5 Replaying a Database Workload
This chapter describes how to replay a database workload on the test system. After a captured workload is preprocessed, it can be replayed repeatedly on a replay system that is running the same version of Oracle Database.
This chapter contains the following sections:
Tip:
Before you can replay a database workload, you must first:-
Capture the workload on the production system, as described in Chapter 3, "Capturing a Database Workload"
-
Preprocess the captured workload, as described in Chapter 4, "Preprocessing a Database Workload"
Setting Up the Test System
Typically, the replay system where the preprocessed workload will be replayed should be a test system that is separate from the production system. Before a test system can be used for replay, it must be prepared properly, as described in the following sections:
Restoring the Database
Before a workload can be replayed, the application data state should be logically equivalent to that of the capture system at the start time of workload capture. This minimizes data divergence during replay. The method for restoring the database depends on the backup method that was used before capturing the workload. For example, if RMAN was used to back up the capture system, you can use RMAN DUPLICATE capabilities to create the test database. For more information, see "Prerequisites for Capturing a Database Workload".
After the database is created with the appropriate application data on the test system, perform the system change you want to test, such as a database or operating system upgrade. The primary purpose of Database Replay is to test the effect of system changes on a captured workload. Therefore, the system changes you make should define the test you are conducting with the captured workload.
Resetting the System Time
It is recommended that the system time on the replay system host be changed to a value that approximately matches the capture start time just before replay is started. Otherwise, an invalid data set may result when replaying time-sensitive workloads. For example, a captured workload that contains SQL statements using the SYSDATE and SYSTIMESTAMP functions may cause data divergence when replayed on a system that has a different system time. Resetting the system time will also minimize job scheduling inconsistencies between capture and replay.
Steps for Replaying a Database Workload
Proper planning of the workload replay ensures that the replay will be accurate. Replaying a database workload requires the following steps:
Setting Up the Replay Directory
The captured workload must have been preprocessed and copied to the replay system. A directory object for the directory to which the preprocessed workload is copied must exist in the replay system.
Resolving References to External Systems
A captured workload may contain references to external systems, such as database links or external tables. Typically, you should reconfigure these external interactions to avoid impacting other production systems during replay. External references that need to be resolved before replay a workload include:
-
Database links
It is typically not desirable for the replay system to interact with other databases. Therefore, you should reconfigure all database links to point to an appropriate database that contains the data needed for replay.
-
External tables
All external files specified using directory objects referenced by external tables need to be available to the database during replay. The content of these files should be the same as during capture, and the filenames and directory objects used to define the external tables should also be valid.
-
Directory objects
You should reconfigure any references to directories on the production system by appropriately redefining the directory objects present in the replay system after restoring the database.
-
URLs
URLs need to be configured so that Web services accessed during the workload capture will point to the proper URLs during replay.
-
E-mails
To avoid resending E-mail notifications during replay, the mail server on the replay system should be configured to ignore requests for outgoing E-mails.
Tip:
To avoid impacting other production systems during replay, Oracle strongly recommends running the replay within an isolated private network that does not have access to the production environment hosts.Remapping Connections
During workload capture, connection strings used to connect to the production system are captured. In order for the replay to succeed, you need to remap these connection strings to the replay system. The replay clients can then connect to the replay system using the remapped connections.
For Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) databases, you can map all connection strings to a load balancing connection string. This is especially useful if the number of nodes on the replay system is different from the capture system. Alternatively, if you want to direct workload to specific instances, you can use services or explicitly specify the instance identifier in the remapped connection strings.
Specifying Replay Options
After the database is restored and connections are remapped, you can set the following replay options as appropriate:
Preserving COMMIT Order
The synchronization parameter controls whether the COMMIT order in the captured workload will be preserved during replay. By default, this option is enabled to preserve the COMMIT order in the captured workload during replay. All transactions will be executed only after all dependent transactions have been committed.
You can disable this option, but the replay will likely yield significant data divergence. However, this may be desirable if the workload consists primarily of independent transactions, and divergence during unsynchronized replay is acceptable.
Controlling Session Logins
The connect_time_scale parameter enables you to scale the elapsed time between the time when the workload capture began and each session connects. You can use this option to manipulate the session connect time during replay with a given percentage value. The default value is 100, which will attempt to connect all sessions as captured. Setting this parameter to 0 will attempt to connect all sessions immediately.
