4 Working with the Cohort Viewer
This chapter contains the following topics:
Introduction
Cohort viewers enables you to view patients or subjects in a variety of formats. With an Oracle Healthcare Omics (OHO, formerly known as ODB) license, you can look at genomic data in a circular genome viewer (using Visquick) or export data into formats acceptable by the Integrative Genome Viewer.
Viewing a Cohort List
After the patient or subject count is displayed, you may want to review the data for these patients or subjects. You can view this data from the Cohort Queries tab as well. For details, see Viewing Patient Count and Patient Data.
You can view a cohort list for:
-
a current active query
-
a query from the library
-
saved patient or subject list
-
on an ad-hoc basis if you have specific patients or subjects you want to examine
Viewing Cohort List for Current Active Query
To view a cohort list for the query currently loaded in the Cohort Query tab:
-
Click the Cohort Viewer tab.
-
On the left side, check that active query is selected under Patient IDs source.
-
Click Submit. The cohort list and details are displayed on the right.
Use the pane on the left to select and filter the data you want to view for the cohort list. For details on filtering data, see Filtering Data in Cohort List.
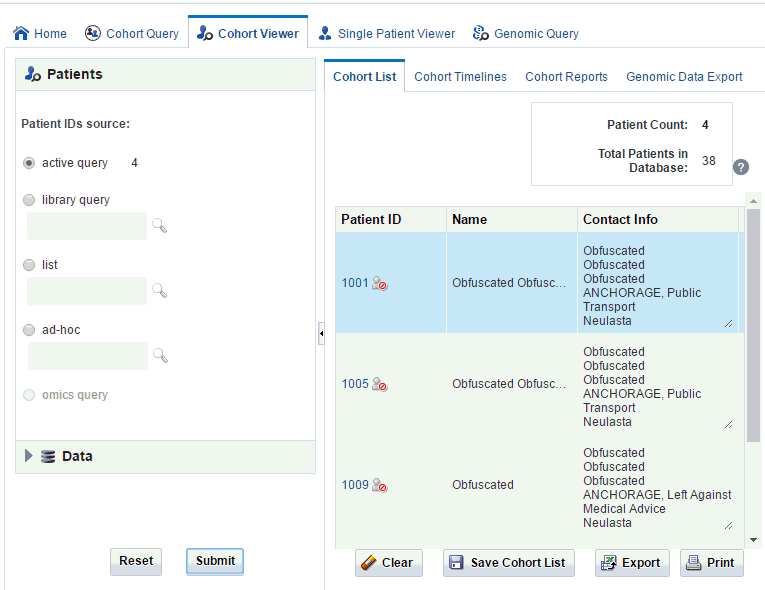
Description of the illustration ''trc27.gif''
Viewing Cohort List for Library Query, List or Ad-hoc
To view the cohort list for a library query or from a saved list or an ad-hoc query:
-
Navigate to the Cohort Viewer tab.
-
On the left side, select one of the following:
-
library query - to view the cohort list for a patient or subject query from the library
-
list - to view the cohort list for a saved patient or subject list
-
ad-hoc - to view list for specific patients or subjects you want to examine
-
-
Click Submit. The cohort list details are displayed on the right.
Filtering Data in Cohort List
The left hand panel contains topics that reflect the query selection criteria from the Clinical Information category. To filter data for the cohort list:
-
Click Data on the left hand panel to view the topics under it.
-
Select one or more check boxes for the data you want to display in your list.
-
Click Submit. The system reruns the query and adds relevant patient or subject data for each patient or subject listed.
A patient or subject may have multiple data for a particular data category, for example, a patient or subject can have more than one procedure or medication. Consequently, the cohort list details may display multiple rows or records for each patient or subject. Selecting several data categories to display may significantly limit your ability to review multiple patients or subject at the same time.
-
To remove data, clear the appropriate boxes and select Submit.
-
To export the list to a Microsoft Excel sheet, click Export. To display the date in the dd/mm/yyyy format, use the formatting option in Microsoft Excel.
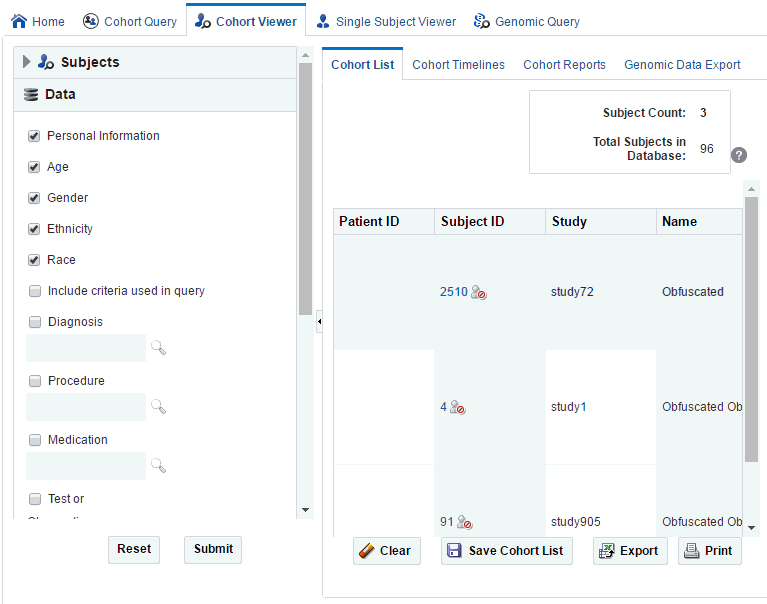
Description of the illustration ''cohortlist.gif''
Displaying Reference Range Values
Cohort List supports displaying Reference Range values, if available, along with numeric results of Observation. To display reference range values:
-
Click Data on the left hand panel to show the topics within it.
-
Select Test or Observation.
-
Enter the value you want to search for.
-
Click Submit. Where available, the reference high and reference low range values are displayed along with numeric results.
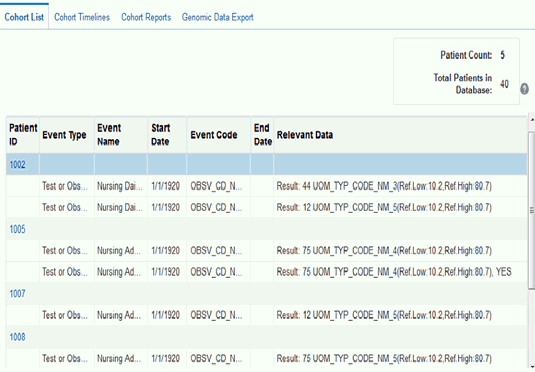
Description of the illustration ''trc80.gif''
Viewing Cohort Timelines
You can view patient or subject data for a small subset of patients in the form of a timeline. This process involves the following steps:
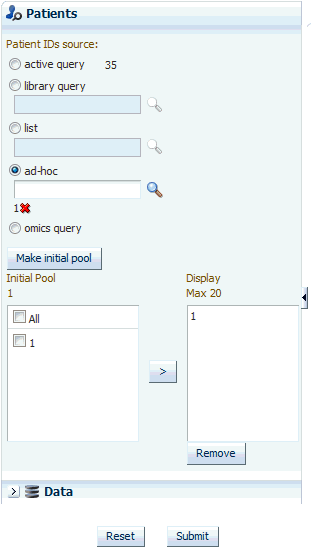
Selecting Patients or Subjects
This step is similar to how you select patients or subjects for the Cohort List. You can select patients or subjects either from the current active query, from a query in the library, or by entering the Patient or Subject ID number.
To select patients or subjects:
-
Navigate to Cohort Viewer > Cohort Timelines.
-
Select the source of your subject ID from among the active query, library query, saved list or an ad-hoc query.
-
Click Make initial pool.All the subjects or patients in the selected query are added to the initial pool.
-
Now select up to 20 patients or subjects and move them from the initial pool to the display list by clicking the arrow button. This selection is what the system will reference for displaying data in the timelines view.
-
Click Submit to view the corresponding data.
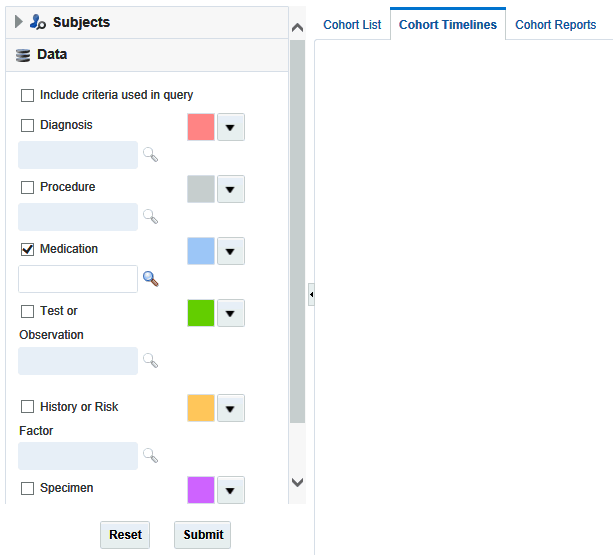
Selecting Data
After you have identified patients or subjects for the Display List, select the clinical information to be displayed in the viewer.
-
In the left hand panel, click Data. The system displays a list of data topics.
Each data topic has a distinct color associated with it. This is so that data can be visually separated for the same patient or subject. You can change the assigned colors by using the drop-down arrow next to each color.
-
Select each data topic you want to view. Then click the magnifying glass icon for each selected topic to search or specify the particular criteria. A popup search window is displayed.
-
For each topic, enter the details for the topic.
-
Click Search.
-
Select one or more items and use the arrow button to move them to the right hand box.
