25 Enabling Runtime Editing of Pages Using Composer
This chapter contains the following topics:
25.1 Designing Editable Pages Using Composer Components
The Composer tag library provides design-time components that you can add to a page in Oracle JDeveloper to enable page editing at runtime. When you create a page with Composer components at design time, at runtime Composer provides options for entering page edit mode and modifying the page according to your requirements.
You can enable customizations in Framework applications and non-Framework applications. Within an application, you can enable customization of the following types of pages:
-
A regular JSPX page, not based on a page template
-
A JSPX template page
-
A JSPX page based on a page template
For more information about Composer components and their attributes, see Composer Components.
This section explains how to add Composer components to a page at design time to make it editable at runtime. It contains the following subsections:
-
How to Enable Runtime Customization Using a Page Customizable Component
-
How to Enable Switching Between Page Modes Using a Change Mode Link or Change Mode Button
-
How to Define Editable Areas of a Page Using Panel Customizable Components
-
How to Enable Layout Customization for a Page Using a Layout Customizable Component
-
How to Enable Component Customization Using Show Detail Frame Components
-
How to Create a Page Template for Creating Customizable Pages
25.1.1 How to Create a Customizable Page
For information about creating a customizable JSPX page in your Framework application.
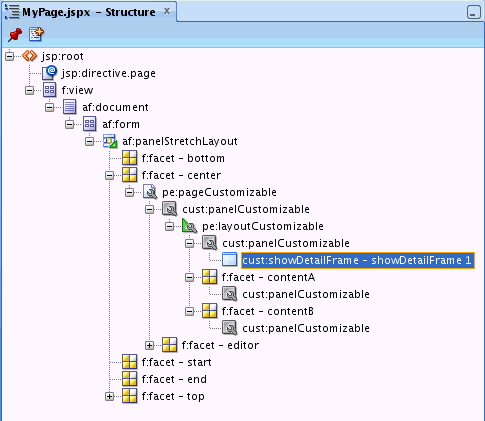
When you create a new page in JDeveloper, it is listed in the Application Navigator under Web Content as shown in Figure 25-1. Additionally, the page is opened in the editor and becomes the active editor panel.
Figure 25-1 A Customizable JSPX Page in the Application Navigator

Description of "Figure 25-1 A Customizable JSPX Page in the Application Navigator"
Security Considerations
By default, a Framework application is configured with ADF security. A default user name and password (weblogic/weblogic1) are created automatically for you.
To enable users to edit a page in a secured application, you must grant Edit or Customize privileges on the page to the required users or roles. For more information about granting permissions, see Managing Users and Application Roles in Administering Oracle WebCenter Portal.
If ADF security is not enabled in your application, you can test how user privileges impact runtime customization capabilities by implementing security and configuring your application to authenticate users so that they have distinct identities. For the steps to implement a basic security model in your application, see Enabling ADF Security in a Fusion WebApplication in Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
25.1.2 How to Enable Runtime Customization Using a Page Customizable Component
Adding a Page Customizable component to the page ensures that Composer is invoked when users switch to Edit mode of the page. When you add a Page Customizable component, some configuration files are updated automatically with the default Composer-specific settings. For more information, see What Happens When You Add Composer Components.
Note:
For considerations you must make before adding Page Customizable to a page, see What You May Need to Know When Designing Editable Pages.
To add a Page Customizable component to a page:
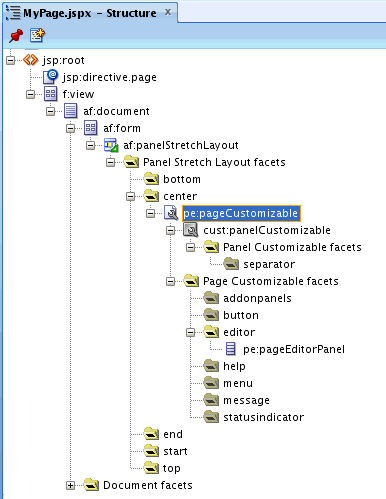
Example 25-1 Page Customizable Component in the Page Source View
<pe:pageCustomizable id="pageCustomizable1"
<cust:panelCustomizable id="panelcustomizable1"
layout="scroll"/>
<f:facet name="editor">
<pe:pageEditor id="pep1"/>
</f:facet>
</pe:pageCustomizable>
25.1.3 How to Enable Switching Between Page Modes Using a Change Mode Link or Change Mode Button
To enable users to switch to Edit mode of a page easily, you must add a Change Mode Link or Change Mode Button component to the page.
