About Options to Ensure High Availability for VMware Workloads in OCI
At first glance, moving to Oracle Cloud VMware Solution (OCVS) seems like the most applicable and convenient approach. However, it requires considering Oracle Database licensing on OCVS, separation of OCVS clusters for Oracle Databases, database migration, management, operations, and ensuring high availability. You must also consider various factors especially when migrating Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) databases that are not available on OCVS.
In this solution playbook, you learn about the architecture options, considerations, and Oracle Maximum Availability Architecture (MAA) compliance levels, to migrate your on-premises Oracle Databases to OCI. With this migration, you benefit from the built-in high availability, automated disaster recovery, migrations, database management and operations, the flexibility, online scalability, cloud licensing model, and the included Oracle Database Enterprise Edition options and packs, especially in Oracle Autonomous Database.
Architecture
OCI offers both managed and autonomous database services with built-in high availability and automated disaster recovery configurations:
- Oracle Base Database Service
- Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure
- Oracle Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure
- Oracle Autonomous Database Serverless
- Oracle Autonomous Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure
Oracle Zero Downtime Migration (ZDM) allows you to migrate your on-premises Oracle Databases to Oracle Database Cloud Services in a simple and automated way while minimizing the migration downtime.
The following architecture shows the various Oracle Database Cloud Services options:
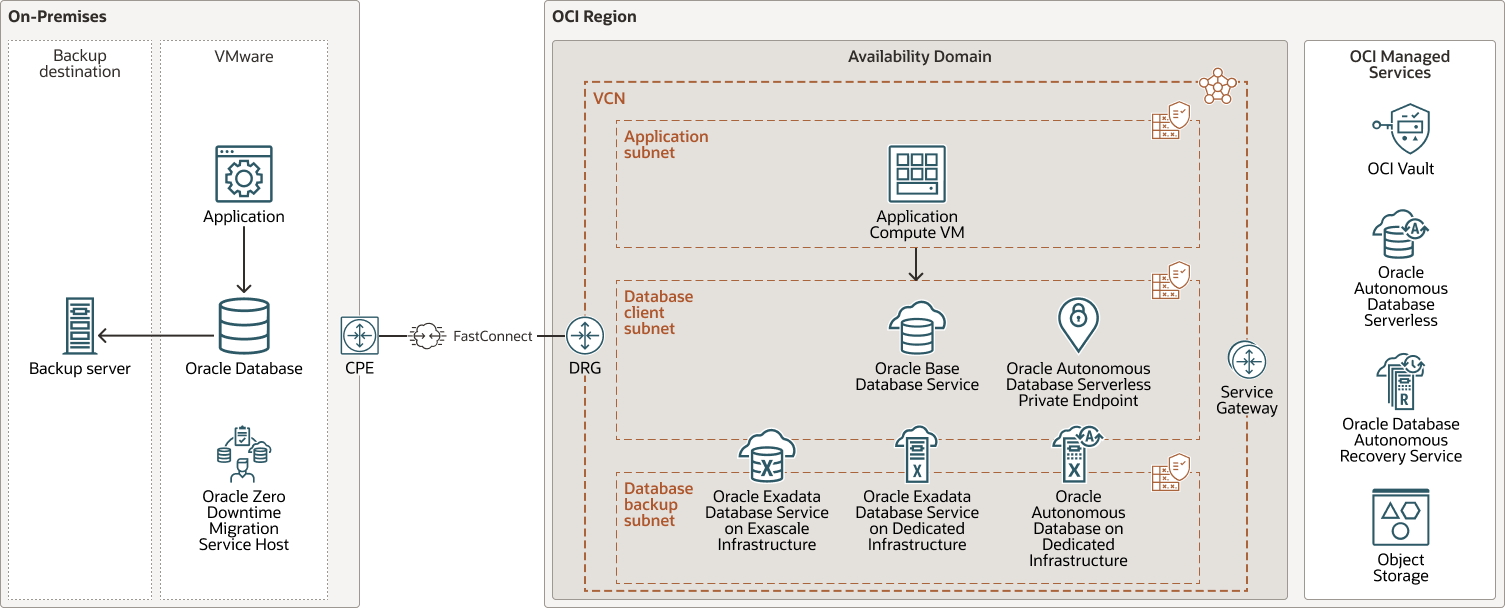
Description of the illustration migrate-vmware-workloads-oci-arch.png
migrate-vmware-workloads-oci-arch-oracle.zip
This architecture consists of the following components:
- Region
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region is a localized geographic area that contains one or more data centers, called availability domains. Regions are independent of other regions, and vast distances can separate them (across countries or even continents).