-
Click Submit.
-
Once you have selected and specified the data you want to view, select Submit at the bottom of the left hand panel. A linear view of the selected data is displayed.
Displaying Patient or Subject Data
The subject and patient data display is divided into two sections.
-
The left side has attributes about the selected patients
-
The right side shows the colored layers of the selected clinical data, in a timeline view.
To move the section divider, hover the cursor on the white vertical line. Select and drag the divider to the desired position. You can hide either section, by clicking the small left hand arrow on the right hand side of the respective area.
Click the Subject ID to navigate to the single patient viewer.
Note:
If you are using Mozilla Firefox, click the patient ID. On Microsoft Internet Explorer and Google Chrome, double-click the patient ID.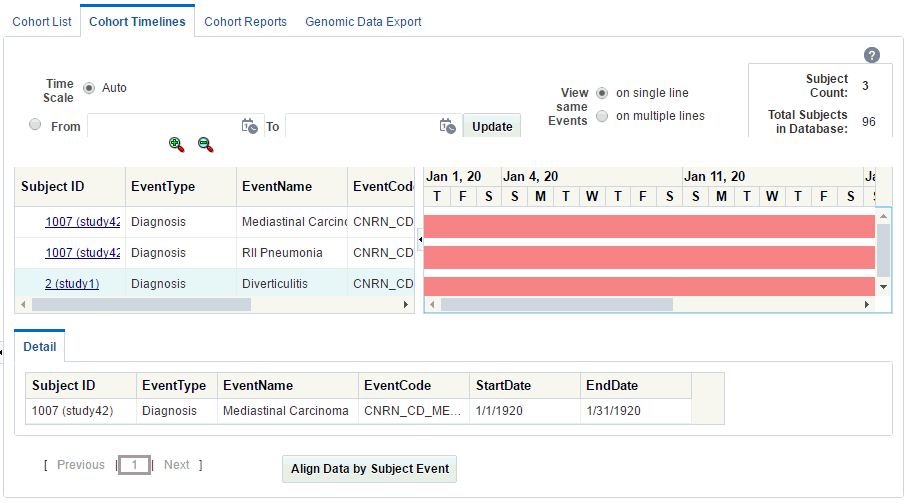
Description of the illustration ''trc32.gif''
-
To view the data for a specific date range, use the Time Scale option for the date range. Enter the From and to dates and click Update.
The default Auto option displays the data without a specific time reference.
-
If an event has both Start Date and End Date values, then the timeline uses the Event Code to mark the start of an event.
-
A tool tip on the timeline provides additional information about the event.
-
On selecting one event in the timeline, the Detail table below the timeline lists all the occurrences of the event and provides additional information such as the start and the end date of the occurrences.
-
For Test or Observation events with numeric result values, the Detail table displays the results of all the occurrences of the event. If two or more occurrences of Test or Observation event have numeric results available, then the Graph tab displays a line graph for those numeric result values.
-
Since the Test or Observation event has only one date event, the user interface uses dummy End Date values that are 1 day later than the corresponding Start Date values to render the graph. The Detail table also displays these dummy End Date values.
-
Events are not displayed on the left hand table or on the timeline in the following conditions:
-
When an event's Start Date is null.
-
When an event has only one Date attribute (for example, Observation has only Observation Date) and the attribute's value is null.
-
-
If an event's End Date is null, then the System Date is used for displaying the event.
Selecting the Timeline Mode
Use the View same Events option to display the events in one of the following modes:
This is the default mode of displaying data on the Timelines tab.
Description of the illustration ''trc110.gif''
In this mode, all instances of a repeating event are displayed on the same line and separate events are displayed on separate lines.
Overlapping occurrences are displayed on separate lines in the timeline. However, the left hand table displays a single row corresponding to all occurrences of the event.
The tabular display on the left side uses alternating background color to visually delineate data of different patients or subjects. All of the rows corresponding to a patient or subject, for a particular Event Type, have one background color and the next set of rows are in a different color.
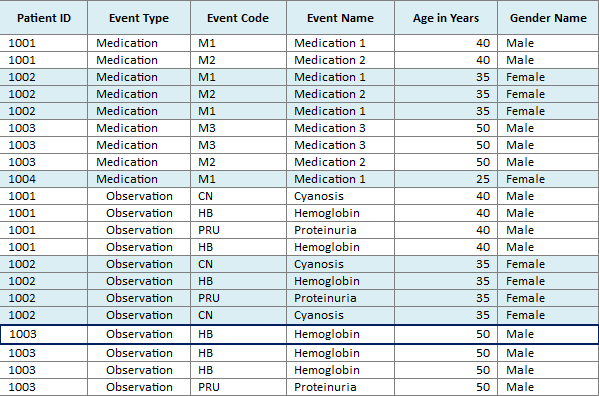
Description of the illustration ''trc111.gif''
Description of the illustration ''trc112.gif''
In this mode, all of the instances of events are displayed on different lines, even if the events are repeating.
Aligning Data by Patient or Subject Event
You can designate a particular piece of clinical data to serve as the anchor, around which the remaining data is adjusted in the viewer. For example, if you choose a particular procedure as the anchor for alignment, the medications or diagnostic tests are adjusted in the display to show how long before (or after) the anchor they were administered. To do this:
-
Click Align Data by Subject Event. The Align Data window is displayed.
-
Enter Subject ID. You can also use the drop-down arrow to select a subject ID.
-
Click the magnifying glass icon next to the Align by field and select the option you want to use.
When you select a particular diagnosis or medication code to align patients, all the event codes at different hierarchical nodes are considered for the selected event code.
-
Click Submit.
Description of the illustration ''trc64.gif''
Including Criteria Used in Query
You can view the data used to define the inclusion criteria of the currently active query by selecting the Include criteria used in query option in the Data section of the left hand panel. The criteria defined in the cohort query is then displayed in the data section of the cohort timeline.
If the inclusion criteria of the active query is not based on any data topics supported on the cohort timeline, a message is displayed to select at least one supported data element.
Note:
The data topic Clinical Encounter can be selected only in conjunction with other data elements that are linked to Clinical Encounter, for example Diagnosis, Procedure and so on.For example, in the Figure 4-3, Diagnosis is selected to be included in the criteria used in the query. After you select it, the corresponding diagnosis criteria is displayed. Click Submit to view the corresponding timeline events.
Figure 4-3 Include Criteria Used in Query
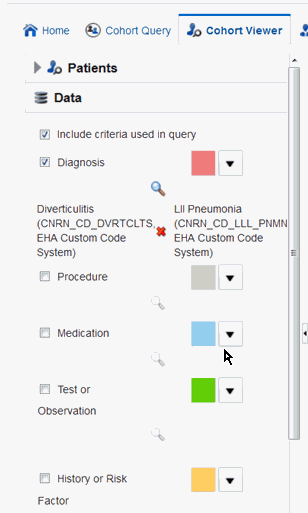
Description of ''Figure 4-3 Include Criteria Used in Query''
Viewing Cohort Reports
The Cohort Reports tab lets you view various cohort reports.
Note:
In the Active Query mode, if no filters have been selected in Cohort Query, then the reports display data of only the first 10,000 patients or subjects. This limit is configurable and can be changed using the DEFAULT_ACTIVE_QUERY_LIMIT property in the TRC.properties file.However, irrespective of the patient or subject selection option, if the count exceeds the value specified in GENOMIC.REPORTS_MAX_PATIENT_COUNT of TRC.properties file, a warning message is displayed. You can either continue to plot with a large number of patient or subjects (might impact performance) or change the selected cohort to a smaller number.
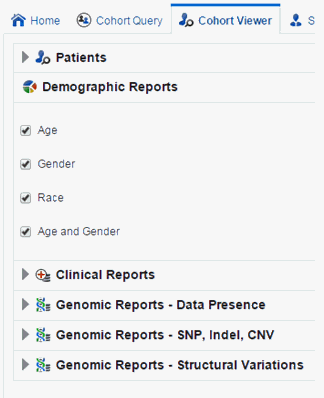
Demographic Reports
You can view demographic reports for a patient list. The queries for these reports can be based on patient list in the cohort query, the library, patient list, ad-hoc query or omics. Perform the following steps to view demographic reports:
-
Navigate to Cohort Viewer > Cohort Reports tab.
-
Expand the Patients node on the left.
-
Select the Patient IDs Source.
-
Expand the Demographic Reports tab.
-
Select the check boxes for the data you want displayed in your list.
-
Select Submit.
