Organization Structures
Organization Structures Overview
Oracle HRMS provides you with organization management functionality to represent the operating structures of your enterprise.
Representing Organization Structures Using Oracle HRMS
Using the Configuration Workbench for your implementation, you can configure the Oracle eBusiness Suite of applications to represent the management and operating structures of your enterprise.
The Configuration Workbench delivers an integrated configuration management toolset for HR systems and assists in the evaluation, configuration, deployment, and maintenance of HR applications. The workbench uses a configuration interview, to review the decisions and operational questions you make about setting up your enterprise using Oracle HRMS.
The Configuration Workbench configuration process suggests a combination of business groups and organizations to satisfy your integrated legal, financial, organization and employee management needs using Oracle HRMS. The suggested combination of business groups and organizations uses one of the following configuration models:
-
A single operating company working within the legislative rules of a single country.
-
A single operating company working within the legislative rules of multiple countries.
-
Multiple operating companies working within the legislative rules of a single country.
-
Multiple operating companies working within the legislative rules of multiple countries.
These configuration models define the basic information model to represent any enterprise. You can add other location and internal work structures that represent your internal organization or reporting structures for specific legal, personnel, and financial management requirements.
Managing your Work Structures Using Graphical Charting Capabilities
You can plan and implement new working structures ahead of time using graphical charts. The hierarchy diagrammer enables you to create organization and position hierarchies to reflect reporting lines and control access to information in your enterprise. See:
-
Organization Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Position Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
The hierarchy diagrammers use the same security model as the other windows in Oracle HRMS and access to them is restricted by your responsibility.
Reporting on Organization Structures
Oracle HRMS and Oracle HRMSi enable you to produce several reports to satisfy the statutory requirements for your legislation and meet your business analysis needs. For example:
-
Oracle HRMS enables employers in the U.S. to generate reports to comply with the VETS government reporting requirements. The report lists the number of special disabled and Vietnam era veterans a U.S. enterprise employs in each of the nine job categories.
-
Oracle HRMS provides you with a standard organization hierarchy report to view the relationships between organizations and their managers within a hierarchy.
-
Oracle HRMSi offers the Organization Separation Report to investigate the performance of your best and worst organizations based on the workforce changes in an organization.
Reporting Costs for Your Organization Structures
With the Oracle eBusiness suite of applications, you can automatically create HR organizations to corresponding company cost center combinations that exist in your GL account combinations. You can use the management reporting functionality in Daily Business Intelligence (DBI) to report on financials information, such as the costs, revenues, and expenses for your organization structures.
Key Concepts
To effectively use Oracle HRMS for organization management, see:
Key Concepts for Representing Enterprises
Extending the Enterprise Framework, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Configuration Models for Your Enterprise Framework, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Organization Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Defaults for the Business Group, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Internal Organizations and Cost Centers, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Organization Structures
Oracle HRMS can represent all the components of your enterprise. You can record the physical locations where your employees work and all the different departments and sections that make up your enterprise. You can even record information about other organizations you work with, such as recruitment agencies or tax authorities.
See: Extending the Enterprise Framework, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
You can view and edit hierarchy diagrams for organizations and positions using:
-
The Organization Hierarchy Diagrammer
-
The Position Hierarchy Diagrammer
How do you represent your enterprise as an employer?
You can use the GRE/Legal Entity and Employer organization classifications to represent the employer in each country you do business. If you use the Configuration Workbench to set up your organization structures, then an employer organization is set up in each country your enterprise operates.
In US and Canada, how do you manage government reporting?
Oracle HRMS enables you to set up one or more Government Reporting Entities (GREs) within each of your Business Groups. GREs represent an employer the government recognizes as being responsible for paying employees and for filing a variety of reports that government agencies require. If your enterprise has a single Employer Identification Number from the Internal Revenue Service, your Business Group and GRE are the same organization.
For Canada, you also need to set up Provincial Reporting Establishments (PREs). GREs and PREs represent an employer the governments recognise as being responsible for paying employees and for filing a variety of reports. There must be a GRE for each Business Number that the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) assigns to an employer. There must be a PRE for each Quebec Identification Number that the Ministere du Revenu assigns to an employer. If your enterprise has a single Business Number from the CRA and a single Quebec Identification Number, your Business Group, GRE and PRE are the same organization.
How do you represent the structure of an enterprise?
Oracle HRMS enables you to build a model of your enterprise showing all the reporting lines and other hierarchical relationships. You can set up reporting hierarchies reflecting all the reporting lines in your enterprise, as established in organization charts.
The Configuration Workbench creates an enterprise structure that suits your operational (management and reporting), and geographical requirements. You can use the enterprise structure the workbench sets up as the basic infrastructure of your company. Once the basic structure is set up, you can define further locations and organizations and add them to your organization hierarchy.
Do I need to run a separate program to create hierarchy diagrams?
No. The hierarchy diagrammers are standard Oracle HRMS windows, with the addition of a graphical area. They work together with the Organization Hierarchy window and Position Hierarchy window so you can create basic hierarchies using these windows and then make intuitive drag-and-drop changes using the diagrammers.
Any changes made using the hierarchy diagrammers are reflected in the hierarchy windows, and are saved in your database.
Can I create multiple versions of a hierarchy, and model different business scenarios?
Yes. You can use the diagrammers together with the organization and position hierarchy windows to:
-
Create new versions of existing hierarchies
-
Create copies of existing hierarchies
-
Create future-dated hierarchies to prepare for reorganizations in advance
Can I print the graphical versions of the hierarchies?
Yes. You can print pictorial representations of organization and position hierarchies.
Can I create hierarchies that contain organizations from multiple business groups?
Yes. If you have the appropriate security access to more than one business group, you can include organizations from more than one business group in your hierarchy.
Organization
Key Concepts for Representing Enterprises
You represent your enterprise using key organization structures in Oracle HRMS. These structures provide the framework so you can perform legal reporting, financial control, and management reporting. You can set up these organization structures yourself, or use the Configuration Workbench.
The Configuration Workbench delivers an integrated configuration management toolset for HR systems and assists in the evaluation, configuration, deployment, and maintenance of HR applications. The workbench suggests a basic structure of organizations for your enterprise based on configuration models.
See: Configuration Models for Your Enterprise Framework, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Once the basic enterprise structure is set up, you add the additional organizations and locations t`hat exist in your enterprise. You define the internal organizations that represent your internal divisions and departments, and you define the external organizations that represent the organizations outside of your enterprise. For example, you can set up an external organization to represent the tax office for which your enterprise uses for reporting purposes.
You can use organizations to represent many levels of your enterprise, from the highest level of organization that represents the whole enterprise, to the lowest level of organization that represents a section or department.
See: Extending the Enterprise Framework, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
See: Organization Classifications
See: Setting Up Organizations, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Business Group
The business group represents a country in which your enterprise operates. You create it as an organization in Oracle HRMS, but it does not represent a specific organization within your enterprise structure, and you do not include it in your organization hierarchies. A business group enables you to group and manage data in accordance with the rules and reporting requirements of each country, and to control access to data.
The critical factors for deciding when to use a separate business group, or an international business group, are based on the following factors:
-
If you use Oracle Payroll
-
The number of people you employ in a country
-
If you require legislative support for Oracle HR
Generally the laws are so different in each country that to be compliant, there must be a different business group for each country in which an enterprise has employees.
Operating Company
An operating company represents a division or line of business within your enterprise that is legally registered for reporting in at least one country. An operating company is a holding company, a company within a company.
Ultimate Legal Entity
The ultimate legal entity represents the enterprise, and typically, the enterprise is the highest (global) level of a business organization. The ultimate legal entity is the parent company or organization for all its subsidiaries and divisions. Oracle HRMS represents the ultimate legal entity with the GRE/Legal Entity organization classification.
Legal Entity/Employer
A legal entity represents the designated legal employer for all employment-related activities. The legal authorities in a country recognize this organization as a separate employer. In an organization hierarchy, a legal entity may report to an operating company or to the ultimate legal entity.
A legal employer is a legal entity that is responsible for employing people in a particular country. Therefore, if you employ people in a country, then you must have at least one organization classified as a legal entity and a legal employer.
The Configuration Workbench classifies an organization as a GRE/Legal Entity where your enterprise operates in a country, and classifies it as an Employer if you employ people in that country also. For example, you can have a legal entity in a country where you do business, but do not employ people in that country.
Consolidated Legal Entity
A consolidated legal entity acts on behalf of multiple operating companies that are not legally registered, or simply on behalf of the enterprise in a country. You typically use the consolidated legal entity for when you have multiple operating companies in your enterprise, but for the purposes of consolidation, you group the information into one organization. For management reporting purposes, the organizations below the consolidated legal entity in an organization hierarchy, such as, your departments and sections, can report to any organization in the enterprise. However, for legal reporting purposes, they report up to the consolidated legal entity.
