8 Adding Application Components
This section describes how to use Application Builder to add pages to an application and add other components (reports, charts, or forms), page controls (buttons, items, list of values), and shared components (breadcrumbs, lists, or tabs).
Creating Reports
In Oracle Application Express, a report is the formatted result of a SQL query. You can generate reports by selecting and running a built-in query, or by defining a report region based on a SQL query.
Creating a Report Using a Wizard
Application Builder includes a number of built-in wizards for generating reports.
To create a report using a wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select the application.
-
Click Create Page and click Next.
-
Select Report and click Next.
-
Select a report type and click Next. Option include:
-
Interactive Report - Creates an interactive report based on a custom SQL
SELECTstatement you provide. For assistance in writing the SQL query, click the Query Builder button. End users can customize the report layout and data displayed by selecting options on the Actions menu. -
Classic Report - Creates a report based on a custom SQL
SELECTstatement or a PL/SQL function returning a SQLSELECTstatement that you provide. For assistance in writing the SQL query, click the Query Builder button. -
Report on Web Service Result - Creates a report based on a Web service result. To learn more, see "Implementing Web Services".
-
Wizard Report - Creates a classic report without requiring any SQL knowledge. Select the appropriate schema, table, columns, and result set display.
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions. To learn more about a specific field, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
Understanding the Difference Between Interactive and Classic Reports
Oracle Application Express includes two main report types, an interactive report and a classic report. The main difference between these two report types is that interactive reports enable the user to customize the appearance of the data through a searching, filtering, sorting, column selection, highlighting, and other data manipulations.
The following is an example of an interactive report.

Description of the illustration rpt_ir.gif
Notice that the interactive report includes a Search Bar, Column Heading Menu links, and Link Column icons in the first column of each row. For a complete description of these components, see "Customizing Interactive Reports".
When using an interactive reports you can:
-
Include one interactive report per page
-
Display 100 columns using report columns. You can edit additional columns using Tree view or paginating through Report Column Attributes.
-
Include 999 rows per column heading filter (if no custom LOV is specified in the column attributes)
In contrast, a classic report does not include any of these customization features. The following is an example of a classic report built on top of the same data.
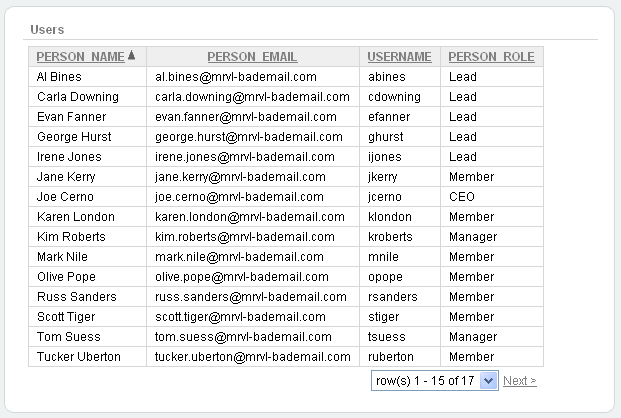
Description of the illustration rpt_classic.gif
Classic reports do not include a Search Bar and the links at the top of each column only support basic sorting.
When using a classic report, you view 100 columns using report columns. You can edit additional columns using Tree view or paginating through Report Column attributes.
Customizing Interactive Reports
Interactive reports enable end users to customize reports. Users can alter the layout of report data by choosing the columns they are interested in, applying filters, highlighting, and sorting. They can also define breaks, aggregations, different charts, group bys, and add their own computations.
Users can also set up a subscription so that an HTML version of the report will be emailed to them a designated interval. Users can create multiple variations of a report and save them as named reports, for either public or private viewing.
An interactive report can be customized in three ways: the Search bar, Actions menu and Column Heading menu.
Tip:
To learn more about controlling what options display in an interactive report, see "Editing Interactive Reports as a Developer"About the Search Bar
Description of the illustration ir_search_bar.gif
A search bar displays at the top of every interactive report and may include the following features:
-
Select Columns icon - Resembles a magnifying glass. Click this icon to narrow your search to specific columns. To search all columns, select All Columns.
-
Text area - Enter case insensitive search criteria (wild card characters are implied) and then click Go.
-
Go button - Executes a search.
-
Reports - Displays alternate default and saved private or public reports.
-
View icons - Switches between icon, report and detail view of the default report (if enabled). May also include Chart and Group By View (if defined).
-
Actions menu - Clicking the icon displays the Actions menu. Use this menu to customize an interactive report. See "Using the Actions Menu".
Using the Select Columns Icon
A Select Columns icon displays to the left of the search bar. Clicking this icon displays a listing of all columns in the current report.
To search specific columns:
-
Click the Select Columns icon and select a column.
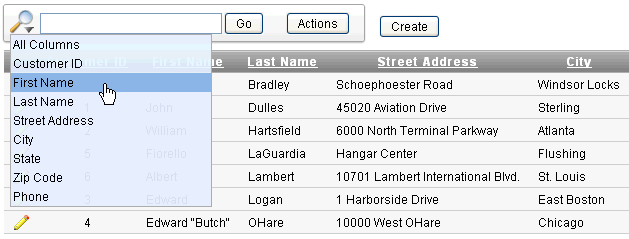
Description of the illustration ir_select_col_rpt.gif
-
Enter keywords in the Text area and click Go.
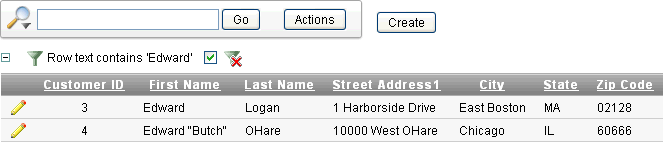
Description of the illustration ir_select_col.gif
Notice in this example the filter
Row text contains 'Edward' displays above the report. -
To disable the filter, select the Enable/Disable Filter check box.
-
To delete the filter, click the Remove Filter icon.
See Also:
"Selecting Columns to Display"Using the Actions Menu
The Actions menu appears to the right of the Go button on the Search bar. Use this menu to customize an interactive report.

Description of the illustration ir_action_menu.gif
The Actions menu contains the following options:
-
Select Columns specifies which columns to display and in what order. See "Selecting Columns to Display".
-
Filter focuses the report by adding or modifying the
WHEREclause on the query. See "Adding a Filter". -
Rows Per Page determines how many rows display in the current report. See "Specifying Rows Per Page".
-
Format contains the following submenu:
-
Sort - Changes the columns to sort on and determines whether to sort in ascending or descending order. See "Selecting Columns and Sort Order".
-
Control Break - Creates a break group on one or several columns. This pulls the columns out of the interactive report and displays them as a master record. See "Creating a Control Break".
-
Highlight - Defines a filter that highlights the rows that meet the filter criteria. See "Adding Highlighting".
-
Compute - Enables users to add computed columns to a report. See "Computing Columns".
-
Aggregate - Enables users to perform mathematical computations against a column. See "Aggregating a Column".
-
Chart - Displays the report data as a chart. See "Creating a Chart from the Actions Menu".
-
Group By - Enables users to group the result set by one or more columns and perform mathematical computations against columns. See "Grouping Columns".
-
-
Flashback - Enables you to view the data as it existed at a previous point in time. See "Executing a Flashback Query".
-
Save Report - Saves the interactive report. Depending upon their user credentials, users can save four different types of reports. See "Saving a Report".
-
Reset - Enables users to reset the report back to the default report settings. See "Resetting a Report".
-
Help - Provides descriptions of how to customize interactive reports.
-
Download - Enables users to download a report. Available download formats depend upon your installation and report definition. See "Downloading a Report".
-
Subscription - Enables users to send themselves an interactive report by email. See "Subscribing to Emailed Reports"
Selecting Columns to Display
To customize a report to include specific columns, select Select Columns on the Actions menu.
To use the Select Columns option:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Select Columns.
The Select Columns region appears.
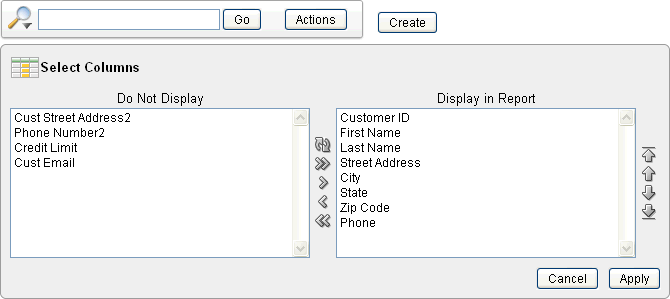
Description of the illustration ir_select_column.gif
-
Select the columns you wish to move. Click the center arrows to move a column from the Display in Report box to the Do Not Display box. To select multiple columns at once, press and hold the CTRL key.
-
To change the order of the columns, click the Top, Up, Down, and Bottom arrows on the right.
-
Click Apply.
A revised report appears.
See Also:
"Resetting a Report"Adding a Filter
You can create a filter on an interactive report by adding or modifying the WHERE clause on the query. You can create two types of filters:
-
Column - Creates a custom column filter. Select a column (it does not need to be one that displays), select a standard Oracle operator (
=, !=, not in,between), and enter an expression to compare against. Expressions are case sensitive. Use % as a wild card. For example:STATE_NAME like A%
-
Row - Creates a custom row filter. This filter creates a complex
WHEREclauses using column aliases and any Oracle functions or operators. For example:G = 'VA' or G = 'CT'
Where
Gis the alias forCUSTOMER_STATE.
Adding a Column Filter
To add a column filter:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Filter.
The Filter region appears.
-
For Filter Type, select Column.
-
In the Filter region, specify a column, an operator, and expression.
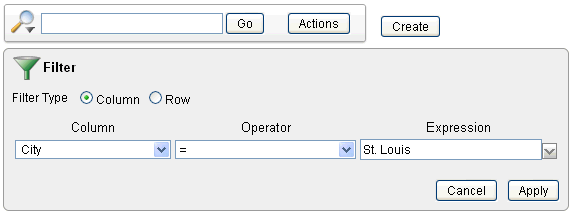
Description of the illustration ir_filter_sel_col.gif
This filter narrows the display to only customers in the city of St. Louis.
-
Click Apply.

Description of the illustration ir_filter.gif
Notice the filter
City = 'St Louis'has been added to the Report Settings area above the report. -
To revise the filter:
-
Click the filter name (in this example,
City = 'St Louis'). -
Edit your selections and click Apply.
-
-
To disable the filter, select the Enable/Disable Filter check box.
-
To delete the filter, click Remove Filter.
Adding a Row Filter
To add a row filter:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Filter.
The Filter region appears.
-
For Filter Type, select Row.
-
In the Filter region:
-
Enter a Name.
-
Enter expression. Select a column and function or operator at the bottom of the region.

Description of the illustration ir_filter_sel_row.gif
-
-
Click Apply.
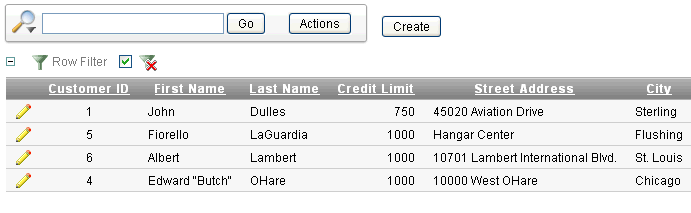
Description of the illustration ir_filter_sel_row_rpt.gif
The filter
K<= 1000narrows the display to customer having credit limit that is less than or equal to 1000. -
To revise the filter:
-
Click Row Filter.
-
Edit your selections and click Apply.
-
-
To disable the filter, select the Enable/Disable Filter check box.
-
To delete the filter, click Remove Filter.
Specifying Rows Per Page
You can specify the number of rows that display on a page by selecting Rows Per Page on the Actions menu.
To specify the number of rows that display:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Rows Per Page.
-
From the submenu, select a number.
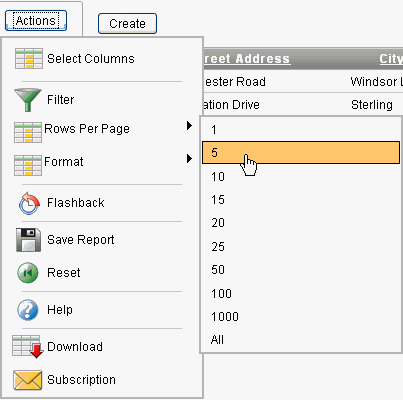
Description of the illustration ir_row_per_page.gif
Selecting Columns and Sort Order
You can specify which columns to display and the sort order (ascending or descending) by selecting Sort on the Format submenu. You can also specify how to handle NULL values. Using the default setting always displays NULL values last or always display them first.
To sort by column:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Format and then Sort.
The Sort region appears.
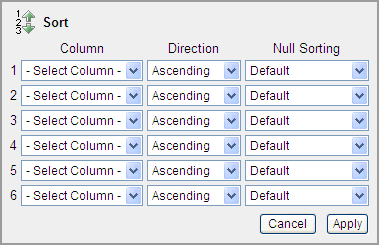
Description of the illustration ir_sort.gif
-
Select a column, the sort direction (Ascending or Descending), and Null Sorting behavior (Default, Nulls Always Last, or Nulls Always First).
-
Click Apply.
Creating a Control Break
You can create a break group of one or several columns by selecting Control Break from the Actions, Format submenu. Creating a break group pulls the columns out of the interactive report and displays them as a master record.
To create a break group:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Format and then Control Break.
The Control Break region appears.

Description of the illustration ir_ctrl_break.gif
-
Select a column and then a status (Enable or Disable)
-
Click Apply.
One or more break groups display in Report Settings area above the report.
-
To expand the break group, click the plus (+) sign.
-
To enable the Control Break filter, select the Enable/Disable Filter check box.
-
To delete the filter, click Remove Filter.
Adding Highlighting
You can customize the display to highlight specific rows in a report by selecting Highlight on the Actions, Format submenu.
To add highlighting:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Format and then Highlight.
The Highlight region appears.

Description of the illustration ir_highlight.gif
-
Enter the following information:
-
Name - Enter a name that describes this filter.
-
Sequence - Enter numeric value to identify the sequence in which the rules are evaluated.
-
Enabled - Select Yes.
-
Highlight Type - Select Cell or Row. If Cell is selected, the column referenced in the Highlight Condition is highlighted.
-
Background Color - Select a new color for the background of the highlighted area.
-
Text Color - Select a new color for the text in the highlighted area.
-
Highlight Condition - Select a column, an operator, and expression.
-
-
Click Apply.
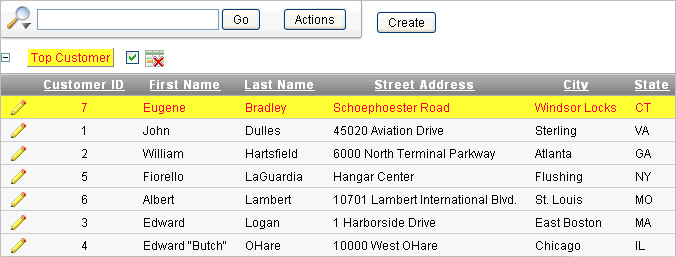
Description of the illustration ir_highlight_rpt.gif
Note a new highlight appears in the Report Settings area above the report.
-
To revise the highlight:
-
Click the highlight name (in this example,
Top Customer). -
Edit your selections and click Apply.
-
-
To disable the highlight, select the Enable/Disable Filter check box.
-
To delete the highlight, click Remove Highlight.
Computing Columns
You can add computations to columns by selecting Compute from the Actions, Format submenu. These computations can be mathematical computations (for example, NBR_HOURS/24) or standard Oracle functions applied to existing columns. Note that some display as examples and others (such as TO_DATE) can also be used).
To create a computation:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Compute.
The Compute region appears.
-
In the Compute region:
-
Computation - Select New Computation.
-
Column Heading - Enter the name of the new column to be created.
-
Format Mask - Select an Oracle format mask to be applied to the new column. (for example,
S9999).Next, create the computation.
-
Create the computation:
-
Columns - Select a column or alias.
-
Keypad - Select a shortcut for commonly used keys.
-
Functions - Select the appropriate function.
The following example, creates a new Commission column. This column calculates at 10% sales commission using the formula
C*.10whereCis the order total.
Description of the illustration ir_compute.gif
-
-
-
Click Apply.
The revised report appears containing a new Commission column.

Description of the illustration ir_compute_eg.gif
Aggregating a Column
You can define a mathematical computation against a column (or aggregate) by selecting Aggregate from the Actions, Format menu. Aggregates are displayed after each control break and at the end of the report within the column in which they are defined.
To aggregate columns:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Format and then Aggregate.
The Aggregate region appears.
-
In the Aggregate region:
-
Aggregation - Select New Aggregation.
-
Function - Select one of the following: Sum; Average, Count, Count Distinct, Minimum, Maximum, or Median.
-
Column - Select a column.

Description of the illustration ir_aggreg.gif
This example creates a sum or Order Total column.
-
-
Click Apply.
The computation appears at the bottom of the report.

Description of the illustration ir_aggreg_rpt.gif
In this example, the aggregate shows the sum of all amounts in the Order Total column.
Creating a Chart from the Actions Menu
To create a chart, select Chart on the Actions, Format menu. You can create one chart for each interactive report. Once defined, you can switch between the chart and report views using links on the Search bar.
To create a chart:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Format and then Chart.
The Chart region appears.
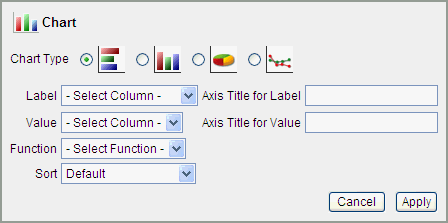
Description of the illustration ir_chart.gif
-
In the Chart region, specify the following:
-
Chart Type - Select the type of chart you wish to create (horizontal bar, vertical bar, pie, or line.).
-
Label - Select the column to be used as the label.
-
Axis for Title for Label - Enter title to be displayed on the axis associated with the column selected for Label (not available for pie chart).
-
Value - Select the column to be used as the Value. If your function is a
COUNT, a Value does not need to be selected. -
Axis Title for Value - Enter the title to display on the axis associated with the column selected for Value (not available for pie chart).
-
Function - (Optional) Select a function to be performed on the column selected for Value.
Click Apply and a View Chart icon appears in Search bar.
-
Grouping Columns
Group By enables users to group the result set by one or more columns and perform mathematical computations against the columns. Once users define the group by, they can switch between the group by and report views using the View Icon on the Search bar.
To use Group By:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Format and then Group By.
The Group By region appears.

Description of the illustration ir_group_by.gif
-
From Group by Column, select the columns to display.
-
To include a computation, select the function, column, label, and format mask.
-
To specify sorting, select a column, sort direction, and preferences for NULL values.
A Group By icon appears in the Search bar.
Executing a Flashback Query
You can execute a flashback query by selecting Flashback from the Actions menu. A flashback query enables you to view the data as it existed at a previous point in time. The default amount of time that you can flashback is 3 hours (or 180 minutes) but the actual amount will differ for each database.
To execute a flashback query:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Flashback.
-
In the Flashback region, enter the number of minutes.
-
Click Apply.
Saving a Report
Both developers and end users can save an interactive reports. However, only a developer can save the report that initially displays, the Primary Default, or create an Alternative Default report.
You can save four types of interactive reports:
-
Primary Default (Developer Only). The Primary Default is the report that initially displays. Primary Default reports cannot be renamed or deleted.
-
Alternative Report (Developer Only). Enables developers to create multiple report layouts. Only developers can save, rename, or delete an Alternative Report.
-
Public Report (End user). Can be saved, renamed, or deleted by the end user who created it. Other users can view and save the layout as another report.
-
Private Report (End user). Only the end user that created the report can view, save, rename or delete the report.
The following shows the Reports list on the Search bar of an interactive report.
Description of the illustration ir_reports_list.gif
See Also:
"Viewing and Deleting Saved Reports"Configuration Dependencies
The Save Report option on the Actions only displays if you:
-
Define an authentication scheme for the current application. See "Establishing User Identity Through Authentication".
-
On the Report Attributes page, scroll down to Search Bar and select Save Report or Save Public Report. See "Customizing the Interactive Report Search Bar".
The Reports select list on the Search Bar only displays if you select Reports Select List under Search Bar on the Report Attributes page. See "Customizing the Interactive Report Search Bar".
Note that many of these options are selected by default.
Saving a Primary or Alternative Interactive Report
Only developers can save a Primary Default interactive report. Primary Default reports cannot be renamed or deleted.
To save a default interactive report:
-
Run the report as a developer.
-
Customize the report (for example, hide columns, add filters, and so on). See "Using the Actions Menu".
-
Click the Actions menu and select Save Report.
The Save Report region appears.
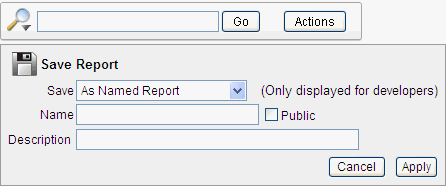
Description of the illustration ir_save_rpt.gif
-
For Save, select As Default Report Settings.
-
For Default Report Type, select either:
-
Primary - This report displays as the primary report when the page runs.
-
Alternative - This report displays as an alternative option on the Reports list on the Search bar. If you select Alternative, enter a name.
-
-
Click Apply.
Saving a Public or Private Interactive Report
End users can save an interactive report and classify it as being either public or private. Public reports can be viewed by all users. Private reports can only be viewed by the user who saves the report.
Tip:
To save a public report, you must select Save Public Report must be selected under Include in Actions Menu on the Report Attributes page. in Include Actions menu list. Developers can also apply authorization scheme to enable or disable Save Public Report. See "Customizing the Interactive Report Search Bar".To save a public or private interactive report:
-
Go to the page containing the interactive report you wish to save.
-
Customize the report (for example, hide columns, add filters, and so on). See "Using the Actions Menu".
-
Click the Actions menu and select Save Report.
The Save Report region appears.
-
In Save Report:
-
Save - Select As Named Report.
-
Public- Select this check box to make the report viewable to all users. Deselect this check box to make the report private.
-
Name - Enter a name for the report.
-
Description - Enter an optional description.
-
Click Apply.
-
Editing or Deleting Primary or Alternative Reports
To edit or delete a primary, alternative, public or private interactive report:
-
Run the report as a developer.
-
Customize the report (for example, hide columns, add filters, and so on). See "Using the Actions Menu".
-
To edit the report:
-
Click the alternative report name link.
-
Edit the attributes (for example, enter a new name).
-
Click Apply.
-
-
To delete the report, click the Delete Report icon next to the alternative report name link.
About Exporting Interactive Reports
When you export an application, the Primary Default, Alternative Default, public reports are included by default. You can also choose to include personal reports during the export process by selecting Yes for Private Interactive Reports. See "Exporting an Application".
Resetting a Report
You can reset a report back to the default settings by selecting Reset from the Actions menu. Resetting a report removes any customizations you have made.
To reset a report:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Reset.
-
Click Apply.
Downloading a Report
You can download an interactive report back by selecting Download from the Actions menu. Available download formats depend upon your installation and report definition. Supported formats include comma-delimited file (CSV) format, HTML, Email, Microsoft Excel (XLS) format, Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF), and Microsoft Word Rich Text Format (RTF). See "Configuring Download Options on the Actions Menu"
To download a report:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Download.
-
Select a report download format and follow the provided instructions.
Subscribing to Emailed Reports
End users can receive updated versions of a report by subscribing to it. To subscribe to a report, click Subscription on the Actions menu.
To utilize Subscription:
-
An Oracle Application Express administrator must configure email at the Instance level. See "Configuring Mail" in Oracle Application Express Administration Guide
-
The application developer must check the Subscription check box on the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Customizing the Interactive Report Search Bar"
To receive updated report results by email:
-
Click the Actions menu and select Subscription.
The Add Subscription region appears.
-
Under Add Subscription:
-
Email Address - Enter the email address to receive the report.
-
Subject - Enter text to display in the email subject line.
-
Frequency - Select the interval at which the report is sent.
-
Starting From - Select a start date and time.
-
Ending - Select a end date and time. Select a day, week, month, or year.
-
Click Apply.
-
Tip:
"Managing Interactive Report Subscriptions" in Oracle Application Express Administration GuideUsing the Column Heading Menu
Clicking a column heading exposes the Column Heading menu.
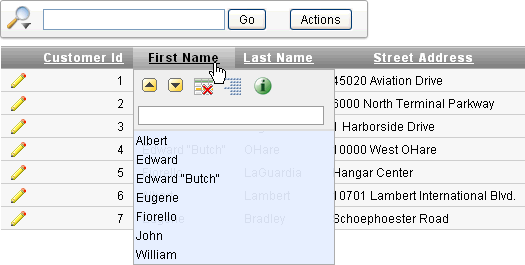
Description of the illustration ir_col_head_menu.gif
Column Heading menu options include:
-
Sort Ascending icon - Sorts the report by the column in ascending order.
-
Sort Descending icon - Sorts the report by the column in descending order.
-
Hide Column - Hides the column. Not all columns can be hidden. If a column cannot be hidden, there will be no Hide Column icon.
-
Break Column - Creates a break group on the column. This pulls the column out of the report as a master record.
-
Column Information - Displays help text about the column, if available.
-
Text Area - Used to enter a case insensitive search criteria (no need for wild cards). Entering a value reduces the list of values at the bottom of the menu. You can then select a value from the bottom. The selected value will be created as a filter using either the
equalsign (=) orcontainsdepending on the List of Values Column Filter Type. Alternatively, you can click the Flashlight icon and enter a value to be created as a filter with theLIKEmodifier (for example, columnLIKE '%ABC%'). -
List of Unique Values - Contains the first 500 unique values that meets your filter criteria. If the column is a date, a list of date ranges is displayed instead.
Editing Interactive Reports as a Developer
By default, an interactive report includes a Search Bar which contains a search icon, text area, Go button, and Actions menu. Users can use these controls to alter the layout of report data by selecting columns, applying filters, highlighting, and sorting. This section describes how developers can customize an interactive report by editing report attributes.
Tip:
To learn more about using interactive reports as a user, see "Customizing Interactive Reports"Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page
You customize an interactive report by editing attributes on the Interactive Report Attributes page.
To access the Report Attributes page:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select the application.
-
Select the page containing the interactive report you wish to edit.
The Page Definition appears.
-
To access the Interactive Report Attributes page:
-
Tree view - Right-click on the Region name and select Edit Report Attributes.
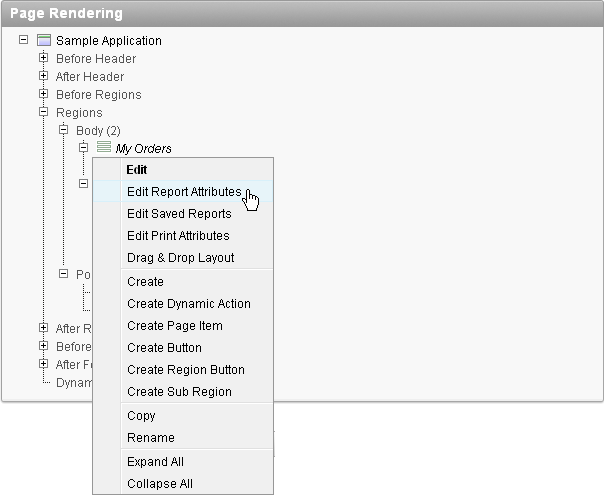
Description of the illustration edit_rpt_attr_tree.gif
-
Component view - Under Regions, click the Interactive Report link next to the name of the report region you want to edit.