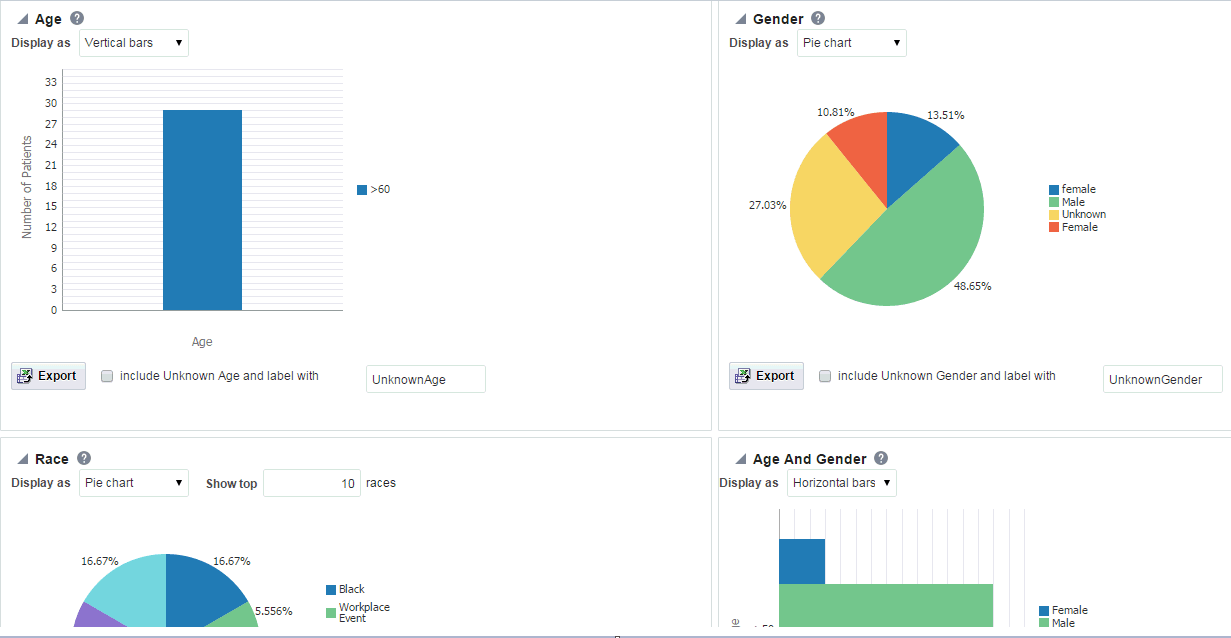
-
The system reruns the query and adds relevant patient or subject data for each patient or subject listed. Depending on you selection, reports age, gender, race and/or age and gender will be displayed. The data will be displayed as pie charts or bar graphs depending on your settings.
Handling Unknown Data
If any missing or unknown data is present, a check box is provided at the bottom of each graph to include missing or unknown data as shown in Figure 4-6.
For the Age, Gender and Race graphs, if the check box is selected, the graph is refreshed with the unknown data. Here unknown data refers to age, gender or race details that are not defined for a particular patient.
For the Age and Gender graph, the unknown age for different genders is combined into one group and the known age is in other group. Both groups are shown in the graph.
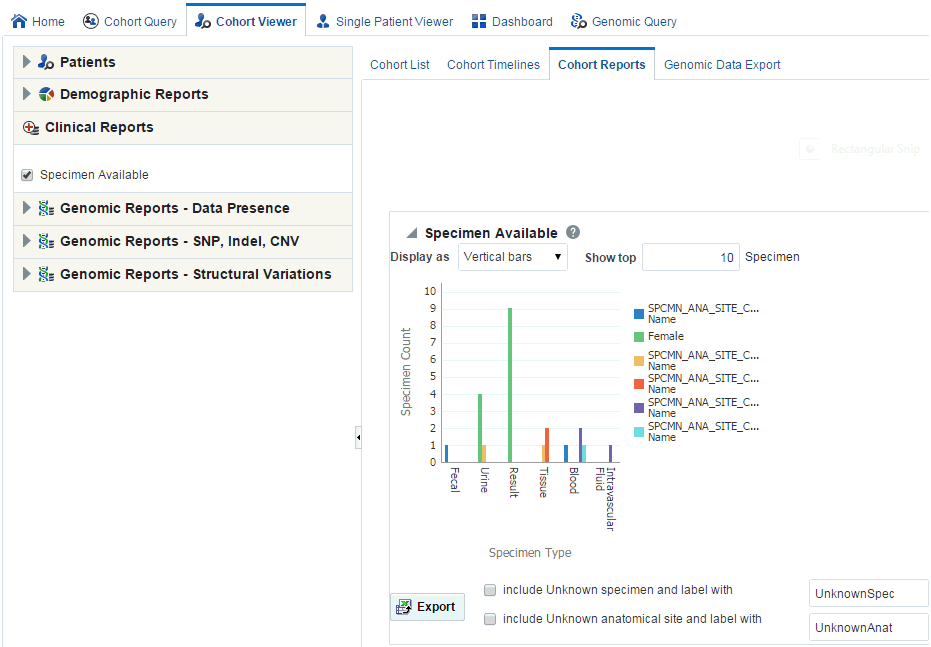
Clinical Reports
You can view clinical reports for a patient list. The queries for these reports can be based on patient list in the cohort query, the library, patient list, ad-hoc query or omics. Perform the following steps to view a clinical reports:
-
Navigate to Cohort Viewer > Cohort Reports tab.
-
Expand the Patients node on the left.
-
Select the Patient IDs Source.
-
Expand the Clinical Reports tab.
-
Select the Specimen Available check box.
-
Select Submit.
-
The system reruns the query and adds relevant patient or subject data for each patient or subject listed. Depending on you selection, reports age, gender, race and (or) age and gender will be displayed. The data will be displayed as pie charts or bar graphs depending on your settings.
Handling Unknown Data
If any missing or unknown data is present, a check box is provided at the bottom of each graph to include missing or unknown data as shown in Figure 4-8.
If Include Unknown Specimen and Label With or Include Unknown Anatomical site and Label With are selected, the graph is refreshed with the unknown data. Here unknown data refers to the specimen and anatomical site data that is not defined for a particular patient.
Genomic Reports
Data Presence
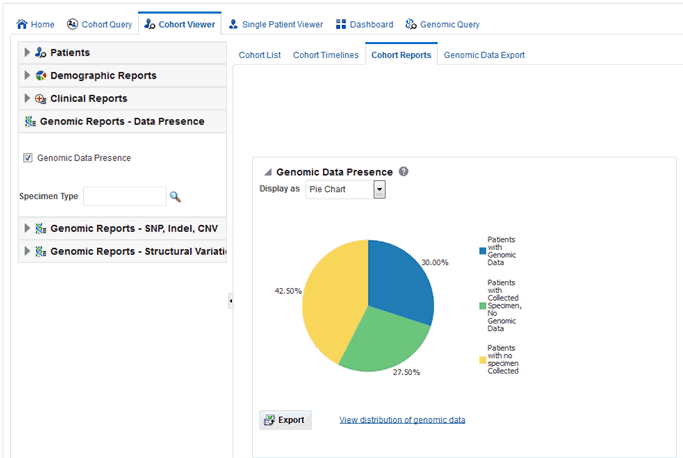
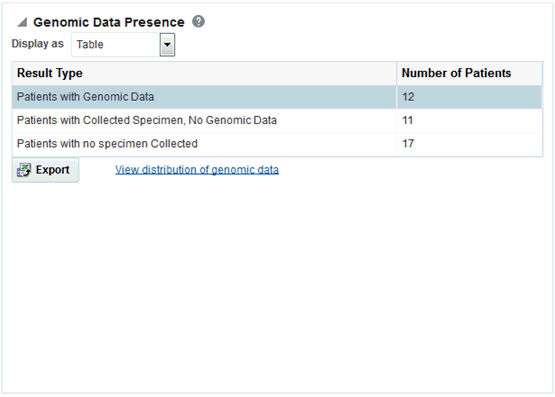
The Genomic Reports - Data presence lets you view a breakup of the patient cohort as follows:
-
Patients in the cohort with specimens collected that have accessible genomic data
-
Patients in the cohort with specimens collected but no genomic data
-
Patients in the cohort with no specimens collected
You can view the Data Presence plot as Pie Chart, Horizontal Bars, Vertical Bars, and Table. The report also provides an option to view the distribution of present genomic data along the following available genomic data types:
-
Sequencing
-
RNA-seq
-
Gene Expression
-
Copy Number Variation
Perform the following steps to view a Genomic data presence report:
-
Navigate to Cohort Viewer > Cohort Reports tab.
-
Expand the Patients node on the left and select the source of patient or subject identifiers.
-
Expand the Genomic Reports - Data Presence node in the left panel.
-
Select the Genomic Data Presence check box. An optional Specimen Type input field appears to allow for filtering the initial cohort on specimen type.
-
Click Submit to generate the report.
-
To change the display type after generating the report, select display option from the Display as drop-down list.
-
To view a breakup of present genomic data by data type, click View distribution of genomic data.
Figure 4-11 Distribution of Genomic Data
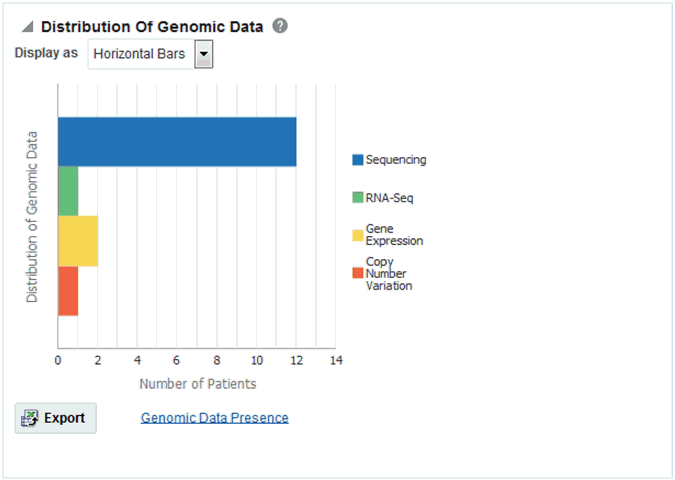
Description of ''Figure 4-11 Distribution of Genomic Data''
-
To export the graphical plot type displays as a PNG image, and the table type displays as a Excel spreadsheet, click Export.
SNP, Indel and CNV
Gene Level Reports - Mutated Gene Frequency and Gene Expression
Genomic Reports - SNP, Indel and CNV display the available SNP Indel genomic reports based on the selected cohort of patients or subjects, if in subject context.