For information on how to model your enterprise using the key organization structures, see: Configuration Models for Your Enterprise Framework, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Organization Classifications
Organization classifications define the purpose of an organization and its functionality within Oracle HRMS. The classifications you assign to an organization control the additional information you can set up at the organization level. The Configuration Workbench automatically assigns the appropriate classifications to the organizations it creates.
For more information on the key organization structures you use to represent your enterprise, see: Key Concepts for Representing Enterprises
You can define one organization with multiple classifications or you can define separate organizations to represent different types of entity. For example, you can classify an organization as a legal entity as well as an HR organization if it's the same organization. If they are different, then you create two organizations.
Note: Oracle HRMS enables you to install your own additional information types for classifications.
You can select the following classifications in the Organization window, depending on your legislation:
All Legislations
All legislations can use the following classifications:
-
Business Group: Use this classification to group, manage, and control access to data in accordance with the rules and reporting requirements of a country.
-
Operating Company: An operating company represents a division or line of business within your enterprise that is legally registered for reporting in at least one country.
-
GRE/Legal Entity: Use this classification to represent the following organizations:
-
Ultimate Legal Entity: this represents the enterprise, and typically, the enterprise is the highest (global) level of a business organization.
-
Legal Entity: this represents the designated legal employer for all employment-related activities. The legal authorities in a country recognize this organization as a separate employer. In an organization hierarchy, a legal entity may report to an operating company or to the ultimate legal entity.
-
Consolidated Legal Entity: this organization acts on behalf of multiple operating companies that are not legally registered, or simply on behalf of the enterprise in a country.
For Chinese users only: Your organization hierarchy must contain at least one GRE with corporate and employer information. Statutory reporting requires this information.
-
-
Employer: Use this along with the GRE/Legal Entity classification to define an organization as a legal entity that is responsible for employing people in a particular country.
For Indian users only: Your organization hierarchy must contain at least one GRE with income tax, challan bank, tax declaration and representative details. This information is used for statutory reporting.
-
HR Organization: Use this classification for all organizations to which you want to assign employees and contingent workers.
-
Payee Organization: Use this when defining an external organization that is the recipient of a third party payment from an employee, for example a court-ordered payment. You can then select this organization on the Personal Payment Method window when entering a third party payment method.
-
Bargaining Association: Use this when defining an organization that is involved in negotiating a collective agreement. A bargaining association could be any organization representing the employees in negotiations, for example a trade union. The UK legislation also enables you to select a bargaining association in the Union Processing window to set up a union element.
-
Representative Body: Use this when defining a representative body. This may be a body defined in legislation, such as a European Works Council, or may be defined by the employer, such as a Sports and Social Club.
-
Disability Organization: Use this when defining an external organization with which employee disabilities are registered.
-
Medical Service Provider: Use this when defining an organization that provides any medical services, such as medical assessments, to the people in your enterprise.
-
Constituency: Use this to define a constituency to group together workers eligible to vote for particular elections.
-
Company Cost Center: Use this to define organizations in Oracle HRMS that map to cost centers in Oracle GL. You can set up your application so that whenever a cost center is defined in GL, a corresponding organization with this classification is defined automatically.
-
Professional Body Information: Use this to define an organization that is a professional body. Organizations with this classification are available to assign to people in the Qualifications window.
-
Operating Unit : Use the operating unit organization classification if you also use Multi-Org applications. You can associate an operating unit with an HR Organization. The application uses the HR Organization to find the operating unit to which a person belongs.
US Legislation
The US legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Reporting Establishment, Corporate Headquarters, or AAP Organization: Use these when defining reporting organizations, that is, organizations required for the production of certain reports for government agencies.
-
Parent Entity: Use this when defining an organization to be included at the top level of an establishment hierarchy. You can then use the hierarchy when producing certain reports for government agencies.
If you are assigning this classification to a Business Group, you must assign it to your default Business Group, that is the one defined in your security profile. If you do not, then your data will not be visible when you attempt to create your hierarchy in the Generic Hierarchy window.
-
Benefits Carrier, Workers' Compensation Carrier, or Beneficiary Organization: Use these when defining an external organization belonging in one of these classifications. You can then select the organization when defining a benefit, entering information for Workers' Compensation calculations, or recording beneficiaries employees have named for certain benefits.
The Federal legislation can also use the Beneficiary Organization classification.
UK Legislation
The UK legislation can use the Education Authority classification to define a Local Education Authority (LEA) that is responsible for education within that council's jurisdiction.
Canadian Legislation
The Canadian legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Provincial Medical Carrier: Use this to define a medical carrier for a province.
-
Provincial Reporting Establishment: Use this to represent employees in the province of Quebec.
French Legislation
The French legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Company: records one or more companies in your business group. A company is a legal entity registered to "Registre du Commerce et des Societes". You must have at least one company.
-
Establishment: identifies the organization that serves as the legal point of contact for settling any disputes and manages the personal details of the workforce.
Note: Do not classify an organization as both a company and an establishment; create two separate organizations.
-
URSSAF Center or ASSEDIC Center: specifies an external organization that is a Social Security organization. You can select the organization when entering additional organization information for an establishment. You can also select URSSAF organizations when entering additional organization information for a company.
-
Insurance Provider or Pension Provider: defines an external organization that provides insurance or pensions. You can select the organization when entering additional organization information for a company or an establishment.
-
OPACIF or OPCA: specifies an external organization that collects the company's yearly training contribution.
-
CPAM: identifies an external organization as a CPAM office. You can select the organization when entering employment information in the People window.
-
Public Sector Other External Organization: records details of the various types of external organizations with whom public-sector companies deal. Be sure to create organizations with this classification as external organizations.
-
Grouping of Employers: identifies the employers (normally establishments) who have decided to group together to make it easier to lend each other workforce and also to list the employees, contingent workers, and employees on loan for an establishment from that grouping in the Personnel Registry report.
-
Tax Group: defines an external tax office.
Dutch Legislation
The Dutch legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Dutch UWV Organization: Use this to indicate if your organization is a social insurance provider. If you enable this classification, you can enter additional information such as the type of provider in the Dutch UWV Organization window.
-
Dutch Tax Office: Use this to define an external tax office.
-
Dutch Private Health Insurance: Use this to define an external organization that provides private health insurance.
-
Pension Provider: Use this to define an external organization that provides pensions to your employees.
German Legislation
The German legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Budget Plan Unit: Use this to define internal organizations for which you can use for the budget plan structure. The budget plan structure defines the different levels of positions in your enterprise, and the budget plan units represent the different levels as organizations. You select which budget plan unit the position belongs to in the Position window.
-
German Additional Second Pension Insurance: Use this to record information about the contributions an organization makes to a second pension.
-
German Capitalized Life Insurance Provider: Use this to indicate if your organization is a provider of German capitalized life insurance.
-
German Mandatory Health/Special Care Insurance Provider: Use this to indicate if your organization is a provider of German mandatory health or special care insurance. If you enable this classification, you can enter additional information using the German Social Insurance Providers window.
-
German Mandatory Pension Insurance Provider: Use this to indicate if your organization is a provider of German mandatory pension insurance. If you enable this classification, you can enter additional information using the German Social Insurance Providers window.
-
German Private Health/Special Care Insurance Provider: Use this to indicate if your organization is a provider of German private health or special care insurance. If you enable this classification, you can enter additional information using the German Social Insurance Providers window.
-
German Public Sector: Use this to indicate if your organization is a public sector organization. If you set this to yes then certain public sector specific windows and fields are made available to you.
-
German Tax Office: Use this to indicate if your organization is a tax office. If you set this to yes then you can enter additional tax office information using the Others button.
-
German Unemployment Insurance Provider: Use this to indicate if your organization is a provider of German unemployment insurance. If you enable this classification, you can enter additional information using the German Social Insurance Providers window.
-
German Voluntary Pension Provider: Use this to indicator if your organization is a provider of German voluntary pensions.
-
German Work Incident Supervising Office: Use this to indicate if your organization is a work incident supervising office.
-
German Workers' Liability Insurance Providers: Use this to indicate if your organization is a provider of German workers' liability insurance.
Hong Kong Legislation
The Hong Kong legislation can use the MPF Trustee Organization classification to set up and enrol employees in an MPF Trustee. This classification allows you to record details of the trustee and details of the scheme provided by the trustee.
Mexico Legislation
The Mexico legislation must use the legal employer classification to define the legal entity. You can add additional organization information for your legal employer, if needed.
Use the GRE/Legal Entity classification to define an organization that is recognized as a separate employer by Social Security or other legal authorities. When you assign a location to a GRE, and you have not already associated them with each other in the generic hierarchy, HRMS will make the association for you.
