4 Enabling SSO Authentication
These topics provide guidelines for configuring single sign-on (SSO) authentication for Oracle Business Intelligence.
This chapter contains the following topics:
- SSO Configuration Tasks for Oracle Business Intelligence
- Understanding SSO Authentication and Oracle Business Intelligence
- SSO Implementation Considerations
- Configuring SSO in an Oracle Access Manager Environment
- Configuring Custom SSO Environments
- Configuring Single Sign-On with Smart View
- Enabling Oracle Business Intelligence to Use SSO Authentication
- Enabling the Online Catalog Manager to Connect
Note:
Oracle recommends using Oracle Access Manager as an enterprise-level SSO authentication provider with Oracle Fusion Middleware. You can assume that Oracle Access Manager is the SSO authentication provider.SSO Configuration Tasks for Oracle Business Intelligence
The table contains SSO authentication configuration tasks and provides links for obtaining more information.
| Task | Description | For More Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Configure Oracle Access Manager as the SSO authentication provider. |
Configure Oracle Access Manager to protect the Oracle Business Intelligence URL entry points. |
Configuring SSO in an Oracle Access Manager Environment Configuring Single Sign-On in Oracle Fusion Middleware in Securing Applications with Oracle Platform Security Services |
|
Configure the HTTP proxy. |
Configure the web proxy to forward requests from Presentation Services to the SSO provider. |
Configuring Single Sign-On in Oracle Fusion Middleware in Securing Applications with Oracle Platform Security Services |
|
Configure a new authenticator for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
Configure the Oracle WebLogic Server domain in which Oracle Business Intelligence is installed to use the new identity store. |
Configuring an OID Authenticator for Oracle WebLogic Server Configuring Oracle Business Intelligence to Use Alternative Authentication Providers Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help |
|
Configure a new identity asserter for Oracle WebLogic Server. |
Configure the Oracle WebLogic Server domain in which Oracle Business Intelligence is installed to use the SSO provider as an asserter. |
Configuring Oracle Access Manager as a New Identity Asserter for Oracle WebLogic Server Configuring Oracle Business Intelligence to Use Alternative Authentication Providers Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help |
|
Configure custom SSO solutions. |
Configure alternative custom SSO solutions to protect the Oracle Business Intelligence URL entry points. |
|
|
Enable Oracle Business Intelligence to accept SSO authentication. |
Enable the SSO provider configured to work with Oracle Business Intelligence. |
Enabling Oracle Business Intelligence to Use SSO Authentication |
Note:
For an example of an Oracle Business Intelligence SSO installation scenario, see Enterprise Deployment Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence.
Understanding SSO Authentication and Oracle Business Intelligence
Integrating a single sign-on (SSO) solution enables a user to log on (sign-on) and be authenticated once. Thereafter, the authenticated user is given access to system components or resources according to the permissions and privileges granted to that user.
You can configure Oracle Business Intelligence to trust incoming HTTP requests authenticated by a SSO solution that is configured for use with Oracle Fusion Middleware and Oracle WebLogic Server. See Configuring Single Sign-On in Oracle Fusion Middleware in Securing Applications with Oracle Platform Security Services.
When Oracle Business Intelligence is configured to use SSO authentication, it accepts authenticated users from whatever SSO solution Oracle Fusion Middleware is configured to use. If SSO is not enabled, then Oracle Business Intelligence challenges each user for authentication credentials. When Oracle Business Intelligence is configured to use SSO, a user is first redirected to the SSO solution's login page for authentication. After the user is authenticated the SSO solution forwards the user name to Presentation Services where this name is extracted. Next a session with the BI Server is established using the impersonation feature, a connection string between the Oracle BI Presentation Server and the BI Server using credentials that act on behalf of a user being impersonated.
After successfully logging in using SSO, users are still required to have the oracle.bi.server.manageRepositories permission to log in to the Administration Tool using a valid user name and password combination. After installation, the oracle.bi.server.manageRepositories permission is granted by being a member of the default BIAdministration application role.