Description of the illustration int_rprt_att.gif
-
-
The Report Attributes page appears and is divided into the following sections:
-
Column Attributes control the report layout. See "Editing Interactive Report Column Attributes".
-
Column Groups attributes enable you to group columns together on the single row view. See "Creating Column Groups".
-
Pagination attributes control report pagination. See "Controlling Interactive Report Pagination".
-
Sorting attributes enable you to define images and image attributes for images that display in report headings to sort values. See "Managing Interactive Report Column Sorting".
-
Search Bar contain attributes that enable you to define the search bar within an interactive report. See "Customizing the Interactive Report Search Bar".
-
Download enables you to add a download option to the Actions menu and export the report as CSV, HTML, Email, XLS, PDF, or RTF file. See "Configuring Download Options on the Actions Menu".
-
Link Column attributes enable you to add a link to a column. See "Understanding Link Columns" and "Creating a Column Link in an Interactive Report".
-
Icon View attributes enable you to add a View Icons icon to the Search bar. See "Enabling Icon View".
-
Detail View attributes enable you to add a View Details icon to the Search bar. See "Enabling Detail View".
-
Advanced Attributes enable you to define the Interactive Report region alias, specify an item whose value stores the saved report id, and define items to set into session state. See "Configuring Advanced Attributes for Interactive Reports".
-
Description lists a textual description of the current report.
-
-
To learn more about a specific attribute, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
See Also:
"Creating a Column Link in a Classic Report" and "Defining an Updatable Column in a Classic Report", and "Defining a Column as a List of Values in a Classic Report", and "Controlling When Columns Display in a Classic Report"About Navigation Alternatives
The Report Attribute page is divided into these sections: Column Attributes, Groups, Pagination, Sorting, Search Bar, Download, Link Column, Icon View, Detail View, Advanced, and Description.
You can access these sections by scrolling down the page, or by clicking a navigation button at the top of the page.
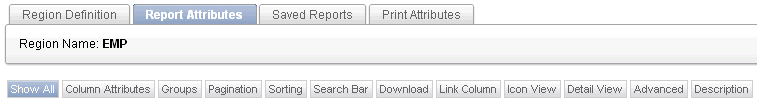
Description of the illustration int_rprt_nav.gif
When you select a button at the top of the page, the selected section appears and all other sections are temporarily hidden. To view all sections of the page, click Show All.
Editing Interactive Report Column Attributes
You can use the Column Attributes section of the Report Attributes page to precisely control the report layout. For example, you can use these attributes to alter column heading text, change column positioning, or hide a column.
To access Column Attributes:
-
On the Workspace home page, click Application Builder.
-
Select the application.
-
Select the page containing the interactive report you wish to edit.
The Page Definition appears.
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears with the Column Attributes section at the top of the page.
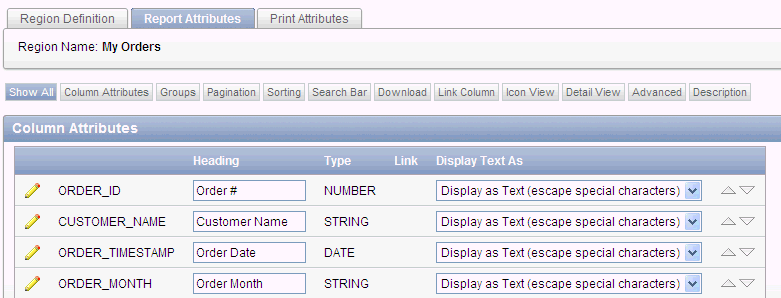
Description of the illustration int_rprt_col.gif
Use the Column Attributes section to control report column appearance and functionality.
Heading displays the heading text to be included in the report. Type indicates the type of query column. The Link column indicates if a link column is currently defined.
Table 8-1 describes common report column edits.
Table 8-1 Common Report Column Edits for Interactive Reports
Description Developer Action Alter column display sequence.
Click the up and down arrows to change the column display sequence.
Note that this display sequence is only used in the Single Row View if enabled. It does not affect report column display. The report column display can be changed when you run the report and save.
Change column group assignment.
If Column Groups are defined, individual columns can be assigned under Column Group.
Change column heading text.
Under Heading, enter different heading text.
Change how columns display.
Select an option from Display Text As.
You can further refine the attributes of a specific column on the Column Attributes page.
-
To access the Column Attributes page, click the Edit icon next to the appropriate column Alias.
The Column Definition appears.
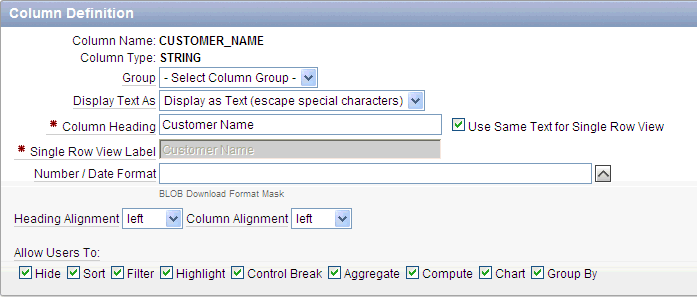
Description of the illustration ir_col_def.gif
Use the check boxes under Allow Users To to control how users manipulate the report. Options include: Hide, Sort, Filter, Highlight, Control Break, Aggregate, Compute, Chart, and Group By.
-
Under Column Definition, Allow Users To, select the appropriate check boxes.
To learn more about a specific attribute, click the item label.
Creating Column Groups
Use column groups to group columns together on a single row view.
To create a column group:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Column Groups.
-
Click Add Group.
-
Under Column Group:
-
Sequence - Enter the display sequence for this column group. This attribute determines the order in which the column groups display in the detail view.
-
Group Name - Enter a column group name. This name displays in the region header in detailed view.
-
Description - Enter an optional description for the column group. This description never displays to the end user.
-
-
Click Create.
Controlling Interactive Report Pagination
You control how pagination displays by making selections from Pagination attributes on the Interactive Report Attributes page.
To access the Pagination section of the Report Attributes page:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Pagination.
You use the Pagination attributes to select a pagination style, determine where pagination occurs, specify the maximum number of rows to query, and messages to display when more than the maximum number of rows are returned or if no rows are returned.
Table 8-2 describes the available Pagination attributes.
Table 8-2 Pagination Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Pagination Type |
Select a pagination type. Pagination provides the user with information about the number of rows and the current position within the result set. Pagination can be displayed above or below the report (or both) and can be positioned on the left or right. Available pagination options include:
|
|
Pagination Display Position |
Defines where pagination occurs. Pagination can be display on the left side, right side, at the bottom, or above the report. |
|
Show Null Values as |
Enter the text you want to display for null columns. The default value is |
|
Maximum Row Count |
Defines the maximum number of rows to query, for example, rows 1 - 10 or 456. If you set this attribute to 200, the result would appear as follows:
Note that this attribute impacts performance. Counting fewer rows can improve performance and counting thousands of rows can degrade performance. |
|
When more than maximum row data found message |
Defines the text message that displays when more than maximum row count are returned. |
|
When No Data Found Message |
Defines the text message that displays when the query does not return any rows. |
Managing Interactive Report Column Sorting
You manage column sorting on the Interactive Report Attributes page.
To manage column sorting:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Under Column Attributes, click the Edit icon for the column for which you want to enable sorting.
-
Under Column Definition, select Sort and click Apply Changes.
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Sorting.
-
Specify ascending and descending image attributes and click Apply Changes.
Customizing the Interactive Report Search Bar
A search bar displays at the top of every interactive report and includes a Search icon, Text area, Go button, and Actions menu.
Description of the illustration ir_search_bar.gif
You can remove or customize the search bar by selecting and deselecting options in the Search Bar section of the Interactive Reports Attributes page.
Customizing the Search Bar
To customize the search bar:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Search Bar.
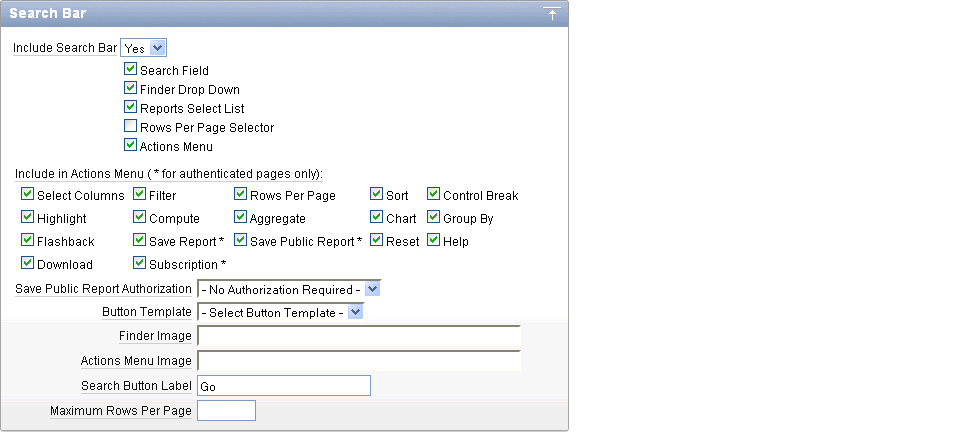
Description of the illustration ir_att_search_bar.gif
Use these attributes to customize how the search bar displays. Table 8-3 describes Search bar attributes:
Table 8-3 Search Bar Attributes
Attribute Description Include Search Bar
Select Yes or No. Selecting No removes the following default components:
-
Search Field - Displays a text field in the search bar in which to enter search criteria.
-
Finder Drop Down - Enables users to search on a selected column or against all columns.
-
Reports Select List - Displays report select list if the report has alternative default, shared report or personal report. See "Saving a Report".
-
Rows Per Page Selector - Displays a select list to enable users to select the number of rows to display per page.
-
Actions Menu - Enables the user to customize the report based on selected Actions.
Include in Actions Menu
Select and deselect functions included in the Actions menu. Available options include:
-
Select Columns - Used to hide, unhide, and order the report columns.
-
Filter - Used to add filters to the report (for example, STATE = VA).
-
Rows Per Page - Used to display rows per page menu.
-
Sort - Used to sort columns.
-
Control Break - Used to build control breaks on report columns.
-
Highlight - Used to define conditions that will highlight certain rows.
-
Compute - Used to add computed columns.
-
Aggregate - Used to include aggregate calculations on report columns.
-
Chart - Used to create a Flash chart based off the data in the report.
-
Group By - Used to create a Group By view based off the data in the report.
-
Flashback - Used to flashback the report data to some time in the past.
-
Save Report - Used to save the report settings for future use. Only available for authenticated pages.
-
Save Public Report * - Used to save Public Report for all users to view. You must select Save Report to enable this option. Only available for unauthenticated pages.
-
Reset - Used to reset the report to the default settings.
-
Help - Used to display instructions for using the Interactive report.
-
Download - Used to download the report in different formats.
-
Subscription * - Used to schedule a subscription to send the report in email. Only available for unauthenticated pages.
See Also: "Using the Actions Menu".
Save Report Public Authorization
Users can save reports and classify them as being either public or private. Public reports can be viewed by all users. Private reports can only be viewed by the user who saved the report.
In addition to enabling Save Public Report under Actions Menu, you can add additional security by defining an Authorization Scheme to determine who has rights to enable Save Public Report.
To enable support for public reports, select an authentication method from this list.
Button Template
Select a template for buttons that display in the search region and in the dialogs.
Finder Image
Specify an image. If no image is defined, the following is used:
/i/htmldb/builder/finder_w_dropdown.gif
Actions Menu Image
Specify an image. If no image is defined, the default button will be used.
Search Button Label
Specify the text to use as search button label.
Maximum Rows Per Page
Enter the maximum number to display in the Rows Per Page Selector.
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
Removing the Search Bar
To remove the search bar:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Search Bar.
-
From Include Search Bar, select No.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Configuring Download Options on the Actions Menu
You can add a Download option to the Actions menu to enable users to download an interactive report as a comma-delimited file (CSV) format, HTML, Microsoft Excel (XLS) format, Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF), Microsoft Word Rich Text Format (RTF), or as HTML attached to an email.

Description of the illustration download.gif
Enabling Download Formats
To configure download formats:
-
Navigate to the page containing the interactive report.
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Search Bar.
-
For Include Search Bar, select Yes and then select Actions Menu.
-
Under Include in Actions menu, select Download.
-
-
Scroll down to Download.
-
Select download formats. Options include:
-
CSV. See "Enabling CSV Download".
-
HTML.
-
Email. See "Enabling Email Download".
-
XLS.
-
PDF. See "About Printing Reports to PDF".
-
RTF.
Tip:
The Download option only appears on the Actions menu if a file format is selected. -
-
Click Apply Changes.
Enabling CSV Download
To enable the Enable CSV download:
-
Enable the CSV output option on the Edit Globalization Attributes page. See "Accessing the Globalization Attributes Page" and "Automatic CSV Encoding".
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Search Bar.
-
For Include Search Bar, select Yes and then select Actions Menu.
-
Under Include in Actions menu, select Download.
-
-
Scroll down to Download.
-
From Download Formats, select CSV.
Tip:
The Download option only appears on the Actions menu if a file format is selected. -
In the CSV Separator, define the column separator. If no value is entered, a comma or semicolon is used depending on your current NLS settings.
-
In the CSV Enclosed By, enter delimiter character. This character is used to delineate the starting and ending boundary of a data value. Default delimiter is double quotation marks (" ").
-
In Filename, enter a name for the downloaded document. Do not specify a file extension, the extension is added automatically. If you leave this blank, the region name is used as the file name.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Enabling Email Download
You can configure the Download option to send static HTML report to specific email addresses.
To enable email download:
-
An Oracle Application Express administrator must configure email at the Instance level. See "Configuring Mail" in Oracle Application Express Administration Guide
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Search Bar.
-
For Include Search Bar, select Yes and then select Actions Menu.
-
Under Include in Actions menu, select Download.
-
-
Scroll down to Download.
-
From Download Formats, select Email.
Tip:
The Download option only appears on the Actions menu if a file format is selected. -
Click Apply Changes.
Understanding Link Columns
A Link Column displays on the left side of an interactive report. It can link to a single row view, a custom target, or be excluded from the report. Note that a Link Column cannot be sorted, hidden, or moved by an end user and does not interact with the standard column link defined on the Column Attributes page.
Linking to a Single Row View
To link to a single row view:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Link Column.
-
For Link Column, select Link to Single Row View.
-
From Single Row View, select the appropriate options:
-
Allow Exclude Null Values - Excludes columns with null values.
-
Allow Displayed Columns - Displays only the columns shown in the report.
-
-
For Uniquely Identify Rows by, select ROWID or Unique Column.
If you select, Unique Column, specify the column in the Unique Column field.
-
For Link Icon, select an icon.
-
For Link Attributes (Optional), specify additional column link attributes to be included in the
<a href= >tag (for example, a link target, classes, or styles). -
Click Apply Changes.
Linking to a Specific Page
To link to a specific page:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Link Column.
-
For Link Column, select Link to Custom Target.
-
For Link Icon, select an icon.
-
For Link Attributes (Optional), specify additional column link attributes to be included in the
<a href= >tag (for example, a link target, classes, or styles). -
For Target, select Page in this Application.
-
For Page, select the target page number. To reset the pagination for this page, select Reset Pagination.
-
For Request, specify the request to be used.
-
For Clear Cache, specify the pages (that is, the page numbers) on which to clear cache. You can specify multiple pages by listing the page numbers in a comma-delimited list. See "Linking to Interactive Reports".
-
For Name and Value, specify session state for a specific item.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Linking to a URL
To link to a URL:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Link Column.
-
For Link Column, select Link to Custom Target.
-
For Link Icon, select an icon.
-
For Link Attributes (Optional), specify additional column link attributes that to be included in the
<a href= >tag (for example, a link target, classes, or styles). -
From Target, select URL.
-
In URL, enter the appropriate address.
-
For Checksum - Select one of the following:
-
Use default
-
Application Level - Link reusable by any user
-
User Level - Link reusable by current user
To learn more about each option, see item Help.
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
Excluding a Link Column
To exclude a column link:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Link Column.
-
For Link Column, select Exclude Link Column.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Creating a Column Link in an Interactive Report
Use Column Attributes to create a link from a report to another page in your application or to a URL.
To create a column link to another page:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Under Column Attributes, locate the column to contain the link.
-
Click the Edit icon next to the column name.
The Column Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Column Link.
-
To create a column link to another page:
-
From Target, select Page in this Application.
-
(Optional) In Link Attributes, specify additional column link attributes to be included in the
<a href= >tag (for example, a link target, classes, or styles). -
In Link Text, enter the text to be displayed as a link, specify an image tag, or pick from the list of default images.
-
In Page, specify the target page number. To reset the pagination for this page, select Reset Pagination.
-
In Request, specify the request to be used.
-
In Clear Cache, specify the pages (that is, the page numbers) on which to clear cache. You can specify multiple pages by listing the page numbers in a comma-delimited list.
-
Use the Name and Value fields to specify session state for a specific item.
-
For Checksum - Select one of the following:
-
Use default
-
Application Level - Link reusable by any user
-
User Level - Link reusable by current user
To learn more about each option, see item Help.
-
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
To create a column link to a URL:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Access the Column Attributes page by clicking the Edit icon next to the appropriate column.
The Column Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Column Link.
-
Under Column Link, specify the following:
-
From Target, select URL.
-
In Link Text, enter the text to be displayed as a link and select a substitution string.
-
(Optional) In Link Attributes, specify additional column link attributes to be included in the
<a href= >tag (for example, a link target, classes, or styles). -
In URL, enter the appropriate address.
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
Displaying Interactive Reports Conditionally
You can choose to have interactive reports display conditionally by editing region attributes on the Edit Region page.
To display an interactive report conditionally:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Edit Region page:
-
Component view - Under Regions, select the region name.
-
Tree view - Right-click the region name and select Edit.
The Edit Region page appears.
-
-
Scroll down to Conditions.
-
From the Condition Type list, make a selection.
-
Enter an expression in the fields provided.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Tip:
Asynchronous JavaScript and XML (AJAX) is used throughout interactive reports. Because AJAX is asynchronous, the value evaluated for conditional display needs to be in the session. To display an interactive report conditionally based on specified value, use a page item instead of using a:REQUEST value. Using :REQUEST in a conditional display causes in the interactive report function incorrectly.Defining a Column as a List of Values in an Interactive Report
In interactive reports you can use a list of values to improve the speed of built-in filter tools.
To define a report column as a list of values:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Access the Column Attributes page by clicking the Edit icon next to the appropriate column.
The Column Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to List of Values.
-
From Column Filter List of Values, specify how to create a list of values as a filter on the report column list. Available options include:
-
None - Disable filter on list of values.
-
Default Based on Column Type -
STRINGandNUMBERcolumns derive the list of values from distinct column values.DATEcolumns derive the list of values from predefined date ranges. -
Use Defined List of Values to Filter Word Contains - Derive the list of values from a defined list of values SQL query to create a contains filter.
-
Use Named List of Values to Filter Exact Match - Derive the list of values from the named list of values to create an equal filter.
-
Use Named List of Values to Filter Word Contains - Derive the list of values from the named list of values to create a contains filter.
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
Enabling Icon View
Be default, most interactive reports display as a report. You can optionally display columns as icons. When configured, a View Icons icon displays on the Search bar.
Description of the illustration ir_search_bar_icon.gif
To utilize Icon view, you must identify the columns used to identify the icon, the label, and the target (that is, the link). As a best practice, set these columns to display as hidden since they are typically not useful for end users.
To add Icon view to an interactive report:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Icon View.
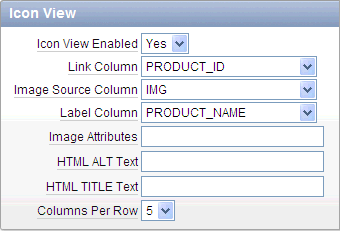
Description of the illustration ir_icon_view.gif
-
For Icon View Enabled, select Yes.
-
Specify the following mandatory attributes:
-
Link Column - Select the column that returns the link target of the icon. See item Help for an example.
-
Image Source Column - Identify the column that returns the image source. See item Help for an example.
-
Label Column - Select the column that returns the image label. See item Help for an example.
-
-
For Columns Per Row, identify the number of icons to be displayed per row. A value of
5would display 5 icons per row. -
Click Apply Changes.
Enabling Detail View
Be default, most interactive reports display as a report. You can optionally display details about each column. When configured, a View Details icon displays on the Search bar.

