) menu option contains settings required for integration with Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
| Setting | Description | Setting |
|---|---|---|
| ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX |
The system uses this property to build the URL for communication with Oracle Retail Customer Engagement. |
http://server:8084/ soap where: server = the name of your Oracle Retail Customer Engagement server 8084 = the port to use on the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement server |
| ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_SUFFIX |
The system uses this property, along with the ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX and the value in the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) to build the URL for communication with Oracle Retail Customer Engagement using the Customer Services API. |
/v2_3/CustomerServices?wsdl where 2_3 is the version of the Customer Services API |
| ORCE_SECURITY_ USER_ID |
The Oracle Retail Customer Engagement user ID with Security Group permission included in the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement API messages. |
Must be a valid user ID in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement that has Security Group permission |
Setup in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement for Purchase History
Order Management System Company > Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Organization
An organization in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement corresponds to a company in Order Administration. You associate a Oracle Retail Customer Engagement organization with an Order Administration company through the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) system control value.
Use system configuration options to define settings for the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement organization that integrates with Order Administration. See the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Configuration Guide for more information on how to define configuration settings for Oracle Retail Customer Engagement using the system configuration options.
Configuration Settings Required for the Loyalty Integration with Oracle Retail Customer Engagement
Use system configuration options to define these settings for the organization that integrates with Order Administration.
| Configuration Option | Setting |
|---|---|
| Default Location ID |
Enter a default location ID of up to 12 positions. |
| Transaction Search Limit |
Enter the maximum number of transaction records that can be returned in the Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Response when making a purchase history lookup request to the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement server. The default value is 50, indicating the 50 most recent transactions will be returned in the results. |
Note: Whenever you makes changes to an organization’s configuration settings, you must stop Oracle Retail Customer Engagement, deploy the configuration settings to Customer Engagement, and restart Oracle Retail Customer Engagement. See:
- Shut Down Services in the Add New Organization section of the Customer Engagement Implementation Guide (Installer Version) for more information on how to stop Customer Engagement.
- the Customer Engagement Configuration Guide for more information on deploying configuration settings to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
- Restart Services in the Add New Organization section of the Customer Engagement Implementation Guide (Installer Version) for more information on how to restart Customer Engagement.
Display Purchase History Screen
Use this screen to review a customer’s purchase history from Oracle Retail Customer Engagement, specifically:
- sales transactions of type:
-
CustomerOrderForDelivery: This sales transaction typically occurs when a customer purchases an item that is not located in the store or the item is out of stock. In this situation, the item is purchased to ship directly to the customer’s home from another location.
-
CustomerOrderForPickup: This sales transaction typically occurs when a customer purchases an item that is not located in the store or the item is out of stock. When the item arrives at the store, the customer picks up the item and a previous customer order is processed to close the transaction.
-
SaleForDelivery: This sales transaction typically occurs when the item is not in stock. In this situation, the item is delivered to an address specified by the customer.
-
- return transactions.
A separate row displays on this screen for each individual item on a sales or return transaction.
When you advance to this screen:
- Order Administration sends a Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Request to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement containing the customer’s Relate ID from the Customer Sold To table.
- Oracle Retail Customer Engagement uses the Relate ID in the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Request to find the customer and returns the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response containing the customer’s information.
- Order Administration sends a Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Request to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
- Oracle Retail Customer Engagement uses the customer information in the Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Request to retrieve the customer’s purchase history.
- Oracle Retail Customer Engagement returns the Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Response to Order Administration, containing the customer’s purchase history.
- Order Administration displays the purchase history information returned from Oracle Retail Customer Engagement on the Display Purchase History screen.
How to display this screen: This screen is available when the ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT and you:
- Select Purch Hist from the Action drop-down menu on the Customer Scan Screen in Work with Customers (WCST) or Order Entry (OEOM).
- Select Purchase History on the Customer Scan Screen after selecting a sold to customer.
- Select Purchase History on the Display More Options Screen.
- Select Purchase History on the More Customer Sold To Options Screen.
When you select the Purchase History option, the system retrieves the sold to customer’s purchase history information from Oracle Retail Customer Engagement to display on the Display Purchase History screen.
The message No purchase history found displays if no purchase history was returned from Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
Column sort: You can sort on the Purchase Date, Transaction ID, Item/SKU, Description, Channel, Transaction Type, Associate ID, Quantity, and Extended Price columns on this screen by clicking the column name. An arrow pointing up displays next to the field when the values for the field display in ascending sequence; an arrow pointing down displays next to the field when the values for the field display in descending sequence.
When you first advance to this screen, purchase history records display in descending Purchase Date sequence.
Note:
The information that displays on this screen is from Oracle Retail Customer Engagement and is not stored in Order Administration.For more information: See the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for details on the Customer Engagement request and response messages.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Customer # |
The number, company name, last name, and first name of the sold to customer whose purchase history you are reviewing. Customer number: Numeric, 9 positions; display-only. Customer name: Alphanumeric, 40 positions; display-only. |
| Purchase History |
A separate row displays on this screen for each individual item on a sales or return transaction. |
| Purchase Date |
The date of the sales or return transaction. From the information in the Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Response. See the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for details. |
| Trans ID |
The transaction ID assigned to the sales or return transaction. If the transaction originated in Order Administration, this is the Order Administration invoice number. From the sequence number for a sale, customer order for delivery, customer order for pickup, sale for delivery, or return line type transaction in the Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Response. See the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for details. |
| Item/SKU |
The item number and SKU code of the item that was purchased or returned. The system uses the itemID with an item type of Stick for a sale, customer order for delivery, customer order for pickup, sale for delivery, or return line type transaction in the Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Response to determine the item and SKU:
|
| Description |
A description of the item. If the item contains SKUs, this is the SKU description. If the item is found in Order Administration, from Description in the SKU or Item table. If the item and SKU is not found in Order Administration, the system defaults Store Only Product to the Description field. |
| Channel |
The channel where the sales or return transaction took place.
|
| Trans Type |
Defines whether the transaction was a sale or return.
|
| Associate ID |
The ID for the user that completed the transaction. Note: This does not have to be a valid user in Order Administration.From operator ID passed in the Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Response for a sale, customer order for delivery, customer order for pickup, sale for delivery, or return transaction. |
| Qty |
The quantity of the item associated with the transaction. From Quantity in the Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Response for a sale, customer order for delivery, customer order for pickup, sale for delivery, or return line type transaction. |
| Ext Price |
The extended merchandise price of the transaction. From ExtendedAmount in the Customer Engagement Get Transaction History Response for a sale, customer order for delivery, customer order for pickup, sale for delivery, or return line type transaction. |
| Lifetime to Date | |
| Sales Amount |
The total life to date sales amount for the customer. From total sales amount in the LifetimeActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Returns Amount |
The total life to date return amount for the customer. From total returns amount in the LifetimeActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Net Amount |
The lifetime to date net purchase amount for the customer. The system uses the following calculation to determine the customer’s lifetime net amount: Lifetime to Date Sales Amount - Lifetime to Date Returns Amount = Lifetime to Date Net Amount From the total sales amount and total returns amount in the LifetimeActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Sales Items |
The total life to date items sold for the customer. From total items sold count in the LifetimeActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Returns Items |
The total life to date items returned for the customer. From total items and returned count in the LifetimeActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Net Items |
The lifetime to date net item count for the customer. The system uses the following calculation to determine the customer’s lifetime net item count: Lifetime to Date Sales Items - Lifetime to Date Returns Items = Lifetime to Date Net Items From the total items sold count and total items returned count in the LifetimeActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Year to Date | |
| Sales Amount |
The total year to date sales amount for the customer. From the year-to-date sales amount in the YearToDateActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Returns Amount |
The total year to date return amount for the customer. From year-to-date returns amount in the YearToDateActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Net Amount |
The year to date net purchase amount for the customer. The system uses the following calculation to determine the customer’s year to date net amount: Year to Date Sales Amount - Year to Date Returns Amount = Year to Date Net Amount From the year-to-date sales amount and the year-to-date returns amount in the YearToDateActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Sales Items |
The total year to date items sold for the customer. From year-to-date items sold count in the YearToDateActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Returns Items |
The total year to date items returned for the customer. From the year-to-date items returned count in the YearToDateActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
| Net Items |
The year to date net item count for the customer. The system uses the following calculation to determine the customer’s year to date net item count: Year to Date Sales Items - Year to Date Returns Items = Year to Date Net Items From the year-to-date items sold count and year-to-date items returned count in the YearToDateActivitySummary class of the Customer Engagement Retrieve Customer Response. |
Reviewing Purchase History in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement
You can view transactions on the Transaction History screen for a customer. To view the details for a transaction, click the transaction to open the Transaction Detail window. See Transaction History Screen in the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement User Guide for screen details.
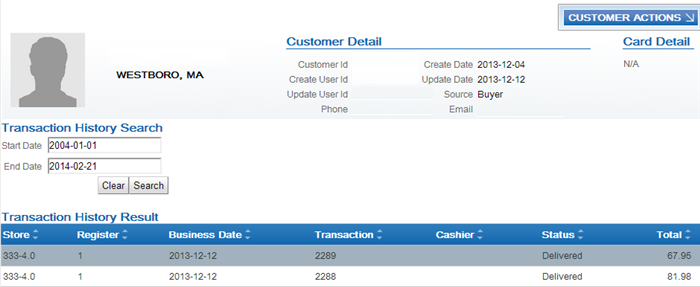
To view the details for a transaction, click the transaction to open the Transaction Detail window. See Transaction Detail Window in the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement User Guide for screen details.
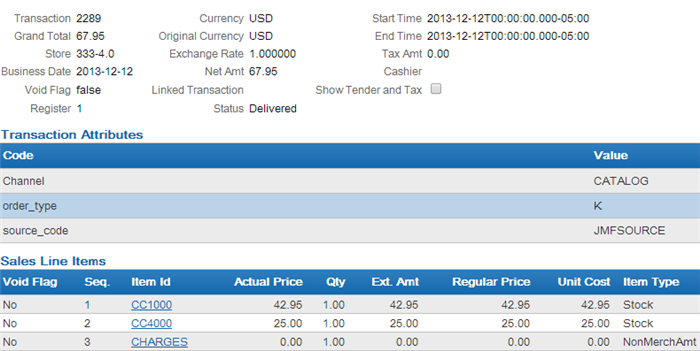
The Purchase Activity section of the Customer Dashboard also provides a summary of the transactions associated with a customer, including:
- Total Sales Amount, Total Sales Item Count, Total Returns Amount, and Total Returns Item Count.
- Year To Date Sales Amount, Year To Date Sales Item Count, Year To Date Returns Amount, and Year To Date Returns Item Count.
See Customer Dashboard in the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement User Guide for screen details.
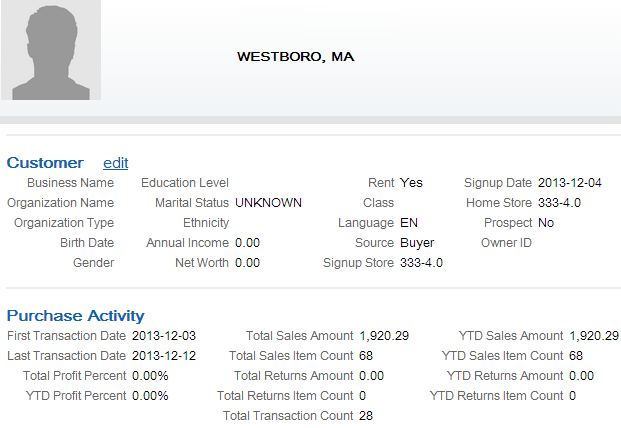
For more information: See the Customer Lookup / Edit section of the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement User Guide for more information on reviewing sales and return transactions for a customer.
Customer Engagement Stored Value Card Integration
Customer Engagement Stored Value Card integration allows you to process stored value cards between Order Administration and Oracle Retail Customer Engagement using point-to-point communication. Processing of stored value cards remains the same in Order Administration; however, in this integration, Order Administration uses Oracle Retail Customer Engagement APIs to send the stored value card transactions directly to the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement system for processing.
Required versions: To use the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement stored value card integration with Order Administration, you must be on version 16.0 or later of Oracle Retail Customer Engagement and Order Management System version 17.0 or later, or Order Administration.
In this topic:
-
Transactions Processed Between Order Administration and Oracle Retail Customer Engagement
-
Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Integration Setup in Order Administration
-
Stored Value Card Integration Setup in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement
-
Oracle Retail Customer Engagement APIs used in the Stored Value Card Integration
For more information: See Stored Value Card Overview and Setup for an overview of stored value card processing, and see the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for details on messages and mapping.
Transactions Processed Between Order Administration and Oracle Retail Customer Engagement
You can process the following transactions for the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement integration with Order Administration:
| OACS | ORCE | See: |
|---|---|---|
|
Activation Virtual card assignment: To assign a number to a virtual card Order Administration sends a Generate Card Request to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement. See Assigning Numbers to Virtual Stored Value Cards. Stored value card refunds: If you process a return against a stored value card pay type that has an alternate pay type or alternate refund category of stored value card defined, the system generates a new stored value card to send to the customer when you process a refund. The card is issued for the refund amount. When you process stored value card refunds, the system adds a stored value card item to the order at no charge and performs pick slip preparation. You can then follow the normal process of generating a pick slip for the stored value card item so that the card can be picked, activated, billed, and shipped to the customer. |
Generate Card (virtual card number assignment)
Recharge (virtual card activation)
Activate Instrument (physical card activation)
See the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for message details. |
|
|
Authorization (both online and batch) |
Preauthorization
See the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for message details. |
Processing Authorizations and Deposits Using Point-to-Point Communication |
|
Deposit Authorization amount mismatch: The deposit request might fail if the amount is different from the original authorization amount. This situation might occur if, for example, the order includes multiple stored value cards and items that were added to the order and billed in a different sequence. To correct:
|
Post Auth (Deposit)
See the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for message details. |
Processing Authorizations and Deposits Using Point-to-Point Communication |
|
Credit Stored value card refunds: If you process a return against a stored value card pay type that does not have an alternate pay type or alternate refund category defined, the system generates a credit card credit refund against the original stored value card pay type, allowing you to reimburse the refund amount to the original stored value card instead of sending a new stored value card to the customer. |
Recharge (Reload)
See the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for message details. |
Generating Stored Value Card Refunds Processing Authorizations and Deposits Using Point-to-Point Communication |
|
Balance Inquiry |
Inquiry
See the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for message details. |
|
|
Authorization Reversal |
Release Auth
See the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for message details. |
Stored Value Card Authorization Reversal |
Oracle Retail Customer Engagement integration stored value card process flow:
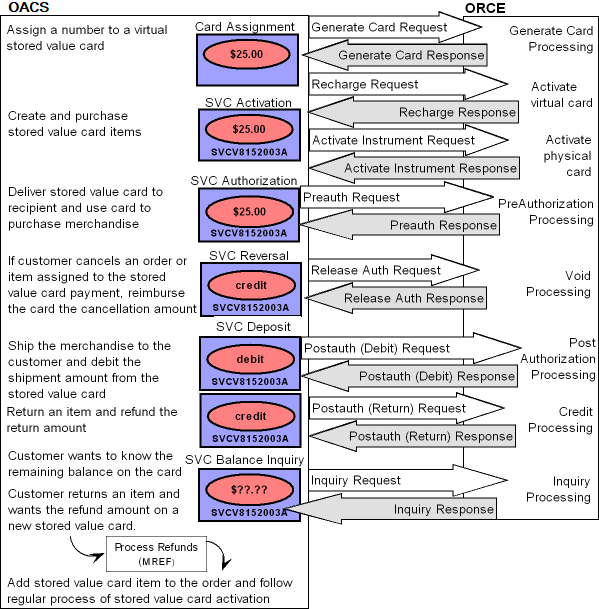
Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Integration Setup in Order Administration
For more information: See Stored Value Card Setup for more information on the setup required to process stored value cards in Order Administration.
Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Service Bureau Setup
Use Defining Authorization Services (WASV) to create the RLT service bureau for the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement system, taking note of these settings:
-
Service code: Must be RLT.
-
Presenter’s ID: The card prefix assigned to virtual stored value cards in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
Important:
When you create virtual card numbers in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement, you must create the numbers using this card prefix number. -
Submitter’s ID: The card series sequence number assigned to virtual stored value cards in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
Important:
When you create virtual card numbers in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement, you must create the numbers using this card series sequence number. -
Send reversal: Select this field to perform authorization reversal processing.
-
Integration layer processes: Leave these fields blank.
-
Batch/online: Select Online or Batch.
-
Immediate response: Must be selected.
-
Selected for deposit: Select this field to include the RLT service bureau in the next deposit run.
-
Primary authorization service: Must be .IL.
-
Communication type: Select Payment Link. to indicate messages sent to and from the service bureau are processed directly.
Response codes: When the Service code is RLT, the system displays the ORCE response field on the Create, Change, and Display Vendor Response screens. This field allows you to map a response from Oracle Retail Customer Engagement to a vendor response code. Use this field to enter the code assigned by the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement service bureau to identify whether the stored value card transaction was approved or declined.
Note:
The INSUFFICIENT_FUNDS response code for the RLT authorization service must be assigned a hold reason code of SV..IL Service Bureau Setup
To send transactions to the service bureau using Point-to-Point communication, create a service bureau using the service code.IL and enter a value in the following fields:
-
Application: ATDP (authorization and deposit)
-
Merchant ID: INTEGRATION LAYER
-
Charge description: Integration Layer
-
Media type: C (communications)
Enter the .IL service bureau in the Primary authorization service field for the RLT service bureau.
Web Service Authentication for Oracle Retail Customer Engagement
If the web services used to process messages to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement require web service authentication, you must provide a valid web service authentication user and password in Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA), or client ID and client secret if using OAuth. In this situation, when Oracle Retail Order Administration generates a message to send to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement it includes the web service authentication information in the HTTP header of the message. See Oracle Retail Omnichannel Web Service Authentication Configuration Guide on My Oracle Support (2728265.1) for more information.
Work with Pay Types (WPAY)
Use Working with Pay Types (WPAY) to create a stored value card pay type to send to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement. Enter RLT as the authorization and deposit service for the stored value card pay type.
Enter 7 in the Reauthorization days for the stored value card pay type used for the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement stored value card integration.
System Control Values
-
Enter RLT in the Stored Value Card Activation Authorization Service (I26) system control value.
-
Leave the Stored Value Card Modulus Checking Method (I24) system control value blank since Oracle Retail Customer Engagement does not perform modulus checking against the digits of a stored value card number.
-
Deselect the Perform Authorization Reversal during Deposit Processing (J20) system control value since this option is not available for the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement stored value card integration.
-
Select the Perform Balance Inquiry during Batch Authorizations (J19) system control value since Oracle Retail Customer Engagement will approve an authorization for an amount that is less than the required authorization amount on the order. If you do not select this system control value, you must require another credit card payment on the order.
-
Select the Retain Unused Stored Value Card Authorization After Deposit (J21) to retain a stored value card authorization after it has been partially deposited.
-
Enter the code that identifies the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement organization that maps to your Order Administration company. The system uses this value when communicating with Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
Stored Value Card Integration Setup in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement
For more information: See the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Configuration Guide for more information on the setup required for gift card processing in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
Card Number Length
The Card Number Length property defines the number of digits used in a card number. This setting applies to all cards generated in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement, regardless of card type. Once an organization has generated card numbers, the Card Number Length setting cannot be changed. Enter a number between 10 and 16. The card number length must match the Order Administration Credit card length in Work with Pay Types (WPAY) for the stored value card pay type you send to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
Card Number Prefix
The Card Number Prefix property specifies the card number prefix character for a card number. Only one character can be used and is counted as part of the card length. This setting applies to all cards generated in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement, regardless of card type. The card number prefix must match the Order Administration Leading digits in Work with Pay Types (WPAY) for the stored value card pay type you send to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
Minimum Activation Amount and Balance
Set the minimum activation amount and balance to 0.00 indicating the amount cannot be a negative amount.
Allow Partial Redemption Setting
Set the Allow Partial Redemption setting for the tender program to No.
Pin
The PIN Required setting for a card definition indicates whether a pin if required for a stored value card.
-
On physical cards, the pin is located on the card. For virtual cards, the pin is provided in the Stored Value Card Notification Email if the program defined in the Stored Value Card Email Notification Program (I30) system control value supports it.
-
If a pin is required, you must provide the pin when using the stored value card as a form of payment. The Pin Length defines the length of the pin.
Oracle Retail Customer Engagement APIs used in the Stored Value Card Integration
The Stored Value Card Transaction Services API v3.1 is used to communicate with Oracle Retail Customer Engagement during the Customer Engagement Stored Value Card integration.
The system uses the value in the ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50) system control value along with the ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX and ORCE_SVC_SERVICE_SUFFIX settings in Work with Customer Properties (PROP) to build the URL for communication with Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.
Note:
In order for transactions to process correctly, the Franchisee feature must be disabled in Oracle Retail Customer Engagement.Reviewing messages for the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement stored value card integration: You can review the messages passed between Order Administration and Oracle Retail Customer Engagement in the ORCE (Oracle Retail Customer Engagement) Log if its Logging Level is set to DEBUG or ALL. Use this log to help troubleshoot the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement integration.
Web service authentication? If the web services used to process inbound messages to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement require web service authentication, you must provide a valid web service authentication user and password in Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA), or client ID and client secret if using OAuth. In this situation, when Oracle Retail Order Administration generates a message to send to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement it includes the web service authentication information in the HTTP header of the message. See Oracle Retail Omnichannel Web Service Authentication Configuration Guide on My Oracle Support (2728265.1) for more information.
Oracle Retail Customer Engagement message formats: For a complete description and message layout of the messages used to communicate with the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement system, see the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement Web Services Guide. Also, see Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for more information on mapping and messages samples.
Data security: Order Administration masks the stored value card number in the Oracle Retail Customer Engagement stored value card messages; for example, ************1111 displays instead of the full stored value card number.
Communication failure: If Order Administration is unable to connect to Oracle Retail Customer Engagement, the response message includes the reason code SU RELATE SERVICE IS UNAVAILABLE.
Error mapping: Regardless of the type of transaction processed, the information returned in the response message if a transaction is declined is the same. Order Administration maps the error code to the ORCE response field in Defining Vendor Response Codes.
Enterprise Order Integration (Future Receipts and Active PO/Pre Order Processing)
Purpose: The enterprise order integration uses enterprise foundation inventory data that originates in Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS) to support creating orders for items on active purchase orders, and submitting the orders to Order Orchestration for fulfillment as these items become available.
In this topic:
-
Importing Future Available Information (OCDSFA Periodic Function)
-
Future Receipts and Active PO Order Processing Configuration
Enterprise Order Flow Overview
The order flow described below takes place if:
-
The Use OROB for Fulfillment Assignment (M31) and Send B/O to OROB (K08) system control values are set to Y, the other system control values at the Order Broker Values (K15) and Order Broker Fulfillment Values are set, and all other related setup for integration with Order Orchestration is completed.
-
You import enterprise data from Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS), as described below (Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS)).
-
Order Orchestration also integrates with OCDS. Order Broker release 18.1 or higher, or Order Orchestration, is required.
Important:
The flow described here typically takes place for brokered backorders, but can also support releasing ship-for-pickup orders to Order Orchestration, provided that the fulfilling system supports this order type.See Future Receipts and Active PO Order Processing Configuration for more configuration requirements.
With this setup:
-
Order Administration submits orders to Order Orchestration for fulfillment rather than reserving the inventory in the warehouse.
-
Certain items are flagged as active PO orders, indicating that:
-
Customers can order these items before you have them in inventory.
-
A limited quantity of each item will be ordered on an active purchase order, and then received in a fulfilling location in Order Orchestration.
-
Optionally, once the full quantity of the item has been received on purchase orders, any additional quantity on orders can be sold out.
-
See below for more discussion.
About Active PO Items
You can take orders for an item that is not currently available, but that you anticipate will be available in the future through an active purchase order. These orders can then be fulfilled through submission to Order Orchestration as the inventory on active purchase orders is received into fulfilling locations and becomes available. The process flows described in this topic provide a means to take orders for these items in advance without selling them out prematurely, in anticipation of the time when they will be in stock in a location where Order Orchestration can assign them for fulfillment.
Order Administration relies on the purchase order information in OCDS to determine when these items can be fulfilled. Only the quantity that has been received on purchase orders is actively eligible for fulfillment; however, Order Administration uses the open quantity on purchase orders (future available quantity) to determine the quantity of each item that it can take in advance.
When an item is flagged as an active PO item:
-
The system does not submit it to Order Orchestration as it normally does. Since the inventory across the enterprise is synchronized, there would be no point to submitting items to Order Orchestration prematurely, because Order Orchestration would not have the inventory to fulfill them, and would respond to Order Administration indicating the order was unfulfillable. Instead, Order Administration uses the processes described below to determine when to submit order lines to Order Orchestration for processing based on the inventory as it becomes available.
-
The item sells out automatically when the order line is created if the active PO calculation indicates that there will not be sufficient inventory to fulfill it based on the on-order quantity, and if a soldout control code is assigned to the item.
Processing takes place through:
Importing Future Available Information (OCDSFA Periodic Function)
Tracking the future availability of active PO items enables Order Administration to determine how many units it will be able to fulfill. In order to track the future availability of pre-order/active PO items, Order Administration communicates with Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS) to determine:
-
The total quantity of the item that is on order in Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS), and,
-
The total quantity of the item that has been received through RMFCS.
Periodic function: The future availability and active PO updates take place through the OCDSFA periodic function, which receives future availability information from OCDS and updates inventory records in Order Administration.
The periodic function receives information on quantities from OCDS and processes the updates described in the table below to manage active PO items that will be fulfilled through the Order Orchestration, and makes the following updates:
Item Warehouse updates based on the quantity information sent from OCDS: The periodic function:
-
Updates:
-
PO On Order: The total quantity on purchase orders for the item. From the on-order quantity sent by OCDS.
-
PO Receipts: The total quantity that has been received against purchase orders, indicating the total quantity on active PO orders that Order Administration can submit to Order Orchestration for fulfillment. A cumulative total, from the received quantity sent by OCDS.
Note:
If the PO On Order quantity is the same as the PO receipts quantity, the periodic function does not make any additional updates. This situation might occur if active PO processing has already taken place, but the records in OCDS were not yet purged at the time the periodic function ran. Otherwise, the periodic function: -
-
Selects the Active PO flag, if it is not already set, to indicate that the item has an active purchase order for which you can accept orders before you expect to have inventory to fulfill. This flag indicates that the system should release units of the item to Order Orchestration for fulfillment as purchase orders are received.
-
Sets the item warehouse on-order quantity to the PO On Order quantity minus the item warehouse Released Qty (the total quantity of the active PO item that has been released to Order Orchestration for fulfillment).
-
Sets the Reservation freeze flag for the item warehouse to N, if it is not already set to N.
-
Updates the PO Updated date.
The function also updates the item/SKU:
-
Sets the soldout control value for the item to the Default Soldout Control Code (D72), if it is not set already.
-
If the PO On Order quantity increases, sets the Active PO flag for the item/SKU to Y if it is not already selected. This is a display-only field on the Create Item (Base Information) Screen and Create SKU 1 of 2 (With Overrides) Screen, as well as the change and display screens.
About increases to PO On Order quantity: Typically, an increase in PO On Order quantity occurs for a new active PO (pre-order) item, although it can also occur for an existing active PO item.
Example: If the PO On Order quantity is 30, Order Administration can take active PO orders for a total of up to 30 units. The Active PO flag for the item is set to Y, indicating that Order Administration should retain orders for up to 30 units, releasing them to Order Orchestration as the purchase orders are received.
If the PO On Order quantity decreases, or stays the same, no additional updates take place besides those described above.
Note:
Active PO order lines are not sold out as a result of OCDSFA processing, regardless of whether there was a decrease in PO On Order quantity or the soldout control code currently assigned to the item.When is Released quantity updated? The PREORDER or ACTPO periodic function updates the Released qty; see the related periodic function under Releasing Eligible Orders to Order Orchestration and Submitting the Backorder Quantity Update Notification for more information. This quantity is 0 for a new active PO item, but the periodic function also accounts for existing active PO items that have had a quantity released to Order Orchestration for fulfillment based on a receipt quantity.
Setup Requirements for the OCDSFA Periodic Function
Required setup for the OCDSFA periodic function includes the following.
-
URL: From the OCDS Future Available URL (M49) system control value.
-
Authentication: From the OCDS Service web service authentication. See Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA).
-
Item number: The Reference # (Reference number)) specified for the item in the SKU table identifies the item warehouse record to update. The retail reference number is set to the same value as the item code when you import items through OCDS, and should not be changed.
-
Warehouse: The Default Warehouse (A04) system control value identifies the item warehouse record to update.
-
Company: From the company submitting the periodic function.
-
Periodic function: Create the OCDSFA (Program name = PFR0203) periodic function and assign it to a periodic process.
Use Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS) to create the item warehouse records.
For more information: See Future Receipts and Active PO Order Processing Configuration for full configuration requirements.
Additional Things to Note about the OCDSFA Periodic Function
When to run: This function should be run after the OCDSITM function described in Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS). Also, it should typically run more often than the OCDSITM function in order to capture frequent inventory updates as they are posted to OCDS.
Errors might occur if:
-
The OCDS Future Available URL (M49) is not correct.
-
The OCDS Service authentication set up through Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA) is not correct.
-
The Default Warehouse (A04) is not set.
-
The item warehouse record does not exist. This situation might occur if the OCDSITM function did not run before the OCDSFA periodic function.
The OCDSFA periodic function also creates Enterprise Data Import History records. You can review these records, with an Import Type of FUTUREAVAILABLE, at the Enterprise Data Import History page in Modern View.
For more information: See Troubleshooting the Enterprise Order Integration for more troubleshooting information.
Releasing Eligible Orders to Order Orchestration and Submitting the Backorder Quantity Update Notification
There are two existing periodic functions that release eligible active PO orders to Order Orchestration:
-
PREORDER Periodic Function for (Order Broker Releases Earlier than 20.2)
-
ACTPO Periodic Function for (Order Broker 20.2 or Higher, or Order Orchestration)
Both the PREORDER periodic function and the ACTPO periodic function also generate the backorder quantity update notification to RMFCS, if needed. See Generating the Backorder Quantity Update Notification Message (PREORDER or ACTPO Periodic Function).
PREORDER Periodic Function for (Order Broker Releases Earlier than 20.2)
When to use the PREORDER periodic function: Use this periodic function for integration with Order Broker releases earlier than 20.2. For integration with Order Broker 20.2 or higher, or Order Orchestration, use the ACTPO Periodic Function for (Order Broker 20.2 or Higher, or Order Orchestration).
PREORDER Processing Steps
Based on the updates made by the OCDSFA periodic function, the PREORDER periodic function performs the following steps.
-
Determining the quantity available to submit to Order Orchestration.
-
Releasing eligible orders to Order Orchestration.
-
Updating Item Warehouse records.
-
Submitting the Backorder Quantity Notification update message to Retail Integration Cloud Service.
Each is described below.
Submits active PO orders to Order Orchestration: Submits eligible active PO orders to the BROKER_ORD process for submission to Order Orchestration for fulfillment, determined by subtracting the released quantity from the PO receipts quantity.
Example: The PO receipts quantity is now set to 15 units, and 10 units have already been released to Order Orchestration. If there are 6 remaining units of the active PO item on open orders that have not yet been submitted to Order Orchestration for fulfillment, the periodic function releases up to 5 units, provided that it would not need to submit a partial quantity of an order line to Order Orchestration. If, for example, the remaining order line quantities are 4 on the oldest order and 2 on a more recent order, only the order line with the quantity of 4 is released.
Note:
-
The order lines are submitted in first-in, first-out order (oldest first).
-
Partial order line quantities are not submitted to Order Orchestration. If the next eligible line would exceed the quantity available to release, it is skipped.
-
The order submission uses the same steps and applies the same updates as the BROKER periodic function.
-
Orders in Error status or Suspended status are not eligible to be submitted. Also, locked orders are not submitted.
-
Each order line for an active PO item is evaluated separately.
The Send Held Orders to OROB (M18) system control value controls whether the PREORDER periodic function includes held orders.
Item warehouse quantity updates: The function:
-
Increases the Released qty for the item warehouse by the quantity of active PO order lines submitted to Order Orchestration.
-
Sets the item warehouse On-order quantity to the PO on-order quantity minus the Released qty. For example, if a total of 30 units are on purchase orders, and 12 units have been released to the Order Orchestration for fulfillment, the item warehouse On-order quantity is set to 18.
Is the item still an active PO item? The following updates take place if the PO On Order quantity is now less than or equal to the PO receipts quantity, indicating that all anticipated units on purchase orders have been received. When this occurs, the item is no longer eligible for active PO processing, so that any additional units ordered can sell out, based on the assigned soldout control code.
Example: If the PO On Order quantity is 30, and the PO Receipts quantity is 25, the Active PO flag remains set to Y, because an additional 5 units can be received and used to fulfill active PO orders. However, if the PO Receipts quantity is 30 or higher, the Active PO flag changes to N, because no additional receipts are expected.
If the item is no longer an active PO item, the periodic process:
-
Sets the Active PO flag for the item to N.
-
Sells out any remaining open lines beyond the PO On Order quantity in last-in, first-out order (sell out the newest first). If the entire line cannot be submitted to Order Orchestration, the entire line sells out.
Example: If the PO On Order quantity and the PO Receipts quantity are both 30, and there are active PO order lines for a total quantity of 35, the additional 5 units sell out. Also, if the newest order line is for a quantity of 6, all 6 units on that line sell out, because order lines are not partially sold out.
-
Sets the PO On Order quantity, PO Receipts quantity, Released qty, and Item Warehouse On-order quantity to 0.
Otherwise, if the item is still an active PO item, the PREORDER function does not update the Active PO flag or sell out any units of the item.
Example: If the PO On Order quantity is 30, there are 29 units on order lines, and the PO Receipts quantity is 15, Order Administration can release up to 15 units to Order Orchestration for fulfillment. The remaining 14 units remain as active PO order lines in Order Administration.
Backorder quantity update notification? If the backorder quantity is not equal to the PO pre-order quantity sent, this means that the backorder quantity has changed, and that RMFCS needs to be notified. In this case, the periodic function submits the backorder quantity update notification message to notify RMFCS of any increase or decrease to the active PO backorder quantity. See Generating the Backorder Quantity Update Notification Message (PREORDER or ACTPO Periodic Function) for information on the backorder quantity update notification generated through the PREORDER periodic function.
Note:
The PO pre-order quantity sent is not displayed on any screen; it is just the current backorder quantity at the time the backorder quantity update notification is generated, and is used only to determine the quantity to send the next time the notification is generated.Setup Requirements for the PREORDER Periodic Function
In addition to the configuration described under Setup Requirements for the OCDSFA Periodic Function, the PREORDER periodic function requires the following:
-
URL: From the OCDS Future Available URL (M49) system control value.
-
Authentication: From the OCDS Service web service authentication. See Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA).
-
Periodic function: Create the PREORDER (Program name = PFR0204) periodic function and assign it to a periodic process.
Additional Things to Note about the PREORDER Periodic Function
When to run: This function should be run after the OCDSFA periodic function, described above under Importing Future Available Information (OCDSFA Periodic Function).
Note:
The PREORDER function needs to run after Order Orchestration receives inventory updates. Otherwise, it is possible for the ACTPO function to submit order lines to Order Orchestration before Order Orchestration recognizes that the location can fulfill orders based on inventory receipts. In this situation, Order Orchestration returns the orders to Order Administration as unfulfillable.Generating the Backorder Quantity Update Notification Message (PREORDER or ACTPO Periodic Function)
Both the PREORDER Periodic Function for (Order Broker Releases Earlier than 20.2) and the ACTPO Periodic Function for (Order Broker 20.2 or Higher, or Order Orchestration) generate the backorder quantity update notification message to RMFCS. This message indicates the net increase or decrease to the backorder quantity for an active PO item, so that RMFCS is aware of the current backorder quantity of the item. The PREORDER periodic function calculates the quantity to send by comparing the current backorder quantity of the active PO item with the current PO pre-order quantity sent that is stored in the Item Warehouse table.
