31 Understanding GST (Release 9.1 Update)
This chapter discusses these topics:
-
Section 31.2, "GST Process Flow for Goods and Services in the P2P Cycle"
-
Section 31.3, "GST Process Flow for Goods and Services in the O2C Cycle"
-
Section 31.4, "JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Software Solution for GST"
31.1 GST Overview
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a destination-based tax applicable to the supply of goods and services or both that is administered concurrently by the central and state governments throughout the value chain. It is levied at all stages starting from manufacture to final consumption with the credit of taxes to be paid at previous stages as offsets against the tax liability of each stage.
The features of GST are:
-
The central government levies the Central GST (CGST) and the state government levies the State GST (SGST) on every supply of goods and services within a state. Both CGST and Integrated GST (IGST) are levied on the same taxable basis.
-
The central government levies the Integrated GST (IGST) on all inter-state supplies and transfers the tax to the destination state. IGST is also levied on imports of goods to India. A portion of the revenue goes to the state government of the consuming state.
|
Note: The government levies GST cess on certain goods and services at a specific rate to collect funds for compensating the states for revenue loss due to the implementation of GST. GST cess is imposed along with the CGST, SGST, and IGST duties levied on the interstate, intrastate, import, and export transactions for these goods and services. |
31.2 GST Process Flow for Goods and Services in the P2P Cycle
This process flow shows the tasks that manufacturers perform to purchase raw materials to run their businesses in the GST regime:
Figure 31-1 GST Process Flow for Goods in the P2P Cycle
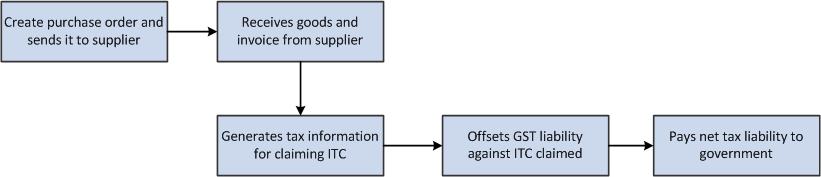
Description of ''Figure 31-1 GST Process Flow for Goods in the P2P Cycle''
This process flow shows the tasks that manufacturers perform to procure services to run their businesses in the GST regime:
Figure 31-2 GST Process Flow for Services in the P2P Cycle

Description of ''Figure 31-2 GST Process Flow for Services in the P2P Cycle''
31.3 GST Process Flow for Goods and Services in the O2C Cycle
This process flow shows the tasks that suppliers perform to sell goods in the GST regime:
Figure 31-3 GST Process Flow for Sales in the O2C Cycle
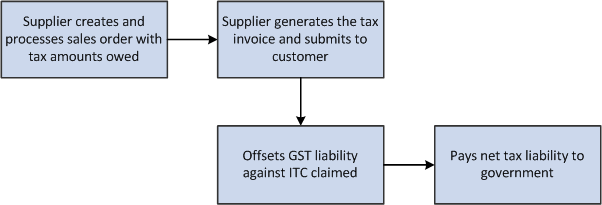
Description of ''Figure 31-3 GST Process Flow for Sales in the O2C Cycle''
This process flow shows the tasks that service providers perform to provide services in the GST regime:
Figure 31-4 GST Process Flow for Services in the O2C Cycle
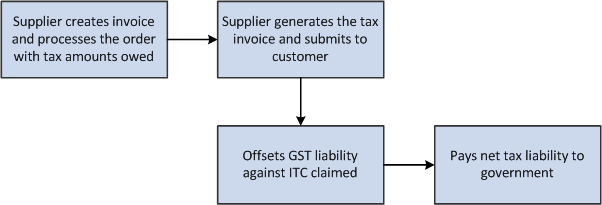
Description of ''Figure 31-4 GST Process Flow for Services in the O2C Cycle''
31.4 JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Software Solution for GST
To meet the GST requirements specified by the tax authorities, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne programs enable you to:
-
Associate all your business units in a state as a GST unit with one GST registration number (GSTIN).
-
Enter and store the GSTIN for purchasers, suppliers, and GST units.
-
Calculate GST for all applicable GST types (CGST, SGST, IGST, and Cess) simultaneously through a single process.
-
Maintain a unified tax table for tracking all tax transactions for all GST types (CGST, IGST, SGST, and Cess).
-
Enable manufacturers and suppliers to work with the GST component of purchases and sales in the P2P and O2C cycles.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Solution for Goods and Services in the P2P Cycle
For a manufacturer in the P2P cycle, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne programs enable you to:
-
Create a purchase order for items that are eligible for GST.
-
Receive goods with a tax component and a receipt note from the supplier.
-
Enable the receiver to declare the goods and services for personal use, for which ITC cannot be claimed.
-
Create an accounts payable voucher for services that are eligible for GST.
-
Compute GST for all applicable GST types (CGST, SGST, IGST, and Cess) to claim ITC.