Controlling Think Time
User think time is the elapsed time while the replayed user waits between issuing calls within a single session. To control replay speed, use the think_time_scale parameter to scale user think time during replay. If user calls are being executed slower during replay than during capture, you can make the database replay attempt to catch up by setting the think_time_auto_correct parameter to TRUE. This will make the replay client shorten the think time between calls, so that the overall elapsed time of the replay will more closely match the captured elapsed time.
Setting Up Replay Clients
The replay client is a multithreaded program (an executable named wrc located in the $ORACLE_HOME/bin directory) where each thread submits a workload from a captured session. Before replay begins, the database will wait for replay clients to connect. At this point, you need to set up and start the replay clients, which will connect to the replay system and send requests based on what has been captured in the workload.
Before starting replay clients, ensure that the:
-
Replay client software is installed on the hosts where it will run
-
Replay clients have access to the replay directory
-
Replay directory contains the preprocessed workload capture
-
Replay user has the correct user ID, password, and privileges (the replay user needs the DBA role and cannot be the
SYSuser)
After these prerequisites are met, you can proceed to set up and start the replay clients using the wrc executable. The wrc executable uses the following syntax:
wrc [user/password[@server]] MODE=[value] [keyword=[value]]
The parameters user and password specify the username and password used to connect to the host where the wrc executable is installed. The parameter server specifies the server where the wrc executable is installed. The parameter mode specifies the mode in which to run the wrc executable. Possible values include replay (the default), calibrate, and list_hosts. The parameter keyword specifies the options to use for the execution and is dependent on the mode selected. To display the possible keywords and their corresponding values, run the wrc executable without any arguments.
The following sections describe the modes that you can select when running the wrc executable:
Calibrating Replay Clients
Since one replay client can initiate multiple sessions with the database, it is not necessary to start a replay client for each session that was captured. The number of replay clients that need to be started depends on the number of workload streams, the number of hosts, and the number of replay clients for each host.
To estimate the number of replay clients and hosts that are required to replay a particular workload, run the wrc executable in calibrate mode.
In calibration mode, the wrc executable accepts the following keywords:
-
replaydirspecifies the directory that contains the preprocessed workload capture you want to replay. If unspecified, it defaults to the current directory. -
process_per_cpuspecifies the maximum number of client processes that can run per CPU. The default value is 4. -
threads_per_processspecifies the maximum number of thread that can run within a client process. The default value is 50.
The following example shows how to run the wrc executable in calibrate mode:
%> wrc mode=calibrate replaydir=./replay
In this example, the wrc executable is executed to estimate the number of replay clients and hosts that are required to replay the workload capture stored in a subdirectory named replay under the current directory. In the following sample output, the recommendation is to use at least 21 replay clients divided among 6 CPUs:
Workload Replay Client: Release 11.1.0.7.0 - Production on Thu March 27 14:06:33 2008 Copyright (c) 1982, 2008, Oracle. All rights reserved. Report for Workload in: /oracle/replay/ ----------------------- Recommendation: Consider using at least 21 clients divided among 6 CPU(s). Workload Characteristics: - max concurrency: 1004 sessions - total number of sessions: 1013 Assumptions: - 1 client process per 50 concurrent sessions - 4 client process per CPU - think time scale = 100 - connect time scale = 100 - synchronization = TRUE
Starting Replay Clients
After determining the number of replay clients that are needed to replay the workload, you need to start the replay clients by running the wrc executable in replay mode on the hosts where they are installed. Once started, each replay client will initiate one or more sessions with the database to drive the workload replay.
In replay mode, the wrc executable accepts the following keywords:
-
useridandpasswordspecify the user ID and password of a replay user for the replay client. If unspecified, these values default to thesystemuser. -
serverspecifies the connection string that is used to connect to the replay system. If unspecified, the value defaults to an empty string. -
replaydirspecifies the directory that contains the preprocessed workload capture you want to replay. If unspecified, it defaults to the current directory. -
workdirspecifies the directory where the client logs will be written. This parameter is only used in conjunction with thedebugparameter for debugging purposes. -
debugspecifies whether debug data will be created. Possible values include:-
onDebug data will be written to both files in the working directory
-
offNo debug data will be written (the default value)
Note:
Before running the wrc executable in debug mode, contact Oracle Support for more information. -
-
connection_overridespecifies whether to override the connection mappings stored in theDBA_WORKLOAD_CONNECTION_MAPview. If set toTRUE, connection remappings stored in theDBA_WORKLOAD_CONNECTION_MAPview will be ignored and the connection string specified using theserverparameter will be used. If set toFALSE, all replay threads will connect using the connection remappings stored in theDBA_WORKLOAD_CONNECTION_MAPview. This is the default setting.