The message does not simply send the current backorder quantity; instead, it indicates the amount of increase or decrease to the backorder quantity.
Backorder update examples:
| Description | Last Backorder Quantity Sent | Current Backorder Quantity | Quantity Sent in Message | New PO Pre-Order Quantity Sent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Backorder quantity increases from 4 to 6 through new order of 2 units. |
4 |
6 |
2 |
6 |
|
Backorder quantity decreases from 5 to 2 through order line cancellation. |
5 |
2 |
-3 |
2 |
|
Backorder quantity decreases from 10 to 4 through PO receipts quantity of 6, and 6 units submitted to Order Orchestration. |
10 |
4 |
-6 |
4 |
|
Backorder quantity of 10 has a net decrease of 6 units:
|
10 |
4 |
-6 |
4 |
|
Backorder quantity has not changed, either because there was no activity, or activity did not result in a net increase or decrease |
10 |
10 |
No message sent |
No change |
The periodic functions submit the backorder quantity update notification to Retail Integration Cloud Service through the RICS Outbound Service URL (M50).
What information is included in the backorder quantity update notification? The information in the notification includes the following:
-
Item: The item’s Retail reference number identifies the item. The retail reference number is set to the item code when Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS), and if the retail reference number is changed in any way, then the pre-order notification process does not succeed.
-
Location type: The message always passes a location type of W (warehouse).
-
Location: The message always passes the Default Warehouse (A04) as the location.
-
Backorder quantity: Calculated as described above.
-
Unit of measure: Set to EA (each).
No other fields are mapped.
ACTPO Periodic Function for (Order Broker 20.2 or Higher, or Order Orchestration)
When to use the ACTPO periodic function: Use this periodic function for integration with Order Broker releases 20.2 or higher, or Order Orchestration. For integration with Order Broker updates earlier than 20.2, use the PREORDER Periodic Function for (Order Broker Releases Earlier than 20.2).
The steps completed by this periodic function are:
-
Checking current availability in Order Orchestration through the inventory availability request.
-
Determining the quantity available to submit to Order Orchestration.
-
Releasing eligible orders to Order Orchestration.
-
Updating Item Warehouse records.
-
Submitting the Backorder Quantity Notification update message to Retail Integration Cloud Service.
Checking Current Availability in Order Orchestration
Overview: The ACTPO periodic function submits the inventory availability request to Order Orchestration to check availability for backordered items whose Active PO flag is selected, as described above under Importing Future Available Information (OCDSFA Periodic Function).
Purpose: The purpose of the inventory availability request is to determine the quantity of each item that should be available to fulfill the backorders in Order Administration. The response from Order Orchestration indicates the Available to Promise quantity for each of the requested items, broken out by the quantity in locations that support:
-
Delivery orders (brokered backorders in Order Administration).
-
Ship-for-pickup orders (included only if the Use OROB for Ship for Pickup Fulfillment Assignment (M34) system control value is set to ALWAYS).
Note that there can be overlap; some locations can support both delivery and ship-for-pickup orders, while others might support just one order type.
Available to Promise quantity calculation: In Order Orchestration, the Available to Promise quantity is the on-hand quantity minus the reserved quantity and any fulfilled quantity.
The response message includes the Available to Promise quantity for each requested item in two ways:
-
Across all product locations (distinct inventory), and
-
For locations that support a requested fulfillment type (either brokered backorders (DELIVERY) or ship-for-pickup orders).
Example: If a location has the item in stock
but does not support fulfilling brokered backorders, the inventory
total is included in distinctInventory but not
in the DELIVERY fulfillmentType.
Used how? The Available to Promise Quantity (availableToPromiseQty) for the DELIVERY fulfillment
type is used to calculate the quantity for brokered backorders, and
the availableToPromiseQty for the SHIPFORPICKUP
fulfillment type is used to calculate the quantity for ship-for-pickup
orders.
Other quantities passed in response not used: The response also includes other quantities, but the Available to Promise Quantity by fulfillment type is the only quantity in the response message that the ACTPO function uses to calculate the quantity available to submit to Order Orchestration.
Which items are included in the request message? Only items whose Active PO flags are selected and that have a backorder quantity in the Default Warehouse (A04) are included in the request. The OROB_INVENTORY_AVAILABILITY_SKU_LIMIT defines the maximum number of items to include in the request message. This limit is set to 500 by default, and cannot be greater than 500, although it can be set to a lower number.
Sample request message:
"messageHeader":
{"datetime": "2021-05-07T13:42:12","source":"OMS"},
"systemCd" : "6",
"fulfillmentTypes":
[
{"fulfillmentType":"DELIVERY"},
{"fulfillmentType":"SHIPFORPICKUP"}
],
"systemProducts":
[
{"systemProduct":"1234567"},
{"systemProduct":"2345678"}
]
}
Sample response message:
{
"messageHeader": {
"datetime": "2021-05-07T20:54:09.259",
"source": "OMS"
},
"itemsProcessed": 1,
"processingTime": 31,
"responseCode": "0",
"responseDescription": "Success",
"systemCd": "6",
"systemProducts": [ {
"systemProduct": "1234567
"distinctInventory": { "availableToPromiseQty":
37, "fulfilledQty": 11, "onHandQty": 235, "reservedQty":
187 },
"fulfillmentTypes": [
{ "fulfillmentType": "DELIVERY", "availableToPromiseQty":
37, "fulfilledQty": 11, "onHandQty": 235, "reservedQty": 187
}],
}
For more information: See Setup Requirements for the ACTPO Periodic Function, below, for setup requirements and troubleshooting information, and see the Inventory Availability Request JSON Message and the Inventory Availability Response JSON Message in the Order Orchestration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (2953017.1) for message details and troubleshooting.
Releasing Eligible Orders to Order Orchestration
Based on the updates made by the OCDSFA periodic function and the available to promise quantity for the order type returned in the inventory availability response, described above, the ACTPO periodic function performs the following steps.
Evaluates the active PO order lines based on date and order (fulfillment) type. The function determines which orders can be submitted to Order Orchestration for fulfillment for each order type:
-
The order lines are submitted in first-in, first-out order (oldest first).
-
Partial order line quantities are not submitted to Order Orchestration. If the next eligible line would exceed the quantity available to release, it is skipped.
-
The order submission uses the same steps and applies the same updates as the BROKER periodic function.
-
Orders in Error status or Suspended status are not eligible to be submitted.
-
Each order line for an active PO item is evaluated separately.
The Send Held Orders to OROB (M18) system control value controls whether the ACTPO periodic function includes held orders.
Example of orders released based on available to promise quantity, order type, order line quantity, and date:
There are 9 units on active PO order lines, in ascending (oldest to newest) order date:
-
Order 1: brokered backorder: 3 units
-
Order 2: ship-for-pickup: 5 units
-
Order 3: ship-for-pickup: 3 units
-
Order 4: brokered backorder: 2 units
-
Order 5: brokered backorder 1 unit
The available to promise quantity for the two fulfillment types returned in the response message indicates:
-
4 units available to promise in locations that support delivery orders (brokered backorders).
-
4 units available to promise in locations that support ship-for-pickup orders.
Note:
The distinct available to promise quantity (across all eligible locations) is actually 7 rather than 8, because one location has a single unit of the item, and supports both delivery orders and ship-for-pickup orders.The following orders are released to Order Orchestration:
-
Order 1: 3 units
-
Order 3: 3 units
-
Order 5: 1 unit
The remaining orders remain on backorder:
-
Order 2 remains on backorder because there are not enough units available in locations that support ship-for-pickup.
-
Order 4 remains on backorder because the full quantity of 2 is not available in any locations that support brokered backorders after allocating 3 units for order 1.
Item warehouse quantity updates: The function then:
-
Increases the Released qty for the item warehouse by the quantity of active PO order lines being released to Order Orchestration, but not to exceed the PO Receipts quantity.
-
Sets the item warehouse On-order quantity to the PO On Order quantity minus the Released qty. For example, if a total of 30 units are on purchase orders, and 12 units have been released to the Order Orchestration for fulfillment, the item warehouse On-order quantity is set to 18.
Is the item still an active PO item? The following updates take place if the PO On Order quantity is now less than or equal to the PO Receipts quantity, indicating that all anticipated units on purchase orders have been received. When this occurs, the item is no longer eligible for active PO processing, so that any additional units ordered are eligible to sell out.
Example: If the PO On Order quantity is 30, and the PO Receipts quantity is 25, the Active PO flag remains set to Y, because an additional 5 units can be received and used to fulfill orders. However, if the PO Receipts quantity is 30 or higher, the Active PO flag changes to N, because no additional receipts are expected.
If the item is no longer an active PO item, the periodic process:
-
Sets the Active PO flag for the item to N.
-
If a soldout control code is assigned to the item, sells out any remaining open lines beyond the PO On Order quantity in last-in, first-out order (sell out the newest first). If the entire line cannot be submitted to Order Orchestration, the entire line sells out.
Example: If the PO On Order quantity and the PO Receipts quantity are both 30, and there are active PO order lines for a total quantity of 35, the additional 5 units can sell out. Also, if the newest order line is for a quantity of 6, all 6 units on that line sell out, because order lines are not partially sold out.
-
If no soldout control code is assigned to the item, the remaining backordered lines are queued for submission to Order Orchestration. If Order Orchestration cannot find a location to fulfill a submitted order line, it closes the order line as unfulfillable.
-
Regardless of whether the remaining lines are sold out, sets the PO On Order quantity, PO Receipts quantity, Released qty, and Item Warehouse On-order quantity to 0.
Otherwise, if the item is still a an active PO item, the ACTPO function does not update the Active PO flag or sell out any units of the item. The item is eligible to be included in the inventory availability request the next time the ACTPO function runs.
Example: If the PO On Order quantity is 30, there are 29 units on active PO order lines, and the PO receipts quantity is 15, Order Administration can release up to 15 units to Order Orchestration for fulfillment. The remaining 14 units remain as active PO items in Order Administration.
Backorder quantity update notification? If the backorder quantity is not equal to the PO pre-order quantity sent, this means that the backorder quantity has changed, and that RMFCS needs to be notified. In this case, the periodic function submits the backorder quantity update notification message to notify RMFCS of any increase or decrease to the active PO backorder quantity. See Generating the Backorder Quantity Update Notification Message (PREORDER or ACTPO Periodic Function) for information on the backorder quantity update notification generated through the ACTPO periodic function.
Note:
The PO pre-order quantity sent is not displayed on any screen; it is just the current backorder quantity at the time the backorder quantity update notification is generated, and is used only to determine the quantity to send the next time the notification is generated.Setup Requirements for the ACTPO Periodic Function
In addition to the configuration described under Setup Requirements for the OCDSFA Periodic Function, the ACTPO periodic function requires the following:
-
Order Broker URL: From the OROB_INVENTORY_AVAILABILITY_URL.
-
Order Broker Authentication: Set up outbound OAuth authentication for OOCS Locate web service. See Setting Up Web Service Authentication for background.
-
SKU Limit for Inventory Availability Request: From the OROB_INVENTORY_AVAILABILITY_SKU_LIMIT. Defaults to 500, and should not be set higher.
-
Periodic function: Assign the ACTPO (Program name = PFR0205) to a periodic process.
Note:
The inventory availability web service request is supported only in Order Broker 20.2 or higher, or Order Orchestration.Additional Things to Note about the ACTPO Periodic Function
When to schedule:
-
This function should be run after the OCDSFA periodic function, described above under Importing Future Available Information (OCDSFA Periodic Function).
-
The BROKER_ORD job needs to be active while you are using the ACTPO function in order for the available to promise quantity returned in the inventory availability response to be accurate. As the BROKER_ORD job submits new orders to Order Orchestration, Order Orchestration updates the available quantities for the assigned locations. If the BROKER_ORD job is not active, there is an increased chance of the available to promise quantities returned in the inventory availability response being overstated.
Reviewing Active PO Status and Quantities
You can use the Display Item/Warehouse Information Screen in Using Inventory Inquiry (DINI) to review the following information:
-
Active PO flag: Selected if the item is currently a pre-order. The OCDSFA periodic function selects this flag, and the PREORDER or ACTPO periodic function clears it if the PO receipts quantity is greater than or equal to the PO on-order quantity.
-
PO on order quantity: The total quantity on purchase orders for an active PO item. From the RMS on-order quantity in the Item Warehouse table. The OCDSFA periodic function updates this quantity, and the PREORDER or ACTPO periodic function uses it in its calculations.
-
PO receipts quantity: The total quantity received on purchase orders for an active purchase order item. From the RMS receipt quantity in the Item Warehouse table. The OCDSFA and PREORDER periodic functions update this quantity to 0 when the purchase order is closed, and use this quantity it in their calculations.
-
Released qty: The total order quantity that has been released to Order Orchestration for fulfillment. The PREORDER or ACTPO periodic function update this field when they release the pre-orders lines to Order Orchestration.
-
PO updated: The last date when the OCDSFA, PREORDER, or ACTPO periodic function updated the Item Warehouse record.
-
On order: The total quantity of this item in this warehouse that is due to be received on open purchase orders. Equal to the PO on order quantity - the PO receipts quantity.
Note:
The PO pre-order quantity sent is also used for active PO calculations, but this quantity is not displayed on any screen; it is just the current backorder quantity at the time the backorder quantity update notification is generated, and is used only to determine the quantity to send the next time the backorder notification is generated.Troubleshooting: See Troubleshooting the Enterprise Order Integration for examples of log entries for the backorder quantity update notification.
Future Receipts and Active PO Order Processing Configuration
A summary of required configuration for enterprise future receipts and active PO processing includes:
System Control Values
Set the following system control values:
-
Included in Enterprise Integration Values (M41):
-
OCDS Future Available URL (M49): Used by the OCDSFA periodic function.
-
RICS Outbound Service URL (M50): Used by the PREORDER periodic function.
-
-
Use OROB for Fulfillment Assignment (M31) and Send B/O to OROB (K08) must be selected.
-
Order Broker Values (K15) and Order Broker Fulfillment Values must be set.
-
Default Warehouse (A04) must be set.
-
Default Soldout Control Code (D72) If you are using the PREORDER Periodic Function for (Order Broker Releases Earlier than 20.2), must be set to a soldout control code with a value of 2, indicating to include the on-order quantity when determining whether to sell out an item; otherwise, if you are using the ACTPO Periodic Function for (Order Broker 20.2 or Higher, or Order Orchestration), optional.
Periodic Functions
The periodic functions supporting enterprise order integration are:
-
OCDSFA (Program name = PFR0203). See Importing Future Available Information (OCDSFA Periodic Function) for background.
-
PREORDER (Program name = PFR0204). See PREORDER Periodic Function for (Order Broker Releases Earlier than 20.2) and Generating the Backorder Quantity Update Notification Message (PREORDER or ACTPO Periodic Function) for background.
-
ACTPO (Program name = PFR0205). See ACTPO Periodic Function for (Order Broker 20.2 or Higher, or Order Orchestration) and Generating the Backorder Quantity Update Notification Message (PREORDER or ACTPO Periodic Function) for background.
Scheduling: You can assign these periodic functions to a periodic process or to separate periodic processes; however, the OCDSFA function needs to run before the PREORDER function, and both functions need to run after the OCDSITM periodic function, described in Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS).
Note:
You should not run both the PREORDER and the ACTPO periodic functions.See Additional Things to Note about the ACTPO Periodic Function for additional notes on scheduling.
Web Service Authentication
-
RICS Service authentication for your company. Required for Generating the Backorder Quantity Update Notification Message (PREORDER or ACTPO Periodic Function).
-
OCDS Service authentication. Required for Importing Future Available Information (OCDSFA Periodic Function).
-
OACS Locate authentication. OAuth is supported. Required for ACTPO Periodic Function for (Order Broker 20.2 or Higher, or Order Orchestration).
For more information: See Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA) for background.
Properties
Use Working with Admin Properties (CPRP) to set up the following properties related to logging for the Pre-order (backorder quantity update) notification:
The following properties are used for the ACTPO periodic function:
Troubleshooting the Enterprise Order Integration
Order Orchestration product locations must be updated: If the PREORDER periodic function runs before Order Orchestration receives inventory updates through OCDS, then Order Administration might submit orders to Order Orchestration for fulfillment before Order Orchestration determines that it has the required inventory to fulfill the orders. In this situation, Order Orchestration returns the orders to Order Administration as unfulfillable.
Do not update items received from OCDS: If you use Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS) as well as Enterprise Order Integration (Future Receipts and Active PO/Pre-Order Processing), it is important not to update the items manually. For example, if the item’s retail reference number is set to the item code. It is important that you do not change the retail reference number to anything other than the item code, or the integration processes, including Generating the Backorder Quantity Update Notification Message (PREORDER or ACTPO Periodic Function), will fail.
Supported Order Orchestration order type: Although Order Administration supports releasing both brokered backorders and ship-for-pickup orders to Order Orchestration in active PO processing, not all fulfilling systems in Order Orchestration support the ship-for-pickup order type.
If the system does not support ship-for-pickup orders, the Ship For Pickup Sourcing Available and Ship For Pickup Receiving/Pickup Available flags should both be set to No at the Preferences screen in Order Orchestration for all of the system’s locations.
Store pickup orders for active PO items: Order Administration does not prevent you from submitting a store pickup order to Order Orchestration for an item currently flagged as an active PO item; however, the active PO functionality does not apply to store pickup orders.
Items must be flagged as OROB eligible: Only items flagged as OROB eligible are submitted to Order Orchestration.
Held orders? If the Send Held Orders to OROB (M18) system control value is selected, it is possible that the sequence in which orders are released to Order Orchestration changes if, for example, a held order does not have a valid authorization, so the next eligible order is released instead.
Enterprise Data Import History: The INT_OCDS_STATUS table tracks activity for both the OCDSFA periodic function and the OCDSITM Periodic Function. You can review this activity, including the FUTUREAVAILABLE records created by the OCDSFA periodic function, at the Enterprise Data Import History page in Modern View.
The OCDSITM periodic function purges records based on the OCDS_JOB_HISTORY_RETENTION_DAYS property; for example, if this property is set to 25 days, each time the OCDSITM function runs, it purges records older than 25 days.
See Additional Things to Note about the OCDSFA Periodic Function for more troubleshooting information.
OCDSFA activity logging: Various messages are written to the OCDS (Omnichannel Cloud Data Service) Log based on the future data import:
-
If the OCDS Future Available URL (M49) system control value is blank:
ERROR com.mr.interfaces.ocds.DataImportConfig - OCDS Import - Valid REST Service Endpoint not configured for SCV: M49. -
If the OCDS Future Available URL (M49) system control value specifies an invalid URL:
ERROR com.mr.interfaces.ocds.DataRetriever - Exception response code InboundJaxrsResponse{context=ClientResponse{method=GET, uri=https://SERVER.com:PORT/ords/ocds/omnichannel/v1/inventory/futurexyz?nodelevel=STORE&nodeid=2019&limit=1000, status=404, reason=Not Found}} from service call {} -
Additional log entries: Samples of additional possible log entries for OCDSFA include:
16:31:13,108 INFO com.mr.interfaces.ocds.impl.FutureAvailDataProcessor - Performing PreOrder quantity Calculation for SKU 12345616:31:13,109 INFO com.mr.interfaces.ocds.impl.FutureAvailDataProcessor - No change - onOrder Qty equals OnReceived Qty and preOrder is N for SKU 12345616:31:13,110 ERROR com.mr.interfaces.ocds.impl.FutureAvailDataProcessor - SKU 123456 does not exists in company 12314:55:18,887 INFO com.mr.interfaces.ocds.impl.FutureAvailDataProcessor - Performing sell out process for Order#1234
Support notification: The system generates a support notification if a submitted periodic function ends in error or goes into message status. See Order Administration Support Notifications for more information.
Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS)
Overview: Use the integration with Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS) to import information and create or update records, including items, item warehouses and locations, prices, and item images, that have been added to the OCDS database from Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS) and Oracle Retail Pricing Cloud Service (RPCS).
About OCDS: Oracle Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS) is a data hub, enabling Oracle Retail Merchandising and Pricing applications to share foundation data with Oracle Retail omnichannel applications through the use of RESTful web services.
OCDS contains the following components:
-
BDI Batch Job Admin: Enables in-bound data flow into OCDS using Oracle Bulk Data Integration (BDI) technology. Job Admin has a User Interface (UI) to support the management of BDI batch Jobs. Handles the initial load into OCDS.
-
RIB Injector: Enables inbound data flow into OCDS from the Oracle Retail Integration Bus (RIB).
-
ORDS: Enables outbound data flow from the OCDS database to omnichannel applications, such as Order Administration, Order Orchestration, and Oracle Retail Customer Engagement, and Xstore.
Enterprise order integration: You can use the data imported from OCDS to support enterprise order integration, including the use of purchase order information originating in RMFCS to control when orders can be fulfilled through submission to Order Orchestration. See Enterprise Order Integration (Future Receipts and Active PO/Pre-Order Processing) for more information.
In this topic:
- Additional Considerations for OCDS Integration
- Troubleshooting Information for OCDS
- Mapping Information into Order Administration
Data Flow from OCDS to Order Administration
If your company is configured for enterprise foundation data integration, processing takes place as follows:
1. When the OCDSITM Periodic Function runs, it uses the system control values listed below to generates a RESTful request for various types of information that is available in OCDS. This information was previously sent to OCDS by enterprise applications, including Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS) and Oracle Retail Pricing Cloud Service (RPCS).
-
Merchandise hierarchy: Requested if the OCDS Merchandise Hierarchy URL (M43) is specified. See Merchandise Hierarchy Import and Mapping for details.
-
Item information: Requested if the OCDS Item URL (M45) is specified. This information updates the item, SKU, item warehouse, and item location tables. See Item-Related Import and Mapping for details.
-
Item image information: Requested if the OCDS Item Image URL (M47) is specified. This information updates the item table. See Item Image Import and Mapping for details.
-
Item location attribute information: Requested if the OCDS Item Location Attributes URL (M46) is specified. This information updates the item and SKU tables. See Item Location Attributes Import and Mapping for details.
-
Pricing information: Requested if the OCDS Initial Item Price URL (M48) is specified. This information updates the item offer and item price tables. See Item Price Import and Mapping for details.
Note:
You need to run the full import before attempting an incremental import. See the OCDSITM Periodic Function for background.GZIP compression: The generated request message indicates that gzip encoding is accepted, and OCDS sends the data in GZIP compression format.
2. The OCDSITM periodic function uses the data in the response messages from OCDS to create or update records in the target tables, as mentioned above. It creates a record if it does not exist; otherwise, it updates the record. However, some fields are never updated for existing records. See Mapping Information into Order Administration for details.
Note:
The periodic function does not delete records. If OCDS passes a delete request, it is ignored.Logging and import history: See Troubleshooting Information for OCDS for a discussion.
Configuration for OCDS Integration
The configuration required in Order Administration to support importing information through OCDS is described below.
System Control Values
The following system control values must be selected:
-
Important:
See Retail Integration (External System into Order Administration) Overview and Setup for background on the additional setup required to support retail item integration. If you do not complete this setup, the import will not be successful.
The following system control values must be unselected:
Enterprise Integration Values: Use the Enterprise Integration Values (M41) screen to define additional values required for integration with OCDS, including URLs and default values for mapping.
Supporting values: Several of these system control values require additional setup of supporting values. For example, you need to configure warehouse and location records in order to specify the defaults to use for the integration. See each system control value for more information.
When you run the import, each type of data is imported only if the related URL is specified at this screen. For example, merchandise hierarchy information is imported only if the OCDS Merchandise Hierarchy URL (M43) system control value specifies a valid URL. See that screen for more information.
Properties
Use the OCDS_JOB_HISTORY_RETENTION_DAYS property to control the number of days to retain records in Enterprise Data Imports History (the INT_OCDS_STATUS table) before thee OCDSITM periodic function automatically deletes them.
Web Service Authentication
Use the Work with Outbound Web Service Authentication Screen to set up authentication for the OCDS Service.
Since the OCDS Service uses basic authentication, only the initial item price is requested.
OCDSITM Periodic Function
Use Working with Periodic Functions (WPER) to set up the periodic function. When setting up the function:
-
Set the Program name to PFR0202.
-
Set the Parameter to:
-
FULL or leave it blank to perform a full load of each type of item-related data.
-
INCREMENTAL to perform a load of new or changed information since the last time you imported data for the company.
-
INCREMENTAL plus a date and time to perform a load of new or changed information since the specified date and time, based on the OCDS server’s local date and time. The date format is based on the locale of the user who configures the periodic function. If the user’s Date Format is set to:
-
DDMMYY, format as INCREMENTAL 31/12/2020 23:59
-
MMDDYY, format as INCREMENTAL 12/31/2020 23:59
-
YYMMDD, format as INCREMENTAL 2020/12/31 23:59
Note:
You need to perform a full load for a company before you can perform an incremental load. -
-
-
Select the Company Parameter flag.
Creation and update only: The periodic function creates new records and updates existing records. It does not delete records.
Periodic Process
Use Working with Periodic Processes (WPPR) to assign the periodic function described above to a periodic process. The Company parameter is required to indicate the company where the records should be created or updated.
Additional Considerations for OCDS Integration
Does not support SKUs: Since RMFCS does not support SKU’s, all items imported from RMFCS are non-SKU’d items.
Using RMFCS Item Level and Tran Level to determine whether to create or update an item: RMFCS uses a different hierarchy than Order Administration for multi-level items. The RMFCS hierarchy supports:
-
A level 1 item: For example, a picture frame that comes in only one finish and size.
-
A level 2 item: For example, an item group that includes a novelty tee shirt in sizes small, medium, and large. Level 1 is the tee shirt, while level 2 includes the sizes.
-
A level 3 item: For example, an item group that includes a polo shirt in red, blue, and yellow, and sizes small, medium, and large. Level 1 is the polo shirt, level 2 is the sizes, and level 3 is the colors.
The records in the itemhdr file that map
to items in Order Administration are identifiable by the fact
that the ItemLevel passed in the file is the same as the TranLevel.
If the ItemLevel and the TranLevel are different, the record is not
used to update the item record in Order Administration.
Troubleshooting Information for OCDS
If the OCDS process ends without successfully importing data, possible explanations include:
-
You submitted an incremental import without first submitting a full import. See OCDSITM Periodic Function for more information.
-
The web service authentication failed. Check that the OCDS Service web service user and password set up through the Work with Outbound Web Service Authentication Screen matches a valid OCDS user.
Enterprise Data Import History: Activity for the OCDSITM periodic function, as well as the OCDSFA periodic function, is also recorded in the INT_OCDS_STATUS table. You can review this data at the Enterprise Data Import History page in Modern View. The periodic function writes a record in this table each time:
-
The import for a feed type begins. The periodic function attempts each import feed type of the system control value defining the feed’s URL is populated. Possible import feed types are:
-
MERCHHEIR: Merchandise hierarchy. See Merchandise Hierarchy Import and Mapping.
-
ITEMSKU: Item and SKU information. See Item-Related Import and Mapping.
-
ITEMIMAGE: Item image information. See Item Image Import and Mapping.
-
ITEMLOCATION: Additional item and SKU information defined in the OCDS ITEM_LOC table. See Item Location Attributes Import and Mapping.
-
-
Item price: Item offer and price information.See Item Price Import and Mapping. The feed requests different price types separately, as follows:
-
ITEMPRICEINI: The initial item price.
-
ITEMPRICEREG: The regular item price.
-
ITEMPRICECLR: The clearance price.
The OCDSFA periodic function creates FUTUREAVAILABLE records.
-
-
The result of each attempted import feed, including:
-
Execution time: The total number of seconds that elapsed while executing the feed.
-
Total rows count: The total number of records that met the selection criteria for the import feed.
-
Updated rows count: The total number of existing records that were updated through the import feed.
Note:
The updated row count might not match the actual number of records changed. -
Inserted rows count: The total number of new records that were created through the import feed.
-
The OCDSITM periodic function clears all outdated Enterprise Data Import History records based on the number of days specified in the OCDS_JOB_HISTORY_RETENTION_DAYS property.
-
When it purges records, it writes an entry in the OCDS (Omnichannel Cloud Data Service) Log:
Purged successfully. -
When there are no eligible records to purge, it writes a log entry:
No Records Available to Purge.
Mapping Information into Order Administration
Mapping details are provided below:
Merchandise Hierarchy Import and Mapping
About merchandise hierarchy: Merchandise hierarchy information in OCDS originates in RMFCS. If the OCDS Merchandise Hierarchy URL (M43) specifies a valid URL, the OCDSITM Periodic Function imports the item hierarchy information. The information that maps to Order Administration through the item hierarchy import is described in the following table.
Note:
The import process creates or updates records. It does not delete item hierarchy records that already exist.| RMFCS Hierarchy Level | Order Administration Hierarchy Level | Menu Option |
|---|---|---|
|
Division |
Not imported |
N/A |
|
Group |
Long SKU Division |
|
|
Department |
Long SKU Department |
|
|
Class |
Retail Class |
|
|
Subclass |
Not imported as part of item hierarchy. Note: The subclass is included in the item import; see Item-Related Import and Mapping. |
N/A |
Mapping: The item hierarchy information is mapped as follows:
| Target Field | Attributes | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
The code identifying the company selected when running the OCDSITM Periodic Function. |
This company code applies to each of the mapped records. |
|
Long SKU Division records |
See Creating and Maintaining Long SKU Divisions (WLDV). Long SKU division records are created where OCDS
passes a |
||
|
Long SKU Division |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
From the NodeID identifying the group. |
If the long SKU division already exists, the description is updated. Note: Although the long SKU division code is alphanumeric in Order Administration, the division code created through the import is always numeric. |
|
Long SKU Division Description |
Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
From the nodename describing the group. |
If no nodename is passed, the description is automatically set
to If the nodename exceeds 30 positions, it is truncated. The nodename is converted to all uppercase. |
|
Long SKU Department records |
See Working with Long SKU Departments (WLSD). Long SKU department records are created where OCDS passes
a hierarchylevel of |
||
|
Long SKU Department |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
From the NodeID identifying the department. |
If the long SKU department already exists, the description is updated. |
|
Long SKU Department Description |
Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
From the nodename describing the department. |
If no nodename is passed, the description is automatically set
to If the nodename exceeds 30 positions, it is truncated. The nodename is converted to all uppercase. |
|
Retail Class |
Use Working with Long SKU Departments (WLSD) to review retail classes that are assigned to long SKU departments. Retail class records are created where OCDS passes a hierarchylevel of |
||
|
Retail Class |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
From the NodeID identifying the class. |
If the retail class already exists, the description is updated. |
|
Retail Class Description |
Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
From the nodename describing the class. |
If no nodename is passed, the description is automatically set
to If the nodename exceeds 30 positions, it is truncated. The nodename is converted to all uppercase. |
|
Long SKU Department |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
From the parentnodeid identifying the long SKU department. |
Identifies the long SKU department to be assigned the retail class. |
Item-Related Import and Mapping
About item, SKU, item warehouse, and item location mapping: Item information in OCDS originates in RMFCS, and additional information in Order Administration, such as SKU, item warehouse, and item location records, is built during the import process using predefined defaults. If the OCDS Item URL (M45) specifies a valid URL, the OCDSITM Periodic Function imports the item information and creates the related records. The information that maps to Order Administration through the item import is described in the following table.
You need to run a full import of the periodic function before you can run an incremental import.
Additional item and SKU information: The ITEMLOCATION feed imports additional item and SKU information that is defined in the ITEM_LOC table in OCDS. See Item Location Attributes Import and Mapping for more information.
Note:
About unmapped fields: Any item, SKU, item warehouse, and item location fields in Order Administration that are not listed below are not mapped through the OCDSITM Periodic Function. Y/N fields are set to N; otherwise, fields are left blank if alphanumeric, or set to 0 if numeric. Also, these fields are not updated after initial record creation.Note:
The import process creates or updates records. It does not delete records that already exist.| Target Field | Value Used | Description/ Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
The code identifying the company selected when running the OCDSITM Periodic Function. |
Note: This company code applies to each of the mapped records. See Item Mapping and Defaults, SKU Mapping and Defaults, Item Warehouse Mapping and Defaults, and Item Location Mapping and Defaults.Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Item Mapping and Defaults |
|||
|
Item |
Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
Item passed. |
Rather than using the item and SKU fields in the same way as Order Administration, RMFCS uses a hierarchical system to identify the relationships between individual items. An item code in the import table creates or updates an item in Order Administration only if the item’s ItemLevel and TranLevel in RMFCS are the same. See Additional Considerations for OCDS Integration for a discussion. Applies to SKU, item warehouse, and item location records. See SKU Mapping and Defaults, Item Warehouse Mapping and Defaults, and Item Location Mapping and Defaults. Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Allow SKUs |
N/A |
Set to N. |
Only non-SKU’d items are created. See Additional Considerations for OCDS Integration for a discussion. |
|
Non-Inventory |
Y/N |
Based on Inventoryind. |
RMFCS uses an Inventoryind of Y to identify an inventoried item, while Order Administration uses a Non-Inventory setting of Y to identify a non-inventoried item. As a result, the Non-Inventory flag is set to N when the Inventoryind flag passed is set to Y, and vice versa. |
|
Ship Alone |
Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
ShipAloneInd passed. |
Set to S if the ShipAloneInd is set to Y; otherwise, blank. |
|
Description |
Alphanumeric, 120 positions. |
Description passed. |
Truncated if it exceeds the maximum field length in Order Administration. |
|
Create Date |
Date |
Date when record is first created. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Last Change Date |
Date |
Most recent create or change date in Order Administration. |
|
|
Retail Style # |
Alphanumeric, 20 positions. |
Item or ItemParent passed. |
If no ItemParent is passed, then set to the Item. |
|
Class (Long SKU Class) |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
Class passed. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. Valid? If the import passes a long SKU class code that has not been set up through Working with Long SKU Classes (WLSC), it is still written to the item record; however, the Change Item screen displays an error. See Performing Initial Item Entry (MITM) for background. |
|
Department (Long SKU Department) |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
Dept passed. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. Valid? If the import passes a long SKU department code that has not been set up through Working with Long SKU Departments (WLSD), it is still written to the item record; however, the Change Item screen displays an error. See Performing Initial Item Entry (MITM) for background. |
|
Long SKU Style |
Alphanumeric, 20 positions. |
ItemParent passed, of any; otherwise, Item passed. |
|
|
Whs (Warehouse) |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
From the Default Warehouse (A04); otherwise, set to 0. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
UOM (Unit of Measure) |
Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration, except through Item Location Attributes Import and Mapping. |
|
|
Updated by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration. |
|
|
Created by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
OROB Eligible |
Y/N |
Y |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Retail Subclass |
Alphanumeric, 4 positions. |
Subclass passed. |
|
|
SKU Mapping and Defaults |
A single SKU record is created for each item record with the same company and item code. |
||
|
Collating Sequence # |
Numeric, 5 positions. |
1 |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Retail Reference # |
Numeric, 15 positions. |
Item passed. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. Note: The retail reference number needs to match the item code, so you should not change it after the SKU record is created. |
|
Short SKU |
Numeric, 7 positions. |
Unique number assigned by Order Administration. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Last Change Date |
Date |
Most recent create or change date in Order Administration. |
|
|
Create Date |
Date |
Date when record is first created. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Whs (Warehouse) |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
From the Default Warehouse (A04); otherwise, set to 0. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Location |
Alphanumeric, 7 positions. |
From the OMS Default Primary Location (M51); otherwise, blank. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Soldout Control Code |
Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
Defaults from the Default Soldout Control Code (D72). |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Updated by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration. |
|
|
Created by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Item Warehouse Mapping and Defaults |
An item warehouse record is created for each item record with the same company, item code, and SKU. |
||
|
Whs (Warehouse) |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
From the Default Warehouse (A04); otherwise, set to 0. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Item Location Mapping and Defaults |
An item location record is created for each item record with the same company, item code, SKU, and warehouse if the OMS Default Primary Location (M51) system control value specifies a value; otherwise, the record is not created. Certain fields, such as the Type, default from the OMS Default Primary Location (M51). |
||
|
Whs (Warehouse) |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
From the Default Warehouse (A04); otherwise, set to 0. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Location |
Alphanumeric, 7 positions. |
From the OMS Default Primary Location (M51). |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
Item Image Import and Mapping
Item image import: Item image URL information in OCDS originates in RMFCS. If the OCDS Item Image URL (M47) system control value specifies a valid URL and the item has been imported from OCDS, the OCDSITM Periodic Function imports the links to item images from OCDS and updates the corresponding field in the item table. The import takes place regardless of the setting of the Use External Item Image (L55) system control value.