To view a SNP, Indel and CNV report:
-
Navigate to Cohort Viewer > Cohort Reports tab.
-
Expand the Patients node on the left and select the source of patient or subject identifiers.
-
Navigate to Genomic Reports - SNP, Indel, CNV and select Gene Level Reports.
-
Select Mutated Gene Frequency and Gene Expression. You can also add additional parameters such Specimen Type, Anatomical Site, Assembly Version which will only consider results linked to the selected categories.
Selecting Include All Specimen includes specimens without genomic data whereas not selecting this returns a result with only genomic data.
-
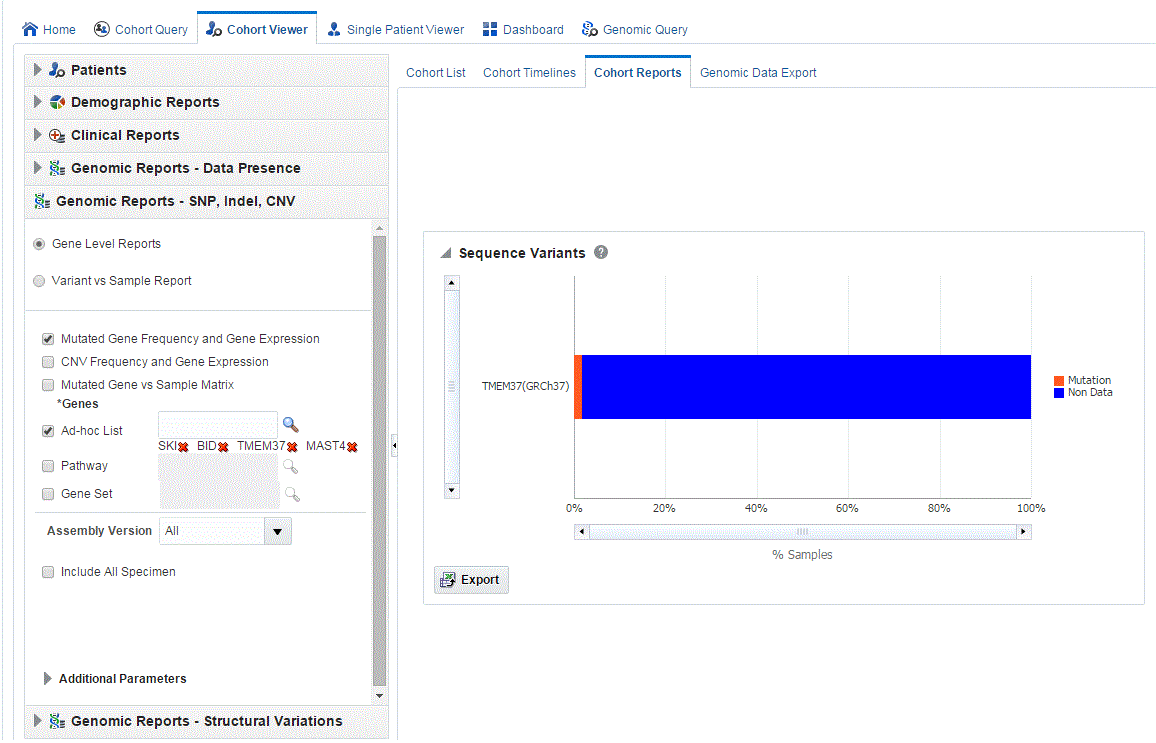
Click Submit. A histogram report appears with the percentage of samples for the relevant cohort, which have sequence variants information within the selected genes.
You can display the results as horizontal bars, vertical bars, or as a table. To export the bar results into PDF or the table results into Excel, click Export.
Note:
When opening the Excel file, you may receive a warning from Excel stating that the file is in a different format than specified by the file extension. This warning can be safely ignored. For more information, seehttp://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23943_01/web.1111/b31973/af_table.htm#autoId34. -
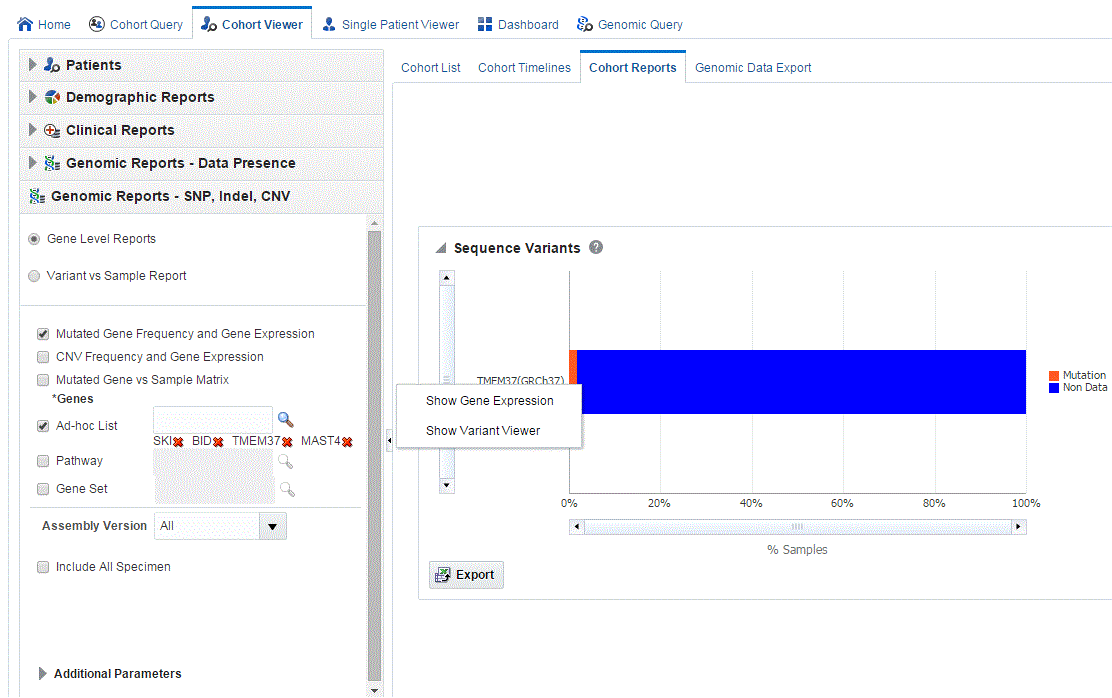
Clicking the histogram for the different selected genes displays a popup to either get the Gene Expression plot or the Variant Viewer to display details of the variant.
-
To view the Gene Expression details for Single Channel or Dual Channel, click Show Gene Expression in the popup. In the Single Channel Expression, you must provide hybridization details.
-
Selecting Show Variant Viewer displays necessary information about all variants present in that gene in the samples belonging to the selected cohort of subjects or patients.
The Mutation plot displays the total number of specimen (on y-axis) having a particular mutation (on y-axis) falling in the selected gene for belonging to a specific reference. The x-axis contain the range of gene region including the flanking region.
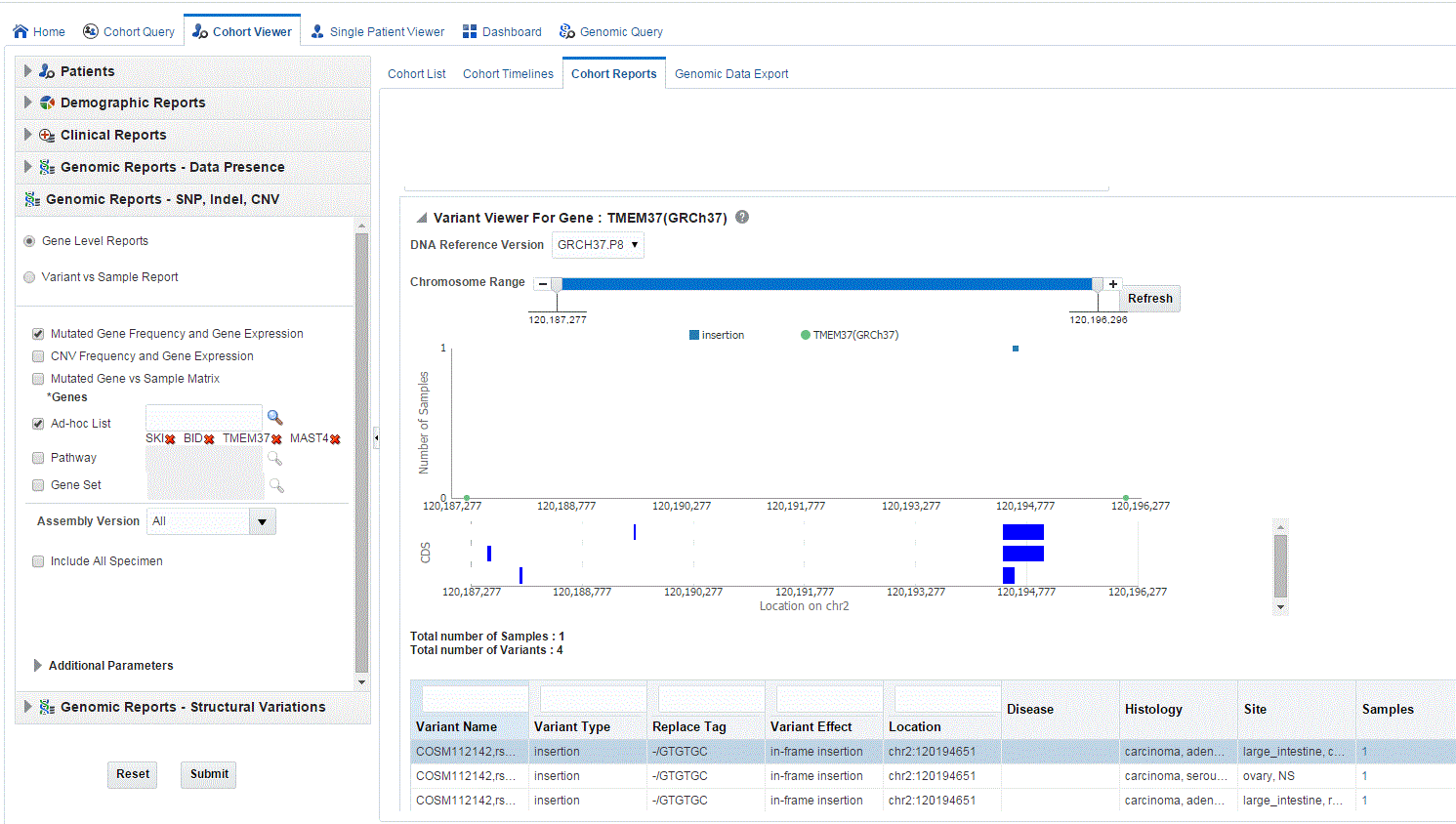
Description of the illustration ''trc66.gif''
The CDS plot displays bars of CDS regions for each of the Ensembl Transcripts belonging to the selected gene of a selected reference version. Each row in the CDS plot represents one Transcript ID of the selected gene and reference version.