The following example shows how to run the wrc executable in replay mode:
%> wrc system/oracle@test mode=replay replaydir=./replay
In this example, the wrc executable starts the replay client to replay the workload capture stored in a subdirectory named replay under the current directory.
After all replay clients have connected, the database will automatically distribute workload capture streams among all available replay clients. At this point, workload replay can begin. After the replay finishes, all replay clients will disconnect automatically.
Displaying Host Information
You can display the hosts that participated in a workload capture and workload replay by running the wrc executable in list_hosts mode.
In list_hosts mode, the wrc executable accepts the keyword replaydir, which specifies the directory that contains the preprocessed workload capture you want to replay. If unspecified, it defaults to the current directory.
The following example shows how to run the wrc executable in list_hosts mode:
%> wrc mode=list_hosts replaydir=./replay
In this example, the wrc executable is executed to list all hosts that participated in capturing or replaying the workload capture stored in a subdirectory named replay under the current directory. In the following sample output, the hosts that participated in the workload capture and three subsequent replays are shown:
Workload Replay Client: Release 11.1.0.7.0 - Production on Thu March 27 13:44:48 2008
Copyright (c) 1982, 2008, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Hosts found:
Capture:
prod1
prod2
Replay 1:
test1
Replay 2:
test1
test2
Replay 3:
testwin
Replaying a Database Workload Using Enterprise Manager
This section describes how to replay a database workload using Enterprise Manager. The primary tool for replaying database workloads is Oracle Enterprise Manager. If for some reason Oracle Enterprise Manager is unavailable, you can also replay database workloads using APIs, as described in "Replaying a Database Workload Using APIs".
To replay a database workload using Enterprise Manager:
-
On the Software and Support page, under Real Application Testing, click Database Replay.
The Database Replay page appears.
-
In the Go to Task column, click the icon that corresponds to the Replay Workload task.
The Replay Workload page appears.
Description of the illustration dbr_replay_empty.gif
-
In the Directory Object list, select a directory that contains the preprocessed workload that you want to replay.
After a directory is selected, the Replay Workload page will be refreshed to display the Capture Summary and the Replay History sections. For more information, see "Setting Up the Replay Directory".
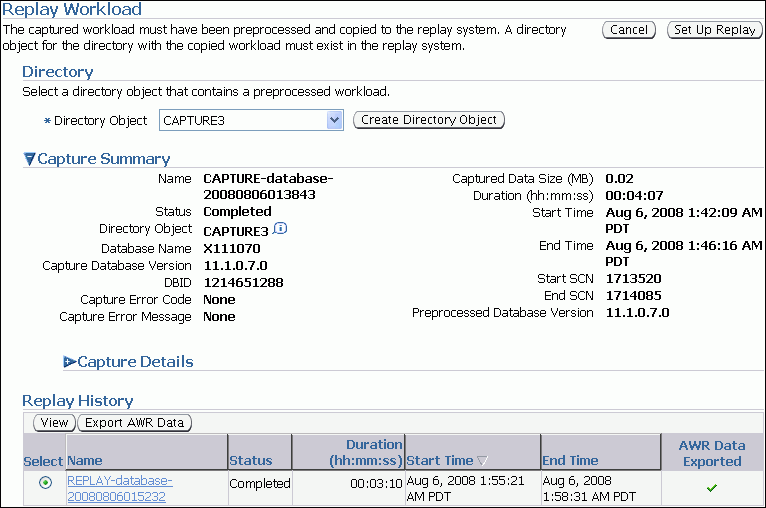
Description of the illustration dbr_replay_capture3.gif
The Capture Summary section displays information about the preprocessed workload capture in the selected directory. To view additional details about the workload capture, expand Capture Details. The expanded Capture Details section displays the workload profile and workload filters used during the workload capture.
-
Click Set Up Replay.
The Replay Workload: Prerequisites page appears.
-
Verify that all prerequisites are met before proceeding.
If you are replaying the workload on a test system, ensure that the test system is properly prepared for replay. For more information, see "Setting Up the Test System".
Once all prerequisites are completed, click Continue.