Description of the illustration ir_search_bar_detail.gif
To add Details view to an interactive report:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Detail View.
-
For Detail View Enabled, select Yes.
-
Specify the following attributes:
-
Before Rows - Enter the HTML to be displayed before report rows. For example:
<TABLE>
-
For Each Row (Use #COLUMN_ALIAS# substitutions) - Use substitution strings for column names and column labels. For example:
<tr><td align="right">#ENAME_LABEL#:</td><td>#ENAME#</td></tr> <tr><td align="right">#JOB_LABEL#:</td><td>#JOB#</td></tr
-
AFter Rows - Enter the HTML to be displayed after report rows. For example:
</TABLE>
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
Configuring Advanced Attributes for Interactive Reports
Use the Advanced Attributes section to define the Interactive Report region alias, specify an item whose value stores the saved report id, and define items to set into session state.
To configure Advanced Attributes:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Advanced Attributes.
Table 8-4 describes the available Advanced Attributes.
Attribute Description Region Alias
Enter an alphanumeric alias for this interactive report region. The alias must be unique within the application.
You can use an alias to reference an interactive report in an API call. For example, you can write a function to return
INTERACTIVE_REPORT_IDby queryingALIAScolumn in theAPEX_APPLICATION_PAGE_IRview). The alias must be unique within the application. Since theINTERACTIVE_REPORT_IDvalue can change when you export or import to different instance, referencing an interactive report region using an alias can be useful.Report ID Item
This attribute enables you to send a user directly to a saved view of the report. You specify an item whose value stores the report ID of the saved view. Report ID's can be retrieved from the
APEX_APPLICATION_PAGE_IR_RPTview.Page Items to Submit
Enter a comma separated list of items to be set into session state when the user clicks the Go button on the search bar. Only items on the current page will be set.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Linking to Interactive Reports
Unlike classic reports which typically use page items as report parameters, the data in an interactive report is driven by declarative filters. However, the developer may desire to set these report parameters by modifying interactive report settings for an end user. These settings only affect the end user's working report and will not affect any saved report settings.
To reset an interactive report in a link, use the string "RIR" in the Clear-Cache section of a URL. This is equivalent to the end user choosing the Reset option from the interactive report actions menu on the target page. The report is returned to the default report settings specified by the developer or saved by the user.
To create a Row text contains filter on an interactive report, use the string IR_ROWFILTER in the Item Names section of the URL. Adding this string passes the filter value in the corresponding location in the Item Values section of the URL.
To create a filter on an interactive report in a link, use the string IR<operator>_<target column alias> in the Item Names section of the URL, and pass the filter value in the corresponding location in the Item Values section of the URL.
Valid operators include:
-
EQ= Equals (this is the default) -
NEQ= Not Equals -
LT= Less than -
LTE= Less then or equal to -
GT= Greater Than -
GTE= Greater than or equal to -
LIKE= SQL Like operator -
N= Null -
NN= Not Null -
C= Contains -
NC= Not Contains
Consider the following examples:
f?p=...:IR_ENAME:KING
The previous example is equivalent to the end user creating a filter on the target page: ENAME = KING. Note that when an operator is not provided, EQ is used because it is the default.
f?p=...:IRGT_SAL:3000
The previous example is equivalent to the end user creating a filter on the target page: SAL > 3000.
Linking to Shared Interactive Reports
You can link to saved primary default, alternative default and public reports using IR_REPORT_[report_alias] in the request value of the URL.
Link Examples to a Primary Report
The following examples demonstrate how to link to a primary report (report_alias=12345):
This example links to a primary report:
f?p=100:1:&APP_SESSION.:IR_REPORT_12345
This example links, resets, and clears primary report settings:
f?p=100:1:&APP_SESSION.:IR_REPORT_12345::RIR,CIR:
This example links, resets, and clears primary report settings. It additionally creates a ENAME = 'KING' filter on the primary report:
f?p=100:1:&APP_SESSION.:IR_REPORT_12345::RIR,CIR:IR_ENAME:KING
Link Examples to Saved Reports
The following examples demonstrate how to link to a saved report (report_alias=12345):
This example links to a saved report:
f?p=100:1:&SESSION.:IR_REPORT_1234
This example links, resets, and clears settings for saved report 12345:
f?p=100:1:&SESSION.:IR_REPORT_12345::RIR,CIR:
This example links, resets, and clears saved report 12345 settings. It additionally creates a ENAME = 'KING' filter on saved report 12345.
f?p=100:1:&SESSION.:IR_REPORT_12345::RIR,CIR::RIR,CIR:IR_ENAME:KING
Note that if you reset, clear, or create filter using URL without the IR_REPORT_[report_alias] request value, it resets, clears, and creates filter on the primary report. For example, this link goes to the primary report:
f?p=100:1:&SESSION.:::RIR,CIR:IR_ENAME:KING
Editing the Saved Report Alias
Developers can edit the report alias or view link examples by going to Saved Reports page.
To access the Saved Reports page.
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select the application.
-
Go to the Page Definition containing the saved interactive report.
The Page Definition appears.
-
To access the Saved Reports page:
-
Tree view - Right-click the Region name and select Edit Saved Reports.
-
Component view - Under Regions, click the Saved Reports link.
The Saved Reports page appears.
-
-
In Report Alias, you can either:
-
Enter a new alias for the saved report
-
Copy and paste the link example to link to a specific saved report
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
Viewing and Deleting Saved Reports
Each interactive report can have multiple default reports. A report categorized as Primary Default displays initially and cannot be renamed nor deleted. A report saved as Alternative Default can be selected from Reports list on the Search bar.
End users can also save reports and classify them as being either public or private. Public reports can be viewed by all users. Private reports can only be viewed by the user who saved the report. To learn more see, "Saving a Report".
To view a listing of Saved Reports:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
Click the Saved Reports tab.
A report displays all saved reports by report type, report name, owner, and report alias.
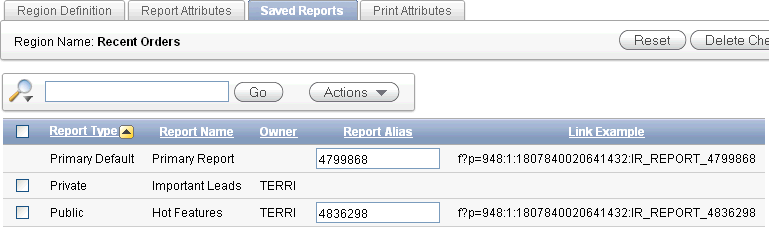
Description of the illustration ir_saved_reports.gif
-
To delete a report, select it and click Delete Checked.
Viewing Saved Report Activity
Developers can view saved report activity by clicking the View Saved Report Activity link under Tasks on the Edit Report Attributes page. This link only displays if saved reports other than the primary default report exist. You can use this page to determine which reports are being used and which ones are not.
To view saved report activity:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing the Interactive Report Attributes Page".
The Interactive Report Attributes page appears.
-
On the Tasks list, click View Saved Report Activity.
Tip:
You can also view saved report activity from the Workspace Administration page. On the Workspace home page, click Administration and then Monitory Activity. Under Page Views, click by Interactive Report.Editing SQL and Classic Reports
Developers can control report layout, pagination, column sorting, error messages, export links, and column break of SQL and Classic reports using the Report Attributes page.
Tip:
With the addition of interactive reports in Oracle Application Express release 3.1, all previous report types are referred to as classic reports. See "Editing Interactive Reports as a Developer".Accessing Classic Report Attributes
To access the Report Attributes page:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select the application.
-
Select a page.
The Page Definition appears.
-
To access the Report Attributes page:
-
Tree view - Right-click the region name and select Edit Report Attributes.

Description of the illustration rprt_edit_tree.gif
-
Component view - Click the Report link next to the report region you want to edit.

Description of the illustration rprt_edit.gif
The Report Attributes page appears and is divided into the following sections:
-
Column Attributes control the report layout. See "Altering Classic Report Layout Using Column Attributes".
-
Layout and Pagination attributes control report pagination. See "Controlling Classic Report Pagination".
-
Sorting attributes enable you to define images and image attributes for images that display in report headings to sort values. See "Enabling Column Sorting in a Classic Report".
-
Messages contain attributes that enable you to define messages that display if no data is found or more data is found than can be displayed.
-
Report Export attributes enable you to add download link to a report or export a report as either an XML file or CSV file. See "Adding a Download Link to a Classic Report" and "Exporting a Classic Report as an XML File or a CSV File".
-
Break Formatting attributes enable you to control if a specific column repeats and how column breaks appear when printed. See "Controlling Column Breaks in a Classic Report".
-
External Processing attributes enable you to specify a URL for post processing and a link label.
-
-
To learn more about a specific attribute, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
To save your changes, click Apply Changes.
See Also:
"Creating a Column Link in a Classic Report" and "Defining an Updatable Column in a Classic Report", and "Defining a Column as a List of Values in a Classic Report", and "Controlling When Columns Display in a Classic Report"About Navigation Alternatives
The Report Attribute page is divided into these sections: Column Attributes, Layout and Pagination, Sorting, Messages, Report Export, Break Formatting, and External Processing.
You can access these sections by scrolling down the page, or by clicking a navigation button at the top of the page.