Details of each variant like Variant name, Variant Type, Replace Tag, Variant Effect if present, Location, Disease if loaded, Histology, Site Total number of samples, Patients are displayed. The results are grouped in descending order of specimen count, such that each row contains unique variants.
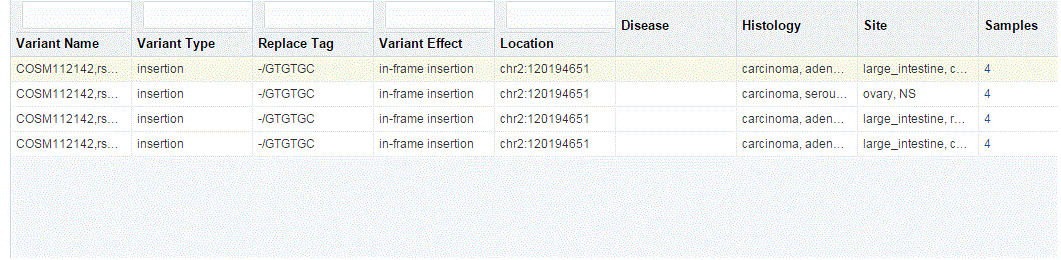
Description of the illustration ''trc67.gif''
-
You can drill down to each mutation by clicking Number of samples present in the samples column of the table. A table and a pie chart are displayed below the table. The table contains details such Sample ID, Study (only in subject context), Anatomical Site and Patient or Subject ID, which contains the selected mutation, number of samples which do not contain this mutation (labeled as Other) from the group of samples having mutations for the selected gene and selected reference version.
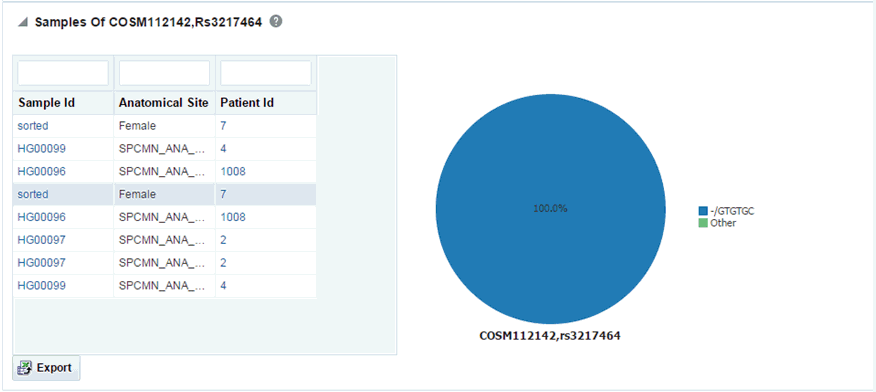
Description of the illustration ''trc68.gif''
Copy Number Variation Frequency and Gene Expression
To view CNV Frequency and Gene Expression reports:
-
Navigate to Cohort Viewer > Cohort Reports tab.
-
Expand the Patients node on the left and select the source of patient or subject identifiers.
-
Navigate to Genomic Reports - SNP, Indel, CNV and select Gene Level Reports.
-
Select CNV Frequency and Gene Expression. You can also add additional parameters such Specimen Type, Anatomical Site, Assembly Version, which will only consider results linked to the selected categories.
Selecting Include All Specimen includes specimens without genomic data whereas not selecting this returns a result with only genomic data.
Figure 4-14 Select Source of Patient or Subject Identifiers
Description of ''Figure 4-14 Select Source of Patient or Subject Identifiers''
-
Click Submit. A histogram report displays the percentage of samples for the relevant cohort, which have copy number variants information within the selected genes.
You can display the results as horizontal bars, vertical bars, or as a table. To export the bar results into or table results into Excel by clicking Export.
Note:
When opening the Excel file, you may receive a warning from Excel stating that the file is in a different format than specified by the file extension. This warning can be safely ignored. For more information, refer tohttp://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23943_01/web.1111/b31973/af_table.htm#autoId34.Figure 4-15 Show the Copy Number Variations
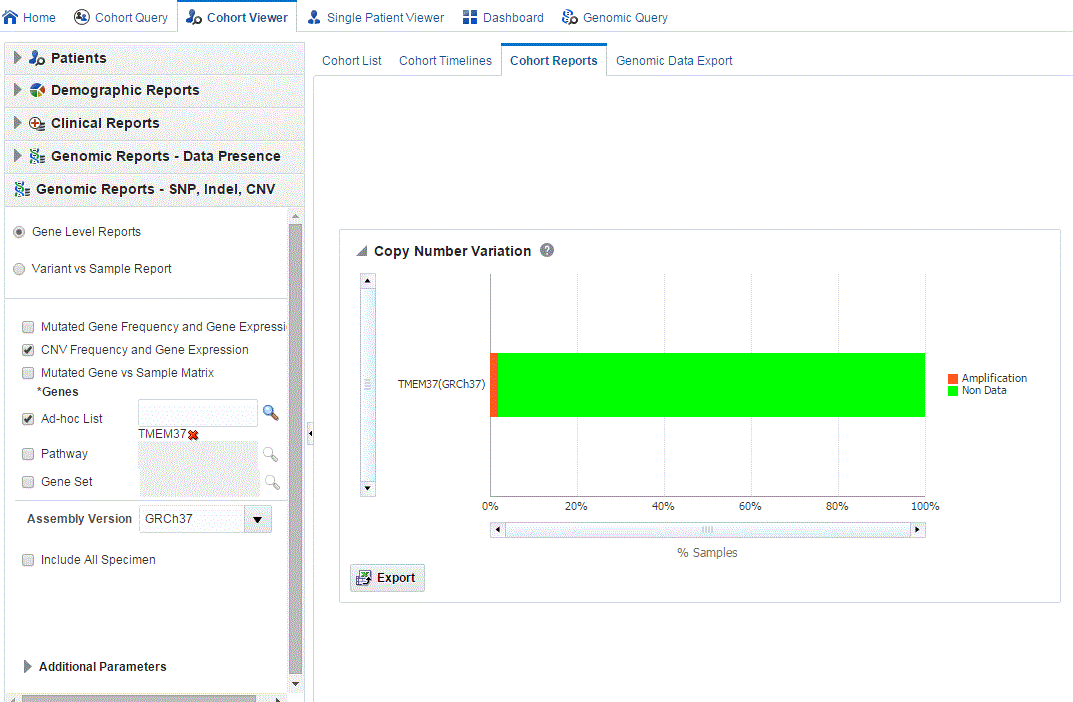
Description of ''Figure 4-15 Show the Copy Number Variations''
-
Clicking the histogram displays a popup is to either get the Gene Expression plot or the CNV Viewer to display details of the variant.
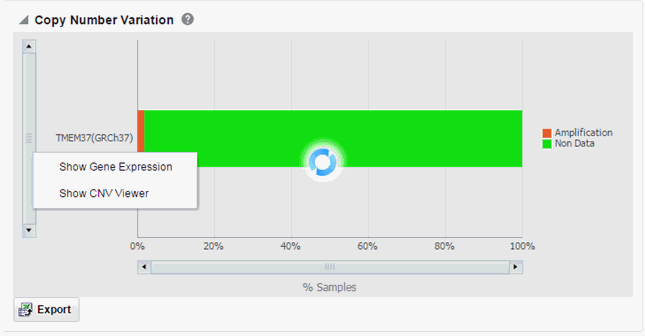
Description of the illustration ''trc70.gif''
-
To display the Gene Expression details for Single Channel or Dual Channel, select Show Gene Expression. In the Single Channel Expression, you must provide hybridization details.
-
Clicking Show CNV Viewer displays necessary information about all CNV variants that are present in that gene in the samples belonging to the selected cohort of subjects or patients.
The CNV plot displays each specimen (on y-axis) and its values falling in the selected gene for belonging to a specific reference.The x-axis plots the range of gene region. The plot is color coded with CNV with Gain (CNV > 0.2) is Red, Normal (-0.2<CNV<0.2) in grey and Loss (CNV < -2) in Green.