Note:
An alternative way to enable switching to Edit mode is by using the Change Mode API. For more information about this API, see Oracle WebCenter Portal Java API Reference.
For things you should consider before adding a Page Customizable component to a page, see What You May Need to Know When Designing Editable Pages.
To add a Change Mode Link or Change Mode Button component:
25.1.4 How to Define Editable Areas of a Page Using Panel Customizable Components
The Panel Customizable component is required for page composition or content management tasks, such as adding, arranging, or removing portlets or regions. By default, one Panel Customizable component is automatically added as a direct child of the Page Customizable component. You can add more Panel Customizable components within this Panel Customizable component according to your requirements.
It is only within a Panel Customizable component that you can drag and drop components at runtime.
Note:
For considerations you must make before adding Page Customizable to a page, see What You May Need to Know When Designing Editable Pages.
To add a Panel Customizable component to the page:
25.1.5 How to Enable Layout Customization for a Page Using a Layout Customizable Component
Use the Layout Customizable component to enable the runtime definition or modification of the layout of components on a page or an area of a page. Use this component only if you want to allow users to customize the layout at runtime. For static layouts, use an alternative component, such as a Panel Group Layout or Panel Stretch Layout.
To add a Layout Customizable component:
25.1.6 How to Enable Component Customization Using Show Detail Frame Components
When you want to enable customizations such as property editing, moving, minimizing, or removing components, you can drop a Show Detail Frame component inside a Panel Customizable component on the page. You can then add a component inside the Show Detail Frame.
Note:
Each Show Detail Frame component should have only one direct child component. If you add multiple child components, then only the first one is rendered. The other direct child components are not rendered at design time or runtime.
If multiple components must be enclosed in a Show Detail Frame, then add a grouping component like Panel Group Layout or Panel Customizable to the Show Detail Frame component and then include the ADF Faces components or other content within this grouping component.
Use the Show Detail Frame component to enable customizations in View and Edit modes of the page. Changes made in View mode are available to that user only, and changes made in Edit mode are available to all application users.
To add a Show Detail Frame component to the page:
For a better understanding of this type of task, see Designing Editable Pages Using Composer Components: Example.
25.1.7 How to Create a Page Template for Creating Customizable Pages
If you plan to create many customizable pages in your application, you can base the pages on an ADF page template in which you have enabled customization. By adding Composer components to the template itself, you can save the effort required to add these components to each customizable page.
To create a page template and enable customization on it:
You can now create customizable pages based on this template. Once you create a page, you can add a Panel Customizable or Layout Customizable component inside the facet displayed on the new page. You can then add page content within the Panel Customizable or Layout Customizable component.
25.1.8 How to Enable Customization in a Populated Page
When you have an existing ADF application with JSPX pages that are populated with content, and you want to enable customization, you can do so by moving all content inside a Page Customizable component.
You must first add the Page Customizable, then a Layout Customizable, and then the required hierarchy of Panel Customizable and Show Detail Frame components. Drag each of the existing components and drop them onto suitable locations inside the Page Customizable.
Note:
-
Ensure that the
Page Customizablecomponent has only one direct child component.When you add multiple direct child components, only the first child component is rendered at runtime. The first child component is stretched to fit the page. All other direct child components are ignored and not rendered on the page.
-
Use a
Layout Customizablecomponent only if you want to allow users to customize the layout at runtime. For static layouts, use an alternative component, such as aPanel Group LayoutorPanel Stretch Layoutcomponent. -
For best results, move components using the Structure window and not by editing the source code.
