30 Composer Component Properties and Files
This chapter provides reference information about Composer-specific tags and configuration files.
This chapter contains the following topics:
30.1 Composer Component Properties
This section is a quick reference for some of the important Composer tags. When you add Composer components to a page, default values are assigned to certain attributes. You can change these default values and define values for the remaining attributes in JDeveloper. For information on the other Composer tags, refer to the 11g WebCenter Portal documentation.
This section contains the following topics:
30.1.1 Page Customizable Component
Use the Page Customizable component to enable page editing at runtime. The Page Customizable component denotes the customizable part of a page and shows the Composer toolbar in Edit mode at runtime. When you enclose components within a Page Customizable component, Composer is enabled in the application page at runtime, allowing the user to customize and edit the components.
In large applications, where you want to enable runtime page editing on multiple pages, you can include the Page Customizable component in the page template, somewhere in the top of the hierarchy. This way, all pages created using the template are editable at runtime.
Geometry Management
View mode: The Page Customizable component can be stretched by a parent layout component that stretches its children, for example, a Panel Stretch Layout or Panel Splitter component. If the Page Customizable component is stretched, it in turn stretches its child component to fill the space available to it. However, if the Page Customizable component is not stretched, its size is determined by the child component.
Edit mode: The Page Customizable component stretches its child component to fill the space available to it.
Attributes
The following table describes the attributes of aPage Customizable component.
Table 30-1 Page Customizable Component Attributes
| Attribute | Type | Supports EL | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Common Attributes |
|||
|
id |
String |
No |
The identifier for the component. The identifier must follow a subset of the syntax allowed in HTML:
|
|
rendered |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether the component is rendered. When set to The default value is |
|
Appearance Attributes |
|||
|
sourceViewPosition |
String |
Yes |
The position of the For more information, see the section, Editing Capabilities in Structure View in Page Edit Mode. |
|
sourceViewSize |
String |
Yes |
The height or width of the Structure view pane in pixels. Use this to specify height if the Since the default for Alternatively, the resize handler on the edge of the Structure view pane enables users to alter the height or width of the pane at runtime. |
|
editModeView |
not applicable |
not applicable |
Specifies the default view in which to open a page in Composer. Valid options are If you select source, the page is opened in |
|
rendered |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether the component is rendered. When set to The default value is |
|
toolbarLayout |
String |
Yes |
The elements to be displayed on the Composer toolbar. This attribute can take a space-separated list of elements. The built in strings the component recognizes are For more information about using this attribute, see Customizing the Composer Toolbar |
|
Style Attributes |
|||
|
styleClass |
String |
Yes |
The CSS style class to use for this component. The style class can be defined in your JSPX page or in a skinning CSS file, for example. |
|
inlineStyle |
String |
Yes |
The CSS styles to use for this component. This is intended for basic style changes. The |
|
Advanced Attributes |
|||
|
binding |
|
Supports only EL |
An EL reference that stores the component instance on a bean. This can be used to give programmatic access to a component from a backing bean, or to move creation of the component to a backing bean. |
|
sourceViewNodeActions |
String |
Yes |
The name of the JPSX file to be called if you want to display custom actions against task flows in the component navigator in Composer Structure view. The For information about using this attribute, see Adding Custom Actions that Display on Task Flows in the Component Navigator |
|
allowLabel |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether label creation must be enabled in the Customization Manager. When This attribute is relevant only if you have configured sandbox support in your application. |
|
catalog |
String |
Yes |
The resource catalog to be used as the default one for the application page. Provide the catalog definition file name. |
|
allowEL |
Boolean |
No |
Specifies whether or not EL can be run in application pages. Default is true. This setting overrides the For more information, see How to Protect Expression Language |
|
protectEL |
Boolean |
No |
Specifies whether or not EL in form elements is read-only. Default is false. This setting overrides the For more information, see How to Protect Expression Language |
|
designViews |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the views available to a user in Composer. By default, This attribute can take a space-separated list of elements. Available options are design, add-content, source, select, preview, and all. If you set the value as all, all the views are rendered except If the For more information see Enabling Direct Select in Design or Add Content View |
|
Customization Attributes |
|||
|
customizationAllowed |
Boolean |
not applicable |
Specifies whether customizations are allowed on this component. Available values are true and false. The default value is true. |
|
customizationAllowedBy |
String |
not applicable |
Specifies the roles for which customization is enabled. |
Supported Facets
The Page Customizable component provides an editor facet, which is prepopulated with a Page Editor Panel component. To ensure that Composer works properly, the editor facet must contain the Page Editor Panel component.
30.1.2 Change Mode Link and Change Mode Button
Use the Change Mode Button or Change Mode Link to enable switching to Edit mode of the page at runtime.
The Change Mode Link and Change Mode Button components share a common set of attributes. The following table describes the attributes of a Change Mode Link or Change Mode Button component
Table 30-2 Change Mode Link and Change Mode Button Attributes
| Attribute | Type | Supports EL? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Common Attributes |
|||
|
id |
String |
Yes |
The identifier for the component. The identifier must follow a subset of the syntax allowed in HTML:
|
|
rendered |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether the component is rendered. When set to The default value is In a secured application, to enable the Edit link or button only for selected users based on specific criteria, you can specify an EL value for the Note: In a secured application, it is recommended that you check all users' privileges and enable the Edit link or button only for privileged users. Unauthenticated users who stumble into page Edit mode can change component properties. |
|
Behavior Attribute |
|||
|
immediate |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether data validation - client-side or server-side - must be skipped when events are generated by this component. When |
|
Advanced Attributes |
|||
|
binding |
or
|
Supports only EL |
An EL reference that stores the component instance in a bean. This can be used to give programmatic access to a component from a backing bean, or to move creation of the component to a backing bean. |
|
Customization Attributes |
|
|
|
|
customizationAllowed |
Boolean |
|
Specifies whether customizations are allowed on this component. Available values are |
|
customizationAllowedBy |
String |
|
Specifies the roles for which customization is enabled. |
|
Other Attribute |
|
|
|
|
customizationId |
|
|
This attribute has been deprecated. Use the |
If you do not want to use the Change Mode Link or Change Mode Button component, you can add your own button or link component and use theChangeModeLinkor ChangeModeButton API to enable the switching of the page mode.
Disabling Runtime Editing in Your Application Pages
To disable runtime editing of pages, you can revoke Edit privileges for users, or delete the Change Mode Link or Change Mode Button component from the page so that the user cannot navigate to the Edit mode of the page.
30.1.3 Layout Customizable Component
The Layout Customizable component applies a predefined layout to its child components. It is a container component that enables end users to lay out its child components in several predefined ways. Use the Layout Customizable component only to enable changing of the page layout at runtime. If you just want container components in which to layout components, but do not want to enable runtime layout changes, then it is recommended that you use ADF Faces layout components like Panel Stretch Layout and Panel Group Layout. It is recommended that you have just one Layout Customizable on the page.
A Layout Customizable component contains a direct child Panel Customizable component and two facets with Panel Customizable components by default to enable users to add content inside them at runtime. However, you can add any components inside the Layout Customizable component and its facets. The content in the three Panel Customizable components can be placed in different ways using predefined layouts. For more information, see the section, Predefined Layout Types.
The following table describes the attributes of a Layout Customizable component.
