Guidelines for Configuring Host-Based Data Replication Between Clusters
This section provides guidelines for configuring data replication between clusters. This section also contains tips for configuring replication resource groups and application resource groups. Use these guidelines when you are configuring data replication for your cluster.
This section discusses the following topics:
Configuring Replication Resource Groups
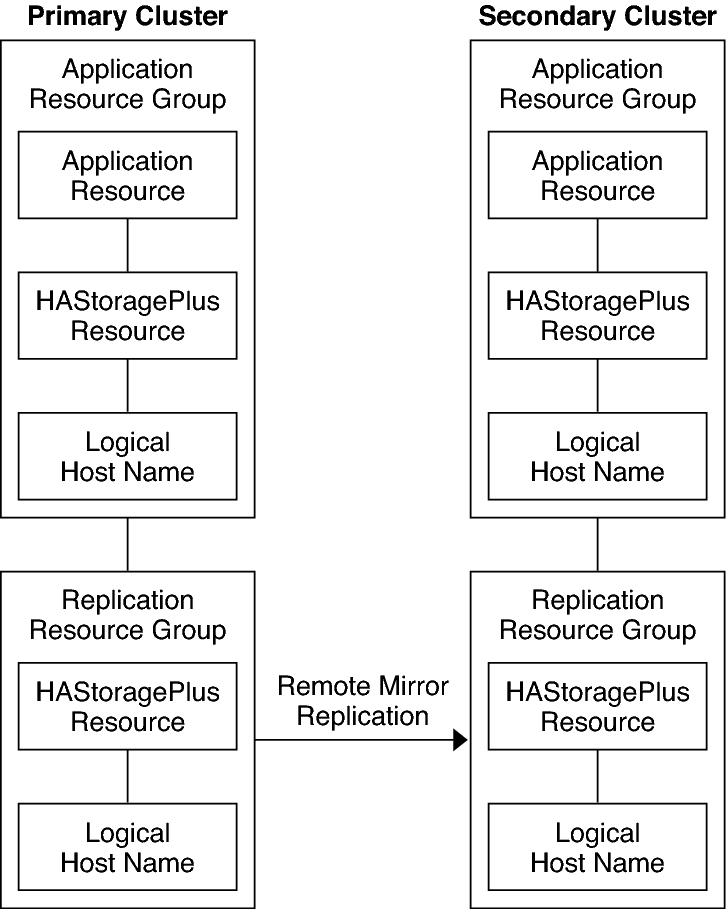
Replication resource groups collocate the device group under Availability Suite software control with a logical hostname resource. A logical hostname must exist on each end of the data replication stream, and must be on the same cluster node that acts as the primary I/O path to the device. A replication resource group must have the following characteristics:
-
Be a failover resource group
A failover resource can run on only one node at a time. When a failover occurs, failover resources take part in the failover.
-
Have a logical hostname resource
A logical hostname is hosted on one node of each cluster (primary and secondary) and is used to provide source and target addresses for the Availability Suite software data replication stream.
-
Have an HAStoragePlus resource
The HAStoragePlus resource enforces the failover of the device group when the replication resource group is switched over or failed over. Oracle Solaris Cluster software also enforces the failover of the replication resource group when the device group is switched over. In this way, the replication resource group and the device group are always colocated, or mastered by the same node.
The following extension properties must be defined in the HAStoragePlus resource:
-
GlobalDevicePaths. This extension property defines the device group to which a volume belongs.
-
AffinityOn property = True. This extension property causes the device group to switch over or fail over when the replication resource group switches over or fails over. This feature is called an affinity switchover.
For more information about HAStoragePlus, see the SUNW.HAStoragePlus(5) man page.
-
-
Be named after the device group with which it is colocated, followed by -stor-rg
For example, devgrp-stor-rg.
-
Be online on both the primary cluster and the secondary cluster
Configuring Application Resource Groups
To be highly available, an application must be managed as a resource in an application resource group. An application resource group can be configured for a failover application or a scalable application.
The ZPoolsSearchDir extension property must be defined in the HAStoragePlus resource. This extension property is required to use the ZFS file system.
Application resources and application resource groups configured on the primary cluster must also be configured on the secondary cluster. Also, the data accessed by the application resource must be replicated to the secondary cluster.
This section provides guidelines for configuring the following application resource groups:
Configuring Resource Groups for a Failover Application
In a failover application, an application runs on one node at a time. If that node fails, the application fails over to another node in the same cluster. A resource group for a failover application must have the following characteristics:
-
Have an HAStoragePlus resource to enforce the failover of the file system or zpool when the application resource group is switched over or failed over.
The device group is colocated with the replication resource group and the application resource group. Therefore, the failover of the application resource group enforces the failover of the device group and replication resource group. The application resource group, the replication resource group, and the device group are mastered by the same node.
Note, however, that a failover of the device group or the replication resource group does not cause a failover of the application resource group.
-
If the application data is globally mounted, the presence of an HAStoragePlus resource in the application resource group is not required but is advised.
-
If the application data is mounted locally, the presence of an HAStoragePlus resource in the application resource group is required.
For more information about HAStoragePlus, see the SUNW.HAStoragePlus(5) man page.
-
-
Must be online on the primary cluster and offline on the secondary cluster.
The application resource group must be brought online on the secondary cluster when the secondary cluster takes over as the primary cluster.
Configuration of Resource Groups in a Failover Application illustrates the configuration of an application resource group and a replication resource group in a failover application.
Figure 5 Configuration of Resource Groups in a Failover Application
Configuring Resource Groups for a Scalable Application
In a scalable application, an application runs on several nodes to create a single, logical service. If a node that is running a scalable application fails, failover does not occur. The application continues to run on the other nodes.