The import process updates the item’s image link only when the response from OCDS indicates that it is flagged as the primary.
-
Company: The code identifying the company selected when running the OCDSITM Periodic Function.
-
Item: The code identifying an item in the OCDS database. If the item does not exist in the specified company in Order Administration, no update takes place.
-
Image link: The image link for the item. See the Item Image/Info Link Screen for more information.
Note:
The import process does not delete item image links that already exist.Item Location Attributes Import and Mapping
Purpose: The item location attributes import through the OCDSITM Periodic Function actually updates certain fields in existing Item and SKU records based on the information in the ITEM_LOC table in OCDS; it does not create or update item location records. These updates take place only if the OCDS Item Location Attributes URL (M46) specifies a valid URL. The information in the Item and SKU tables that the function updates in Order Administration is described in the following table:
-
Item Fields Updated through the Item Location Attributes Import
-
SKU Fields Updated through the Item Location Attributes Import
Identifying the items to update: The OCDSITM Periodic Function uses the OCDS RMS Location Identifier (M52) system control value to determine which records to update with item location attributes. Only OCDS ITEM_LOC records with a LOCATION that matches the system control value are used to update the Order Administration item and SKU records.
How are item locations updated? The OCDSITM Periodic Function creates and updates item location records through the Item and SKU import. See Item-Related Import and Mapping, including Item Location Mapping and Defaults, above, for more information.
Important:
About unmapped fields: Any item, SKU, item warehouse, and item location fields in Order Administration that are not listed below are not mapped through the OCDSITM Periodic Function. Y/N fields are set to N; otherwise, fields are left blank if alphanumeric, or set to 0 if numeric. Also, these fields are not updated after initial record creation.Note:
The import process updates existing item and SKU records. It does not delete records that already exist.| Target Field | Attributes | Value Used | Description/ Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
The code identifying the company selected when running the OCDSITM Periodic Function. |
The company code used to identify the item and SKU records to update. |
|
Item |
Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
Item passed |
The item code used to identify the item and SKU records to update. |
|
Item Fields Updated through the Item Location Attributes Import |
|||
|
Item Status |
Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
The status passed. |
A code that represents an item's status, such as obsolete, discontinued, etc. This information is used for inventory reporting purposes; also, items that are assigned the Item Status for Suppressing Item During Item Selection (L21) at the item level are not listed at the Item Selection screen. Valid? If the import passes a status code that has not been set up through Working with Item Status (WIST), it is still written to the item record; however, the Change Item screen displays an error. See Performing Initial Item Entry (MITM) for background. |
|
Unit of Measure |
Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
The sellinguom passed. |
A standard by which an item/SKU is sold. Typical units of measure include:
Also updates the SKU record; see below. Valid? If the import passes a unit of measure code that has not been set up through Working with Units of Measure (WUOM), it is still written to the item record; however, the Change Item screen displays an error. See Performing Initial Item Entry (MITM) for background. |
|
Updated by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration |
|
|
Last Change Date |
Date |
Most recent create or change date in Order Administration. |
|
|
SKU Fields Updated through the Item Location Attributes Import |
|||
|
Restrict |
Y/N |
From the stopsaleind passed. |
Indicates whether this item can be ordered.
Any existing orders before the item becomes restricted are processed normally. |
|
Unit of Measure |
Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
The sellinguom passed. |
A standard by which an item/SKU is sold. Typical units of measure include:
Also updates the item record; see above. Valid? If the import passes a unit of measure code that has not been set up through Working with Units of Measure (WUOM), it is still written to the item record; however, the Change Item screen displays an error. See Performing Initial Item Entry (MITM) for background. |
|
Updated by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration |
|
|
Last Change Date |
Date |
Most recent create or change date in Order Administration. |
Item Price Import and Mapping
Identifying the items to update: The OCDSITM Periodic Function uses:
-
The OCDS RMS Location Identifier (M52) system control value to determine which items are eligible to have item offer and item price records created or updated. Only OCDS ITEM_LOC records with a LOCATION that matches the system control value are used to update the Order Administration item offer and item price records.
-
The retail reference number in Order Administration, which needs to match the Item passed from OCDS. Ordinarily, the retail reference number and the item code in Order Administration are the same, as the periodic function sets them both to the same Item code.
Default offer: The periodic function creates item offer and item price records using the Current Offer (A33) system control value. This system control value must be set to a valid, current offer in order to create the item offer and item price records correctly.
Important:
About unmapped fields: Any item offer or item price fields in Order Administration that are not listed below are not mapped through the OCDSITM Periodic Function. They are set to N if a Y/N value; otherwise, they are left blank if alphanumeric, or set to 0 if numeric. Also, these fields are not updated after initial record creation.Note:
The import process updates existing item offer and item price records. It does not delete records that already exist.| Target Field | Properties | Value Used | Description/ Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
The code identifying the company selected when running the OCDSITM Periodic Function. |
The company code used to identify the item and SKU records to update. |
|
Item |
Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
Item passed |
The item code used to identify the record to update. Matched based on retail reference number: The periodic function uses the retail reference number for the item to determine whether the item matches a record received from OCDS. The function sets the retail reference number to the same value as the item code, so ordinarily they are the same. The periodic function creates item offer and item price records only for items that exist in OCDS and have been imported into Order Administration. Also, the item price is updated only if the retail reference number is numeric, because a non-numeric reference number indicates that the item is not sellable. |
|
Item Offer Field Updated through the Price Import |
Any additional item offer fields in Order Administration besides the item and offer are not mapped through the OCDSITM Periodic Function. They are set to N if a Y/N value; otherwise, they are left blank if alphanumeric, or set to 0 if numeric. Also, these fields are not updated after initial record creation. |
||
|
Offer |
Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
From the Current Offer (A33). |
Valid? If the system control value is not set to a valid offer, the item offer and item price records are not created correctly. |
|
Item Price Fields Updated through the Price Import |
In addition to the company, item, and offer, described above, the following Item Price fields are created as follows. If the periodic function retrieves updated price information for an item with a different effective date, a new item price record is created. |
||
|
Effective Date |
Date |
From the effective date passed. |
If no effective date is passed, the date is set to January 1 2000. Ordinarily, an effective date is passed only when there was an item price change recorded in OCDS. In that case, there are records in the CLEARANCE and PRICE_CHANGE tables. |
|
Quantity |
Numeric, 7 positions. |
Set to 1. |
|
|
Price |
Numeric, 13 positions with a 2-place decimal. |
From the price passed. |
If multiple prices are passed with the same effective date, the last price passed is used. If the price passed is not greater than zero, it is ignored. The item price record is not created or updated. |
Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services
Overview: Use the integration with Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services to import information and create or update records, including items, item warehouses and locations, prices, and item images, that are in Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS) and Oracle Retail Pricing Cloud Service (RPCS).
Enterprise order integration: You can use the data imported to support enterprise order integration, including the use of purchase order information originating in RMFCS to control when orders can be fulfilled through submission to Order Orchestration. See Enterprise Order Integration (Future Receipts and Active PO/Pre-Order Processing) for more information.
Data Flow from Merchandising Cloud Services to Order Administration
If your company is configured for enterprise foundation data integration, processing takes place as follows:
-
When the OCDSITM Periodic Function runs, it uses the system control values listed below to generates a RESTful request for various types of information from Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS) and Oracle Retail Pricing Cloud Service (RPCS).
-
Merchandise hierarchy: Requested if the OCDS Merchandise Hierarchy URL (M43) is specified. See Merchandise Hierarchy Import and Mapping for details.
-
Item information: Requested if the OCDS Item URL (M45) is specified. This information updates the item, SKU, item warehouse, and item location tables. See Item-Related Import and Mapping for details.
-
Item image information: Requested if the OCDS Item Image URL (M47) is specified. This information updates the item table. See Item Image Import and Mapping for details.
-
Item location attribute information: Requested if the OCDS Item Location Attributes URL (M46) is specified. This information updates the item and SKU tables. See Item Location Attributes Import and Mapping for details.
-
Pricing information: Requested if the OCDS Initial Item Price URL (M48) is specified. OCDS Regular Item Price URL (M68) and OCDS Clearance Item Price URL (M69) are used instead if the OCDS Service is set to OAuth. This information updates the item offer and item price tables. See Item Price Import and Mapping for details.
Note:
You need to run the full import before attempting an incremental import. See the OCDSITM Periodic Function for background. -
-
The OCDSITM periodic function uses the data in the response messages to create or update records in the target tables, as mentioned above. It creates a record if it does not exist; otherwise, it updates the record. However, some fields are never updated for existing records. See Mapping Information into Order Administration for details.
Logging and import history: See Troubleshooting Information for Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services for a discussion.
Configuration for Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services Integration
The configuration required in Order Administration to support importing information through Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services is described below.
System Control Values
The following system control values must be selected:
-
Important:
See Retail Integration (External System into Order Administration) Overview and Setup for background on the additional setup required to support retail item integration. If you do not complete this setup, the import will not be successful.
The following system control values must be unselected:
Enterprise Integration Values: Use the Enterprise Integration Values (M41) screen to define additional values required for integration with Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services, including URLs and default values for mapping.
Supporting values: Several of these system control values require additional setup of supporting values. For example, you need to configure warehouse and location records in order to specify the defaults to use for the integration. See each system control value for more information.
When you run the import, each type of data is imported only if the related URL is specified at this screen. For example, merchandise hierarchy information is imported only if the OCDS Merchandise Hierarchy URL (M43) system control value specifies a valid URL. See that screen for more information.
Properties
Use the OCDS_JOB_HISTORY_RETENTION_DAYS property to control the number of days to retain records in Enterprise Data Imports History (the INT_OCDS_STATUS table) before thee OCDSITM periodic function automatically deletes them.
Web Service Authentication
Use the Work with Outbound Web Service Authentication Screen to set up authentication for the Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services.
Since the Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services are configured to use OAuth for authentication, the OCDSITM periodic function requests not only the initial item price, but also the regular item price and the clearance item price, using the URLs specified in the related system control values at the Enterprise Integration Values (M41) screen.
OCDSITM Periodic Function
Use Working with Periodic Functions (WPER) to set up the periodic function. When setting up the function:
-
Set the Program name to PFR0202.
-
Set the Parameter to:
-
FULL or leave it blank to perform a full load of each type of item-related data.
-
INCREMENTAL to perform a load of new or changed information since the last time you imported data for the company.
-
INCREMENTAL plus a date and time to perform a load of new or changed information since the specified date and time, based on the Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services server’s local date and time. The date format is based on the locale of the user who configures the periodic function. If the user’s Date Format is set to:
-
DDMMYY, format as INCREMENTAL 31/12/2020 23:59
-
MMDDYY, format as INCREMENTAL 12/31/2020 23:59
-
YYMMDD, format as INCREMENTAL 2020/12/31 23:59
Note:
You need to perform a full load for a company before you can perform an incremental load. -
-
-
Select the Company Parameter flag.
Creation and update only: The periodic function creates new records and updates existing records. It does not delete records.
Periodic Process
Use Working with Periodic Processes (WPPR) to assign the periodic function described above to a periodic process. The Company parameter is required to indicate the company where the records should be created or updated.
Additional Considerations for Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services Integration
Does not support SKUs: Since RMFCS does not support SKU’s, all items imported from RMFCS are non-SKU’d items.
Using RMFCS Item Level and Tran Level to determine whether to create or update an item: RMFCS uses a different hierarchy than Order Administration for multi-level items. The RMFCS hierarchy supports:
-
A level 1 item: For example, a picture frame that comes in only one finish and size.
-
A level 2 item: For example, an item group that includes a novelty tee shirt in sizes small, medium, and large. Level 1 is the tee shirt, while level 2 includes the sizes.
-
A level 3 item: For example, an item group that includes a polo shirt in red, blue, and yellow, and sizes small, medium, and large. Level 1 is the polo shirt, level 2 is the sizes, and level 3 is the colors.
The records in the itemhdr file that map
to items in Order Administration are identifiable by the fact
that the ItemLevel passed in the file is the same as the TranLevel.
If the ItemLevel and the TranLevel are different, the record is not
used to update the item record in Order Administration.
Troubleshooting Information for Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services
If the Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services process ends without successfully importing data, possible explanations include:
-
You submitted an incremental import without first submitting a full import. See OCDSITM Periodic Function for more information.
-
The web service authentication failed. Check that the Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services user and password set up through the Work with Outbound Web Service Authentication Screen matches a valid Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services user.
Enterprise Data Import History: Activity for the OCDSITM periodic function, as well as the OCDSFA periodic function, is also recorded in the INT_OCDS_STATUS table. You can review this data at the Enterprise Data Import History page in Modern View. The periodic function writes a record in this table each time:
-
The import for a feed type begins. The periodic function attempts each import feed type of the system control value defining the feed’s URL is populated. Possible import feed types are:
-
MERCHHEIR: Merchandise hierarchy. See Merchandise Hierarchy Import and Mapping.
-
ITEMSKU: Item and SKU information. See Item-Related Import and Mapping.
-
ITEMIMAGE: Item image information. See Item Image Import and Mapping.
-
ITEMLOCATION: Additional item and SKU information defined in the Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services ITEM_LOC table. See Item Location Attributes Import and Mapping.
-
-
Item price: Item offer and price information. See Item Price Import and Mapping. The feed requests different price types separately, as follows:
-
ITEMPRICEINI: The initial item price.
-
ITEMPRICEREG: The regular item price.
-
ITEMPRICECLR: The clearance price.
The OCDSFA periodic function creates FUTUREAVAILABLE records.
-
-
The result of each attempted import feed, including:
-
Execution time: The total number of seconds that elapsed while executing the feed.
-
Total rows count: The total number of records that met the selection criteria for the import feed.
-
Updated rows count: The total number of existing records that were updated through the import feed.
Note:
The updated row count might not match the actual number of records changed. -
Inserted rows count: The total number of new records that were created through the import feed.
-
The OCDSITM periodic function clears all outdated Enterprise Data Import History records based on the number of days specified in the OCDS_JOB_HISTORY_RETENTION_DAYS property.
-
When it purges records, it writes an entry in the OCDS (Omnichannel Cloud Data Service) Log:
Purged successfully. -
When there are no eligible records to purge, it writes a log entry:
No Records Available to Purge.
Mapping Information into Order Administration
Mapping details are provided below:
Merchandise Hierarchy Import and Mapping
About merchandise hierarchy: If the OCDS Merchandise Hierarchy URL (M43) specifies a valid URL, the OCDSITM Periodic Function imports the item hierarchy information. The information that maps to Order Administration through the item hierarchy import is described in the following table.
Note:
The import process creates or updates records. It does not delete item hierarchy records that already exist.| RMFCS Hierarchy Level | Order Administration Hierarchy Level | Menu Option |
|---|---|---|
|
Division |
Not imported |
N/A |
|
Group |
Long SKU Division |
|
|
Department |
Long SKU Department |
|
|
Class |
Retail Class |
|
|
Subclass |
Not imported as part of item hierarchy. Note: The subclass is included in the item import; see Item-Related Import and Mapping. |
N/A |
Mapping: The item hierarchy information is mapped as follows:
| Target Field | Attributes | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
The code identifying the company selected when running the OCDSITM Periodic Function. |
This company code applies to each of the mapped records. |
|
Long SKU Division records |
See Creating and Maintaining Long SKU Divisions (WLDV). Long SKU division records are created where RMFCS
passes a |
||
|
Long SKU Division |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
From the NodeID identifying the group. |
If the long SKU division already exists, the description is updated. Note: Although the long SKU division code is alphanumeric in Order Administration, the division code created through the import is always numeric. |
|
Long SKU Division Description |
Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
From the nodename describing the group. |
If no nodename is passed, the description is automatically set
to If the nodename exceeds 30 positions, it is truncated. The nodename is converted to all uppercase. |
|
Long SKU Department records |
See Working with Long SKU Departments (WLSD). Long SKU department records are created where RMFCS passes
a hierarchylevel of |
||
|
Long SKU Department |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
From the NodeID identifying the department. |
If the long SKU department already exists, the description is updated. |
|
Long SKU Department Description |
Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
From the nodename describing the department. |
If no nodename is passed, the description is automatically set
to If the nodename exceeds 30 positions, it is truncated. The nodename is converted to all uppercase. |
|
Retail Class |
Use Working with Long SKU Departments (WLSD) to review retail classes that are assigned to long SKU departments. Retail class records are created where RMFCS passes a hierarchylevel of |
||
|
Retail Class |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
From the NodeID identifying the class. |
If the retail class already exists, the description is updated. |
|
Retail Class Description |
Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
From the nodename describing the class. |
If no nodename is passed, the description is automatically set
to If the nodename exceeds 30 positions, it is truncated. The nodename is converted to all uppercase. |
|
Long SKU Department |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
From the parentnodeid identifying the long SKU department. |
Identifies the long SKU department to be assigned the retail class. |
Item-Related Import and Mapping
About item, SKU, item warehouse, and item location mapping: Item information in Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services originates in RMFCS, and additional information in Order Administration, such as SKU, item warehouse, and item location records, is built during the import process using predefined defaults. If the OCDS Item URL (M45) specifies a valid URL, the OCDSITM Periodic Function imports the item information and creates the related records. The information that maps to Order Administration through the item import is described in the following table.
You need to run a full import of the periodic function before you can run an incremental import.
Additional item and SKU information: The ITEMLOCATION feed imports additional item and SKU information that is defined in the ITEM_LOC table in Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services. See Item Location Attributes Import and Mapping for more information.
Note:
About unmapped fields: Any item, SKU, item warehouse, and item location fields in Order Administration that are not listed below are not mapped through the OCDSITM Periodic Function. Y/N fields are set to N; otherwise, fields are left blank if alphanumeric, or set to 0 if numeric. Also, these fields are not updated after initial record creation.Note:
The import process creates or updates records. It does not delete records that already exist.| Target Field | Value Used | Description/ Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
The code identifying the company selected when running the OCDSITM Periodic Function. |
Note: This company code applies to each of the mapped records. See Item Mapping and Defaults, SKU Mapping and Defaults, Item Warehouse Mapping and Defaults, and Item Location Mapping and Defaults.Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Item Mapping and Defaults |
|||
|
Item |
Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
Item passed. |
Rather than using the item and SKU fields in the same way as Order Administration, RMFCS uses a hierarchical system to identify the relationships between individual items. An item code in the import table creates or updates an item in Order Administration only if the item’s ItemLevel and TranLevel in RMFCS are the same. See Additional Considerations for Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services Integration for a discussion. Applies to SKU, item warehouse, and item location records. See SKU Mapping and Defaults, Item Warehouse Mapping and Defaults, and Item Location Mapping and Defaults. Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Allow SKUs |
N/A |
Set to N. |
Only non-SKU’d items are created. See Additional Considerations for Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services Integration for a discussion. |
|
Non-Inventory |
Y/N |
Based on Inventoryind. |
RMFCS uses an Inventoryind of Y to identify an inventoried item, while Order Administration uses a Non-Inventory setting of Y to identify a non-inventoried item. As a result, the Non-Inventory flag is set to N when the Inventoryind flag passed is set to Y, and vice versa. |
|
Ship Alone |
Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
ShipAloneInd passed. |
Set to S if the ShipAloneInd is set to Y; otherwise, blank. |
|
Description |
Alphanumeric, 120 positions. |
Description passed. |
Truncated if it exceeds the maximum field length in Order Administration. |
|
Create Date |
Date |
Date when record is first created. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Last Change Date |
Date |
Most recent create or change date in Order Administration. |
|
|
Retail Style # |
Alphanumeric, 20 positions. |
Item or ItemParent passed. |
If no ItemParent is passed, then set to the Item. |
|
Class (Long SKU Class) |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
Class passed. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. Valid? If the import passes a long SKU class code that has not been set up through Working with Long SKU Classes (WLSC), it is still written to the item record; however, the Change Item screen displays an error. See Performing Initial Item Entry (MITM) for background. |
|
Department (Long SKU Department) |
Numeric, 4 positions. |
Dept passed. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. Valid? If the import passes a long SKU department code that has not been set up through Working with Long SKU Departments (WLSD), it is still written to the item record; however, the Change Item screen displays an error. See Performing Initial Item Entry (MITM) for background. |
|
Long SKU Style |
Alphanumeric, 20 positions. |
ItemParent passed, of any; otherwise, Item passed. |
|
|
Whs (Warehouse) |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
From the Default Warehouse (A04); otherwise, set to 0. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
UOM (Unit of Measure) |
Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration, except through Item Location Attributes Import and Mapping. |
|
|
Updated by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration. |
|
|
Created by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
OROB Eligible |
Y/N |
Y |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Retail Subclass |
Alphanumeric, 4 positions. |
Subclass passed. |
|
|
SKU Mapping and Defaults |
A single SKU record is created for each item record with the same company and item code. |
||
|
Collating Sequence # |
Numeric, 5 positions. |
1 |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Retail Reference # |
Numeric, 15 positions. |
Item passed. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. Note: The retail reference number needs to match the item code, so you should not change it after the SKU record is created. |
|
Short SKU |
Numeric, 7 positions. |
Unique number assigned by Order Administration. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Last Change Date |
Date |
Most recent create or change date in Order Administration. |
|
|
Create Date |
Date |
Date when record is first created. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Whs (Warehouse) |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
From the Default Warehouse (A04); otherwise, set to 0. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Location |
Alphanumeric, 7 positions. |
From the OMS Default Primary Location (M51); otherwise, blank. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Soldout Control Code |
Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
Defaults from the Default Soldout Control Code (D72). |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Updated by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration. |
|
|
Created by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Item Warehouse Mapping and Defaults |
An item warehouse record is created for each item record with the same company, item code, and SKU. |
||
|
Whs (Warehouse) |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
From the Default Warehouse (A04); otherwise, set to 0. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Item Location Mapping and Defaults |
An item location record is created for each item record with the same company, item code, SKU, and warehouse if the OMS Default Primary Location (M51) system control value specifies a value; otherwise, the record is not created. Certain fields, such as the Type, default from the OMS Default Primary Location (M51). |
||
|
Whs (Warehouse) |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
From the Default Warehouse (A04); otherwise, set to 0. |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
|
Location |
Alphanumeric, 7 positions. |
From the OMS Default Primary Location (M51). |
Not updated after initial record creation in Order Administration. |
Item Image Import and Mapping
Item image import: Item image URL information in Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services originates in RMFCS. If the OCDS Item Image URL (M47) system control value specifies a valid URL and the item has been imported from Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services, the OCDSITM Periodic Function imports the links to item images from Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services and updates the corresponding field in the item table. The import takes place regardless of the setting of the Use External Item Image (L55) system control value.
The import process updates the item’s image link only when the response from Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services indicates that it is flagged as the primary.
-
Company: The code identifying the company selected when running the OCDSITM Periodic Function.
-
Item: The code identifying an item in the Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services database. If the item does not exist in the specified company in Order Administration, no update takes place.
-
Image link: The image link for the item. See the Item Image/Info Link Screen for more information.
Note:
The import process does not delete item image links that already exist.Item Location Attributes Import and Mapping
Purpose: Item Location Attributes URL information in Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services originates in RMFCS. The item location attributes import through the OCDSITM Periodic Function actually updates certain fields in existing Item and SKU records based on the information in the ITEM_LOC table in Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services; it does not create or update item location records. These updates take place only if the OCDS Item Location Attributes URL (M46) specifies a valid URL. The information in the Item and SKU tables that the function updates in Order Administration is described in the following table:
-
Item Fields Updated through the Item Location Attributes Import
-
SKU Fields Updated through the Item Location Attributes Import
Identifying the items to update: The OCDSITM Periodic Function uses the OCDS RMS Location Identifier (M52) system control value to determine which records to update with item location attributes. Only Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services ITEM_LOC records with a LOCATION that matches the system control value are used to update the Order Administration item and SKU records.
How are item locations updated? The OCDSITM Periodic Function creates and updates item location records through the Item and SKU import. See Item-Related Import and Mapping, including Item Location Mapping and Defaults, above, for more information.
Important:
About unmapped fields: Any item, SKU, item warehouse, and item location fields in Order Administration that are not listed below are not mapped through the OCDSITM Periodic Function. Y/N fields are set to N; otherwise, fields are left blank if alphanumeric, or set to 0 if numeric. Also, these fields are not updated after initial record creation.Note:
The import process updates existing item and SKU records. It does not delete records that already exist.| Target Field | Attributes | Value Used | Description/ Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
The code identifying the company selected when running the OCDSITM Periodic Function. |
The company code used to identify the item and SKU records to update. |
|
Item |
Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
Item passed |
The item code used to identify the item and SKU records to update. |
|
Item Fields Updated through the Item Location Attributes Import |
|||
|
Item Status |
Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
The status passed. |
A code that represents an item's status, such as obsolete, discontinued, etc. This information is used for inventory reporting purposes; also, items that are assigned the Item Status for Suppressing Item During Item Selection (L21) at the item level are not listed at the Item Selection screen. Valid? If the import passes a status code that has not been set up through Working with Item Status (WIST), it is still written to the item record; however, the Change Item screen displays an error. See Performing Initial Item Entry (MITM) for background. |
|
Unit of Measure |
Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
The sellinguom passed. |
A standard by which an item/SKU is sold. Typical units of measure include:
Also updates the SKU record; see below. Valid? If the import passes a unit of measure code that has not been set up through Working with Units of Measure (WUOM), it is still written to the item record; however, the Change Item screen displays an error. See Performing Initial Item Entry (MITM) for background. |
|
Updated by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration |
|
|
Last Change Date |
Date |
Most recent create or change date in Order Administration. |
|
|
SKU Fields Updated through the Item Location Attributes Import |
|||
|
Restrict |
Y/N |
From the stopsaleind passed. |
Indicates whether this item can be ordered.
Any existing orders before the item becomes restricted are processed normally. |
|
Unit of Measure |
Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
The sellinguom passed. |
A standard by which an item/SKU is sold. Typical units of measure include:
Also updates the item record; see above. Valid? If the import passes a unit of measure code that has not been set up through Working with Units of Measure (WUOM), it is still written to the item record; however, the Change Item screen displays an error. See Performing Initial Item Entry (MITM) for background. |
|
Updated by User |
Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
User ID flagged as the Default User during system configuration |
|
|
Last Change Date |
Date |
Most recent create or change date in Order Administration. |
Item Price Import and Mapping
Identifying the items to update: The OCDSITM Periodic Function uses:
-
The OCDS RMS Location Identifier (M52) system control value to determine which items are eligible to have item offer and item price records created or updated. Only Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services ITEM_LOC records with a LOCATION that matches the system control value are used to update the Order Administration item offer and item price records.
-
The retail reference number in Order Administration, which needs to match the Item passed from Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services. Ordinarily, the retail reference number and the item code in Order Administration are the same, as the periodic function sets them both to the same Item code.
Default offer: The periodic function creates item offer and item price records using the Current Offer (A33) system control value. This system control value must be set to a valid, current offer in order to create the item offer and item price records correctly.
Important:
About unmapped fields: Any item offer or item price fields in Order Administration that are not listed below are not mapped through the OCDSITM Periodic Function. They are set to N if a Y/N value; otherwise, they are left blank if alphanumeric, or set to 0 if numeric. Also, these fields are not updated after initial record creation.Note:
The import process updates existing item offer and item price records. It does not delete records that already exist.| Target Field | Properties | Value Used | Description/ Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Numeric, 3 positions. |
The code identifying the company selected when running the OCDSITM Periodic Function. |
The company code used to identify the item and SKU records to update. |
|
Item |
Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
Item passed |
The item code used to identify the record to update. Matched based on retail reference number: The periodic function uses the retail reference number for the item to determine whether the item matches a record received from Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services. The function sets the retail reference number to the same value as the item code, so ordinarily they are the same. The periodic function creates item offer and item price records only for items that exist in Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services and have been imported into Order Administration. Also, the item price is updated only if the retail reference number is numeric, because a non-numeric reference number indicates that the item is not sellable. |
|
Item Offer Field Updated through the Price Import |
Any additional item offer fields in Order Administration besides the item and offer are not mapped through the OCDSITM Periodic Function. They are set to N if a Y/N value; otherwise, they are left blank if alphanumeric, or set to 0 if numeric. Also, these fields are not updated after initial record creation. |
||
|
Offer |
Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
From the Current Offer (A33). |
Valid? If the system control value is not set to a valid offer, the item offer and item price records are not created correctly. |
|
Item Price Fields Updated through the Price Import |
In addition to the company, item, and offer, described above, the following Item Price fields are created as follows. If the periodic function retrieves updated price information for an item with a different effective date, a new item price record is created. |
||
|
Effective Date |
Date |
From the effective date passed. |
If no effective date is passed, the date is set to January 1 2000. Ordinarily, an effective date is passed only when there was an item price change recorded in Merchandising Omnichannel Web Services. In that case, there are records in the CLEARANCE and PRICE_CHANGE tables. |
|
Quantity |
Numeric, 7 positions. |
Set to 1. |
|
|
Price |
Numeric, 13 positions with a 2-place decimal. |
From the price passed. |
If multiple prices are passed with the same effective date, the last price passed is used. If the price passed is not greater than zero, it is ignored. The item price record is not created or updated. |
Integration with the Sales Audit Module of the Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service
Overview: Use the integration with Sales Audit module of the Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (Sales Audit module) to export information on sales and returns.
Types of information sent for transactions: The following information is included:
-
transaction header
-
customer
-
items
-
discounts
-
tax
-
payment
-
tenders
-
transaction tail
The file also includes transaction open and close records, and file header and trail records.
Tracking shipments and credits: If you enable the Sales Audit module sales audit integration in Order Administration, the system writes records in the INT_RESALOG table in the database, and updates the table with records as shipments and order credits bill throughout the day.
Packaging the DAT file into a ZIP file: On a daily basis, you use a periodic process to add file header and trailer records to “wrap” the transaction information, and convert the contents of the INT_RESALOG table into a DAT file that is ready for Sales Audit module to retrieve and process. This file is named RTLOG_6_20190721145902950.DAT, where 6 is the company number or the store number, and 20190721145902950 is the date and time stamp. The DAT file is then packaged into a ZIP file of the same name, for example, RTLOG_6_20190721145902950.ZIP.
In this topic:
Data Flow from Order Administration to Sales Audit Module
If your company is configured for Sales Audit module integration, processing takes place as follows:
-
Sale or credit invoices are created through the day and are processed by the billing async job in Background Job Control (MBJC).
-
Outbound Interface Transaction trigger records with a File setting of IHD are created based on the invoices. You can review these trigger records in Working with Outbound Interface Transactions (WOIT).
-
The INVOIC_OUT process in Working with Integration Layer Processes (IJCT) works through the IHD trigger records to collect the required information for each invoice, and creates records in the INT_RESALOG database table for transactions in each company that is configured for the Sales Audit module integration.
-
When the RTLOG periodic function runs, it:
-
Consolidates multiple records for the same invoice found in the INT_RESALOG table. This can occur if, for example, you ship multiple ship-alone items on a single order and you have the Consolidated Invoice (B49) system control value selected.
Note:
In Order Management System 21.0 or higher, or Order Administration, you cannot select the Consolidated Invoice system control value if it is not already selected. If the system control value is currently selected (set to Y) and you deselect it (change it to N or blank), you cannot then change it back to selected. The option to consolidate invoices will be removed at a later date. -
Uses the records in the INT_RESALOG table to create a DAT file that contains the transaction data from the temporary file for the company specified for the function, as well as the header, close store, and footer records. The DAT file name is
RTLOG_1234_20190621140400561.DAT, where:-
1234is the Parameter specified for the periodic function. This needs to be the store number assigned by the Sales Audit module. If no store number is specified as the parameter, the company number is used. -
20190621140400561is the date and time.
-
-
Creates a compressed ZIP file containing the DAT file, using the same naming convention as described above the for DAT file and places the ZIP file in the CWDIRECTCP_FTP_FOLDER.
-
Transmitting the RTLOG File to Object Storage
Use the following process to transmit the RTLOG file to object storage.
Note:
Object storage is supported in Sales Audit module version 21.0 and later.Run the RTLOG periodic function, as described above, to create the RTLOG file and place it in the CWDIRECTCP_FTP_FOLDER.
Run the SNDRTLG periodic function. If there is an RTLOG file in the CWDIRECTCP_FTP_FOLDER, and if the Sales Audit File Service URL (M64) and Sales Audit Import Folder Path (M65) are populated, this function:
-
Sends a POST request message for each RTLOG file to the Sales Audit module, using the authentication set up for the Sales Audit File Service through the Work with Outbound Web Service Authentication Screen.
-
If the Sales Audit module returns a response indicating that the pre-authentication request (PAR) was successful, the periodic function processes a PUT to the URL that was returned in the Sales Audit module response.
-
After processing the PUT, the periodic function:
-
Removes the RTLOG file from the CWDIRECTCP_FTP_FOLDER.
-
Saves a copy of the RTLOG zip file in the OMS-SALES-AUDIT container of the FILE_STORAGE table. This copy is available in case there was an issue with the Sales Audit module receiving the file, so it will be available to be resent, if necessary, through the RCVRTLG periodic function, described below.
-
-
If no pre-authentication response is received, the Order Administration Support Notification is generated. Possible reasons for an unsuccessful process include an invalid setting for any of the Additional System Control Values Related to Transmitting to Object Storage.
Resending the RTLOG file: If the pre-authentication response was received during SNDRTLG processing, but the Sales Audit module did not actually receive the RTLOG file, you can use the RCVRTLG periodic function to resend the file.
For example, Sales Audit module staff indicate the date and time when the RTLOG file was expected but not received. In this case:
-
Use the
getFilesfile storage request to obtain a list of files in the OMS-SALES-AUDIT container of the FILE_STORAGE table. See File Storage API for information on the file storage API and the FILE_STORAGE table. -
Based on the date and time when the missing RTLOG file was generated, obtain the exact file name to send.
-
Enter the exact RTLOG file name as the Parameter for the RCVRTLG periodic function, and run the function.
Note:
The records in the OMS-SALES-AUDIT container of the FILE_STORAGE table are not purged automatically. You can use thedeleteFile file storage request to delete these records.
Configuration for the Sales Audit Module Integration
Configuration within Order Administration
The configuration required in Order Administration to support the integration with Sales Audit module includes the following.
System Control Values
Set the following system control values:
-
ReSA RTLOG Format (M39): Must be set to RTLOG or RTLOGQ.
-
Consolidated Invoice (B49): Needs to be unselected. Otherwise, if this system control value is selected, it is possible to generate multiple transaction heads with the transaction numbers, as individual lines on the order are billed. The items that bill first could then accumulate and repeat on each subsequent transaction: for example, if 3 items ship separately, invoice 1 contains item 1; invoice 2 contains items 1 and 2; invoice 3 contains invoice 1, 2, and 3.
Note:
In Order Management System 21.0 or higher, or Order Administration, you cannot select the Consolidated Invoice system control value if it is not already selected. If the system control value is currently selected (set to Y) and you deselect it (change it to N or blank), you cannot then change it back to selected. The option to consolidate invoices will be removed at a later date. -
Create Generic Invoice Download Trigger Records (I17): Must be selected in order to create the IHD trigger records for processing.