Table 30-3 Layout Customizable Component Attributes
| Attribute | Type | Supports EL? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Common Attributes |
|||
|
id |
String |
No |
The identifier for the component. The identifier must follow a subset of the syntax allowed in HTML:
|
|
rendered |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether the component is rendered. When set to false, no output is delivered for this component (the component is not in any way rendered, and cannot be made visible on the client). The default value is true. The rendering of a component can also be defined at runtime using the Show Component and Hide Component options. |
|
type |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the layout to be used for the page. You can choose from a list of eight predefined layouts. For more information, see the table in Predefined Layout Types. Default value is threeColumn. You can define customization restrictions on a |
|
Appearance Attributes |
|||
|
text |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the text to be displayed for the Change Layout menu. Use the text attribute to provide a descriptive label for the For example: text="Change Layout" |
|
accessKey |
Char |
Yes |
A character used to gain quick access to this button. For accessibility reasons, this functionality is not supported in screen reader mode. If the same access key appears in multiple input fields in the same page of output, the rendering user agent cycles among the elements accessed by the similar keys. Note that user agents are inconsistent about dealing with two links having same access key, and so the cycling behavior is dependent on what the user agent provides. This attribute is sometimes referred to as the "mnemonic". The character specified by this attribute must exist in the Text attribute of this button instance. If it does not, the user receives no visual indication of the existence of the Note that the accessKey is triggered by browser-specific and platform-specific modifier keys. It even has browser-specific meaning. For example, Internet Explorer 7.0 sets focus when you press Alt+<accessKey>. Firefox 2.0 on some operating systems sets focus when you press Alt+Shift+<accessKey>. Firefox 2.0 on other operating systems set focus when you press Control+<accessKey>. Refer to your browser's documentation for how it treats accessKey. |
|
showIcon |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether the default Change Layout icon is visible or not. The default value is |
|
showLayoutChanger |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether the Change Layout icon or text must be displayed. The default value is When set to
|
|
showTypes |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the names of predefined layouts that must be displayed in the layout changer. Use this attribute to control the layout options displayed to users. You can provide a space-separated list of layout types. By default, all eight layouts are displayed when a user clicks the Change Layout icon or link. |
|
shortDesc |
String |
Yes |
The short description of the component. This text is commonly used by user agents to display tooltip help text, in which case the behavior for the tooltip is controlled by the user agent, for example, Firefox 2 truncates long tooltips. For form components, the |
|
Style Attributes |
|||
|
styleClass |
String |
Yes |
A CSS style class to use for this component. The style class can be defined in your JSPX page or in a skinning CSS file, for example. |
|
inlineStyle |
String |
Yes |
The CSS styles to use for this component. This is intended for basic style changes. The |
|
Advanced Attribute |
|||
|
binding |
oracle.adf.view.page.editor.component.LayoutCustomizable |
Supports only EL |
An EL reference that stores the component instance in a bean. This can be used to give programmatic access to a component from a backing bean, or to move creation of the component to a backing bean. For example: binding="#{yourManagedBean.Binding}" |
|
Customization Attributes |
|||
|
customizationAllowed |
Boolean |
|
Specifies whether customizations are allowed on this component. Available values are |
|
customizationAllowedBy |
String |
|
Specifies the roles for which customization is enabled. |
|
Other Attribute |
|||
|
customizationId |
|
|
This attribute has been deprecated. Use the id attribute. |
Supported Facets
The following table describes the facets provided for a Layout Customizable component.
Table 30-4 Layout Customizable Component Facets
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
|
contentA |
Prepopulated with a |
|
contentB |
Prepopulated with a |
|
facetSeparator |
Content to be rendered once between each facet. |
|
separator |
Content to be rendered once between each of the other children. |
Predefined Layout Types
When you add a Layout Customizable component to the page, three child Panel Customizable components are added by default; one direct child and two Panel Customizable in the two facets. However, you can replace the child Panel Customizable components with any container components of your choice. When you select the layout type, the components in these Panel Customizable are arranged according to the layout type chosen.
The following table describes the eight layouts that you can apply to your page or an area of the page at design time. To easily describe how components are laid out, let us assume the following:
-
The child
Panel CustomizableofcontentAfacet is called A. -
The child
Panel CustomizableofcontentBfacet is called B. -
The primary
Panel Customizable, which is a direct child of theLayout Customizable, is called C.
| Layout Type | Image Showing Content Arrangement |
|---|---|
|
oneColumn |

Note: In a oneColumn layout, A and B are rendered only if they contain child components. |
|
threeColumn |
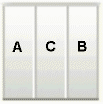 |
|
threeColumnNarrow |
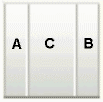 |
|
twoColumn |
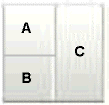 |
|
twoColumnBottom |
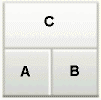 |
|
twoColumnNarrowLeft |
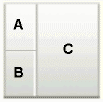 |
|
twoColumnNarrowRight |
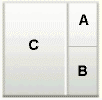 |
|
twoColumnTop |
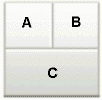 |
30.1.4 Show Detail Frame Component
Add Show Detail Frame components inside Panel Customizable components to enable runtime customizations like move, minimize, restore, and delete of child components. You can move Show Detail Frame components only if they are added inside a Panel Customizable component.
Geometry Management
A Show Detail Frame component can be stretched by a parent layout component that stretches its children, for example, Panel Customizable.
A Show Detail Frame component stretches its child component to fill the height and width available to it. It is recommended that you add only one child component inside a Show Detail Frame component. However, if you have more than one child component, the first child component is stretched to the height and width of the Show Detail Frame's content area and subsequent child components are ignored.
The resize handler at the lower right corner of a Show Detail Frame enables you to resize the component vertically. From then on, the Show Detail Frame cannot be stretched by its parent.
The following table describes the attributes of a Show Detail Frame component.