Description of the illustration classic_rprt_nav.gif
When you select a button at the top of the page, the selected section appears and all other sections are temporarily hidden. To view all sections of the page, click Show All.
Altering Classic Report Layout Using Column Attributes
You can use the Column Attributes section of the Report Attributes page to precisely control the report layout. For example, you can use these attributes to alter column heading text, change column positioning, hide a column, create a sum of a column, or select a sort sequence.
To access the Column Attributes:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select the application.
-
Select a page.
The Page Definition appears.
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears with the Column Attributes section at the top of the page.
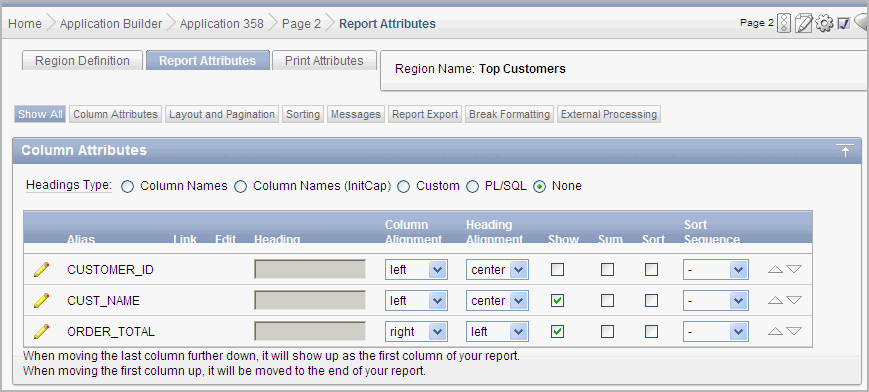
Description of the illustration rpt_att.gif
Use the Column Attributes section to control report column appearance and functionality.
Heading Type identifies how the heading is generated for the report. The Link column indicates if a column link is currently defined. The Edit column indicates whether a column is currently updatable.
Table 8-5 describes common report column edits.
Table 8-5 Common Report Column Edits for Classic Reports
Description Developer Action Alter column display sequence.
Click the up and down arrows to change the column display sequence.
Alter heading alignment.
Under Column Alignment, select a column alignment.
Change column heading text.
Under Heading, enter different heading text.
Control which columns display.
Click Show to indicate a column should display.
Enable a unique sort sequence.
Click Sort and select a sequence number from Sort Sequence.
Any number of columns can be sort enabled. However, at least one column must have a Sort Sequence defined.
Enable the sum of a column.
Click Sum to enable the sum of a column.
You can further refine the attributes of a specific column on the Column Attributes page.
-
To access the Column Attributes page, click the Edit icon next to the appropriate column Alias.
To learn more about a specific attribute, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
Controlling Classic Report Pagination
You control report pagination by:
-
Including a pagination substitution string in the report template
-
Making selections from the Layout and Pagination section on the Report Attributes page
You control how pagination displays by making selections from the Layout and Pagination attributes on the Report Attributes page.
Accessing and Understanding Layout and Pagination Attributes
To access the Layout and Pagination section of the Report Attributes page:
-
Create a report. See "Creating a Report Using a Wizard".
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Layout and Pagination.
You use the Layout and Pagination attributes to select a pagination style, determine where pagination occurs, and specify the number of rows that display on each page. Table 8-6 describes the most commonly used Layout and Pagination attributes.
To learn more about a specific attribute, click the item label. When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
Table 8-6 Layout and Pagination Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Report Template |
Specifies a template to be applied to this report. Report templates provide control over the results of a row from your SQL query. You can choose from a number of default templates, or pick a custom build template. |
|
Report Attributes Substitution |
Enter a value to be in place of the |
|
Show Null Values as |
Enter the text you want to display for null columns. The default value is |
|
Pagination Scheme |
Specifies a pagination scheme for this report. Pagination provides the user with information about the number of rows and the current position within the result set. Pagination also defines the style of links or buttons used to navigate to the next or previous page. For more information, see the Help information for this attribute. |
|
Enable Partial Page Refresh |
If enabled, this attribute refreshed the report region when paginating forward and backward in your result set. |
|
Display Position |
Defines where pagination occurs. If you choose to display pagination above a report, the selected report template needs to support that type of display. |
|
Number of Rows |
Defines the maximum number of rows to display on each page. |
|
Number of Rows (Item) |
Defines the number of rows displayed by default per page for SQL queries (obtained dynamically from an item). Identify the item in this attribute. |
|
Maximum Row Count |
Defines the maximum number of rows to query, for example, rows 1 - 10 of 456. If you set this attribute to 200, the result would appear as follows:
Note that this attribute impacts performance. Counting fewer rows can improve performance and counting thousands of rows can degrade performance. |
|
Strip HTML |
Specify whether to remove HTML tags from the original column values for HTML expressions, column links and report data exported as CSV files. If you select values from the database that contain HTML tags, then those tags can cause conflicts with the HTML generated for your columns links or HTML expressions. When this option is enabled, only the actual data portion of your column value is used. |
|
Sort Nulls |
For reports with column heading sorting, specify if you want null valued columns to sort first or last. |
Including Pagination After the Rows in a Classic Report
To include pagination after the rows in a report:
-
Create a report. See "Creating a Report Using a Wizard".
Next, select the appropriate Layout and Pagination attributes.
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Under Layout and Pagination, select the following:
-
Report Template - Select a report template (optional).
-
Pagination Scheme - Select a pagination scheme.
-
Display Position - Select a display position.
-
Number of Rows - Specify how many rows display on each page.
-
Click Apply Changes.
-
-
Edit the report template:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Templates, select the report template name.
-
Include the
#PAGINATION#substitution string in the After Rows attribute. -
Click Apply Changes.
-
-
Run the page.
Including Pagination Before the Rows in a Classic Report
To include pagination before the rows in a report:
-
Create a report. See "Creating a Report Using a Wizard".
Next, select the appropriate Layout and Pagination attributes.
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Under Layout and Pagination:
-
Report Template - Select a report template (optional).
-
Pagination Scheme - Select a pagination scheme.
-
Display Position - Select a position that contains the word top.
-
Number of Rows - Specify how many rows display on each page.
-
Click Apply Changes.
-
-
Edit the report template.
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Templates, select the report template name.
-
Include the
#TOP_PAGINATION#substitution string in the Before Rows attribute. -
Click Apply Changes.
-
-
Run the page.
Enabling Column Sorting in a Classic Report
You enable column sorting on the Report Attributes page.
To enable column sorting:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Under Column Attributes, select the Sort check box next to the columns to be sorted.
-
From Sort Sequence, select a sequence number.
Sort Sequence is optional. However, if there are one or more sort enabled columns, then at least one column needs a defined Sort Sequence.
-
Scroll down to Sorting.
-
Specify ascending and descending image attributes or click set defaults.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Tip:
Note that column sorting must be enabled if you want columns with null values to display at the top or end of the report. To learn more about the Sort Nulls attribute, see "Accessing and Understanding Layout and Pagination Attributes".Adding a Download Link to a Classic Report
You can create a link within a report that enables users to export the report as a comma-delimited file (.csv) file. To add a CSV link to a report you must enable the CSV output option. When using the CSV output option, the report template is not important. You can include a CSV link with any report template that has the CSV export substitution string defined.
See Also:
"Automatic CSV Encoding"Enabling the CSV Output Option in a Classic Report
To use the enable the CSV output option:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Report Export.
-
From Enable CSV output, select Yes.
-
(Optional) In the Separator and Enclosed By fields, define the separator and delimiter.
The default Enclosed By by characters are a double quotation marks (" "). The default delimiter is either a comma or a semicolon depending upon your current NLS settings.
-
In the Link Label field, enter link text. This text will display in your report and enable users to invoke a download.
-
(Optional) To specify a default export file name, enter a name in the Filename field.
By default, the Application Express engine creates an export file name by taking the region name and adding the appropriate file name extension (
.csvor.xml). -
Click Apply Changes.
Exporting a Classic Report as an XML File or a CSV File
You can export a report as an XML file by selecting a report template.
To export a report as a file:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Layout and Pagination.
-
From the Report Template list, select export: XML or export: CSV.
Selecting export: XML prevents the Application Express engine from rendering the page and dumps the content to an XML file.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Creating a Column Link in a Classic Report
Use the Column Link attributes to create a link from a report to another page in your application or to a URL.
To create a column link to another page:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Under Column Attributes, locate the column to contain the link.
-
Click the Edit icon next to the column name.
The Column Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Column Link.
-
To create a column link to another page:
-
From Target, select Page in this Application.
-
(Optional) In Link Attributes, specify additional column link attributes to be included in the
<a href= >tag (for example, a link target, classes, or styles). -
In Link Text, enter the text to be displayed as a link, specify an image tag, or pick from the list of default images.
-
In Page, specify the target page number. To reset the pagination for this page, select Reset Pagination.
-
In Request, specify the request to be used.
-
In Clear Cache, specify the pages (that is, the page numbers) on which to clear cache. You can specify multiple pages by listing the page numbers in a comma-delimited list. See "Linking to Interactive Reports".
-
Use the Name and Value fields to specify session state for a specific item.
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
To create a column link to a URL:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Access the Column Attributes page by clicking the Edit icon next to the appropriate column.
The Column Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Column Link.
-
Under Column Link, specify the following:
-
From Target, select URL.
-
In Link Text, enter the text to be displayed as a link and select a substitution string.
-
(Optional) In Link Attributes, specify additional column link attributes to be included in the
<a href= >tag (for example, a link target, classes, or styles). -
In URL, enter the appropriate address.
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
Defining an Updatable Column in a Classic Report
You can make a column updatable by editing Tabular Form Element attributes on the Column Attributes page. Note that the Application Express engine can only perform updates if:
-
A multirow update is defined
-
A PL/SQL process is implemented to process updated data
-
When using the built-in tabular form elements and display types, then the report has to be defined using the type SQL Query (updatable report)
To define updatable column attributes:
-
Access the Classic Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Access the Column Attributes page by clicking the Edit icon next to the appropriate column.
The Column Attributes page appears.
-
Under Column Attributes, specify the following:
-
Display As - Select a type of updatable column.
Use this option to make a column updatable. Updates can only be performed if a multirow update is defined, or a PL/SQL process is implemented to process updated data.
-
Number/Date Format - Make a selection if you selected the Display As type of Date Picker.
-
Element Width - Specify the width of the form item.
-
Number of Rows - Specify the height of a form item (applicable to text areas).
-
Element Attributes - Define a style or standard form element attribute.
-
Element Option Attributes - Specify form element attributes for items in a radio group or check box.
-
-
Tabular Form Attributes, specify the following:
-
Default Type - Identify the default type.
-
Default - Identify the default source.
-
Reference Table Owner - Identify the owner of the referenced table. This attribute is used to compare references to columns across applications against User Interface Defaults. This reference is manually maintained after being initialized by a wizard, whenever possible.
-
Reference Table Name - Specify the table or view that this column references. This attribute is used to compare references to columns across applications against User Interface Defaults. This reference is manually maintained after being initialized by a wizard, whenever possible.
-
Reference Column Name - Specify the column name that this report column references. This attribute is used to compare references to columns across applications against User Interface Defaults. This reference is manually maintained after being initialized by a wizard, whenever possible.
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
Defining a Column as a List of Values in a Classic Report
A column can be rendered as Radio Group or a static, named, or query-based LOV. For example, a column can be rendered using a select list or a popup list of values. Or, a column can be rendered as read-only text based on a list of values.
This last approach is an effective strategy when creating display lookup values and is particularly useful in regular, nonupdatable reports. This approach enables you to display the value of a column without having to write a SQL JOIN statement.
To render a report column as a list of values:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Access the Column Attributes page by clicking the Edit icon next to the appropriate column.
The Column Attributes page appears. Next, specify how the column is rendered (radio group, LOV, select list, and so on).
-
Under Column Attributes, make a selection from the Display As list.
-
Scroll down to List of Values.
-
From Named LOV, make a selection from the List of Values repository. See "Creating Lists of Values at the Application Level".
-
To include a null value in a list of values:
-
In Display Null - Select Yes.
-
Null display value - Enter the display value for the
NULLoption here. -
Null return value - Enter the
NULLvalue to be used for this item's list of values. If you do not specify a value, the default is%null%.
A column can also have a value that does not display in its list of values.
-
-
To define a value that does not display in the list of values:
-
From Display Extra Value, select Yes.
The extra value is used if the actual column value is not part of the LOV. In that situation, the actual value is shown. If you do not display extra values, you may end up with the wrong value and unintentionally update your data incorrectly.
-
In Null Value, specify the value that displays.
-
If you have not selected a Named LOV, enter the query used to display a select list in the LOV Query field.
-
-
If you have not selected a Named LOV, enter the query used to display a select list in List of values definition.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Controlling When Columns Display in a Classic Report
You can use the Authorization and Condition attributes to control when a column displays.
Authorization enables you to control access to resources (such as a report column) based on predefined user privileges. For example, you could create an authorization scheme in which only managers can view a specific report column. Before you can select an authorization scheme, you must first create it.
A condition is a small unit of logic that enables you to control the display of a column based on a predefined condition type. The condition evaluates to true or false based on the values you enter in the Expressions fields.
To specify Authorization and Condition attributes:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Access the Column Attributes page by clicking the Edit icon next to the appropriate column.
The Column Attributes page appears.
-
Under Authorization, make a selection from the Authorization Scheme list.
-
Under Conditions, make a selection from the Condition Type list, and depending upon your selection, enter an expression or value in the appropriate Expression fields.
If the authorization is successful and the condition type display evaluates to true, the column displays.
Controlling Column Breaks in a Classic Report
You can control if a specific column repeats and how column breaks appear when printed using Break Formatting attributes. For example, suppose your report displays employee information by department number. If multiple employees are members of the same department, you can increase the readability by specifying the department number only appears once.
To create this type of column break:
-
Access the Interactive Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
The Report Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Break Formatting.
-
Make a selection from the Breaks list.
Printing Report Regions
You can configure a classic report region to print by exporting it to a number of different formats. Oracle BI Publisher supports Adobe Portable Document Format (PDF), Microsoft Word Rich Text Format (RTF), or Microsoft Excel format (XLS), or Extensible Markup Language (XML). The supplied OC4J with Apache FOP alternative only supports PDF and XML. If you choose to use other third-party rendering engines, other output formats can also be configured.
By taking advantage of region report printing, your application users can view and print reports that have a predefined orientation, page size, column headings, and page header and footer. Interactive reports also have the ability to export to PDF, RTF, Microsoft Excel and Comma Separated Values (CSV). Note that for interactive reports, it is not possible to define a custom report layout.
Tip:
If you are running Oracle Application Express with Oracle Database 11g Release 1 (11.1), you must enable network services in order to use report printing. See "Enabling Network Services in Oracle Database 11g"About Printing Reports to PDF
When printing to a PDF, the report data is transformed using an externally defined report server. When the application end user clicks a print link, a request is sent to the Application Express engine. The Application Express engine then generates the report data in XML format and report template in XSL-FO or RTF format. The external reporting engine then transforms the data and the template into a PDF which displays to the end user using the conversion servlet that ships with BI Publisher 10.1.3.2 (formerly known as Oracle XML Publisher). Fortunately, this architectural complexity is transparent to both end users and developers. End users just click a print link, and developers just declaratively set regions to support PDF printing. Output to other formats operates in the same manner using the necessary conversion servlet.
About Report Printing Configuration Options
Your report server can be Oracle BI Publisher, OC4J with Apache FOP, or another standard XSL-FO processing engine. Oracle BI Publisher provides a higher level of functionality and facilitates "high fidelity" output requirements including master-detail reports, charts, and so on. To accommodate the difference in functionality, Oracle Application Express provides two report printing configuration options:
-
Standard Support. Enables you to print report regions and report queries using either the built-in templates (provided with a standard XSL-FO processing engine), or other XSL-FO compatible formats you provide. This setting does not support RTF.
Standard Support provides declarative formatting of report regions and report queries with basic control over page attributes, including page orientation, page size, column heading formats, page header, and page footer.
-
Advanced Support. Requires a valid license of Oracle BI Publisher (also known as Oracle XML Publisher). This setting, provides you with all the capabilities of the Standard configuration plus the ability to define RTF-based report layouts developed using the BI Publisher Word Template Builder.
To learn more about installing and configuring Oracle BI Publisher, see PDF Printing in Application Express 3.1. Go to:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/products/database/application_express/html/configure_printing.html
Note:
To use the full functionality of report printing, your Oracle Application Express service administrator must enable it for your site. See "Configuring Report Printing" in Oracle Application Express Administration Guide.About Classic Report Printing Methods
There are two ways to print classic report regions:
-
Configure Printing Attributes for a Report Region. You can print a report region by configuring the Printing Attributes for the region. See "Configuring Classic Report Region Print Attributes".
-
Create a Report Query. You can print a report by defining a report query as a Shared Component. See "About Report Queries".
Both report regions and report queries can be downloaded in the following formats:
-
PDF - Adobe Portable Document Format.
-
RTF - Microsoft Word Rich Text Format.
-
XLS - Microsoft Excel format. Note that this is not a true
.xlsfile because the content is HTML-based. -
HTML
-
XML - Extensible Markup Language.
To format either a report region or report query, you associate it with a report layout. To learn more, see "About Report Layouts".
Tip:
You can also have the output format specified by an item that determines the output format at runtime. Select the item that will hold the format value. Valid values are PDF, RTF (to open the document in Microsoft Word), XLS (to open the document in Microsot Excel) and HTM (to download the document as an HTML file).About Report Queries
You can print a report region by defining a report query as a Shared Component. A report query identifies the data to be extracted. Unlike SQL statements contained in regions, report queries contain SQL statements that are validated when you save the query. Note that report queries must be SQL statements, not functions returning SQL statements.
You can associate a report query with a report layout and download it as a formatted document. If no report layout is selected, a generic layout is used. The generic layout is intended to be used to test and verify a report query. When using the generic layout option and multiple source queries are defined, only the first result set is included in the print document. The reports can include session state of the current application.
To make these reports available to end users, you then integrate them with an application. For example, you can associate a report query with a button, list item, branch, or other navigational component that enables you to use URLs as targets. Selecting that item then initiates the printing process.
Creating a Report Query
Note that the availability of the report query options depends on how your service administrator configures report printing for your instance. All options described in these steps may not be available to you.
To create a report query:
-
Navigate to the Shared Components page. See "Accessing the Shared Components Page".
-
Under Reports, click Report Queries.
-
Click Create.
-
For Query, specify the following information:
-
Report Query Name - Enter a name to identify the report query. When referencing a report query as a link target, the report query name is part of the request string.
-
Output Format - Select the report output format. Valid options include:
-
PDF - Adobe Portable Document Format.
-
Word - Microsoft Word Rich Text Format.
-
Excel - Microsoft Excel format. Note that this is not a true
.xlsfile because the content is HTML-based. -
HTML
-
XML - Extensible Markup Language.
-
-
Item - Select the item to hold the format value. This can be used to determine the output format at runtime.
-
View File As - Select how the Web browser opens the report query document. Options include:
-
Attachment - Displays a File Open/Save dialog box when the user clicks the report query download button.
-
Inline - Displays the report query document inside the Browser window.
-
-
Session State - Select this check box to reference session state values, such as the values of page items in the XML structure of your report.
-
Click Next.
-
-
For SQL Query, enter a SQL statement directly or click Query Builder to build a SQL statement by clicking and pointing.
To reference applications and page items in the SQL statement, reference them as bind variables. Click Set Bind Variables to be able to enter in values for each bind variable and test the query to ensure the expected output is returned.
-
For Download Definition, specify the following:
-
Data Source for Report Layout - Use this option to download a report definition export file. Select XML Data or XML Schema and then click Download.
XML Schema creates XSD file (that is, a XML schema definition of your XML structure.)
-
Add Query - Click this button to add another query to the report query. Adding another query enables the production of complex reports with more than one output component (for example, a chart and a report based on two different queries).
-
Create Report Query - Click this button to exit the wizard early. The Report Layout Source will default to use the generic report layout.
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Upload Report Layout, specify the following:
-
Report Layout Source - Specify how the report layout is derived. If you choose the report based file layout then the layout name and report layout file must be provided.
-
Layout Name - Enter a layout name (optional). The default is the report query name.
-
Report Layout File - Click Browse and select a Rich Text Format (RTF).
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Confirm:
-
Query Name - Identifies the query.
-
Report Layout - Identifies the report layout you selected.
-
Output Format - Identifies the format for this report query.
-
Derive from Item - Identifies the item to hold the format information.
-
URL - To integrate this report with your application, use the displayed URL as the target for a button, list item, link, or other navigational component. End users can click a button, for example, to start the printing process.
-
Test Report - Click this to preview your report. If you have chosen to use a generic report layout then the Test Report will not produce an output.
-
Click Finish.
The Report Query is created and saved to Shared Components.
-
Editing Report Queries
To edit a report query:
-
Navigate to the Shared Components page. See "Accessing the Shared Components Page".
-
Under Reports, click Report Queries.
-
On the Report Queries page, you can use the Navigation bar at the top of the page to search for a query by name or change the page display. For example, you can change the default display by making a selection from View list. Available options include:
-
Icons (the default) displays each query as a large icon. To edit a query, click the appropriate icon.
-
Details displays each query as a line in a report. To edit a query, click the name.
-
-
Select the appropriate report query. On the Edit Report Query page, edit the information.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Copying Report Queries
To copy a report query:
-
Navigate to the Shared Components page. See "Accessing the Shared Components Page".
-
Under Reports, click Report Queries.
-
On the Report Queries page, click Copy.
-
On the Copy Report Query, select the query you want to copy, enter a name for the report query, and click Copy.
The copy appears in the query list.
About Report Layouts
To format either a classic report region or report query, you associate it with a report layout. Using report layouts renders the data in a printer-friendly format. If you do not select a report layout, a default XSL-FO layout is used. The default XSL-FO layout is always used for rendering Interactive Report regions.
When creating and using report layouts, you can:
-
Take advantage of the default layouts for report regions and generic layouts for report queries provided with Oracle Application Express.
-
Utilize the built-in XSL-FO-based layouts for report regions by copying and customizing the code. You can edit a number of attributes for report regions that control page size, fonts, colors, and so on.
-
Create RTF or XSL-FO report layouts to customize the report look and feel. To use RTF report layouts, your Oracle Application Express service administrator must select the Advanced setting for your site. See "Configuring Report Printing" in Oracle Application Express Administration Guide.
About Report Layout Options
You can create a report layout based on one of these options:
-
Generic Columns - A generic report layout works with most query result sets. With this layout, the number of columns is automatically adjusted when generating the printable document.
A number of report layout attributes can be defined declaratively for report regions using the built-in XSL-FO default layout. This step allows for creating customizable copies of the built-in default XSL-FO layout, if additional control over the report layout is needed.
-
Named Columns - A named column report layout is a query-specific report layout designed to work with a defined list of columns in the query result set. This type of layout is used for custom-designed layouts when precise control of the positioning of page items and query columns is required.
Note that the availability of the Report Layout options depends on how your site administrator configured the report printing settings at your site. All options described in these steps may not be available to you.
See Also:
"Configuring Report Printing" in Oracle Application Express Administration Guide.Creating a Report Layout
To create a report layout:
-
Navigate to the Shared Components page. See "Accessing the Shared Components Page".
-
Under Reports, click Report Layouts.
-
Click Create.
The Create Report Layout wizard appears.
-
For Report Layout Type, select an option and click Next:
-
Generic Columns (XSL-FO) - This layout is pre-populated with a default template, which you can edit to fit your needs.
-
Named Columns (RTF) - This layout is uploaded as an RTF file.
-
Named Columns (XSL-FO) - This layout is uploaded as an XSL-FO file.
-
-
For Layout Source, review and edit the appropriate information. The options that appear on this page depend on the layout type you select:
-
If you selected Generic Columns:
-
Report Layout Name - Enter a name to identify the report layout when associating it with a report query or report region.
-
Report Layout - The report layout is the XSL-FO based definition of the page formatting. All attributes defining page size, orientation, fonts, styles, and so on, are defined in this section.
To see a list of valid substitution strings and other information, click the item label, Report Layout. This opens a separate Help window.
-
Report Column Heading - Defines the look of each cell in the report heading row.
-
Report Column - Defines the look of each cell for all report rows.
-
Report Column Width - This width is computed at runtime time or can be derived from the report column definition of a report region.
-
If you selected Named Columns:
-
Layout Name - Enter a name to identify the report layout when associating it with a report query or report region.
-
8.b) Report Layout File - Upload the file containing the report layout.
-
Editing Report Layouts
You can edit a generic column report layout directly in Application Express. However, to edit a named column report layout, you must download the current file, edit it, and then upload it again.
To edit a report layout:
-
Navigate to the Shared Components page. See "Accessing the Shared Components Page".
-
Under Reports, click Report Layouts.
-
On the Report Layouts page, select the layout you want to edit.
-
For generic column layouts, edit the layout directly on the Edit Report Layout page and then click Apply Changes.
-
For named column layouts, click Download and save the file to your computer.
Edit the file and then upload the updated version as a new report layout.
Copying Report Layouts
You can copy a report layout to edit and save.
To copy a report layout:
-
Navigate to the Shared Components page. See "Accessing the Shared Components Page".
-
Under Reports, click Report Layouts.
-
On the Report Layouts page, click Copy.
-
On the Copy Report Layout page, select the layout you want to copy, enter a name for the copy, and click Copy.
The copy appears in the layout list.
Configuring Classic Report Region Print Attributes
One approach to printing a report region is to configure Print Attributes. Once configured, these attributes only apply only to current region and cannot be used outside the context of the region.
If the printing feature is set up for your instance, you can configure a report region to print in various formats.
See Also:
"About Classic Report Printing Methods" and "Configuring Report Printing" in Oracle Application Express Administration GuideTo configure a classic report region for printing:
-
In your application, select the page containing the classic report region you want to print.
The Page Definition appears.
-
Access the Report Attributes page. See "Accessing Classic Report Attributes".
-
Click the Print Attributes tab.
-
Under Printing, specify the appropriate information:
-
Enable Report Printing - Select Yes.
-
Link Label - Enter the text for the link that starts the printing process.
-
Response Header - Specify whether the response header generated by Oracle Application Express is based on your Report Settings or the Print Server. The response header is the information the server sends back to the Web browser in response to receiving an HTTP request. It contains the date, size and type of file that the server is sending back to the client and also data about the server itself. To specify content disposition (using the attribute View File As) and file name, the response header needs to be based on Report Settings.
-
View File As - Select how the Web browser opens the report query document. Options include:
-
Attachment - Displays a File Open/Save dialog box when the user clicks the report query download button.
-
Inline - Displays the report query document inside the Browser window.
-
-
(Optional) File Name - Enter a name for the downloaded file. If you leave this blank, the region name is used as the file name.
-
Output Format - Select an output option.
-
Item - Only enabled, if you select the Output Format Derived from Item. If enabled, select the application or page item that holds format value.
-
Report Layout - Select Default Report Layout to use the built-in generic report layout, or an available report layout you or your administrator created. See item Help for a listing of the supported substitution strings available when building custom XSL-FO report layouts.
-
Print Server Overwrite - Specify an alternate print server. A print server is typically configured centrally for all workspaces in Oracle Application Express Administration Services. See "Configuring Report Printing" in Oracle Application Express Administration Guide.
Configuring an alternative print server at the report level makes debugging and diagnosis of potential printing problems easier and supports the use of specific custom built end points to perform custom XSLT transformations.
-
Print URL - Report regions can be printed using the standard print link or using a page button. To use a button, remove the Link Label, create a button on your page, and use the URL shown in this attribute as the button target.
-
-
In the remaining sections, define page size, paper orientation, page headers and footers, fonts, text color, and background color.
-
Under Report Columns, specify the width for each column.
The default is to make each column the same width. The Total Width is a display only field that shows the sum of all column width values. When changing the width for an individual column the Total Width is automatically recalculated. If Column Width Units is set to Percentage, rather than Points, then the total column width must be less than or equal to 100.
Use the Reset Column Width button to reset the Column Width Units to Percentage and change all column widths back to their default value. The Recalculate button maintains the current ratios between column widths but reduce all column widths such that the Total Width is less than or equal to 100%.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Configuring Interactive Report Region Print Attributes
Unlike classic reports, the Interactive Report Print Attributes can only utilize the default XSL-FO layout and is initiated from the Report Attributes, Download section rather than directly from this screen. Once configured, these attributes only apply only to the current region and cannot be used outside the context of the region.
If the printing feature is set up for your instance, you can configure a report region to print in various formats
To configure a interactive report region for printing:
-
In your application, select the page containing the interactive report region you want to print.
The Page Definition appears.
-
Under Regions, click Interactive Report next to the region you want to print.
-
Click the Print Attributes tab.
-
Under Printing, specify the appropriate information:
-
Response Header - Specify whether the response header generated by Oracle Application Express is based on your Report Settings or the Print Server. The response header is the information the server sends back to the Web browser in response to receiving an HTTP request. It contains the date, size and type of file that the server is sending back to the client and also data about the server itself. To specify content disposition (using the attribute View File As) and file name, the response header needs to be based on Report Settings.
-
Content Disposition - Select how the Web browser opens the report query document. Options include:
-
Attachment - Displays a File Open/Save dialog box when the user clicks the report query download button.
-
Inline - Displays the report query document inside the Browser window.
-
-
Print Server Overwrite - Specify an alternate print server. A print server is typically configured centrally for all workspaces in Oracle Application Express Administration Services. See "Configuring Report Printing" in Oracle Application Express Administration Guide.
Configuring an alternative print server at the report level allows for easier debugging and diagnosis of potential printing problems and supports the use of specific custom built end points to perform custom XSLT transformations.
-
-
In the remaining sections, define page size, paper orientation, page headers and footers, fonts, text color, and background color.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Creating Forms
You can include a variety of different types of forms in your applications. You can include forms that enable users to update just a single row in a table or multiple rows at once. Application Builder includes a number of wizards you can use to create forms automatically, or you can create forms manually.
Creating a Form Using a Wizard
The easiest way to create a form is to use a wizard. For example, the Form on Table or View Wizard creates one item for each column in a table. It also includes the necessary buttons and processes required to insert, update, and delete rows from the table using a primary key. Each region has a defined name and display position; all other attributes are items, buttons, processes, and branches.
To create a form using a wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Form and click Next.
-
Under Forms, select a type of form page as described in Table 8-7.
Form Page Type Description Builds a form based on stored procedure arguments. Use this approach when you have implemented logic or data manipulation language (DML) in a stored procedure or package.
Creates a form that enables users to update a single row in a database table.
Creates two pages. One page displays a report. Each row provides a link to the second page to enable users to update each record.
Note: This wizard does not support tables having more than 127 columns. Selecting more than 127 columns generates an error.
Creates a form that displays a master row and multiple detail rows within a single HTML form. With this form, users can query, insert, update, and delete values from two tables or views.
See Also: "Creating a Master Detail Form"
Creates a form in which users can update multiple rows in a database.
See Also: "Creating a Tabular Form"
Creates a form based on the columns returned by a SQL query such as an
EQUIJOIN.Creates a read-only version of a form. Typically used to provide a confirmation page at the end of a wizard.
Creates a page with items based on a Web service definition. This wizard creates a user input form, a process to call the Web service, and a submit button.
See Also: "Creating a Form on a Web Service"
Creates a page with items based on a Web service definition. This wizard creates a user input form, a process to call the Web service, a submit button, and displays the results returned in a report.
See Also: "Creating an Input Form and Report on a Web Service"
-
Follow the on-screen instructions. To learn more about a specific field, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
Creating a Tabular Form
A tabular form enables users to update multiple rows in a table at once from a single page. If created using a wizard, a tabular forms enables you to perform update, insert, and delete operations on multiple rows in a database table. This form includes a built-in multiple row update process that performs optimistic locking behind the scenes to maintain the data integrity.
About Tabular Forms
There are two primary methods for creating tabular forms:
-
Create Application Wizard
-
Create Page Wizard
Tabular forms created using these wizards include automatic DML processes. These wizards create a form that performs update, insert, and delete operations on multiple rows in a database table. Alternatively, you can build a tabular form manually either by creating a updatable report region or standard report region with updatable columns in conjunction with custom PL/SQL page processes to process the tabular form data.
Note:
Any modification of the select list of a SQL statement of a tabular form after it has been generated using a wizard is not recommended. If you do modify the query, make sure the values of the updateable columns are not altered after being queried from the database by the Application Express engine.Running a Tabular Form
When running a tabular form, data is rendered as a report having updateable columns shown using various form elements (including text fields, text areas, date pickers, select lists, radio groups, and so on).
Description of the illustration rprt_tabular_form.gif
By default, date columns are created using the Date Picker item type. If user interface defaults are defined, other columns can be automatically created as select lists based on lists of values, or numeric fields and large text areas.
See Also:
"Managing User Interface Defaults" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop GuideFor numeric and date fields, you can also pre-define date and number format masks, or apply those format masks after generating the initial form.
Each report also includes a check box column (called a row selector). Users use this row selector to select one or more columns and update or delete data. To add a row, users click Add Row.
Tip:
You can control the appearance of a specific column by editing column attributes. See "Altering Classic Report Layout Using Column Attributes" and "Editing SQL and Classic Reports".How Tabular Forms Work
Tabular forms are based on a SQL query in which the query columns are tied to the underlying table columns. Unlike a single record from, tabular forms do not store data in session state. When a tabular form page is submitted, the tabular form data is processed using built-in data manipulation language (DML), or a custom PL/SQL page processes.
A tabular form with automatic DML has two processes for multi-row operations:
-
A Multi Row Update (MRU) process performs create and update operations
-
Multi Row Delete (MRD) process deletes requests on one or more rows
MRU and MRD processes reference the underlying table name and the primary key columns. The primary key columns must be part of the tabular form SQL query, and the report columns must be either hidden or display-only (save state) in order for the DML processes to be able to identify the correct records. For new records, the primary key values must be NULL in order to be identified as new records. Delete operations are performed by referencing row number of the row to be deleted. Users can check one or more rows on the current page and when they press the Delete button, the row numbers are used to identify the corresponding primary key value(s) and the matching rows are deleted.
Wizard generated tabular forms built-in DML, include a checksum column to prevent lost updates. Using a method called optimistic locking, a checksum is computed for each row when rendering a tabular form. This checksum is stored in an extra hidden tabular form column. Upon submission of the form for update, an additional set of checksums is computed on the then current data stored in the database. The new checksums are compared to those built when the tabular form was first rendered, and if there are any mismatches, the update is rejected, because the data in the database was either modified by another user or anther process in the time between the tabular form was rendered and the time the data was submitted.
Wizard generated tabular forms also automatically create validations for some columns. Validations are created for columns that are set to NOT NULL in the underlying table and columns of type NUMBER, DATE or TIMESTAMP. Note that validations are not created for columns if the column is set to read-only, either based on the user's selection, or defined user interface defaults.
Creating a Tabular Form Using the Create Application Wizard
The Create Application Wizard is designed to quickly create a basic Oracle Application Express application consisting of multiple pages and components. For that reason, this wizard uses general best practices to generate the application and does not include several advanced options included in the Create Page Wizard.
To create a tabular form using the Create Application Wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Click the Create button.
-
For Application Type, select Database.
-
For Method, select From Scratch.
-
For Name, enter the following and click Next:
-
Name - Enter a name to identify the application.
-
Application - Enter a unique integer value to identify the application.
-
Create Application - Select a creation method:
-
Select From scratch to manually add all pages
-
Select Based on existing application design model to copy page definitions from a previous application model.
Note that you will still have to define all other application attributes, or you can choose to copy some attributes by choosing to copy shared components from another application (See step 11).
-
-
Schema - Your application will obtain its privileges by parsing all SQL as a specific database schema. Identify the database schema owner.
Next, select a page type and table on which to build the tabular form.
-
-
For Pages:
-
Select Page Type - Select Tabular Form.
-
Table Name - Select a table.
Select the operations to be performed on the table (for example, Update, Insert and Delete).
-
Click Add Page.
The new page appears at the top of the page.
-
Click Next.
-
-
On Tabs, specify a tab implementation and click Next.
-
For Shared Components, determine whether to import shared components from another application. Shared components are common elements that can display or be applied on any page within an application.
To include shared components, select the following:
-
Copy Shared Components from Another Application - Select Yes.
-
Copy from Application - Select the application from which you want to import shared components.
-
Select Components to Import - Select the components to import.
-
Click Next.
Next, select a default authentication scheme. Authentication is the process of establishing a user's identity before they can access an application. See "Establishing User Identity Through Authentication".
-
-
For Authentication Scheme, select one of the following:
-
Application Express - Uses the user account credentials created and maintained with the Application Express Service Administration application. These are the accounts you use to log in to the Application Express development environment. You can also create accounts in this user account repository for end users of your applications.
-
No Authentication - Also known as database authentication, this option enables users to access your application using the account credentials stored in the
modplsqlDAD definition. In most cases this results in users not having to login when accessing your application. This is the quickest way to create a "public" application. -
Database Account - Requires users logging into your application to enter a database schema name (or user name) and a password in order to authenticate. This account information is managed entirely within the Oracle database.
-
-
Next, specify the following attributes:
-
Language - Select the primary language for this application.
This attribute identifies the language in which an application is developed. This language is the base language from which all translations are made.
-
User Language Preference Derived From - Specifies how the engine determines the application language. The application primary language can be static (that is, derived from the Web browser language) or determined from a user preference or item. The database language setting determines date display and sorting characteristics.
You can alter the Language and User Language Preference Derived From attributes later on the Edit Globalization attributes page. See "Configuring Globalization Attributes".
-
Date Format - Specifies the date format to be used in the application.
This date format is used to alter the
NLS_DATE_FORMATdatabase session setting before showing or submitting any page within the application. This value can be a literal string containing a valid Oracle date format mask or an item reference via substitution syntax. If no value is specified, the default date format is derived from the database session at runtime. If supplied, this is also used as the date format for any items resulting from columns of typeDATE. -
Click Next.
-
-
For User Interface, select a theme and click Next.
Themes are collections of templates that can be used to define the layout and style of an entire application. See "Managing Themes".
-
Confirm your selections and click Create.
See Also:
"Managing User Interface Defaults" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop GuideCreating a Tabular Form Using the Create Page Wizard
Use the Create Page Wizard to add a tabular form to an existing application. Once you provide a table name on which to build the tabular form, the wizard reads the table columns from the database data dictionary. You then choose which columns to include in the tabular form, either as display-only columns or as updatable columns. Unlike the Create Application Wizard, you can choose between three different primary key source types: trigger, PL/SQL function, and sequence.
To create a tabular form using the Create Page Wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Form and click Next.
-
Select Tabular Form and click Next.
The Create Tabular Form Wizard appears.
-
For Table/View Owner:
-
Specify the table or view owner on which you want to base your tabular form.
-
Select the operations to be performed on the table (for example, Update, Insert and Delete).
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Table/View Name, select a table and click Next.
-
For Displayed Columns:
-
Select the columns (updatable and nonupdatable) to include in the form.
Note that you can modify the column order or your SQL query after you create the page.
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Primary Key, select the Primary Key column and a secondary Primary Key column (if applicable) and click Next.
-
For Primary Key Source, select a source type for the primary key column and click Next. Valid options include:
-
Existing trigger - Select this option if a a before-insert trigger populates the primary key. You can also select this option if you plan on specifying the primary key column source later after completing the form.
-
Custom PL/SQL function - Select this option if you want to provide a PL/SQL function to generate returning key value.
-
Existing sequence - Select this option if you want to pick the sequence from a list of sequences available in the selected schema.
-
-
On Updatable Columns, select which columns should be updatable and click Next.
-
On Page and Region Attributes:
-
Specify a page name and region information.
-
Specify a region title.
-
Select a region template.
-
Select a report template.
-
Determine whether to include breadcrumbs.
-
Click Next.
-
-
On Tab, specify a tab implementation for this page and click Next.
-
On Button Labels, enter the display text to appear for each button and click Next.
-
On Branching, specify the pages to branch to after the user clicks the Submit and Cancel buttons and click Next.
-
Click Finish.
A success message appears.
Creating a Master Detail Form
A master detail form reflects a one-to-many relationship between two tables in a database. Typically, a master detail form displays a master row and multiple detail rows within a single HTML form. With this form, users can insert, update, and delete values from two tables or views.
About Master Detail Forms
When running a master detail form, data is rendered as a report using various form elements (including text fields, text areas, date pickers, select lists, radio groups, and so on).
Description of the illustration rprt_master_detail.gif
By default, date columns are created using the Date Picker item type. If user interface defaults are defined, other columns can be automatically created as select lists based on lists of values, or numeric fields and large text areas.
Click Create to add a new row. Click the Edit icon to edit row details.