25.1.9 What Happens When You Add Composer Components
When you add a Page Customizable component to the page, the following configurations are performed automatically:
-
A default Resource Catalog definition file,
default-catalog.xml, is configured in the application. Thedefault-catalog.xmlfile is located in theApplication_Root/Portal/src/portaldirectory.In a Framework application, the
default-catalog.xmlfile is located in theApplication_Root/Portal/public_html/oracle/webcenter/portalapp/catalogsdirectory out-of-the-box, even without creating a page and adding aPage Customizablecomponent. -
A Resource Catalog Viewer is configured for the application. At runtime, Composer provides users the option to add resources from this viewer to the page.
-
The
web.xmlfile available in theApplication_Root/Project_Name/public_html/WEB-INFdirectory is updated to configure the MDS JSP provider. -
The
ComposerChangeManageris configured in the application'sweb.xmlfile. For more information, see Configuring the Persistence Change Manager. -
When you create an application, a minimal
adf-config.xmlfile is also created. When you add aPage Customizablecomponent to an application page, the required configuration is added to theadf-config.xmlfile. For example, change persistence is configured in theadf-faces-configsection in this file. For more information, see Configuring the Persistence Change Manager. -
The
DataBindings.cpxfile in theApplication_Root/Portal/adfmsrc/portaldirectory is updated to enable the presence of task flows on the page. -
The page definition file is updated with the binding for the Composer task flow, which is available as part of the Oracle WebCenter Portal extension JAR file. Example 25-2 shows the code in the page definition file after a
Page Customizablecomponent is added to an application page.
See Also:
Composer-Specific Files and Configurations for information about files that are created or modified when you add Composer components.
Example 25-2 Page Definition File After Adding Page Customizable Component
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<pageDefinition xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adfm/uimodel"
version="11.1.1.57.95" id="rcpagePageDef"
Package="portal.pageDefs">
<parameters/>
<executables>
<variableIterator id="variables"/>
<taskFlow id="pageeditorpanel"
taskFlowId="#{pageEditorBean.pageEditorPanel}"
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/controller/binding"/>
</executables>
<bindings/>
</pageDefinition>
25.1.10 What Happens at Runtime
At runtime, users can perform all the tasks described in Customizing Capabilities in Page View Mode and Editing Capabilities in Design View and Add Content View in Page Edit Mode.
Each Composer component provides runtime capabilities that are described in Composer Components.
Note:
Runtime customizations that you perform on a page are not carried over when you deploy the application to a target server.
25.1.11 What You May Need to Know When Designing Editable Pages
When adding Composer components to your customizable page, consider the following:
-
To enable users to edit a page in a secured application, you must explicitly grant Edit or Customize privileges on the page to the required users or roles. For more information about granting permissions, see Managing Roles and Permissions for a Portal
-
To enable runtime customization of components, add only one
Page Customizablecomponent to a page.Note:
Do not add a second
Page Customizablecomponent to your page. Only the firstPage Customizablecomponent is picked up when you run the page. -
Ensure that the
Page Customizablecomponent has only one direct child component.When you add multiple direct child components, only the first one is rendered at runtime. The first child component is stretched to fit the page. All other direct child components are ignored.
-
Place all components you want to be customizable within the
Page Customizablecomponent. -
To enable runtime editing, you must ensure that the
IDattribute is defined on all components on the page. Runtime editing of components that have noIDvalue is not supported in Composer.If your page includes components with no
IDvalue, then you may encounter problems while editing the page in Composer. -
To enable View mode user customization, place a
Show Detail Framecomponent within aPanel Customizablecomponent. -
Use a
Show Detail Frameto enclose a single child only. If you must enclose multiple components in aShow Detail Frame, then place a grouping component, such as aPanel Group LayoutorPanel Customizable, within theShow Detail Framecomponent and then place the ADF Faces components or other content within this grouping component. -
Portlets need not be placed within
Show Detail Framecomponents. Portlets come equipped with a header and display options that are similar toShow Detail Framecomponents.
25.2 Designing Editable Pages Using Composer Components: Example
In this example, assume you want to create a page that is customizable at runtime. The page is named MyPage.jspx in a Framework application named MyWebCenterApp.