The Replay Workload: References to External Systems page appears.
-
Verify potential references to all external systems and modify any invalid references.
Use the links available on the Replay Workload: References to External Systems page to verify the database links, directory objects, and Oracle Streams that may be referenced during the workload capture process. There may be other references to external systems that are not included in these categories. For more information, see "Resolving References to External Systems".
Once all references to external systems have been verified and modified as necessary, click Continue.
The Replay Workload: Choose Initial Options page appears.
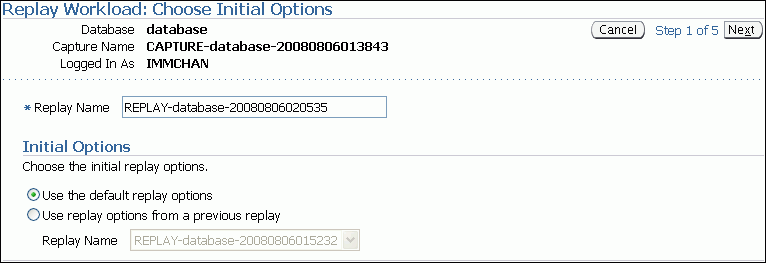
Description of the illustration dbr_replay_init_options.gif
-
In the Replay Name field, you may enter a name for the replay, or simply use the name generated by the system.
-
Under Initial Options, select whether to use default replay options or replay options from a previous replay (if one is available). If more than one previous replay exist, select the replay you want to use from the Replay Name list.
Click Next.
The Replay Workload: Customize Options page appears.
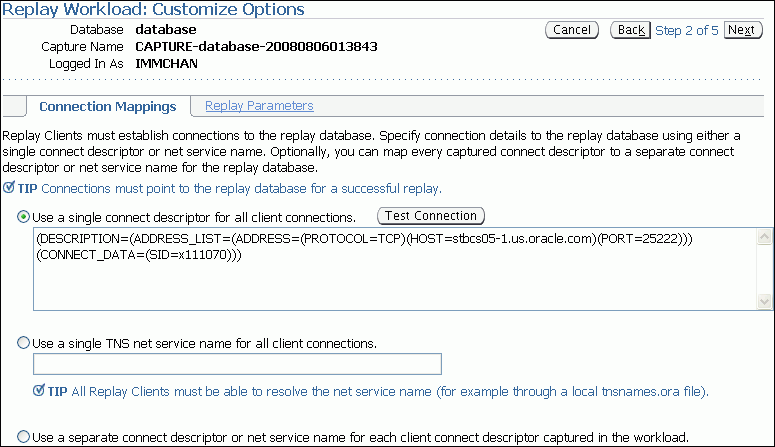
Description of the illustration dbr_replay_cust_options.gif
-
Remap captured connection strings to connection strings that point to the replay system.
Click the Connection Mappings tab. There are several methods you can use to remap captured connection strings. You can choose to:
-
Use a single connect descriptor for all client connections by selecting this option and entering the connect descriptor you want to use. The connect descriptor should point to the replay system.
To test the connection, click Test Connection. If the connect descriptor is valid, an Information message is displayed to inform you that the connection was successful.
-
Use a single TNS net service name for all client connections by selecting this option and entering the net service name you want to use. All replay clients must be able to resolve the net service name, which can be done using a local tnsnames.ora file.
-
Use a separate connect descriptor or net service name for each client connect descriptor captured in the workload by selecting this option and, for each capture system value, entering a corresponding replay system value that will be used by the replay client.
For more information, see "Remapping Connections".
-
-
Specify the replay options using the replay parameters.
To modify the replay behavior, click the Replay Parameters tab and enter the desired values for each replay parameter. Using the default values is recommended. For information about setting the replay parameters, see "Specifying Replay Options".

Description of the illustration dbr_replay_params.gif
After setting the replay parameters, click Next.
The Replay Workload: Prepare Replay Clients page appears.
-
Ensure that replay clients are prepared for replay.
Before proceeding, the replay clients need to be prepared. For more information, see "Setting Up Replay Clients".
After all replay clients are ready to start, click Next.
The Replay Workload: Wait for Client Connections page appears.
Description of the illustration dbr_replay_client.gif
-
Start the replay clients.
For information about starting replay clients, see "Setting Up Replay Clients".
As replay clients are started, the replay client connections will be displayed under Client Connections. When all replay clients have connected, click Next.