-
Use Async Start Date for Billing Transactions (E95): Oracle recommends leaving this system control value unselected.
-
Item for Non-Merchandise Amounts (L39): Used as the non-merchandise item (NMITEM) in the DAT file for Sales Audit module.
-
ReSA Warehouse for Non-Inventory Returns (M56): Used as the return warehouse for a credit invoice for a return that does not affect inventory. Must map to a Physical Warehouse defined in the Sales Audit module.
-
Default Warehouse (A04): Used as the return warehouse for a credit invoice for a return that does not affect inventory, if no ReSA Warehouse for Non-Inventory Returns (M56) is specified.
Additional System Control Values Related to Transmitting to Object Storage
Set the following additional required system control values for Transmitting the RTLOG File to Object Storage:
-
Sales Audit File Service URL (M64): Defines the endpoint for the SNDRTLG periodic function to use when submitting the RTLOG file to object storage. Order Administration supports multiple File Transfer methods with ReSA. The endpoint configured in this system control value determines which method is used.
-
If ‘/RmsReSTServices/’ is in the URL, the RMFCS exposed FTS Service URL is used.
-
If ‘/RmsPlatformServices/’ is in the URL, the Platform FTS Service URL is used.
-
-
Sales Audit Import Folder Path (M65): Defines the folder where RTLOG files should be placed when you are using object storage.
-
IDCS Enterprise Endpoint Scope (M66): Defines the limits that control where the OAuth token can be used to support posting to object storage.
-
IDCS Enterprise Endpoint URL (M67): Defines the endpoint to use for OAuth authentication to support posting to object storage.
Property
The process uses the CWDIRECTCP_FTP_FOLDER, displayed in Working with Admin Properties (CPRP), for the RTLOG function to place the ZIP file for the Sales Audit module.
Periodic Functions and Processes
Use Working with Periodic Functions (WPER) to set up:
-
The RTLOG periodic function. If the function needs to run in more than one company, mapping to more than one store in the Sales Audit module, you can name the function RTLOGN, where N is a unique number. When setting up the function:
-
Set the Program name to PFR0201
-
Set the Parameter to the store number assigned by the Sales Audit module, but if not passed, uses company number
-
-
The SNDRTLG periodic function for Transmitting the RTLOG File to Object Storage. When setting up the function:
-
Set the Program name to PFR0206
-
Set the Parameter to the store number assigned by the Sales Audit module, but if not passed, uses company number
-
-
The RCVRTLG periodic function for Transmitting the RTLOG File to Object Storage. When setting up the function:
-
Set the Program name to PFR0208
-
Set the Parameter to the name of the RTLOG file that you are resubmitting to object storage, but if not passed, uses company number. See Transmitting the RTLOG File to Object Storage for more information
-
Use Working with Periodic Processes (WPPR) to assign each periodic function to a periodic process. The RTLOG and SNDRTLG processes should run at the end of day, because records accumulate in a temporary file until the function runs.
Authentication
In order to use the process described under Transmitting the RTLOG File to Object Storage, you need to use the Work with Web Service Authentication screen (WWSA) to set up authentication for the Sales Audit File Service, using an authentication type of OAuth. See the Work with Outbound Web Service Authentication Screen for background.
Miscellaneous Setup
Do not set Trigger Rules or XML Inclusion rules for the INVOIC_OUT job in Working with Integration Layer Processes (IJCT).
Mapping Configuration between Order Administration and the Sales Audit Module
In addition to the Configuration within Order Administration, described above, you need to map the following information from the Sales Audit module:
-
Store number: Specify as the Parameter for the RTLOG periodic function. This store number is used as part of the DAT file name, as described above, and also populates the Location Number in the FHEAD record. If no Parameter is specified for the periodic function, the company number is used.
-
Return Reason Codes: The return reason codes used must map to SARR codes defined in the Sales Audit module.
-
Return Warehouse Codes: Any warehouse codes that might be passed as return warehouses must map to Physical Warehouses defined in the Sales Audit module.
-
Pay Types: Each pay type sent must map to a Pay Type in the Sales Audit module.
-
Items: The Reference # for the item must map to an item in the Sales Audit module. Items are ordinarily imported from Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS) into the Sales Audit module and Order Administration, and the Reference # is set to the same value as the item code. The Reference # should not be changed.
Considerations for the Sales Audit module Integration
Cross-channel orders are not excluded from the RTLOG file for the Sales Audit module, and as a result can be submitted by multiple systems that integrate with the Sales Audit module.
Example: Xstore submits an order to Order Orchestration, and the order is fulfilled through assignment to Order Administration; in this case, both Xstore and Order Administration submit the order to the Sales Audit module. Similarly, if the Use OROB for Fulfillment Assignment (M31) system control value is selected, Order Administration sends invoices for both the originating order and fulfilling order, or there could be multiple transactions sent for same order if a line splits in Order Orchestration.
The Cross Channel Orders to Exclude in Sales Feed (L35) does not affect the selection of orders to include in the export file.
If the Consolidated Invoice (B49) system control value is selected, the RTLOG periodic function consolidates the records for an invoice into a single record in the RTLOG file.
Important:
In Order Management System 21.0 or higher, or Order Administration, you cannot select the Consolidated Invoice system control value if it is not already selected. If the system control value is currently selected (set to Y) and you deselect it (change it to N or blank), you cannot then change it back to selected. The option to consolidate invoices will be removed at a later date.Additional Things to Note
It is not necessary to create queues for the INVOIC_OUT job in Working with Integration Layer Processes (IJCT) if the trigger records are required only for the Sales Audit module integration. In this case, you should set the ReSA RTLOG Format (M39) to RTLOG, and no invoice out message is generated or logged. If you set the ReSA RTLOG Format (M39) to RTLOGQ rather than RTLOG, errors will be logged if no queues have been created.
The invoice amount passed in the RTLOG file may not be the same as the paid amount in the case of an underpayment, overpayment, or canceled return.
Invoice to RTLog Mapping
The file type record descriptors for each record type included in the RTLog file, and a brief summary of their contents:
-
FHEAD: The header for the file, indicating basic information such as the originating system, the store number, and the file creation date and time. Added through the RTLOG periodic function. One header per file.
-
THEAD (SALE or RETURN transaction): This File Type Descriptor contains the header for each transaction, indicating the date and time generated, the invoice (transaction) number, and whether the transaction was a shipment (SALE) or refund (RETURN).
-
The first THEAD record in the file is the THEAD (OPEN transaction) following the initial FHEAD, and the last THEAD record is the THEAD (CLOSE transaction) at the end of the transactions. Unlike the OPEN transaction, the CLOSE transaction is created through the RTLOG periodic function.
-
TCUST: Information about the customer, including customer number and name and address.
-
TITEM: Information about each item sold or returned, including item number, quantity, and pricing, as well as the order number and invoice number.
-
IDISC: Discount line information for sales transactions.
-
IGTAX: Item-level tax amounts.
-
TTAX: Tax amounts.
-
TPYMT: Payment amounts for sales, exclusive of tax.
-
TTEND: Tender information for each transaction.
-
TTAIL: Indicates the total number of lines in the transaction.
-
FTAIL: The total number of lines in the file. The last entry in the file. Added through the RTLOG periodic function.
The following table describes the fields that are mapped into the RTLog file, or that are hard-coded.
Note:
Fields that are left blank are not included in the following table.| Field | Data Type and Length | Value Passed | Description/ Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
FHEAD |
This File Type Descriptor identifies a single record at the beginning of the file. Created by the RTLog periodic function, and not found in the temporary file. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
0000000001 |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. Set to 0000000001 for the FHEAD. |
|
File Type Definition |
Character (4) |
RTLG |
Hard-coded. |
|
File Create Date |
Character (14) |
System date and time |
The date and time when the file was created. Example: 20190621140400, where 2019 is the year, 06 is the month, 21 is the date, and 140400 is the time. |
|
Business Date |
Character (8) |
System date |
The date when the file was created. Example: 20190621, where 2019 is the year, 06 is the month, and 21 is the date. |
|
Location Number |
Character (10) |
Location ID |
The location ID assigned in the Sales Audit module. From the Parameter defined for the RTLOG periodic function. If no Parameter was defined, this is the company number. |
|
RTLOG Originating System |
Character (3) |
OMS |
Hard-coded. |
|
THEAD (OPEN transaction) |
The first record in the file with a File Type Descriptor of THEAD is an OPEN transaction, and follows the initial FHEAD record in the DAT file created by the RTLOG periodic function. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Next sequential number in the file. |
Identifies the line number in the file. Ordinarily set to 0000000002, since this line follows the FHEAD record. Zero-padded. |
|
Register |
Character (5) |
01 |
Hard-coded. |
|
Transaction Date |
Character (14) |
System date and time |
The date and time when the record was created. Example: 20190621140400, where 2019 is the year, 06 is the month, 21 is the date, and 140400 is the time. |
|
Transaction Number |
Number (10) |
Next transaction number in the file. |
Zero-padded. Ordinarily set to 0000000002 for the OPEN transaction type. |
|
Transaction Type |
Character (6) |
OPEN |
Hard-coded. |
|
Sub-transaction Type |
Character (6) |
OSTORE |
Hard-coded. |
|
THEAD (SALE or RETURN transaction) |
Records with this File Type Descriptor contains the header for each transaction, indicating the date and time generated, the invoice (transaction) number, and whether the transaction was a shipment (SALE) or refund (RETURN). The first THEAD record in the file is an OPEN transaction following the initial FHEAD, and the last THEAD record is a CLOSE transaction at the end of the transactions. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Next sequential number |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
Register |
Character (5) |
01 |
Hard-coded. |
|
Transaction Date |
Character (14) |
System date and time |
The date and time when the INVOIC_OUT job processed the transaction record. Example: 20190621140400, where 2019 is the year, 06 is the month, 21 is the date, and 140400 is the time. |
|
Transaction Number |
Number (10) |
Invoice number |
The unique number identifying the invoice in Order Administration. |
|
Cashier |
Character (10) |
Salesman number |
The unique number identifying the salesman, if any, associated with the order. |
|
Salesperson |
Character (10) |
Salesman number |
The unique number identifying the salesman, if any, associated with the order. |
|
Transaction Type |
Character (6) |
SALE or RETURN |
Set to SALE if the merchandise was shipped; otherwise, set to RETURN if the merchandise was returned, or if a negative additional charge was applied and express-billed. NOTE: Typically, if the merchandise was shipped, the invoice type is I, but it is possible that negative additional charges, applied through the non-inventory item, could exceed the value of the shipped items. Similarly, if the merchandise is returned, the invoice type is C, but it is possible that positive additional charges could exceed the value of the returned items. |
|
Value Sign |
Character (1) |
P |
Set to P for both sales and credit invoices. |
|
Rounded Amount Sign |
Character (1) |
P |
Set to P for both sales and credit invoices. |
|
Rounded Off Sign |
Character (1) |
P |
Set to P for both sales and credit invoices. |
|
Transaction Processing System |
Character (3) |
POS or OMS |
Passes POS:
Otherwise, passes OMS. |
|
TCUST |
Records with this File Type Descriptor contains information about the sold-to customer, including customer number and name and address. TCUST records follow THEAD records with File Type Descriptors of SALE or RETURN. The information in this record type is primarily from the Sold To Customer record. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Line number |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
Customer ID |
Character (16) |
Sold-to customer number. |
The sold-to customer on the order. |
|
Customer Type ID |
Character (6) |
CUSTID |
Hard-coded. |
|
Customer Name |
Character (120) |
Customer first name, last name, and company. |
Values are concatenated, with spaces between each. |
|
Address 1 |
Character (240) |
First address line |
All address and phone number information is for the sold-to customer. |
|
Address 2 |
Character (240) |
Second address line |
Blank if no second address line exists. Apartment number is not passed. |
|
City |
Character (120) |
City |
|
|
State |
Character (12) |
State or province code |
If blank, spaces are passed. |
|
Zip Code |
Character (30) |
Zip or postal code |
If blank, spaces are passed. |
|
Country |
Character (3) |
Country code |
Two positions. |
|
Home Phone |
Character (20) |
Day phone |
|
|
Work Phone |
Character (20) |
Evening phone |
|
|
|
Character (100) |
Email address |
The sold-to customer’s primary email address. |
|
TITEM |
Records with this File Type Descriptor contains information about each item sold or returned, including item number, quantity, and pricing, as well as the order number and invoice number. The information for this record type is primarily from the Invoice Detail table. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Line number |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
Item Status |
Character (6) |
ORD or C |
Set to ORD if the invoice is for a shipment; otherwise, set to R if the invoice is for a return, or for a negative additional charge that was express-billed. |
|
Item Type |
Character (6) |
ITEM or NMITEM |
Set to NMITEM for the Item for Non-Merchandise Amounts (L39); otherwise, set to ITEM. |
|
Item Number Type |
Character (6) |
ITEM |
Hard-coded. |
|
Item |
Character (25) |
Item code |
The item’s Reference # (retail reference number) from the SKU table. The Reference # is automatically populated with the item number through Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS). If for any reason the Reference # is blank, the base item code is passed instead. The item code passed does not include a SKU. SKUs are not supported in the Sales Audit module. NOTE: Each item must map to an item in the Sales Audit module. |
|
Non-Merchandise Item |
Character (25) |
Non-merchandise item code |
From the Item for Non-Merchandise Amounts (L39) system control value. This must be a valid item code in the Sales Audit module. |
|
Quantity Sign |
Character (1) |
P or N |
Typically set to P for a sale invoice; otherwise, set to N for a credit invoice. However, if this is the NMITEM, the Quantity Sign indicates the effect of the charge, for example:
|
|
Quantity |
Number (12) |
Shipped or returned unit quantity |
Zero-padded with a 4-position implied decimal; for example, a quantity of 2 is passed as 000000020000. Absolute value. Quantity of 1 is passed for the Item for Non-Merchandise Amounts. |
|
Selling Unit of Measure |
Character (4) |
EA |
Hard-coded. |
|
Unit Retail |
Number (20) |
Pre-discount price |
Zero-padded with a 4-position implied decimal; for example, a price of 1.50 is passed as 00000000000000015000. Absolute value. If the selling price is less than the offer price on a sales transaction, an IDISC record provides details on the discount. NOTE Ordinarily the same as the Original Unit Retail, except for the following scenarios.
|
|
Override Reason |
Character (6) |
OMS |
Hard-coded. |
|
Original Unit Retail |
Number (20) |
Offer price from the Order Detail record |
The original offer price. Set to 0.00 if no offer price is defined. See Overriding the Item/SKU Offer Price for a discussion of how the offer price for an Order Detail record is determined when offers are not set up, and a price override reason code is used to set the price for the order line. If the selling price is lower than the original offer price, the Unit Discount Amount specified in the IDISC record indicates the unit amount of the discount. |
|
Taxable Indicator |
Character (1) |
Y or N |
Set to Y, unless:
|
|
Item_swiped_ind |
Character (1) |
N |
Hard-coded. |
|
Return Reason Code |
Character (6) |
Return reason code |
The return reason code used for a return of an order line. See Establishing Return Reason Codes (WRTR) for background. NOTE The return reason codes used MUST map to SARR codes defined in the Sales Audit module |
|
Salesperson |
Character (10) |
Salesman number |
The unique number identifying the salesman, if any, associated with the order. |
|
Drop Ship Ind |
Character (1) |
Y or N |
Set to Y for a drop ship item on a sale transaction; otherwise, set to N. Set to N for a return. |
|
Uom_qty |
Number (12) |
Shipped quantity |
The shipped quantity on the invoice detail. Zero-padded with a 4-position implied decimal; for example, a quantity of 2 is passed as 000000020000. Absolute value. Quantity of 1 passed for the Item for Non-Merchandise Amounts. |
|
Catchweight_ind |
Character (1) |
N |
Hard-coded. |
|
Total_igtax_amount |
Number (21) |
Invoice detail tax amount |
The total tax for the invoice detail line. |
|
Selling item |
Character (25) |
Item code |
The base item code. Does not include a SKU. SKUs are not supported in the Sales Audit module. |
|
Customer Order Number |
Character (48) |
Order number |
The Order Administration order number. Does not include the ship-to suffix. |
|
Customer Order Date |
Character (14) |
Order date |
The order date from the Order Header. YYYYMMDD format. |
|
Fulfillment Order Number |
Character (48) |
Invoice number |
Included only for sales transactions. Not included for returns. |
|
No Inventory Return |
Character (1) |
Y or N |
Used only for credit invoice records. Set to Y when inventory was not updated for the transaction creating the invoice detail record (there is no Item Transaction History record, as indicated in Display Inventory Transaction History (DITH)). For example, this flag is selected when a negative additional charge express bills against a closed order. Otherwise, set to N if inventory was updated, or if this is a non-merchandise item (NMITEM). |
|
Sales Type |
Character (1) |
E |
Hard-coded. |
|
Return Warehouse |
Character (10) |
Warehouse code |
Used only for return records that are not for the non-merchandise item (NMITEM):
Note: Any warehouse codes that might be passed MUST map to Physical Warehouse defined in the Sales Audit module. |
|
Return Disposition |
Character (10) |
COR |
Sent only when No Inventory Return is set to N, or the record is for the NMITEM. |
|
Location Type |
Character (2) |
Location type identifier |
Not passed for returns. |
|
Location Number |
Character (10) |
Code identifying fulfilling or pickup location |
Not passed for returns. |
|
IDISC |
Records with this File Type Descriptor contain discount line information for sales transactions when the selling price is lower than the offer price. These records are not created for returns. Also, if the offer price is lower than the selling price, such as when the offer price is zero, no discount record is created. This record follows the TITEM record for the discounted item. The information for this record type is primarily from the Invoice Detail table. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Line number |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
RMFCS Promotion Number |
Character (6) |
2000 |
Hard-coded. |
|
Discount Type |
Character (6) |
ITEM |
Hard-coded. |
|
Quantity Sign |
Character (1) |
P |
Hard-coded. A quantity sign of N is not used, since only sales transactions create these records. |
|
Quantity |
Number (12) |
Shipped quantity |
The shipped quantity on the invoice detail. Zero-padded with a 4-position implied decimal; for example, a quantity of 2 is passed as 000000020000. |
|
Unit Discount Amount |
Number (20) |
Discount amount divided by shipped quantity |
The discount amount shipped quantity on the invoice detail. Zero-padded with a 4-position implied decimal; for example, a unit discount amount of 2.5 is passed as 000000025000. |
|
Uom_qty |
Number (12) |
Shipped quantity |
The shipped quantity on the invoice detail. Zero-padded with a 4-position implied decimal; for example, a quantity of 2 is passed as 000000020000. |
|
Catchweight_ind |
Character (1) |
N |
Hard-coded. |
|
IGTAX |
Records with this File Type Descriptor contain item-level tax amounts. This record type follows the IDISC, if any; otherwise, follows the TITEM. NOTE VAT amounts are not passed in this record type, since they are included in item prices. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Line number |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
Tax Authority |
Character (10) |
TOTALTAX |
Hard-coded. |
|
Igtax Code |
Character (6) |
TOTAX |
Hard-coded. |
|
Igtax Amount Sign |
Character (1) |
P or N |
Set to P for a sale invoice; otherwise, set to N for a credit invoice. |
|
Igtax Amount |
Number (21) |
Tax amount |
The total tax amount for the invoice detail line, including any GST or PST as well as tax on any special handling or gift wrap for the item. For the NMITEM, includes the total order-level freight tax from the Invoice Payment Method record for all payment methods. Zero-padded with a 5-position implied decimal; for example, a tax amount of 2.38 is passed as 000000000000000238000. Absolute value. |
|
TTAX |
Records with this File Type Descriptor contain tax amounts. NOTE VAT amounts are not passed in this record type, since they are included in item prices. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Line number |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
Tax Code |
Character (6) |
TOTAX |
Hard-coded. |
|
Tax Sign |
Character (1) |
P or N |
Set to P for a sale invoice; otherwise, set to N for a credit invoice. |
|
Tax Amount |
Number (20) |
Tax amount |
The total tax amount for the invoice, including any GST or PST. Zero-padded with a 4-position implied decimal; for example, a tax amount of 2.38 is passed as 00000000000000023800. Absolute value. |
|
TPYMT |
Records with this File Type Descriptor contain payment amounts for sales, exclusive of tax, although VAT is not subtracted if the order is subject to VAT. These records are not created for return or credit transactions. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Line number |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
Payment Sign |
Character (1) |
P |
Hard-coded. A payment sign of N is not used, since only sales transactions create these records. |
|
Payment Amount |
Number (20) |
Deposit amount minus tax |
The deposit amount for the invoice payment method, exclusive of tax. Zero-padded with a 4-position implied decimal; for example, a payment amount of 37.60 is passed as 00000000000000376000. |
|
TTEND |
Records with this File Type Descriptor contain tender information for each transaction. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Line number |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
Tender Type Group |
Character (6) |
CHECK, CCARD, or VOUCH |
Set to:
|
|
Tender Type ID |
Number (6) |
Pay type code |
The pay type code, as set up in Work with Pay Types (WPAY). NOTE Each pay type must map to a Pay Type in the Sales Audit module. |
|
Tender Sign |
Character (1) |
P or N |
Set to P for a sale invoice; otherwise, set to N for a credit invoice. |
|
Tender Amount |
Number (20) |
Deposit amount |
The deposit amount for the invoice payment method, including tax. Zero-padded with a 4-position implied decimal; for example, a payment amount of 39.98 is passed as 00000000000000399800. |
|
CC_no |
Character (40) |
Last 4 positions of the credit card number |
The last 4 positions of the credit card or stored value card. From the Order Payment Method table. Included only if the Send Payment Card Data in ReSA RTLOG (M74) system control value is selected, and only if numeric; otherwise, blank. |
|
cc_token |
Character (40) |
Character (40) |
The tokenized credit card number, if any, from the Invoice Payment Method table. A stored value card or gift card number is not passed in this field. Included only if the order payment method is a credit card and is tokenized, and if the Send Payment Card Data in ReSA RTLOG (M74) system control value is selected; otherwise, blank. |
|
Voucher_no |
Character (25) |
Gift card number or stored value card number |
The stored value card number from the Invoice Payment Method table. Included only for a gift card or stored value card, and if the Send Payment Card Data in ReSA RTLOG (M74) system control value is selected; otherwise, blank. |
|
TTAIL |
A Type Record Descriptor for the transaction trailer record following each transaction, including an OPEN or CLOSE transaction. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Line number |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
Transaction Record Counter |
Number (10) |
Number of records in the transaction |
Set to 0000000000 for an OPEN or CLOSE transaction. Zero-padded. |
|
THEAD (CLOSE transaction) |
The last record in the file with a File Type Descriptor of THEAD is a CLOSE transaction. This record is followed by the TTAIL and FTAIL records. Created by the RTLog periodic function, and not found in the temporary file. The CLOSE THEAD record is followed by a TTAIL record, and then the FTAIL record. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Next sequential number in the file. |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
Register |
Character (5) |
01 |
Hard-coded. |
|
Transaction Date |
Character (14) |
Date and time |
The date and time when the RTLOG function created the DAT file. |
|
Transaction Number |
Number (10) |
Next transaction number in the file. |
Identifies the transaction number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
Transaction Type |
Character (6) |
DCLOSE |
Hard-coded. |
|
Sub-transaction Type |
Character (6) |
DSTORE |
Hard-coded. |
|
FTAIL |
The total number of lines in the file. The last entry in the file. Added through the RTLOG periodic function. |
||
|
File Line Identifier |
Number (10) |
Next sequential number in the file |
Identifies the line number in the file. Zero-padded. |
|
File Record Counter |
Number (10) |
Next sequential number in the file |
Identifies the transaction number in the file. Zero-padded. |
File Storage API
File Storage API
File storage for imports: You can use the file storage API to:
-
upload files for import
-
obtain a list of files that have been uploaded, or that are in error
-
download a file, such as an error file (does not automatically delete the file)
-
delete files
Note:
Use of the file storage API is required for new installations of Order Administration 17.x and later.
File storage for exports: Use the file storage API to:
-
obtain a list of export files that have been generated
-
download an export file
-
delete files
Use of the FILE_STORAGE table: The FILE_STORAGE table stores data on import files and export files, as well as errors that occur during import or export processing. The web service requests files from, deletes files in, and puts files in this table.
Import processing example: To import Catalog Requests through the file storage API:
-
Create or obtain the Catalog Request file named IXCRIN.txt. See the Sample Catalog Requests Upload Data for sample contents.
-
Use the putFile web service request to place the IXCRIN.txt file data in the OMS-IMPORTS container of the FILE_STORAGE table.
-
Run the UPCATRQ Upload Catalog Request File (Program name PFR0134, Parameter IXCRIN) periodic function to use the contents of the FILE_STORAGE record to populate the Catalog Request Interface table (IXCRIN).
-
This deletes the record from the FILE_STORAGE table. Also, the system creates a file upload record, viewable at the Work with File Upload Screen.
-
Use the Work with Catalog Request Interface (WCRU) menu option to process the records in the Catalog Request Interface table; see Working with the Catalog Request Interface (WCRU).
When the uploaded file record is processed by the related import function, the record is deleted. It is not archived in the FILE_STORAGE folder.
Export processing example: To export marketing download data through the file storage API:
-
The system creates records in the Marketing Download Trigger table as a result of certain actions in Order Administration.
-
Run the MDEXTR Marketing Download Order and Customer Extract (CSX1041) periodic function to extract order and customer-related records in the Marketing Download Trigger table to the appropriate Marketing Download table.
-
Run the MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) periodic function to extract the data in the Marketing Download tables to a pipe delimited text file that is included in a zip file, which is placed in the OMS-MARKETING container of the FILE_STORAGE table. The zip file has the same name as the text file, except for the .zip extension.
-
Use the getFiles web service request to determine the names of the zip files that are in the OMS-MARKETING container.
-
Use the getFile web service request to download one or more marketing download files from the FILE_STORAGE table.
-
Use the deleteFile web service request to delete the files from the FILE_STORAGE table once they are downloaded.
Web service requests: Requests supported by the file storage API and their purposes are:
-
getFile: Download an error or export file that has been generated by Order Administration.
-
deleteFile: Delete a file record, such as an error file or export file that has already been downloaded.
-
putFile: Upload an import file to Order Administration. The file format can be text (.TXT file extension) or compressed (.zip file extension, or the .MOMZIP file extension for the Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS) and Oracle Retail Pricing Cloud Service (RPCS) Integration). If the file is compressed, Order Administration extracts the information from the zip file when processing the import. No other file extensions are supported.
Note:
If you are uploading a zip file, then it must contain a text file of the same name as the zip file, which be in the base level of the zip file, with no subfolders. For example, the EXAMPLE123.ZIP file contains a single EXAMPLE123.TXT file.
The file storage API returns an error if there is already an existing file in the table with the same name, regardless of whether the suffix is different. For example, the API returns an error if you attempt to upload a file named VENDORS.ZIP if there is currently a FILE_STORAGE record named VENDORS.TXT.
-
getFiles: Request a list of file records in the FILE_STORAGE table.
URL: The URL is http://server:port/oms/sxrs/SerenadeREST/FileStorage, where server:port identifies the application server where the RESTful service is located.
Every web service request needs to specify a container. The types of containers are:
-
OMS-IMPORTS: Contains import file records from the integrating system that can be processed by the appropriate Order Administration function. For example, use the putFile request to create an OMS-IMPORTS record so that Order Administration can import the data.
-
OMS-ERRORS: Contains error file records that resulted from a process through the file storage API. For example, use the getFiles request to retrieve a list of error files that have been created.
-
OMS-MARKETING: Contains zip file records, each containing a single text file of marketing download data. See Working with the Marketing Download Extract.
-
OMS-ECOMMERCE: Contains zip file records, each including a single text file of ecommerce-related data. The following options create records in this container:
-
Downloading E-Commerce Offer Files (EOFR): Contains the E-Commerce Product Web XML File (ProductWeb).
-
Working with Merge/Purge Sold-to Names (MMCS): Contains the E-Commerce Customer Merge Web XML File (CustomerMergeWeb).
-
E-Commerce Availability Web Request XML Message (AvailabilityWebRequest).
For more information see the Order Administration Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1).
-
-
OMS-POSLOG: Contains zip file records, each containing a single text file of POSLog data for Xlink generated through the POSLOGX periodic function.
-
OMS-SALES-AUDIT: Contains RTLOG zip file records that the SNDRTLG periodic function copied to file storage after sending the files to the Sales Audit module of Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service. These files are retained in the FILE_STORAGE table in case you need to resend a file through the RCVRLG periodic function. See Data Flow from Order Administration to Sales Audit Module for an overview of the data flow, and see Transmitting the RTLOG File to Object Storage for information on how the records are written to the FILE_STORAGE table and used.
Web authorization required: All request messages also need to use a valid Storage web service user ID with a valid password. See Working with Web Service Authentication (WWSA).
File cleanup:
-
Import file records: The import process removes records from the OMS-IMPORTS container when populating the staging or destination database table.
-
Error records: The integrating system is responsible for deleting error records.
-
Export records: The integrating system is responsible for deleting export records, including the OMS-MARKETING, OMS-ECOMMERCE, OMS-POSLOG, and OMS-SALES-AUDIT containers.
Summary of file storage API responses: The response codes that might be returned to file storage requests include:
-
200 = The getFile or getFiles request was successful.
-
204 = The putFile or deleteFile request was successful.
-
401 = The request failed because the web service user and password were not correct.
-
403 = The putFile request included a file that exceeded the FILE_STORAGE_MAX_SIZE property, or that was empty.
-
404 = The request failed for other reasons.
-
409 = A putFile failed because a file with the same name already exists in the FILE_STORAGE table.
-
500 = Server error.
Maximum file size for uploads: The FILE_STORAGE_MAX_SIZE property defines the maximum file size that you can upload through the file storage API. This property should not be set larger than 1G.
Uploading multiple files: If the amount of data for a particular upload exceeds the maximum size defined in the FILE_STORAGE_MAX_SIZE property, you can break the data out into multiple files. To upload multiple files of the same type, append a unique sequence number, such as a date/time suffix, to the file name, preceded by an underscore. The date/time suffix indicates the sequence in which to upload the contents of each file.
Example: To upload more than one file containing vendor data, you can create and upload a file named VNDUPL_20180702010203.ZIP and another named VNDUPL_20180702010204.ZIP. When the vendor upload program runs, the contents of both files will be extracted and loaded into the Vendor Upload table. Each zip file must include a single file using the same name, but with the TXT extension.
Note:
When an upload uses multiple files, the file names MUST include a unique sequence number suffix, such as a date/time stamp, preceded by an underscore. If the file names do not follow this convention, the upload will fail, and no subsequent uploads for the same file type will succeed until the incorrectly named files are removed from the CWDIRECTCP_UPLOAD_ DIRECTORY.
Upload directories: If the file storage API is enabled for imports, files that are placed in the CWDIRECTCP_UPLOAD_ DIRECTORY, or the other directories that are used for the are not processed by the related function; however, you can still upload a file for processing through the Work with File Uploads (WUPL) option.
Even though the system does not retrieve import files from the upload directories such as the CWDIRECTCP_UPLOAD_ DIRECTORY, import functions still use these directories for certain processing steps.
Merchandising Integration
Topics in this part: The following topics describe the integration between Order Administration and Oracle Retail merchandising applications.
-
Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS) and Oracle Retail Pricing Cloud Service (RPCS) Integration: Provides information on importing items and pricing from Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service (RMFCS) and from Oracle Retail Pricing Cloud Service (RPCS).
Note:
This integration will be deprecated in a future release. Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS) can be used instead to import items and pricing. -
Integration with the Sales Audit Module of the Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service; Provides information on transmitting sales and returns information to the Sales Audit module of the Oracle Retail Merchandising Foundation Cloud Service, details on the information mapped, and the setup required to support the integration.
-
Importing Enterprise Foundation Data through Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS): Provides information on importing enterprise foundation data, including items, prices, merchandise hierarchy, and item images from other retail applications through Oracle Omnichannel Cloud Data Service (OCDS).
-
Enterprise Order Integration (Future Receipts and Active PO/Pre-Order Processing): Provides information on importing future availability information for pre-orders, processing updates as pre-order items become available, and controlling the submission of these orders to Order Orchestration.
Order Orchestration Integration
Topics in this part: This part describes integration between Order Administration and Order Orchestration.
-
Order Orchestration Integration Overview describes the components of the integration between Order Orchestration and Order Administration, including the extract processes that occur automatically as well as the Order Orchestration and Merchandise Locator API’s, and describes required setup.
-
Order Orchestration Integration provides details on how the integration with Order Orchestration handles each order type.
-
Merchandise Locator API describes how to search for a store location where the customer can pick up an item.
Order Orchestration Integration
Order Orchestration: Integration with the Routing Engine module in Order Orchestration supports fulfilling orders across the enterprise.
Use the Order Orchestration integration for the following:
-
brokered backorders: Automatically send backordered lines to the Routing Engine module in Order Orchestration, so the orders can be assigned to locations for fulfillment.
-
If the Use OROB for Fulfillment Assignment (M31) system control value is selected, the system bypasses reservation in order to send all eligible items to Order Orchestration for fulfillment assignment, even if the item is available in the warehouse. In this situation, the fulfilling location may be a store location or an Order Administration warehouse.
-
If the Use OROB for Ship for Pickup Fulfillment Assignment (M34) system control value is set to ALWAYS, the system bypasses reservation in order to send eligible items on a ship-for-pickup order to Order Orchestration for fulfillment assignment. In this situation, the fulfilling location may be a store location or an Order Administration warehouse.
-
-
receive retail pickup (including ship-for-pickup) or delivery orders from Order Orchestration: Receive and fulfill orders in Order Administration. If the order is a retail pickup order, Order Administration sends the merchandise to the customer’s selected store for pickup. If the order is a delivery order, Order Administration ships the merchandise to the customer’s ship-to address. Typically, retail pickup and delivery orders originated in an external retail location. In addition:
-
If the Use OROB for Fulfillment Assignment (M31) system control value is selected, Order Orchestration may send a delivery order to Order Administration that originated as a brokered backorder in Order Administration. In this situation, Order Orchestration determined that an Order Administration warehouse was the best location to fulfill the order.
-
If the Use OROB for Ship for Pickup Fulfillment Assignment (M34) system control value is set to ALWAYS, Order Orchestration may send a retail pickup order to Order Administration that originated as a ship-for-pickup order in Order Administration. In this situation, Order Orchestration determined that an Order Administration warehouse was the best location to fulfill the order.
-
-
send ship-for-pickup orders during pick slip generation/drop ship processing to Order Orchestration: If the Use OROB for Ship for Pickup Fulfillment Assignment (M34) system control value is set to NEVER, ship orders to an external retail location for customer pickup if the merchandise is not already available at that location.
-
send store pickup orders to Order Orchestration: Notify an external retail location that has inventory available that a customer will pick up an order.
Version compatibility: Fulfillment assignment and ship-for-pickup functionality is available in release 16.0 or higher of Order Management System, or Order Administration, and release 16.0 or higher of Order Broker, or Order Orchestration. Also, in order to use ship-for-pickup processing, you must select the Enable Ship For Pickup option on the Organization window in Order Orchestration. Once you enable ship for pickup, the Organization window in Order Orchestration displays the Ship for Pickup Enabled Date, and you cannot deselect this option.
An OROB_MESSAGE_VERSION of 16.0 or higher is required to use the Ship-for-Pickup Orders integration with Order Orchestration.
A message version of 19.0 or higher is required to include the shipment_date tag in the status inquiry response message from Order Orchestration. This date indicates the actual date when the order line was shipped by the fulfilling location, provided the fulfilling system passed this date when it submitted the status update to Order Orchestration when reporting the fulfillment. The shipment date is available to include in shipment notifications to the customer; see Outbound Email API in the Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for more information.