To create a customizable page:
-
Create a Framework application named
MyWebCenterApp. -
Create a JSPX page named
MyPage.jspx. -
Add a
Panel Stretch Layoutfrom the ADF Faces tag library toMyPage.jspx.Note:
The
Panel Stretch Layoutcomponent stretches the child in the center facet to fill all the available space in the browser. This is true even if you resize the browser. Therefore, by placing your components within this child component, you can ensure that the customizable portion of your page occupies the complete browser area. -
Add
Page Customizablefrom the Composer tag library to the center facet by following the steps in How to Enable Runtime Customization Using a Page Customizable Component. -
Set the border color of
Page Customizabletoblueto differentiate the editable area from other noneditable areas.Under the Style category in the Property Inspector for
Page Customizable, click the Box tab and set theBorder Colorattribute toBlue. -
Set the border color of child
Panel Customizabletored.Under the Style category in the Property Inspector for
Panel Customizable, click the Box tab and set theBorder Colorattribute toRed. -
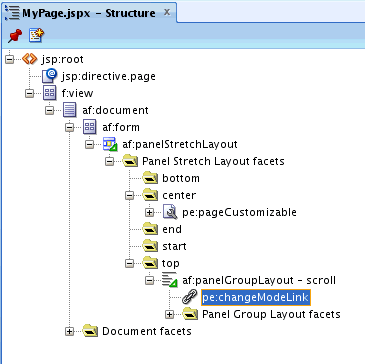
Add a
Change Mode Linkcomponent to the top facet of thePanel Stretch Layoutby performing the steps in How to Enable Switching Between Page Modes Using a Change Mode Link or Change Mode Button. -
In the center facet, in the
Panel Customizablethat is a direct child of thePage Customizable, add aLayout Customizablecomponent by following the steps in How to Enable Layout Customization for a Page Using a Layout Customizable Component. -
Add
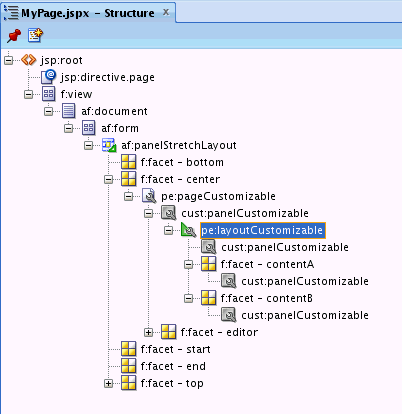
Show Detail Framecomponents inside eachPanel Customizableon the page by performing the steps in How to Enable Component Customization Using Show Detail Frame Components.Figure 25-8 shows
Show Detail Framecomponents insidePanel Customizablethat is a direct child ofLayout Customizable, and insidePanel Customizablecomponents that are direct children of theContentAandContentBfacets. -
For the sake of this example, add a
Rich Text Editorand anImagecomponent inside two of theShow Detail Framecomponents nested in theLayout Customizable. Drag and drop each of these components from the ADF Faces tag library to the required location on the page.The hierarchy of components on the page is as shown in Figure 25-8.
Figure 25-8 Component Hierarchy in MyPage.JSPX
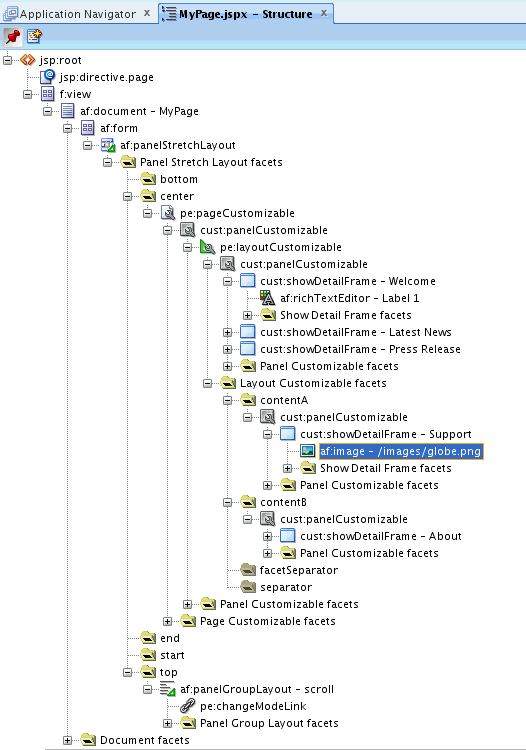
Description of "Figure 25-8 Component Hierarchy in MyPage.JSPX " -
Grant Edit or Customize permission on the page to the required users and roles. For more information about granting permissions, see Managing Roles and Permissions for a Portal
-
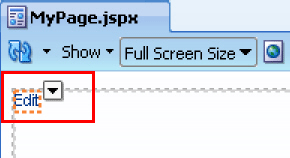
Run
MyPage.jspx.The page opens in View mode. Click the Edit link on the page to enter Edit mode. The page opens in Composer. In Composer, you can perform all editing tasks described in Editing Capabilities in Design View and Add Content View in Page Edit Mode.