The Replay Workload: Review page appears.
Description of the illustration dbr_replay_review.gif
-
Review the options and parameters that have been defined for the workload replay.
Before starting replay, reset the system clock to a value that is as close to the capture start time as possible. This minimizes any data divergence that may result from replaying a time-sensitive workload. For more information, see "Resetting the System Time".
To begin replay, click Submit. If no replay clients are connected, this button will be disabled. To make changes, click Back. To cancel replay without saving changes, click Cancel.
Once the replay is started, the View Workload Replay page appears. For information about monitoring an active workload replay, see "Monitoring an Active Workload Replay".
Monitoring Workload Replay Using Enterprise Manager
This section describes how to monitor workload replay using Enterprise Manager. The primary tool for monitoring workload replay is Oracle Enterprise Manager. Using Enterprise Manager, you can:
-
Monitor or stop an active workload replay
-
View a completed workload replay
If for some reason Oracle Enterprise Manager is unavailable, you can monitor workload replay using views, as described in "Monitoring Workload Replay Using Views".
This section contains the following topics:
Monitoring an Active Workload Replay
This section describes how to monitor an active workload replay using Enterprise Manager.
To monitor an active workload replay:
-
On the Software and Support page, under Real Application Testing, click Database Replay.
The Database Replay page appears.
-
Under Active Capture and Replay, select the workload replay you want to monitor and click View.
The View Workload Replay page appears.
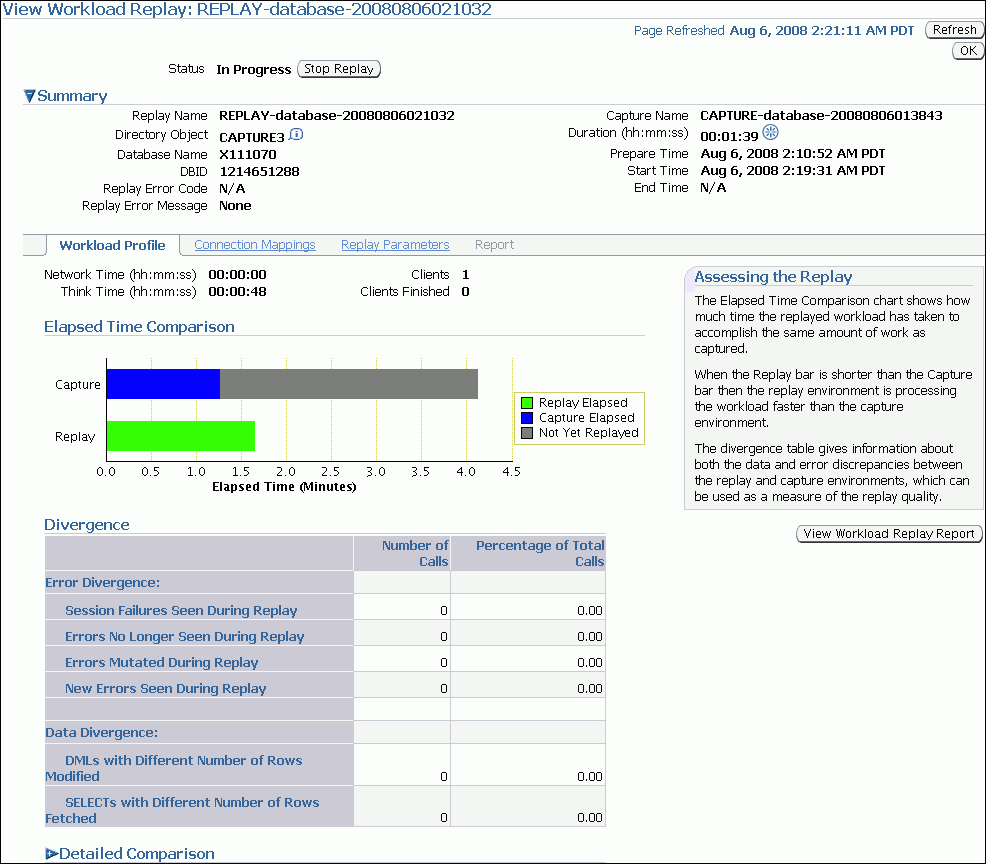
Description of the illustration dbr_replay_view_active.gif
-
Under Summary, information about the workload replay is displayed.