Table 30-5 Show Detail Frame Component Attributes
| Attribute | Type | Supports EL? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Common Attributes |
|||
|
id |
String |
No |
The identifier for the component. The identifier must follow a subset of the syntax allowed in HTML:
|
|
rendered |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether the component is rendered. When set to false, no output is delivered for this component (the component is not in any way rendered, and cannot be made visible on the client). The default value is true. The rendering of a component can also be defined at runtime using the |
|
text |
String |
Yes |
A title for the You can change the style of this text using the |
|
icon |
String |
Yes |
If you decide to add an icon on the header of the For example: icon="http://source-pc/images/accessability.gif" Note: An image that is stored at the document root does not require a full path. For example: icon="detail.gif" |
|
Appearance Attributes |
|||
|
text |
String |
Yes |
A title for the You can change the style of this text using the |
|
shortDesc |
String |
Yes |
The short description of the component. This text is commonly used by user agents to display tooltip help text, in which case the behavior for the tooltip is controlled by the user agent, for example, Firefox 2 truncates long tooltips. For form components, the shortDesc is displayed in a note window. |
|
icon |
String |
Yes |
If you decide to add an icon on the header of the For example: icon="http://source-pc/images/accessability.gif" Note: An image that is stored at the document root does not require a full path. For example: icon="detail.gif" |
|
background |
String |
Yes |
Working with the skin CSS, provides a means of applying a different look and feel for this Available values are The |
|
displayHeader |
Boolean |
Yes |
Indicates whether the header of the The default value is If you choose to set |
|
displayShadow |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether a shadow is cast by the The default value is |
|
expansionMode |
String |
Yes |
The default state of the Available values are minimized and normal. The default display mode is normal. |
|
rendered |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether the component is rendered. When set to false, no output is delivered for this component (the component is not in any way rendered, and cannot be made visible on the client). The default value is The rendering of a component can also be defined at runtime using the |
|
Actions Attributes |
|||
|
displayActions |
String |
Yes |
Specifies when seeded interactions are displayed. Available options are |
|
inheritGlobalActions |
Boolean |
Yes |
This attribute is of significance if you add child custom action components, and the attribute specifies whether the global action value of a custom action must override the local value. The default value is For information about global custom actions, see Defining Custom Actions at the Global Level |
|
showMoveAction |
String |
Yes |
Specifies whether the Move action is available for the component. Available values are:
The default value is Note: The disabled option is applicable only in View mode. |
|
showRemoveAction |
String |
Yes |
Renders a Remove icon on the Show Detail Frame header. Clicking this icon removes the component from the page. Available values are chrome and none. The default value is none. Note: In page Edit mode, the Remove icon appears regardless of this setting, provided other restrictions have not been applied. |
|
showResizer |
String |
Yes |
Specifies whether a resize handle is displayed on the lower right corner of the Available values are |
|
showMinimizeAction |
String |
Yes |
Specifies whether the minimize action is displayed on the header. Available values are |
|
showEditAction |
Boolean |
Yes |
While in This is relevant only in a Composer-enabled page, that is, if the |
|
Style Attributes |
|||
|
contentStyle |
String |
Yes |
The CSS style to apply to the The CSS styles in this attribute are commonly used to define the Note: If the |
|
styleClass |
String |
Yes |
The CSS style class to use for this component. The style class can be defined in your JSPX page or in a skinning CSS file, for example. |
|
inlineStyle |
String |
Yes |
The CSS styles to use for this component. This is intended for basic style changes. The |
|
headerStyle |
String |
Yes |
The CSS style to apply to the The CSS styles in this attribute are commonly used to define the font, size, and color of the title text. |
|
Behavior Attributes |
|||
|
partialTriggers |
String |
Yes |
The IDs of the components that should trigger a partial update. This component listens on the trigger components. If a trigger component receives an event that causes it to update in some way, this component requests to be updated too. Identifiers are relative to the source component (this component), and must account for NamingContainers. If your component is inside of a naming container, you can use a single colon to start the search from the root of the page, or multiple colons to move up through the NamingContainers - "::" pop out of the component's naming container (or itself if the component is a naming container) and begin the search from there, ":::" pop out of two naming containers (including itself if the component is a naming container) and begin the search from there. |
|
disclosureListener |
|
Yes |
A method reference to a disclosure listener. A disclosure event is fired when the user expands or collapses the |
|
stretchContent |
String |
Yes |
Specifies whether the Available options are You can use the If you select true, then the child component is stretched to the height and width of the The default height of the If you select auto, the child component is stretched only if the |
|
Advanced Attributes |
|||
|
binding |
|
Supports only EL |
An EL reference that stores the component instance in a bean. This can be used to give programmatic access to a component from a backing bean, or to move creation of the component to a backing bean. |
|
attributeChangeListener |
|
Yes |
A method reference to an attribute change listener. Attribute change events are not delivered for any programmatic change to a property. They are only delivered when a renderer changes a property without the application's specific request. An example of an attribute change event might include the width of a column that supported client-side resizing. |
|
selectChild |
String |
Yes |
Specifies whether runtime selection and customization are enabled on child components. This is relevant only in a Composer-enabled page, that is, if the Default value is If you select |
|
Customization Attributes |
|||
|
customizationAllowed |
Boolean |
|
Specifies whether customizations are allowed on this component. Available values are |
|
customizationAllowedBy |
String |
|
Specifies the roles for which customization is enabled. |
|
childCreation |
String |
Yes |
Specifies when the children (contents) of the
|
|
Other Attributes |
|||
|
customizationId |
|
|
This attribute has been deprecated. Use the |
|
helpTopicID |
String |
Yes |
Specifies a Help topic ID that is used to link to a custom Help topic from the component. To link to a Help topic from your |
30.1.5 Show Property
Use the Show Property component to display an attribute or parameter in a custom property panel at runtime. Use one Show Property component for each attribute or parameter that you want to display to users at runtime.
The following table describes the new attributes of a Show Property component.
Table 30-6 Attributes of a Show Property Component
| Attribute | Type | Supports EL? | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Common Attributes: |
|
|
|
|
id |
String |
No |
The identifier for the component. The identifier must follow a subset of the syntax allowed in HTML:
|
|
rendered |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether the component is rendered. When set to The default value is The rendering of a component can also be defined at runtime using the Show Component and Hide Component options. |
|
attributeType |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the property type. Supported values are |
|
value |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the current value of the property. If the EL binding for the "value" points to a bean property with a getter but no setter, and this is an editable component, the component will be rendered in read-only mode. |
|
label |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the label of the component. If you want the label to appear above the control, use a |
|
Data Attributes: |
|
|
|
|
value |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the current value of the property. If the EL binding for the "value" points to a bean property with a getter but no setter, and this is an editable component, the component will be rendered in read-only mode. |
|
selectItem |
|
|
Specifies the list of values to be displayed if |
|
Appearance Attributes: |
|
|
|
|
columns |
Int |
Yes |
Specifies the size of the text control specified by the number of characters shown. The number of columns is estimated based on the default font size of the browser. |
|
rows |
Int |
Yes |
Specifies the height of the text control specified by the number of characters shown. The default value is 1, which generates a one-row input field. The number of rows is estimated based on the default font size of the browser. |
|
label |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the label of the component. If you want the label to appear above the control, use a |
|
shortDesc |
String |
Yes |
Provides a short description of the component. This text is commonly used by user agents to display tooltip help text, in which case the behavior for the tooltip is controlled by the user agent, for example, Firefox 2 truncates long tooltips. For form components, the This is applicable only for a custom action rendered as a toolbar icon. |
|
simple |
Boolean |
Yes |
A boolean value that controls whether the component provides label support; when set to "true", the component will not display the label (these may be ignored: label, labelAndAccessKey, accessKey, showRequired, help facet) and may use simpler layout primitives. One of the use cases can be when the component is used in repeatable elements like in table, for-each etc., where label is not required. |
|
unselectedLabel |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the label for the option that represents a value of null, meaning nothing is selected. If |
|
Behavior Attributes: |
|
|
|
|
required |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether a non-null, non-empty value must be entered. If |
|
autoSubmit |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies an attribute which if set to TRUE on a form element, the component will automatically submit when an appropriate action takes place (a click, text change, etc.). Since |
|
disabled |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether the property should be shown as disabled. This is useful if the |
|
validator |
String |
Yes |
Specifies a method reference to a validator method. |
|
valueChangeListener |
javax.faces.el.MethodBinding |
EL only |
Specifies a method reference to a value change listener. |
|
Advanced Attributes: |
|
|
|
|
binding |
|
Supports only EL |
Specifies an EL reference that stores the component instance in a bean. This can be used to give programmatic access to a component from a backing bean, or to move creation of the component to a backing bean. |
|
clientComponent |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether a client-side component will be generated. A component may be generated whether or not this flag is set, but if client Javascript requires the component object, this must be set to true to guarantee the component's presence. Client component objects that are generated today by default may not be present in the future; setting this flag is the only way to guarantee a component's presence, and clients cannot rely on implicit behavior. However, there is a performance cost to setting this flag, so clients should avoid turning on client components unless absolutely necessary. |
|
componentId |
|
|
If you use the |
|
showELBuilder |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether to display the EL builder for the property. |
|
showResourceEditor |
Boolean |
Yes |
Specifies whether to display the resource string editor for the property. However, this option is enabled only if you have configured resource string editing in the application and the property is of type String. |
|
taskFlowId |
String |
Yes |
If |
|
taskFlowParam |
String |
Yes |
If |
|
customizationId |
|
|
This attribute has been deprecated. Use the |
|
Customization Attributes |
|
|
|
|
customizationAllowed |
Boolean |
|
Specifies whether customizations are allowed on this component. Available values are |
|
customizationAllowedBy |
String |
|
Specifies the roles for which customization is enabled. |
|
Other Attribute |
|
|
|
|
text |
String |
Yes |
Specifies the text used for the check box. This is used only when |
Supported Facets
The Show Property component supports a customLink facet, which can be used to include a Command Menu Item. The Command Menu Item specified in this facet appears as a custom link in the dropdown next to the property field, along with Resource String editor and EL Builder.