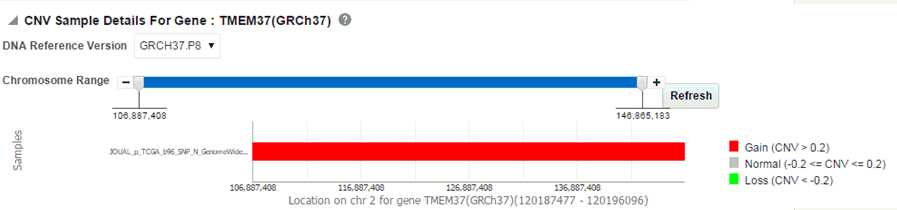
Description of the illustration ''trc71.gif''
The CNV table provides details of CNV data such as Samples, File Type, Chromosome, Anatomical Site, Start Position, End Position, CNV Value and Patient or Subject ID.

Description of the illustration ''trc72.gif''
Mutated Gene vs Sample Matrix
The Mutated Gene vs Sample Matrix plot displays a high-level pictorial view of the presence of specific variants in genes of interest across various specimens of patients or subjects in a cohort. You can see if a particular gene from a specimen has selected mutations or no-mutations or no-data loaded. The same plot lets you view CNV data on the genes for the specimens.
The specimens are grouped together for each patient or subject and are ordered based on their collection date.
You can also view patient_id:specimen_number(specimen_vendor_number):collection_dt:no of variants in the tooltip for each data point.
Variant selection is based on variant impact, implying that the depiction of mutations on genes for each specimen is based on the variants having selected variant impacts. For example, if you select frameshift mutation for EGFR, then the query searches for variants causing frameshift impact for EGFR gene and reports as mutation if it finds any such variants. If there is only non-variant information, then it reports as non-mutation in the plot. If there is no data, then it shows no-data in the plot.
Following are the definitions of various types of data in the plot.
| Data | Definition |
|---|---|
| Mutation | If any of the variants are present in the selected gene of a specimen, then it is reported as mutation. |
| No Mutation | If none of the variants are present in the selected gene of a specimen and there is non-variant information available for that gene, then it is reported as No Mutation. |
| No data | If there are no variants and also no non-variant information and there is no-call data for the selected gene of a specimen or there is no-data loaded for this specimen, then it will be reported as no data. |
| Amplification | If there is CNV data, which has seg_mean value more than zero, then it is reported as amplification. |
| Deletion | If there is CNV data which has seg_mean value less than zero, then it is reported as deletion. |
To view this plot:
-
Navigate to Cohort Viewer > Cohort Reports tab.
-
Expand the Patients node on the left and select the source of patient or subject identifiers.
-
Navigate to Genomic Reports - SNP, Indel, CNV and select Gene Level Reports.
-
Select Mutated Gene vs Sample Matrix.
-
Select genes either by ad-hoc list, pathway or gene set. Data is filtered using the Variant Impact or the cosmic mutation selected.You can also add additional parameters such Specimen Type, Anatomical Site, Assembly Version, which will only consider results linked to the selected categories.
Selecting Include All Specimen includes specimens without genomic data whereas not selecting this returns a result with only genomic data.
-
Click Submit. A report displays the percentage and details of samples for the relevant cohort which have sequence variants and copy number variants information within the selected genes.
Figure 4-16 Mutated Gene vs Sample Matrix Report
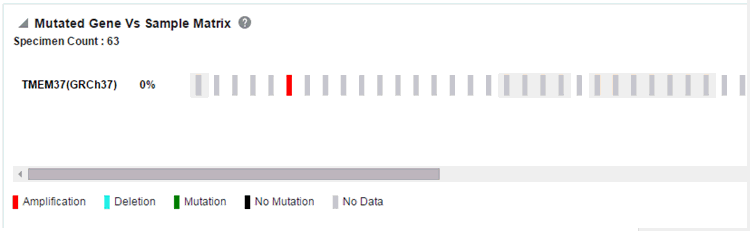
Description of ''Figure 4-16 Mutated Gene vs Sample Matrix Report''
Each bar represents a specimen, which is grouped patient-wise and in the order of the specimen collection date. The Sequence Variants and CNV information for each specimen is displayed. The percentage of specimens with mutation on the gene is also mentioned. Export functionality is provided at each specimen level.
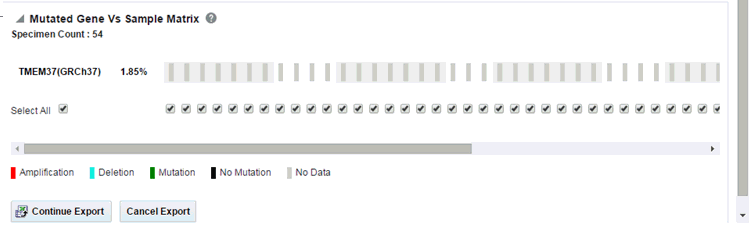
Description of the illustration ''trc89.gif''
Note:
When opening the Excel file, you may receive a warning from Excel stating that the file is in a different format than specified by the file extension. This warning can be safely ignored. For more information, refer tohttp://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23943_01/web.1111/b31973/af_table.htm#autoId34.There is a limit to the number of specimens that can be seen in the gene matrix plot. This is an application level parameter called 'MAX_SPEC_REPORT' that is defined in the TRC.properties file. The default value of this parameter is 1000. If the number of specimens in the cohort used for this analysis is greater than the specified value, then the following warning message is displayed:
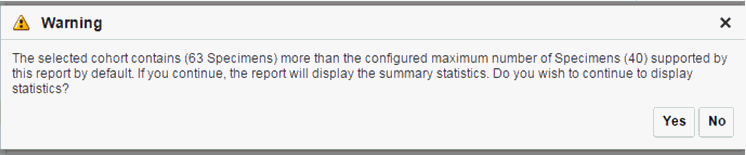
Description of the illustration ''trc90.gif''
If you continue from this warning message, the report displays the summary statistics instead of the matrix plot. You may have to decrease the cohort size based on some criteria like specimen type or anatomical site or otherwise use cohort query to view the matrix plot. Alternatively, you can also change the default value of MAX_SPEC_REPORT parameter to a desired value and rebuild the plot. However, rebuilding maybe affect the performance of the plot generation.
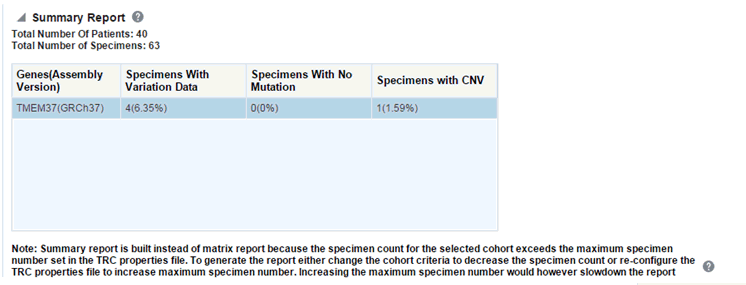
Description of the illustration ''trc91.gif''
The summary report only displays the percentage of specimens with different categories of data as shown in the image above.
Variant vs Sample Reports
This option is displayed on the Genomic Reports - SNP Indel genomic reports available, based on the selected cohort of patients or subjects, if in subject context. It provides a high level pictorial view of the presence of specific variants of interest across various specimens of patients or subjects in a cohort.
The specimens are grouped together for each patient or subject and are ordered based on their collection date. You can also view patient_id:specimen_number(specimen_vendor_number):collection_dt in the tooltip for each data point.
To generate the plot:
-
Navigate to Cohort Viewer > Cohort Reports tab.
-
Expand the Patients node on the left and select the source of patient or subject identifiers.
-
Navigate to Genomic Reports - SNP, Indel, CNV and select Variant vs Sample Report.
Description of the illustration ''trc92.gif''
-
Select Variant ID.
You can also add additional parameters such Specimen Type, Anatomical Site, Assembly Version, which will only consider results linked to the selected categories.
Selecting Include All Specimen includes specimens without genomic data whereas not selecting this returns a result with only genomic data.
-
Click Submit. A report displays the percentage and details of samples for the relevant cohort, which have mutation within the selected genes.
Each bar represents a specimen, which is grouped together patient wise and in the order of the specimen collection date. The mutation information for each specimen is displayed. Each row represents one variant and the label represents reference_id, assembly version and the variant replace_tag value to maintain the uniqueness of the variant. The percentage of specimens for each mutation is also mentioned.

Description of the illustration ''trc94.gif''
Note:
When opening the Excel file, you may receive a warning from Excel stating that the file is in a different format than specified by the file extension. This warning can be safely ignored. For more information, refer tohttp://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23943_01/web.1111/b31973/af_table.htm#autoId34.There is a limit on the number of specimens that can be seen in matrix plot. This is an application level parameter called 'MAX_SPEC_REPORT' that is defined in the TRC.properties file. The default value of this parameter is 1000. If the number of specimens in the cohort used for this analysis is greater that the specified value then the following warning message is shown below:

Description of the illustration ''trc90.gif''
If you continue from this warning message, the report will display the summary statistics instead of the matrix plot. You may have to decrease cohort size based on some criteria like specimen type or anatomical site or otherwise using cohort query to view the matrix plot. Alternatively, you can also change the default value of MAX_SPEC_REPORT parameter to a desired value and rebuild the plot but the performance of the plot generation may be effected. The summary report will only display the percentage of specimens with different categories of data as shown below.
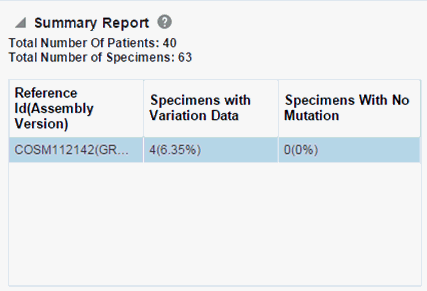
Description of the illustration ''trc95.gif''
Structural Variations
Structural Variations in Genes
To view the structural variations in genes:
-
Navigate to Cohort Viewer > Cohort Reports tab.