- Availability domain
Availability domains are standalone, independent data centers within a region. The physical resources in each availability domain are isolated from the resources in the other availability domains, which provides fault tolerance. Availability domains don’t share infrastructure such as power or cooling, or the internal availability domain network. So, a failure at one availability domain shouldn't affect the other availability domains in the region.
- Fault domain
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each availability domain has three fault domains with independent power and hardware. When you distribute resources across multiple fault domains, your applications can tolerate physical server failure, system maintenance, and power failures inside a fault domain.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN) and subnet
A VCN is a customizable, software-defined network that you set up in an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region. Like traditional data center networks, VCNs give you control over your network environment. A VCN can have multiple non-overlapping CIDR blocks that you can change after you create the VCN. You can segment a VCN into subnets, which can be scoped to a region or to an availability domain. Each subnet consists of a contiguous range of addresses that don't overlap with the other subnets in the VCN. You can change the size of a subnet after creation. A subnet can be public or private.
- Route table
Virtual route tables contain rules to route traffic from subnets to destinations outside a VCN, typically through gateways.
- Security list
For each subnet, you can create security rules that specify the source, destination, and type of traffic that must be allowed in and out of the subnet.
- Service gateway
The service gateway provides access from a VCN to other services, such as Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage. The traffic from the VCN to the Oracle service travels over the Oracle network fabric and does not traverse the internet.
- Dynamic routing gateway (DRG)
The DRG is a virtual router that provides a path for private network traffic between VCNs in the same region, between a VCN and a network outside the region, such as a VCN in another Oracle Cloud Infrastructure region, an on-premises network, or a network in another cloud provider.
- FastConnect
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect creates a dedicated, private connection between your data center and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. FastConnect provides higher-bandwidth options and a more reliable networking experience when compared with internet-based connections.
- Zero
Downtime Migration Service Host
The Oracle Zero Downtime Migration service host should be a dedicated system, but can be shared for other purposes. Oracle ZDM software requires a standalone Oracle Linux host running on any one of the following platforms: Oracle Linux 7, Oracle Linux 8, or Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8. The Oracle ZDM service host must be able to connect to the source and the target database servers; as long as connectivity is guaranteed, the service host can be located anywhere.
- Oracle Base Database Service
Oracle Base Database Service is an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) database service that enables you to build, scale, and manage full-featured Oracle databases on virtual machines. Oracle Base Database Service uses OCI Block Volumes storage instead of local storage and can run Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) to improve availability.
- Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure
Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure enables you to leverage the power of Exadata in the cloud. Oracle Exadata Database Service delivers proven Oracle Database capabilities on purpose-built, optimized Oracle Exadata infrastructure in the public cloud. Built-in cloud automation, elastic resource scaling, security, and fast performance for all Oracle Database workloads helps you simplify management and reduce costs.
- Exadata Database
Service on Exascale
Infrastructure
Oracle Exadata Database Service on Exascale Infrastructure provides the same cloud service experience as Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure, but without requiring you to subscribe to dedicated infrastructure. You can start with a small virtual machine (VM) cluster, and easily scale as your needs grow. Oracle manages all of the physical infrastructure in a shared multitenancy infrastructure service model.
- Autonomous Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure
Oracle Autonomous Database on Dedicated Exadata Infrastructure is a fully managed, preconfigured database environment that you can use for transaction processing and data warehousing workloads. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure handles creating, backing up, patching, upgrading, and tuning the database.
- Autonomous Database Serverless
Oracle Autonomous Database Serverless is an Oracle Autonomous Database. You have a fully elastic database where Oracle autonomously operates all aspects of the database lifecycle from database placement to backup and updates.
- Oracle Database Autonomous
Recovery Service
Oracle Database Autonomous Recovery Service is an Oracle Cloud service that protects Oracle databases. With backup automation and enhanced data protection capabilities for OCI databases, you can offload all backup processing and storage requirements to Oracle Database Autonomous Recovery Service, thereby eliminating backup infrastructure costs and manual administration overhead.
- Object storage
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage provides quick access to large amounts of structured and unstructured data of any content type, including database backups, analytic data, and rich content such as images and videos. You can safely and securely store and then retrieve data directly from the internet or from within the cloud platform. You can scale storage without experiencing any degradation in performance or service reliability. Use standard storage for "hot" storage that you need to access quickly, immediately, and frequently. Use archive storage for "cold" storage that you retain for long periods of time and seldom or rarely access.
- Full Stack Disaster Recovery
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Full Stack Disaster Recovery is an orchestration and management service that provides comprehensive disaster recovery capabilities for all layers of an application stack, including infrastructure, middleware, database, and application.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Vault
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Vault enables you to centrally manage the encryption keys that protect your data and the secret credentials that you use to secure access to your resources in the cloud. You can use the Vault service to create and manage vaults, keys, and secrets.
OCI Vault also offers a rich set of Rest APIs to manage vaults and keys.