Release 9.0.1
Part Number A88784-01
Home |
Book List |
Contents |
Index | Master Index | Feedback |
| Oracle interMedia Annotator User's Guide Release 9.0.1 Part Number A88784-01 |
|
interMedia Annotator is packaged along with several sample multimedia files. They are included in the <ORACLE_HOME>\ord\Annotator\media_data directory. You can use interMedia Annotator on these files (or on files of your own choosing) to perform a number of operations. These operations include:
To create an annotation, perform the following operations:
The Make a Selection window appears (Figure 3-1).
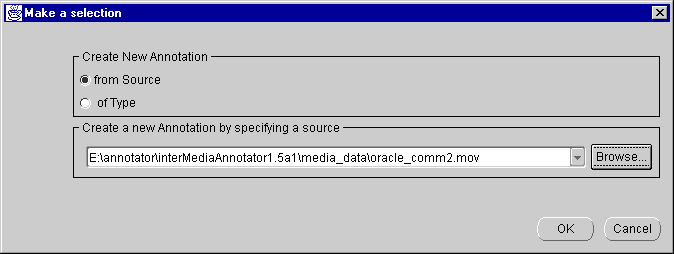
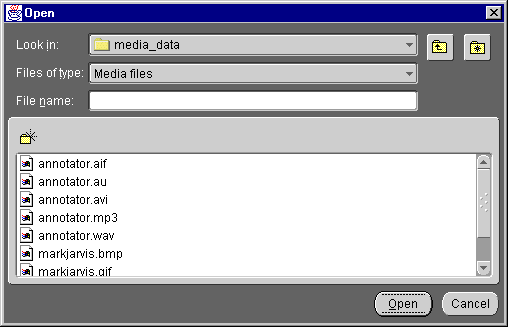
If the media file does not appear in the pull-down menu, click the Browse button and select a media file in the Open window (Figure 3-2).
See Figure 1-1 for more information on how interMedia Annotator builds an annotation.
interMedia Annotator can parse media sources accessible through the URL protocols shown in Table 3-1.
If you are parsing a local file or a file available over the Internet through the http protocol, interMedia Annotator extracts the time-independent attributes from the media file and inserts them into a logical annotation.
If you are parsing an audio CD, interMedia Annotator can connect to a CDDB, find the entry corresponding to your CD, and create a logical annotation.
If you are parsing a media source with multiple tracks, such as a video source or audio CD, an annotation is created for each track.
When the parsing is complete, the annotation type appears in the Annotation Tree View of the Annotations pane. The attribute names and values for the currently selected annotation are displayed in the Attributes tab of the interMedia Annotator window (Figure 2-1). The Annotations pane contains an expandable list, which shows the hierarchy of annotations and sub-annotations (Figure 3-3).
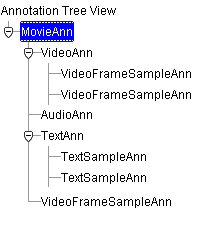
In order to display the attributes of another annotation, select it in the Annotation Tree View.
Some JPEG files contain additional metadata in the Information Interchange Model (IIM) format. This metadata can optionally be extracted into an IpctIimAnn sub-annotation, which appears as a sub-annotation of your main annotation. In order to create an IpctIimAnn sub-annotation, perform the following operations:
The Parsers tab of the Preferences window appears (Figure 2-7).
You can edit the value that appears for each attribute by performing the following operations:
A solid outline will appear around the table cell and an I-beam cursor will appear.
You can save your changes to the annotation. See Section 3.6 for more information.
interMedia Annotator defines a given number of attributes (see Appendix C for a complete list of attributes). However, not all media sources will provide values for every attribute. You can use interMedia Annotator to add a value to your annotation for any attribute that does not have a value.
interMedia Annotator cannot write any new attribute values back to the media sources. The current annotation will contain the value, but any annotations created later by interMedia Annotator will not contain the new value.