-
Expand the Patients node on the left and select the source of patient or subject identifiers.
-
Navigate to Genomic Reports - Structural Variations and select Structural Variations in Genes.
You can also add additional parameters such as specimen type, anatomical site, DNA version, which will only consider results linked to the selected categories.
Figure 4-18 Select Source of Patient or Subject Identifiers
Description of ''Figure 4-18 Select Source of Patient or Subject Identifiers''
-
Click Submit. A histogram report shows the occurrence of structural variations involving genes sorted from the gene involved in most SVs for a given cohort, and subsequently display genes with decreasing frequency of Structural Variations. By default, the top 10 genes are shown and you can increase or decrease the number of genes displayed.
-
You can display the results as horizontal bars, vertical bars, or as a table. To export the bar results into PDF or table results into Excel, click Export.
Note:
When opening the Excel file, you may receive a warning from Excel stating that the file is in a different format than specified by the file extension. This warning can be safely ignored. For more information, refer tohttp://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23943_01/web.1111/b31973/af_table.htm#autoId34.Figure 4-19 Show the Structural Variations
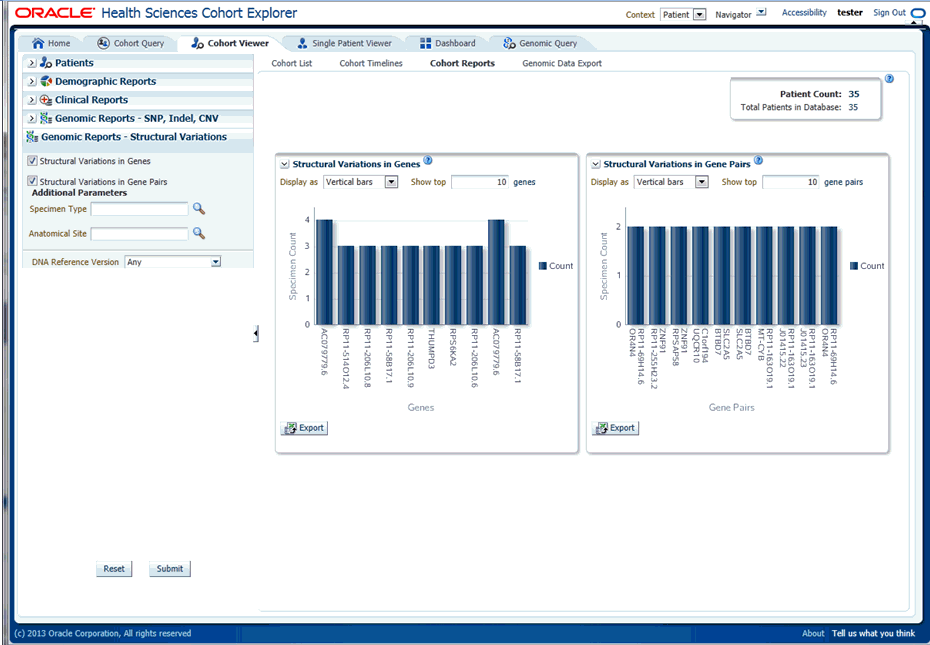
Description of ''Figure 4-19 Show the Structural Variations''
Structural Variations in Gene Pairs
Structural Variations in Gene Pairs is one of the SV genomic reports available to you based on the selected cohort of patients or subjects, if it is in the subject context.
-
Navigate to Cohort Viewer > Cohort Reports tab.
-
Expand the Patients node on the left and select the source of patient or subject identifiers.
-
Navigate to Genomic Reports - Structural Variations and select Structural Variations in Gene Pairs.
You can also add additional parameters such as specimen type, anatomical site, DNA version, which will only consider results linked to the selected categories.
Figure 4-20 Select Source of Patient or Subject Identifiers

Description of ''Figure 4-20 Select Source of Patient or Subject Identifiers''
-
Click Submit. A histogram report displays the frequency of occurrence of structural variations in a cohort among gene pairs. The histogram is automatically sorted from the gene pair with most SVs as per cohort and the incidence decreases or at best stays the same for each subsequent gene pair. By default, top 10 gene pairs are shown and you can change the default number of bars shown.
-
You can display the results as horizontal bars, vertical bars, or as a table. To export the bar results into PDF or the table results into Excel, click Export.
Note:
When opening the Excel file, you may receive a warning from Excel stating that the file is in a different format than specified by the file extension. This warning can be safely ignored. For more information, refer tohttp://docs.oracle.com/cd/E23943_01/web.1111/b31973/af_table.htm#autoId34.Figure 4-21 Show the Structural Variations

Description of ''Figure 4-21 Show the Structural Variations''
Exporting Genomic Data
The Genomic Data Export page is used to export the genomic data for patients or subjects filtered based on Study, Specimen type and Anatomical Site in a specific file format.
Currently, exporting variation data from sequencing platform, single and double channel gene expression and Copy Number Variation data in VCF, SEG, RES and GCT file formats are supported. These formats are supported by the IGV browser.
Selecting Patients or Subjects
You can download data for patients or subjects already selected in an active query or from a query library or from ad-hoc list of patients ID. There is no upper limit on the number of patients or subjects to be selected, however the performance slows down as more and more patients are selected.
Selecting Results to Export
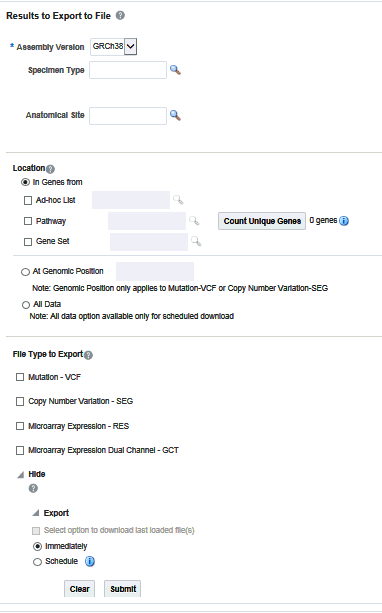
After selecting Patients, select the Assembly Version, Specimen Type, and Anatomical Site. These selection criteria will help you filter out patients based on the requirements. Specimen Type and Anatomical Site also have multiselect options. Currently only one version of data can be exported at a time.
Selecting Location
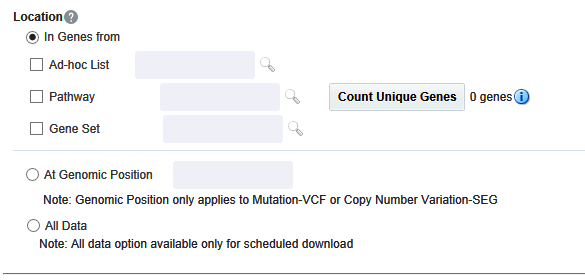
You can download genomic data for either a list of genes or pathway or a gene set for a defined region in chromosome. You can also export the genomic data for a specific chromosome region and also the complete genomic data for the patient using the All Data option.
On Exadata, the code takes advantage of chromosome based partitioned data for VCF and SEG export. This enables more accurate results to be exported, including intergenic result. On non-Exadata systems, only the results that lie within any gene boundary are exported.
In Genes From
You can select genes from one or more of the provided three options.
-
Using ad-hoc List, you can select one or more genes.
-
Using Pathway, you can select one or more pathways which in turn will get the list of genes associated with the selected pathway internally for querying.
-
With Gene Set, you can use the user-defined collection of genes.
The genomic data to be downloaded is based on the above selected genes.
At Genomic Position
You can alternatively download genomic data using the genomic co-ordinates. You specify the chromosome region in a standard format for the Variation and CNV data to be exported. The Gene Expression - RES and Gene Expression - GCT download option would be disabled for genomic region criteria. You can specify a complete chromosome or a part of chromosome as criteria. Currently, only one chromosome region at a time is implemented for search.
The following chromosome region formats are supported.
-
CHR15:10000-200000: Considers region between 10000 to 200000 in chromosome 15.
-
CHR15:1,200,000+5000 - Considers 5000 bases upstream from 1,200,000 position in chromosome 15.
-
CHR15 - Considers whole of the chromosome 15.
-
CHR15:1000 - Considers 1000th nucleotide position of chromosome 15.
Selecting File Type
This panel lists out four file type options to export. You can select all four options at a time. For Genomic Region criteria, the Gene Expression – RES, and Gene Expression Dual Channel options are disabled.
Click Submit. The data is generated and a link is provided in the bottom panel separately for each result type.
Mutation - VCF
This option exports the sequencing variation data for the selected patients or subjects for either the selected genes, pathway, geneset or for a given chromosome region as selected in the previous option. VCF supports multiple specimens' data in a single file.
The metadata header gives the following information that differs based on the search criteria:
-
##fileformat=VCFv4.1
-
##fileDate: Date and time of the VCF file generated.