Saudi Legislation
The Saudi legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Saudi GOSI Office: Use this to represent the General Office of Social Insurance (GOSI) which the employer is registered. The GOSI office requires employers to make deductions for eligible employees and send all payments and reports to this office.
-
Saudi Employment Office: Use this to represent an office to which the employer reports the status of its disabled employees.
Hungary Legislation
The Hungary legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Draft Agency: Use this to represent an external defense organization to which you send employee military service details.
-
Company Information: Use this to represent the organization which is legally entitled to hire employees.
-
Pension Provider: Use this to indicate an external organization that provides pensions to your employees.
Spanish Legislation
The Spanish legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Work Center: Use this to define an internal organization that represents a facility within your enterprise. You use these organizations for statutory reporting purposes.
-
Section: Use this to define an internal organization that represents the place where people work. You use these organizations for internal reporting purposes only.
-
Tax Office: Use this to indicate if the organization is an external tax office.
-
Tax Administration Office: Use this to indicate if the organization is an external tax administration office.
-
Social Security Office: Use this to define a social security office as an external organization. If you enable this classification, you can record the social security office details.
-
Social Security Province Office: Use this to define an organization as an external social security office. If you enable this classification, you can enter the social security province office details.
-
Health Care Organization: Use this to define an organization as an external health care organization. If you enable this classification, you can enter the insurance company details.
Korea Legislation
The Korean legislation can use the following classification:
-
Business Place: Use this classification to define an organization as an employer to which you assign employees. You set up information such as the registration number, representative information, and the health insurance number for the National Tax Service (NTS).
Indian Legislation
Your organization hierarchy should contain at least one GRE/Legal Entity (Tax Organization) and Registered Company.
The Indian legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Registered Company: Records your company's Legal Name, Registration Number, Corporate Identity Number, Permanent Account Number (PAN) of the company and company's representative details.
-
Factory: Records your factory's Registration Number, License Number, National Industrial Code, Production Commencement Date and factory's representative details.
-
Shops/Establishment: Records your shops/establishment's registration number and representative details.
-
Contractor Details: Records a contractor's details, work details, and representative details. A contractor supplies contingent workers to an enterprise and can be either an individual or an external organization.
-
ESI Organization: Use this to define an external organization that provides Employee State Insurance (ESI) to your employees. Records your Employee State Insurance (ESI) organization's Challan Information, General Information and Representative Details. You can have multiple ESI organizations and select an employee's ESI organization in the Assignment window.
-
Provident Fund Organization: Records your PF organization's PF challan information, PF information, and PF representative details. You can have multiple PF organizations and select an employee's PF organization in the Assignment window.
-
Professional Tax Organization: Records your Professional Tax organization's information, Professional Tax Challan information, and Representative Details information. You can have multiple professional tax organizations and select an employee's professional tax organization in the Assignment window.
-
Income Tax Office: Records your income tax organization's information. You can enter the location details of the income tax office. You can select the income tax organization in the GRE/Legal Entity: Income Tax Details window.
-
National Pension Scheme: Records the National Pension office information. You can enter the corporate registration account number and the corporate branch account number in the NPS Account Set Up window.
Polish Legislation
The Polish legislation can use the following classifications:
-
PL SII Branch: Use this classification to represent a local branch of the Social Insurance Institute (SII), a public organization that deals with the social insurance benefits, such as sickness allowance, maternity allowance, and rehabilitation benefits. You use the SII branch information for social insurance reporting.
-
PL Statistic Office: Use this to represent a local statistic office. You use this information in reports sent to the statistic office.
-
PL Tax Office: Use this to define the tax office bank accounts for the employer and for the tax collected from the employees. You use this information in statutory reports.
Norwegian Legislation
The Norwegian legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Local Unit: Use this classification to identify and report on the different work centers, within your enterprise, to which you assign employees.
-
Payee Organization: Use this classification to define an external organization which receives third party payment from an employee
-
Social Security Office: Use this to define external social security office organizations.
-
Pension Provider: Use this classification to define an external organization that provides pensions to your employees.
-
Statement Provider: Use this classification to define an external organization that provides reports on behalf of the legal employer.
-
Tax Office: Use this classification to define an external tax organization.
Finnish Legislation
The Finnish legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Local Unit: Use this classification to identify and report on the different work centers, within your enterprise, to which you assign employees.
-
External Company: Use this to record details of the various types of external organizations with whom your organization deals. Ensure to create organizations with this classification as external organizations.
-
Pension Provider: Use this to record the basic information about pension insurance providers to which you transfer the appropriate pension insurance deductions.
-
Accident Insurance Provider: Use this to identify organizations that provide accident insurance coverage, group life insurance, and unemployment insurance.
-
Finnish Magistrate Office: Use this for identifying the authority responsible for processing the employee court orders.
-
Finnish Trade Union: Use this to record the basic information about the employees' trade unions to process employee deductions.
-
Provincial Tax Office: Use this to identify the legal employer's tax office.
Danish Legislation
The Danish legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Service Provider: Use this classification to record details of the various types of external service providers with whom your organization deals.
-
Pension Provider: Use this classification to define external pension providers.
Swedish Legislation
The Swedish legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Local Unit: Use this classification to identify and report on the different work centers, within your enterprise, to which you assign employees.
-
Social Security Office: Use this to define external social security office organizations with which you coordinate medical reimbursements for the employees.
-
Swedish Enforcement Office: Use this to define external enforcement office organizations with which you coordinate the attachment of earnings deductions for the employees.
South African Legislation
The South African legislation can use the following classification:
-
Training Provider: Use this to indicate if an organization is a training provider.
UAE Legislation
The UAE legislation can use the Legal Employer classification to define and enter additional organization information for your legal employer.
Irish Legislation
The Irish legislation can use the following classifications:
-
Legal Employer: Use this classification to define and enter additional organization information for your legal employer.
-
Pension Provider: Use this classification to define external pension provider.
Dutch Organizations and Additional Information
Within Oracle HRMS you can enter the following information for each HR organization within a Dutch organization hierarchy:
-
social insurance provider
-
tax office
To store this information, you first need to define each separate provider as an external organization with the corresponding organization classification.
You can create multiple external organizations for each organization classification depending on the requirements of your enterprise. For example, you may have two internal organizations that require different tax offices or tax numbers. Therefore, you can set up two Dutch tax offices as external organizations and assign them to each internal organization.
Linking External and Internal Organizations
When you have defined your external organizations, you define links to your internal organizations. However, you do not need to define the information for each individual organization. As long as you maintain the information for at least the top-level HR organization, the values will be inherited by the subordinate organizations.
You specify the preferred hierarchy for your organization in the Dutch Business Group window.
See: Creating Organization Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
See: Entering Dutch Business Group Information
The following diagram illustrates how values entered against the top-level organizations are inherited by the subordinate organizations. The Social Insurance Providers H1 and H2 are stored against the top-level organization. This means that the list of possible social insurance providers for the second-level organization (Company A) is the inherited values (H1 and H2) plus H3.
Inherited Information for External Organizations
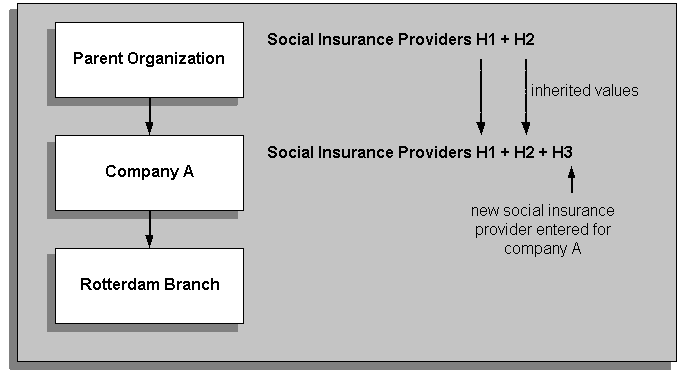
For more information on defining the organizational links between external and internal organizations, see: HR Organization: Entering Social Insurance Provider Information and HR Organization: Entering Dutch Organization Information
When you link your external organizations to your internal organizations, you select SI classifications that identify which types of social insurance the external organization provides. The employees assigned to that internal organization inherit the social insurances from that provider. You can set up all of the mandatory social insurances for a particular provider and assign the provider to your internal organization for all of the mandatory insurances. The SI classification All Mandatory Insurances ensures that the employees within your internal organization inherit all of the mandatory social insurances.
For examples of assigning social insurance types and providers to your internal organizations and how your employees inherit the information, see: Examples of Assigning Social Insurance Types and Providers to Employees
Employees and External Organization Information
It is important that your hierarchy includes the relevant internal organizations with links to applicable external organizations. If this information is not set up correctly, the social insurance information that you record for your employees may result in incorrect social insurance calculations for Oracle Payroll.