Note:
Up to version 21.1 of OROB_MESSAGE_VERSION is supported. but this property cannot be set higher than 19.9 for integration with Order Broker 19.x, or higher than 21.1 for integration with Order Orchestration 22.2.301.0 or higher.For more information: See:
-
Order Orchestration Integration Overview for general background on integration between Order Orchestration and Order Administration.
-
Order Orchestration Configuration for required setup in Order Administration.
-
the Order Orchestration Operations Guide for details on each request and response message, as well as details on logging and troubleshooting in Order Orchestration.
-
the Order Orchestration online help for step-by-step instructions on populating the Order Orchestration database and on scheduling item and inventory imports.
For information on Order Orchestration processing in Order Administration, see:
Order Orchestration Integration Overview
Purpose: The integration between Order Orchestration and Order Administration enables you to share information on items’ availability and create orders across the enterprise, including:
-
providing periodic item and inventory import from Order Administration to Order Orchestration.
-
providing real-time, on-demand inventory availability information for specific items from the Order Administration warehouse to the point of sale or the web storefront, and vice versa.
-
using Order Orchestration’s routing engine to automatically assign backordered items to one or more locations for fulfillment. In addition:
-
If the Use OROB for Fulfillment Assignment (M31) system control value is selected, you can use the Order Orchestration routing engine to determine the fulfilling location for all eligible items.
-
If the Use OROB for Ship for Pickup Fulfillment Assignment (M34) system control value is set to ALWAYS and the Send B/O to OROB (K08) system control value is selected, you can use the Order Orchestration routing engine to determine the fulfilling location for eligible items on a ship-for-pickup order.
-
-
searching for store locations that stock a requested item so that the customer can pick up the item at the store.
-
using Order Administration to fulfill ship-for-pickup, retail pickup, or delivery orders that originated in a retail store location or in Order Administration.
-
creating ship-for-pickup orders in Order Administration during pick slip generation/drop ship processing and shipping the merchandise to a retail store location for customer pickup.
-
creating store pickup orders so the customer can pick up the order at a retail store location where the merchandise is already in stock.
Integrated systems: Order Orchestration provides visibility into items and inventory across all integrated systems. Typically, you would integrate Order Orchestration with Order Administration and a POS system, such as Xstore.
Setting up the integration: See Order Orchestration Configuration.
Version compatibility: Fulfillment assignment and ship-for-pickup functionality is available in release 16.0 or higher of Order Management System, or Order Administration, and release 16.0 or higher of Order Broker, or Order Orchestration. Also, in order to use ship-for-pickup processing, you must select the Enable Ship For Pickup option on the Organization window in Order Orchestration. Once you enable ship for pickup, the Ship for Pickup Enabled Date displays on the Organization window and this option cannot be changed.
Integration with releases of Order Broker earlier than 5.0 is not supported.
In this topic:
-
Order Orchestration’s Product, Product Location, and Incremental Inventory Import Process
-
Retail Pickup (including Ship-for-Pickup) and Delivery Orders from Order Orchestration
Order Orchestration’s Product, Product Location, and Incremental Inventory Import Process
Overview: The Order Orchestration product import process allows you to extract and import item and inventory information from Order Administration to Order Orchestration.
How does the import work? The following periodic functions allow you to generate output files to import into Order Orchestration.
-
The OBPROD OB Product Output File (program name PFR0127) periodic function allows you to generate a Product output file for import into Order Orchestration. This file contains product information for a specified company. See Order Orchestration Product Output File for details.
-
The OBPRLOC OB Product Location Output File (program name PFR0128) periodic function allows you to generate a Product Location output file for import into Order Orchestration. This file contains product location and availability information for a specified company. See Order Orchestration Product Location Output File for details.
-
The OBINCIN OB Incremental Inventory Output File (program name PFR0129) periodic function allows you to generate an Incremental Inventory output file for import into Order Orchestration. This file contains inventory updates for a specified company. See Oracle Retail Order Orchestration Incremental Inventory Output File for details.
Only items and SKU’s whose OROB eligible flags are selected are eligible for extract. This flag is selected by default.
Required setup: See Order Orchestration Configuration.
For more information: See the Order Orchestration online help and the Order Orchestration Operations Guide.
Location of files: The OROB_DIRECTORY_PATH in Working with Admin Properties (CPRP) defines the location where the system creates the output files.
Import process: When running an Order Orchestration import, the system
-
deletes any matching import file in the OROB-Imports location in Order Orchestration.
-
creates a zip file for the import text file in the OROB_DIRECTORY_PATH and then deletes the text file in the OROB_DIRECTORY_PATH.
-
calls the OACS Import RESTful web service using the setting in the OROB_IMPORTS_URL and the authentication defined for the OACS Imports web service, to automatically upload the import file to the OROB-Imports location in Order Orchestration.
-
deletes the zip file in the OROB_DIRECTORY_PATH.
Application log: The system writes any messages related to the Order Orchestration import process to the application log.
Scheduling the import or running it on demand:
-
In Order Administration, you can use the job scheduler to schedule when a periodic process runs. See Scheduling Jobs for instructions.
-
In Order Orchestration, you use the Schedule Import Process screen in Order Orchestration to set up a schedule for importing item and inventory information from Order Administration. You can also run the import on demand from this screen.
Before you can run the import, you need to complete the required setup in Order Orchestration as well as the Order Orchestration Configuration.
Mapping the Order Administration item and SKU code to the Order Orchestration product or system product code:
-
The Order Administration item and SKU maps to the Order Orchestration system product code. The system maps the full 12 positions for the item and the full 14 positions for the SKU; for example:
SKU YELW SML WMNS. -
The setting of the OROB Product Code ID (K66) system control value defines which field in Order Administration is used as the product code in Order Orchestration. You can map the item and SKU, reference number, or UPC code to the product code.
Order Orchestration Product Output File
Use the OBPROD OB Product Output File (program name PFR0127) periodic function to generate the Order Orchestration Product Output file. This file contains product information for a specified company to import into Order Orchestration. See Order Orchestration’s Product, Product Location, and Incremental Inventory Import Process for processing details.
Location of file: The OROB_DIRECTORY_PATH in Working with Admin Properties (CPRP) defines the location where the system creates the output file. See Order Orchestration’s Product, Product Location, and Incremental Inventory Import Process for processing details.
Name of file: The system names the file PRODUCT_SYS.TXT, where SYS is the
company code where you submitted the periodic function.
Sample file:
system_cd|department|class|sub_class|system_product|product_cd|product_description|master_style
7|7777 LONG SKU DEPARTMENT|7777 LONG SKU CLASS|777 LONG
SKU DIVISION|SKU YELW
SML WMNS|SKU YELW
SML WMNS|SKU ITEM DESCRIPTION|SKU
The system includes empty pipes in the file for data that is not included.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
system_cd |
The company code where the periodic function was submitted. Maps to the Order Orchestration system code. |
|
department |
The code and description of the long SKU department assigned to the item. Maps to the Order Orchestration Department field if the Order Administration company is the default system. |
|
class |
The code and description of the long SKU class assigned to the item. Maps to the Order Orchestration Class field if the Order Administration company is the default system. |
|
subclass |
Depending on the setting of the OROB Item Category Value (M54) system control value:
Maps to the Order Orchestration Category field if the Order Administration company is the default system. |
|
system_product |
The item
and SKU. The system includes the full 12 positions for the item and
the full 14 positions for the SKU; for example: |
|
product_cd |
The item’s product code in Order Orchestration. The setting of the OROB Product Code ID (K66) system control value defines which field in Order Administration is used as the product code in Order Orchestration. Note: When mapping the item and SKU, the system includes the full 12 positions for the item and the full 14 positions for the SKU; for example:SKU YELW
SML WMNS.
|
|
product_description |
A description of the item. Maps to the product description if the Order Administration company is the default system. |
|
master_style |
The item code if the item contains SKUs. Maps to the Order Orchestration master style code if the item has SKU’s. |
Order Orchestration Product Location Output File
Use the OBPRLOC OB Product Location Output File (program name PFR0128) periodic function to generate the Order Orchestration Product Location Output file. This file contains product location, attribute, and availability information for a specified company to import into Order Orchestration. See Order Orchestration’s Product, Product Location, and Incremental Inventory Import Process for processing details.
Location of file: The OROB_DIRECTORY_PATH in Working with Admin Properties (CPRP) defines the location where the system creates the output file. See Order Orchestration’s Product, Product Location, and Incremental Inventory Import Process for processing details.
Name of file: The system names the file PRODUCT_LOCATION_SYS.TXT, where SYS is
the company code where you submitted the periodic function.
Note:
It is important to use Purchase Order Layering to update the PO Layering table before running the import; otherwise, the Next PO date and Next PO quantity sent to Order Orchestration will not be up to date.Send inventory by warehouse? You can either map inventory information for individual item warehouses to the related locations in Order Orchestration, or aggregate item warehouse totals across all allocatable warehouses for an item or SKU into a default location representing your distribution center.
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is:
-
selected: the import process includes each Item Warehouse record for items flagged OROB eligible if the warehouse has an OROB location specified and the warehouse is flagged as Allocatable. Any purchase order information is related to that warehouse only.
-
unselected: the import process sends the total available quantity for the item in all allocatable warehouses, regardless of whether the warehouse has an OROB location specified, and updates the product location in Order Orchestration using the OROB Default Location (K51). Any purchase order information is the earliest eligible purchase order across all allocatable warehouses.
Example:
Item AB100 is stocked in:
-
Warehouse 1 (allocatable, OROB location = DC1)
-
Available quantity = 100
-
Next purchase order date = 6/30
-
Next purchase order quantity = 15
-
-
Warehouse 2 (allocatable, OROB location = S2)
-
Available quantity = -10
-
No open purchase orders
-
-
Warehouse 3 (allocatable, no OROB location)
-
Available quantity = 5
-
Next purchase order date = 6/28
-
Next purchase order quantity = 50
-
OROB Default Location (K51) is set to DC.
Results when sending by warehouse:
If Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) is selected, update:
OROB location DC1:
-
Available quantity = 100
-
Next purchase order date = 6/30
-
Next purchase order quantity = 15
OROB location S2:
-
Available quantity = -10
-
No purchase order information is included
Warehouse 3 is not included because there is no OROB location.
Results when sending sum:
If Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) is unselected, update:
OROB location DC:
-
Available quantity = 95 (warehouse 1 + warehouse 2 + warehouse 3)
-
Next purchase order date = 6/28
-
Next purchase order quantity = 50
Availability for Drop Ship and Non-Inventory Items, including Main Set Items
-
Drop ship items: If an item is flagged as Drop ship, the available quantity passed to Order Orchestration is 9999, unless you actually have an available quantity of the drop ship item in the warehouse; in this case, the available quantity sent to Order Orchestration is based on the standard availability calculation described above. Also, in this case, if there are any open purchase orders for the drop ship item tracked in the Purchase Order Layering table, then the next PO date and quantity from the first Purchase Order Layering record is also passed to Order Orchestration. (Purchase orders for drop ship items are in the Purchase Order Layering table only if they are not generated through customer orders, but are requesting shipment to the warehouse.)
Example:
12 units in warehouse 2 (OROB location = 2)
0 units in warehouse 3 (OROB location = DC; this is the OROB Default Location (K51))
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is:
-
selected: the available quantity reported for each OROB location:
-
2 = 12
-
DC = 9999
-
-
unselected: the available quantity reported for OROB location DC = 12
Note:
If there is a quantity on-hand in the warehouse, but it is not currently available (for example, because it is reserved against an order), then the available quantity reported is 9999.-
Main set items and other non-inventory items: The available quantity reported for the main set item is typically 0; however, if you actually have an available quantity of the item in the warehouse, this quantity is used. To determine the true availability of a set, check the set components and the set quantity of each component required to make up a set, or look up the main set item in Entering Set Information (WSET).
Sample file:
system_cd|location_cd|product_cd|available_qty|next_po_qty|next_po_date|daily_sell_through_qty|sell_qty_multiple|minimum_sell_qty|shrink_rate|sales_velocity
7|1|SKU YELW
SML WMNS|1000|200|2015-12-07||1|||
The system includes empty pipes in the file for data that is not included.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
system_cd |
The company code where the periodic function was submitted. Maps to the Order Orchestration system code. |
|
location_cd |
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is unselected, this is from the OROB Default Location (K51), even if the item is not stored in this warehouse, but is stored in another allocatable warehouse; otherwise, this is the OROB location specified for the warehouse. If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) is selected and the warehouse does not have a OROB location, the information is not sent to Order Orchestration. Maps to a Order Orchestration location. |
|
product_cd |
The item
and SKU. The system includes the full 12 positions for the item and
the full 14 positions for the SKU; for example: |
|
available_qty |
If the Send
Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is
unselected, this is the total quantity available across all allocatable
warehouses; otherwise, this is the total quantity available for the
warehouse. Calculated as: |
|
next_po_qty |
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is unselected, this is the quantity expected on the next open purchase order that might be able to fulfill a new backorder; otherwise, this is the quantity expected on the next eligible open purchase order for that warehouse only. From the Purchase Order Layering table. |
|
next_po_date |
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is unselected, this is the date of the next open purchase order that might be able to fulfill a new backorder; otherwise, this is the date of the next eligible open purchase order for that warehouse only. From the Purchase Order Layering table. |
|
daily_sell_through_qty |
This value is not populated. |
|
sell_qty_multiple |
The Sell Quantity defined for the item. |
|
minimum_sell_qty |
This value is not populated. |
|
shrink_rate |
This value is not populated. |
|
sales_velocity |
This value is not populated. |
Item Availability Updates
The Order Orchestration item availability update process allows Order Orchestration to obtain up-to-date inventory information from Order Administration.
How does the update work?
-
The OBINCIN OB Incremental Inventory Output File (program name PFR0129) periodic function allows you to generate an Incremental Inventory output file for import into Order Orchestration. This file contains inventory updates for a specified company since the last time the periodic function was run. See Oracle Retail Order Orchestration Incremental Inventory Output File for details.
-
The Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability API returns location availability information for a specific product, based on a request from Order Orchestration.
Oracle Retail Order Orchestration Incremental Inventory Output File
Use the OBINCIN OB Incremental Inventory Output File (program name PFR0129) periodic function to generate an Incremental Inventory output file to send to Order Orchestration. This file contains inventory updates for a specified company to send to Order Orchestration.
Include only items with changed availability: When you run this periodic function, the system calculates
the quantity currently available and updates the Virtual current
available field in the Item Warehouse table. If the Send Inventory
by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is unselected,
this is the total quantity available across all allocatable warehouses;
otherwise, this is the total quantity available for the warehouse.
Calculated as: On hand - Protected - Reserved - Reserve Transfer
- Backordered = Quantity available. See Availability for Drop Ship and Non-Inventory Items, including Main
Set Items for a discussion on drop ship and non-inventory
items, such as main set items.
The system compares the quantity in the Virtual current available to the quantity in the Last available sent field in the Item Warehouse table. If the quantities do not match, the system:
-
includes the item in the incremental inventory output file, updating the available_qty in the file with the Virtual current available quantity.
-
updates the Last available sent field with the quantity defined in the Virtual current available field.
Note:
If the quantities in the Virtual current available and Last available sent match, the system does not include the item in the incremental inventory output file.Send inventory by warehouse? You can either map inventory information for individual item warehouses to the related locations in Order Orchestration, or aggregate item warehouse totals across all allocatable warehouses for an item or SKU into a default location representing your distribution center.
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is:
-
selected: the import process includes availability for items flagged OROB eligible if the warehouse has an OROB location specified and the warehouse is flagged as Allocatable. Any purchase order information is related to that warehouse only. Only warehouses whose available quantity has changed are included.
-
unselected: the import process sends the total available quantity for the item in all allocatable warehouses, regardless of whether the warehouse has an OROB location specified, and updates the product location in Order Orchestration using the OROB Default Location (K51). Any purchase order information is the earliest eligible purchase order across all allocatable warehouses.
Example:
Item AB100 is stocked in:
-
Warehouse 1 (allocatable, OROB location = DC1)
-
Available quantity = 100
-
Next purchase order date = 6/30
-
Next purchase order quantity = 15
-
-
Warehouse 2 (allocatable, OROB location = S2)
-
Available quantity = -10
-
No open purchase orders
-
-
Warehouse 3 (allocatable, no OROB location)
-
Available quantity = 5
-
Next purchase order date = 6/28
-
Next purchase order quantity = 50
-
OROB Default Location (K51) is set to DC.
Results when sending by warehouse:
If Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) is selected, update:
OROB location DC1:
-
Available quantity = 100
-
Next purchase order date = 6/30
-
Next purchase order quantity = 15
OROB location S2:
-
Available quantity = -10
-
No purchase order information is included
Warehouse 3 is not included because there is no OROB location.
Results when sending sum:
If Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) is unselected, update:
OROB location DC:
-
Available quantity = 95 (warehouse 1 + warehouse 2 + warehouse 3)
-
Next purchase order date = 6/28
-
Next purchase order quantity = 50
See Availability for Drop Ship and Non-Inventory Items, including Main Set Items for more information on how the system determines the available quantity for drop ship items, non-inventory items, and main set items.
Location of file: The OROB_DIRECTORY_PATH in Working with Admin Properties (CPRP) defines the location where the system downloads the Incremental Inventory output file. See Order Orchestration’s Product, Product Location, and Incremental Inventory Import Process for processing details.
Name of file: The system names the file
INCREMENTAL_INVENTORY_999_YYMMDDHHMMSS.TXT, where 999 is the company code where you submitted the periodic function
and YYMMDDHHMMSS is the date and time when the
download occurred. The file has a .tmp suffix while it is being generated.
Application log: The system writes any messages related to the download to the application log.
Sample file:
system_cd|location_cd|product_cd|available_qty|next_po_qty|next_po_date
9|1|2006 PINK
S REG|10|20|2015-10-31
The system includes empty pipes in the file for data that is not included.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
system_cd |
The company code where the periodic function was submitted. Maps to the Order Orchestration system code. |
|
location_cd |
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is unselected, this is from the OROB Default Location (K51), even if the item is not stored in this warehouse, but is stored in another allocatable warehouse; otherwise, this is the OROB location specified for the warehouse. If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) is selected and the warehouse does not have a OROB location, the information is not sent to Order Orchestration. Maps to a Order Orchestration location. |
|
product_cd |
The item
and SKU. The system includes the full 12 positions for the item and
the full 14 positions for the SKU; for example: |
|
available_qty |
If the Send
Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is
unselected, this is the total quantity available across all allocatable
warehouses; otherwise, this is the total quantity available for the
warehouse. Calculated as: |
|
next_po_qty |
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is unselected, this is the quantity expected on the next open purchase order that might be able to fulfill a new backorder; otherwise, this is the quantity expected on the next eligible open purchase order for that warehouse only. From the Purchase Order Layering table. |
|
next_po_date |
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is unselected, this is the date of the next open purchase order that might be able to fulfill a new backorder; otherwise, this is the date of the next eligible open purchase order for that warehouse only. From the Purchase Order Layering table. |
Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability API
Use the Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability API to return location availability information for a specific product, based on a request from Order Orchestration.
Process overview: When a remote system requests inventory information, Order Orchestration checks for current inventory information from Order Administration if:
-
the system representing Order Administration is configured in Order Orchestration as an online system, and
-
there is a product location record in Order Orchestration indicating that the item is stocked in a Order Administration warehouse. This record is normally created automatically through Order Orchestration’s Product, Product Location, and Incremental Inventory Import Process.
If the above conditions are true, Order Orchestration automatically checks the item’s inventory information in Order Administration, and updates the product location record for the product in the OROB Default Location (K51) if the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is unselected; otherwise, it updates the location matching the warehouse’s OROB location. The rules used to update the product location’s Available quantity, Next PO quantity, and Next PO date are the same as those used for Order Orchestration’s Product, Product Location, and Incremental Inventory Import Process.
Setup:
-
Complete all the setup required for Order Orchestration’s Product, Product Location, and Incremental Inventory Import Process.
-
Flag the Order Administration system in Order Orchestration as Online.
-
Complete the setup required for the Order Orchestration Availability API.
Order Orchestration Availability API setup: The CWServiceIn Web Service allows an external system to post the Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability Request directly to Order Administration.
Web service authentication? Use the Work with Web Service Authentication (WWSA) menu option to define a valid user and password for basic web service authentication, or client ID and client secret if using OAuth.
Web service type? You can use the CWServiceIn RESTful web service for the Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability API. You POST the Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability Request to the web service’s URL, or endpoint, of the RESTful service. The web service routes the messages sent to the endpoint and dispatches them to the Item Availability Update process. When the Item Availability Update process generates an Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability Response, the CWServiceIn web service routes the response.
Determine the endpoint: The individual
URL for the CWServiceIn RESTful service used for the Order Orchestration
Product Inventory Availability API uses the following format: http://server/oms/sxrs/Inventory, where server identifies the application server where the RESTful service
is located.
Errors: If the Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability Request fails, the response returns with an error message. Possible errors are:
| Error Message | Reason |
|---|---|
|
Message is Invalid |
The message is not in the correct JSON format. |
|
Product Code in Invalid |
The product code must be a valid item in Order Administration. |
|
System Code in Invalid |
The system code must be a valid company code in Order Administration. |
Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability Request
See Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability: Sample Messages for sample messages.
| Name | Type | Length | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
urlString |
Identifies
the URL for the Order Administration web service. The individual
URL for the CWServiceIn RESTful service uses the following format: |
||
|
productCd |
alpha |
12 |
The Order Administration item number and SKU. |
|
systemCd |
numeric |
3 |
The Order Administration company code. |
|
Response |
Not used. |
||
|
systemId |
Not used. |
||
|
timeOut |
Not used. |
Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability Response
See Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability: Sample Messages for sample messages.
| Name | Type | Length | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ProductCode |
alpha |
12 |
The item
and SKU. The system includes the full 12 positions for the item and
the full 14 positions for the SKU; for example: |
|
LocationCode |
numeric |
3 |
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is unselected, this is from the OROB Default Location (K51), even if the item is not stored in this warehouse, but is stored in another allocatable warehouse; otherwise, this is the OROB location specified for the warehouse. If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) is selected and the warehouse does not have a OROB location, the information is not sent to Order Orchestration. Maps to a Order Orchestration location. |
|
AvailableQuantity |
If the Send
Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is
unselected, this is the total quantity available across all allocatable
warehouses; otherwise, this is the total quantity available for the
warehouse. Calculated as: A negative quantity indicates the item in on backorder. See Availability for Drop Ship and Non-Inventory Items, including Main Set Items for a discussion on drop ship and non-inventory items, such as main set items. |
||
|
NextPOQuantity |
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06)system control value is unselected, this is the quantity expected on the next open purchase order that might be able to fulfill a new backorder; otherwise, this is the quantity expected on the next eligible open purchase order for that warehouse only. From the Purchase Order Layering table. |
||
|
NextPODate |
If the Send Inventory by Warehouse to OROB (L06) system control value is unselected, this is the date and time, in YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS format, of the next open purchase order that might be able to fulfill a new backorder; otherwise, this is the date of the next eligible open purchase order for that warehouse only. From the Purchase Order Layering table. |
Order Orchestration Product Inventory Availability: Sample Messages
Samples of the Order Orchestration Availability messages are presented below.
Successful Order Orchestration Availability Request:
{"urlString":"https://wbooms55app2/oms/sxrs/Inventory","productCd":"LOCATE","systemCd":"7","response":"-1","systemId":425430,"timeOut":30000}
Order Orchestration Availability Response:
[
{
"ProductCode": "LOCATE",
"LocationCode": "S2",
"AvailableQuantity": -10,
"NextPOQuantity": 0,
"NextPODate": ""
},
{
"ProductCode": "LOCATE",
"LocationCode": "1",
"AvailableQuantity": 100,
"NextPOQuantity": 15,
"NextPODate": "2016-01-30
12:00:00 AM"
}
]
Unsuccessful Order Orchestration Availability Request:
{"urlString":"https://wbooms55app2/oms/sxrs/Inventory","productCd":"ITM","systemCd":"7","response":"-1","systemId":425430,"timeOut":30000}
Order Orchestration Availability Response:
{"error": "Product Code is Invalid"}
Brokered Backorder Integration with Order Broker
Brokered backorder: Use the brokered backorder integration with Order Orchestration to automatically send backordered lines to the Order Broker module in Order Orchestration for fulfillment.
-
If the Use OROB for Fulfillment Assignment (M31) system control value is unselected, the system sends eligible backordered items to the Order Broker for fulfillment. The Order Broker will choose the best store location to fulfill and ship the item to the customer. Items that are in stock follow normal reservation and fulfillment processing.
-
If the Use OROB for Fulfillment Assignment (M31) system control value is selected, the system bypasses reservation and places all eligible items on backorder, even if the item is available in an Order Administration warehouse. The Order Broker will choose the best store location or Order Administration location to fulfill and ship the item to the customer.
-
If the Use OROB for Ship for Pickup Fulfillment Assignment (M34) system control value is set to ALWAYS, the system bypasses reservation in order to send eligible items on a ship-for-pickup order to the Order Broker for fulfillment assignment. In this situation, the fulfilling location may be a store location or an Order Administration warehouse and the merchandise is shipped to the customer’s selected store for pickup.
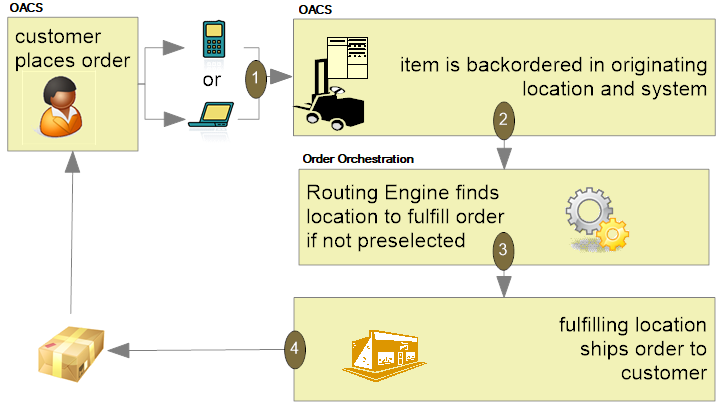
When using Order Orchestration for fulfillment assignment, the fulfilling location can be a store location or an OACS warehouse location. In addition, for ship-for-pickup orders, the fulfilling location ships the order to the customer’s selected store for pickup.
Unlike the merchandise locator API, the brokered backorder integration with Order Orchestration enables you to fulfill these orders automatically “behind the scenes” using business rules you have configured in Order Orchestration and Order Administration, without the need to select a fulfilling location; the Order Broker selects the location for you.
For more information: See Order Orchestration Configuration and Brokered Backorders.
Ship-for-Pickup Orders
Ship-for-pickup order: Use the ship-for-pickup integration with Order Orchestration to send the merchandise for an order to a designated store, where the customer can pick it up. The Order Orchestration integration facilitates communication between Order Administration and the designated store location, so the store receives notification that the order is in transit, and sends notification back to Order Administration after the merchandise is received and when the customer picks up the order.
The items on the order do not need to be stocked in the store. In addition, the Use OROB for Ship for Pickup Fulfillment Assignment (M34) system control value controls whether Order Administration fulfills the order or whether the order is sent to Order Orchestration for fulfillment assignment.
-
If this system control value is set to NEVER, Order Administration fulfills the order and sends the items on the order to the store selected for customer pick up during pick slip generation and/or drop ship processing. In this situation, if an item on the order is not in stock, the item is placed on backorder until it can be fulfilled by Order Administration. The order can include up to two locations for processing:
-
the originating, or placed, location that creates the order. For ship-for-pickup orders, the originating location is always an Order Administration warehouse.
-
the fulfilling, or sourcing, location that provides the inventory for the order. If the Use OROB for Ship for Pickup Fulfillment Assignment (M34) system control value is set to NEVER, this is always an Order Administration warehouse.
-
the pickup location where the customer picks up the items on the order. For ship-for-pickup orders, this is always the store location the customer selected for pickup.
-
-
If this system control value is set to ALWAYS, the system sends the order to Order Orchestration for fulfillment assignment after the order is created. In this situation, Order Orchestration determines the best location to fulfill the order and the order can include up to three locations for processing:
-
the originating, or placed, location that creates the order. For ship-for-pickup orders, the originating location is always an Order Administration warehouse.
-
the fulfilling, or sourcing, location that provides the inventory for the order. If the Use OROB for Ship for Pickup Fulfillment Assignment (M34) system control value is set to ALWAYS, this is the location the Order Broker selected for fulfillment of the order. This location can be a store location or an Order Administration warehouse.
-
the pickup location where the customer picks up the items on the order. For ship-for-pickup orders, this is always the store location the customer selected for pickup.
-
If Order Orchestration determines that Order Administration is the best location to fulfill the order, the system creates a new retail pickup order in Order Administration to fulfill the ship-for-pickup order.
Important:
Regardless of when you send ship-for-pickup orders to Order Orchestration, in order to use ship-for-pickup processing, you must select the Enable Ship For Pickup option on the Organization window in Order Orchestration. Once you enable ship for pickup, the Ship for Pickup Enabled Date displays on the Organization window and cannot be changed.Examples: Examples of ship-for-pickup include the following.
Example 1 (three different locations; Order Orchestration determines fulfilling location):
The customer places an order on the web site (originating location A, Order Administration) and wants to pick the order up at store location B. Order Orchestration selects store location C as the fulfilling, or sourcing, location. Store location C ships the inventory to store location B, where the customer can pick it up.
Example 2 (fulfillment location and pickup location are the same; Order Orchestration determines fulfilling location):
The customer places an order on the web site (originating location A, Order Administration) and wants to pick the order up at store location B. Order Orchestration selects store location B as the fulfilling, or sourcing, location. Once the order is ready at store location B, the customer can pick it up.
Example 3 (originating location and fulfillment location are the same); Order Orchestration determines fulfilling location:
The customer places an order on the web site (originating location A, Order Administration) and wants to pick the order up at store location B. Order Orchestration selects warehouse location A, Order Administration, as the fulfilling, or sourcing, location. Order Administration ships the items on the order to store location B. Once the order is ready at store location B, the customer can pick it up.
Example 4 (originating location and fulfillment location are the same; items on the order are shipped to the store during pick slip generation/drop ship processing):
The customer places an order on the web site (originating location A, Order Administration) and wants to pick the order up at store location B. Order Administration fulfills the items on the order and during pick slip generation, ships the items on the order to store location B. Order Orchestration manages communication between Order Administration and store location B. Once the order is ready at store location B, the customer can pick it up.
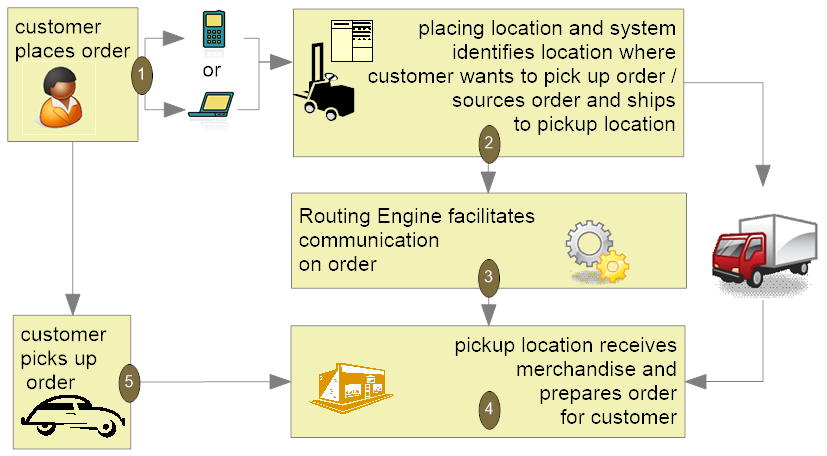
For more information: See Order Orchestration Configuration and Ship-for-Pickup Orders.
Retail Pickup (including Ship-for-Pickup) and Delivery Orders from Order Orchestration
Purpose: Use the retail pickup and delivery order integration with Order Orchestration to fulfill orders received from Order Orchestration. The originating location may be a store location or an Order Administration order.
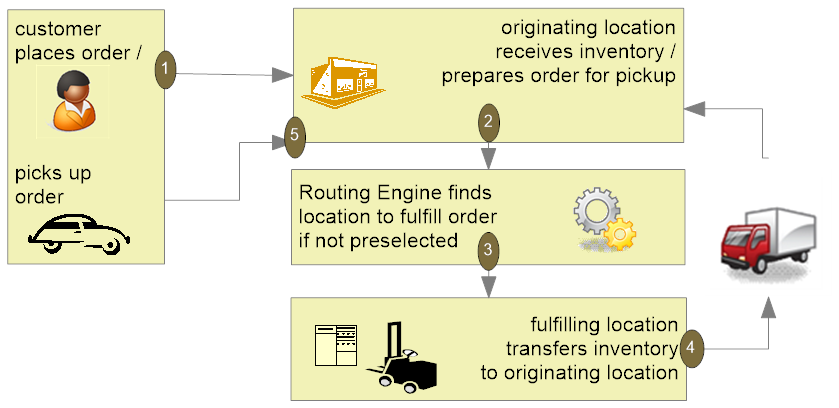
Retail pickup or ship-for-pickup order: The Order Broker sends a retail pickup order or ship-for-pickup order to Order Administration for fulfillment when the customer would like to pick up the order at a retail location. The ship-to address on the order sent to Order Administration for fulfilment is the name and address of the pickup store location. If Order Orchestration sends a ship-for-pickup order to Order Administration for fulfillment, the system treats the ship-for-pickup order the same as a retail pickup order.
Delivery order: The Order Broker sends a delivery order to Order Administration for fulfillment when the customer would like the order shipped to his or her address. The ship-to address on a delivery order is the name and address of the customer.
For more information: See Order Orchestration Configuration and Retail Pickup (including Ship-for-Pickup) or Delivery Orders.
Store Pickup Orders
Store pickup order: Use the store pickup integration with Order Orchestration to send orders to an external retail location where the merchandise is already available for pickup. Unlike a ship-for-pickup order, a store pickup order does not require Order Administration to transfer the inventory to the store. The ship-to address on a store pickup order sent from Order Administration to the Order Broker is the name and address of the originating store location.
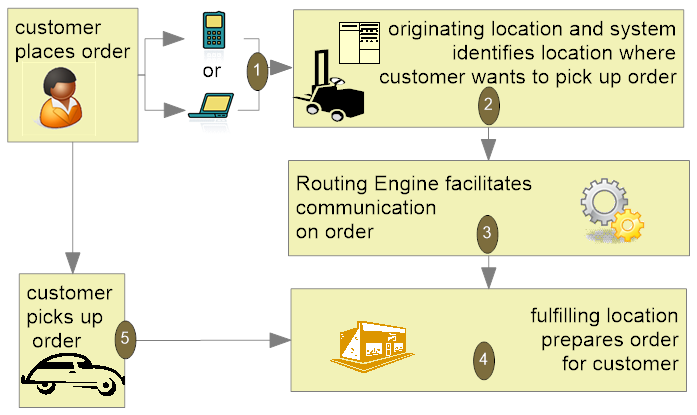
For more information: See Order Orchestration Configuration and Store Pickup Orders.
Merchandise Locator Searching
Merchandise locator searching: This integration with Order Orchestration provides a way to search for a location across the enterprise where the customer can pick up an item. This option is available in item availability, order entry, and order maintenance. The results are informational only.
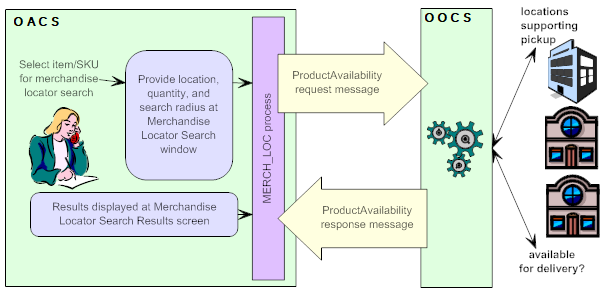
For more information: See Order Orchestration Configuration, and the Merchandise Locator API.