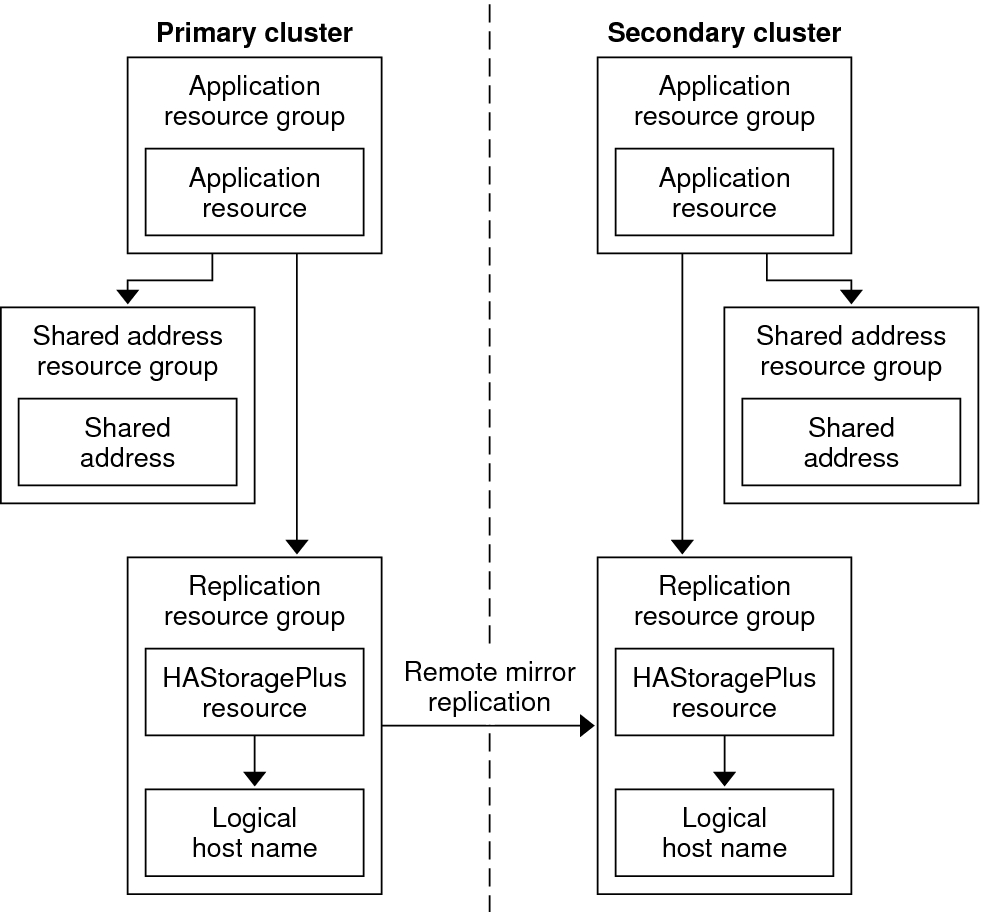
When a scalable application is managed as a resource in an application resource group, it is not necessary to collocate the application resource group with the device group. Therefore, it is not necessary to create an HAStoragePlus resource for the application resource group.
-
Have a dependency on the shared address resource group
The nodes that are running the scalable application use the shared address to distribute incoming data.
-
Be online on the primary cluster and offline on the secondary cluster
A resource group for a scalable application must have the following characteristics:
Configuration of Resource Groups in a Scalable Application illustrates the configuration of resource groups in a scalable application.
Figure 6 Configuration of Resource Groups in a Scalable Application
Guidelines for Managing a Takeover
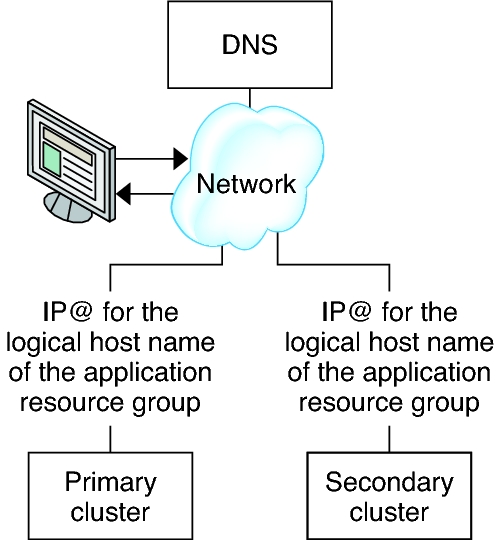
If the primary cluster fails, the application must be switched over to the secondary cluster as soon as possible. To enable the secondary cluster to take over, the DNS must be updated.
Clients use DNS to map an application's logical hostname to an IP address. After a takeover, where the application is moved to a secondary cluster, the DNS information must be updated to reflect the mapping between the application's logical hostname and the new IP address.
Figure 7 DNS Mapping of a Client to a Cluster
To update the DNS, use the nsupdate command. For information, see the nsupdate(1M) man page. For an example of how to manage a takeover, see Example of How to Manage a Takeover.
After repair, the primary cluster can be brought back online. To switch back to the original primary cluster, perform the following tasks:
-
Synchronize the primary cluster with the secondary cluster to ensure that the primary volume is up-to-date. You can achieve this by stopping the resource group on the secondary node, so that the replication data stream can drain.
-
Reverse the direction of data replication so that the original primary is now, once again, replicating data to the original secondary.
-
Start the resource group on the primary cluster.
-
Update the DNS so that clients can access the application on the primary cluster.