-
Maintain the inbound GSTR2 report provided by the government (based on input by the supplier).
-
Summarize and format the calculated GST amounts to match with the inbound GSTR2 report.
-
Avail partial or full claim of the calculated GST amounts for all applicable GST types (CGST, IGST, SGST, and Cess) through a single claim process.
-
Process the claim for a single tax settlement for all business units sharing the same GST registration number (GSTIN).
-
Update credit balances.
-
Track and report tax liability separately for different GST types.
-
Distribute GST lTC to decrease tax liability.
-
Create vouchers for the supplier to pay the balance liability to the tax authorities.
-
Make ledger adjustments, and credit or debit adjusted amounts.
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Solution for Goods and Services in the O2C Cycle
To meet the GST requirements specified by the tax authorities for a supplier in the O2C cycle, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne programs enable you to:
-
Create a sales order for items that are eligible for GST.
-
Compute the GST amounts for the items during the sales order creation taking into account any adjustments and discounts.
-
Create accounts receivable invoices for services that are eligible for GST.
-
Facilitate advance payments by customers and compute the tax on advance payment.
-
Apply GST to inter-branch transactions.
-
Create legal tax invoice templates.
-
Authorize the shipment of items after verification of the items.
-
Make ledger adjustments, and credit or debit adjusted amounts.
-
Perform the sales update to maintain accurate inventory, accounts receivable, and ledger records.
-
Declare manufactured goods for internal consumption and for other categories where ITC is not applicable.
-
Record the bill of export information when you export goods.
31.5 Setup Requirements for India GST
This table lists the GST setup requirements for India:
| Setup Requirement | Details | Cross-Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Activating the GST module for India. | Before you can work with the GST component of goods and services, you must activate the GST module in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system by using the Activate GST Module program (P75I833). | See Activating the GST Module for India. |
| Associate tax types to tax regimes. | You use the Relation Tax Reg/Tax Type Inf program (P75I005) to specify the GST types (CGST, IGST, SGST, and GCESS) for the GST regime. | See Assigning Tax Types to Tax Regimes. |
| Set up landed cost rules. | Use the Landed Cost Revisions - IND - 43B program (P75I791) to set up landed cost rules for the item and branch plant combination in the Landed Cost Revisions - IND - 43B program (P75I791). | See Setting Up Landed Costs. |
| Create GST rules. | You use the GST Rules Setup program (P75I802) to create GST rules with attributes, such as recoverable and reverse charge. | See Setting Up GST Rules. |
| Associate GST rules to level costs. | You use the GST P2P Setup program (P75I801) to associate GST rules with level costs. | See Linking GST Rules to Level Costs. |
| Set up GST identification number for GST units. | You use the Work With Address Book Additional Information program (P75I210) to enter the GST identification number for customers, suppliers, or GST units. | See Setting Up Tax Registration Details. |
| Set up GST account details. | You use the GST Account Master Setup program (P75I805) to set up accounts for various types of GST duties. | See Setting Up the GST Account Master. |
| Create cross-references between GST units and business units. | You use the GST Cross Reference Setup program (P75I803) to create a relationship between a GST unit and a business unit. | See Associating Business Units with GST Units. |
| Upload CL, ITC, and TL Opening and Closing Balances | You use the GST Ledgers Setup program (P75I804) to enter opening balances for Cash Ledger (CL), Input Tax Credit (ITC), and Tax Liability (TL) ledgers. You use this program only once before the India Localization system goes live. If you leave the opening balance for an account blank, the system considers the opening balance as zero. | See Entering Opening Balances for Cash Ledger, Input Tax Credit, and Tax Liability Ledgers. |
| Define the attributes for an item. | Verify that the item attribute values (HSN and SAC) exist in the Item Attribute UDC table (75I/IA). The values for this UDC are hard-coded. You enter values from this UDC table when you work with the Service Tax Category Codes Mapping program (P75I009). | N/A |
| Associate item attributes with items. | You use the GST Category Type Setup program (P75I806) to define and associate the HSN code (harmonized system for goods) and SAC code (service account code) with items. | See Assigning Category Codes to Item Attributes. |
| Set up GST tax rates. | You use the GST Tax Rate Setup program (P75I809) to set up tax rates for HSN and SAC. | See Setting Up Tax Rates for GST |
| Map Adjustment Schedules to GST Rules. | You use the GST Adjustment Schedules Setup program (P75I826) to link GST rules with adjustment schedules. | See Linking GST Rules to Adjustment Schedules for Sales Transactions. |
| Create GST offset rules. | You use the GST Credit Distribution Setup program (P75I830) to create GST offset rules. | See Setting Up Rules to Offset the GST ITC. |
| Set up information for printing legal documents. | To populate information that you need to print the legal invoice document, run the Legal Doc Default Setup program (R75I807). Also, set up the next numbering sequence for invoices using the GST Legal Document Next Numbers program (P75I818). | See Setting Up Legal Documents for GST Invoices (Release 9.1 Update). |