Store Connect
Overview: Store Connect is a module of Order Orchestration that provides store associates with a suite of screens to process delivery orders (brokered backorders from Order Administration) or store pickup orders. Store Connect is represented in Order Orchestration as a separate integrated system, and stores using Store Connect identified as locations; however, the Order Broker assigns and tracks orders assigned to Store Connect locations as it does for any other orders.
Types of orders: When using Order Administration, only delivery orders (brokered backorders) and store pickup orders can be fulfilled through Store Connect:
-
Brokered backorders (delivery orders): When Order Orchestration receives a brokered backorder from Order Administration, it assigns the order to a fulfilling location using standard Order Orchestration rules. If the selected location is part of the Store Connect system, the associates use Store Connect to accept, print, pick, and ship the order, and Order Administration tracks the activity as with any other brokered backorder.
-
Store pickup orders: Selecting a fulfilling location for a store pickup order uses standard Order Orchestration rules; however, since Store Connect is represented in Order Orchestration as a separate system, you need to associate Store Connect store locations with that system code, either through the Store Cross Reference record or through a default specified in a system control value. The store associate uses Store Connect to accept, print, and pick the order, and to confirm customer pickup.
For more information: See:
-
the Order Orchestration Operations Guide and online help
Summary of Order Types for the Order Orchestration Integration
The different types of orders that Order Administration sends to or receives from Order Orchestration are summarized below. This summary is from the Order Administration perspective.
| Brokered Backorder | Delivery | Store Pickup | Retail Pickup | Ship-for-Pickup | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
used to: |
Create an
order in Order Administration and send backordered items to the
Order Broker so that the items can be assigned to locations for fulfillment.
Additional settings allow you to send all items to Order Broker to
determine the fulfilling location even if the item is in stock in
the warehouse.
Note: A brokered backorder order type does not exist in Order Orchestration. |
Receive and fulfill an order from Order Orchestration and ship the order to the customer’s ship to address. |
Create an order in Order Administration and send the order to Order Orchestration to notify a store location that already has the inventory available that a customer will pick up the order. |
Receive and fulfill an order from Order Orchestration and ship the order to the customer’s selected store for pickup. Ship-for-pickup orders that originate in a store come into Order Administration as retail pickup orders. |
Create an order in Order Administration and ship the order to a store location for customer pickup if the inventory is not already available at that store location. A system control value setting defines whether ship-for-pickup orders are immediately sent to Order Orchestration to determine the fulfilling location, similar to a brokered backoder, or are fulfilled by an Order Administration warehouse and then sent to Order Orchestration to complete the process. |
|
originating location is where the order is placed: |
This is an Order Administration warehouse. |
This is a store location but can be an Order Administration warehouse if the order originated in Order Administration and Order Orchestration assigned an Order Administration warehouse as the fulfilling location. |
This is an Order Administration warehouse. |
This is a store location. |
This is an Order Administration warehouse. |
|
fulfilling location is where the order is fulfilled: |
This can be a store location or an Order Administration warehouse. |
This is an Order Administration warehouse. |
This is a store location. |
This is an Order Administration warehouse. |
This can be an Order Administration warehouse or a store location. |
|
pickup location is where the order is picked up by the customer: |
Not applicable if the order is shipped to the customer. |
Not applicable; the order is shipped to the customer. |
This is a store location. |
This is a store location. |
This is a store location. |
|
order shipped to: |
Customer. |
Customer. |
Not applicable; the fulfilling location and pickup location are always the same. |
Store location; this is typically the originating store location. |
Pickup store location. |
Note:
-
When Order Administration is the originating location of a delivery order, the order is identified as a brokered backorder in Order Administration. To Order Orchestration it is considered a delivery order.
-
When Order Administration is fulfilling a delivery order, the order is identified as a delivery order in Order Administration.
-
When Order Administration is the originating location of a ship-for-pickup order, the order is identified as a ship-for-pickup order. A system control value setting defines whether ship-for-pickup orders are immediately sent to Order Orchestration to determine the fulfilling location, similar to a brokered backorder, or are fulfilled by an Order Administration warehouse and then sent to Order Orchestration to complete the process.
-
When Order Administration is the fulfilling location of a ship-for-pickup order, the order is identified as a retail pickup order in Order Administration.
-
Order Administration can only be the fulfilling location of a retail pickup order.
-
Order Administration can only be the originating location of a store pickup order.
Oracle Retail Promotion Engine Integration
Order Administration is integrated to the Oracle Retail Promotion Engine Cloud Service (ORPE) following the v23.2.401.0 update. When configured, Order Administration will bypass some of the inherent promotional pricing options during order entry, making a REST call to provide the order (cart) details for evaluation by ORPE. The promotion engine performs a comprehensive evaluation of the cart, identifies the applicable offers, and responds with the discounted price applied for qualifying merchandise lines. If shipping rewards are included in the response, Order Administration performs additional validation and calculations before they are applied to the order.
Retailers define deals and promotions using Customer Engagement and then automatically propagate the promotion data to ORPE. This allows the retailers to submit orders (carts) from various external systems (ecommerce, point of sale, order management, and so on) to be centrally evaluated against a single source of promotion data.
The following features in Order Administration will communicate with ORPE for applying promotions:
-
Modern View Order Entry
-
Classic View Order Entry when editing / accepting a batch of orders in error
-
CWOrderIn version 12.0 when it indicates discounts are not already applied
-
Customer Membership Child Order Generation (EGMO)
The following features will not communicate with ORPE: Order Maintenance, OB Fulfillment Order Creation, and ChannelAdvisor.
Note:
Order Administration Modern View Order Summary does NOT communicate with ORPE when an existing order is maintained. If a new line is added in maintenance, it will be priced based on the Order Administration price method hierarchy. If an existing line quantity is changed in maintenance, the price will remain unchanged. The line will not be re-evaluated by Order Administration, and it will not be sent to ORPE for evaluation.Order Administration Classic View does not allow the reprice function with ORPE enabled, nor does it call ORPE during interactive order entry or order maintenance. However the Edit/Accept batch process triggered from Classic View does call ORPE to evaluate orders which have corrected within the Error Batch.
All promotion details successfully applied by ORPE are stored for display within the Modern View user interface (UI) and incorporated into various outbound API’s and integration files including:
-
Modern View Order Summary and Invoice tabs
-
CWInvoiceOut version 7.0
-
CWOrderOut version 12.0
-
CWEmailOut version13.0
-
ReSA RTLog Output File
-
ORCE POSLog Output File
ORPE Setup Requirements
Required Properties: The following properties are available to configure the integration with ORPE:
-
oms.promotion.engine.service.url (PROP): The full URL for the promotion engine service. Provided by your Oracle representative. Defaults to blank.
-
oms.promotion.engine.service.timeout (CPRP): The number of seconds to wait before deal requests from Order Administration to the ORPE Promotion time out. Defaults to 500 seconds.
-
oms.promotion.engine.service.token.url (CPRP): The URL to use when requesting a token for Oauth authentication. Provided by your Oracle representative. Defaults to blank.
-
orce.coupon.service.url.suffix (PROP): The suffix to append to the ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX for Serialized ORCE Coupon Service for validation and redemption of a serialized coupon.
Note:
When calling the ORCE Coupon Service, Order Administration builds the URL using the ORCE_CUSTOMER_SERVICE_PREFIX, SCV L50 and the orce.coupon.service.url.suffix value.Authentication configuration: To configure the promotion engine integration, use ORPE Promotion and ORCE Coupon Service at the Work with Outbound Web Service Authentication screen (WWSA). Only OAuth authentication is supported. Client ID and Client Secret will be delivered blank by default for each company.
Required system control value settings: Use the following system control values to enable use of ORPE:
-
Use ORPE Promotion Engine (M77): Select this system control value to enable use of ORPE for a specific company. Required for ORPE Integration.
-
Price Override Reason for ORPE Discounts (M78): Select the price override reason code to apply to order lines that are discounted through use of the Promotion Engine. Required for ORPE Integration.
-
Use ORCE Serialized Coupons (M79): Select this system control value to use Serialized Coupons with ORPE.
-
ORCE Serialized Coupon Prefix Length (M80): This system control value stores the Serialized coupon codes prefix length value. It must match the value defined in Property Configuration Promotion Coupon Length within ORCE.
Also, the following existing system control values are used:
-
Allow Manual Entry of Promotion Code (I63): Must be selected to see the new Coupons section within in the Order Summary panel.
-
ORCE Integration Item ID (L38): Required for ORPE Integration.
-
ORCE Organization Descriptor (L50): Required for Serialized Coupons with ORPE.
-
Display Order Line Discount Messages (F01): Impacts display of ORPE promotion details.
-
Display Discount On Order Recap Screen (D38): Impacts display of ORPE promotion details.
-
Default Location for ORCE Integration (K69): Required for integration with ORCE and ORPE.
Order API Enhancements
The Order API (CWOrderIn) now allows the ability to indicate the order should be sent to ORPE for promotions to be applied. Additionally, it includes new attributes to allow an external merchant application to pass discount details already applied by ORPE externally. The changes include:
-
The already_eval_by_promote attribute was renamed to already_eval_by_promo_engine.
-
A new repeating element (Shipping_Rewards) was added within the ship to element, allowing retailers to include shipping award details that were already applied by an external system.
A new repeating element (Discount_Rewards) was added within the item element, allowing retailers to include order line discount details that were already applied by an external system.
Note:
The Order API does not currently support ORCE coupon codes or targeted customer promotions when passed in from an external merchant application. See the Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1) for more information.For more information on Order API documentation and for a comprehensive list of available attributes, sample XML messages, DTD’s and XSD’s, see the Web Services Guide on My Oracle Support (ID 2953017.1).
Deal Types and Promotions
The Order Administration integration now supports the ORPE deal types included below. These deal types are configured in Customer Engagement.
-
BOGO: Buy X Get X and Buy X Get Y
-
LINE ITEM: Line Item Discount
-
GROUP PRICE: Kit
-
SUBTOTAL: Transaction Discount
For each supported deal type, Order Administration will allow shipping awards to optionally apply an Override Shipping Method (Ship Via) and/or the ability to define a discount from the following options:
-
an Override Price (flat shipping fee),
-
an Amount Off (Order Administration deducts the value from the shipping calculation) or
-
a Percent Off (Order Administration calculates the discount percentage amount then deducts the value from the shipping calculation)
Note:
All Shipping Award discount options are applied within Order Administration as a shipping override.The Order Administration integration currently supports product and coupon promotion types (both single-use and multi-use coupons) and incorporates cart data for evaluation of location qualifiers and promotion audience rules (exclusive and non-exclusive).
Note:
Coupon Codes are not supported through the Order API. They are only supported when entered through Modern View Order Entry.Coupons the integration with ORPE supports two options for coupon promotions, (Serialized and Non-Serialized).
-
A Serialized Coupon allows the retailer to generate coupons, each with a unique serial number, generally for a one-time use. Depending on user authority, a contact center agent may have the ability to allow a previously redeemed serialized coupon to be submitted to ORPE. In this situation, ORPE will apply the coupon discount as long as the cart meets the coupon requirements.
-
If the Contact Center user has authority to the Allow Redeemed ORCE Serialized Coupon to be Overridden secured feature, they can submit a previously redeemed serialized coupon to ORPE by clicking a new attempt Reuse button. For example: If the coupon represented a 10% discount on handbags, it would be automatically applied as long as the cart included a handbag.
-
-
A Non-Serialized Coupon allows a retailer to define a coupon code for the promotion which can be used multiple times. For example, the coupon code ‘SHOE20’ may represent a coupon code that a customer can use multiple times to receive a 20% discount on a shoe purchase.
For Failed redeems due to a communication failure with ORCE or another issue, the retailer can generate a report through Customer Reports or RDS based on the Order Transaction History record where the serialized coupon was not redeemed.
About location qualifiers: When submitting the cart information to ORPE, Order Administration includes location identifier (value from SCV K69 – Default Location for ORCE Integration), so that ORPE can evaluate and either qualify or exclude the cart based on location rules defined for the promotion in ORCE.About audience rules: Audience rules can be defined within each promotion created from the ORCE UI. By default, the audience defaults to All which means that the promotion is available to anyone. (Everyone who buys the items included in the promotion, gets the offer discount.) However, the retailer can optionally define the promotion audience as Exclusive or Non-Exclusive and include additional selections options.
Note:
To identify customers that are included in exclusive promotions, Order Administration first makes a call to ORCE using the retrieveCustomer method. Any Exclusive Promotion details included in the response are then submitted with the cart for ORPE evaluation. If the cart qualifies for the exclusive promotion, the respective discounts are applied to the order.Targeted Customer Promotions: the integration with ORPE supports applying customer targeted promotions tied to a customer in ORCE. These promotions are set up as Audience Rules within the promotion in ORCE.
-
Exclusive Audience: When the retailer defines the promotion audience as Exclusive, this means that only the customers identified in the target group (segment) are eligible to receive the promotion.
-
Non-Exclusive Audience: When the retailer defines the promotion audience as Non-Exclusive, this means that all customers are eligible to receive the promotion.
During Modern View Order Entry, if the customer exists in ORCE and qualifies for an Exclusive Promotion, that will automatically be passed into ORPE as additional qualifiers in the cart and the respective discounts are applied to the order.
Entitlement Coupons
Order Administration supports Entitlement coupons to be included from an external system when submitting the order using the Order API as well as providing the ability to retrieve and apply available entitlement coupons based on a customer's loyalty cards during Modern View Order Entry.
Entitlements are a type of coupon code that triggers an offer/deal that is tied to a loyalty program. Entitlements are not set up the same as coupons. First the customer must be set up/enrolled in a loyalty program in Customer Engagement (ORCE), then based on points earned an entitlement coupon is issued, specific to that customer.
Entitlements are supported when:
-
ORCE Customer Integration (L37) system control value is set to INTERACT
-
Use ORCE Loyalty (M06) system control value is set to Yes
-
Use ORPE Promotion Engine (M77) system control value is set to Yes
-
The Source Code assigned to the Order has the Price Method set to Regular Plus Reprice
-
There is at least one Entitlement coupon for the selected Loyalty Card
Within Order Entry, the number of available entitlement coupons is displayed on the Select Card window. Once a loyalty card is assigned, entitlement coupons will be retrieved from Customer Engagement (ORCE) for that specific card only. You cannot apply entitlements associated to other loyalty cards not assigned to the order.
In the Order Summary panel, if entitlement coupons are available, an Entitlement Coupons available link or edit icon will be displayed within the Customer section. Advance into the Entitlement Coupons window to select/deselect which coupons should be submitted for evaluation during the order review step.
At final order submit, each Entitlement coupon that is successfully applied by ORPE is:
-
Redeemed in ORCE. An Order Activity record is written for each successful or failed redemption request.
-
Stored in discount history coupon tables.
-
Displayed in a tooltip for a specific order line in MV Order Summary and Invoice tabs. Additionally, is included in the merchandise and shipping discount totals within the Order Totals section of the Order Summary tab. Only displayed if Display Order Line Discount Message (F01) system control value is set to Y.
-
Displayed in the Promotion Details drawer in MV Order Summary. Only displayed if Display Discount on Order Recap Screen (D38) system control value is set to Y.
Entitlement coupons that apply merchandise and shipping discounts are included in:
-
Customer Engagement POSLog within the RetailPriceModifier object.
-
ReSA RTLog within the IDISC record. The Coupon Reference Number value is populated with a coupon_type of ‘entitlementCoupon’.
Order Entry Changes in Modern View
Modern View Order Entry has been changed when SCV Use ORPE Promotion Engine (M77) is enabled to support the deal types and promotions. The following now occurs:
-
The Promotion Code and the Discount Percent fields are hidden from view.
-
When Allow Manual Entry of Promotion Code (I63) system control value is enabled there is a new Coupons section in the Order Summary panel.
-
When using a source code with price method Reg Plus Reprice and the Add Coupon Code button is selected from the Coupons section of the Order Summary panel, a modal window opens so that the user can enter coupon codes. Entered coupons are evaluated during order review, rather than immediately upon closing the modal window, since additional order changes may be incorporated.
-
If the source code used at order entry has price method other than Reg Plus Reprice, a warning message is displayed within the Coupons section advising Source code does not support Coupons and the Add Coupon Code button is not displayed.
-
-
At the Review step, or after Refresh Order if changes were added, the Coupons section may display a message indicating that Codes were not applied; this occurs if any serialized coupons were previously redeemed or coupons were submitted for evaluation but were not applied.
-
At the Final Submit step, a System Update entry is written in the Order Activity tab when:
-
a coupon code is entered but not successfully applied by ORPE.
-
a serialized coupon is successfully applied by ORPE and it is successfully redeemed or not.
-
If the Contact Center user has authority to the Allow Redeemed ORCE Serialized Coupon to be Overridden secured feature, they can submit a previously redeemed serialized coupon to ORPE by clicking a new Attempt Reuse link. For example: If the coupon represented a 10% discount on handbags, it would be automatically applied as long as the cart included a handbag.
Discount Display in Modern View Order Entry and Summary
Item Level Discounts
When the offer price is greater than the unit price, the system now displays the offer price with a strike through before the discounted Unit Price. This is controlled by Display Order Line Discount Messages (F01) system control value.
Additionally, hovering over a new icon will display the discount details for each promotion applied, including the unit discount amount and the associated deal description. If the promotion was triggered by a coupon, the coupon code is included in parenthesis following the deal description.
Order Level Discounts
The Order Total section now displays an icon in front of each of the labels that include an ORPE discount (Merchandise and/or Shipping). This is controlled by Display Discount On Order Recap Screen (D38) system control value.
Additionally, an informational message will display below the totals for each ORPE discount type (Merchandise and/or Shipping) showing the total promotion discounts for the order.
Note:
The calculated Merchandise Discounts and Shipping Discounts are limited to discounts applied by ORPE. If additional discounts were applied based on price methods, manual price overrides, and so on, those discounts would not be reflected in the Merchandise Discounts or Shipping Discounts.When no ORPE promotion discounts have been applied to the order, but there is a delta between the offer price and the actual selling price (due to price method discount, price overrides, and so on) an Order Discount informational message will display below the totals. The Order Discount value is a calculation of the sum of the extended offer prices for all lines, minus the total extended selling price for all lines.
Promotion Details
For orders including promotional discounts applied by ORPE (or submitted through the Order API with the already_eval_by_promo_engine attribute set to Y and containing reward data) a Promotion Details button will display within the Ship To section of Modern View Order Summary. Summary level promotion details per ship-to will be displayed in this panel.
From the Invoices tab, once an invoice has been selected the same item level and order level promotion discount data is available, however the lines displayed will be limited to those included on that specific invoice.
When there is a communication failure (error response, timeout) preventing Order Administration from successfully receiving the applyDeals response (via Modern View Order Entry, Error Batch Edit/Accept Processing or the Order API),details are written to the ORPE log.
If the error results from an order that was submitted from MV Order Entry, prior to the 'final submit', communication message advising that a communication error occurred is displayed.
If the error results from an order that was submitted from MV Order Entry, during the 'final submit', a snackbar message advising that a communication error occurred is displayed.
Discount History
When ORPE is enabled, additional order line discounts are captured and stored in the discount history tables. This includes automatic pricing/discounting as well as manual discounting performed in Modern View Order Entry and Maintenance, Classic View Order Entry and Maintenance, discounts relating to loyalty awards applied and discounts assessed on orders submitted via the CWOrderIn API. Individual discount details are displayed within Modern View Order Summary and passed in CWInvoiceOut and CWOrderOut.
The ReSA RTLog and the ORCE POSLog includes individual discount details for promotions and writes a delta record to make up the difference between the offer price and the discounted price, after the promotion discounts have been incorporated.
Pricing Upload Interface
Pricing Upload Interface allows you to upload Special Pricing by Source records and Quantity Price Matrix Detail records from an external system.
Special pricing by source allows you to define special pricing for an item that is ordered for the specified source code. The system applies the item discount automatically when the customer orders the item in the required quantity from the source code. You can define a discount price for regular customers and associate customers; the system updates the order line with *Special Source Price as the pricing method. You can create, review, and update special pricing by source on the Work with Special Source Price Screen in the Working with Source Codes (WSRC) menu option.
Quantity price matrix pricing allows you to define special pricing for a specific item and SKU, item, or item category. You can define additional pricing for a specific sold to customer, customer price group, source code, and item category. The system updates the order line with *Qty Price Matrix as the pricing method. You can create, review, and update quantity price matrix pricing on the Work with Quantity Price Matrix Details Screen and Work with Quantity Price Matrix Specials Screen in the Working with Quantity Price Matrix (WQPM) menu option.
In this topic:
- Pricing Upload Process
- Pricing Upload Table
- Pricing Upload Interface Errors
- Uploading Special Pricing by Source Records
- Special Pricing by Source Table Updates
- Uploading Quantity Price Matrix Detail Records
- QPM Detail Table Updates
For more information: See Work with Pricing Upload (WPUP).
Pricing Upload Process
Use the following steps to upload Special Pricing by Source records and Quantity Price Matrix Detail records from an external system.
| # | Step |
|---|---|
|
1. |
Populate the Pricing Upload Table with Special Pricing by Source and Quantity Price Matrix Detail records from an external system. |
|
2. |
Review, and optionally change, the Pricing Upload records in the Work with Pricing Upload (WPUP) menu option. |
|
3. |
When you are ready to upload the records from the Pricing Upload table, use the Work with Pricing Upload Screen to submit the Pricing Upload process. The Record Type field indicates whether the record is a Special Pricing by Source Upload record or Quantity Price Matrix Detail Upload record.
Scheduling the Pricing Upload process: You can also schedule the Pricing Upload process to run periodically by setting up the RIPRCUP periodic function using the PFRRIPRCUP program. See Scheduling Jobs for background. |
Pricing Upload Table
This table contains Special Pricing by Source Upload records and QPM Detail Upload records. You need to populate this table to create, update, and delete Special Pricing by Source records and QPM Detail records through the Pricing Upload Process.
Note:
It is your responsibility to populate this table with pricing information from an external system.| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Company # |
A code for the company associated with the Pricing Upload record. Company codes are defined in and validated against the Company table. Special Pricing by SourceCorresponds to the Company field in the Special Pricing by Source table. QPM DetailCorresponds to the Company field in the QPM Detail table. Numeric, 3 positions; required. |
| Sequence # |
A unique number assigned to each Pricing Upload record. Numeric, 9 positions; required. |
| Record Date |
The date the Pricing Upload record was created. Numeric, 7 positions (CYYMMDD format); optional. |
| Record Type |
The type of Pricing Upload record. Valid values:
Alphanumeric, 3 positions; required. |
| Request Type |
Indicates whether the Pricing Upload record creates, updates, or deletes a record in the Special Pricing by Source table or QPM Detail table. Valid values:
Alphanumeric, 1 position; required. |
| Item |
A code for the item defined for the Pricing Upload record. Item codes are defined in and validated against the Item table. Special Pricing by SourceThe item associated with the special source price. Corresponds to the ITM Number field in the Special Pricing by Source table. QPM DetailThe item associated with the quantity price matrix detail. You must define an item category or item for a quantity price matrix price, but not both. Corresponds to the Item field in the QPM Detail table. Alphanumeric, 12 positions; required. |
| SKU |
The SKU of the item associated with the Pricing Upload record. SKU codes are defined in and validated against the SKU table. Special Pricing by SourceLeave this field blank. If the item contains SKUs, the price will apply to all SKUs defined for the item. Note: If you define a SKU for a Special Pricing by Source Upload record, the system ignores the value.Corresponds to the SKU field in the QPM Detail table. A code for the SKU of the item associated with the quantity price matrix detail.
Alphanumeric, 14 positions; optional. |
| Quantity | Special Pricing by Source The quantity of the item that must be purchased to receive the specified price break. Corresponds to the Qty field in the Special Pricing by Source table. QPM DetailThe quantity of the item that must be ordered to qualify for the quantity price matrix detail. The item qualifies for the quantity price matrix detail if the order line quantity is less than or equal to the quantity pice matrix detail. You cannot create more than one quantity price matrix price break for the same item category and quantity, item and quantity, or item and SKU and quantity. Corresponds to the Quantity field in the QPM Detail table. Numeric, 5 positions; required. |
| Price |
The price at which the item will be sold if the pricing requirements are met. Special Pricing by SourceCorresponds to the Price field in the Special Pricing by Source table. Note: For Special Pricing by Source records, the price cannot be greater than 7 positions with a 2 place decimal.Corresponds to the Price field in the QPM Detail table. Numeric, 7 positions with a 2 place decimal; required for Record Type SRC. |
| Source |
The source code associated with the pricing upload record. Source codes are defined in and validated against the Source Code table. Special Pricing by SourceThe source code associated with the Special Pricing by Source record. Corresponds to the Source Code field in the Special Pricing by Source table. QPM DetailThe source code that must exist on the order header in order to qualify for the QPM price. Corresponds to the Source field in the QPM Detail table. Alphanumeric, 9 positions; required for Record Type SRC. |
| Associate price |
The price at which the item will be sold to associate customers if the pricing requirements are met. Special Pricing by SourceCorresponds to the Associate Price field in the Special Pricing by Source table. Note: For Special Pricing by Source records, the associate price cannot be greater than 7 positions with a 2 place decimal.Leave this field blank. Numeric, 7 positions with a 2 place decimal; optional. |
| QPM Code | Special Pricing by Source Leave this field blank. QPM DetailThe quantity price matrix code associated with the QPM Detail price. QPM codes are defined in and validated against the QPM Header table. Corresponds to the Code field in the QPM Detail table. Alphanumeric, 4 positions; required for Record Type QPM. |
| Item Category | Special Pricing by Source Leave this field blank. QPM DetailA code for the item category associated with the quantity price matrix detail. You must define an item category or item for a quantity price matrix price, but not both. Item category codes are defined in and validated against the Item Category table. Corresponds to the Item Category field in the QPM Detail table. Alphanumeric, 4 positions; optional. |
| Customer Sold To # | Special Pricing by Source Leave this field blank. QPM DetailThe sold to customer that must exist on the order header in order to qualify for the QPM price. Customer sold to numbers are defined in and validated against the Customer Sold To table. Corresponds to the Customer field in the QPM Detail table. Numeric, 9 positions; optional. |
| Customer Price Group | Special Pricing by Source Leave this field blank. QPM DetailThe customer price group for the sold to customer on the order header in order to qualify for the QPM price. Customer price group codes are defined in and validated against the Customer Price Group table. Corresponds to the Price Group field in the QPM Detail table. Alphanumeric, 4 positions; optional. |
| Expire Date | Special Pricing by Source Leave this field blank. QPM DetailThe date the QPM price expires. The expiration date cannot be earlier than the current date. Corresponds to the Exp Date field in the QPM Detail table. Numeric, 7 positions (CYYMMDD format); optional. |
| Discount % | Special Pricing by Source Leave this field blank. QPM DetailThe percentage of the quantity price matrix detail price when the item ordered is eligible for the quantity price matrix special. For example, 10 means the item qualifies for a 10% discount. Example: The % discount is based on the following criteria:
The 10% discount is based on the quantity price matrix detail defined for item category HG and quantity 2:
In this example, the 10% discount is a 1.00 discount (10.00 QPM detail - 10% QPM special = 9.00 discount price) If a quantity price matrix detail is not defined for item category HG and quantity 2, the system uses the next lowest quantity for the item category (in this example, the system uses item category HG and quantity 1). See Calculating the QPM Price for more information on how the system finds the price for a quantity price matrix detail and quantity price matrix special. Corresponds to the Discount % field in the QPM Detail table. Numeric, 4 positions with a 2 place decimal; optional. |
| Tax Price |
The price at which the item will be sold to customers if the order is subject to VAT and if the pricing requirements are met. Special Pricing by Source Corresponds to the Tax Price field in the Special Pricing by Source table. Displays on the Work with Special Source Price Screen only if the Tax Included in Price (E70) system control value is selected. Note: For Special Pricing by Source records, the tax price cannot be greater than 7 positions with a 2 place decimal.Corresponds to the Tax Price field in the QPM Detail table. Displays on the Work with Quantity Price Matrix Details Screen and Work with Quantity Price Matrix Specials Screen only if the Tax Included in Price (E70) system control value is selected. Numeric, 7 positions with a 2 place decimal; optional. |
| Associate Tax Price |
Special Pricing by Source The price at which the item will be sold to associate customers if the order is subject to VAT and if the pricing requirements are met. Corresponds to the Associate Tax Price field in the Special Pricing by Source table. Displays on the Work with Special Source Price Screen only if the Tax Included in Price (E70) system control value is selected. Note: For Special Pricing by Source records, the associate tax price cannot be greater than 7 positions with a 2 place decimal.Leave this field blank. Numeric, 7 positions with a 2 place decimal; optional. |
| Status |
The status of the Pricing Upload record. Valid values:
Alphanumeric, 1 position; updated by the system. |
| Error |
The reason why the Pricing Upload record has been placed in an error status. See Pricing Upload Interface Errors. Alphanumeric, 30 positions; updated by the system. |
Pricing Upload Interface Errors
The system includes Pricing Upload records that are in error on the Pricing Upload Error Records Report. You can correct records that are in error using the Work with Pricing Upload (WPUP) menu option.
| Error | Reason |
|---|---|
| General Errors | |
|
Invalid Request Type |
The Record Type field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is invalid. Valid values for Record Type are SRC (Special Pricing by Source upload) or QPM (QPM Detail upload). Note: If the Request Type field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is missing or invalid, the system looks for a match to the record in the Order Administration table and either creates a new record (no match found) or updates the existing record (match found).To correct this error: If the Record Type is missing or invalid, the system places the record in an error status; however, you cannot correct this error using the Change Pricing Upload screen. You must correct the error in the Pricing Upload Table. |
|
Qty is required |
The Quantity field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is blank and it is a required field. |
|
Record does not exist for Dlt |
The Request Type field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is D (Delete) and the system could not match the upload record to an existing record in the Order Administration database. |
|
Item does not exist |
The Item field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is invalid. Item codes are defined in and validated against the Item table. |
|
Source does not exist |
The Source field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is invalid. Source codes are defined in and validated against the Source Code table. |
| Special Pricing by Source Errors The following errors can occur if the Record Type for the record in the Pricing Upload table is SRC. |
|
|
Source is required |
The Source field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is blank and it is a required field. |
|
Item is required |
The Item field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is blank and it is a required field. |
|
Price is required |
The Price field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is blank and it is a required field. |
|
Price value is too large |
The entry in the Price field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is greater than 7 positions with a 2-place decimal. |
|
Tax Price value is too large |
The entry in the Tax Price field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is greater than 7 positions with a 2-place decimal. |
| Quantity Price Matrix Detail Errors The following errors can occur if the Record Type for the record in the Pricing Upload table is QPM. |
|
|
QPM Code is required |
The QPM Code field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is blank and it is a required field. |
|
QPM Code does not exist |
The QPM Code field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table is invalid. QPM codes are defined in and validated against the QPM Header table. |
|
Category or Item is required |
The Item Category field and Item field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table are either blank or both contain a value. You must define an item category or item for a QPM Detail record, but not both. |
|
SKU does not exist |
The SKU field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table contains an invalid value. SKU codes are defined in and validated against the SKU table. |
|
SKU requires Item |
The SKU field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table contains a value and the Item field is blank. |
|
Category does not exist |
The Item Category field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table contains an invalid value. Item category codes are defined in and validated against the Item Category table. |
|
Customer does not exist |
The Customer Sold To # field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table contains an invalid value. Customer sold to numbers are defined in and validated against the Customer Sold To table. |
|
Price Group does not exist |
The Customer Price Group field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table contains an invalid value. Customer price group codes are defined in and validated against the Customer Price Group table. |
|
Price or Disc % is required |
The Price field and Discount % field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table are either blank or both contain a value. You must define a price or discount % for a QPM Detail record, but not both. Also, if you define a discount % you must also specify a Customer Sold To # or Customer Price Group, and/or Source. |
|
Disc % missing Src/Cust#/CPG |
The Discount % field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table contains a value and a Customer Sold To # or Customer Price Group, and/or Source has not been specified. |
|
Cust# or CPG is required |
The Customer Sold To # field and Customer Price Group field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table are either blank or both contain a value. You must define an item category or item for a QPM Detail record, but not both. |
|
Exp Date missing Src/Cust#/CPG |
The Expire Date field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table contains a value and a Customer Sold To # or Customer Price Group, and/or Source has not been specified. |
|
Exp Date < today |
The Expire Date field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table contains a date that is earlier than the current date. |
|
Tax Price missing Price |
The Tax Price field for the record in the Pricing Upload Table contains a value and the Price field is blank. |
Uploading Special Pricing by Source Records
The system performs the following validation when you upload a Special Pricing by Source record (Record Type SRC) through the Pricing Upload Interface.
| # | Step |
|---|---|
|
1. |
Validates that the required fields for the Special Pricing by Source upload record in the Pricing Upload table contain information and the fields that require a valid value contain a valid value. The minimum fields required for a Special Pricing by Source upload record in the Pricing Upload Table are:
In addition, you can also define:
See Pricing Upload Interface Errors for more information on the validation the system performs. |
|
2. |
Determines whether the Special Pricing by Source upload record in the Pricing Upload table creates, updates, or deletes a Special Pricing by Source record in the Order Administration database. The system uses the Company #, Item, Source, and Quantity fields for the Pricing Upload record to determine if a match exists in the Special Pricing by Upload table.
|
|
3. |
Failed Special Pricing by Source
Upload If the Special Pricing by Source Upload record in the Pricing Upload table does not pass validation, the system:
|
|
4. |
Successful Special Pricing by Source
Upload If the Special Pricing by Source Upload record in the Pricing Upload table passes validation, the system:
You can review or maintain Special Pricing by Source records on the Work with Special Source Price Screen in the Working with Source Codes (WSRC) menu option. |
Special Pricing by Source Table Updates
The system uses the information defined in the Pricing Upload table to create, update, or delete a record in the Special Pricing by Source table in the Order Administration database.
You can review Special Pricing by Source records on the Work with Special Source Price Screen in the Working with Source Codes (WSRC) menu option. See this screen for complete field descriptions.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Company |
A code for the company where the special source price applies. From the Company # field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
| Item Number |
The item to which the special source price applies. From the Item field in the Pricing Upload Table. Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
| Source Code |
The source code for which the special source price applies. From the Source field in the Pricing Upload Table Alphanumeric, 9 positions. |
| Quantity |
The quantity of the item that must be purchased to receive the specified price break. From the Quantity field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 5 positions. |
| Price |
The price at which the item will be sold if the pricing requirements are met. From the Price field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 13 positions with a 2 place decimal. |
| Associate Price |
The price at which the item will be sold to associate customers if the pricing requirements are met. From the Associate price field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 13 positions with a 2 place decimal. |
| Tax Price |
The price at which the item will be sold to customers if the order is subject to VAT and if the pricing requirements are met. Note: Displays on the Work with Special Source Price Screen only if the Tax Included in Price (E70) system control value is selected.From the Tax Price field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 13 positions with a 2 place decimal. |
| Associate Tax Price |
The price at which the item will be sold to associate customers if the order is subject to VAT and if the pricing requirements are met. Note: Displays on the Work with Special Source Price Screen only if the Tax Included in Price (E70) system control value is selected.From the Associate Tax Price field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 13 positions with a 2 place decimal. |
Uploading Quantity Price Matrix Detail Records
The system performs the following validation when you upload a Quantity Price Matrix Detail record (Record Type QPM) through the Pricing Upload Interface.
| # | Step |
|---|---|
|
1. |
Validates that the required fields for the QPM Detail upload record in the Pricing Upload table contain information and the fields that require a valid value contain a valid value. The minimum fields required for a QPM Detail upload record in the Pricing Upload Table are:
In addition, you can also define:
Note: You cannot create more than one quantity price matrix detail for the same item category and quantity, item and quantity, or item and SKU and quantity.See Pricing Upload Interface Errors for more information on the validation the system performs. |
|
2. |
Determines whether the QPM Detail upload record in the Pricing Upload table creates, updates, or deletes a QPM Detail record in the Order Administration database. The system uses the Company #, QPM Code, Quantity, Source, either the Item Category or Item and SKU, and either the Customer Sold To # or Customer Price Group, for the Pricing Upload record to determine if a match exists in the Special Pricing by Upload table. See
|
|
3. |
Failed QPM Detail Upload If the QPM Detail Upload record in the Pricing Upload table does not pass validation, the system:
|
|
4. |
Successful Special Pricing by Source
Upload If the QPM Detail Upload record in the Pricing Upload table passes validation, the system:
You can review or maintain QPM Detail records in the Working with Quantity Price Matrix (WQPM) menu option.
|
QPM Detail Table Updates
The system uses the information defined in the Pricing Upload table to create, update, or delete a record in the QPM Detail table in the Order Administration database.