You select a classification of social insurance that a person is entitled to at the assignment level. The application checks if the organization the employee is assigned to has a social insurance provider that offers this type of social insurance classification for the dates selected. If an appropriate social insurance provider is not found, then the application continues to search up through the hierarchy.
For example, if you select WAO disability insurance as the social insurance classification for the employee at the assignment level, the application will look at the employee's internal organization to see if that organization has a social insurance provider that provides the social insurance type with the classification of WAO disability insurance.
Note: When searching for external organizations, the application only travels up the organizational hierarchy in the direction of the parent organization.
Organization Hierarchy and Employee Data
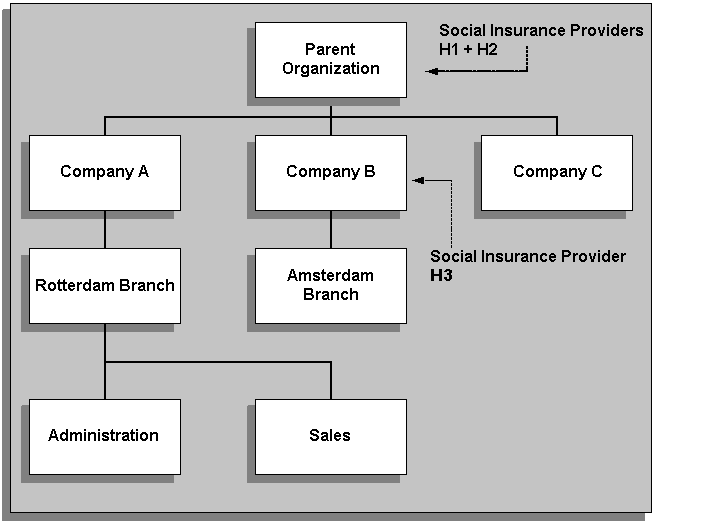
The previous diagram shows that the Social Insurance Providers H1 and H2 that have been assigned to the Parent Organization are available for the employees in Companies A, B and C, and their subordinate branches (Rotterdam and Amsterdam) and departments (Administration and Sales). The Social Insurance Provider H3 has been assigned to Company B, and is therefore only available for the employees at Company B and the Amsterdam Branch.
If an employee at the Amsterdam Branch is eligible for a social insurance classification that required a social insurance type that Social Insurance Provider H3 did not provide, the application would search up through the hierarchy at the next parent organization (Parent Organization) in the organization hierarchy to find the relevant social insurance type.
Examples of Assigning Social Insurance Types and Providers to Employees
This topic explains the possible scenarios that might occur when you assign social insurance (SI) types and SI providers to your internal organizations, and how your employees inherit this information.
Scenario 1
The following table describes a scenario of SI types and SI providers in an organization hierarchy. The text following the table explains how an employee from each organization inherits the information.
| Internal Organization | Order in Hierarchy | SI Provider | SI Classification | Primary Provider |
| HR Org 1 | First | UWV Org 1 | ZVW | Yes |
| UWV Org 2 | ZW | Yes | ||
| HR Org 101 | Second | UWV Org 3 | ZVW | Yes |
| UWV Org 4 | ZW | No |
You assign Employee 1 to the internal organization HR Org 1. Employee 1 inherits the values for the ZVW social insurance type from the SI provider UWV Org 1, and inherits the values for social insurance ZW from the SI provider UWV Org 2.
You assign Employee 2 to the internal organization HR Org 101. Employee 2 inherits the values for the ZVW social insurance type from the SI provider UWV Org 3. UWV Org 3 is the primary provider of this social insurance for the employee's internal organization.
Employee 2 inherits the values for social insurance ZW from the SI provider UWV Org 2. The SI provider UWV Org 4 assigned to the HR Org 101 that provides the social insurance ZW, is not the primary provider for this SI type. The application searches up the hierarchy to the parent organization that has a primary SI provider that offers the ZW social insurance type (UWV Org 2).
Scenario 2
The following table describes another scenario of SI types and SI providers set up in an organization hierarchy. The following text explains how an employee from each organization inherits the information. In this scenario, the SI classification All Mandatory Insurances applies all of the mandatory insurances to the SI provider's internal organization.
Note: All mandatory insurances include the following six types of social insurance: WAO Base, WAO diff, We Wa, We We, ZVW and ZW.
| Internal Organization | Order in Hierarchy | SI Provider | SI Classification | Primary Flag Checked? |
| HR Org 1 | First | UWV Org 1 | All Mandatory Insurances | Yes |
| UWV Org 2 | ZW | Yes | ||
| HR Org 101 | Second | UWV Org 3 | All Mandatory Insurances | No |
| UWV Org 4 | ZW | No |
You assign Employee 3 to the internal organization HR Org 1. Employee 3 inherits the values for the ZVW social insurance from the SI provider UWV Org 1, and inherits the values for social insurance ZW from the SI provider UWV Org 2. Employee 3 inherits the SI type ZVW from the SI provider UWV Org 1 because the SI provider has an SI classification of All Mandatory Insurances, which includes the social insurance ZVW. The employee automatically inherits the SI type ZW from a separate SI provider (UWV Org 2).
Note: Every separate record you identify for a type of social insurance automatically overrides a primary provider that offers all of the mandatory insurances.
You assign Employee 4 to the internal organization HR Org 101. Employee 4 inherits the values for the ZVW social insurance from the SI provider UWV Org 2. For the employee's internal organization (HR Org 101), the SI provider UWV Org 3 offers the social insurance type ZVW, however as this is not the primary provider the application searches up the organization hierarchy to find a primary SI provider that offers the social insurance type of ZVW. As the SI provider UWV Org 1 has all of the mandatory insurances identified as the SI classification and as the primary provider, the application uses this SI provider with the values it has for the SI type of ZVW for the employee.
Note: If the SI provider UWV Org 1 had not been identified as the primary provider, the application would use the first SI provider that offered this type of social insurance, UWV Org 3.
Employee 4 inherits the values for social insurance ZW from the SI provider UWV Org 4. The social insurance type ZW is an individual record and assigned to HR Org 101.
Scenario 3
The following table describes a further scenario of SI types and SI providers in an organization hierarchy. The text that follows the table explains how an employee from each organization inherits the information.
| Internal Organization | Order in Hierarchy | SI Provider | SI Classification | Primary Flag Checked? |
| HR Org 1 | First | UWV Org 1 | ZVW | Yes |
| UWV Org 2 | ZW | No | ||
| HR Org 101 | Second | UWV Org 3 | All Mandatory Insurances | Yes |
| UWV Org 4 | ZW | No |
You assign Employee 5 to the internal organization HR Org 1. The employee inherits the values for the ZVW social insurance type from the SI provider UWV Org 1. The SI provider UWV Org 1 is the primary provider for this type of social insurance assigned to this organization.
Employee 5 inherits the values for social insurance ZW from the SI provider UWV Org 2. UWV Org 2 is the only provider that offers this type of social insurance for this organization.
Note: When searching for SI types and SI providers, the application only travels up the organizational hierarchy in the direction of the parent organization.
You assign Employee 6 to the internal organization HR Org 101. This employee inherits the values for the ZVW social insurance from the SI provider UWV Org 3. The SI provider has the SI classification of All Mandatory Insurances is the primary provider for the employee's internal organization.
Employee 6 inherits the values for social insurance ZW from the SI provider UWV Org 4. A separate SI provider (UWV Org 4) provides the SI type of ZW. This separate record automatically overrides the primary provider that offers all of the mandatory insurances.
Methods for Deriving Social Insurance Days
Oracle HRMS for the Netherlands enables you to derive the number of social insurance (SI) days used in the SI contribution calculations, using the following methods:
-
Average SI days: This method calculates a constant figure for SI days for each payroll period.
-
Average SI days with work schedules: This method uses the average constant figure and divides the number of days an employee works by the number of days in the employee's work pattern and multiplies it by the average number of days in a payroll period.
-
Real SI days: This method uses the employee's work schedule to count the number of days an employee actually worked during a payroll period.
Note: If you enable Law Walvis, the application does not use these methods. Instead, calculations are based on period amounts for SI thresholds and maximum wages.
The Average SI Days Methods
The average SI days method calculates a constant average days figure for SI days for each payroll period. The average SI days with work schedules method uses the average days value and the employee's work pattern.
To derive the number of SI days in a period according to the average days method, the application uses the global value for average days. To derive the number of SI days in a period according to the average days with work schedules method, the formula performs the following steps:
-
Checks if the employee has a work pattern attached to their assignment. The application uses the average SI days method if it does not find a work pattern for the employee.