Configuring Oracle Business Intelligence to work with SSO authentication requires minimally that the following be done:
- Oracle Fusion Middleware and Oracle WebLogic Server are configured to accept SSO authentication. Oracle Access Manager is recommended in production environments.
- Oracle BI Presentation Services is configured to trust incoming messages.
- The HTTP header information required for identity propagation with SSO configurations, the user identity and SSO cookie, is specified and configured.
How an Identity Asserter Works
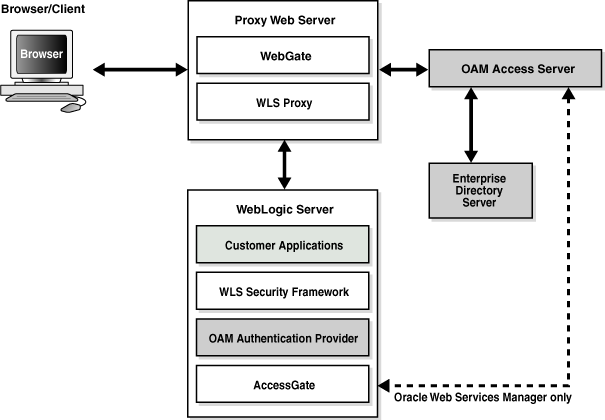
This section describes how Oracle Access Manager authentication provider works with Oracle WebLogic Server using Identity Asserter for single sign-on, providing the following features:
- Identity Asserter for Single Sign-on
This feature uses the Oracle Access Manager authentication services and validates already-authenticated Oracle Access Manager users through a suitable token and creates a WebLogic-authenticated session. It also provides single sign-on between WebGate and portals. WebGate is a plug-in that intercepts web resource (HTTP) requests and forwards them to the Access Server for authentication and authorization.
- Authenticator
This feature uses Oracle Access Manager authentication services to authenticate users who access an application deployed in Oracle WebLogic Server. Users are authenticated based on their credentials, for example a user name and password.
After the authentication provider for Oracle Access Manager is configured as the Identity Asserter for single sign-on, the web resources are protected. Perimeter authentication is performed by WebGate on the web tier and by the appropriate token to assert the identity of users who attempt access to the protected WebLogic resources.
All access requests are routed to a reverse proxy web server. These requests are in turn intercepted by WebGate. The user is challenged for credentials based on the authentication scheme configured within Oracle Access Manager (form-based login recommended).
After successful authentication, WebGate generates a token and the web server forwards the request to Oracle WebLogic Server, which in turn invokes Oracle Access Manager Identity Asserter for single sign-on validation. Oracle Access Manager is able to pass various types of heading token, the simplest being an HTTP header called OAM_REMOTE_USER containing the user ID that has been authenticated by Oracle Access Manager. The WebLogic Security Service invokes Oracle Access Manager Identity Asserter for single sign-on, which next gets the token from the incoming request and populates the subject with the WLSUserImpl principal. The Identity Asserter for single sign-on adds the WLSGroupImpl principal corresponding to the groups the user is a member of. Oracle Access Manager then validates the cookie.
The diagram depicts the distribution of components and the flow of information when the Oracle Access Manager Authentication Provider is configured as an Identity Asserter for SSO with Oracle Fusion Middleware.
How Oracle Business Intelligence Operates with SSO Authentication
After SSO authorization has been implemented, Presentation Services operates as if the incoming web request is from a user authenticated by the SSO solution. Presentation Services next creates a connection to the BI Server using the impersonation feature and establishes the connection to the BI Server on behalf of the user. User personalization and access controls such as data-level security are maintained in this environment.
SSO Implementation Considerations
When implementing a SSO solution with Oracle Business Intelligence you should consider the following:
When accepting trusted information from the HTTP server or servlet container, you must secure the machines that communicate directly with Presentation Services. In the instanceconfig.xml file, specify the list of HTTP Server or servlet container IP addresses in the Listener\Firewall node. The Firewall node must include the IP addresses of all Oracle BI Scheduler instances, Oracle Presentation Services instances, and Oracle Business Intelligence JavaHost instances.