Description of the illustration rprt_master_detail2.gif
On the Master Detail, the master record displays as a standard form and the detail records display in a tabular form at the bottom of the page.
See Also:
"Managing User Interface Defaults" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop GuideFor numeric and date fields, you can also pre-define date and number format masks, or apply those format masks after generating the initial form. Wizard generated master detail forms also automatically create validations for some columns. Validations are created for columns that are set to NOT NULL in the underlying table and columns of type NUMBER, DATE or TIMESTAMP. Note that validations are not created for columns if the column is set to read-only, either based on the user's selection, or defined user interface defaults.
Tip:
You can control the appearance of a specific column by editing column attributes. See "Altering Classic Report Layout Using Column Attributes" and "Editing SQL and Classic Reports".Creating a Master Details form Using the Create Application Wizard
The Create Application Wizard is designed to quickly create a basic Oracle Application Express application consisting of multiple pages and components. This wizard uses general best practices to generate the application and does not include several advanced options included in the Create Page Wizard.
To create a tabular form using the Create Application Wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Click the Create button.
-
For Application Type, select Database.
-
For Method, select From Scratch.
-
For Name, enter the following and click Next:
-
Name - Enter a name to identify the application.
-
Application - Enter a unique integer value to identify the application.
-
Create Application - Select a creation method:
-
Select From scratch to manually add all pages
-
Select Based on existing application design model to copy page definitions from a previous application model.
Note that you will still have to define all other application attributes, or you can choose to copy some attributes by choosing to copy shared components from another application (See step 11).
-
-
Schema - Your application will obtain its privileges by parsing all SQL as a specific database schema. Identify the database schema owner.
Next, select a page type and table on which to build the tabular form.
-
-
For Pages:
-
Select Page Type - Select Master Detail.
-
Master Table Name - Select a table.
This table will be used to create a report page and used as the master form on the master detail page.
-
Detail Table Name - Select a table.
Only tables and views that are associated to your selected Master Table via a foreign key are displayed.
-
Click Add Page.
The new page appears at the top of the page.
-
Click Next.
-
-
On Tabs, specify a tab implementation and click Next.
-
For Shared Components, determine whether to import shared components from another application. Shared components are common elements that can display or be applied on any page within an application.
To include shared components, select the following:
-
Copy Shared Components from Another Application - Select Yes.
-
Copy from Application - Select the application from which you want to import shared components.
-
Select Components to Import - Select the components to import.
-
Click Next.
Next, select a default authentication scheme. Authentication is the process of establishing a user's identity before they can access an application. See "Establishing User Identity Through Authentication".
-
-
For Authentication Scheme, select one of the following:
-
Application Express - Uses the user account credentials created and maintained with the Application Express Service Administration application. These are the accounts you use to log in to the Application Express development environment. You can also create accounts in this user account repository for end users of your applications.
-
No Authentication - Also known as database authentication, this option enables users to access your application using the account credentials stored in the
modplsqlDAD definition. In most cases this results in users not having to login when accessing your application. This is the quickest way to create a “public” application. -
Database Account - Requires users logging into your application to enter a database schema name (or user name) and a password in order to authenticate. This account information is managed entirely within the Oracle database.
-
-
Next, specify the following attributes:
-
Language - Select the primary language for this application.
This attribute identifies the language in which an application is developed. This language is the base language from which all translations are made.
-
User Language Preference Derived From - Specifies how the engine determines the application language. The application primary language can be static (that is, derived from the Web browser language) or determined from a user preference or item. The database language setting determines date display and sorting characteristics.
You can alter the Language and User Language Preference Derived From attributes later on the Edit Globalization attributes page. See "Configuring Globalization Attributes".
-
Date Format - Specifies the date format to be used in the application.
This date format is used to alter the
NLS_DATE_FORMATdatabase session setting before showing or submitting any page within the application. This value can be a literal string containing a valid Oracle date format mask or an item reference via substitution syntax. If no value is specified, the default date format is derived from the database session at runtime. If supplied, this is also used as the date format for any items resulting from columns of typeDATE. -
Click Next.
-
-
For User Interface, select a theme and click Next.
Themes are collections of templates that can be used to define the layout and style of an entire application. See "Managing Themes".
-
Confirm your selections and click Create.
Create a Master Detail Form Using the Create Page Wizard
The Create Page Wizard provides support for creating a master detail from two tables that do not have foreign key relationship defined in the database. Although Oracle recommends the use of foreign keys and properly defined relationships in the underlying database, developers do not always have the ability to modify their database model.
When created using a wizard, the master form on a master detail form page includes buttons that enable the user to move forward and backward with in the master result set. While running the wizard, you choose which columns determine the navigation order. You also have the option to choose whether to create a two-page or three-page master detail form, with the detail records shown in a report with single-record editing on a separate page.
To create a master detail form using the Create Page Wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Form and click Next.
-
Select Master Detail Form and click Next.
The Master Detail Wizard appears.
-
On Master Table:
-
Select the table or view owner.
-
Select a table or view name.
The columns in that object appear under Available Columns.
-
Select the columns to display in the form and then click the arrow keys to move them to Displayed Columns.
-
Click Next.
-
-
On Detail Table:
-
Specify whether to show only related tables by selecting Yes or No.
-
Select the table or view owner.
-
Select a table or view name.
The columns in that object appear under Available Columns.
-
Select the columns to display in the form and then click the arrow keys to move them to Displayed Columns.
-
Click Next.
-
-
On Primary Key Source, select the primary key column for the master table and click Next. Then select the primary key column for the detail table and click Next. Options include:
-
Existing trigger - Select this option if a trigger is defined to populate the primary key, or if the user will be expected to enter the primary key value manually. Detail tables do not support user entered primary key values.
-
Custom PL/SQL function - Select this option if you want to provide a PL/SQL function to populate the primary key.
-
Existing sequence - Select this option if an existing sequence will be used to generate the primary key.
-
-
On Master Options, specify whether to include master row navigation and click Next.
If you include master row navigation, define navigation order columns. If a navigation order column is not defined, the master update form navigates by the primary key column.
-
On Layout, specify how to build the master detail and click Next. Options include:
-
Edit detail as tabular form on same page creates a two page master detail. Edit detail on separate page creates a three page master detail.
-
Edit detail on separate page creates a three page master detail.
-
-
On Page Attributes, review and edit the master page and detail page information and then click Next.
-
On Tab, specify whether to include a tab set and click Next.
-
Click Create.
Creating a Form Manually
You can also create a form manually by performing the following steps:
-
Create an HTML region (to serve as a container for your page items)
-
Create items to display in the region
-
Create processes and branches
To create a form manually by creating and HTML region:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Create an HTML region:
-
Under Regions, click the Create icon.
-
Select the region type HTML.
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
-
-
Start adding items to the page:
-
Under Items, click the Create icon.
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
-
Processing a Form
Once you create a form, the next step is to process the data a user types by inserting into or updating the underlying database tables or views. There are three ways to process a form:
Creating an Automatic Row (DML) Processing Process
One common way to implement a form is to manually create an Automatic Row Processing (DML) process. This approach offers three advantages. First, you are not required to provide any SQL coding. Second, Oracle Application Express performs DML processing for you. Third, this process automatically performs lost update detection. Lost update detection ensures data integrity in applications where data can be accessed concurrently.
To implement this approach you need to:
-
Add items, define the Item Source Type as Database Column, and specify a case-sensitive column name.
-
Select the option Always overrides the cache value.
To create an Automatic Row Processing (DML) process:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition"
-
Access the Create Page Process Wizard:
-
Tree view - Under the appropriate location, right-click and click Create Process.
-
Component view - Under Processes, click the Create icon.
-
-
Under Processes, click the Create icon.
-
Select the process Data Manipulation.
-
Select the process category Automatic Row Processing (DML).
-
Specify the following process attributes:
-
In the Name field, enter a name to identify the process.
-
In the Sequence field, specify a sequence number.
-
From the Point list, select the appropriate processing point. In most instances, select Onload - After Header.
-
From the Type list, select Automated Row Processing (DML).
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
Creating a Process that Contains One or More Insert Statements
In this approach to form handling, you create one or more processes to handle insert, update, and delete actions. Instead of having the Application Express engine handling everything transparently, you are in complete control.
For example, suppose you have a form with three items:
-
P1_ID- A hidden item to store the primary key of the currently displayed row in a table. -
P1_FIRST_NAME- A text field for user input. -
P1_LAST_NAME- A text field for user input.
Assume also there are three buttons labeled Insert, Update, and Delete. Also assume you have a table T that contains the columns id, first_name, and last_name. The table has a trigger that automatically populates the ID column when there is no value supplied.
To process the insertion of a new row, you create a conditional process of type PL/SQL that executes when the user clicks the Insert button. For example:
BEGIN
INSERT INTO T ( first_name, last_name )
VALUES (:P1_FIRST_NAME, :P1_LAST_NAME);
END;
To process the updating of a row, you create another conditional process of type PL/SQL. For example:
BEGIN
UPDATE T
SET first_name = :P1_FIRST_NAME,
last_name = :P1_LAST_NAME
WHERE ID = :P1_ID;
END;
To process the deletion of a row, you create a conditional process that executes when the user clicks the Delete button. For example:
BEGIN
DELETE FROM T
WHERE ID = :P1_ID;
END;
Using a PL/SQL API to Process Form Values
For certain types of applications, it is appropriate to centralize all access to tables in a single or a few PL/SQL packages. If you created a package to handle DML operations, you can call procedures and functions within this package from an After Submit PL/SQL process to process insert, updates, and delete requests.
Populating Forms
Oracle Application Express populates a form either on load or when the Application Express engine renders the page. You can populate a form in the following ways:
-
Create a process and define the type as Automated Row Fetch.
-
Populate the form manually by referencing a hidden session state item.
To create an Automated Row Fetch process:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Create Page Process Wizard:
-
Tree view - Under the appropriate location, right-click and click Create Process.
-
Component view - Under Processes, click the Create icon.
-
-
Select the process type Data Manipulation.
-
Select the process category Automatic Row Fetch.
-
Specify the following process attributes:
-
In the Name field, enter a name to identify the process.
-
In the Sequence field, specify a sequence number.
-
From the Point list, select the appropriate processing point.
-
From the Type list, select Automated Row Fetch.
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
You can also populate a form manually by referencing a hidden session state item. For example, the following code in an Oracle Application Express process of type PL/SQL would set the values of ename and sal. The example also demonstrates how to manually populate a form by referencing a hidden session state item named P2_ID.
FOR C1 in (SELECT ename, sal
FROM emp WHERE ID=:P2_ID)
LOOP
:P2_ENAME := C1.ename;
:P2_SAL := C1.sal;
END LOOP;
In this example:
-
C1is an implicit cursor. -
The value of
P2_IDhas been set. -
The process point for this process would be set to execute (or fire) on or before Onload - Before Regions.
Validating User Input in Forms
You can use validations to check data a user enters before processing. Once you create a validation and the associated error message, you can associate it with a specific item. You can choose to have validation error messages display inline (that is, on the page where the validation is performed) or on a separate error page.
Creating an inline error message involves these steps:
-
Create a validation and specify error message text.
-
Associate the validation with a specific item.
Creating a Validation
To create a validation:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Create Validation Wizard:
-
Tree view - Under Page Processing, right-click Validating and click Create Validation.
-
Component view - Under Processes, click the Create icon.
-
-
For Level, select the validation level:
-
Item Level Validation
-
Tabular Form Validation
-
Page Level Validation
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
Note:
Validations cannot contain more than 3,950 characters.Associating a Validation with a Specific Item
To associate an item with a validation and specify error message text:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Navigate to the Edit Page Validations page:
-
Tree view - Right-click the validation name and click Edit.
-
Component view - Under Validations, select the validation item you want to associate.
The attributes page for the validation appears.
-
-
Scroll down to Error Message:
-
Error message display location - Verify the display location.
-
Associated Item - Select the item you want to associate with this validation.
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
About Error Message
Error message display location identifies where a validation error message displays. Validation error messages can display on an error page or inline within the existing page. Inline error messages can display in a notification area (defined as part of the page template) or within the field label.
To create a hard error that stops processes, including any remaining validations, you must display the error on an error page.
Creating Calendars
Application Builder includes a built-in wizard for generating a calendar with monthly, weekly, and daily views. Once you specify the table on which the calendar is based, you can create drill-down links to information stored in specific columns. Note that Oracle Application Express supports the creation of only one calendar per page.
About Creating Calendars
Application Builder supports two calendar types:
-
Easy Calendar creates a calendar based on schema, table, and columns you specify. The wizard prompts you to select a date column and display column.
-
SQL Calendar creates a calendar based on a SQL query you provide. The SQL SELECT statement you provide must include at least two columns: a date column and display column.
See Also:
"Calendar Display"Supported Calendar Substitution Strings
Application Builder supports a number of date format substitution strings. You can view a complete list of supported substitution strings on the Calendar Templates page.
To view a list of supported substitution strings for calendars:
-
Navigate to the appropriate calendar template.
-
View the Substitution Stings list on the right side of the page.
See Also:
"Managing Themes"Creating a New Calendar
How you create a calendar depends on if you are adding a calendar to an existing page or adding a calendar on a new page. When creating calendars remember:
-
You can only create one calendar for each page. The calendar includes daily, weekly, and monthly views.
-
The date column determines which days on the calendar will contain entries.
-
The display column defines a specific row that will display a calendar date.
Tip:
In Oracle Application Express release 3.1, the Create Calendar Wizard includes a new Display Type option. Standard submits the page along with the associated request. Partial Page Refresh only refreshes the Calendar region. Once the calendar is created, the display type cannot be changed. To change the display type, you must delete the calendar and then recreate it.Adding a Calendar to an Existing Page
Oracle Application Express supports the creation of one calendar per page.
To add a calendar to an existing page:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
On the Page Definition, create a new Calendar region:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, right-click Regions and select Create.
-
Component view - Under Region, click the Create icon.
-
-
Select Calendar and click Next.
-
Select the type of calendar you want to create and click Next:
-
Easy Calendar creates a calendar based on the date column and display column you specify.
-
SQL Calendar creates a calendar based on a SQL query you provide.
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
Adding a Calendar to a New Page
To create a calendar on a new page:
-
Navigate to the Workspace home page.
-
Click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Calendar and click Next.
-
Select the type of calendar you want to create and click Next:
-
Easy Calendar creates a calendar based on the date column and display column you specify.
-
SQL Calendar creates a calendar based on a SQL query you provide.
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
See Also:
"Editing Calendar Attributes"Editing a Calendar Title
The title that appears at the top of calendar corresponds to the region title.
To alter the region title:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Region Definition:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, double-click the region name.
-
Component view - Under Region, select the region name.
The Region Definition appears.
-
-
Under Identification, edit the Title attribute.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Editing Calendar Attributes
Once you create a calendar, you can alter the display by editing attributes on the Calendar Attributes page.
Note that to disable a view of a calendar, you must delete the Monthly, Weekly, or Daily buttons on the calendar page.
Accessing the Calendar Attributes Page
To access the Calendar Attributes page:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Calendar Attributes page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, double-click the region name.
-
Component view - Under Region, select the region name.
The Region Definition appears.
-
-
Click Calendar Attributes.
-
Edit the appropriate attributes. To learn more about a specific item on a page, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark.
-
Click Apply Changes.
About Navigation Alternatives
The Calendar Attribute page is divided into sections.
You can access these sections by scrolling down the page, or by clicking a navigation button at the top of the page. When you select a button at the top of the page, the selected section appears and all other sections are temporarily hidden. To view all sections of the page, click Show All.
About the Calendar Attributes Page
The topics that follow describe specific sections of the Calendar Attributes page. You can use these attribute to specify general calendar formatting, define the dates included in the calendar, or create a link on the column or a day in the calendar.
Calendar Display
Use Calendar Display to specify a calendar template, date columns, and general calendar formatting. Table 8-8 describes Calendar Display attributes.
Table 8-8 Calendar Display Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Calendar Template |
Determines what template is used when the Application Express engine renders a calendar. |
|
Date Column |
Defines the column from the table or query containing the dates to be placed on the calendar. |
|
Date Item |
Defines the item which holds the date on which the calendar is based |
|
End Date Item |
Specifies the item which holds the end date on which the calendar of type Custom is based |
|
Calendar Type Item |
Specifies the item which holds the calendar type. |
|
Display Type |
Defines the display type. Options include:
If the Display Type is Column, use the Display Column attribute to select the column to display in the day cell of the monthly calendar. If the Display Type is Custom, in Column Format enter a custom column format using HTML expressions and supported substitution strings. |
|
Display Column |
Defines a specific row that displays on a calendar date. |
|
Column Format |
Enter HTML expressions to be shown in this column. Use #EMPLOYEE_NAME# This following example demonstrates how to display images in a column. <img src="#IMAGE_NAME#"> |
Display Attributes
Use Display Attributes to define the dates that are included in the calendar. Table 8-9 describes Display attributes.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
Begin at Start of Interval |
Determines when the calendar should start. Selecting this option creates a calendar that spans an entire interval (such as a month). For example:
|
|
Item Containing Start Date Item Containing End Date |
These attributes define which items hold the calendar start date and end date. You can use these attributes to create calendars that span multiple months at a time. Note that the format of the date of either item must be
|
|
Start of Week for Monthly Calendar |
Determines the day on which the calendar starts for the monthly view. |
|
Start Day for Weekly Calendar |
Determines the day on which the calendar starts for the weekly view. |
|
End Day for Weekly Calendar |
Determines the day on which the calendar ends for the weekly view. Time Format determines if the time displays in a 12-hour or 24-hour format. Start Time and End Time determine the start and end times to display in the weekly and daily calendar views. |
|
Time Format |
Determines if the time displays in a 12-hour or 24-hour format. |
|
Start Time |
Determines the start times to display in the weekly and daily calendar views. |
|
End Time |
Determines the end times to display in the weekly and daily calendar views. |
Column Link
Use Column link to create a link on the column in the calendar.
To create a column link to another page:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Calendar Attributes page.
-
Scroll down to Column Link.
-
From Target is a, select Page in this Application.
-
In Page, specify the target page number. To reset the pagination for this page, select reset pagination for this page.
-
In Request, specify the request to be used.
-
In Clear Cache, specify the pages (that is, the page numbers) on which to clear cache. Specify multiple pages by listing the page numbers in a comma-delimited list.
You can set session state (that is, give a listed item a value) using the next two attributes: the Set these items attribute and the With these values attribute.
-
To set session state:
-
Set these items - Enter a comma-delimited list of item names for which you would like to set session state.
-
With these values - Enter a comma-delimited list of values for the items specified in the previous step.
You can specify static values or substitution syntax (for example,
&APP_ITEM_NAME.). Note that item values passed tof?p=in the URL cannot contain a colon (:). Additionally, item values cannot contain commas unless you enclose the entire value in backslashes (for example,\1234,56\).
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
To create a column link to a URL:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Calendar Attributes page.
-
Scroll down to Column Link.
-
From Target is a, select URL.
-
In URL, enter the appropriate address.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Day Link
Use Day link to create a link on a day in the calendar. This attribute creates a link on an actual number (or day) on the calendar.
To create a day link to another page:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Calendar Attributes page.
-
Scroll down to Day Link.
-
From Target is a, select Page in this Application.
-
In Page, specify the target page number.
To reset the pagination for this page, select reset pagination for this page.
-
In Request, specify the request to be used.
-
In Clear Cache, specify the pages (that is, the page numbers) on which to clear cache. Specify multiple pages by listing the page numbers in a comma-delimited list.
You can set session state (that is, give a listed item a value) using the next two attributes: Set these items and With these values.
-
To set session state:
-
Set these items - Enter a comma-delimited list of item names for which you would like to set session state.
-
With these values - Enter a comma-delimited list of values for the items specified in the previous step.
You can specify static values or substitution syntax (for example,
&APP_ITEM_NAME.). Note that item values passed tof?p=in the URL cannot contain a colon (:). Additionally, item values cannot contain commas unless you enclose the entire value in backslashes (for example,\1234,56\).
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
To create a day link to a URL:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Calendar Attributes page.
-
Scroll down to Day Link.
-
From Target is a, select URL.
-
In URL, enter the appropriate address.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Upgrading a Calendar Created in a Previous Releases
By default, calendars you create in Oracle Application Express 3.0 include daily, weekly, and monthly views. To update calendars created in a previous release to include these views, you can either:
-
Create a calendar:
-
Create a calendar page and integrate the SQL query from your previous calendar.
-
Replace the previous calendar page with the new one in your application.
-
-
Upgrade the theme:
-
Change the identification number of the existing theme. See "Changing a Theme Identification Number".
-
Recreate the theme. See "Creating a Theme".
-
Apply the new theme to your application. See "Switching the Active Theme".
-
Converting an Easy Calendar to a SQL Calendar
Creating an Easy Calendar is the simplest way to create a calendar. However, if you find the resulting calendar does not meet your needs, you can quickly convert it to a SQL Calendar.
To convert an Easy Calendar to a SQL Calendar:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Regions, click Calendar next to the region name.
The Calendar Attributes page appears.
-
On the Tasks list, click Convert to SQL Based calendar.
Converting an Easy Calendar to a SQL Calendar adds a Region Source section to the Region Definition. The Region Source contains the original SQL query that creates the calendar. By accessing the Region Source, you can edit the query to meet your needs.
Creating Maps
Application Builder includes built-in wizards for generating Flash maps. How you create a flash map depends upon whether you are adding the map to an existing page, or adding a map on a new page.
About Flash Map Support
Flash map support in Oracle Application Express is based on the AnyChart AnyMap Interactive Maps Component. AnyMap is a flexible Macromedia Flash-based solution that enables developers to visualize geographical related data. Flash maps are rendered by a browser and require Flash Player 9 or later. For more information about AnyChart, go to
http://www.anychart.com
AnyChart stores map data in files with a *.amap extension, and supports 300 map files for the United States of America, Europe, Asia, Europe, Africa, Oceania, North America, and South America. To render a desired map, you select the map source in the wizard (for example, Germany) and the map XML automatically references the desired map source .amap file, germany.amap. To browse through the available maps, see "Map Reference" in AnyChart User's Guide:
http://anychart.com/products/anychart/docs/users-guide/
Adding a Flash Map to an Existing Page
To add a flash map to an existing page.
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
On the Page Definition, create a new region:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, right-click Regions and select Create.
-
Component view - Under Region, click the Create icon.
-
-
Select Map and click Next.
-
For Map Type, select a map type (for example, Europe), and click Next.
-
For Map Source, a Tree lists the map source files for the selected Map Type. Click the Map Source you wish to use (for example, Denmark).
-
For Display Attributes:
-
Specify the following:
-
Title
-
Region Template
-
Parent Region
-
Display Point
-
Sequence
-
Column
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Display Attributes, select the appropriate map attributes and click Next.
To learn more about a specific attribute, click the item label. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
For Source:
-
Specify a query by either:
-
Entering a SQL query in the field provided. See "About Creating SQL Queries for Maps".
-
Clicking the Build Query button. When the Build Chart Query Wizard appears, follow the on-screen instructions.
-
-
Specify relevant attributes. To view map reference information associated with your selected Map Source, expand the Map Region Information region at the bottom on of the page.
In order to associate data with geographical locations, you must incorporate information from the Region Name or Region ID columns into the Map query. See "About Creating SQL Queries for Maps".
-
-
Click Create Region.
Adding Flash Maps to a New Page
To create an flash chart on a new page:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Map and click Next.
-
For Map Type, select a map type (for example, Europe), and click Next.
-
For Map Source, a Tree lists the map source files for the selected Map Type. Click the Map Source you wish to use (for example, Denmark).
-
For Page Attributes:
-
Specify the following:
-
Page Number
-
Page Name
-
Region Template
-
Region Name
-
Breadcrumb
To learn more, click the item label. When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
Specify whether to include tabs and click Next.
-
For Map Attributes, select the appropriate attributes and click Next.
To learn more about a specific attribute, click the item label. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
For Query:
-
Specify a query by either:
-
Entering a SQL query in the field provided. See "About Creating SQL Queries for Maps".
-
Clicking the Build Query button. When the Build Chart Query Wizard appears, follow the on-screen instructions.
-
-
Specify relevant attributes. To view map reference information associated with your selected Map Source, expand the Map Region Information region at the bottom on of the page.
In order to associate data with geographical locations, you must incorporate information from the Region Name or Region ID columns into the Map query. See "About Creating SQL Queries for Maps".
-
Click Next.
-
-
Click Finish.
About Creating SQL Queries for Maps
You define a map in Application Builder using a wizard. For most chart wizards, you select a map type, map source, and provide a SQL query using the following syntax:
SELECT link, label, value FROM ...
Where:
-
linkis a URL. -
labelis the text that identifies the point on the map that you wish to associate data with. The Region ID or Region Name of the map should be used as the label. -
valueis the numeric column that defines the data to be associated with a point on the map.
Consider the following example when creating a new page:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Map and click Next.
-
For Map Type, select United States of America and click Next.
-
For Map Source, expand Country Maps and select States.
Description of the illustration maps_source1.gif
-
For Page Attributes specify the appropriate attributes and click Next.
-
Specify whether to include tabs and click Next.
-
For Map Attributes, select the appropriate attributes and click Next.
The Query page appears.
-
Expand and review the Map Region Information region at the bottom of the page.
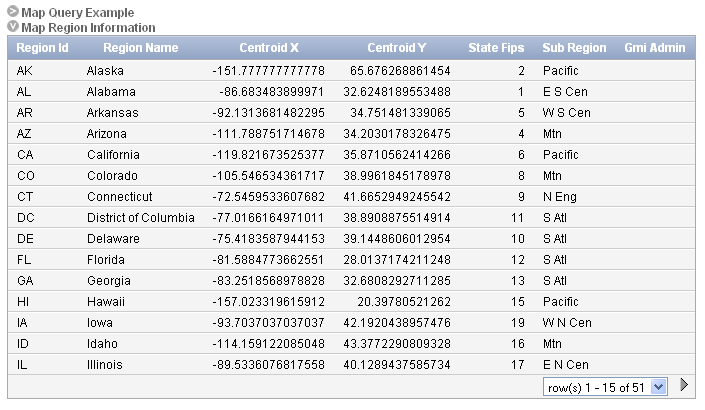
Description of the illustration maps_source2.gif
-
For Query,
-
Specify a query by either:
-
Entering a SQL query in the field provided. See "About Creating SQL Queries for Maps".
-
Clicking the Build Query button. When the Build Chart Query Wizard appears, follow the on-screen instructions.
-
-
When you create your query, you must incorporate the region name information. The following example includes information for Florida and Alaska:
SELECT null link, region label, value Populations FROM ( SELECT 'Florida' region, 18328340 value FROM dual UNION ALL SELECT 'Alaska' region, 686293 value FROM dual)
Note:
If you are referencing geographical information stored in a database table, the information must correspond with the Region information associated with the map source. For more information, see AnyChart User's Guide:http://anychart.com/products/anymap/docs/
-
Click Next.
-
-
Click Finish.
Editing Flash Map Attributes
Once you create a map, you can alter its display by editing map attributes on the Map Attributes page.
To access the Map Attributes page:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Chart Attributes page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, double-click the region name.
-
Component view - Under Region, select the region name.
The Region Definition appears.
-
-
Click Map Attributes.
-
Edit the appropriate attributes.
To learn more about a specific item on a page, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
Click Apply Changes.
About Navigation Alternatives
The Map Attributes page is divided into sections. You can access these sections by scrolling down the page, or by clicking a navigation button at the top of the page. When you select a button at the top of the page, the selected section appears and all other sections are temporarily hidden. To view all sections of the page, click Show All.
Using Custom XML with Flash Maps
There are additional map settings that cannot be controlled using the standard attributes on the Map Attributes page. To further control the look and feel of a chart, you can use custom XML.
To use custom XML:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Map Attributes page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, double-click the region name.
-
Component view - Under Region, select the region name.
The Region Definition appears.
-
-
Click Map Attributes.
-
Scroll down to Map XML.
-
From Use Custom XML, select Yes.
Note that when you select to use custom XML, regions with attributes that no longer appear are hidden. To display these regions again, select No for Use Custom XML.
-
Edit the XML.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Tip:
For more information on supported XML format for maps, see the Online Map XML Reference at:http://www.anychart.com/
Enabling Asynchronous Updates
You can create Flash maps that monitor information by enabling the Asynchronous Update attribute on the Map Attributes page. Enabling this attribute updates the map to reflect changes in the underlying data within a specified time interval.
To enable asynchronous updates:
-
Create a Flash map. See "About Flash Map Support" and "About Flash Map Support".
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Map Attributes page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, double-click the region name.
-
Component view - Under Region, select the region name.
The Region Definition appears.
-
-
Click Map Attributes.
-
Scroll down to Refresh.
-
From Asynchronous Update, select Yes.
-
In Update Interval (Seconds), enter the interval in seconds between map updates. For optimal performance, select an interval that is greater than 2 seconds.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Creating Charts
Application Builder includes built-in wizards for generating HTML and Flash charts, and supports the editing of SVG charts. Oracle Application Express supports only those three types of graphical charts.
About Creating SQL Queries for Charts
You define a chart in Application Builder using a wizard. For most chart wizards, you select a chart type and provide a SQL query using the following syntax:
SELECT link, label, value FROM ...
Where:
-
linkis a URL. -
labelis the text that displays in the bar. -
valueis the numeric column that defines the bar size.
For example:
SELECT null, last_name, salary FROM employees WHERE DEPARTMENT_ID = :P101_DEPARTMENT_ID
To create a dial chart, select a dial chart type and provide a SQL query using the following syntax:
SELECT value , maximum_value [ ,low_value [ ,high_value] ] FROM ...
Where:
-
valueis the starting point on the dial. -
maximum_valueis the possible highest point on the dial. -
low_valueandhigh_valueare the historical low and high values.
For example:
SELECT dbms_random.value(500, 1200), 1300, dbms_random.value(100, 200) FROM DUAL
Multiple Series Syntax (Flash only)
For column charts and line Flash charts, you can define multiple series in one SQL query. The series names for these chart types are derived from the corresponding column aliases in the query. To define a multiple series Flash chart, use the following syntax:
SELECT link, label, series_1_value [, series_2_value [, ...]] FROM ...
Range Chart Syntax (Flash only)
Range charts require two values for each bar. To create a range chart, create a Flash chart and provide a SQL query using the following syntax:
SELECT link, label, low_value, high_value FROM ...
Scatter Chart Syntax (Flash only)
Scatter charts require an x value and y value for each point. To create a range chart, create a Flash chart and provide a SQL query using the following syntax:
SELECT link, label, x_value, y_value FROM ...
Candlestick Chart Syntax (Flash only)
Candlestick charts require open, low, high, and close values for each candlestick. To create a candlestick chart, create a Flash chart and provide a SQL query using the following syntax:
SELECT link, label, open, low, high, close FROM ...
Project Gantt charts require a task name, task id, parent task id, actual start date, actual_end_date, and progress value for each task. Two optional values for planned start date and planned end date can also be used. To create a Project gantt chart, create a Flash chart and provide a SQL query using one of the following syntax:
SELECT link, task_name, task_id, parent_task_id, actual_start_date, actual_end_date, progress FROM ...
Resource Gantt charts require a resource id, resource name, parent resource id, actual start date, and actual end date value for each task. To create a Resource gantt chart, create a Flash chart and provide a SQL query using the following syntax:
SELECT link, resource_id, resource_name, resource_parent_id, actual_start_date, actual_end_date FROM ...
Creating an HTML Chart
How you create a chart depends upon whether you are adding the chart to an existing page, or adding a chart on a page. This chart type creates a bar chart showing one data series with each data point represented by a bar.
Adding an HTML Chart to an Existing Page
To add an HTML chart to an existing page:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
On the Page Definition, create a new region:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, right-click Regions and select Create.
-
Component view - Under Region, click the Create icon.
-
-
Select Chart and click Next.
-
For Region, select HTML Chart and click Next.
-
For Display Attributes:
-
Specify the following:
-
Title
-
Region Template
-
Parent Region
-
Display Point
-
Sequence
-
Column
To learn more, click the item label. When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Source:
-
Specify a query by either:
-
Entering a SQL query in the field provided. See "About Creating SQL Queries for Charts".
-
Clicking the Build Query button. When the Build Chart Query Wizard appears, follow the on-screen instructions.
-
-
Specify relevant chart attributes. To learn more, click the item label.
-
-
Click Create Region.
Adding an HTML Chart to a New Page
To create an HTML chart on a new page:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Chart and click Next.
-
For Region, select HTML Chart and click Next.
-
For Page Attributes:
-
Specify the following:
-
Title
-
Region Template
-
Parent Region
-
Display Point
-
Sequence
-
Column
To learn more, click the item label. When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
Specify whether to include tabs and click Next.
-
For Chart Definition:
-
Specify a query by either:
-
Entering a SQL query in the field provided. See "About Creating SQL Queries for Charts".
-
Clicking the Build Query button. When the Build Chart Query Wizard appears, follow the on-screen instructions.
-
-
Specify relevant chart attributes. To learn more, click the item label.
-
Click Next.
-
-
Click Finish.
Creating a Flash Chart
Flash chart support in Oracle Application Express is based on the Anychart Flash Chart Component.
About Flash Charts
Flash chart support in Oracle Application Express is based on the Anychart Flash Chart Component. Anychart is a flexible Macromedia Flash-based solution that enables developers to create animated, compact, interactive flash charts. Flash charts are rendered by a browser and require Flash player 9 or later.
http://www.anychart.com
Adding a Flash Chart to an Existing Page
To add a flash chart to an existing page:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
On the Page Definition, create a new region:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, right-click Regions and select Create.
-
Component view - Under Region, click the Create icon.
-
-
Select Chart and click Next.
-
Select Flash Chart and click Next.
-
For Chart Type:
-
Select a chart style (for example, Column) and click Next.
-
Select a specific chart type (for example, 3D Column) and click Next.
-
-
For Display Attributes
-
Specify the following:
-
Title
-
Region Template
-
Parent Region
-
Display Point
-
Sequence
-
Column
To learn more, click the item label. When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Display Attributes, select the appropriate attributes and click Next.
To learn more about a specific attribute, click the item label.
-
For Source:
-
Specify a query by either:
-
Entering a SQL query in the field provided. See "About Creating SQL Queries for Charts".
-
Clicking the Build Query button. When the Build Chart Query Wizard appears, follow the on-screen instructions.
-
-
Specify relevant chart attributes. To learn more, click the item label.
-
-
Click Create Region.
Adding a Flash Chart to a New Page
To create a flash chart on a new page:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page.
-
Select Chart and click Next.
-
Select Flash Chart and click Next.
-
For Chart Type:
-
Select a chart style (for example, Column) and click Next.
-
Select a specific chart type (for example, 3D Column) and click Next.
-
-
For Display Attributes
-
Specify the following:
-
Page Number
-
Page Name
-
Region Template
-
Region Name
-
Breadcrumb
To learn more, click the item label. When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
Specify whether to include tabs and click Next.
-
For Display Attributes, select the appropriate attributes and click Next.
To learn more about a specific attribute, click the item label.
-
For Query:
-
Specify a query by either:
-
Entering a SQL query in the field provided. See "About Creating SQL Queries for Charts".
-
Clicking the Build Query button. When the Build Chart Query Wizard appears, follow the on-screen instructions.
-
-
Specify the remaining attributes. To learn more, click the item label.
-
Click Next.
-
-
Click Finish.
Upgrading all Flash 3 Charts to Flash 5
To upgrade all Flash 3 charts in an application to Flash 5:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