-
Finds the number of days in the employee's work pattern, and determines which are regular working days.
-
Determines the average number of days in the period.
-
Calculates the average SI days: divides the regular working days by the number of days in a work pattern, and multiplies it by the number of days in a period.
-
Reduces the adjusted average days value by the number of days of unpaid leave that are deemed to be a non-SI absence.
The Real SI Days Method
The real SI days method uses the employee's work pattern to determine the number of days an employee has actually worked. A day is counted as an SI day if an employee worked on that day, regardless of how many hours they actually worked. Only unpaid leave days which are not deemed as SI days, reduce the number of real SI days.
You decide the method for deriving the maximum of SI days allowed for each period in the employee's assignment. This maximum is either five days per week for the weeks that the employee works, or the number of week days in the period. Whichever maximum SI days method you choose, the maximum possible number of SI days in the year is 260, 261 or 262, depending on the year.
To derive the number of real SI days in a period according to the real SI days method, the fast formula performs the following steps:
-
Determines the maximum number of SI days in the payroll period, using one of two methods: either the number of week days (Monday to Friday) in the period, or five days per week that the employee works.
-
Determines the regular working days in the period. This number indicates how many days an employee actually worked in the period.
-
Compares the regular working days to the maximum number of SI days, and uses the lowest value.
-
Reduces the real SI days value by the number of days of unpaid leave, that are deemed to be a non-SI absence.
Note: If both a Standard run and a Process Separate run are processed for an assignment, only the SI days will be shown in the Standard run and will be zero in the Process Standard run, even though the correct value is used in the calculation for the Process Separate run.
Override Requirements
The application always calculates two values for the SI days, one value is the real SI days, and the other value is calculated for use in the calculations depending on what day method or override has been specified. The real SI days value is stored in the application as you need it to perform an end of year adjustment for an employee's last payroll period or at the end of a calender year. The application must adjust and recalculate the SI days and the SI contributions according to the real SI days method and the normal cumulative recalculation SI calculation rule at the end of the year, if the real SI days method of calculation has not been used.
If you need to override the calculated or the adjusted figure for the SI days, for example the derived SI days figure for the payroll period is wrong, you can use the employee's assignment to manually enter a figure or a percentage of average or maximum SI days . This figure or percentage overrides the number of SI days for the payroll period.
You can also override the derived real SI days figure, and any manually entered figure or percentage of SI days for the assignment, at the payroll run level using input values on the social insurance element.
Alternatively, you can override real SI days by defining a fast formula titled NL_REAL_INSURANCE_DAYS that returns a parameter Real_Social_Insurance_Days with a two-digit SI days value. The formula can use any of the application database items, and input values are not mandatory.
Caution: When you use a fast formula to override real SI days, ensure that you account for multiple assignment aggregates. The application uses the override value that the fast formula returns in the calculation without making any adjustments for multiple assignments.
The following table describes the override hierarchy for the information you enter in order to determine the number of SI days in a period. Therefore, it shows the top level in the hierarchy as the manual entry at the payroll run level. The application overrides any information that you enter below this level in the hierarchy by the values entered at the payroll run level.
| Position in Hierarchy | Entry Level |
|---|---|
| 1 | Manual entry using input values at the payroll run level. |
| 2 | Manual entry of the override real SI days at the assignment level |
| 3 | Value derived from a user-defined fast formula |
| 4 | Percentage of average or maximum SI days entry of the overriding day method at assignment level. |
| 5 | Derivation method for the SI type at assignment level. |
| 6 | Derivation method for the SI type at SI provider organization level. |
See: Setting Up Social Insurance Days for more information.
Multiple Assignments
For employees that have more than one assignment on the same payroll, the application can aggregate the number of SI days across the assignments.
See: Multiple Assignment Processing for Social Insurance for more information about the impact of multiple assignments.
Creating and Maintaining Organizations
Creating an Organization
Use the Organization window to create:
-
Business groups
-
External organizations (for example, tax offices, pension providers, insurance carriers, disability organizations, benefit carriers, or recruitment agencies)
-
Internal organizations (for example, departments, sections or cost centers)
-
GREs/Legal Entities
If you use the Configuration Workbench to configure your enterprise structure, then you only need to create the additional internal and external organizations you require. For example, you can set up additional organizations to represent the internal divisions or departments, and external organizations for reporting or third party payments.
See: Extending the Enterprise Framework, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
To create an organization
-
Navigate to the Organization window and click New to create a new organization.
Note: For information about querying existing organizations, see: Finding an Organization
-
Enter a name for your organization in the Name field. A check is performed to see if organizations with the same name already exist.
All Oracle applications you install share the information entered in the Organization window. Therefore organization names must be unique within a business group, and business group names must be unique across your applications network.
You can create two organizations with the same name in different business groups but this can cause confusion later, if the HR: Cross business group profile option is set to Yes and you decide to share certain information across all business groups. If you decide to create two organizations with the same name, be sure that this will not cause you problems in the future.
-
Optionally, select an organization type in the Type field.
Organization types do not classify your organization, you use them for reporting purposes only. The type may identify the function an organization performs, such as Administration or Service, or the level of each organization in your enterprise, such as Division, Department or Cost Center. You create the organization types you require by entering values for the Lookup Type ORG_TYPE.
-
Enter a start date in the From field. This should be early enough to include any historical information you need to enter.
Note: You cannot assign an employee to an organization before the start date of the organization.
-
Enter a location, if one exists. You can also enter an internal address to add more details such as floor or office number.
Dutch only: If you are setting up external organizations for a tax office, a social insurance provider or a private health insurance provider, you must enter the postal address and contact details using the NL_POSTAL_ADDRESS Location EIT.
Mexico only: When defining a GRE/Legal Entity, if you select a location here, HRMS automatically associates it with this GRE in the Generic Hierarchy.
US only: If you are using Oracle Payroll in the US, every organization to which employees can have assignments, including business groups, must have on record a location with a complete address. This is because the system uses the location of the organization of the employee's primary assignment to determine employee work locations for tax purposes. This does not apply to GREs, because the assignment to a GRE exists in addition to the assignment to an organization.
India only: You can define an income tax organization and enter its location details. You can then select this organization at the GRE/Legal Entity Income Tax Office.
Note: If you are an Oracle Inventory user, then you must not assign a location to more than one organization classified as an Inventory Organization.
-
Enter internal or external in the Internal or External field. You cannot assign people to an external organization.
Examples of external organizations that may require entry are disability organizations, benefits carriers, insurance carriers, organizations that employees name as beneficiaries of certain employee benefits, and organizations that are recipients of third party payments from employees' pay.
-
Save the basic organization details.
Entering Organization Classifications
To determine the purpose and use of each organization you create, you give it one or more classifications. The setup information you enter for an organization depends in large part on its classification.
See: Organization Classifications
Note: If you classify an organization as a business group, it is not reversible.
To enter organization classifications:
-
Enter the classification for your organization in the Name field.
-
Enable the classification by checking the Enable box. This allows you to use and enter the essential additional information for your organization.
-
Save the classification details.
-
You can either enter additional information for the classification type or enter another classification.
Note: Save each classification after entering and enabling it.
Entering Additional Information
For each classification you set up you can enter additional information. This information can be different for each classification.
For business group see: Business Group
For HR organization see: HR Organization
For representative body see: Representative Body
For constituency see: Constituency
For bargaining association see: Bargaining Association
For Dutch UWV organization see: Dutch UWV organization
For professional body information see: Professional Body Information
For pension providers, use the Framework Pension pages--rather than the Organization window--to assign pension types to each provider. Also use these pages to assign providers and types to your HR organizations. See: Setting Up Pension Schemes.
See Organization Classifications if you need to check which classification to select.
To enter Business Group additional information
-
Click on the organization classification for which you want to enter additional information.
-
Choose the Others button to open the Additional Organization Information window.
-
Select one of the following:
-
Business Group Information, see: Entering Business Group Information, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide.
-
Budget Value Defaults, see: Business Groups: Entering Budget Value Defaults.
-
Work Day Information, see: Business Groups and HR Organizations: Work Day Defaults.
-
Benefits Defaults, see: Business Groups: Defining a Default Monthly Payroll.
-
PTO Balance Type, see Business Groups: Selecting a PTO Balance Type.
-
Recruitment Information, see Business Groups: Entering Recruitment Information
-
Dutch Business Group, see Business Groups: Entering Dutch Business Group Information
-
Payslip Balances, see: Identifying Balances for the Payslip
-
Payslip Elements, see: Identifying Elements for the Payslip
-
ABP Pension Types, see: Assigning ABP Pension Types to an Organization
Important: Do not edit the NL ER Pension Types EIT from the Organization window. Instead, use the Pension pages to assign pension types to employers.