-
##source=Oracle Healthcare Omics (OHO, formerly known as Omics Data Bank)
-
##Total Number of patients included in this VCF file
-
##Total Number of samples included in this VCF file
-
7. ##INFO=<ID=NS, Number=1, Type=Integer, Description=Number of Samples With Data>
-
##FORMAT=<ID=GT,Number=1,Type=String,Description=Genotype>
-
##FORMAT=<ID=GQ, Number=1, Type=Integer, Description=Genotype Quality>
-
##FORMAT=<ID=GQVAF, Number=2, Type=Integer, Description=Genotype_quality_X>
-
##FORMAT=<ID=DP, Number=1, Type=Integer, Description=Read Depth>
-
##FORMAT=<ID=AD,Number=.,Type=Integer,Description=Allelic depths for the ref and alt alleles in the order listed >
-
##FORMAT=<ID=HQ, Number=2, Type=Integer, Description=Haplotype Quality>
-
##FORMAT=<ID=BQ,Number=.,Type=Integer,Description=Average base quality >
-
##FORMAT=<ID=MQ,Number=.,Type=Integer,Description=Average mapping quality >
-
##FORMAT=<ID=SS,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description=Variant status relative to non-adjacent Normal,0=wildtype,1=germline,2=somatic,3=LOH,4=post-transcriptional modification,5=unknown>
-
##FORMAT=<ID=SSC,Number=1,Type=Integer,Description=Somatic Score>
The following data types are imported to VCF file:
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| CHROM | chromosome |
| POS | position of the variation |
| ID | dbSNP ID or COSMIC ID associated with a variant |
| REF | reference allele |
| ALT | variant alleles |
| QUAL | not populated. Will have '.' specified in this column. |
| FILTER | is populated as PASS |
| INFO | Not populated. Will have '.' specified in this column. |
| FORMAT:GT | genotypic data for each specimen. |
| FORMAT:GQ | genotype quality. If not value available in DB, then '.' is specified in the file. |
| FORMAT:GQX | mapped to GENOTYPE_QUALITY_X column |
| FORMAT:DP | this stores the TotalReadCount for a specific variant |
| FORMAT:AD | this stores the reference read count and Allele read count for a specific variant. |
| FORMAT:HQ | not populated as of now. Will have '.' specified in this column. |
| FORMAT:FT | this stores GENOTYPE_FILTER column value |
| FORMAT:BQ | stores the RMS base quality |
| FORMAT:MQ | stores the RMS mapping quality |
| FORMAT:SS | stores the somatic status |
| FORMAT:SSC | stores the somatic status score value |
| Flex field format | If any custom formats are available, they are also included in the export. |
1000 Genomes VCF 4.1 conventions are followed while exporting variation data, however certain datatypes, which are non-standard, like BQ and MQ, may differ in convention for some customers since there is no standard way to represent them.
Handling Non-variant and No-call Data
If NON_VARIANT and (or) NOCALL records exist for any given position, the zygosity is checked to determine if the format information from these tables is used.
Note:
For het-ref or half zygosity values, these other format fields are compared with the existing SEQUENCING information. This information is then used with zygosity to create the format string.The NON_VARIANT data allows for GQ, GQX, MQ, BQ and the first reference read count of AD. The NOCALL data allows for all format fields to be compared. Both NON_VARIANT and NOCALL do not support exporting flex fields. The GT value of the format string reflects the stored zygosity as follows:
| Zygosity | FORMAT string GT:GQ:GQX:BQ:MQ:AD:DP |
|---|---|
| het-ref | 1/0:99:98:38:45:20:10,10 |
| Half | 1/.:99:98:34,34:45,45:20:10,5 |
| Het-alt | 1/2:99:98:43,44:56,67:20:0,10,10 |
| Hom | 1/1:99:98:34,34:45,45:20:0,19 |
If there are no result records for any specimen, the export displays "." with no other information for the format.
Handling Ambiguous Sequencing Data in Export
There could be cases where users reload genetic information multiple times for the same specimen. This may create ambiguous values for the different fields that exist in the VCF export file. The export code deals with such ambiguous numerical values that represent the quality (that is, GQ, GQX, AD, BQ, MQ). This code now computes minimum values and ensure that the value of least confidence is reported. There could be more complex cases, for instance, if there are 2 different alleles for the same position belonging to the same specimen, or variants with same position for same specimen with different zygosity. The export code uses MIN functions on all values including all the text fields. This allows for VCF export to create a valid file that can be loaded into genome browsers.
Alternatively, you can choose not to consider data from a specific specimen or a specific file using following methods:
-
Using DELETE_FLG - A user may load results for a specimen more than once that can completely contradict previous results. Users can set the DELETE_FLG as 'Y' on W_EHA_RSLT_SPECIMEN and (or) W_EHA_SPEC_PATIENT or W_EHA_SPEC_SUBJECT to have previous loads excluded, and then reload the correct result files. When the user now exports the data, only the latest loaded specimen data is considered for export.
-
Using FILE_URI - Oracle recommends using this method since you need not reload the data again as opposed to the above method. When there are multiple files loaded with contradicting data for the same specimen, user can set some files as obsolete by changing the W_EHA_FILE_LOAD.FILE_WID column. For example, if you have loaded the same specimen data 3 times and would like to consider the latest file loaded for export, then you must first identify the latest FILE_WID from W_EHA_FILE_LOAD table. Then change the FILE_WID of two old files in W_EHA_FILE_LOAD table to the latest FILE_WID. Now, all the three records belonging to the three file loads contain same FILE_WID, which represents the latest file load and only the latest file export data is exported.
Allele depth values represented under the AD datatype are in the order of the alleles represented in the GT. Refer to the following table with examples:
| ALT | FORMAT | SAMPLE1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| G,C,T | GT:AD | 1/2:0,4,6 | 0 represents reference_read_count
4 represents allele_read_count of 'G' 6 represents allele_read_count of 'C' |
| G,T | GT:AD | 2/2:0,4 | 0 represents reference_read_count
4 represents allele_read_count of 'T' |
| G,T | GT:AD | 1/0:10,5 | 10 represents reference_read_count
5 represents allele_read_count of 'G' |
Copy Number Variation - SEG
The copy number variation data is exported in SEG format. Currently, CNV data from any array based system like Affymetrix Genome Wide SNP 6 array whose data is in SEG format while loading in OHO is supported. The main requirement for exporting CNV data is to have the SEG_MEAN value in the CNV table of OHO.
For exporting data that is not loaded from SEG files, for example, data from CGI CNV files or any other source of CNV data, users have to create their own loader. The loader is expected to calculate the SEG_MEAN value since this value is most important for export.
-
ID: specimen ID of the reported CNV segment
-
chrom: chromosome name
-
loc.start: start position of the CNV segment
-
loc.end: end position of the CNV segment
-
num.mark: for array based CNV data, this stores the number of probes details
-
seg.mean: this stores the segment mean value from SEG_MEAN column in CNV table.
Gene Expression - RES
RES is one of the gene expression formats supported by IGV browser. Currently, only microarray gene expression data is exported to this format. Following data types are imported to RES format:
-
Description: hugo name of a specific probe
-
Accession: probe ID
-
Intensity: intensity value of the associated probe
-
Call: call of the associated probe
Gene Expression Dual Channel - GCT
GCT is one of the gene expression formats supported by IGV browser. Currently, only AgilentG4502A platform microarray gene expression data is exported to this format. Following data types are imported to GCT format:
-
Description: Gene symbol of a specific probe
-
Accession: probe ID
-
Intensity: intensity value of the associated probe
-
Call: call of the associated probe
Note:
The GCT file takes its gene symbol for the probe from the 2-channel composite element of ADF file. This is input into the ADF composite table in OHO. This value may not match with HUGO name in certain cases as OHTR associates 2-channel records in the result table that has partial (which includes a flanking region set by the user) genomic coordinate. The coordinate overlaps between composite elements and gene segments in the reference. This may also result in some cases in more than one unique gene in the reference mapping to a gene composite element.Export Options
You can export data in the following two ways:
-
Select option to download last loaded file(s)
-
Immediately, which is the default option
-
Schedule
Figure 4-26 Export Options - Schedule Mode
Description of ''Figure 4-26 Export Options - Schedule Mode''
The Immediately option gives you the file link on the same screen and you can click to download it immediately. The link provided has a specific naming convention: <file type>_OHO_<date:MM-DD-YYYY>_<time:HH24*-MI-SS>.<file_type_extension>. For example, RES_OHO_09-14-2014_04-26.res. A short description of the file stating data type and advise on the expected count of features is displayed below the created link.
The Schedule option runs the process as a job. You can track the status of the job from the Home > Jobs tab. This option is best suited for exporting large data set like All Data, whole chromosome variants and so on. For schedule option, you must provide a job name and description. Then click Submit to start the process. For more details, see Working with Jobs.
There is a possibility of replicate and duplicate data in the database. This could be due to loading multiple files belonging to the same specimen_number. This can happen if the same library is sequenced multiple times or the data is reanalyzed, for example, the reads were realigned using the new reference version and hence new VCF or gVCF files are created for same sample. In this scenario, you can use the option to export VCF data only from last loaded files. For example if variation data has been loaded for a specimen in Jan 2015, Mar 2015 and July 2015, then using this option you can export data from the file loaded in July 2015 and it would not consider variants from the file loaded in Jan and Mar 2015.
Note:
The Schedule Jobs option uses an asynchronous approach to store the file in DBFS. As an alternative to downloading the file using the link in the Oracle Healthcare Translational Research Jobs page, there are other ways to access DBFS. From a Linux OS, you can mount DBFS using dbfs_client application and then browse the directories. Windows OS does not support the FUSE interface and cannot mount DBFS directly. However, there is a dbfs_client application for Windows that can execute commands to access DBFS. The Windows version of dbfs_client lets you use the command line to execute normal directory commands. You can list the DBFS directories as well as copy data from DBFS to the local drive. The dbfs_client application is part of the standard Oracle client software.For more information about using dbfs_client, see http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E11882_01/appdev.112/e18294/adlob_client.htm#ADLOB0006.