30.2 Composer-Specific Files and Configurations
This section describes the various files that you can modify to extend Composer capabilities. While some files, for example the Composer extension file, pe_ext.xml, are entirely relevant to Composer only, others are ADF configuration files that can take entries for Composer-specific configurations.
30.2.1 pe_ext.xml
You can create a pe_ext.xml file and add elements in it to register new Composer add-ons and custom property panels, selectively render panels, register event handlers, and define property filters. This file is not available by default when you add Oracle Components to a page. You can create this file in the META-INF directory in your Portal project; for example, in the APPLICATION_HOME\Portal\src\META-INF directory. This section describes the different elements of the Composer extension file schema and explain when you may want to use the schema elements.
Note:
In applications that use shared libraries with their own pe_ext.xml file, use the sequence element within the pe-extension tag to define the order of execution. Use sequence="first" to lay down default settings, and sequence="last" to load the file last and override settings defined by files loaded previously.
addon-config
Use the addon-config element to include entries for new Composer add-ons and custom property panels. For example, to add a new About button to your page that invokes a panel displaying information about your application, you must first create a task flow containing the information and then register this task flow in the pe_ext.xml file. Composer add-ons declared inside the addon-config element are configured in the adf-config.xml file, whereas custom property panels declared within the addon-config element are configured within the property-panels element in the extension file itself.
Insert the addon-config element within the pe-extension tag. You can add only one addon-config element in the XML file. Within the addon-config element you can have a panels element to define add-ons.
panels
Use the panels element to register new add-ons or property panels in Composer. Add the panels element within the addon-config element. You can have only one panels element in an extension file, and all custom panels must be defined inside this element.
panel
Use panel elements to define individual add-ons and property panels to display to users. Within the panels element you can insert any number of individual panel elements that define the add-ons or property panels to be displayed in Composer. You must have one panel element for every add-on or property panel you want to display.
Table 30-7 panel Element Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
An identifier that is used while referencing the new add-on in |
|
|
The title to display on the button used to invoke the task flow in Composer. You can use EL for this property to show a localized title. For custom property panels, the title to display on the new tab for that panel. |
|
|
The icon that appears next to the title on the button. This is optional. |
|
|
The ID of the task flow that defines the add-on or property panel. |
|
|
A help topic ID that links to a custom help topic from the add-on or property panel. This is optional. |
When a panel element is deleted from the file, that add-on or property panel is not displayed on the page.
The following example shows how to use the addon-config, panels, and panel elements:
<addon-config>
<panels>
<panel name="oracle.fod.custom.panel" title="About FOD"
icon="adf/webcenter/images/about.gif"
taskflow-id="/WEB-INF/about-fod.xml#about-fod"
/>
</panels>
</addon-config>
Optionally, to register an event handler for a specific add-on panel, you can also add an event-handlers element inside a panel element, as shown in the following example:
<event-handlers>
<event-handler event="close">
oracle.fod.custom.TaskFlowEventHandler
</event-handler>
</event-handlers>
The XML code is the same as for any generic event handler.
property-panels
Use the property-panels element to register custom property panels. Add the property-panels element within the addon-config element. You can have only one property-panels element in an extension file.
property-panel
Use the property-panel element to define a custom property panel to display for a particular component in Composer. Within the property-panels element you can insert any number of individual property-panel elements to define custom property panels to display as tabs in the Component Properties dialog. To specify the component or task flow for which you want to register a custom property panel, you must add a component or taskflow-id element respectively within the property-panel.
Table 30-8 property-panel Element Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
name |
An identifier for the custom property panel you want to display in the Component Properties dialog. |
|
rendered |
Whether this panel is displayed to users in the Component Properties dialog. This can take an EL value. |
component
Use the component element to specify the fully qualified class name of the component for which you are registering the custom property panel. You can have only one component inside a property-panel element.
taskflow-id
Use the taskflow-id element to specify the name of the task flow for which you are registering the custom property panel. You can have only one taskflow-id inside a property-panel element.
panel
Use the panel element to specify a custom property panel to display as a tab in the Component Properties or Page Properties dialog for the component. Within a property-panel element, you can have any number of panel elements. The following table describes the attributes of a panel element.
Table 30-9 panel Element Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
name |
Name with which you declared the panel in the addon-config section. |
|
rendered |
Whether the custom property panel must be rendered or not. |
|
parameter |
Parameters to be passed to the implementing task flow. Takes an EL only and must return a Map<String, String>. |
When a panel element is deleted from the file, that property panel is no longer displayed in the Component Properties dialog.
The following example shows how to register a custom property panel for a Command Button component:
<property-panels>
<property-panel name="cmdbtn"><component>oracle.rich.CommandButton</component>
<panel name="prop.panel.cmdbtn"/>
</property-panel>
</property-panels>
The following example shows how to register a custom property panel for a task flow:
<property-panels>
<property-panel name="dashboard"><taskflow-id>/WEB-INF/dashboard-taskflow#prop-panel</taskflow-id>
<panel name="dashboard.prop-panel" />
</property-panel>
</property-panels>
lov-config
Use the lov-config element to register a custom List of Values or picker for a task flow parameter. Add the lov-config element directly under the pe-extension tag. You can have only one lov-config element in an extension file. Within this element, you can add a task-flow-definition element for each task flow that you want to register for LOV usage. Add an input-parameter-definition for each parameter that provides an LOV. Use enumeration elements to list the LOV options for a parameter, as shown in the following example:
<lov-config <task-flow-definition taskflow-id="/WEB-INF/employee-details.xml#employee-details"> <input-parameter-definition> <name>Designation</name> <enumeration> <item> <name>Accounts Manager</name> <value>Accounts Manager</value> <description>Accounts Manager</description> </item> <item> <name>Accounts Assistant</name> <value>Accounts Assistant</value> <description>Accounts Assistant</description> </item> <item> <name>Payroll Executive</name> <value>Payroll Executive</value> <description>Payroll Executive</description> </item> <item> <name>Senior Manager</name> <value>Senior Manager</value> <description>Senior Manager</description> </item> </enumeration> </input-parameter-definition> </task-flow-definition></lov-config
event-handlers
Use the event-handler element to register an event handler in Composer. Within event-handlers you can have any number of event-handler elements to register handlers for save, close, deletion, addition, and selection events. For example, if you have implemented the processSave method in a Java class called SaveHandler to perform a specific action when a Save event is invoked, then you can register that implementation in Composer by adding an event-handler entry in the pe_ext.xml file as follows:
<event-handlers>
<event-handler event="save">view.SaveHandler</event-handler>
</event-handlers>
drop-handlers
Use the drop-handlers element to register drop handlers to handle addition of components to the page from the resource catalog. Add the drop-handlers element directly under the pe-extension tag. You can have only one drop-handlers element in an extension file.
drop-handler
Use the drop-handler element to register a drop handler in Composer. Within drop-handlers you can have any number of drop-handler elements to register drop handlers that you created in the application. For example, if you created a drop handler called TestDropHandler to handle addition of XML components on the page, then you can register that implementation in Composer by adding a drop-handler entry in the pe_ext.xml file as follows:
<drop-handlers> <drop-handler>test.TestDropHandler</drop-handler> </drop-handlers>
filter-config
Use the filter-config element to define property filters for components that can be edited at runtime. For a selected component, the Component Properties dialog displays properties that can be edited. If you do not want to expose all properties for editing, you can filter specific properties so that they are not displayed in the Component Properties dialog. You can specify global-level filters to filter common attributes across all components, or you can define tag-level filters to filter properties for a particular component only.