-
-
Repeat these steps to enter further information.
To enter HR organization additional information
-
Click on the organization classification for which you want to enter additional information.
-
Choose the Others button to open the Additional Organization Information window.
-
Select one of the following:
-
Reporting Information, see: Entering Reporting Information for an HR Organization or a Company Cost Center.
-
Costing Information, see: HR Organizations: Entering Costing Information
-
Parent Organization, see: HR Organizations: Entering Parent Organizations
-
Work Day Information, see: Business Groups and HR Organizations: Entering Work Day Defaults
-
Dutch Organization, see HR Organizations: Entering Dutch Organization Information
-
Dutch SI Provider, see HR Organizations: Entering Dutch SI Provider Information
-
Dutch ABP Provider, see: HR Organizations: Entering Dutch ABP Provider Information
-
ABP Pension Types, see: Assigning ABP Pension Types to an Organization
Important: Do not edit the NL ER Pension Types EIT from the Organization window. Instead, assign pension types to employers using the Pension pages.
-
ABP Pensions General Information, see: HR Organizations: Entering ABP Pensions General Information
-
ABP Sender Details, see: HR Organizations: Entering ABP Sender Details
-
Related Organizations Information, see: Entering Related Organizations Information for an HR Organization
-
-
Repeat these steps to enter further information.
To enter representative body additional information
-
Click on the organization classification for which you want to enter additional information.
-
Choose the Others button to open the Additional Organization Information window.
-
Select one of the following:
-
Representative Body Information, see: Entering Representative Body Information
-
Constituency information, see: Entering Constituency Information for a Representative Body
-
Work Day Information, see: Business Groups and HR Organizations: Entering Work Day Defaults
-
-
Repeat these steps to enter further information.
To enter constituency additional information
-
Click on the organization classification for which you want to enter additional information.
-
Choose the Others button to open the Additional Organization Information window.
-
Select one of the following:
-
Location, see Entering Location Information for Constituencies
-
Organization, see Entering Organization Information for Constituencies
-
Organization Hierarchy, see Entering Organization Hierarchy information for Constituencies
-
Bargaining Unit, see Entering Bargaining Unit information for Constituencies
-
Collective Agreement Grade, see Entering Collective Agreement Grade information for Constituencies
-
-
Repeat these steps to enter further information.
To enter Dutch UWV organization additional information
-
Click on the organization classification for which you want to enter additional information.
-
Choose the Others button to open the Additional Organization Information window.
-
Select one of the following:
-
Dutch UWV Organization, see Dutch UWV Organization: Entering Dutch SI Provider Information
-
Dutch SI Type, see Dutch UWV Organization: Entering Dutch SI Type Information
-
-
Repeat these steps to enter further information.
To enter bargaining association information
-
Click on the organization classification for which you want to enter additional information.
-
Choose the Others button to open the Additional Organization Information window.
-
Select Trade Union Information, see: Entering Trade Union Information for a Bargaining Association
-
Repeat these steps to enter further information.
To enter company cost center information
-
Click on the organization classification for which you want to enter additional information.
-
Choose the Others button to open the Additional Organization Information window.
-
Select one of the following:
-
GL Company Cost Center, see: Entering GL Company Cost Center Information for a Company Cost Center
-
Reporting Information, see: Entering Reporting Information for an HR Organization or a Company Cost Center.
-
-
Repeat these steps to enter further information.
To enter professional body information
-
Click on the organization classification for which you want to enter additional information.
-
Choose the Others button to open the Additional Organization Information window.
-
Select Professional Body Info, see: Entering Additional Information for a Professional Body.
-
Repeat these steps to enter further information.
Finding an Organization
Use the Find Organization window to find the organizations you want to review or amend. If you want to set up a new organization, rather than querying an existing organization, select the New button. For more information about creating a new organization, see Creating an Organization.
Note: When you navigate to the Organization window, the Find Organization window automatically displays.
To query an organization using the Find Organization window
-
Do one, a selection, or all of the following:
-
Enter a full or partial query on the organization's name. If more than one name matches the selection criteria, select one of the names.
-
Enter a full or partial query on the organization type and/or location. If more than one organization type or location matches the selection criteria, select the type and/or location to query.
-
Enter a full or partial query on the classification name. If more than one classification name matches the selection criteria, select the name to query.
For the classification you have selected indicate whether you want to query on:
-
Enabled classifications: This only returns those organizations that match your selection criteria and have your selected classification enabled.
-
Disabled classification: This only returns those organizations that match your selection criteria and have your selected classification disabled.
-
Both: This returns organizations that match your selection criteria and have your selected classification, regardless of whether the classification is enabled or disabled.
-
-
-
Choose the:
-
Find button to run the query.
The organization or organizations found by the query display in the Organization window. If the query finds more than one organization, you can use the [Down Arrow] key or choose Next Record from the Go menu to display the next organization.
-
Clear button to remove the existing selection criteria. You can then enter new information on which to perform a query.
-
Removing and Deleting Organizations
Remove an organization if you want to prevent it being available for employee assignments. This still leaves a history of the organization. Only delete an organization if you want to completely remove it from your system.
To remove an organization
-
Select the organization you want to remove.
-
Enter an end date (Date To) on the organization record.
To delete an organization
-
Remove any employee assignments to the organization.
-
Remove the organization from any hierarchies.
-
Disable its organization classifications in the Organization window.
-
Delete the organization in the Organization window.
Entering Additional Organization Information
Entering Business Group Information
To enter Business Group information
-
In the Organization window, query the Business Group if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group, choose the Others button, and select Business Group Information.
-
Click in a field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Business Group Information window.
-
You can enter a short name for the Business Group. This name is no longer used in Oracle HRMS it is provided for compatibility with earlier releases, where it appeared in the header line of each form.
-
Select the method of creating identifying numbers for employees, applicants, and contingent workers. The choices are:
-
Automatic number generation.
If you choose the automatic entry method of number generation you can at a later date decide to switch to global sequencing. Global sequencing enables you to use a single sequence of person numbers for applicants, employees or contingent workers across multiple business groups.
See: Running the Global Sequencing for Person Number Generation Process, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
You can switch from local automatic numbering to manual numbering for a person type by editing the business group information and selecting Manual.
Note: If you are using Oracle iRecruitment, ensure to set the applicant numbering to Automatic.
-
Manual entry.
If you choose the manual entry method of number generation, but at a later date decide to change to the Automatic method of number generation, you can run the Change Person Numbering to Automatic process.
See: Running the Change Person Numbering to Automatic Process, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Automatic use of the national identifier (for example, the social security number in the US, and the NI number in the UK). If you choose this option you must ensure that a national identifier is entered for each new person. This option is not available for applicants.
Note: For whichever method of number generation you choose, it is important to be aware that the number is displayed in various windows and reports. Therefore, if you choose the national identifier method, the person's national identifier is displayed.
-
Employee numbering for contingent worker. This option allows you to use the same sequence of numbers for contingent workers as you use for your employees. For example, you enter an employee and the application gives the employee number 101. If the next person entered is a contingent worker they receive the number 102.
-
-
Select the names of the key flexfield structures you want to use in this Business Group.
-
Select the appropriate Legislation Code and default currency. The Legislation Code determines the startup data you can access and the contents of some legislation-specific windows.
Mexico only: Specify MXN as the currency. Do not select MXP.
Important: Selecting the correct legislation code is essential for the correct functioning of Oracle HRMS. You cannot change the legislation code after entering employees against the Business Group.
-
US users: To maintain fiscal year balances in Oracle Payroll if your fiscal year is different from the calendar year, enter the fiscal year start date.
The application does not provide a connection between the fiscal year functionality in Oracle General Ledger and in Oracle HRMS. In Oracle General Ledger you specify how the fiscal calendar is broken down in the Accounting Calendar view. Oracle HRMS calculates a fiscal quarter as a three month period. The application calculates four equal three month periods beginning from the fiscal year start date.
South African users: You must enter the fiscal year start date for your Business Group, or you will not be able to define payrolls later.
-
You can enter a Minimum and Maximum Working Age for the Business Group. When you enter or hire employees, you receive a warning if the person's age is outside this range.
-
Save your work.
Entering Dutch Business Group Information
You use the Dutch Business Group window to define the organization hierarchy for your business group, and to override the Replacement method of retropay you may have previously enabled.
For further information on how to enable your retropay method of choice, see: Enabling the Method of Retropay
To enter Dutch business group information
-
Query the business group if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region select Business Group, choose the Others button and select Dutch Business Group.
-
Click in the field in the Additional organization Information window to open the Dutch Business Group window.
-
Select the preferred hierarchy for your business group in the Organization Hierarchy field.