If any of these components are co-located with Oracle BI Presentation Services, you must add the 127.0.0.1 address in Firewall node. Setting the list of HTTP Server or servlet container IP addresses does not control end-user browser IP addresses. When using mutually-authenticated SSL, you must specify the Distinguished Names (DNs) of all trusted hosts in the Listener\TrustedPeers node.
Configuring SSO in an Oracle Access Manager Environment
Review the overview about how to configure SSO in an Oracle Access Manager environment, and these additional references.
After the Oracle Fusion Middleware environment is configured, you must do the following to configure Oracle Business Intelligence:
-
Configure the SSO provider to protect the Oracle Business Intelligence URL entry points.
-
Configure the web server to forward requests from the Presentation Services to the SSO provider.
-
Configure the new identity store as the main authentication source for the Oracle WebLogic Server domain whereOracle Business Intelligence has been installed. See Configuring an OID Authenticator for Oracle WebLogic Server.
-
Configure the Oracle WebLogic Server domain where Oracle Business Intelligence is installed to use an Oracle Access Manager identity asserter. See Configuring Oracle Access Manager as a New Identity Asserter for Oracle WebLogic Server.
-
After the SSO environment configuration is complete, enable SSO authentication for Oracle Business Intelligence. See Enabling SSO Authentication Using Fusion Middleware Control.
See Configuring Single Sign-On in Oracle Fusion Middleware in Securing Applications with Oracle Platform Security Services.
See Configuring BI Publisher to Use Oracle Access Manager (OAM) Single Sign-On in Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Publisher.
Configuring an OID Authenticator for Oracle WebLogic Server
After installing Oracle Business Intelligence, the Oracle WebLogic Server embedded LDAP server is the default authentication source (identity store).
To use a new identity store such as Oracle Internet Directory (OID) as the main authentication source, you must configure the Oracle WebLogic Server domain, where Oracle Business Intelligence is installed.
See Administering Security for Oracle WebLogic Server and Using Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
See Setting the JAAS Control Flag Option.
For the field details to complete the Provider Specific tab, see Authentication Provider Specific Reference.
- Click the newly added authenticator in the authentication providers table.
- Navigate to Settings, then select the Configuration\Common tab:
- Select SUFFICIENT from the Control Flag list.
- Click Save.
- Display the Provider Specific tab and specify the following settings using appropriate values for your environment:
- Click Save.
- Perform the following steps to set up the default authenticator for use with the Identity Asserter:
- At the main Settings for myrealm page, display the Providers tab, then display the Authentication tab, then select DefaultAuthenticator to display its configuration page.
- Display the Configuration\Common tab, from the Control Flag list, select SUFFICIENT.
- Click Save.
- Perform the following steps to reorder providers:
- Display the Providers tab.
- Click Reorder to display the Reorder Authentication Providers page
- Select a provider name and use the arrow buttons to order the list of providers as follows:
- OID Authenticator (SUFFICIENT)
- OAM Identity Asserter (REQUIRED)
- Default Authenticator (SUFFICIENT)
- Click OK to save your changes.
- In the Change Center, click Activate Changes.
- Restart Oracle WebLogic Server.
- Log in to Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
- In the Change Center, click Lock & Edit.
- From Domain Structure, select Security Realms and click myrealm.
- In Settings for myrealm, click the Providers tab, and then click the Authentication tab.
- In Authentication Providers, click New.
- In Create a New Authentication Provider, type the Name for the authentication providers such as OID Provider.
- From the Type list, select OracleInternetDirectoryAuthenticator, and click OK.
- From the Authentication Providers table, select the provider you just created.
- Click the Common tab, from the Control Flag list, select Sufficient, and click Save.