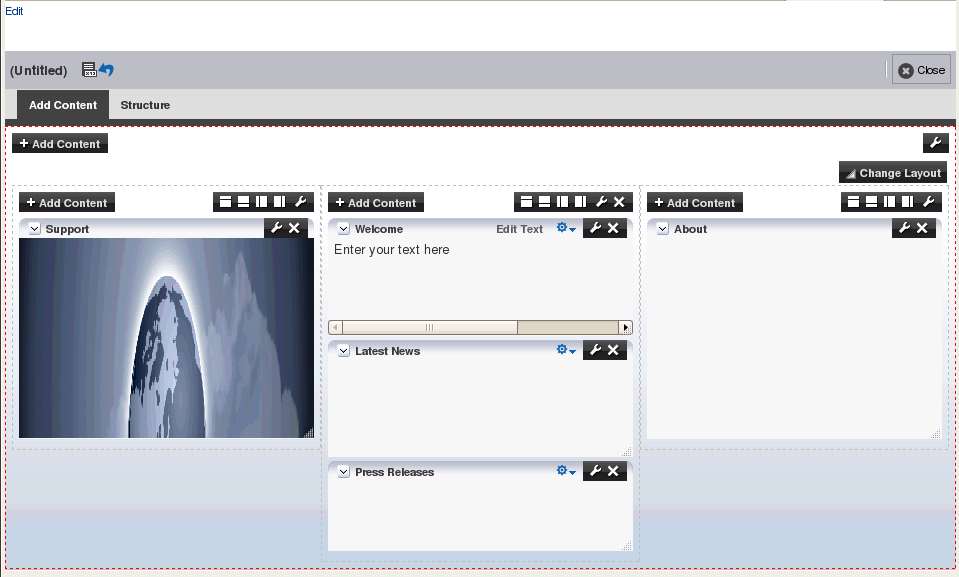
Figure 25-9 shows how the page appears in Edit mode at runtime.
If your application is not configured with ADF security, then to use this sample page in other examples in this guide, configure ADF security on the application.
To configure security in your application:
-
Configure ADF Security with form-based authentication, generating a default login page.
For more information, see Enabling ADF Security
-
Create three users
ahunold,sking, andjdoe.For the detailed procedure, see About Application Roles and Permissions and How to Create Application Roles
When you run MyPage.jspx, a login screen is displayed. You can log in with any of the three user names that you created.
25.3 Populating Pages with Content
After you create an editable page with the required Composer components, you can populate the page with content just like a regular JSPX page. However, there are certain limitations and recommendations that you must be aware of when adding content to your Composer-enabled page.
Populating editable pages at design time is like populating any other ADF Faces page. You can drag and drop components from different areas of the IDE onto the page. You can add components like portlets, task flows, and ADF Faces components.
When you drag and drop a component anywhere inside a Page Customizable component, the Id attribute is set to a unique value. The Id attribute is required for editing a component and persisting its changed state. When you add a component to a page at runtime, the Id attribute is set automatically.
25.3.1 What You May Need to Know When Adding Content to a Page
Consider the following when adding content to your editable page:
-
Add components inside
Panel Customizablecomponents that are nested in thePage Customizablecomponent. This ensures that the components can be edited at runtime. -
You can include any Oracle ADF Faces component or task flow as child component of a
Show Detail Framecomponent. However, portlets contain headers similar to those provided byShow Detail Framecomponents and can be added toPanel Customizablecomponents directly. There are no additional benefits to including portlets inShow Detail Framecomponents. -
For components that you want to make selectable in Structure view in Composer, ensure that the component is compliant with rich client framework and generates a client-side component.