Add the filter-config element directly under the pe-extension tag. You can have only one filter-config element in an extension file.
global-attribute-filter
Use the global-attribute-filter element to filter specific properties across all components. You can have only one global-attribute-filter element in the extension file. Within this element you can include any number of attribute elements to define property filters for components from different libraries.
taglib-filter
Use the taglib-filter element to define property filters for components within a particular library. You can include multiple taglib-filter elements to filter properties for components in different libraries. Within this element you can include tag elements for every component belonging to the library.
Table 30-10 tag Element Attribute
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
namespace |
Namespace of the tag library containing the component whose properties you want to filter. |
tag
Use the tag element to specify a component whose properties you want to filter. You can include multiple tag elements within a taglib-filter element. Within this element you can include attribute elements for all properties you want to filter.
The following table describes the attribute the tag element can take.
Table 30-11 tag Element Attribute
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
name |
Name of the component whose properties you want to filter, for example, commandButton,portlet. |
attribute
Use the attribute element to specify a property to filter either across all components or for the specified component only. To define global-level filters, you must include attribute elements inside the global-attribute-filter. To define property filters for a particular component, you must include attribute elements inside the taglib-filter element.
The following table describes the attributes the attribute element can take.
Table 30-12 attribute Element Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
name |
Name of the property you want to filter. |
|
filtered |
Whether the property must be filtered or not. Takes a value of true or false. To filter the property in a specific view, use the view attribute. |
|
label |
The label for the property in the UI. To retrieve localized strings or show a different label depending on the view, use EL. |
|
view |
(Optional) The view in which to show/hide this property. Takes a value of design or source. |
The following example shows how you can define global and component-level property filters:
<filter-config> <global-attribute-filter> <attribute name="readOnly" filtered="false" label="Read Only"/> <attribute name="required" filtered="false" label="Mandatory"/> <attribute name="shortDesc" filtered="false" label="#{composerBundle.PNL_TB_SHORTDESC}"/> </global-attribute-filter> <taglib-filter namespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/rich"> <tag name="goLink"> <attribute name="accessKey" view="design"/> <attribute name="targetFrame" filtered="false" view="source"/> <attribute name="destination" filtered="false" label="#{pageEditorPanelBean.layoutView ? 'Where do you want to surf?' : 'Destination'}"/> </tag> <tag name="inputText"> <attribute name="all" view="design"/> <attribute name="label" label="Field Name" filtered="false" /> <attribute name="readOnly" filtered="false" /> <attribute name="required" filtered="false" /> <attribute name="rendered" filtered="false" /> <attribute name="wrap" filtered="false" /> </tag> </taglib-filter> </filter-config>
elbuilder-config
Use the elbuilder-config element to configure custom values for the expression builder. The expression builder invoked from Composer's Component Properties dialog enables users to specify EL values for component properties. Users can either select for a set of predefined values or enter an EL value in the text box. You can customize the expression builder to provide more options to users.
Add the elbuilder-config element directly under the pe-extension tag. You can have only one elbuilder-config element in an extension file.
selector
Use selector elements to define and include custom options, as shown in the following example:
<elbuilder-config> <!-- define selector --> <selector id="CustomELParameter"> view.CustomELParameter </selector> <!-- include selector --> <selectors> <selector id="CustomELParameter"/> </selectors> </elbuilder-config>
You can include many selector elements inside a selectors element.
selection-config
Use the selection-config element to enable or disable direct select for specific components and define associated operations. To make a component selectable, you must define operations within this tag.
Within the <selection-config> tag, you can configure selection globally using <global-filter> and by namespace and tag using <selection-taglib-filter>.
selection
The selection tag is used to enable direct select view.
operation
Available operations are defined within <operation> tags under each specific component. The following elements are used to define operations:
-
name: Defines the operation to be executed. (Use standard or custom operations.) -
label(optional): Overrides the operation name as the tab label in the popup window. -
filtered: Set tofalseto include the operation in the popup window.
<selection-config>
<global-filter>
<selection view="design" enabled="false"/>
</global-filter>
<selection-taglib-filter
namespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/customizable">
<tag name="showDetailFrame">
<selection view="design" enabled="true"/>
<operation name="oracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.sdfprop"
label="SDF Change Property"
filtered="false"/>
</tag>
</selection-taglib-filter>
</selection-config>
Sample pe_ext.xml File
Following is a sample pe_ext.xml file with different elements used to extend Composer capabilities.
<pe-extension xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/pageeditor/extension">
<addon-config>
<!-- Composer add-on panels configuration -->
<panels>
<panel name="oracle.fod.custom.panel" title="About FOD"
icon="adf/webcenter/images/about.gif"
taskflow-id="/WEB-INF/about-fod.xml#about-fod"/>
</panels>
<!-- Composer property panels configuration -->
<property-panels>
<property-panel name="cmdbtn">
<component>oracle.rich.CommandButton</component>
<panel name="prop.panel.cmdbtn" />
</property-panel>
</property-panels>
</addon-config>
<Save event handler configuration -->
<event-handlers>
<event-handler event="save">view.SaveHandler</event-handler>
</event-handlers>
<!-- Test drop handler configuration -->
<drop-handlers>
<drop-handler>test.TestDropHandler</drop-handler>
</drop-handlers>
<!-- Property filter configuration. Properties defined here are not displayed in Composer. -->
<filter-config>
<global-attribute-filter>
<attribute name="accessKey" />
<attribute name="attributeChangeListener" />
<attribute name="autoSubmit" />
<attribute name="binding" />
</global-attribute-filter>
<taglib-filter namespace="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/rich">
<tag name="commandButton">
<attribute name="text" />
<attribute name="icon" />
</tag>
</filter-config>
</pe-extension>
30.2.2 adf-config.xml
The adf-config.xml file specifies application-level settings that are usually determined at deployment and are often changed at runtime. This file is created when you create your application and is located in the ADF META-INF folder under Descriptors in the Application Resources panel. The following example shows the minimal adf-config.xml file created when you create a Portal Framework application:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252" ?>
<adf-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config"
xmlns:adf="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config/properties">
<adf:adf-properties-child xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config/properties">
<adf-property name="adfAppUID" value="Application4-2138"/>
</adf:adf-properties-child>
</adf-config>
When you add the Page Customizable component to a page, certain required configurations are added to the adf-config.xml file.
You must update the adf-config.xml file when you perform tasks such as registering new add-ons and custom property panels, selectively rendering add-ons, creating customization layers, enabling and disabling the Composer sandbox, creating custom resource catalogs, and disabling Structure view. The following sections describe the various adf-config.xml elements used for Composer-specific configurations.
page-editor-config
Use the <pe:page-editor-config> element to include Composer-specific configurations such as add-on panel registration, sandbox configuration, resource string editor configuration, and so on. Add the <pe:page-editor-config> element within the adf-config tag as shown in the following example:
<adf-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config"
xmlns:adf="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config/properties"
xmlns:mdsC="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mds/config">
. . .
<pe:page-editor-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/pageeditor/config">
. . .