The Application Builder home page appears.
-
Select an application.
The Application home page appears.
-
Click Utilities and then click Upgrade Application.
The Upgrade Application Summary report appears.
-
For Upgrade Flash Charts to Flash Chart 5, click the number of candidate objects.
-
Select the objects to upgrade and click Upgrade.
Upgrading a Flash 3 Chart to Flash 5
To upgrade a Flash 3 charts Flash 5:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Chart Attributes page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, double-click the region name.
-
Component view - Under Region, select the region name.
The Region Definition appears.
-
-
From the Tasks list, click Upgrade to New Flash Chart.
-
Click Upgrade.
About SVG Charts
Previous releases of Oracle Application Express supported the creation of SVG charts. Although existing SVG charts are still supported, Oracle Application Express no longer supports the creation of new SVG charts.
About Upgrading SVG Charts to Flash
You can automatically upgrade single or multiple SVG charts to Flash.
About SVG Chart Upgrade Restrictions
Note that SVG charts can be upgraded with the following restrictions:
-
Only number formats defined in axis format strings will be migrated. Date and time formats will be ignored.
-
Number format elements containing the following will be migrated:
0,9,D,G,, (comma),. (period),$,C,L,FM
-
The label for each series in the Flash chart will be derived from each series' column alias. This differs from SVG charts, where the label for each series was derived from the Series Name attribute.
-
Flash Dial charts display actual values instead of percentages.
-
In SVG charts, only the labels for the first series are used for the x-axis. In Flash charts, this has been enhanced so that all data appears, even if the data's label does not occur in the first series.
Upgrading a SVG Chart to Flash
To upgrade a SVG chart to Flash:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Chart Attributes page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, double-click the region name.
-
Component view - Under Region, select the region name.
The Region Definition appears.
-
-
From the Tasks list, click Upgrade to New Flash Chart.
-
Click Upgrade.
Upgrading all SVG Charts in a Application to Flash
To upgrade all SVG Charts to Flash charts:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
The Application Builder home page appears.
-
Select an application.
The Application home page appears.
-
Click Utilities and then click Upgrade Application.
The Upgrade Application Summary report appears.
-
For Upgrade SVG Charts to Flash Chart 5, click the number of candidate objects.
-
Select the objects to upgrade and click Upgrade.
Understanding SVG Chart Cascading Style Sheet Classes
When you create a SVG chart, Oracle Application Express renders it based on cascading style sheet (CSS) classes associated with the current theme. You can change the appearance of a chart by referencing another CSS or by overriding individual classes in the CSS section of the Edit Attributes page
The following sample contains the CSS classes for the dial chart in Sample Application. This example contains all the available CSS classes. Class names appear in boldface.
text{font-family:Verdana, Geneva, Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;fill:#000000;} tspan{font-family:Verdana, Geneva, Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;fill:#000000;} text.title{font-weight:bold;font-size:14;fill:#000000;} text.moredatafound{font-size:12;} rect.legend{fill:#EEEEEE;stroke:#000000;stroke-width:1;} text.legend{font-size:10;} #background{fill:#FFFFFF;stroke:none;} rect.chartholderbackground{fill:#ffffff;stroke:#000000;stroke-width:1;} #timestamp{text-anchor:start;font-size:9;} text.tic{stroke:none;fill:#000000;font-size:12} line.tic{stroke:#000000;stroke-width:1px;fill:none;} #dial{stroke:#336699;stroke-width:2px;fill:#336699;fill-opacity:.5;} #dial.alert{fill:#FF0000;fill-opacity:.5;} #dialbackground{stroke:#000000;stroke-width:none;fill:none;filter:url(#MyFilter);} #dialcenter{stroke:none;fill:#111111;filter:url(#MyFilter);} #dialbackground-border{stroke:#DDDDDD;stroke-width:2px;fill:none;filter:url (#MyFilter);}#low{stroke-width:3;stroke:#336699;} #high{stroke-width:3;stroke:#FF0000;} #XAxisTitle{letter-spacing:2;kerning:auto;font-size:14;fill:#000000;text-anchor:middle;} #YAxisTitle{letter-spacing:2;kerning:auto;font-size:14;fill:#000000;text-anchor:middle;writing-mode:tb;} .XAxisValue{font-size:8;fill:#000000;} .YAxisValue{font-size:8;fill:#000000;text-anchor:end;} .nodatafound{stroke:#000000;stroke-width:1;font-size:12;} .AxisLine{stroke:#000000;stroke-width:2;fill:#FFFFFF;} .GridLine{stroke:#000000;stroke-width:0.3;stroke-dasharray:2,4;fill:none;} g.dataholder rect{stroke:#000000;stroke-width:0.5;} .legenditem rect{stroke:#000000;stroke-width:0.5;}
Table 8-10 describes all supported CSS classes. Note that certain classes only apply to specific chart types.
Table 8-10 Available SVG Chart CSS Classes
| Class | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Defines the appearance of text that displays in a chart. |
|
|
Defines the appearance of text that displays in a chart. |
|
|
Overrides the default chart text. Use this class for title text. |
|
|
Defines the appearance of more datafound text. |
|
|
Creates the rectangular box that holds the chart legend. To remove the legend border, change
rect.legend{fill:#CCCC99;stroke:none;}
|
|
|
Defines the text that appears in the chart legend. |
|
|
Creates the entire background for the SVG plug-in. For a solid white background with no border, change
#background{fill:#FFFFFF;stroke:#FFFFFF;stroke-width:2;}
|
|
|
Not applicable to pie and dial charts. Creates the background of the rectangle that holds the chart data. For a clear background, change rect.chartholderbackground(display:none;) |
|
|
Only applicable if the Asynchronous Update chart attribute is set to Yes. Controls the appearance of the update timestamp test. To disable the display of the timestamp, use defines
"#timestamp{display:none;}"
See Also: "Enabling Asynchronous Updates" |
|
|
Dial charts only. Defines the numbers on a dial chart. |
|
|
Dial charts only. Defines the graduation mark that displays directly beneath the number on a dial chart. |
|
|
Dial charts only. Defines the value that displays on the dial chart. |
|
|
Dial charts only. Defines a value (called an alert value) that renders in a dial chart using a different display. |
|
|
Dial charts only. Creates the background of a dial chart. |
|
|
Dial charts only. Creates the center of the dial on a dial chart. |
|
|
Dial charts only. Works with |
|
|
Dial charts only. Defines the historical low watermark of the data being displayed on a chart. |
|
|
Dial charts only. Defines the historical high watermark of the data being displayed on a chart. |
|
|
Defines the title that appears on the x-axis |
|
|
Defines the title that appears on the y-axis. |
|
|
Defines the value that appears on the x-axis. |
|
|
Defines the value that appears on the y-axis. |
|
|
Similar to the axis value. |
|
|
Defines the text element that displays if no information is available. |
|
|
Indicates zero on charts that have negative values. |
|
. |
Creates the horizontal and vertical lines on the chart. |
|
|
Applies a blanket style to all data that displays in the chart. |
|
|
Applies a blanket style to all rectangular items in the legend. |
Referencing a Custom SVG Chart Cascading Style Sheet
You can reference a custom cascading style sheet for a chart using the CSS section of the Chart Attributes page. When you reference an external CSS, you can reference it entirely or simply override specific styles.
To reference a custom chart CSS:
-
Upload the CSS to Application Builder. See "Uploading Cascading Style Sheets".
-
Navigate to the Page Definition containing the chart. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Regions, click Chart next to the region name.
The Chart Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to the CSS section.
-
From Use Custom CSS, select Yes.
-
To reference an external CSS exclusively:
-
In Custom CSS, Link, enter a link to a custom CSS. For example:
#IMAGE_PREFIX#themes/theme_4/svg.css
-
Specify that the CSS should be used exclusively. In Custom CSS, Inline enter the following:
/**/
-
-
To reference a custom CSS and override specific styles:
-
In Custom CSS, Link, enter a link to a custom style sheet. For example:
#IMAGE_PREFIX#themes/theme_4/svg.css
-
In Custom CSS, Inline, enter the custom CSS styles you want to override.
-
Specifying Custom CSS Styles Inline for SVG Charts
You can override specific styles within the default CSS, using the Custom CSS, Inline attribute on the Chart Attributes page.
To override specific styles within the default CSS:
-
Create a chart. See "About SVG Charts".
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Regions, click Chart next to the region name.
The Chart Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to CSS.
-
From Use Custom CSS, select Yes.
-
In Custom CSS, Inline, enter the custom CSS styles you want to override.
Displaying SVG Charts in Other Languages
To display an SVG chart in another language, you edit the text and tspan classes to reflect the correct language.
To display an SVG chart in another language:
-
Navigate to the Chart Attributes page. See "Editing Chart Attributes".
-
Scroll down to CSS.
-
From Use Custom CSS, select Yes.
-
In Custom CSS, Inline, edit the
textandtspanclasses to reflect the correct language. The following example demonstrates how to change a chart to Korean:text{font-family:Batang;fill:#000000;} tspan{font-family:Batang;fill:#000000;}
Editing Chart Attributes
Once you have created a chart, you can alter its display by editing chart attributes on the Chart Attributes page.
To access the Chart Attributes page:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Chart Attributes page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, double-click the region name.
-
Component view - Under Region, select the region name.
The Region Definition appears.
-
-
Click Chart Attributes.
-
Edit the appropriate attributes.
-
To learn more about a specific item on a page, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
Click Apply Changes.
Tip:
Removing the chart title of an SVG chart (that is, the Chart Title attribute) may negatively impact the location and display of the chart legend.About Navigation Alternatives
The Chart Attributes page is divided into sections. You can access these sections by scrolling down the page, or by clicking a navigation button at the top of the page. When you select a button at the top of the page, the selected section appears and all other sections are temporarily hidden. To view all sections of the page, click Show All.
Using Custom XML with Flash Charts
There are additional chart settings that cannot be controlled using the standard attributes on the Chart attributes page. To further control the look and feel of a chart, you can use custom XML.
To use custom XML:
-
Navigate to the Chart Attributes page:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Regions, click the chart type, Flash Chart.
The Chart Attributes page appears.
-
-
Scroll down to Chart XML.
-
From Use Custom XML, select Yes.
Note that when you select to use custom XML, regions with attributes that no longer apply are hidden. To display these regions again, select No for Use Custom XML.
-
Edit the XML.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Tip:
For more information on supported XML format for charts, see the Online XML Reference at:http://www.anychart.com
Enabling Asynchronous Updates
SVG and Flash charts can monitor information by enabling the Asynchronous Update attribute on the Chart attributes page. Enabling this attribute updates the chart to reflect changes in the underlying data within a specified time interval.
To enable asynchronous updates:
-
Edit an existing SVG or Flash chart. See "About SVG Charts".
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Regions, click Chart next to the region name.
The Chart Attributes page appears.
-
Scroll down to Refresh.
-
From Asynchronous Update, select Yes.
-
In Update Interval (Seconds), enter the interval in seconds between chart updates. For optimal performance, select an interval that is greater than 2 seconds.
When Asynchronous Update is enabled for an SVG chart, a timestamp displays on the chart indicating the last update.
To disable the Asynchronous Update timestamp:
-
Navigate to the Chart Attributes page.
-
Locate the CSS section.
-
From Use Custom CSS, select Yes.
-
In Custom CSS, Inline edit
#timestampas follows:#timestamp{display:none;}
Creating Buttons
As you design your application, you can use buttons to direct users to a specific page or URL, or to post or process information (for example, by creating Create, Cancel, Next, Previous, or Delete buttons).
Buttons can perform two different types of actions. A button can submit a page and then redirect to a URL. Alternately, a button can branch to a URL without submitting the page, such as for a Cancel button.
Creating a Button Using a Wizard
You create a button by running the Create Button Wizard from the Page Definition. Each button resides in a region. A region is an area on a page that serves as a container for content. How you create a button depends upon whether the Page Definition is in tree or component view. To learn more, see "About Tree and Component View".
Creating a Button in Component View
To create a button in Component view:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
If necessary, create region. See "Understanding Regions".
-
Under Buttons, click the Create icon.
-
Select a region to contain the button and click Next.
-
Select a position for the button and click Next:
-
Create a button in a region position - Select this option to place the button in a region position. A region position is a position defined by a region template.
-
Create a button displayed among this region's items - Select this option to display the button within or between page items (for example, to add a button directly to the right of a form field).
-
-
If you select Create a button in a region position:
-
For Button Attributes:
-
Button Name - Enter a name for this button. Note that the button name becomes the page request value.
-
Label - Enter a label to be displayed for the button.
-
Button Style - Select HTML Button, Image, or Template Based Button
If the button is an image, you will need to supply an image name. If the button is template controlled, you will need select a template name.
-
Button Template - Define which template controls the display of the button. Button templates are defined on the templates page. You must have at least one button template defined to use button templates. If you wish to no longer use a button template, change the button template to the
NULL. -
Button Attributes - Text entered is added to the HTML element definition. The following example sets the class of a text button:
class="myclass"
For buttons based on templates your template will need to include the
#BUTTON_ATTRIBUTES#substitution string. You can use this to control tab stops. For example:tabindex="3"
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Display Properties, select a position, sequence, and alignment and click Next.
-
For Action When Clicked:
-
Action - Select the action to be performed when button is clicked.
-
Execute Validations - Select Yes or No. See item Help for more details.
-
-
-
If you select Create a button displayed among this region's items:
-
Button Name - Enter a button name.
-
Sequence - Enter the sequence for this button. The sequence determines the order of evaluation amongst the other items in this region.
-
Show - Select Beginning on New Line or Beginning on New Field. See item Help for more details.
-
Label - Enter a label for this button. This will become the HTML alt tag if the button is an image.
-
Request - Enter a
Requestvalue to be associated with this button. When the button is pressed the page will be submitted and the page request will be set to this value. -
Execute Validations - Select Yes or No. See item Help for more details.
-
Button Style - Specify the button style.
-
Image Name - Enter a optional button image name. The button image should be just the image file name, no prefix. The image prefix will be prepended to the image name. This application currently has an image prefix of "
/i/". -
Image Attributes - Enter button image attributes if you have entered a button image name. The button image attributes are not required however identifying the height and width will allow browsers to paint the page faster. For example:
width=16 height=14
-
-
Click Create Button.
Creating a Button in Tree View
To create a button in Tree view, you select a region and then one of two options:
-
Create Region Button displays a button in a region position (for example, to add a button directly to the right of a form field).
-
Create Button displays a button within or between button items (for example, to place a button after a page item.
Creating a Region Button
To create a region button in Tree view:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
If necessary, create region. See "Understanding Regions".
-
Right-click the region to contain the button and select Create Region Button.
-
For Button Attributes, specify the following:
-
Button Name - Enter a name for this button. Note that the button name becomes the page request value.
-
Label - Enter a label to be displayed for the button.
-
Button Style - Select HTML Button, Image, or Template Based Button
If the button is an image, you will need to supply an image name. If the button is template controlled, you will need select a template name.
-
Button Attributes - Text entered is added to the HTML element definition. The following example sets the class of a text button:
class="myclass"
For buttons based on templates your template will need to include the
#BUTTON_ATTRIBUTES#substitution string. You can use this to control tab stops. For example:tabindex="3"
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Display Properties, specify the following:
-
Position - Identifies the button position.
-
Sequence - Specify the sequence for this component. The sequence determines the order of evaluation.
-
Button Style - Select HTML Button, Image, or Template Based Button
If the button is an image, you will need to supply an image name. If the button is template controlled, you will need select a template name.
-
Alignment - Choose the button alignment.
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Action When Clicked, specify the following:
-
Action - Select action to be performed when button is clicked.
-
Execute Validations - Select Yes or No. See item Help for more details.
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Conditional Display, select a condition type from the list that must be met in order for this component to be rendered processed.
-
Click Create Button.
Creating a Button Among Region Items
To create a button that displays within or between button items:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
If necessary, create a region. See "Understanding Regions".
-
Click the region to contain the button, right-click and select Create Button.
-
For the button attributes, specify the following:
-
Button Name - Enter a button name.
-
Sequence - Enter the sequence for this button. The sequence determines the order of evaluation amongst the other items in this region.
-
Show - Select Beginning on New Line or Beginning on New Field. See item Help for more details.
-
Label - Enter a label for this button. This will become the HTML alt tag if the button is an image.
-
Request - Enter a
Requestvalue to be associated with this button. When the button is pressed the page will be submitted and the page request will be set to this value. -
Execute Validations - Select Yes or No. See item Help for more details.
-
Button Style - Specify the button style.
-
Image Name - Enter a optional button image name. The button image should be just the image file name, no prefix. The image prefix will be prepended to the image name. This application currently has an image prefix of "
/i/". -
Image Attributes - Enter button image attributes if you have entered a button image name. The button image attributes are not required however identifying the height and width will allow browsers to paint the page faster. For example:
width=16 height=14
-
-
Click Create Button.
Creating Multiple Buttons in Component View
In Component view, you can create multiple buttons within the same region at once using the Create Multiple Buttons Wizard.
To create multiple buttons at once:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition in Component view. See "Switching Between Tree and Component View".
-
If necessary, create an HTML region. See "Understanding Regions".
-
In Component view, locate the Buttons section and click the Create icon.
The Create Button wizard appears.Create icon.
-
From the Tasks list, click Create Multiple Buttons.
The Create Multiple Button Wizard appears.
-
From Place Buttons in Region, select the region to contain the buttons.
-
From Template, select a template.
-
In HTML Attributes, specify HTML attributes for these buttons. This text will be added to the HTML element definition. For example, you could set the class of a text button as follows:
class="myclass"
-
To quickly populate the remaining fields, make a selection from the Quick Button list on the right side of the page.
-
Click Create Buttons.
Editing Buttons
When you want to edit a button, you start from the Buttons section on the Page Definition. You can edit the attributes of a button, edit multiple buttons at once, or change a button position within a region.
Editing Button Attributes
You can edit button attributes on the Edit Pages Buttons page.
To edit attributes for an existing button:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Edit Page Buttons page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, double-click the button name.
-
Component view - Under Button, select the button name.
The Edit Page Buttons page appears.
-
-
To learn more about a specific item on a page, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
Click Apply Changes.
About Execute Validations
The Execute Validations attribute controls the execution of validations when a page is submitted. Set this attribute to No to prevent the execution of validations and associated error messages (for example, in the case of a Cancel button or Delete button). Set this attribute to Yes to execute all page and built-in validations and associated error messages when the page is submitted.
Use this attribute in conjunction with the validation attribute, Always Execute. To learn more, see "Creating a Validation".
Editing Multiple Buttons a Once
Use the Buttons page to delete multiple buttons or view a history of recent changes.
To edit multiple buttons at once:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Edit Page Buttons page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, right-click the button name and select Edit All.
-
Component view - Click the Edit All icon. The Edit All icon resembles a small grid with a pencil on top of it.
The Buttons page appears. The Buttons page contains a table listing the buttons in the region.
-
Deleting Multiple Buttons
To delete multiple buttons at once:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Edit Page Buttons page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, right-click the button name and select Edit All.
-
Component view - Click the Edit All icon. The Edit All icon resembles a small grid with a pencil on top of it.
The Buttons page appears. T
-
-
Click Delete Multiple Buttons.
The Delete Multiple Buttons page appears.
-
Select the buttons to delete and click Remove Buttons.
Using the Reorder Buttons Icon in Component View
In Component view, you can quickly edit a button label or change a button position within a region on the Reorder Buttons page. The Reorder Region Buttons icon resembles a light gray downward arrow and upward arrow and displays next to the region name.
To edit buttons using the Reorder Region Buttons icon:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition in Component view. See "Switching Between Tree and Component View".
-
Under Buttons, click the Reorder Region Buttons icon.
The Reorder Buttons page appears. Use this page to edit the button label, select a region position, or change the button order.
-
To edit the button label, enter a name in the Label field.
-
To change the region position, make a selection from the Position list.
-
To change the order in which buttons display, click the up and down arrows in the far right column.
Note that you can also control the order in which buttons display by editing the Sequence attribute. See "Editing Button Attributes".
-
Click Apply Changes.
Note:
To change the region where a button resides, you must edit the button attributes. See "Editing Button Attributes".Understanding the Relationship Between Button Names and REQUEST
The name you give a button determines the value of the built-in attribute REQUEST. You can reference the value of REQUEST from within PL/SQL using the bind variable :REQUEST. By using this bind variable, you can conditionally process, validate, or branch based on which button the user clicks. You can also create processes that execute when the user clicks a button. And you can use a more complex condition as demonstrated in the following examples:
If :REQUEST in ('EDIT','DELETE') then ...
If :REQUEST != 'DELETE' then ...
These examples assume the existence of buttons named EDIT and DELETE. You can also use this syntax in PL/SQL Expression conditions. Be aware, however, that the button name capitalization (case) is preserved. In other words, if you name a button LOGIN, then a request looking for the name Login will fail. For example:
<input type="BUTTON" value="Finish" onClick="javascript:doSubmit('Finish');">
Note that in this example Finish is the name of the REQUEST and this example is case-sensitive.
About Branching with Buttons
Each page can include any number of branches. A branch links to another page in your application or to a URL. The Application Express engine considers branching at different times during page processing. You can choose to branch before processing, before computation, before validation, and after processing. Like any other control in Application Builder, branching can be conditional. For example, you can branch when a user clicks a button. When you create a branch, you associate it with a specific button. The branch will only be considered if a user clicks the button.
See Also:
"Controlling Navigation Using Branches"Displaying Buttons Conditionally
You can choose to have a button display conditionally by editing attributes on the Edit Pages Button page.
To have a button display conditionally:
-
Create the button. See "Creating a Button Using a Wizard".
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Edit Page Buttons page:
-
Tree view- Under Page Rendering, locate the button and double-click the button name.
-
Component view - Under Buttons, click the button name.
-
-
Scroll down to Conditions.
-
Make a selection from the Condition Type list.
-
Enter an expression in the fields provided.
-
Click Apply Changes.
See Also:
"About Bind Variable Syntax"Creating Lists of Values at the Application Level
A list of values (LOV) is a static or dynamic set of values used to display a specific type of page item, such as popup lists of values, a select list, a check box, a radio group, or multiple select lists.
Creating a LOV as a shared component has a number of advantages:
-
It can be added to any page within an application.
-
All LOV definitions are stored in one location, making them easy to locate and update.
See Also:
"Creating a Static List of Values", "Creating a Cascading List of Values", and "Working with Shared Components"Creating a Named LOV at the Application Level
You define named (or shared) LOVs at the application level by running the Create LOV Wizard and adding them to the List of Values repository. All LOVs can be defined as static or dynamic. Static lists are based on predefined pairs of display values and return values. Dynamic lists are based on a SQL query you write that selects values from a table.
To create a named LOV:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
The Application home page appears.
-
Click the Shared Components icon.
-
Under User Interface, select Lists of Values.
The Lists of Values page appears.
-
To create a LOV, click Create.
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
New named LOVs are added to the List of Values repository. Note to add the LOV to a page you must edit the appropriate item or column and select the named LOV.
About the List of Values Page
Once you create an LOV, it appears on the List of Values page.
Description of the illustration lov_page.gif
A navigation bar appears at the top of the page and contains the following controls:
-
Search icon - Resembles a magnifying glass. Click this icon to narrow your search to only specific columns. To search all columns, select All Columns.
-
Text area - Enter case insensitive search criteria (wild card characters are implied) and then click Go.
-
View icons. Use this control to toggle between icon and report views. To change the view, click the following icons:
-
View Icons (default) displays each lists of value as a large icon.
-
View Report displays each lists of value as a line in a report.
-
-
Go button - Executes a search.
-
Actions menu - Displays the Actions menu. Use this menu to customize an interactive report. See "Using the Actions Menu".
About Static LOVs
Static LOVs are based on a static list of display values and return values you specify when you run the Create LOV Wizard. To create a static LOV, run the Create LOV Wizard and select the LOV type Static. Oracle Application Express stores the display values, return values, and sort sequence you specify in the List of Values repository. Once you add a static LOV to the repository, you can create an item and display it as a check box, radio group, select list, or popup list based on this definition.
Editing an Existing LOV
To edit an existing LOV, select the LOV on the Lists of Values page.
To edit an LOV:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Shared Components.
-
Under User Interface, select Lists of Values.
-
Select an LOV.
The Edit List of Values page appears.
-
To learn more about a specific item on a page, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
Click Apply Changes.
About Navigation Alternatives
The Edit List of Values page is divided into the following sections: Name, Subscription, Source, and Comments.
You can access these sections by scrolling down the page, or by clicking a navigation button at the top of the page. When you select a button at the top of the page, the selected section appears and all other sections are temporarily hidden. To view all sections of the page, click Show All.
Bulk Edit of Static LOVs
You can edit the display values of all static LOVs by clicking the Grid Edit button on the Edit List of Values page.
To perform a bulk edit of static LOVs:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Shared Components.
-
Under User Interface, select Lists of Values.
By default, LOVs display as icons.
-
Click the Grid Edit tab.
-
Edit the appropriate display values and click Apply Changes.
Referencing Session State Within an LOV
You can reference session state by using bind variables. Keep in mind that referencing session state makes an LOV a bit less reusable, but is still a recommended development practice. In the following example, this LOV only works if the item called my_deptno contains a valid department number.
SELECT ename, empno FROM emp WHERE deptno = :P1_DEPTNO
Accessing LOV Reports
Application Builder includes a number of reports designed to help you better manage LOVs.
To access LOV reports:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
When Application Builder appears, click Shared Components.
-
Under User Interface, select Lists of Values.
-
Select one of the following tabs at the top of the page:
-
Edit Null Text
-
Locally Defined
-
Grid Edit
-
Conditional Entries
-
Subscription
-
Utilization
-
History
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
Locally Defined
Click Locally Defined to view all LOVs that are defined locally with the definition of an item. LOVs that are usable by multiple pages can be converted into shared lists of values. Converting locally defined lists of values into a shared list of values promotes reuse.
Using Shortcuts
By using shortcuts you can avoid repetitive coding of HTML or PL/SQL functions. You can use a shortcut to define a page control such as a button, HTML text, a PL/SQL procedure, or HTML. Once defined, you can invoke a shortcut using specific syntax unique to the location in which the shortcut is used. Shortcuts can be referenced many times, thus reducing code redundancy.
About Shortcut Types
When you create a shortcut, you must specify the type of shortcut you want to create. Oracle Application Express supports the following shortcut types:
Text with JavaScript Escaped Single Quotes
Use this type of shortcut to reference a shortcut inside of a JavaScript literal string. This shortcut defines a text string. When the shortcut is referenced, it escapes the single quotation marks required for JavaScript.
Message
Use this type of shortcut to reference a translatable message at run time. Note that since this shortcut does not have a shortcut body, the name of the shortcut must match the corresponding message name. At run time, the name of the shortcut expands to the text of the translatable message for the current language.
Defining Shortcuts
Before you can incorporate a shortcut in your application, you must define it and add it to the Shortcuts repository. You reference shortcuts using the following syntax:
"MY_SHORTCUT"
Note that the shortcut name must be capitalized and enclosed in quotation marks.
To define a shortcut:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
When Application Builder appears, click Shared Components.
-
Under User Interface, select Shortcuts.
-
Click Create.
-
Select one of the following creation methods:
-
From Scratch
-
As a Copy of an Existing Shortcut
-
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
New shortcuts are added to the Shortcut repository and are available for use within the following locations:
-
The Region Source attribute of regions defined as HTML Text (with shortcuts). See "Understanding Regions".
-
Region Header and Footer Text attribute. See "Specifying a Region Header and Footer".
-
Item Label attributes and Default Value attribute.
-
Region Templates attributes. See "Customizing Templates".
About the Shortcuts Page
Once you create a shortcut, it appears on the Shortcuts page. You control how the page displays by making a selection from the View list. Available options include:
-
Icons (the default) displays each shortcut as a large icon. To edit a shortcut, click the appropriate icon.
-
Details displays each shortcut as a line in a report. To edit a shortcut, click the name.
Editing Existing Shortcuts
Once you create a shortcut, you can alter it by editing attributes on the Edit Shortcut page.
To edit an existing shortcut:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Shared Components.
-
Under User Interface, select Shortcuts.
-
Select a shortcut.
The Edit Shortcut page appears.
-
To learn more about a specific item on a page, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
Click Apply Changes.
About Navigation Alternatives
The Edit Shortcut page is divided into the following sections: Name, Subscription, Source, Configuration, and Comments.
You can access these sections by scrolling down the page, or by clicking a navigation button at the top of the page. When you select a button at the top of the page, the selected section appears and all other sections are temporarily hidden. To view all sections of the page, click Show All.
Accessing Shortcut Reports
Application Builder includes a number of reports designed to help you better manage shortcuts.
To access shortcut reports:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
When Application Builder appears, click Shared Components.
-
Under User Interface, select Shortcuts.
-
Click one of the following tabs:
-
Subscription
-
History
Note:
The Subscription and History tabs only appear after you create a shortcut. -
Subscribed Shortcuts
Click Subscription to display the Subscribed Shortcuts page. This page displays all subscribed shortcuts in your application.
Creating Trees
Application Builder includes a built-in wizard for generating a tree. Trees utilize jsTree, a JavaScript-based, cross browser tree component that features theme support, optional keyboard navigation, and optional state saving. You can create a Tree from a query that specifies a hierarchical relationship by identifying an ID and parent ID column in a table or view.The tree query utilizes a START WITH .. CONNECT BY clause to generate the hierarchical query.
Creating a Tree
To create a tree using a wizard:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Create Page and click Next.
-
For Page Type, select Tree.
-
For Page Attributes, specify the following:
-
Page Number - Specify the page on which the tree should be created.
-
Page Name - If the tree will be created on a new page, enter the page name.
-
Region Template - Select a region template for the tree region.
-
Region Name - Enter a name for the region to contain the tree.
-
Breadcrumb - Select whether you want to use a breadcrumb navigation control on your page, and which breadcrumb navigation control you want to use. If you select Breadcrumb, enter the following:
-
Entry Name - Enter a name for the breadcrumb entry.
-
Select Parent Entry - Select a parent entry.
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Tab, specify whether the page should have tabs and click Next.
-
For Tree Templates, select a tree template and click Next.
-
For Table/View Owner, select the table or view owner on which to base the tree and click Next.
-
For Table/View Name, select the table or view and click Next.
-
For Query, select the columns to include in the tree:
-
ID - Select the column to use as the ID.
-
Parent ID - Select the column to use as the parent ID.
-
Node Text - Select the text to appear on the tree nodes.
-
Start With - Select the column to be used to specify the root of the hierarchical tree query.
-
Start Tree - Choose how to start your query. Options include:
-
Based on Existing Item - Select an existing application or page item.
-
Based on a SQL Query - Enter a SQL query that returns a single row or single column.
-
Based on a Static Value - Enter a static value.
-
Value is
NULL.
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Where and Order by, specify the following:
-
Where Clause - Enter an optional
WHEREclause. -
Order Siblings By - Select the columns by which siblings are ordered.
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Tree Attributes, specify the following:
-
Include following buttons - Select the buttons to include.
-
Link Option:
-
Existing Application Item - Makes the leaf node text a link. If you select this option, you must specify a page to link to in the next step.
-
Nothing
-
-
Existing Application Item - Can be used to hold the selected node value. If you select an application item, this item can be used to save the tree state, by holding the last selected node of the tree.
-
Tooltip - Displays a tooltip when the mouse hovers over a leaf node. Options include:
-
Static Assignment - Specifies a static value to be used as the tooltip text. Substitution strings can be used in the static text, to incorporate information from the SQL query in the tooltip text. The following substitution strings can be used:
#VALUE#- refers to the value of ID column.#TITLE#- refers to the value of Node Text column#LINK#- refers to the value of Link option -
Database Column - Select the column to use as the tooltip text.
-
-
Click Next.
-
-
For Link, select a page the leaf node links to.
Note that this option only appears if you want make the leaf node text a link.
-
Confirm your selections and click Finish.
Editing a Tree as a Developer
By default, a tree does not have focus and node links are activated with a single click action. This section describes how developers can customize a tree by editing tree attributes.
Accessing the Tree Attributes Page
Developers can customize a tree by editing attributes on the Tree Attributes page.
To access the Tree Attributes page:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Access the Tree Attributes page:
-
Tree view - Right-click on the Region name and select Edit Tree.
-
Component View - Under Regions, click the Tree link next to the name of the tree region you want to edit.
The Tree Attributes page appears and is divided into the following sections:
-
Display Settings enable you control a tree's appearance and functionality. Use these settings to define a tree template, tooltip, a page item to hold the last selected node value for saving tree state, determine whether the tree has focus on page load, and what action activates node links on a tree.
-
Query enables you to edit the SQL query underlying the tree. The query must be in the following format:
SELECT status, level, name, icon, id, tooltip, link FROM ... WHERE ... START WITH... CONNECT BY PRIOR id = pid ORDER SIBLINGS BY ...
-
-
To learn more about a specific attribute, click the item label.
When Help is available, the item label changes to red when you pass your cursor over it and the cursor changes to an arrow and question mark. See "About Field-Level Help".
-
Click Apply Changes.
Using the Find Icon
You can search for items, pages, queries, tables, PL/SQL code, images, or cascading style sheets by clicking the Find icon on numerous pages within Application Builder.
See Also:
"Debugging an Application"About the Find Icon
The Find icon resembles a flashlight and often displays to the right of the Run Page and Edit Page icons as shown in the following illustration. The Find icon displays on many pages in Application Builder, including the Application Home page, the Page Definition, application attribute pages, and numerous pages for creating and managing shared components.
Description of the illustration find_icon.gif
See Also:
"About the Application Home Page"About the Item Finder
In Application Builder, an item can be a text field, text area, password, select list, check box, and so on. You can use the Item Finder to search for items within the current application or within the schema associated with the workspace.
See Also:
"Understanding Page-Level Items"To search for an item using the Item Finder:
-
Click the Find icon.
The Item Finder appears. A search bar displays at the top of the page and contains the following controls:
-
Select Columns icon - Resembles a magnifying glass. Click this icon to narrow your search to specific columns. To search all columns, select All Columns.
-
Text area - Enter case insensitive search criteria (wild card characters are implied) and then click Go.
-
Go button - Executes a search.
-
Actions menu - Clicking the icon displays the Actions menu. Use this menu to customize an interactive report. See "Using the Actions Menu".
Description of the illustration item_finder.gif
-
-
To restrict the report to display just items on a specific page, click the appropriate page number in the far right column.
Note the page number you select appears in the Page field at the top of the page. To expand the view to all pages, delete the page number in the Page field and click Go.
-
To edit a specific item, navigate to the appropriate item. See "Understanding Page-Level Items" and "Editing Multiple Items Simultaneously".
Using the Page Finder
A page (or Page Definition) is the basic building block of an application. You can use the Page Finder to search for pages within the current application or within the schema associated with the workspace.
To search for a page:
-
Click the Find icon.
-
Click the Pages tab.
The Page Finder report appears, displaying the page number, page name, page alias, title, tab set, and counts of the number of items and regions on the page.
A search bar displays at the top of the page and contains the following controls:
-
Select Columns icon - Resembles a magnifying glass. Click this icon to narrow your search to specific columns. To search all columns, select All Columns.
-
Text area - Enter case insensitive search criteria (wild card characters are implied) and then click Go.
-
Go button - Executes a search.
-
Actions menu - Clicking the icon displays the Actions menu. Use this menu to customize an interactive report. See "Using the Actions Menu".
Description of the illustration pages_finder.gif
-
-
To link to the Items page, click the page number.
Using the Queries Finder
You can use the Queries Finder to locate a query within your application or within the schema associated with the workspace.
To search for a query using the Queries Finder:
-
Click the Find icon.
-
Click the Queries tab.
The Query Finder report appears, displaying the page number, page name, the region containing the query, and the query source.
A search bar displays at the top of the page and contains the following controls:
-
Select Columns icon - Resembles a magnifying glass. Click this icon to narrow your search to specific columns. To search all columns, select All Columns.
-
Text area - Enter case insensitive search criteria (wild card characters are implied) and then click Go.
-
Go button - Executes a search.
-
Actions menu - Clicking the icon displays the Actions menu. Use this menu to customize an interactive report. See "Using the Actions Menu".
Description of the illustration query_finder.gif
-
-
To link to the Items page, click the page number.
Using the Table Finder
You can use the Table Finder to view tables within the schema associated with the workspace.
To view tables associated within the current schema:
-
Click the Find icon.
-
Click the Tables tab.
The Table Finder appears.