-
To view the workload profile, click the Workload Profile tab.
Under Elapsed Time Comparison, the chart shows how much time it has taken to replay the same workload compared to the elapsed time during the workload capture. If the Replay bar is shorter than the Capture bar, the replay system is processing the workload faster than the capture system. If the workload replay is still running, a portion of the Capture bar will be shown as not yet replayed.
Under Divergence, any error and data discrepancies between the replay system and the capture system are displayed. This information can be used as a measure of the replay quality.
To view a detailed comparison of the workload during capture and replay, expand Detailed Comparison.
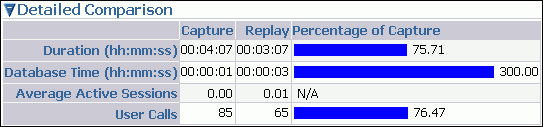
Description of the illustration dbr_replay_view_detail.gif
This section displays the following information:
-
Duration
The duration that was captured in a workload is compared to the amount of time it is taking to replay the workload. In the Capture column, the duration of the time period that was captured is shown. In the Replay column, the amount of time it is taking to replay the workload is shown. The Percentage of Capture column shows the percentage of the captured duration that it is taking to replay the workload. If the value is under 100 percent, the replay system is processing the workload faster than the capture system. If the value is over 100 percent, the replay system is processing the workload slower than the capture system.
-
Database time
The database time that is consumed in the time period that was captured is compared to the amount of database time that is being consumed while replaying the workload.
-
Average active sessions
The number of average active sessions captured in the workload is compared to the number of average active session that are being replayed.
-
User calls
The number of user calls captured in the workload is compared to the number of user calls that are being replayed.
To view the workload capture report, click View Workload Replay Report.
-
-
To view the connection strings used in the capture and the replay systems, click the Connection Mappings tab.
-
To view replay parameters used by the workload replay, click the Replay Parameters tab.
-
To stop the workload replay, click Stop Replay.
-
To return to the Database Replay page, click OK.
Viewing a Completed Workload Replay
This section describes how to view a completed workload replay using Enterprise Manager.
To view a completed workload replay:
-
On the Software and Support page, under Real Application Testing, click Database Replay.
The Database Replay page appears.
-
In the Go to Task column, click the icon that corresponds to the Replay Workload task.
The Replay Workload page appears.
-
In the Directory Object list, select a directory that contains the preprocessed workload that was used for the replay.
After a directory is selected, the Replay Workload page will be refreshed to display the Capture Summary and the Replay History sections.
-
The Replay History section displays previous replays of the workload capture. To view details about a previous replay, select the replay and click View.
The View Workload Replay page appears.
-
Under Summary, information about the workload replay is displayed.
-
To view the workload profile, click the Workload Profile tab.
Under Elapsed Time Comparison, the chart shows how much time it has taken to replay the same workload compared to the elapsed time during the workload capture. If the Replay bar is shorter than the Capture bar, the replay system is processing the workload faster than the capture system.
Under Divergence, any error and data discrepancies between the replay system and the capture system are displayed. This information can be used as a measure of the replay quality.
To view a detailed comparison of the workload during capture and replay, expand Detailed Comparison. This section displays the following information:
-
Duration
The duration that was captured in a workload is compared to the amount of time it took to replay the workload. In the Capture column, the duration of the time period that was captured is shown. In the Replay column, the amount of time it took to replay the workload is shown. The Percentage of Capture column shows the percentage of the captured duration that it took to replay the workload. If the value is under 100 percent, the replay system processed the workload faster than the capture system. If the value is over 100 percent, the replay system processed the workload slower than the capture system.
-
Database time
The database time that is consumed in the time period that was captured is compared to the amount of database time that is consumed when replaying the workload.
-
Average active sessions
The number of average active sessions captured in the workload is compared to the number of average active session that are replayed.
-
User calls
The number of user calls captured in the workload is compared to the number of user calls that are replayed.
To view the workload capture report, click View Workload Replay Report.
-
-
To view the connection strings used in the capture and the replay systems, click the Connection Mappings tab.
-
To view replay parameters used by the workload replay, click the Replay Parameters tab.
-
To run a report, click the Report tab.