Use Reordering Authentication Providers to make the OID authenticator the primary authentication used by Oracle WebLogic Server. Reorder the authenticators as follows:
-
OID Authenticator (SUFFICIENT)
-
OAM Identity Asserter (REQUIRED)
-
Default Authenticator (SUFFICIENT)
Authentication Provider Source Reference
This table provides a reference for adding an authentication provider.
| Section Name | Field Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Connection |
Host |
The LDAP host name. For example, <localhost>. |
|
Connection |
Port |
The LDAP host listening port number. For example, 6050. |
|
Connection |
Principal |
The distinguished name (DN) of the user that connects to the LDAP server. For example, cn=orcladmin. |
|
Connection |
Credential |
The password for the LDAP administrative user entered as the Principal. |
|
Users |
User Base DN |
The base distinguished name (DN) of the LDAP server tree that contains users. For example, use the same value as in Oracle Access Manager. |
|
Users |
All Users Filter |
The LDAP search filter. For example, (&(uid=*) (objectclass=person)). The asterisk (*) filters for all users. Click More Info... for details. |
|
Users |
User From Name Filter |
The LDAP search filter. Click More Info... for details. |
|
Users |
User Name Attribute |
The attribute that you want to use to authenticate, for example, cn, uid, or mail. Set as the default attribute for user name in the directory server. For example, uid. The value that you specify here must match the User Name Attribute that you are using in the authentication provider, as described in the next task Configuring User Name Attributes. |
|
Groups |
Group Base DN |
The base distinguished name (DN) of the LDAP server tree that contains groups (same as User Base DN). |
|
General |
GUID attribute |
The attribute used to define object GUIDs in LDAP. orclguid You should not change this default value, in most cases the default value here is sufficient. |
Configuring Oracle Access Manager as a New Identity Asserter for Oracle WebLogic Server
The Oracle WebLogic Server domain in which Oracle Business Intelligence is installed must be configured to use an Oracle Access Manager asserter.
-
Log in to Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
-
In Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, select Security Realms from the left pane and click the realm you are configuring, for example, myrealm.
-
Select Providers.
- Click New. Complete the fields as follows:
- Name: OAM Provider, or a name of your choosing.
- Type: OAMIdentityAsserter.
- Click OK.
- Click Save.
- In the Providers tab, perform the following steps to reorder Providers:
- Click Reorder
- In the Reorder Authentication Providers page, select a provider name, and reorder the list of providers as follows:
- OID Authenticator (SUFFICIENT)
- OAM Identity Asserter (REQUIRED)
- Default Authenticator (SUFFICIENT)
- Click OK to save your changes.
- In the Change Center, click Activate Changes.
- Restart Oracle WebLogic Server.
You can verify that Oracle Internet Directory is the new identity store (default authenticator) by logging back into Oracle WebLogic Server and verifying the users and groups stored in the LDAP server appear in the console.
- Enable SSO authentication.
.
Configuring Custom SSO Environments
This section contains references to information about setting up custom SSO environments.
For information about configuring Oracle Business Intelligence to participate in custom SSO environments, for example, setting up SSO using SiteMinder, see article 1287479.1 on My Oracle Support at:
Configuring Single Sign-On with Smart View
This topic describes the steps required to configure Single Sign-On (SSO) with Smart View. It applies to Smart View clients that are integrated with an Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition server that is SSO-enabled with Microsoft Active Directory and Native Authentication.
These steps allow Smart View users to launch Smart View on their Windows PCs and connect to Oracle Business Intelligence analytics without being prompted for a login username and password. The SSO login information is passed seamlessly from Microsoft Active Directory to Oracle Business Intelligence to Smart View.
Before you begin, you must have configured Oracle Business Intelligence to use Windows Server Active Directory as an LDAP Authentication source and to use Windows Native Authentication in an SSO environment. This process is described in the white paper Configuring authentication and SSO with Active Directory and Windows Native Authentication in Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition available as part of article 1274953.1 on My Oracle Support.
-
Verify that you can sign in and connect to Oracle Business Intelligence using the Microsoft Active Directory username and password.
-
Install the Smart View client on any Windows machines running Smart View. You can download the most current Smart View version from Oracle Technology Network (OTN).