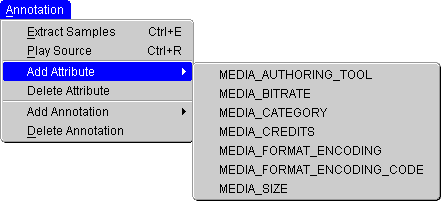
To add a value for an attribute that has not been automatically set, perform the following operations:
The Add Attribute submenu appears (Figure 3-4), listing the attributes that have no values.
The new attribute appears in the Attributes tab with no value in the right-hand column.
Validation of the annotation type is done at this time.
To delete an attribute from your annotation, perform the following operations:
The Please Confirm window opens (Figure 3-5).
The attribute and its value are deleted from the annotation.
An annotation will usually contain one or more sub-annotations, which contain the metadata associated with a portion of the media source, such as a text track or an audio track. In addition to these populated sub-annotations, you can create your own sub-annotations by adding an empty annotation and then populating it with your own values.
To create an empty annotation, perform the following operations:
The Add Annotation submenu appears (Figure 3-6).
Your new annotation appears in the Annotation Tree View.
You can populate an empty annotation with attribute values in the same way you would add attribute values to a populated annotation. See Section 3.3 for more information.
You can delete annotations and sub-annotations. You can delete sub-annotations that you have created and sub-annotations that were created automatically in the parsing process. To delete an annotation, perform the following operations:
The Please Confirm window opens (Figure 3-7).
The selected annotation is removed from the Annotation Tree View.
You can use interMedia Annotator to extract three types of samples: text selections (or tracks) from a QuickTime movie file, images from a QuickTime movie file, or audio tracks from a compact disc.
To extract a text track from a QuickTime movie, perform the following operations:
oow_annotator.mov (included with interMedia Annotator). See Section 3.1 for more information on creating an annotation.
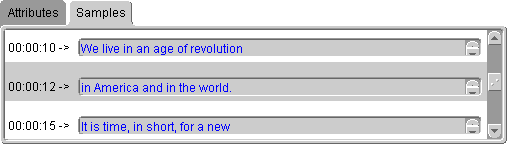
View the extracted text information by clicking the Samples tab when the text annotation is selected (Figure 3-8).
To extract a video track from a QuickTime movie, perform the following operations:
The Parsers tab of the Preferences window appears (Figure 2-7).
View the extracted video information by clicking the Samples tab when the video annotation is selected (Figure 3-9).

interMedia Annotator can extract audio data from a CD track. You can specify the start and end points of your extracted sample.
To extract samples from a CD, perform the following operations:
The Parsers tab of the Preferences window appears (Figure 2-7).
The audio sample is extracted and stored in the Sun AU sound file format.
After extraction, media source attributes will be modified in order to refer to the extracted sample. These attributes include file format, MIME type, file name, directory, and URL, among others.
See Section 3.8 for more information on playing back the extracted sample.
Once you have parsed a media source, you can save the annotation as an XML document by performing the following operations:
The Save window opens (Figure 3-10).
The XML document can be viewed through any text editor or through interMedia Annotator. See Section 3.7 for more information.
The default folder where interMedia Annotator will save annotations is set in the General tab of the Preferences window. To change the default folder, perform the following operations:
If you have a saved annotation, you can open it in interMedia Annotator by performing the following operations:
The Make a Selection window opens (Figure 3-11).
The Open window appears (Figure 3-2).
The annotation and its sub-annotations appear in the Annotation Tree View.
You can use interMedia Annotator to play your media source and any text or video sample that you have extracted.
Before playing a media source or sample, check the Mime-Types tab of the Preferences window to ensure that each MIME type is paired with the correct path to the appropriate helper application. See Section 2.2.5 for more information.
Play a media source or an extracted sample by performing the following operations:
The appropriate media player opens and plays the media source.
Play an extracted media sample by performing the following operations:
The appropriate media player opens and plays the media source.
You can view a text sample without opening a separate viewer.
After extracting the text sample, click the Samples tab in the right-hand window pane. The text sample appears, along with a time line indicating roughly where each piece of text appears in the video or song.
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2001, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|