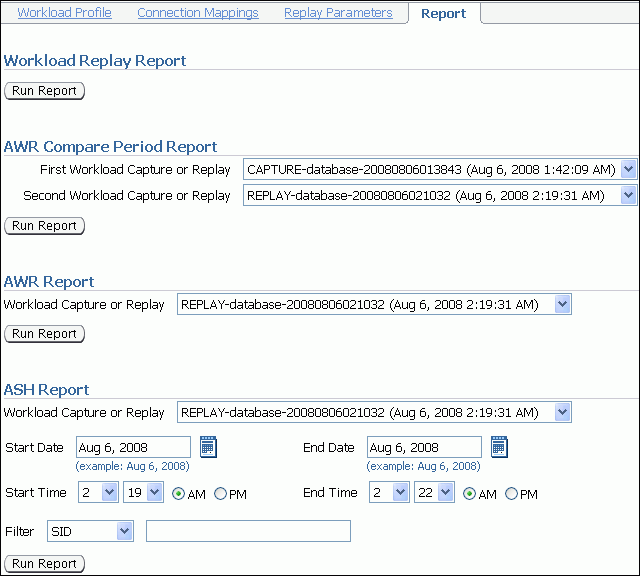
Description of the illustration dbr_replay_view_report.gif
There are several types of reports you can run for a completed workload replay:
-
Workload Replay
The Workload Replay report contains information that can be used to measure data and performance divergence between the capture system and the replay system. To run this report, under Workload Replay Report, click Run Report. For information about using the Workload Replay report, see "Using a Workload Replay Report".
-
AWR Compare Period
The AWR Compare Period report can be used to compare the AWR data in one workload capture or replay with another. Before running this report, AWR data for the captured or replayed workload must have been previously exported. To run this report, under AWR Compare Period Report, select the first and second workload captures or replays you want to compare and click Run Report. If AWR data is not previously exported from the captured or replayed workload, you will be prompted to import the AWR data before continuing. For more information about the AWR Compare Period report, see Oracle Database 2 Day + Performance Tuning Guide.
-
AWR
The AWR report shows the AWR data contained in a workload that was captured or replayed. Before running this report, AWR data must have been previously exported from the captured or replayed workload. To run this report, under AWR Report, select the workload capture or replay for which you want to generate an AWR report and click Run Report. If AWR data is not previously exported from the captured or replayed workload, you will be prompted to import the AWR data before continuing. For more information about the AWR report, see Oracle Database Performance Tuning Guide.
-
ASH
The ASH report contains active session history (ASH) information for a specified duration of a workload that was captured or replayed. Before running this report, AWR data must have been previously exported from the captured or replayed workload. To run this report, under ASH Report, select the workload capture or replay for which you want to generate an ASH report. Specify the duration using the Start Date, Start Time, End Date, and End Time fields. You can also apply filters using the Filter field. Once the duration and filters are specified, click Run Report. If AWR data is not previously exported from the captured or replayed workload, you will be prompted to import the AWR data before continuing. For more information about the ASH report, see Oracle Database 2 Day + Performance Tuning Guide.
The Report window opens while the report is being generated. Once the report is generated, you can save the report by clicking Save to File.
-
-
To return to the Database Replay page, click OK.
Replaying a Database Workload Using APIs
This section describes how to replay a database workload using the DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY package. You can also use Oracle Enterprise Manager to replay a database workload, as described in "Replaying a Database Workload Using Enterprise Manager".
Replaying a database workload using the DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY package is a multi-step process that involves:
See Also:
Oracle Database PL/SQL Packages and Types Reference for information about theDBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY packageInitializing Replay Data
After the workload capture is preprocessed and the test system is properly prepared, the replay data can be initialized. Initializing replay data loads the necessary metadata into tables required by workload replay. For example, captured connection strings are loaded into a table where they can be remapped for replay.
To initialize replay data, use the INITIALIZE_REPLAY procedure:
BEGIN
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.INITIALIZE_REPLAY (replay_name => 'dec06_102',
replay_dir => 'dec06');
END;
/
In this example, the INITIALIZE_REPLAY procedure loads preprocessed workload data from the dec06 directory into the database.
The INITIALIZE_REPLAY procedure in this example uses the following parameters:
-
The
replay_namerequired parameter specifies a replay name that can be used with other APIs to retrieve settings and filters of previous replays. -
The
replay_dirrequired parameter specifies the directory that contains the workload capture that will be replayed.