</pe:page-editor-config>
</adf-config>
addon-panels
Use a <pe:addon-panel> element to register an add-on in the adf-config.xml file. A <pe:addon-panel> element must only be included inside the <pe:addon-panels> element. You can have any number of <pe:addon-panel> elements to register custom panels. The following example shows how you can register a new add-on using these elements:
<pe:page-editor-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/pageeditor/config">
<pe:addon-panels>
<!-- Page Properties add-on -->
<pe:addon-panel name="oracle.adf.pageeditor.addonpanels.page-settings" />
<!-- Page Reset add-on -->
<pe:addon-panel name="oracle.adf.pageeditor.addonpanels.page-reset" /><pe:addon-panel name="oracle.fod.custom.panel" />
</pe:addon-panels>
. . .
</pe:page-editor-config>
The <pe:addon-panel> element also supports the rendered attribute. This attribute can take an EL value and specifies whether the panel must be rendered in Composer or not.
When registering custom add-ons, you must also include entries for the default add-ons. If the default add-ons are not registered, then only your custom add-on is available in Composer.
The <pe:addon-panel> element supports the following parameters:
-
rendered: Use to specify whether the add-on must be rendered or not. The rendered attribute can take true, false, or an EL value. Use this attribute to display an add-on conditionally based on specific criteria. -
parameters: Use to declaratively pass parameters to the add-on task flow. The parameters attribute takes an EL value as shown in the following example:
<pe:addon-panels>
<pe:addon-panel name="oracle.adf.pageeditor.addonpanels.customization-manager" parameters="#{AppUtilBean.customizationManagerParams}"/>
. . .
</pe:addon-panels>
where AppUtilBean provides the logic to pass parameters to the add-on task flow.
sandbox-namespaces
Use the <pe:sandbox-namespaces> element to register namespaces for all metadata for which you want to enable sandbox creation at runtime. For more information about enabling sandbox creation, see How to Enable Composer Sandbox Creation
Insert the <pe:sandbox-namespaces> element within the <pe:page-editor-config> element. The following example shows how to use the sandbox-namespaces element:
<pe:page-editor-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/pageeditor/config">
. . .
<pe:sandbox-namespaces>
<pe:namespace path="/pages"/>
<pe:namespace path="/pageDefs"/>
</pe:sandbox-namespaces>
</pe:page-editor-config>
session-options-factory
When creating customization layers in your application, use the <pe:session-options-factory> element to register the ComposerSessionOptionsFactory implementation with Composer. This class contains the logic to save customizations in different layers based on the specified criteria. For more information, see Adding Customization Layers to View and Edit Modes: Example.
The following example shows how to register a class named AppsSessionOptionsFactoryImpl:
<pe:page-editor-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/pageeditor/config"> . . . <pe:session-options-factory>view.AppsSessionOptionsFactoryImpl</pe:session-options-factory> </pe:page-editor-config>
enable-design-views
To enable Composer direct select, you must first enable Select view. For more information on direct select functionality, see Enabling Direct Select in Design or Add Content View. Add the <pe:enable-design-views> tag inside the <pe:page-editor-config> tag to define the available views. The possible values are: design, add-content, select, source, preview, and all. The all value will show design, select, source, and preview only since add-content is a subset of design.
allow-el and protect-el
You can configure Composer to disable EL or protect existing EL from overwrite. Use <pe:allow-el> to define whether or not EL can be run in application pages. The default is true. Use <pe:protect-el> to define whether or not EL in form elements can be edited. The default is false. For more information, see How to Protect Expression Language
The following example disables EL:
<pe:page-editor-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/pageeditor/config"> . . . <pe:allow-el>false</pe:allow-el> </pe:page-editor-config>
rcv-config
Use the <rcv-config> element to register custom resource catalogs with Composer and to register the ResourceCatalogSelector implementation when using multiple resource catalogs.
If you want to display a custom resource catalog to users in place of the default one, you must first create a catalog definition file with the required content and then register this catalog definition in the Composer extension file and adf-config.xml file. The custom resource catalog is then displayed when a user clicks an Add Content button on the page.
Insert the <rcv-config> element within the adf-config tag. The following example shows how you can use the <rcv-config> element to register a custom catalog called users-catalog:
<adf-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config"
xmlns:adf="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config/properties"
xmlns:mdsC="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mds/config">
. . .
<rcv-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/rcs/viewer/adf-config">
<default-catalog catalog-name="users-catalog"/>
</rcv-config>
</adf-config>
You can also configure multiple resource catalogs with Composer so that different catalogs are displayed to different users depending on the specified criteria. When configuring multiple resource catalogs, use the <rcv-config> element with a <catalog-selector> element to register the ResourceCatalogSelector implementation, which contains the logic for selecting a resource catalog.
The following example shows how you can use the <rcv-config> element to register a ResourceCatalogSelector implementation called CatalogSelector:
<adf-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config"
xmlns:adf="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config/properties"
xmlns:mdsC="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mds/config">
. . .
<rcv-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/rcs/viewer/adf-config">
<catalog-selector class-name="webcenter.CatalogSelector"/>
<default-catalog catalog-name="default-catalog"/>
</rcv-config>
</adf-config>
customizableComponentsSecurity
Use the <customizableComponentsSecurity> element to apply restrictions on Show Detail Frame actions. Insert the <customizableComponentsSecurity> element within the adf-config tag.
Within the <customizableComponentsSecurity> element, you can specify the <enableSecurity>, <actionsCategory>, <actions>, and <custom-actions> elements.
enableSecurity
Use the <enableSecurity> element to override the security inheritance behavior on Show Detail Frame actions. This element can take a value of true or false. If set to true, then the ability for a user to modify a component is first determined from the page permissions and then adjusted according to the current set of actions defined for that type of permission. If set to false, then all actions are available to users. A user's page permissions and actions configured in adf-config.xml are ignored.
actionsCategory
Use the <actionsCategory> element to apply restrictions on a group of Show Detail Frame actions simultaneously. Within the <actionsCategory> element, you can have <actionCategory> elements for the supported categories. For more information about action categories, see Defining Security at the Actions Category Level.
The following example shows how actionsCategory can be used:
<adf-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config"
xmlns:adf="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config/properties"
xmlns:mdsC="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mds/config">
. . .
<cust:customizableComponentsSecurity
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/customizable/config">
<cust:enableSecurity value="true"/>
<cust:actionsCategory>
<cust:actionCategory name="personalizeActionsCategory" value="false"/>
<cust:actionCategory name="editActionsCategory" value="true"/>
</cust:actionsCategory>
<cust:actions>
. . .
</cust:actions>
</cust:customizableComponentsSecurity>
</adf-config>
actions
Use the <actions> element to apply restrictions on individual actions. Within each actions element, you can have <action> elements for all supported actions.
The following example shows how <actions> can be used:
<adf-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config"
xmlns:adf="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config/properties"
xmlns:mdsC="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mds/config">
. . .
<cust:customizableComponentsSecurity
xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/customizable/config">
<cust:enableSecurity value="true"/>
<cust:actionsCategory>
. . .
</cust:actionsCategory>
<cust:actions>
<cust:action name="showMinimizeAction" value="true"/>
<cust:action name="showMoveAction" value="false"/>
</cust:actions>
</cust:customizableComponentsSecurity>
<adf-config>
For more information about applying action-level restrictions, see Applying Action-Level Restrictions on Panel Customizable and Show Detail Component Actions.
custom-actions
Use the <custom-actions> element to define custom actions to display along with the other Show Detail Frame actions. You must add only one <custom-actions> element inside the customizableComponentsSecurity section. Within this you can add any number of <custom-action> elements to define individual custom actions.
Note:
Alternatively, you can add a <custom-actions> element inside an <adf-config-child> element instead of inside the <customizableComponentsSecurity> section.