Note: The named hierarchy defines the way in which additional information is stored for your internal organizations. Information that is defined for a particular organization also applies to all child organizations within the named hierarchy.
-
To override the Replacement method of retropay enabled, select Yes in the Override Replacement Method field. Select No if you wish to continue running this method.
For further information on the methods of retropay available for the Netherlands, see: Retropay for the Netherlands
-
In the Sender Tax Reporting Name field, enter the name of your sender for tax reporting purposes. You can enter up to 22 characters.
-
In the Sender Tax Registration Number field, enter your sender's tax registration number. You can enter up to 12 digits.
-
Optionally, enter a start date from when the application must use the Adjustment and Correction retro components to identify the Correction periods in the Dutch wage report. Leave this field blank, if you want to report Corrections using the New Wage Override element.
-
In the Assignment Process Group field, select Employer to process multiple assignments according to employer. Alternatively, select Payroll to perform Payroll-based processing.
-
Specify whether you want the application to perform late hire processing. Select Yes to ensure the application uses the salary-earned date instead of salary-paid date for the calculation of SI and tax deductions for new hires and retrospective reversal of employee terminations.
Before processing previous period payroll for late hires, ensure you setup the predefined Late Hire Indicator element using the Element Entries window. Use the predefined Late Hire Indicator element only with the late hire employees. After you finish processing payroll for the previous periods, specify an end date so that the application starts calculating the current period payroll using the salary-paid date. Do not use the adjustment component of the RetroPay for late hires as it will result in incorrect payroll calculation.
Note: For retrospective reversal of employee terminations, ensure that you create an element entry for the predefined element Late Hire Indicator for the valid period between the termination and reversal. For example, if you terminate an employee in February2006 and reverse the termination in May 2006, you need to create an element entry for the employee valid from 1st February 2006 to 31st May 2006.
-
Save your work.
Business Groups: Entering Budget Value Defaults
You can set up budgets for non-monetary measures such as headcount or full-time equivalent. When you enter employee assignments to define the work an employee does for your enterprise, you can specify the value of the assignment towards these budgets. For example, all assignments typically count as one for headcount budgets, but may count as less than one for full-time equivalent budgets.
To remove the requirement to enter these values for every assignment, you can enter defaults for the whole Business Group. You can override the defaults for individual assignments.
To define budget value defaults
-
In the Organization window, query the Business Group if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group, choose the Others button, and select Budget Value Defaults.
-
Click in a field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Budget Value Defaults window.
-
In the Units field, select a measurement type, such as Full Time Equivalent or Headcount.
-
Enter a default value in the Value field.
You can enter a default value for as many budgetary units as you plan to use for the Business Group.
To find out more about budgets see: Budgeting Overview, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
Business Groups: Selecting a PTO Balance Type
If you use Oracle Payroll, you can choose to use a payroll balance to store gross accruals for an accrual plan. The payroll balance is maintained by the payroll run. It calculates accruals from the day after either the Date Earned or the Date Paid of the last payroll period in which the assignment was processed
To specify whether to use Date Earned or Date Paid for all your accrual plans, select a PTO Balance Type for your business group. The default is Date Paid.
To select a PTO balance type
-
In the Organization window, query the business group if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group, choose Others, and select PTO Balance Type.
-
Click in the field on the Additional Organization Information window to open the PTO Balance Type window.
-
Select Date Paid or Date Earned in the PTO Balance Type field.
-
Save your work.
Business Groups and HR Organizations: Entering Work Day Defaults
To enter schedule information for a person, you can:
-
Set up extensive availability information such as, shifts, schedules, and calendar events using integrated features from HRMS and Common Application Components (CAC).
See: Setting Up Availability, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
Set up holiday calendars, shifts, and work plans in OTL.
See: Time Management Structures, Oracle Time and Labor Implementation and User Guide
Alternatively, you can enter basic schedule information in various areas of Oracle HRMS, such as here in the Organization window. You can set up default working hours for all employees in the Business Group or in an HR Organization, saving data entry at lower levels. When necessary, you can override the defaults at lower levels, for example, for individual positions or employee assignments.
Important: The application does not use the schedule information that you can enter here to determine a worker's availability. This is for information purposes only.
The decision for which method to set up is based on knowledge of which applications use which information.
The Salary Administration process uses working hours information to prorate the salary values against which it validates any salary proposals.
To define work day defaults
-
In the Organization window, query the Business Group or HR Organization if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group or HR Organization, choose the Others button, and select Work Day Information.
-
Click in the field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Work Day Information window.
-
Enter the normal start and end times in 24 hour format. For example, for 5.30 p.m., enter 17:30.
-
Enter a number in the Working Hours field, and select the corresponding period of time in the Frequency field. For example, enter 40 and select Week.
You can add to the list of available frequencies by making entries for the Lookup Type FREQUENCY, using the Application Utilities Lookups window.
Defining Benefits Defaults for a Business Group
Follow this procedure to define a default payroll for benefits administration and to configure the use of benefits assignments.
You use both the Payroll Description window and the Organization window to assign a default payroll to a business group.
When a benefits assignment is created for an employee, due to their termination or other qualifying event, the benefits assignment must have a default payroll. US and Canadian customers should define a default payroll with a periodicity of monthly.
You can indicate if you want the application to auto-generate benefits assignments for qualifying events. For US and Canadian customers, the application creates benefits assignments by default.
To define benefits defaults for a business group
-
For monthly payrolls, create a payroll with a period type of Calendar Month using the Payroll Description window.
-
Save your work and exit the Payroll Description window.
-
Select the business group for which you want to define a default payroll using the Find Organization window.
-
Place the cursor in the Organization classifications block on the Business Group field and choose the Others button.
-
Select Benefits Defaults from the Additional Organization Information lookups.
-
Choose the Next button to display the Benefits Defaults window.
-
Select a default payroll for this business group.
-
In the Benefits Assignment field, select Yes if you want to record benefits assignments for continuing benefits eligibility.
If your enterprise uses Oracle HRMS solely for compensation management--or if you do not want the application to automatically create benefits assignments--select No.
See: Continuing Eligibility: Benefits Assignments, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
-
Save your work.
Business Group: Setting Up Public Sector-type Functionality
Oracle HR enables you to set up a particular business group for Commercial or Public Sector-type functionality.
To set up public sector-type functionality
-
In the organization window, query the Business Group if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group, choose the Others button, and select Public Sector Details.
-
Click in a field of the Additional Organization information window to open the Public Sector Details window.
-
In the Installed field, select Yes or No.
The default value is No, hence there is no impact on existing business groups. Select Yes if you want to use the public sector-type functionality of Oracle HR. You need to manually change this value for each business group.
-
Save your work.
Business Groups: Entering Recruitment Information
You enter recruitment information at the business group level to define various default values for iRecruitment.
You enter additional information for iRecruitment in the Organization window of Oracle HRMS.
To enter Recruitment information
-
In the Organization window, query the business group. In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group, choose the Others button, and select Recruitment.
-
Click in a field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Recruitment information window.
-
Specify how the vacancy code is allocated. The choices are:
-
Manual - the Vacancy Name field is displayed when you create a vacancy. You must manually enter a name for the vacancy.
-
Automatic - the application assigns a unique vacancy name automatically. The Vacancy Name field is not displayed when you create a vacancy.
-
-
Enter the default number of openings for a vacancy. The default number is displayed in the Total Openings field when you create a vacancy. You can overwrite the default value if required.
-
You can specify the organization defaulting method. The choices are:
-
Creator - The default organization for a vacancy is the organization for the person who has created the vacancy (employee who has logged in).
-
Manager - The default organization for a vacancy is the organization for the manager of the vacancy.
You can overwrite these defaults when you create a vacancy. Both methods use the primary assignment.
-
-
Specify the location defaulting method. The choices are:
-
Manager - The default location for the vacancy is the same location as the manager for the vacancy.
-
Position - The default location for the vacancy is the same location as the position for the vacancy.
-
-
You can select a default budget measurement type, for example, FTE or headcount.
To find out more about budgets, see Budgeting Overview, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
-
Select a default status which is assigned to a candidate when a candidate withdraws an application. If you do not specify a particular status here, the candidate receives the Terminate status.
-
Specify a user-defined person type as a default for candidates who register in iRecruitment. Oracle HRMS creates a record with this default person type when a candidate registers in iRecruitment. If you do not specify a value, the default person type is Candidate.
Note: The user person type that you define here is associated with the External system person type. The internal code for this system person type is OTHER.
-
Select Yes if you want to exclude this business group from the list of business groups available on the Create Vacancy page. You should do this if you do not want managers or recruiters to be able to create vacancies for this business group.
-
Select a default resume template that iRecruitment can use to create resumes for candidates. When candidates register, they can use the default template or select a template of their choice in the Create Resume page.
