Network Administration by Functional Area
Oracle Solaris network administration features are designed to meet specific networking needs by providing support in the following functional areas: high availability, network virtualization, performance, resource management, security, and storage. Knowing which functional area a particular feature supports is helpful for evaluating which networking strategy or strategies to implement at your site.
The following table describes the various network administration features that are supported in Oracle Solaris according to functional area. Information about the administrative interface that is used to administer the feature and at which layer of the network protocol stack the feature is administered, is also provided.
|
In many cases, you can obtain optimal results by using a combination of networking features. For example, the following figure shows how you might combine multiple networking features for high availability.
Figure 1-2 Combining the Use of Aggregations With VNICs
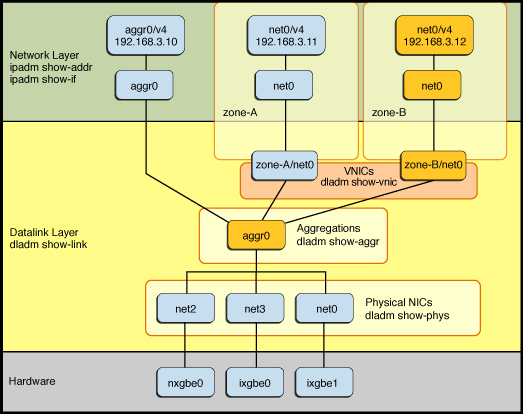
In the figure, multiple physical datalinks (net0, net2, and net3) are combined into a single link aggregation (aggr0). The aggregation datalink is then directly configured from IP in the global zone through the aggr0 and aggr0 IP interface and IP address, respectively. For another example, see Combining Aggregations With VNICs for High Availability.
You can also virtualize the aggregation datalink by using it as the underlying link for the VNICs. In this figure, two VNICs are configured and then assigned to two non-global zones. This particular configuration makes the VNICs highly available because any failures of the underlying physical NICs that occur are automatically handled by the link aggregation layer and are transparent to the zones.