For more information about custom actions, see Adding a Custom Action on a Show Detail Frame Enclosing a Task Flow.
mds-config
When defining type-level application customization restrictions on components, use the <mds-config> element to register a standalone XML file describing the restrictions to be applied on specific components. For information about applying type-level restrictions, see How to Define Type-Level Customization Policies.
Insert the <mds-config> element within the <adf-config> tag. You can add the <mds-config> element as follows:
<mds-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/mds/config">
<type-config>
<standalone-definitions>
<file>Directory_Name/standalone.xml</file>
</standalone-definitions>
</type-config>
</mds-config>
resource-string-editor
Use a <pe:resource-string-editor> element to enable resource string editing in your application. Insert the <pe:resource-string-editor> element within the <pe:page-editor-config> section, as shown in the following example:
<pe:page-editor-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/pageeditor/config">
. . .
<pe:resource-string-editor>
<pe:enabled>true</pe:enabled>
</pe:resource-string-editor>
</pe:page-editor-config>
For more information, see Configuring Runtime Resource String Editing.
enable-source-view
Use the <pe:enable-source-view> element to enable or disable Structure view in Composer. Insert the <pe:enable-source-view> element within the <pe:page-editor-config> section. Structure view is enabled by default in Composer. You can disable it by setting <pe:enable-source-view> to false, as shown in the following example:
<pe:page-editor-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/pageeditor/config"> . . . <pe:enable-source-view>false</pe:enable-source-view> </pe:page-editor-config>
For more information, see Disabling Structure View for the Application.
enable-zoom
Use the <pe:enable-zoom> element to enable or disable the capability to zoom into task flows in Composer. Insert the <pe:enable-zoom> element within a <pe:source-view> tag in the <pe:page-editor-config> section. Task flow zoom is enabled by default in Composer. You can disable it by setting <pe:enable-zoom> to false, as shown in the following example:
<pe:page-editor-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/pageeditor/config">
. . .
<pe:source-view>
<pe:enable-zoom>false</pe:enable-zoom>
</pe:source-view>
</pe:page-editor-config>
For more information, see Disabling Task Flow Zoom Capability.
persistent-change-manager
Use this to configure the change manager to be used for persisting changes made in Composer. Insert the <persistent-change-manager> element within the <adf-faces-config> section. You must set <persistent-change-manager> to MDSDocumentChangeManager as follows if you want to persist application customizations to MDS:
<adf-faces-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/config">
<persistent-change-manager>
<persistent-change-manager-class>oracle.adf.view.rich.change.MDSDocumentChangeManager</persistent-change-manager-class>
</persistent-change-manager>
. . .
</adf-faces-config>
For more information about change persistence in Composer, see Configuring the Persistence Change Manager.
For more information about the <persistent-change-manager> element, see What Happens When You Enable User Customizations in Fusion Middleware Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
taglib-config
Use the <taglib-config> element to specify the component tags that must be persisted by default. This element is relevant only when you define change persistence using <persistent-change-manager> in your adf-config.xml file.
When you add Composer components to the page, the adf-config.xml file is populated with the <taglib-config> element containing a list of tags and attributes that must be persisted. You can add more elements and attributes to the default list.
For more information about this element, see What Happens When You Enable User Customizations in Fusion Middleware Developing Fusion Web Applications with Oracle Application Development Framework.
Insert the <taglib-config> element within the <adf-faces-config> section. The <taglib-config> element appears as shown in the following example:
<adf-faces-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/config">
. . .
<taglib-config>
<taglib uri="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/customizable">
<tag name="showDetailFrame">
<persist-operations>all</persist-operations>
<attribute name="expansionMode">
<persist-changes>true</persist-changes>
</attribute>
<attribute name="contentStyle">
<persist-changes>true</persist-changes>
</attribute>
</tag>
<tag name="panelCustomizable">
<persist-operations>all</persist-operations>
</tag>
</taglib>
</taglib-config>
</adf-faces-config>
For more information, see Configuring the Persistence Change Manager.
security-config
Use this to override Composer-specific security configurations, specifically if you want to override the default security policies with application-level checks. Insert the <pe:security-config> element inside the <pe:page-editor-config> section. Within the security-config element, you can define <pe:security-policies>, <pe:security-policy>, <pe:policy-class>, and <pe:task-flow-security> elements.
security-policies
Use this to encompass all the security policies and policy overrides for Composer. You can have only one <pe:security-policies> element under the <pe:page-editor-config> section.
security-policy
Use this to override an existing policy. Add one <pe:security-policy> element for each policy that you want to override.
The <pe:security-policy> element supports the name and override attributes, where name is used to specify a name with which to register the custom policy and override is used to specify the name of the default policy that you want to override.
policy-class
Use this to specify the name of the custom security policy.
task-flow-security
Use this element, along with the check-permission attribute, to enable Composer to check for a task flow's permissions so that only users with appropriate privileges are allowed to edit or customize the task flow at runtime.
For more information, see Implementing Task Flow Security.
Example 30-1 Sample adf-config.xml File
shows a sample adf-config.xml file with Composer-specific configurations.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="windows-1252" ?>
<adf-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config"
xmlns:adf="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config/properties"
xmlns:mdsC="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/mds/config">
<adf:adf-properties-child xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config/properties">
<adf-property name="adfAppUID" value="configfilesapp-7198"/>
</adf:adf-properties-child>
<mdsC:adf-mds-config version="11.1.1.000">
<mds-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/mds/config">
<persistence-config>
<metadata-namespaces>
<namespace path="/oracle/adf/rc/metadata"
metadata-store-usage="WebCenterFileMetadataStore"/>
<namespace path="/persdef/"
metadata-store-usage="WebCenterFileMetadataStore"/>
<!-- Namespace definitions for Composer sandbox -->
<!-- Your jspx customizations alone go here -->
<namespace path="/pages" metadata-store-usage="WebCenterFileMetadataStore">
<namespace-restriction type="CUSTOMIZATIONS"/>
</namespace>
<!-- Your pagedef customizations alone go here -->
<namespace path="/pageDefs" metadata-store-usage="WebCenterFileMetadataStore">
<namespace-restriction type="CUSTOMIZATIONS"/>
</namespace>
</metadata-namespaces>
<metadata-store-usages>
<metadata-store-usage id="WebCenterFileMetadataStore"
default-cust-store="true">
<metadata-store class-name="oracle.mds.dt.persistence.stores.file.SrcControlFileMetadataStore">
<property name="metadata-path" value="../../mds"/>
</metadata-store>
</metadata-store-usage>
</metadata-store-usages>
</persistence-config>
<cust-config>
<match>
<customization-class name="oracle.adf.share.config.SiteCC"/>
</match>
</cust-config>
<cache-config>
<max-size-kb>100000</max-size-kb>
</cache-config>
<!-- Registration of a standalone XML file used for type-level customization policies -->
<type-config>
<standalone-definitions>
<file>Directory_Name/standalone.xml</file>
</standalone-definitions>
</type-config>
</mds-config>
</mdsC:adf-mds-config>
<pe:page-editor-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/pageeditor/config">
<!-- Composer add-on panel configuration -->
<pe:addon-panels>
<pe:addon-panel name="oracle.adf.pageeditor.addonpanels.page-settings" />
<pe:addon-panel name="oracle.adf.pageeditor.addonpanels.page-reset" />
<pe:addon-panel name="oracle.fod.custom.panel" />
</pe:addon-panels>
<!-- Composer sandbox configuration -->
<pe:sandbox-namespaces>
<pe:namespace path="/pages"/>
<pe:namespace path="/pageDefs"/>
</pe:sandbox-namespaces>
<!-- ComposerSessionOptionsFactory class registration for implementing customization layers -->
<pe:session-options-factory>view.AppsSessionOptionsFactoryImpl</pe:session-options-factory>
<!-- Resource string editor configuration -->
<pe:resource-string-editor>
<pe:enabled>true</pe:enabled>
</pe:resource-string-editor>