-
If your page has the ADF Faces components
Output TextandOutput Formattednested inside aPage Customizablecomponent, then ensure that you set theclientComponentattribute value. If this attribute value is not set, then you may encounter errors while trying to move or rearrange components on the page at runtime. -
To consume portlets in your editable page, you must first register the portlet producers with your application. For information, see Managing Portlet Producers.
25.3.1.1 Considerations for Adding Task Flows
Users can personalize, customize, and edit task flows that are added to a customizable page. In a secured application, users with Customize permission on the task flow can also edit components on the task flow's page.
Consider the following points when adding task flows to your customizable page:
-
To provide a consistent user experience in terms of look and feel, layout design, and interaction, and to avoid problems, such as too much white space, too many scroll bars, or slow, jerky, and unpredictable responses when displaying large data sets, ensure that the task flows are created as reusable building blocks in Oracle ADF.
-
In a secured application, to enable users to view task flow content in Composer, ensure that the task flow has a
TaskFlowPermissiongrant in the application'sjazn-data.xmlfile, with at leastViewaction provisioned. You must set this explicitly as it is not enabled by default. -
In a secured application, to enable users to edit components on the task flow's page, ensure that the task flow has a
TaskFlowPermissiongrant in the application'sjazn-data.xmlfile, withCustomizeaction provisioned. You must set this explicitly as it is not enabled by default. -
Ensure that you specify valid values for all required parameters on the task flow.
For more information, see Implementing Task Flow Security
25.4 Troubleshooting Composer Problems
This section provides information to assist you in troubleshooting problems you may encounter while using Composer.
Configuring ADF Logging for Composer
While creating your applications in JDeveloper, you can use the JDeveloper debugging tools to easily find errors in your web pages or page definition files. You can also set up the Java logger to display Java diagnostic messages. For detailed information about configuring logging, see the Testing and Debugging ADF Components chapter in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework. To configure logging for Composer, perform the tasks in that guide and ensure that the oracle.adf.view.page.editor and oracle.adfinternal.view.page.editor packages are configured in the logging.xml file, with the desired logging level.
Problem
When you run a page, the following error displays:
java.lang.IllegalStateException: The expression "#{bindings.pageeditorpanel.regionModel}"
(that was specified for the RegionModel "value" attribute of the region component with id "pePanel")
evaluated to null. This is typically due to an error in the configuration of the
objects referenced by this expression. If it helps, the expression
"#{bindings.pageeditorpanel}" evaluates to "null". If it helps, the expression
"#{bindings}" evaluates to "view_untitled1PageDef". Now using an empty RegionModel instead.
Solution
This error occurs if a page containing the Page Customizable component does not have the required task flow binding in its page definition file. Ensure that the page definition file contains the following valid entry under the <executables> node:
<taskFlow id="pageeditorpanel" taskFlowId="#{pageEditorBean.pageEditorPanel}"xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/controller/binding"/>
This error may also occur if your page is based on a page template and that page template contains the Page Customizable component. In such a case, the af:pageTemplate tag does not contain the value="#{bindings.pageTemplateBinding}" attribute.
Ensure that the page definition file has the following entry under the <executables> node:
<page path="view.pageDefs.templateDef1PageDef" id="pageTemplateBinding" Refresh="ifNeeded"/>
Problem
Users cannot switch to Edit mode. The Edit link (Change Mode Link or Change Mode Button) appears disabled.
Solution
The user may have only view privilege on the page. Ensure that the user has the edit privilege on the page. For the page template on which the page is based, it is sufficient to have only view privilege.
Problem
Users encounter an exception while wiring events in the Component Properties dialog in Composer.
Solution
This error occurs if your application page includes both ADF Data Visualization components and Composer components.
Register the DvtElementObjectFactory class with the Oracle ADF FactoryManager object by adding the following code to the application class that gets loaded the earliest:
...
import oracle.adfdt.model.dvt.objects.DvtElementObjectFactory;
import oracle.adfdt.model.managers.FactoryManager;
...
static
{
FactoryManager.getInstance().registerFactory(new DvtElementObjectFactory());
}