Description of the illustration table_finder.gif
A search bar displaying the selected tab appears at the top of the page and contains the following controls:
-
Select Columns icon - Resembles a magnifying glass. Click this icon to narrow your search to specific columns. To search all columns, select All Columns.
-
Text area - Enter case insensitive search criteria (wild card characters are implied) and then click Go.
-
Go button - Executes a search.
-
Actions menu - Clicking the icon displays the Actions menu. Use this menu to customize an interactive report. See "Using the Actions Menu".
-
-
Select a table name.
A table definition appears.
This report displays the column names, data type, length, precision, and scale and the SQL necessary to re-create the table appears at the bottom of the page.
See Also:
"Managing Tables" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop GuideUsing the PL/SQL Finder
You can use the PL/SQL Finder to locate and view details about stored procedures, functions, and packages associated with each object within the schema associated with the workspace.
To search for PL/SQL code in the current schema:
-
Click the Find icon.
-
Click the PL/SQL tab.
The PL/SQL Finder appears.
A search bar displays at the top of the page and contains the following controls:
-
Select Columns icon - Resembles a magnifying glass. Click this icon to narrow your search to specific columns. To search all columns, select All Columns.
-
Text area - Enter case insensitive search criteria (wild card characters are implied) and then click Go.
-
Go button - Executes a search.
-
Actions menu - Clicking the icon displays the Actions menu. Use this menu to customize an interactive report. See "Using the Actions Menu".
-
-
To view additional details, select the procedure, function, or package name.