See Also:
-
"Preprocessing a Database Workload Using APIs" for information about preprocessing a workload capture
-
"Setting Up the Test System" for information preparing the test system
Connection Remapping
After the replay data is initialized, connection strings used in the workload capture need to be remapped so that user sessions can connect to the appropriate databases and perform external interactions as captured during replay. To view connection mappings, use the DBA_WORKLOAD_CONNECTION_MAP view. For information about connection remapping, see "Remapping Connections".
To remap connections, use the REMAP_CONNECTION procedure:
BEGIN
DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.REMAP_CONNECTION (connection_id => 101,
replay_connection => 'dlsun244:3434/bjava21');
END;
/
In this example, the connection that corresponds to the connection ID 101 will use the new connection string defined by the replay_connection parameter.
The REMAP_CONNECTION procedure in this example uses the following parameters:
-
The
connection_idrequired parameter is generated when initializing replay data and corresponds to a connection from the workload capture. -
The
replay_connectionoptional parameter specifies the new connection string that will be used during workload replay.
Setting Workload Replay Options
After the replay data is initialized and the connections are appropriately remapped, you need to prepare the database for workload replay. For information about workload replay preparation, see "Steps for Replaying a Database Workload".
To prepare workload replay on the replay system, use the PREPARE_REPLAY procedure:
BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.PREPARE_REPLAY (synchronization => TRUE); END; /
In this example, the PREPARE_REPLAY procedure prepares a replay that has been previously initialized. The COMMIT order in the workload capture will be preserved.
The PREPARE_REPLAY procedure uses the following parameters:
-
The
synchronizationrequired parameter determines if synchronization will be used during workload replay. If this parameter is set toTRUE, theCOMMITorder in the captured workload will be preserved during replay and all replay actions will be executed only after all dependentCOMMITactions have completed. The default value isTRUE. -
The
connect_time_scaleoptional parameter scales the elapsed time from when the workload capture started to when the session connects with the specified value and is interpreted as a % value. Use this parameter to increase or decrease the number of concurrent users during replay. The default value is 100. -
The
think_time_scaleoptional parameter scales the elapsed time between two successive user calls from the same session and is interpreted as a % value. Setting this parameter to 0 will send user calls to the database as fast as possible during replay. The default value is 100. -
The
think_time_auto_correctoptional parameter corrects the think time (based on thethink_time_scaleparameter) between calls when user calls take longer to complete during replay than during capture and can be set to eitherTRUEorFALSE. The default value isTRUE.
For more information about setting these parameters, see "Specifying Replay Options".
Starting a Workload Replay
Before starting a workload replay, you must first:
-
Preprocess the captured workload, as described in "Preprocessing a Database Workload Using APIs"
-
Initialize the replay data, as described in "Initializing Replay Data"
-
Specify the replay options, as described in "Setting Workload Replay Options"
-
Start the replay clients, as described in "Starting Replay Clients"
To start a workload replay, use the START_REPLAY procedure:
BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.START_REPLAY (); END; /
Stopping a Workload Replay
To stop a workload replay, use the CANCEL_REPLAY procedure:
BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.CANCEL_REPLAY (); END; /
Exporting AWR Data for Workload Replay
Exporting AWR data enables detailed analysis of the workload. This data is also required if you plan to run the AWR Compare Period report on a pair of workload captures or replays.
To export AWR data, use the EXPORT_AWR procedure:
BEGIN DBMS_WORKLOAD_REPLAY.EXPORT_AWR (replay_id => 1); END; /
In this example, the AWR snapshots that correspond to the workload replay with a replay ID of 1 are exported. The EXPORT_AWR procedure uses the replay_id required parameter, which specifies the ID of the replay whose AWR snapshots will be exported. This procedure will work only if the corresponding workload replay was performed in the current database and the AWR snapshots that correspond to the original replay time period are still available.
Monitoring Workload Replay Using Views
This section summarizes the views that you can display to monitor workload replay. You need DBA privileges to access these views.
-
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_CAPTURESview lists all the workload captures that have been captured in the current database. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_FILTERSview lists all workload filters, for both workload captures and workload replays, defined in the current database. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAYSview lists all the workload replays that have been replayed in the current database. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_REPLAY_DIVERGENCEview enables you to monitor workload replay divergence. -
The
DBA_WORKLOAD_CONNECTION_MAPview lists the connection mapping information for workload replay. -
The
V$WORKLOAD_REPLAY_THREADview lists information about all sessions from the replay clients.
See Also:
Oracle Database Reference for information on these views