<!-- Switch to enable or disable Composer Source view -->
<pe:enable-source-view>false</pe:enable-source-view>
</pe:page-editor-config>
<!-- Multiple resource catalog configuration -->
<rcv-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/rcs/viewer/adf-config">
<catalog-selector class-name="webcenter.CatalogSelector"/>
<default-catalog catalog-name="users-catalog"/>
</rcv-config>
<!-- Composer and WebCenter Portal Customizable Components actions security configuration -->
<cust:customizableComponentsSecurity xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/customizable/config">
<cust:enableSecurity value="true"/>
<cust:actionsCategory>
<cust:actionCategory name="personalizeActionsCategory" value="false"/>
<cust:actionCategory name="editActionsCategory" value="true"/>
</cust:actionsCategory>
<cust:actions>
<cust:action name="showMinimizeAction" value="true"/>
<cust:action name="showMoveAction" value="false"/>
</cust:actions>
</cust:customizableComponentsSecurity>
<adf-faces-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/config">
<!-- Composer persistence change manager configuration -->
<persistent-change-manager>
<persistent-change-manager-class>oracle.adf.view.rich.change.MDSDocumentChangeManager</persistent-change-manager-class>
</persistent-change-manager>
<!-- Composer default persistence configuration -->
<taglib-config>
<taglib uri="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/faces/customizable">
<tag name="showDetailFrame">
<persist-operations>all</persist-operations>
<attribute name="expansionMode">
<persist-changes>true</persist-changes>
</attribute>
<attribute name="contentStyle">
<persist-changes>true</persist-changes>
</attribute>
</tag>
<tag name="panelCustomizable">
<persist-operations>all</persist-operations>
</tag>
</taglib>
</taglib-config>
</adf-faces-config>
</adf-config>
30.2.3 web.xml
The web.xml file is a Java EE standard descriptor that contains details about web applications. When you add a Page Customizable component to your page, the web.xml file available in the Application_Root\Project_Name\public_html\WEB-INF directory is updated to enable change persistence among other settings.
You must update web.xml further when creating an application that uses multiple customization layers and when enabling Composer sandbox. The following sections describe the web.xml configurations specific to Composer.
CHANGE_PERSISTENCE Context Parameter
The CHANGE_PERSISTENCE context parameter in the application's web.xml file specifies how application customizations are persisted. To enable changes in a Composer-enabled page to be persisted in MDS, you must ensure that the CHANGE_PERSISTENCE context parameter is set to ComposerChangeManager, as shown in the following example:
<context-param> <param-name>org.apache.myfaces.trinidad.CHANGE_PERSISTENCE</param-name> <param-value>oracle.adf.view.page.editor.change.ComposerChangeManager</param-value> </context-param>
This context parameter registers the ChangeManager class to be used to ensure persistence to MDS. This configuration happens automatically when you add a Page Customizable component to a page in a new Portal Framework application. However, in an existing ADF application, this context parameter may be set to some other value, for example session or oracle.adf.view.rich.change.FilteredPersistenceChangeManager. Therefore, when you add Composer components to such an application, you must ensure that the CHANGE_PERSISTENCE parameter is set to ComposerChangeManager.
For more information, see Configuring the Persistence Change Manager
WebCenterComposerFilter
Use WebCenterComposerFilter in the web.xml file to register Composer's ComposerSessionOptionsFactory with Oracle ADF for every HTTP request. The request is then handled depending on your implementation of ComposerSessionOptionsFactory. This filter can be defined as shown in the following example:
<filter-mapping> <filter-name>WebCenterComposerFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/faces/*</url-pattern> <dispatcher>FORWARD</dispatcher> <dispatcher>REQUEST</dispatcher> </filter-mapping>
You must use WebCenterComposerFilter if you are performing the following tasks:
-
Creating customization layers. For information, see Adding Customization Layers to View and Edit Modes: Example
-
Enabling sandbox creation in Composer. For more information, see How to Enable Composer Sandbox Creation
30.3 Composer Default Add-Ons and Property Panels
This section lists the add-ons and property panels available by default in Composer.
Default Add-Ons
This section lists the add-ons available in Composer and provides the names with which these add-ons are registered in the adf-config.xml file. It is useful to know these names as you will need them to enable or disable the display of the add-ons in your application.
-
Page Properties
Used to edit page properties and create page parameters.
This add-on is registered with the name
oracle.adf.pageeditor.addonpanels.page-settingsin theadf-config.xmlfile. -
Reset Page
Used to reset page customizations.
This add-on is registered with the name
oracle.adf.pageeditor.addonpanels.page-resetin theadf-config.xmlfile. -
Customization Manager
Used to manage customizations made to pages and task flows.
This add-on is registered with the name
oracle.adf.pageeditor.addonpanels.customization-managerin theadf-config.xmlfile.
The Page Properties and Reset Page add-ons are rendered by default. If you create custom add-ons in your application, while registering those add-ons in adf-config.xml, you must also include the entries for the default add-ons. Without these, the default add-ons are not displayed in Composer.
Default Property Panels
This section lists the property panels available by default in the Component Properties and Page Properties dialogs and provides the names with which these panels are registered in the pe_ext.xml file. These names are useful if you choose to override the default panels with custom property panels, or hide some or all of the default panels. You can also enable specific panels for display in Composer Add Content or Design view; for details.
-
Display Options
Used to define display-related behavior of a component. This panel is displayed in the Component Properties dialog for all components.
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.generic-property-inspector. -
Display Options (Show Detail Frame)
Used to define display-related behavior of a
Show Detail Framecomponent. This panel is displayed in the Component Properties dialog for aShow Detail Framecomponent only.In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.sdfprop. -
Tabs
Used to define the display properties and order of tabs on a Panel Customizable or Box component. This panel is displayed in the Component Properties dialog for a Panel Tabbed orPanel Customizable component. The panel is displayed for a Panel Customizable component only if the component has tabs on it.
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.panel-tabbed. -
Style
Used to define the appearance of the component instance. This panel is displayed in the Component Properties dialog for all components.
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.inline-style-editor. -
Content Style
Used to define the appearance of content inside a component instance. This panel is displayed in the Component Properties dialog for all components.
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.content-style-editor. -
Events
Used to wire a contextual event to an action handler to enable the passing of values from a producer component to a consumer component when the event is triggered on the producer. This panel displays in the Component Properties dialog for all components.
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.events. -
Region Parameters
Used to define parameters for the task flow region. This panel displays in the Component Properties dialog only for task flow regions.
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.region-param. -
Portlet Parameters
Used to define portlet parameters. This panel displays in the Component Properties dialog only for portlets.
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.portlet-param. -
Layout Customizable
Used to define the layout for page components by selecting from a set of predefined layouts. This panel displays in the Component Properties dialog only for Layout Customizable components.
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.layout-cust-prop. -
Child Components
Used to rearrange and show or hide child components inside a Panel Customizable component. This panel displays only for Panel Customizable components
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.adf.pageeditor.pane.child-navigator. -
Page Parameters
Used to define the page parameters that can be wired to components on the page. This panel displays in the Page Properties dialog.
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.webcenter.page.pane.page-param. -
Page Security
Used to define page permissions. This panel displays in the Page Properties dialog for secured application pages.
In the
pe_ext.xmlfile, this panel is referenced with the nameoracle.webcenter.page.pane.page-sec.