-
On the Oracle Business Intelligence server, make a backup copy of the existing
jbips.earfile. -
Use the
jarcommand to unpack thejbips.earfile into a temporary directory.jar –xvf jbips.ear
-
Add the following to the
web.xmlfile before the<welcome-file-list>section of the document:<security-constraint> <web-resource-collection> <web-resource-name>JBIPS</web-resource-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </web-resource-collection> <auth-constraint> <role-name>SSORole</role-name> </auth-constraint> </security-constraint> <login-config> <auth-method>CLIENT-CERT</auth-method> </login-config> <security-role> <role-name>SSORole</role-name> </security-role> -
Modify the
weblogic.xmlfile and add the following:<context-root>jbips</context-root> <security-role-assignment> <role-name>SSORole</role-name> <principal-name>BIUsers</principal-name> <principal-name>BIAdmins</principal-name> <principal-name>Domain Users</principal-name> <principal-name>Users</principal-name> </security-role-assignment> </weblogic-web-app> -
Modify the
MANIFEST.MFfile to add the version:Weblogic-Application-Version: 12.2.1
-
Recreate the
jbips.earfile using thejarcommand:jar –cfm jbips.ear /META-INF/MANIFEST.MF
-
Sign in to the WebLogic Server console and delete the existing
jbips.earfile. -
Use the WebLogic Server console to deploy the newly created
jbips.earfile . When deploying, don’t enter the version. The version number is picked up by the changes to theMANIFEST.MFfile. -
Restart the servers and retest Smart View to confirm that SSO is working as expected.
Enabling Oracle Business Intelligence to Use SSO Authentication
After you configure Oracle Business Intelligence to use the SSO solution, you must enable SSO authentication for Oracle Business Intelligence.
After you enable SSO, the default Oracle Business Intelligence login page is not available.
Enabling and Disabling SSO Authentication Using WLST Commands
Use WLST commands to enable or disable SSO authentication for Oracle Business Intelligence.
In Oracle Business Intelligence 12.2.1.3.0, lightweight SSO is enabled by default. If you are using legacy authentication methods such as session variables in initialization blocks, you need to disable lightweight SSO using the disableBISingleSignOn command.
- You must have file system and WebLogic Administrator permissions.
- You must perform the enable or disable SSO authentication as an offline activity.
- Validation is limited to URL format. Connectivity and WebLogic configuration is not validated.
- Changing the URL for log off requires that you disable, and then re-enable with new URL.
- A logon URL is not required.
Pre-requisites:
- Configure WebLogic security providers, see About Configuring WebLogic Security Providers in Administering Security for Oracle WebLogic Server.
See Using the WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) in System Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
See Starting Oracle Business Intelligence Component Processes in System Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
Use the table to learn the arguments appropriate for each command.
| Command | Arguments | Return | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
DOMAIN_HOME, <logoff-url> |
None |
Enable SSO and configure logoff URL. |
|
|
DOMAIN_HOME |
None |
Disable SSO. |
Enabling SSO Authentication Using Fusion Middleware Control
How you enable SSO authentication for Oracle Business Intelligence using the Security tab in Fusion Middleware Control.
See Using Oracle Fusion Middleware Control, and Starting and Stopping the Oracle Business Intelligence Components in System Administrator's Guide for Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition.
Enabling the Online Catalog Manager to Connect
How you enable online Catalog Manager to point to a new URL when analytics becomes protected when using SSO.
The online Catalog Manager might fail to connect to Oracle BI Presentation Services when the HTTP web server for Oracle Business Intelligence is enabled for SSO. When you enable SSO in Enabling SSO Authentication Using Fusion Middleware Control, the Oracle Business Intelligence URL http://hostname:port_number/analytics becomes protected, and you must point the online Catalog Manager to the URL http://hostname:port_number/analytics-ws instead. The URL should remain unprotected. It is configured only to accept SOAP access as used by Oracle BI Publisher, Oracle BI Add-in for Microsoft Office, and the online Catalog Manager.
To log in to the online Catalog Manager when SSO is enabled you must change the URL suffix to point to analytics-ws/saw.dll.