Description of the illustration plsql_finder.gif
The procedure, package, or function name appears and additional information including the owner, source name, source type, return type, argument names, data types, and IN/OUT parameters.
See Also:
"Managing Database Objects with Object Browser" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop GuideUsing the Images Finder
You can use the Images Finder to identify images available to the current application.
To view available images:
-
Click the Find icon.
-
Click the Images tab.
The Images Finder appears.

Description of the illustration image_finder.gif
A search bar displays at the top of the page and contains the following controls:
-
Select Columns icon - Resembles a magnifying glass. Click this icon to narrow your search to specific columns. To search all columns, select All Columns.
-
Text area - Enter case insensitive search criteria (wild card characters are implied) and then click Go.
-
Go button - Executes a search.
-
Actions menu - Clicking the icon displays the Actions menu. Use this menu to customize an interactive report. See "Using the Actions Menu".
-
-
From Show, select the type of images to view. Options include:
-
Standard Images
-
Workspace Images
-
Application Images
-
See Also:
"Managing Database Objects with Object Browser" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop GuideControlling Access to Applications, Pages, and Page Components
You can control access to an application, individual pages, or page components by creating an access control list. To create an access control page, the application schema needs to have CREATE TABLE, CREATE TRIGGER, CREATE SEQUENCE privileges.
See Also:
"Building Queries with Query Builder" in Oracle Application Express SQL Workshop GuideHow the Access Control List Works
You create an access control list by running the Access Control Wizard. The Access Control Wizard creates a page named Access Control Administration. This page contains a list of application modes and an Access Control List. Once you create the Access Control Administration page, you:
-
Run the Access Control Administration page.
-
Select one of the following application modes:
-
Full access to all, access control list not used.
-
Restricted access. Only users defined in the access control list are allowed.
-
Public read only. Edit and administrative privileges controlled by access control list.
-
Administrative access only.
-
-
Add users to the Access Control List.
In addition to creating the Access Control Administration page, the Access Control Wizard also creates:
-
two tables within the application's default schema to manage the access control
-
the authorization schemes that correspond to the application mode list options
-
the privileges available in the Access Control List
You can control access to a specific page or page component by selecting one of these authorization schemes on the page or component attributes pages. Once you create an Access Control, you can customize the page, tables and values to suit the specific needs of your application.
Creating an Access Control List
You create an access control list by creating a page. You can create a page on the Application home page, while viewing a Page Definition, or by clicking Create on the Developer toolbar.
Creating an Access Control from the Application Home Page
To create an access control list from the Application home page:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
The Application home page appears.
-
Click Create Page.
-
For page type, select Access Control and click Next.
The Access Control Wizard appears.
-
Specify a page number and click Next.
-
Select a tab option and click Next.
-
Review the confirmation page and click Finish.
Creating an Access Control from the Page Definition
To create an access control list from the Page Definition:
-
Navigate to the appropriate Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Click the Create button next to the navigation bar at the top of the page.
-
Click New page and Select New Page.
-
For page type, select Access Control and click Next.
The Access Control Wizard appears.
-
Specify a page number and click Next.
-
Select a tab option and click Next.
-
Review the confirmation page and click Finish.
Creating an Access Control List from the Developer Toolbar
To create an access control list from the Developer toolbar:
-
Run the application. See "Running a Page or Application".
-
On the Developer toolbar, click Create.
-
Select New page and click Next.
-
For page type, select Access Control and click Next.
The Access Control Wizard appears.
-
Specify a page number and click Next.
-
Select a tab option and click Next.
-
Review the confirmation page and click Finish.
Selecting an Application Mode and Adding Users
You can control access to an application by running the Access Control Administration page, selecting an application mode, and then adding users to the Access Control list.
Selecting an Application Mode
To select an application mode:
-
Create an access control list. See "Creating an Access Control List".
The wizard creates a page named Access Control Administration.
-
Run the Access Control Administration page. See "Running a Page or Application".
-
Select an Application Mode. Options include:
-
Full access to all, access control list not used.
Select this option to enable all users access to an application.
-
Restricted access. Only users defined in the access control list are allowed.
Select this option to restrict access to users on the Access Control List. Only users on the Access Control List can view pages and components associated with an authorization scheme.
-
Public read only. Edit and administrative privileges controlled by access control list.
Provides public access to pages and components associated with the access control - view authorization scheme.
-
Administrative access only.
Only users with Administrator privileges can access pages or components associated with an authorization scheme.
-
-
Click Set Application Mode.

Description of the illustration access_control_1.gif
Note that the user interface of your page is dependent upon the theme you selected for your application. See "Managing Themes".
Next, add users to the Access Control List.
Adding Users to the Access Control List and Selecting Privileges
To add users to the Access Control List:
-
Under Access Control List, click Add User.
A new row appears.
Description of the illustration access_control_2.gif
-
Enter a user in the Username field.
-
Associate a privilege with the user. Available options include:
-
Administrator
-
Edit
-
View
-
-
Click Apply Changes.
-
Repeat steps 1 to 5 for all users.
Controlling Access for Pages and Page Components
The Access Control Wizard creates authorization schemes that correspond to the application mode list options and the privileges available in the Access Control List.
You can control access to a specific page or page component by selecting one of the following authorization schemes on the page or component attributes pages:
-
access control administrator. Only users with Administrator privileges can view the page or component.
-
access control - edit. Users with both Edit and Administrator privileges can view the page or component. Users with View privileges cannot view the page or component.
-
access control - view. Users with Administrator, Edit, or View privileges can view the page or component.
-
Not access control administrator. Users with Administrator privileges cannot view the page or component.
-
Not access control - edit. Users with both Edit and Administrator privileges cannot view the page or component. Users with View privileges can view the page or component.
-
Not access control - view. Users with Administrator, Edit, or View privileges cannot view the page or component.
Incorporating JavaScript into an Application
Adding JavaScript to a Web application is a great way to add features that mimic those found in client/server applications without sacrificing all the benefits of Web deployment. Oracle Application Express includes multiple built-in interfaces especially designed for adding JavaScript.
Remember that JavaScript is not appropriate for data intensive validations. For example, to verify that a name is contained within a large database table, you would need to pull down every record to the client, creating a huge HTML document. In general, complex operations are much better suited for server-side Application Express validations instead of JavaScript.
See Also:
"Understanding Validations"Referencing Items Using JavaScript
When you reference an item, the best approach is to reference by ID. If you view the HTML source of an Oracle Application Express page in a Web browser, you would notice that all items have an id attribute. This id corresponds to the name of the item, not the item label. For example, if you create an item with the name P1_FIRST_NAME and a label of First Name, the ID will be P1_FIRST_NAME.
You can get and set item attributes and values using the JavaScript function $v('P1_FIRST_NAME'). Consider the following example:
function firstName(){
alert('First Name is ' +$v('P1_FIRST_NAME'));
}
// or a more generic version would be
function displayValue(pId){
alert('The Value is ' + $v(pId));
}
// Then add the following to the "Form Element Attributes" Attribute of the item:
onchange="displayValue('P1_FIRST_NAME');"
Incorporating JavaScript Functions
You can include JavaScript functions by incorporating JavaScript
-
Editing the JavaScript attribute of the page
-
Calling the .js file from the HTML Header attribute of the page
-
Calling the .js file from the page template
See Also:
"Text with JavaScript Escaped Single Quotes" for information about referencing a shortcut inside of a JavaScript literal stringIncorporating JavaScript Utilizing the JavaScript Attribute
You can include JavaScript into your application by adding it to the JavaScript attribute of the page. This is a good approach for functions that are very specific to a page and a convenient way to test a function before you include it in the .js file.
In the following example, adding the code would make the test function accessible from anywhere on the current page.
To add JavaScript code to the JavaScript attribute:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
To access the Edit Page:
-
Tree view - Under Page Rendering, double-click the page title at the top of the tree.
-
Component view- Under Page, click the Edit icon.
-
-
Scroll down to JavaScript.
-
Enter code into the following:
-
Function and Global Variable Declaration - Enter JavaScript code (for example, functions or global variable declarations) for code to be used on this page. If the code is used on multiple pages, consider putting it into an external JavaScript file to avoid duplication.
Code you enter here replaces the
#JAVASCRIPT_CODE#substitution string in the page template. -
Execute When Page Loads - Enter JavaScript code to execute when the page loads. The code is executed after the JavaScript code generated by Oracle Application Expresss.
For example, adding the following would test a function accessible from anywhere on the current page.
function test(){ window.alert('This is a test.'); } -
-
Apply Changes.
Calling the JavaScript File from the HTML Header Attribute
To call a .js file from the HTML Header attribute:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
To access the Edit Page:
-
Tree view - Under Page Rendering, double-click the page title at the top of the tree.
-
Component view- Under Page, click the Edit icon.
-
-
Scroll down to HTML Header and Body Attribute.
-
In HTML Header, call the JavaScript file using the following syntax:
<script src="/my_images/custom.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
-
Apply Changes.
Calling the JavaScript File from the Page Template
In Oracle Application Express, you can reference a .js file in the page template. This approach makes all the JavaScript in that file accessible to the application. This is the most efficient approach since a .js file loads on the first page view of your application and is then cached by the browser.
The following demonstrates how to include a .js file in the header section of a page template. Note the line script src= that appears in bold.
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>#TITLE#</title>
#HEAD#
<script src="/my_images/custom.js" type="text/javascript"></script>
</head>
<body #ONLOAD#>#FORM_OPEN#
See Also:
"Page Templates"Calling JavaScript from a Button
Calling JavaScript from a button is a great way to confirm a request. Oracle Application Express uses this technique for the delete operation of most objects. For example, when you delete a button, a JavaScript message appears asking you to confirm your request. Consider the following example:
function deleteConfirm(msg)
{
var confDel = msg;
if(confDel ==null)
confDel= confirm("Would you like to perform this delete action?");
else
confDel= confirm(msg);
if (confDel== true)
doSubmit('Delete');
}
This example creates a function to confirm a delete action and then calls that function from a button. Note that the function optionally submits the page and sets the value of the internal variable :REQUEST to Delete, thus performing the deletion using a process that conditionally executes based on the value of the request.
Note that when you create the button, you would need to select Action Redirect to URL without submitting page. Then, you would specify a URL target such as the following:
javascript:confirmDelete('Would you like to perform this delete action?');
See Also:
"Creating a Button Using a Wizard"Calling JavaScript Using a Dynamic Action
You can also execute JavaScript code by creating a dynamic action of type Execute JavaScript Code. To learn more, see "Implementing Dynamic Actions".
Optimizing a Page for Printing
You can optimize a page for printing by creating a specific Printer Friendly template and selecting that template on the Create/Edit Theme page. See "Changing the Default Templates in a Theme".
Generally, a Printer Friendly template optimizes a page for printing. For example, a Printer Friendly template might:
-
Not display tabs or navigation bars
-
Display items as text instead of as form elements
If the theme you select does not include a printer friendly template, you can create a Printer Friendly template by creating a new page template.
See Also:
"Changing the Default Templates in a Theme", "Creating a Theme", and "Printing Report Regions"Selecting a Printer Friendly Template for an Application
To select a Printer Friendly template:
-
Navigate to the Themes page:
-
On the Workspace home page, click Application Builder.
-
Select an application.
-
Click Shared Components.
-
Under User Interface, select Themes.
The Themes page appears.
-
-
Change to a report view by clicking the View Report icon.
-
In the Themes list, click the theme name.
The Create/Edit Theme page appears.
-
Scroll down to Component Defaults and locate the Printer Friendly Page list.
-
Make a selection from the Printer Friendly Page list.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Using f?p Syntax to Toggle to Printer Friendly Mode
Once you create a Printer Friendly template and select it, you can use f?p syntax to toggle to Printer Friendly mode. Including the ninth f?p syntax argument (PrinterFriendly) renders the page in printer friendly mode (optimizing printed output). For example, you could include this argument when coding a link or creating a navigation bar icon.
See Also:
"Using f?p Syntax to Link Pages"Creating a Help Page
Application Builder includes built-in attributes to create Help for your application. Creating Help for your application involves the following steps:
-
Create a dedicated Help page and Help region.
-
Define page Help text.
-
Define item Help text.
-
Create a navigation bar icon to link to your Help page.
Help created in Application Builder displays on a dedicated Help page. To access Help, users click a link that takes them to a dedicated Help page. This Help page displays page and item Help topics specific to the page they are viewing.
Creating a Help Page and Region
The first step in creating Help for your application is to create a dedicated page and Help Text region.
To create a Help Text region:
-
Create a page for your Help. See "Managing Pages in a Database Application".
-
Navigate to the Page Definition of your Help page. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Regions, the Create icon.
-
When prompted to select a region type, select Help Text.
-
Follow the on-screen instructions.
Defining Help Text
You define Help text for a page or single item by editing attributes. Ideally, you would define these attributes as you create your application. For simplicity, however, the following procedures describe how to define this text after the fact.
Defining Help for a Page
To define page Help text:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition for the page for which you want to add page Help. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Page, click the Edit page attributes icon to view the existing page attributes.
-
Scroll down to Help.
-
Enter your Help text in the field provided.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Repeat the previous procedure for each page requiring page Help text.
Defining Help Text for an Item
To define item Help text for an item:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition for the page for which you want to add item Help. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Items, click the name of the item you want to edit.
-
Scroll down to Help Text.
-
Enter your Help text in the field provided.
-
Click Apply Change.
Repeat the previous procedure for each item requiring Help text.
Editing Multiple Item Help Topics Simultaneously
If you are including item Help in your application, you can edit multiple item Help topics at once using the Bulk Edit Item Help report.
Accessing the Bulk Edit Item Help Report
To view the Bulk Edit Item Help report:
-
On the Workspace home page, click the Application Builder icon.
-
Select an application.
-
On the Tasks list, click Application Reports.
-
Click the Utilities icon.
-
From Page Specific Utilities, select Item Utilities.
-
Click Grid Edit of All Item Help Text.
-
In Bulk Item Help Report, you can:
-
Update existing Help topics. Edit the Help text that appears and click Apply Changes.
-
Link to the Page Definition containing the item by clicking the page number.
-
Link to the Page Item by clicking the item name.
-
Seeding Item Help Topics
If your application does not yet contain item Help, you can perform a mass update of default Help text.
To seed item Help topics:
-
Access the Bulk Edit Item Help report as described in "Accessing the Bulk Edit Item Help Report".
-
Click Seed Item Help Text.
-
In Default Help Text, enter the default text to appear in all Help topics.
-
Click Apply Changes.
Searching for Existing Item Help Topics
You can search for existing Help text, or for an item label.
To search for existing item Help topic:
-
Access the Bulk Edit Item Help report as described in "Accessing the Bulk Edit Item Help Report".
-
In Help Contains, enter keywords.
-
Click Go.
Searching for an Item Label
To search for an item label:
-
Access the Bulk Edit Item Help report as described in "Accessing the Bulk Edit Item Help Report".
-
In Help Contains, enter keywords.
-
Click Go.
See Also:
"Viewing Utilities and Reports"Creating a Help Navigation Bar Entry
Once you have created your Help, the next step is to create a navigation bar entry so users can link to it.
To create a navigation bar entry:
-
Navigate to the Page Definition. See "Accessing the Page Definition".
-
Under Navigation Bar, click the Create icon.
-
For Attributes:
-
Sequence - Specify the sequence for this component. The sequence determines the order of evaluation.
-
Alt Tag Text - Enter ALT text for navigation icons that are images. If you do not specify an image name, then this text displays.
-
Icon Image Name - Enter the name of the image that displays.
-
Image Height - Enter the height of the image.
-
Image Width - Enter the width of the image.
-
Text - Enter additional text to display with the image. You can include text or use icons with no text. This attribute is optional and can be translated.
-
Click Next.
Next, specify the target location.
-
-
For Target:
-
Target is a - Select Page in this application.
-
Page - Specify the page number of the help page you created in "Creating a Help Page and Region".
-
Request - Enter the following:
&APP_PAGE_ID.
By specifying substitution string
&APP_PAGE_IDas the Request, you are instructing the Application Express engine to display Help text for the current page when the user clicks this icon. -
Click Next.
-
-
Click Create.