You can review QPM Details on the Work with Quantity Price Matrix Details Screen and Work with Quantity Price Matrix Specials Screen in the Working with Quantity Price Matrix (WQPM) menu option. See these screens for complete field descriptions.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Company |
A code for the company where the quantity price matrix price applies. From the Company # field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
| Code |
The quantity price matrix code for which the quantity price matrix price applies. From the QPM Code field in the Pricing Upload Table. Alphanumeric, 4 positions. |
| Item |
The item to which the quantity price matrix price applies. From the Item field in the Pricing Upload Table. Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
| SKU |
The SKU to which the quantity price matrix price applies. From the SKU field in the Pricing Upload Table. Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
| Item Category |
The item category code to which the quantity price matrix price applies. From the Item Category field in the Pricing Upload Table. Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
| Quantity |
The quantity of the item that must be purchased to receive the specified price break. From the Quantity field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 5 positions. |
| Price |
The price at which the item will be sold if the pricing requirements are met. From the Price field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 13 positions with a 2 place decimal. |
| Tax Price |
The price at which the item will be sold to customers if the order is subject to VAT and if the pricing requirements are met. From the Tax Price field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 13 positions with a 2 place decimal. |
| Customer |
The sold to customer to which the quantity price matrix price applies. From the Customer Sold To # field in the Pricing Upload Table. Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
| Price Group |
The customer price group to which the quantity price matrix price applies. From the Customer Price Group field in the Pricing Upload Table. Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
| Expiration Date |
The date the quantity price matrix price expires. From the Expire Date field in the Pricing Upload Table. Numeric, 7 positions (CYYMMDD format). |
| Discount % |
The percentage of the quantity price matrix detail price when the item ordered is eligible for the quantity price matrix special. For example, 10 means the item qualifies for a 10% discount. Example: The % discount is based on the following criteria:
The 10% discount is based on the quantity price matrix detail defined for item category HG and quantity 2:
In this example, the 10% discount is a 1.00 discount (10.00 QPM detail - 10% QPM special = 9.00 discount price) If a quantity price matrix detail is not defined for item category HG and quantity 2, the system uses the next lowest quantity for the item category (in this example, the system uses item category HG and quantity 1). See Calculating the QPM Price for more information on how the system finds the price for a quantity price matrix detail and quantity price matrix special. Numeric, 4 positions with a 2 place decimal. |
| Source |
The source code to which the quantity price matrix price applies. From the Source field in the Pricing Upload Table. Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
| Sort |
Used to correctly display QPM detail records on the Work with Quantity Price Matrix Specials Screen.
Numeric, 1 position. |
Store Upload
Purpose: The Store Upload allows you to upload store information from an external system to create or update records the Store Cross Reference table.
Note:
You cannot use the Store Upload process to delete a record from the Store Cross Reference table.In this topic:
For more information: See Work with Store Cross Reference (WSCR) for more information on creating, updating, and deleting store cross references in Order Administration.
Store Upload Setup
The setup required to use the store upload includes:
Store File
Create a Store flat file for the store information you wish to create or update.
-
The fields in this flat file are fixed length, each record separated by a carriage return.
-
The name of the file must start with ST and have a .TXT file extension; for example: ST99999.txt, where 99999 is a unique value for each Store file.
-
Include only one record for each store you wish to upload. However, if multiple records exist for the same store number, the system creates or updates the record in the Store Cross Reference table using the information in the last record processed.
-
If you wish to leave any field in the upload file blank, pass a space in the field so that the file can be processed without errors. Leaving a field with no space is interpreted as null in the database and causes errors.
File contents:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Store # |
Updates Store# in the Store Cross Reference table. Alphanumeric, 10 positions; Required. |
|
Store Name |
Updates Description in the Store Cross Reference table. Alphanumeric, 40 positions; Required. |
|
Store Active Indicator |
Updates Active? in the Store Cross Reference table. Valid values are:
Alphanumeric, 1 position; Required. |
|
Address 1 |
Updates Address Line 1 in the Store Cross Reference table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions; Required when updating an existing record whose Ship for Pickup flag is selected. |
|
Address 2 |
Updates Address Line 2 in the Store Cross Reference table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions; Optional. |
|
Address 3 |
Updates Address Line 3 in the Store Cross Reference table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions; Optional. |
|
Address 4 |
Updates Address Line 4 in the Store Cross Reference table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions; Optional. |
|
City |
Updates City in the Store Cross Reference table. Alphanumeric, 25 positions; Required when updating an existing record whose Ship for Pickup flag is selected. |
|
State |
Updates State in the Store Cross Reference table. The state code must be defined for the SCF associated with the postal code. Alphanumeric, 2 positions; Required when updating an existing record whose Ship for Pickup flag is selected. |
|
Postal Code |
Updates Postal Code in the Store Cross Reference table. The postal code must be at least 5 characters and its first three positions must exist in the SCF table. Alphanumeric, 10 positions; Required when updating an existing record whose Ship for Pickup flag is selected. |
|
Country |
Updates Country in the Store Cross Reference table. Alphanumeric, 3 positions; Required when updating an existing record whose Ship for Pickup flag is selected. |
|
Phone |
Updates Telephone # in the Store Cross Reference table. Alphanumeric, 14 positions; Optional. |
Sample record in Store file:
STORE#777 THIS IS STORE#777 NAME/DESCRIPTION YSTORE#777 STREET ADDRESS LINE 1 STORE#777 STREET ADDRESS LINE 2 STORE#777 STREET ADDRESS LINE 3 STORE#777 STREET ADDRESS LINE 4CITY MA01468 USATELEPHONENUMBR
Work with File Upload (WUPL)
You will use the Work with File Uploads (WUPL) menu option to upload the Store file to the STORE_FILE_PATH folder (CPRP).
Note:
Using the File Storage API to upload stores is not currently supported.
STRUPLD Upload Store Periodic Function
You will use the STRUPLD periodic function to submit the Store Upload Process.
| Function Setting | How to Set |
|---|---|
|
Function: |
STRUPLD |
|
Description: |
UPLOAD STORES |
|
Program name: |
PFR0110 |
|
Company |
The Company flag must be selected. The Store Upload process creates records in the Store Cross Reference table using the company you entered when you submitted the STRUPLD periodic function. |
-
The STRUPLD periodic function is delivered with the system. Use the Working with Periodic Functions (WPER) menu option to review it.
-
Use the Working with Periodic Processes (WPPR) menu option to assign the STRUPLD periodic function to a periodic process.
-
Once you have created the periodic process, you can use the Execute Periodic Process screen (located in the Working with Periodic Processes (WPPR) or Executing Periodic Processes (EPRO)) to define a schedule for the job. See Defining the Job Schedule.
For more information: See Scheduling Jobs for more information on How to Schedule a Job.
Store Upload Process
After you use WUPL to upload the store file, then submit the STRUPLD Store Upload periodic function to have the system perform the following steps.
| # | Step |
|---|---|
|
1. |
Looks in the directory defined in the STORE_FILE_PATH property (CPRP) for new store files to process. If a file exists in the STORE_FILE_PATH directory whose file name begins with ST and has a .TXT file extension, the syistem selects the file for processing. |
|
2. |
Validates each record in the file.
|
|
3. |
Creates or updates records in the Store Cross Reference table for the company you entered when you submitted the STRUPLD periodic function. The system uses the Store # in the Store File to determine if the record is an add or a change.
You can review the store cross reference records that have been created and updated in the Work with Store Cross Reference (WSCR) menu option. |
|
4. |
Once all of the records in the Store file are processed, the system changes the file extension of the file from .TXT to .PRC to indicate that the file has been processed. It is your responsibility to delete files with the .PRC file extension. |
Using the Financial Data Interface
Purpose: Use the financial data interface to extract invoice information for the current date or for a range of dates.
Periodic function: To perform the extract as part of a periodic process, you must first create a periodic function for the program FNR0008. You can then assign the periodic function to a periodic process, which you can run daily to capture all invoices for that system date. See Working with Periodic Functions (WPER) for an overview on working with periodic functions.
For more information: :
Financial Sales Download Table (IXSLDL)
Note:
Each of the fields listed below contains data only if indicated for the record type; otherwise, the field is blank.
| Field | Attributes | Comments | Record Types |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Company |
Numeric, 3 positions |
From Invoice Header table. |
all |
|
Invoice number |
Numeric, 7 positions |
From Invoice Header table. |
all |
|
Invoice type |
Alphanumeric, 1 position |
From Invoice Header table: I = invoice C = credit |
all |
|
Record type |
Alphanumeric, 1 position |
01 = sale (one record for each Invoice Detail record) 02 = credit (one record for each Invoice Detail record) 03 = Shipping and handling 04 = Pay type (one record for each invoice payment method) 05 = additional charges |
all |
|
Sequence number |
Numeric, 4 positions |
Generated by the extract; restarts at 1 with each extract. |
all |
|
Customer number |
Numeric, 9 positions |
From Order Header table. |
all |
|
Order number |
Numeric, 8 positions |
From Invoice Header table. |
all |
|
Entity |
Numeric, 3 positions |
From the division associated with the source code on the Order Header. |
all |
|
Internet order |
Alphanumeric, 1 position |
I = internet order; otherwise blank. Based on the setting of the Internet order (Future use sts 1) field in the Order Header table; if this field is set to I, then the order is considered an internet order. |
all |
|
Invoice date |
Numeric, 8 positions; YYYYMMDD format |
From Invoice Header table. |
all |
|
Item |
Alphanumeric, 12 positions |
From Order Detail table. |
01 (sale) and 02 (credit) |
|
SKU |
Alphanumeric, 14 positions |
Three 4-position fields, separated by blank spaces. |
01 (sale) and 02 (credit) |
|
Long SKU style |
Alphanumeric, 20 positions |
From the L/S style (Long SKU style) SKU table. If no long SKU style is specified for the SKU, then this field is blank. |
01 (sale) and 02 (credit) |
|
Long SKU color |
Alphanumeric, 5 positions |
From the L/S color (Long SKU color) in the SKU table. If no long SKU color is specified for the SKU, then this field is set to 00000. Note: The L/S color in the SKU table is a numeric field. |
01 (sale) and 02 (credit) |
|
Long SKU size |
Alphanumeric, 5 positions |
From the L/S size (Long SKU size) in the SKU table. If no long SKU size is specified for the SKU, then this field is set to 00000. Note: The L/S size in the SKU table is a numeric field. |
01 (sale) and 02 (credit) |
|
Long SKU width |
Alphanumeric, 5 positions |
From the L/S width (Long SKU width) in the SKU table. If no long SKU width is specified for the SKU, then this field is set to 00000. Note: The L/S width in the SKU table is a numeric field. |
01 (sale) and 02 (credit) |
|
SKU second language description |
Alphanumeric, 40 positions |
From the Second language description if no second language description is specified for the SKU; otherwise, from the Second language description. If no second language description is specified for the SKU or the base item, then this field is blank. |
01 (sale) and 02 (credit) |
|
Retail style number |
Alphanumeric, 20 positions |
From the Rtl style (Retail Style #) in the Item table. From the base item, if specified; otherwise, this field is blank. |
01 (sale) and 02 (credit) |
|
Quantity shipped |
Numeric, 4 positions |
The quantity shipped or returned, from the Ship qty (Shipped quantity) in the Invoice Detail table. Absolute value (i.e., both credits and invoices have positive quantities). |
01 (sale) and 02 (credit) |
|
Dollar amount |
Numeric, 13 positions with a 2-place decimal |
Depending on record type:
|
all |
|
Tax amount |
Numeric, 13 positions with a 2-place decimal |
Note: Absolute value (i.e., both credits and invoices have positive amounts). |
01 (sale) and 02 (credit) |
|
Additional charge code |
Alphanumeric, 2 positions |
From the Code in the Order Additional Charge table. |
05 (additional charges) |
|
Pay type |
Numeric, 2 positions |
From the Pay method in the Invoice Payment Method table. Not zero-filled (for example, pay type 9 is represented as 9, not 09). |
04 (pay type) |
|
Credit card number |
Alphanumeric, 16 positions |
From the Credit card # in the Invoice Payment Method table. Used only for credit card payment methods (payment category 2). Note: If you use credit card encryption, the credit card number will not be encrypted because the information in this table is extracted to an outside system. |
04 (pay type) |
|
Credit card expiration date |
Alphanumeric, 4 positions |
From the CC expiration date in the Invoice Payment Method table. Used only for credit card payment methods (payment category 2); otherwise, this field is set to 0000 for an 04 record. |
04 (pay type) |
|
Credit card authorization code |
Alphanumeric, 6 positions |
From the Auth # in the Invoice Payment Method table. Used only for credit card payment methods (payment category 2). Included on invoice records only. |
04 (pay type) |
Working with the Marketing Download Extract
Purpose: The Marketing Download Extract allows you to download order and customer information from Order Administration to an external system.
To download order and customer-related data: The system creates records in the Marketing Download Trigger table as a result of certain actions in Order Administration. You can then:
-
Run the MDEXTR Marketing Download Order and Customer Extract (CSX1041) periodic function to extract order and customer-related records in the Marketing Download Trigger table to the appropriate Marketing Download table.
-
Run the MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) periodic function to extract the data in the Marketing Download tables to a pipe delimited text file.
The text file is then included in a zip file that is placed in the OMS-MARKETING container of the FILE_STORAGE table.
For more information: See Creating Marketing Download Trigger Records and Populating the Marketing Download Tables and Extract Files, and see File Storage API for background on using the file storage API.
Marketing Download reports: You can print reports to review the data in the Marketing Download tables before the data is downloaded to an external system; see Setting up the Marketing Download Extract for more information.
Note:
Because the Marketing Download extract process clears old trigger records from the table, back up the contents of the table before running the extract if you will need the data later.
In this topic:
-
Marketing Download Customer Status Change Table and Extract File
-
Marketing Download Customer Address Change Table and Extract File
-
Marketing Download Customer Ownership Table and Extract File
Setting up the Marketing Download Extract
System control values: The following system control values control trigger creation logic:
-
Populate Marketing Download Trigger File (G33): controls the type(s) of triggers to create.
-
Include All Customer Inquiry Triggers for Marketing Download (I09): controls whether to create customer inquiry triggers if there are corresponding order header triggers.
Periodic functions: The Marketing Download extract uses the following periodic functions:
-
MDEXTR Marketing Download Order and Customer Extract (CSX1041) populates the Marketing Download order-related and customer-related tables based on the records in the Marketing Download Trigger table.
-
MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) exports the data in the Marketing Download order-related and customer-related tables to pipe-delimited files and places the files in the Marketing folder of the directory defined in the CWDIRECTCP_FTP_FOLDER property (CPRP). Once the extract files are created, the system deletes the records in the associated Marketing Download tables.
How to set up: To set up the Marketing Download periodic functions for periodic processing:
-
Use Working with Periodic Functions (WPER) to set up each of the required Marketing Download periodic functions (for example, enter CSR1033 as the Program name for the function that populates the Marketing Download Source Download table).
-
Use Working with Periodic Processes (WPPR) to assign each of the periodic functions to a periodic process.
-
Use Scheduling Jobs to indicate when and how often to run the periodic process.
Generating reports: You can also set up periodic functions for the Marketing Download reports and assign them to the Marketing Download periodic process:
-
MDADRCG (CSX1069): Marketing Download Change of Address Interface Report
-
MDCSCHG (CSX1061): Marketing Download Customer Status Change Interface Report
-
MDINQSM (CSX1066): Marketing Download Customer Inquiry Interface Report
-
MDORDHD (CSX1044): Marketing Download Order Header Interface Summary Report
-
MDORDTL (CSX1058): Marketing Download Order Detail Interface Summary Report
Note:
To make sure the report prints correctly, select an option that reduces the page or fits the content to the printer margins at the Print dialog box.
Marketing Download Extract Process
Creating Marketing Download Trigger Records
Which activity creates a trigger? The setting of the Populate Marketing Download Trigger File (G33) system control value determines which type of activity in Order Administration causes the system to populate the Marketing Download Trigger table. Valid values are:
-
ORDER: order entry or maintenance
-
CUSTOMER: customer maintenance or catalog requests
-
ORD/CUST: order entry or maintenance, customer maintenance, or catalog requests
Marketing download trigger type: When the system creates a record in the Marketing Download Trigger table, the record is assigned a trigger type based on the type of activity that was performed. The trigger type determines which fields are populated in the Marketing Download Trigger table and which Marketing Download table is populated when you run the marketing download trigger program. The following table lists the trigger type created based on the setting of the Populate Marketing Download Trigger File (G33) system control value and the action you performed.
| SCV value: | creates trigger type: | when you: | trigger includes: | Marketing Download table populated: |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ORDER or ORD/CUST |
OH (order header) |
|
Customer sold to # Customer ship to # (if a permanent ship-to address is used) Entity Order # Order ship-to # |
Marketing Download Order Header Table and Extract File, Marketing Download Order Detail Table and Extract File Marketing Download Customer Inquiry Table and Extract File (only for a recipient customer) |
|
ORDER or ORD/CUST |
LH (order line history) |
create order line history (for example, adding, cancelling, changing, exchanging, returning, shipping, or selling out an item on an order; or billing an order). Note: The system does not create an LH record if the original OH record for the order is in the Marketing Download Trigger table. |
Order # Order ship-to # Order detail sequence # Order line history sequence # |
|
|
CUSTOMER or ORD/CUST |
CI (customer inquiry) |
|
Customer sold to # Entity #, if the activity was associated with a specific entity (for example, creating a new customer in order entry) |
|
|
CUSTOMER or ORD/CUST |
CO (customer ownership) |
create a customer ownership record. |
Customer sold to # |
Marketing Download Customer Ownership Table and Extract File |
|
CUSTOMER or ORD/CUST |
CS (customer status change) |
change one or more of these fields for a customer sold-to:
Note: The system may change one of the above fields when you create a catalog request for an existing customer. |
Customer sold to # Entity #, if the activity was related to a specific entity |
Marketing Download Customer Status Change Table and Extract File |
|
CUSTOMER or ORD/CUST |
CA (customer address change) |
change a customer sold-to or change or create a permanent customer ship-to address, including phone numbers and email address. |
Customer sold to # Customer ship to, if the activity was related to a ship-to address |
Marketing Download Customer Address Change Table and Extract File |
|
CUSTOMER or ORD/CUST |
CN (customer action note) |
create, work with, or resolve a customer action note. Note: The system populates the Marketing Download Customer Inquiry table only if a reason has been defined for the customer action note. |
Customer sold to # Customer action sequence # |
|
|
CUSTOMER or ORD/CUST |
CP (customer profile) |
create or change a customer profile record. |
Customer sold to # |
In addition to the fields listed above, each marketing download trigger record also includes company number, trigger type, trigger sequence number, status, date created, and time created.
When is the trigger created? Each of the trigger record types indicated are created when the update in the system is complete. For an interactive process, such as creating or updating a customer in order entry, the trigger is created immediately. For an update that is handled by an asynchronous job, such as order creation, the trigger is not created until the job processing is complete.
Marketing Download Trigger Table
The system creates a a marketing download trigger record based on the Populate Marketing Download Trigger File (G33) system control value and the action you perform.| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Company |
The code for the company where you performed the action that created the marketing download trigger. OH: the company from the Order Header table. LH: the company from the Order Line History table. CI: the company from the Catalog Request processing. CN: the company from the Customer Action Note table. CO: the company from the Customer Ownership table. CP: the company from the Customer Profile table. CS: the company from the Customer Sold To table. CA: the company from the Customer Sold To table. Numeric, 3 positions; required. |
|
Trigger type |
The type of action that created the marketing download trigger. Valid values are: OH = order header LH = order line history CI = customer inquiry CO = customer ownership CP = customer profile CS = customer status change CA = customer address change CN = customer action note Alphanumeric, 2 positions; required. |
|
Trigger seq # |
A unique sequence number to distinguish records with the same company number and trigger type. Numeric, 7 positions; required. |
|
Customer Sold To |
The customer sold-to number associated with the activity that created the trigger. Populated for trigger types OH (order header), CS (customer status change), CI (customer inquiry), CA (customer address change), CO (customer ownership), CP (customer profile), and CN (customer action note). OH: the customer sold-to number from the Order Header table. CI: the customer sold-to number from the Catalog Request processing. CN: the customer sold-to number from the Customer Action Note table. CO: the customer sold-to number from the Customer Ownership table. CP: the customer sold-to number from the Customer Profile table. CS: the customer sold-to number from the Customer Sold To table. CA: the customer sold-to number from the Customer Sold To table. Numeric, 9 positions; optional. |
|
Customer Ship To |
The customer ship-to number associated with the activity that created the trigger. Populated only for trigger types OH (order header) and CA (customer address change). The OH trigger type includes customer ship-to only if a permanent ship-to address is used on the order. The CA trigger type includes customer ship-to only if a permanent ship-to address was created or changed. OH: The customer ship-to number from the Order Ship To table. CA: The customer ship-to number from the Customer Ship To table. Numeric, 3 positions; optional. |
|
Customer action seq # |
The sequence number associated with the activity that created the trigger. Populated for trigger type CN (customer action note). The customer action sequence number from the Customer Action table. Numeric, 2 positions; optional. |
|
Entity |
The entity associated with the activity that created the trigger. Populated only for trigger types OH (order header), CS (customer status change) or CI (customer inquiry). OH: The entity from the Division table for the division associated with the source code on the order header. CI: The entity from the Division table for the division associated with the source code on the catalog request. CS: The entity from the Customer Sold To Entity table. Numeric, 3 positions; optional. |
|
Order # |
The order number associated with the activity that created the trigger. Populated only for trigger types OH (order header) or LH (order line history). OH: The order number from the Order Header table. LH: The order number from the Order Line History table. Numeric, 8 positions; optional. |
|
Order ship to # |
The ship-to number on the order associated with the activity that created the trigger. Populated only for trigger types OH (order header) or LH (order line history). OH: The order ship-to number from the Order Ship To table. LH: The order ship-to number from the Order Line History table. Numeric, 3 positions; optional. |
|
Order detail seq # |
The order line associated with the activity that created the trigger. Populated only for trigger type LH (order line history). The order detail sequence number from the Order Line History table. Numeric, 5 positions; optional. |
|
Order line hist seq # |
The order line history record associated with the activity that created the trigger. Populated only for trigger type LH (order line history). The order line history sequence number from the Order Line History table. Numeric, 2 positions; optional. |
|
Warehouse |
The code for the warehouse associated with the activity that created the trigger. Not populated for any of the trigger types. Numeric, 3 positions; optional. |
|
PO number |
The purchase order number associated with the activity that created the trigger. Not populated for any of the trigger types. Numeric, 7 positions; optional. |
|
PO detail seq # |
The purchase order line number associated with the activity that created the trigger. Not populated for any of the trigger types. Numeric, 5 positions; optional. |
|
Status |
Indicates whether the trigger has been downloaded to the Marketing Download tables. U = unprocessed; the trigger has not been downloaded to the Marketing Download tables. P = processed; the trigger has been downloaded to the Marketing Download tables. The periodic function deletes the marketing download trigger record once it is extracted to the Marketing Download tables. Alphanumeric, 1 position; required. |
|
Date created |
The date the trigger was created; this is the date when the activity was performed that created the trigger record. Numeric, 7 positions (CYYMMDD format); required. |
|
Time created |
The time the trigger was created; this is the time when the activity was performed that created the trigger record. Numeric, 6 positions (HHMMSS format); required. |
|
Date processed |
The date the trigger was downloaded to the Marketing Download tables. Numeric, 7 positions (CYYMMDD format); required. |
Populating the Marketing Download Tables and Extract Files
You can run the MDEXTR Marketing Download Order and Customer Extract (CSX1041) periodic function to create records in the Marketing Download tables.
You can also run the periodic function on demand through Working with Periodic Processes (WPPR).
If there is already data in the download tables: If you run the Marketing Download (CSX1041) periodic function while there are still records in the Marketing Download order or customer tables, the function writes an error to the APP.log: Data already exists in Marketing Download files. Please clear the files before running Download. See the Application Log for information on how to review this log.
You must first download or delete the records that are already in the Marketing Download order and customer tables before you can populate these tables with new information.
Order and customer-related tables: The MDEXTR Marketing Download Order and Customer Extract (CSX1041) periodic function creates records in these Marketing Download tables:
-
Marketing Download Customer Status Change Table and Extract File
-
Marketing Download Customer Address Change Table and Extract File
-
Marketing Download Customer Ownership Table and Extract File
During processing, the function changes the status of each selected trigger record to P (processed). Once the Marketing Download records are created, the function deletes the processed marketing download triggers.
You can then run the MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) periodic function to export the data in the Marketing Download order-related and customer-related tables to pipe-delimited files. The text file is included in a zip file that is placed in the OMS-MARKETING container of the FILE_STORAGE table. See File Storage API for background.
The table below indicates the validation performed for different unprocessed (status = U) trigger types in the Marketing Download Trigger table.
| For trigger type: | the Marketing Download function: |
|---|---|
|
OH (order header) |
|
|
LH (order line history) |
|
|
CS (customer status change) |
|
|
CI (customer inquiry) |
|
|
CN (customer action note) |
|
|
CO (customer ownership) |
|
|
CP (customer profile) |
|
|
CA (customer address change) |
|
When you extract the records in the Marketing Download Trigger table to the Marketing Download order and customer tables, you can also print reports to review the data in the Marketing Download tables; see Setting up the Marketing Download Extract for setup information.
Marketing Download Order Header Table and Extract File
Marketing Download Order Header table: The MDEXTR Marketing Download Order and Customer Extract (CSX1041) periodic function creates a record for each marketing download trigger record with a trigger type of order header (OH); see Populating the Marketing Download Tables and Extract Files for more information on how the function determines when to create a record in the Marketing Download Order Header table
Note:
The MDEXTR periodic function also creates a record in the Marketing Download Order Detail Table and Extract File for each order detail line associated with the order ship-to in the Marketing Download Order Header table.
Marketing Download Order Header Export file: The MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) periodic function creates a pipe-delimited text file based on the records in the Marketing Download Order Header table.
Name of file: The name of the file is 999.ORDER_HEADER.DATETIME.TXT, where 999 is the company code where you submitted the MDEXPRT periodic function and DATETIME is the date and time when the extract occurred, including an abbreviation, such as EDT, indicating the time zone. For example: 7.ORDER_HEADER.Mon-Apr-25-11-28-03-EDT-2016.TXT.
Location of file: The Marketing Download Order Header Export text file is included in a zip file that is placed in the OMS-MARKETING container of the FILE_STORAGE table. The zip file in the FILE_STORAGE table has the same name as the text file that it contains, except for the ZIP extension.
Example of file: In this example, the first row is a header record indicating the name of each column and the second row contains the actual data; see the Marketing Download Order Header Table for a description of the contents of this file.
Company|Order#|Ship To#|Customer#|Entity|CST Prefix||CST Last Name|CST First Name|CST Initial|CST Company Name|CST Internet Address|CST Address Line 1|CST Address Line 2|CST Apartment|CST City|CST State|CST Zip|CST Country|CST Phone #1 Day|CST Phone #2 Eve|CST Phone #3 Fax|Customer Class|CST Mail name?|CSE Mail name?|CST Rent name?|CST Mail code 1|CST Call code 1|Order Amount|Order Date|Payment Code #1|Payment Code #2|Order Type|Offer|Source Code|Ship Via|OST Customer#|OST CSH Ship To#|OST Recipient#|Gift Flag|Ship To Flag|Station ID|CST Deliverable Code|FPO Type|CST Hold/Bypass/Fraud|CSH Prefix|CSH Last Name|CSH First Name|CSH Initial|CSH Company Name|CSH Internet Address|CSH Address Line 1|CSH Address Line 2|CSH Apartment|CSH City|CSH State|CSH Zip|CSH Country|CSH Phone #1 Day|CSH Phone #2 Eve|CSH Phone #3 Fax|Alternate Customer#|CSH Address line 3|CSH Address line 4|Email Sts
7|19|1|4|777|||LAST|FIRST|R|||1234 SAMPLE STREET|||WESTBOROUGH|MA|01581|US|5083310100|5085550101|0||Y||Y|Y||303.96|20160425|4|0|P|OFR|SOURCE|1|0|0|0|N||0|||||||||||||||||0|0|0||||O1
Note:
When you run the MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export periodic function, the system creates the Marketing Download Order Header Export file even if there is no data to extract from the Marketing Download Order Header table; in this situation, the text file contains only a header record indicating the column names.
Marketing Download Order Header Table
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Company |
The code for the company where the order is located. From the Company in the Order Header table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Order number |
The order number associated with the order you created or for which you created a new ship-to address. From the Order number in the Order Header table. Numeric, 8 positions. |
|
Order ship to number |
The order ship-to number associated with the order you created or for which you created a new ship-to address. From the Order ship to number in the Order Ship To table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Customer number |
The sold-to customer on the order. From the Customer number in the Order Header table. Numeric, 9 positions. |
|
Entity |
The entity associated with the order. From the Entity number in the Division table for the division associated with the source code on the order header. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Name prefix |
The prefix of the sold-to customer. From the Prefix in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Gender code |
Not mapped. |
|
Last name |
The last name of the sold-to customer. From the Last name in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 25 positions. |
|
First name |
The first name of the sold-to customer. From the First name in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 15 positions. |
|
Initial |
The middle initial of the sold-to customer. From the Initial in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Company name |
The company name of the sold-to customer. From the Company name in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
|
Internet address |
The email address of the sold-to customer. From the Email in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 50 positions. |
|
Address line 1 |
The sold-to customer’s street address. From the Street address in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Address line 2 |
Address line 2 of the sold-to customer’s address. From the Address line 2 in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Apartment |
The apartment of the sold-to customer’s address. From the Apartment in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
City |
The city of the sold-to customer’s address. From the City in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 25 positions. |
|
State |
The state code of the sold-to customer’s address. From the State in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
|
Zip |
The postal code of the sold-to customer’s address. From the Zip in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
Country |
The country code of the sold-to customer’s address. From the Country in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Phone number 1 day |
The sold-to customer’s day phone number. From the Phone in the Customer Sold To Phone Number table for phone type D. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Phone number 2 evening |
The sold-to customer’s evening phone number. From the Phone in the Customer Sold To Phone Number table for phone type E. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Phone number 3 fax |
The sold-to customer’s third (fax or mobile) number. From the Phone in the Customer Sold To Phone Number table for phone type F. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
Customer class |
The class of the sold-to customer. From the Customer class in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
|
Mail name? |
Indicates whether the sold-to customer receives future catalogs. selected = mail catalogs to the customer. unselected = Do not mail catalogs to the customer. From the Mail name in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. |
|
Customer entity mail name? |
Indicates whether the sold-to customer receives future catalogs. This field is used if the Track Customer History at Entity Level (F89) system control value is selected. Selected = mail catalogs to the customer. Unselected = Do not mail catalogs to the customer. This field is unselected if there is no customer information at the entity level (the Track Customer History at Entity Level (F89) system control value is unselected). From the Mail name in the Customer Sold To Entity table for the customer number on the order header and the entity for the division associated with the source code on the order header. |
|
Rent name? |
Indicates whether you can include the customer’s name in lists you sell to other companies for their own catalog mailings. Selected = Sell the customer’s name to another company. Unselected = Do not sell the customer’s name to another company. From the Rent name in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. |
|
Mail code |
Indicates how often, and under what conditions, to send mail to the customer. From the Mail code in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Call code |
Specifies how often, and under what conditions, to call the customer. From the Call code in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Order amount |
The total merchandise amount on the order for the order ship-to, including soldout and cancelled order lines if the cancel reason code has Reduce demand unselected. The system multiplies the Quantity ordered by the Price from the Order Detail table for the order shipping address to determine the merchandise amount. Numeric, 20 positions with a 2-place decimal. |
|
Order date |
The date the order was created. From the Order date in the Order Header table. Numeric, 8 positions (YYYYMMDD format). |
|
Payment code 1 |
The code identifying the first form of payment on the order, based on charge sequence. The payment method must be active. From the Pay type code in the Order Payment Method table for the payment on the order with a charge sequence of 1. Numeric, 2 positions. |
|
Payment code 2 |
The code identifying the second form of payment on the order, based on charge sequence. The payment method must be active. From the Pay type code in the Order Payment Method table for the payment on the order with a charge sequence of 2. Numeric, 2 positions. |
|
Order type |
The order type of the order, such as phone or mail. From the Order type in the Order Header table. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Offer code |
The offer code associated with the source code on the order header. From the Offer in the Offer table for the source code on the order header. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Source code |
The source code on the order header. From the Source code in the Order Header table. Alphanumeric, 9 positions. |
|
Ship via |
The ship via code on the order ship-to. From the Ship via in the Order Ship To table. Numeric, 2 positions. |
|
Customer number |
The sold-to customer number on the order. Populated only if a permanent ship-to customer has been selected for the sold-to customer on the order (the Ship To option in order entry). From the Customer number in the Order Ship To table. Numeric, 9 positions. |
|
Order ship to number |
The permanent ship-to customer number for the sold-to customer on the order. Populated only if a permanent ship-to customer has been selected for the sold-to customer on the order (the Ship To option in order entry). From the Ship to number in the Order Ship To table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Recipient number |
The recipient customer number on the order. Populated only if a recipient customer number has been selected for the sold-to customer on the order (Sold To/Recip in order entry). From the Customer number in the Order Ship To table. Numeric, 9 positions. |
|
Gift flag |
Identifies a gift order. Selected = This is a gift order. Unselected = This is not a gift order. From the Gift order flag in the Order Ship To table. |
|
Ship to flag |
Selected indicates a permanent ship-to address is selected for the order. Populated only if a permanent ship-to customer has been selected for the sold-to customer on the order (the Ship To option in order entry). |
|
Station ID |
Blank. Numeric, 4 positions. |
|
Deliverable code |
The deliverable code for the ship-to customer. From the Deliverable code in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Flexible payment option type |
The flexible payment option on the credit card on the order. The payment method must be active. D = deferred billing. I = installment billing. blank = regular billing. From the FPO payment code in the Order Payment Method table for the credit card payment on the order. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Hold/bypass/fraud |
Controls how credit checking is performed for the sold-to customer during order entry. H = Hold; place the customer’s orders on hold automatically. B = Bypass; orders for the customer are not included in the credit check function in order entry; however, the customer is still subject to other fraud-checking, as described in for the Fraud Checking (A68) system control value. F = Fraud; the system places the customer’s orders on fraud hold automatically. blank = normal fraud checking occurs in order entry. From the Hold/bypass/fraud flag in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Ship to name prefix |
Prefix of the permanent ship-to customer on the order. From the Prefix in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Ship to last name |
Last name of the permanent ship-to customer on the order. From the Last name in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 25 positions. |
|
Ship to first name |
First name of the permanent ship-to customer on the order. From the First name in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 15 positions. |
|
Ship to initial |
Middle initial of the permanent ship-to customer on the order. From the Initial in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Ship to company name |
Company name of the permanent ship-to customer on the order. From the Company name in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
|
Ship to internet address |
Email address of the permanent ship-to customer on the order. From the Email address in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 50 positions. |
|
Ship to address line 1 |
Street address of the permanent ship-to customer address. From the Street address in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Ship to address line 2 |
Address line 2 of the permanent ship-to customer’s address. From the Address line 2 in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Ship to apartment |
Apartment of the permanent ship-to customer’s address. From the Apartment in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
Ship to city |
City of the permanent ship-to customer’s address. From the City in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 25 positions. |
|
Ship to state |
State code of the permanent ship-to customer’s address. From the State in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
|
Ship to zip |
Postal code of the permanent ship-to customer’s address. From the Zip in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
Ship to country |
Country code of the permanent ship-to customer’s address. From the Country in the Customer Ship To table for the order ship-to on the order. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Ship to phone number day |
Day phone number of the permanent ship-to customer on the order. From the Phone in the Customer Ship To Phone Number table for phone type D. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Ship to phone number evening |
Evening phone number of the permanent ship-to customer on the order. From the Phone in the Customer Ship To Phone Number table for phone type E. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Ship to phone number fax |
Third (fax or mobile) phone number of the permanent ship-to customer on the order. From the Phone in the Customer Ship To Phone Number table for phone type F. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Alternate customer number |
Alternate customer number of the sold-to customer. From the Interface customer code in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 15 positions. |
|
Address line 3 |
Address line 3 of the sold-to customer’s address. From the Address line 3 in the Customer Sold To Extended table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Address line 4 |
Address line 4 of the sold-to customer’s address. From the Address line 4 in the Customer Sold To Extended table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Email status |
Indicates the preferred method of correspondence. O1 (Email): Email is the preferred method of correspondence. O2 (Order-only email): Use email for order-related correspondence only; generate a document for other correspondence. O3 (No email): Do not use email for any correspondence; generate a document instead. O4 (Do not ask customer): Do not ask the customer for his/her email address; the customer has already been asked and has declined to provide it. The system does not generate any email correspondence to the customer, even if an email address is specified. From the Email status in the Customer Sold To table for the customer number on the order header. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
Marketing Download Order Detail Table and Extract File
Marketing Download Order Detail Table: This table contains a record for each marketing download trigger with a trigger type of order header (OH) or trigger type of LH (line history); see Populating the Marketing Download Tables and Extract Files for more information on how the MDEXTR Marketing Download Order and Customer Extract (CSX1041) periodic function determines when to create a record in the Marketing Download Order Detail table.
Note:
Marketing Download order detail records are associated with a record in the Marketing Download Order Detail Table and Extract File if the order is newly created; a record does not exist in the Marketing Download Order Header table for Marketing Download order detail records that are associated with a maintenance transaction that created an order line history record.
Marketing Download Order Detail Export file: The MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) periodic function creates a pipe-delimited text file based on the records in the Marketing Download Order Detail table.
Name of file: The name of the file is 999.ORDER_DETAIL.DATETIME.TXT, where 999 is the company code where you submitted the MDEXPRT periodic function and DATETIME is the date and time when the extract occurred, including an abbreviation, such as EDT, indicating the time zone. For example: 7.ORDER_DETAIL.Mon-Apr-25-11-28-03-EDT-2016.TXT.
Location of file: The Marketing Download Order Detail Export file text file is included in a zip file that is placed in the OMS-MARKETING container of the FILE_STORAGE table. The zip file in the FILE_STORAGE table has the same name as the text file that it contains, except for the ZIP extension.
Example of file: In this example, the first row is a header record indicating the name of each column and the subsequent rows contain the actual data; see the Marketing Download Order Detail Table for a description of the contents of this file.
Company|Order#|Ship To#|Line#|Customer#|Entity|Item/SKU|Qty Ordered|Qty Shipped|Qty Returned|Qty Canceled|Qty Sold Out|Qty Exchanged|Unit Price|Unit Offer Price|Return Reason Cd|Cancel Reason Code|Exchange Reason Code|Item Class|Long SKU Dept|Item Categ|Backorder Flag|Order Dt|Ship Dt|Return Dt|Cancel Dt|Sold Out Dt|Exchange Dt|Merch Loaded Cost|Price Meth|Disc Applied|Price Override Code|Promotion Code|Source Code|Offer
7|19|1|1|4|777|ITEM|6|0|0|0|0|0|31.66|80|000|000|000|1|7777|ICAT|N|20160425|0|0|0|0|0|40|6|A|||SOURCE|OFR
7|19|1|2|4|777|SKU BLUE SML WMNS|1|0|0|0|0|0|47.5|50|000|000|000|1|7777||N|20160425|0|0|0|0|0|0|6|A|||SOURCE|OFR
7|19|1|3|4|777|SKU RED|1|0|0|0|0|0|66.5|70|000|000|000|1|7777|ICAT|Y|20160425|0|0|0|0|0|45|6|A|||SOURCE|OFR
Note:
When you run the MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export periodic function, the system creates the Marketing Download Order Detail Export file even if there is no data to extract from the Marketing Download Order Detail table; in this situation, the text file contains only a header record indicating the column names.
Marketing Download Order Detail Table
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Company |
The code for the company where the order is located. OH: From the Company in the Order Detail table. LH: From the Company in the Order Line History table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Order number |
The order number of the order you created or maintained. OH: From the Order number in the Order Detail table. LH: From the Order number in the Order Line History table. Numeric, 8 positions. |
|
Order ship to number |
The order ship-to number associated with the order you created or maintained. OH: From the Ship to number in the Order Detail table. LH: From the Ship to number in the Order Line History table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Order detail number |
The order line number on the order you created or maintained. OH: From the Sequence number in the Order Detail table. LH: From the Sequence number in the Order Line History table. Numeric, 5 positions. |
|
Customer number |
The sold-to customer number on the order. From the Customer number in the Order Header table. Numeric, 9 positions. |
|
Entity |
The entity associated with the order. From the Entity number in the Division table for the division associated with the source code on the order detail; otherwise order header. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Item |
The item number on the order line. From the Item number in the Order Detail table. Alphanumeric, 12 positions. |
|
SKU |
The SKU code for the item on the order line. From the SKU code in the Order Detail table. Alphanumeric, 14 positions. |
|
Qty ordered |
The number of units of the item ordered. If the quantity is negative (a return), this field is blank. The Marketing Download function checks the associated order line history record to determine if the transaction was a return or exchange.
OH: From the Quantity ordered in the Order Detail table. Order maintenance transactions The quantity ordered is populated if the order maintenance transaction increased the order quantity; in this case, the quantity ordered represents the additional amount. If the order maintenance transaction decreased the quantity ordered, the function updates the quantity cancelled. However, if the cancel reason code used has Reduce demand selected, the quantity cancelled updates the quantity ordered with a negative number. LH: From the Quantity in the Order Line History table. Numeric, 5 positions. |
|
Qty shipped |
The number of units of the item shipped. OH: From the Quantity shipped in the Order Detail table. LH: From the Quantity in the Order Line History table for the order line history record with an activity code of S (shipped) or B (express billed). Numeric, 5 positions. |
|
Qty returned |
The number of units of the item returned, including returns entered as a negative order quantity in order entry. OH: From the Quantity returned in the Order Detail table. LH: From the Quantity for the order line history record with an activity code of R (return). Numeric, 5 positions. |
|
Qty cancelled |
The number of units of the item cancelled. The function updates this field if the cancel reason code used has Reduce demand unselected; however, if the cancel reason code has Reduce demand selected, the quantity cancelled updates the quantity ordered with a negative number. OH: From the Quantity cancelled in the Order Detail table. LH: From the Quantity for the order line history record with an activity code of C (cancel). Numeric, 5 positions. |
|
Qty sold out |
The number of units of the item soldout. OH: From the Quantity sold out in the Order Detail table. LH: From the Quantity for the order line history record with an activity code of O (soldout). Numeric, 5 positions. |
|
Qty exchanged |
The number of units of the item exchanged. OH: From the Quantity returned in the Order Detail table. LH: From the Quantity for the order line history record with an activity code of E (exchange). Numeric, 5 positions. |
|
Unit price |
The actual selling price of a single unit of the item on this order. From the Pre-discount amount in the Order Detail table. Numeric, 13 positions with a 2-place decimal. |
|
Unit offer price |
The actual selling price of a single unit of the item, as defined in the offer. From the Price in the Item Price table for the offer associated with the order detail line. Numeric, 13 positions with a 2-place decimal. |
|
Return reason code |
The return reason code used to return a quantity of this item. From the Return reason code for the order line history record with an activity code of R (return). Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Cancel reason code |
The cancel reason code used to cancel a quantity of this item. From the Cancel reason code for the order line history record with an activity code of C (cancel). Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Exchange reason code |
The exchange reason code used to exchange a quantity of this item. From the Exchange reason code for the order line history record with an activity code of E (exchange). Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Item class |
The item class associated with the item. From the Item class in the Item table for the item on the order detail line. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Long SKU department |
The long SKU department associated with the item. From the Long SKU department in the Item table for the item on the order detail line. Numeric, 4 positions. |
|
Item category |
The item category associated with the item. From the Category in the SKU table for the item on the order detail line. Alphanumeric, 4 positions. |
|
Backorder flag |
Indicates whether the item is on backorder. Selected = A quantity of the item is on backorder. Unselected = The item is not on backorder and can be reserved. Selected if there is a Backorder reason in the Order Detail table. |
|
Order date |
The date the order was created. From the Entered date in the Order Detail table. Numeric, 8 positions (YYYYMMDD format). |
|
Ship date |
The date a quantity of this item shipped. From the Date for the most recent order line history record with an activity code of S (shipped) or B (express billed). Numeric, 8 positions (YYYYMMDD format). |
|
Return date |
The date a quantity of this item was returned. From the Date for the most recent order line history record with an activity code of R (return). Numeric, 8 positions (YYYYMMDD format). |
|
Cancel date |
The date a quantity of this item was cancelled. From the Date for the most recent order line history record with an activity code of C (cancel). Numeric, 8 positions (YYYYMMDD format). |
|
Sold out date |
The date a quantity of this item was soldout. From the Date for the most recent order line history record with an activity code of O (soldout). Numeric, 8 positions (YYYYMMDD format). |
|
Exchange date |
The date a quantity of this item was exchanged. From the Date for the most recent order line history record with an activity code of E (exchange). Numeric, 8 positions (YYYYMMDD format). |
|
Merch loaded cost |
The loaded merchandise cost of this item. The function adds the vendor item cost (for the primary vendor defined for the item) to all of the vendor item additional charges associated with the vendor item to determine the loaded merchandise cost. This is the sum of Price from the Vendor Item table and the Percent or Unit amount from the Vendor Item Additional Charge table for each additional charge associated with the vendor item. The function first converts any vendor item additional charge percentages to a unit amount. Numeric, 13 positions with a 2-place decimal. |
|
Price method |
The price method used on the order detail line. 5 = column price 3 = contract price * = converted price 1 = coupon item price 2 = customer discount % 7 = offer price R = price override Y = price table K = price table default L = price table level override T = price table premium M = promotional item 6 = quantity break price |
|
|
I = repriced quantity break/item Q = repriced quantity break/offer V = repriced volume discount 4 = special source price U = upsell item N = no charge O = no charge/no cost E = price code P = regular hierarchy D = regular plus reprice C = use item cost SB = the Sale book item flag for the SKU/offer or item/offer is selected. From the Price method in the Order Detail table. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
|
Discount applied |
Indicates whether a discount has been applied to the order line. A = source discount B = order discount C = source and order discount blank = no discount From the Discount applied in the Order Detail table. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Price override code |
The price override reason code for the order line. From the Price override code in the Order Detail table. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Promotion code |
The promotion that applies to the order. Defaults from the Order Promotion table, where it is stored only if the Allow Manual Entry of Promotion Code (I63) system control value is selected, and the operator selected a promotion code when creating the order. If more than one Order Promotion record exists for the order, the system uses the first promotion code. If the Allow Manual Entry of Promotion Code (I63) system control value is unselected, this field is blank even if one or more promotions apply to the order. Alphanumeric, 7 positions. |
|
Source code |
The source code saved in the Order Detail table, if any. See the Default Offer Source Code to Order Detail Line (G28) system control value for a discussion of when the system saves the source code in the Order Detail table. Alphanumeric, 9 positions. |
|
Offer |
The offer associated with the order detail line. See Override Offer on Order Detail Line (D49) for a discussion on which offer is saved in the Order Detail table. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
Marketing Download Customer Status Change Table and Extract File
Marketing Download Customer Status Change table: This table contains a record for each marketing download trigger with a trigger type of customer status change (CS); see Populating the Marketing Download Tables and Extract Files for more information on how the MDEXTR Marketing Download Order and Customer Extract (CSX1041) periodic function determines when to create a record in the Marketing Download Customer Status Change table.
Marketing Download Customer Status Change Export file: The MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) periodic function creates a pipe-delimited text file based on the records in the Marketing Download Customer Status Change table.
Name of file: The name of the file is 999.CUST_STATUS_CHANGE.DATETIME.TXT, where 999 is the company code where you submitted the MDEXPRT periodic function and DATETIME is the date and time when the extract occurred, including an abbreviation, such as EDT, indicating the time zone. For example: 7.CUST_STATUS_CHANGE.Mon-Apr-25-11-28-03-EDT-2016.TXT.
Location of file: The Marketing Download Customer Status Change Export text file is included in a zip file that is placed in the OMS-MARKETING container of the FILE_STORAGE table. The zip file in the FILE_STORAGE table has the same name as the text file that it contains, except for the ZIP extension.
Example of file: In this example, the first row is a header record indicating the name of each column and the subsequent row contains the actual data; see the Marketing Download Customer Status Change Table for a description of the contents of this file.
Company|Customer#|Entity|Trans Dt|Prefix|Last Name|First Name|Initial|Company Name|Address Line 1|Address Line 2|Apartment|City|State|Zip|Country|Customer Class|Mail Name?|CSE Mail Name?|Rent Name?|Mail Code|Call Code|Deliverable Code|Hold/Bypass/Fraud|Alt Customer#|Address Line 3|Address Line 4|Email Sts
555|122|0|20160210||BROWN|T|||1234 SAMPLE ST|ADD 2|250|NATICK|MA|01760|US|C1|Y||Y|N|||||ADD3|ADD4|O1
Note:
When you run the MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export periodic function, the system creates the Marketing Download Customer Status Change Export file even if there is no data to extract from the Marketing Download Customer Status Change table; in this situation, the text file contains only a header record indicating the column names.
Marketing Download Customer Status Change Table
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Company |
The code for the company where the customer status change took place. From the Company in the Customer Sold To table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Customer number |
The sold-to customer number that was changed. From the Customer number in the Customer Sold To table. Numeric, 9 positions. |
|
Entity |
The entity associated with the sold-to customer. Used only if the Mail name in the Customer Sold To Entity table changed. From the Entity in the Marketing Download Trigger table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Transaction date |
The date when the customer sold-to was changed. From the Date created in the Marketing Download Trigger table. Numeric, 8 positions. |
|
Prefix |
The prefix of the sold-to customer. From the Prefix in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Last name |
The last name of the sold-to customer. From the Last name in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 25 positions. |
|
First name |
The first name of the sold-to customer. From the First name in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 15 positions. |
|
Initial |
The middle initial of the sold-to customer. From the Initial in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Company name |
The company name for the sold-to customer. From the Company name in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
|
Address line 1 |
The street address for the sold-to customer. From the Street address in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Address line 2 |
Address line 2 for the sold-to customer. From the Address line 2 in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Apartment |
The apartment for the sold-to customer. From the Apartment in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
City |
The city for the sold-to customer. From the City in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 25 positions. |
|
State |
The state code for the sold-to customer. From the State in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
|
Zip |
The postal code for the sold-to customer. From the Zip in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
Country |
The country code for the sold-to customer. From the Country in the Customer Sold to table. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Customer class |
The customer class for the sold-to customer. From the Customer class in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
|
Mail name? |
Indicates whether the customer receives future catalogs. Selected = Mail catalogs to the customer. Unselected = Do not mail catalogs to the customer. From the Mail name in the Customer Sold To table. |
|
Customer entity mail name? |
Indicates whether the sold-to customer, at the entity level, receives future catalogs. Selected = mail catalogs to the customer. Unselected = Do not mail catalogs to the customer. This field is unselected if there is no customer information at the entity level (the Track Customer History at Entity Level (F89) system control value is unselected). From the Mail name in the Customer Sold To Entity table. |
|
Rent name? |
Indicates whether to include the customer’s name in lists you sell to other companies for their own catalog mailings. Selected = Sell the customer’s name to another company. Unselected = Do not sell the customer’s name to another company. From the Rent name in the Customer Sold To table. |
|
Mail code |
A code that specifies how often, and under what conditions, to send mail to the customer. From the Mail code in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Call code |
A code that specifies how often, and under what conditions, to call the customer. From the Call code in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Deliverable code |
The deliverable code for the sold-to customer. From the Deliverable code in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Hold/bypass/fraud |
A code that controls how credit checking is performed for the customer during order entry. H = hold; the system places the customer’s orders on hold automatically. B = bypass; orders for the customer are not included in the credit check function in order entry. F = fraud; the system places the customer’s orders on “fraud” hold automatically. blank = normal fraud checking occurs in order entry. From the Hold/bypass/fraud in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Alternate customer number |
Alternate customer number for the sold-to customer. From the Interface customer code in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 15 positions. |
|
Address line 3 |
Address line 3 for the sold-to customer’s address. From the Address line 3 in the Customer Sold To Extended table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Address line 4 |
Address line 4 for the sold-to customer’s address. From the Address line 4 in the Customer Sold To Extended table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Email status |
Indicates the preferred method of correspondence. O1 (Email): Email is the preferred method of correspondence. O2 (Order-only email): Use email for order-related correspondence only; generate a document for other correspondence. O3 (No email): Do not use email for any correspondence; generate a document instead. O4 (Do not ask customer): Do not ask the customer for his/her email address; the customer has already been asked and has declined to provide it. The system does not generate any email correspondence to the customer, even if an email address is specified. From the Email status in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
Marketing Download Customer Inquiry Table and Extract File
Marketing Download Customer Inquiry table: This table contains a record for each marketing download trigger with a trigger type of customer inquiry (CI), customer action note (CN; only if a reason has been defined for the customer action), or order header (OH; only for a recipient customer); see Populating the Marketing Download Tables and Extract Files for more information on how the MDEXTR Marketing Download Order and Customer Extract (CSX1041) periodic function determines when to create a record in the Marketing Download Customer Inquiry table.
Marketing Download Customer Inquiry Export file: The MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) periodic function creates a pipe-delimited text file based on the records in the Marketing Download Customer Inquiry table.
Name of file: The name of the file is 999.CUST_INQUIRY.DATETIME.TXT, where 999 is the company code where you submitted the MDEXPRT periodic function and DATETIME is the date and time when the extract occurred, including an abbreviation, such as EDT, indicating the time zone. For example: 7.CUST_INQUIRY.Mon-Apr-25-11-28-03-EDT-2016.TXT.
Location of file: The Marketing Download Customer Inquiry Export text file is included in a zip file that is placed in the OMS-MARKETING container of the FILE_STORAGE table. The zip file in the FILE_STORAGE table has the same name as the text file that it contains, except for the ZIP extension.
Example of file: In this example, the first row is a header record indicating the name of each column and the subsequent row contains the actual data; see the Marketing Download Customer Inquiry Table for a description of the contents of this file.
Company|Customer#|Entity|CAC Seq#|Trans Dt|Prefix||Last Name|Initial|First Name|Company Name|Address Line 1|Address Line 2|Apartment|City|State|Zip|Country|Internet Address|Phone #1 Day|Phone # Eve|Phone #3 Fax|Customer Class|Mail Name?|CSE Mail Name?|Rent Name?|Mail Code|Mail Type|Offer|Source Code|Station ID|Deliverable Code|Hold/Bypass/Fraud|Action Entry Dt|Action Reason Code|Action Resolved Dt|Alt Customer#|Address Line 3|Address Line 4|Email Sts
7|4|777|0|20160425|||BROWN|R|THOMAS||1234 SAMPLE STREET|||WESTBOROUGH|MA|01581|US||5083310100|5083310101|0||Y||Y|Y|||||0|||0||0||||O1
Note:
When you run the MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export periodic function, the system creates the Marketing Download Customer Inquiry Export file even if there is no data to extract from the Marketing Download Customer Inquiry table; in this situation, the text file contains only a header record indicating the column names.
Marketing Download Customer Inquiry Table
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Company |
The company where the customer inquiry took place. From the Company in the Customer Sold To table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Customer number |
The sold-to customer associated with the customer inquiry. From the Customer sold to in the Customer Sold To table. Numeric, 9 positions. |
|
Entity |
The entity associated with the sold-to customer. From the Entity in the Marketing Download Trigger table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Customer action sequence number |
The customer action sequence number of the customer action note that was updated. From the Customer action sequence number in the Marketing Download Trigger table. Numeric, 2 positions. |
|
Transaction date |
The date the customer inquiry took place. From the Date created in the Marketing Download Trigger table. Numeric, 8 positions. |
|
Prefix |
The prefix of the sold-to customer. From the Prefix in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Gender code |
Not mapped. |
|
Last name |
The last name of the sold-to customer. From the Last name in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 25 positions. |
|
Initial |
The middle initial of the sold-to customer. From the Initial in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
First name |
The first name of the sold-to customer. From the First name in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 15 positions. |
|
Company name |
The company name of the sold-to customer. From the Company name in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
|
Address line 1 |
The street address of the sold-to customer. From the Street address in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Address line 2 |
Address line 2 of the sold-to customer. From the Address line 2 in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Apartment |
The apartment of the sold-to customer. From the Apartment in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
City |
The city of the sold-to customer. From the City in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 25 positions. |
|
State |
The state code of the sold-to customer. From the State in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
|
Zip |
The postal code of the sold-to customer. From the Zip in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
Country |
The country code of the sold-to customer. From the Country in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Internet address |
The email address of the sold-to customer. From the Email in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 50 positions. |
|
Phone number 1 day |
The day phone number of the sold-to customer. From the Phone in the Customer Sold To Phone Number table for phone type D. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Phone number 2 evening |
The evening phone number of the sold-to customer. From the Phone in the Customer Sold To Phone Number table for phone type E. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Phone number 3 fax |
The third (fax or mobile) phone number of the sold-to customer. From the Phone in the Customer Sold To Phone Number table for phone type F. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Customer class |
The customer class of the sold-to customer. From the Customer class in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
|
Mail name? |
Indicates whether the customer receives future catalogs. Selected = Mail catalogs to the customer. Unselected = Do not mail catalogs to the customer. From the Mail name in the Customer Sold To table. |
|
Customer entity mail name? |
Indicates whether the sold-to customer receives future catalogs. Selected = mail catalogs to the customer. Unselected = Do not mail catalogs to the customer. This field is unselected if there is no customer information at the entity level (the Track Customer History at Entity Level (F89) system control value is unselected). From the Mail name in the Customer Sold To Entity table. |
|
Rent name? |
Indicates whether to include the customer’s name in lists you sell to other companies for their own catalog mailings. Selected = Sell the customer’s name to another company. Unselected = Do not sell the customer’s name to another company. From the Rent name in the Customer Sold To table. |
|
Mail code |
A code that specifies how often, and under what conditions, to send mail to the customer. From the Mail code in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Call code |
A code that specifies how often, and under what conditions, to call the customer. From the Call code in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Mail type |
The code that identifies how you and the customer first established contact. B = buyer; the customer has placed an order. C = catalog requester; the customer has requested a catalog. L = list rental; the customer’s name was purchased from another company. R = recipient; the customer has received an order. S = suspect; the customer’s name was acquired through a telemarketing effort. Also, a customer that has placed an order, but then rejected the order. From the Current mail type in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Offer |
The offer associated with the current source code for the customer sold-to. From the Offer number in the Source code table for the source code for the customer sold-to. Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Source code |
The source code on the marketing download trigger record. From the Source code in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 9 positions. |
|
Station ID |
This field is blank. Numeric, 4 positions. |
|
Deliverable code |
Identifies whether the address is a business (commercial) or residential address. B = business address. R = residential address. N = no distinction between business and residential address. From the Delivery code in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Hold/bypass/fraud |
A code that controls how credit checking is performed for the customer during order entry. H = hold; the system places the customer’s orders on hold automatically. B = bypass; orders for the customer are not included in the credit check function in order entry. F = fraud; the system places the customer’s orders on “fraud” hold automatically. blank = normal fraud checking occurs in order entry. From the Hold/bypass/fraud in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
Action entry date |
The date the customer action note was created for the sold-to customer. From the Entry date in the Customer Action table. Numeric, 8 positions. |
|
Action reason code |
The reason code for the customer action note. From the Reason code in the Customer Action table. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
|
Action resolved date |
The date the customer action note was resolved. From the Resolved date in the Customer Action table. Numeric, 8 positions. |
|
Alternate customer number |
Alternate customer number for the sold-to customer. From the Interface customer code in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 15 positions. |
|
Address line 3 |
Address line 3 of the sold-to customer’s address. From the Address line 3 in the Customer Sold To Extended table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Address line 4 |
Address line 4 of the sold-to customer’s address. From the Address line 4 in the Customer Sold To Extended table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Email status |
Indicates the preferred method of correspondence. O1 (Email): Email is the preferred method of correspondence. O2 (Order-only email): Use email for order-related correspondence only; generate a document for other correspondence. O3 (No email): Do not use email for any correspondence; generate a document instead. O4 (Do not ask customer): Do not ask the customer for his/her email address; the customer has already been asked and has declined to provide it. The system does not generate any email correspondence to the customer, even if an email address is specified. This is the Email status in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
Marketing Download Customer Address Change Table and Extract File
Marketing Download Customer Address Change table: This table contains a record for each marketing download trigger with a trigger type of customer address change (CA); see Populating the Marketing Download Tables and Extract Files for more information on how the MDEXTR Marketing Download Order and Customer Extract (CSX1041) periodic function determines when to create a record in the Marketing Download Customer Address Change table.
Marketing Download Customer Address Change Export file: The MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) periodic function creates a pipe-delimited text file based on the records in the Marketing Download Customer Address Change table.
Name of file: The name of the file is 999.CUST_ADDRESS_CHANGE.DATETIME.TXT, where 999 is the company code where you submitted the MDEXPRT periodic function and DATETIME is the date and time when the extract occurred, including an abbreviation, such as EDT, indicating the time zone. For example: 7.CUST_ADDRESS_CHANGE.Mon-Apr-25-11-28-03-EDT-2016.TXT.
Location of file: The Marketing Download Customer Address Change Export text file is included in a zip file that is placed in the OMS-MARKETING container of the FILE_STORAGE table. The zip file in the FILE_STORAGE table has the same name as the text file that it contains, except for the ZIP extension.
Example of file: In this example, the first row is a header record indicating the name of each column and the subsequent row contains the actual data; see the Marketing Download Customer Address Change Table for a description of the contents of this file.
Company|Customer#|CSH Ship To#|Trans Dt|Prefix||Last Name|Initial|First Name|Company Name|Address Line 1|Address Line 2|Apartment|City|State|Zip|Country|Internet Address|Phone #1 Day|Phone # Eve|Phone #3 Fax|Alt Customer#|Address Line 3|Address Line 4|Email Sts
7|4|0|20160425|||BROWN|R|THOMAS||1234 SAMPLE STREET|||WESTBOROUGH|MA|01581|US||5083310100|5083310101|0||||O1
Note:
When you run the MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export periodic function, the system creates the Marketing Download Customer Address Change Export file even if there is no data to extract from the Marketing Download Customer Address Change table; in this situation, the text file contains only a header record indicating the column names.
Marketing Download Customer Address Change Table
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Company |
The company where the customer address change took place. From the Company in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Customer number |
The customer sold-to number associated with the customer address change. From the Customer Sold To in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Numeric, 9 positions. |
|
Ship to number |
The ship-to number associated with the customer address change. Included only if the address change is for the ship-to customer. From the Ship to number in the Customer Ship To table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Transaction date |
The date the customer address was changed. From the Date created in the Marketing Download Trigger table. Numeric, 8 positions. |
|
Prefix |
The prefix of the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Prefix in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Gender code |
Not mapped. |
|
Last name |
The last name of the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Last name in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 25 positions. |
|
Initial |
The middle initial of the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Initial in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 1 position. |
|
First name |
The first name of the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the First name in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 15 positions. |
|
Company name |
The company name for the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Company name in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
|
Address line 1 |
The street address of the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Street address in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Address line 2 |
Address line 2 of the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Address line 2 in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Apartment |
The apartment of the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Apartment in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
City |
The city of the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the City in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 25 positions. |
|
State |
The state code for the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the State in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
|
Zip |
The postal code for the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Zip in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
Country |
The country code for the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Country in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 3 positions. |
|
Internet address |
The email address for the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Email in the Customer Sold To table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To table (ship-to address change). Alphanumeric, 50 positions. |
|
Phone number 1 day |
The day phone number for the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Phone in the Customer Sold To Phone Number table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To Phone Number table (ship-to address change) for phone type D. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Phone number 2 evening |
The evening phone number for the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Phone in the Customer Sold To Phone Number table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To Phone Number table (ship-to address change) for phone type E. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Phone number 3 fax |
The third (fax or mobile) phone number for the sold-to customer or ship-to customer, depending on which address changed. From the Phone in the Customer Sold To Phone Number table (sold-to address change) or Customer Ship To Phone Number table (ship-to address change) for phone type F. Numeric, 10 positions. |
|
Alternate customer number |
Alternate customer number for the sold-to customer. From the Interface customer code in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 15 positions. |
|
Address line 3 |
Address line 3 for the sold-to customer’s address.From Address line 3 in the Customer Sold To Extended table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Address line 4 |
Address line 4 for the sold-to customer’s address. From Address line 4 in the Customer Sold To Extended table. Alphanumeric, 32 positions. |
|
Email status |
Indicates the preferred method of correspondence. O1 (Email): Email is the preferred method of correspondence. O2 (Order-only email): Use email for order-related correspondence only; generate a document for other correspondence. O3 (No email): Do not use email for any correspondence; generate a document instead. O4 (Do not ask customer): Do not ask the customer for his/her email address; the customer has already been asked and has declined to provide it. The system does not generate any email correspondence to the customer, even if an email address is specified. From the Email status in the Customer Sold To table. Alphanumeric, 2 positions. |
Marketing Download Customer Ownership Table and Extract File
Marketing Download Customer Ownership table: This table contains a record for each marketing download trigger with a trigger type of customer ownership (CO). If a customer has more than one ownership record, the system creates an ownership trigger record each time there is a change to either ownership. See Populating the Marketing Download Tables and Extract Files for more information on how the periodic function determines when to create a record in the Marketing Download Customer Ownership table.
Marketing Download Customer Ownership Export file: The MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) periodic function creates a pipe-delimited text file based on the records in the Marketing Download Customer Ownership table.
Name of file: The name of the file is 999.CUST_OWNERSHIP.DATETIME.TXT, where 999 is the company code where you submitted the MDEXPRT periodic function and DATETIME is the date and time when the extract occurred, including an abbreviation, such as EDT, indicating the time zone. For example: 7.CUST_OWNERSHIP.Mon-Apr-25-11-28-03-EDT-2016.TXT.
Location of file: The Marketing Download Customer Ownership Export text file is included in a zip file that is placed in the OMS-MARKETING container of the FILE_STORAGE table. The zip file in the FILE_STORAGE table has the same name as the text file that it contains, except for the ZIP extension.
Example of file: In this example, the first row is a header record indicating the name of each column and the subsequent row contains the actual data; see the Marketing Download Customer Ownership Table for a description of the contents of this file.
Company|Customer#|Ownership ID|Active Flag|Entry Dt|Confirm Dt|Description
555|276|A123456789|Y|20160201|20160201|BANKER OWNERSHIP RECORDS
Note:
When you run the MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export periodic function, the system creates the Marketing Download Customer Ownership Export file even if there is no data to extract from the Marketing Download Customer Ownership table; in this situation, the text file contains only a header record indicating the column names.
Marketing Download Customer Ownership Table
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Company |
The company where the customer ownership record was created. From the Company in the Customer Ownership table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Customer # |
The customer sold-to number associated with the customer ownership record. From the Customer # in the Customer Ownership table. Numeric, 9 positions. |
|
Ownership ID |
A code that represents a product the customer owns or previously owned. From the Ownership ID in the Customer Ownership table. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
Act Flag |
Indicates if the customer currently owns the product. Selected (default) = The customer currently owns the product. Unselected = The customer previously owned the product. From the Act in the Customer Ownership table. |
|
Entry Date |
The date the customer ownership record was created. From the Entry date in the Customer Ownership table. Numeric, 6 positions (MM/DD/YY format). |
|
Confirm Date |
The most recent date when the customer confirmed ownership of the product. From the Confirm date in the Customer Ownership table. Numeric, 6 positions (MM/DD/YY format). |
|
Description |
A description of the product the customer owns or previously owned. From the Description in the Customer Ownership table. Alphanumeric, 120 positions. |
Marketing Download Customer Profile Table and Extract File
Marketing Download Customer Profile table: This table contains a record for each marketing download trigger with a trigger type of customer profile (CP). If a customer has more than one profile record, the system creates a Marketing Download Customer Profile record for each Customer Profile record defined for the sold to customer. See Populating the Marketing Download Tables and Extract Files for more information on how the periodic function determines when to create a record in the Marketing Download Customer Profile table.
Marketing Download Customer Profile Export file: The MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export (PFR0130) periodic function creates a pipe-delimited text file based on the records in the Marketing Download Customer Profile table.
Name of file: The name of the file is 999.CUST_PROFILE.DATETIME.TXT, where 999 is the company code where you submitted the MDEXPRT periodic function and DATETIME is the date and time when the extract occurred, including an abbreviation, such as EDT, indicating the time zone. For example: 7.CUST_PROFILE.Mon-Apr-25-11-28-03-EDT-2016.TXT.
Location of file: The Marketing Download Customer Profile Export text file is included in a zip file that is placed in the OMS-MARKETING container of the FILE_STORAGE table. The zip file in the FILE_STORAGE table has the same name as the text file that it contains, except for the ZIP extension.
Example of file: In this example, the first row is a header record indicating the name of each column and the subsequent row contains the actual data; see the Marketing Download Customer Profile Table for a description of the contents of this file.
Company|Customer#|Profile Code|Profile Code Desc|Profile Data Code|Profile Data Code Desc
555|123456798|1|||
Note:
When you run the MDEXPRT Marketing Download Export periodic function, the system creates the Marketing Download Customer Profile Export file even if there is no data to extract from the Marketing Download Customer Profile table; in this situation, the text file contains only a header record indicating the column names.
Marketing Download Customer Profile Table
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Company |
The company where the customer profile record was created. From the Company in the Customer Profile table. Numeric, 3 positions. |
|
Customer # |
The customer sold-to number associated with the customer profile record. From the Customer # in the Customer Profile table. Numeric, 9 positions. |
|
Profile Code |
A number that represents a demographic profile category. From the Profile code in the Customer Profile table. Alphanumeric, 10 positions. |
|
Profile Code Description |
The description of the demographic profile category. From the Description in the Profile table. Alphanumeric, 20 positions. |
|
Profile Data Code |
A user-defined code that represents a valid response for the profile category. From the Profile data code in the Customer Profile table. Alphanumeric, 30 positions. |
|
Profile Data Code Description |
Text that describes the profile data response. Example: For the profile category of Income level, you might have profile data codes such as the following: 1 = less than $20,000 2 = $20,000-$29,000 3 = $30,000-$39,000 4 = $40,000-$49,000 5 = more than $49,000 From the Description in the Profile Data table. Alphanumeric, 40 positions. |