-
Select Yes to record and track applicant data for compliance purposes. When you enable the applicant tracking functionality, Oracle iRecruitment creates snapshots of applicants who apply for vacancies in that business group. The snapshots include personal information, skills, qualifications, and work preferences.
-
Save your work.
Assigning ABP Pension Types to an Organization
Employees participate in ABP pension types that are assigned to their organization or parent organizations in the default organization hierarchy. You can assign pension types to a business group or HR organization.
-
In the Organization window, query the Business Group or HR Organization if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group or HR Organization, choose the Others button, and select Dutch ABP Pension Types.
-
Click in the field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Dutch ABP Pension Types window.
-
In the Date From field, enter the first day on which the pension type becomes valid for this organization. You can also enter an end date in the Date To field.
-
Select the pension type.
-
Optionally enter or change the employee and employer contribution percentages to provide a default for the employees assigned to this organization, or its child organizations.
-
Change the Valid field from Yes to No if you do not want this pension type to be available for all employees assigned to this organization, or its child organizations.
-
Choose OK and save your work.
-
You can repeat these steps to assign another pension type to this organization.
Assigning PGGM Pension Types to an Organization
To record PGGM pension information for employees, you assign PGGM pension types to their organization or parent organizations in the default organization hierarchy. You assign pension types to a business group or HR organization.
To Assign PGGM Pension Types to an Organization
-
In the Organization window, query the business group or HR organization. In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group or HR Organization, click Others, and select PGGM Pension Types.
-
Click in the field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the PGGM Pension Types window.
-
In the Date From field, enter the first day on which the pension type becomes valid for this organization. Optionally, enter an end date.
-
Select the pension type.
-
To provide default values for employees assigned to this organization or its child organizations, enter or change the employee and total-contribution percentages.
Additional Information: The application calculates the employer contribution as the difference between the total and employee contributions.
-
Click OK, and save your work.
Entering Payslip Information
-
In the Organization window, query the Business Group if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select either Business Group or HR Organization, choose Others, and select Payslip Information.
-
Click in a field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Payslip Information window.
-
Select the type of extra information to be displayed on the payslip. The choices are:
-
Balance
-
Element
-
Message
Your selection determines which other fields you must complete in this window.
-
To enter Balance extra information
-
Select a balance name.
-
Select a dimension.
-
Optionally, enter a display name for the balance.
-
Optionally, enter a message text.
-
Save your work.
To enter Element extra information
-
Select the element you want to display.
-
Select the input value for the element.
-
Optionally, enter a display name for the element.
-
Optionally, enter a message text.
-
Save your work.
To enter Message extra information
-
Enter a display name for the message.
-
Enter a message text. This message will be displayed on the employees' online payslip.
-
Save your work.
Entering Self-Service Preference Information
You enter self-service preference information to define whether documents such as the online payslip is available in either or both online and paper version.
Note: You can also enter this information at the Person or Location level.
See: Person Extra Information Types, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide and Location Extra Information Types, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
These information levels are arranged in a hierarchy. If you define self-service preferences at the person level, the settings will override any other settings made at the location, business group, or HR organization level. Similarly, if you define self-service preferences at the location level, the settings override any settings at the business group or HR organization level. Settings at the HR organization level will override settings at the business group level.
To enter Self-Service Preference information
-
In the Organization window, query the Business Group or HR Organization if it does not already appear there.
-
In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group or HR Organization, choose Others, and select Self Service Preference.
-
Click in a field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Self Service Preference window.
-
Select the document type for which you want to define preferences.
Australia users: Select payslip, payment summary, or payslip modeler.
If Payslip Modeler functionality is available, you must select the document type as Payslip Modeler.
-
Select whether you want the document to be available online.
-
Select whether you want the document to be available on paper.
-
If you are providing payslips in PDF format:.Select the appropriate localization template. If you do not select the a payslip template, then the web web-based payslip is displayed
Note: Australia, China, India, Hong Kong, Singapore, Korea, and New Zealand users should select the appropriate predefined localization template.
-
You can append custom data to the generated XML. Specify the custom package and procedure in the XML Code field as : <custom package>.<custom procedure>.
-
Specify the dates these changes are to take effect.
Note: Template, XML Code and Effective Date fields in Self-Service Preference can be configured at the Business Group, HR Organization, and Location levels.
The application generates either an Oracle Applications Framework (OAF)-based payslip or PDF payslip depending on the values entered in the Template and Effective Date fields. A PDF Payslip is generated when you select the template and enter the effective date on or before the payroll payment date.
For example, consider the effective date of PDF payslip as 01-Jun-2016:
If the payment date is prior to the effective date (31-May-2016), then the application generates an OAF payslip.
If the payment date is later than the effective date (30-Jun-2016), then the application generates a PDF payslip.
-
-
If payslip modelling is enabled for your localization, then select the template that you want to use for payslip modeling process to use, if you do not want the application to use the default template.
-
Select the element set for elements that you want to exclude from selection when you run a payslip modeling process.
-
Payslip Employer Address – Select either a GRE/Legal Entity Address or an HR Organization Address (default) to display on the payslip.
Note: You can configure this segment only at the Business Group level.
For Canada only – Both the OAF and PDF payslips display the HR Organization as the Employer Address.
-
Display Payslip GRE Addr From – If you selected GRE/Legal Entity Address for the Payslip Employer Address field, select the effective date after which the GRE address displays on the payslip.
Note: You can configure this segment only at Business Group level.
For Canada: – This field is not applicable.
-
Specify the Offset Criteria – Select either Payslip View Date or Date Paid to configure the date to be used for displaying Online Payslips. If this field is left blank or if the Payslip View Date is selected then the online payslip will be displayed based on the Payslip View Date that is defined for the payroll period. If Date Paid is selected, then the payslip will be displayed based on the Date Paid of the payroll run.
Note: By default, Payslip View Date – Check Date for any period will be equal to the Payslip offset defined for the payroll. However, if the user manually changes these dates for any period, then the Payslip Offset for that period will be considered as the Payslip View Date – Check Date and not the Offset defined for the Payroll.
If the Payslip View Date or the Payslip Offset is set to null, then all payslips (prior, current and future) will be available to the employee. By default, the Payslip Offset is set to zero when creating the Payroll definition.
-
Select whether you want to display the rate details section.
-
Save your work.
Identifying Balances for the Payslip
You enter payslip balances information to determine the balances you want to archive and display on the payslip. You can define multiple balances for archive.
Enter the payslip balances information using the Organization window.
To identify balances for the payslip
-
In the Organization window, query the Business Group if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group, choose the Others button, and select Payslip Balances.
-
Click in the Additional Organization Information window to open the Payslip Balances window.
-
Select the Balance Name and Balance Dimension. In the Balance Narrative field enter a description of the balance information. This appears on the payslip. The order you define the balances determines the sequence the application picks them up and displays on the payslip.
Note: Netherlands users: You can select the Social Insurance Type from the list of values, but only if you have selected entries for both the Balance Name and Balance Dimension fields.
-
Save your work.
Identifying Elements for the Payslip
You enter payslip elements information to determine the elements you want to archive and appear on the payslip. You can define multiple element input values for archive.
Enter the payslip elements information using the Organization window.
To identify elements for the payslip
-
In the Organization window, query the Business Group if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Business Group, choose the Others button, and select Payslip Elements.
-
Click in the Additional Organization Information window to open the Payslip Elements window.
-
Select the Element Name and Input Value. In the Narrative field enter a description of the element information. This appears on the payslip. The order you define the elements, determines the sequence the application picks them up and displays them on the payslip.
Note: Netherlands users: You can select the Social Insurance Type from the list of values, but only if you have selected entries for both the Balance Name and Balance Dimension fields.
-
Save your work.
HR Organizations: Entering Costing Information
-
In the Organization window, query the HR Organization if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select HR Organizations, choose Others, and select Costing Information.
-
Click in the Additional Information window to display the segments of the Cost Allocation flexfield set up with the qualifier of Organization.
-
Select the appropriate cost code in each segment.
For individual employees, you can override these organization-level codes by entering costing information on their assignments.
Entering Reporting Information for an HR Organization or a Company Cost Center
Use the Reporting Information window to enter information that can be used when reporting on the organization.
If you want to enter managers for a number of organizations, or want to see an historical record of the managers for an organization, then you can use the Organization Manager Relationship window. See: Selecting and Viewing Managers for Organizations, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
To enter reporting information
-
Query the Company Cost Center in the Organization window, if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Company Cost Center, choose the Others button, and select GL Company Cost Center Information.
-
Click in the field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the GL Company Cost Center Information window.
-
Enter a reporting name. This could be a short name that enables you to easily identify the organization in a report.
-
Select the manager of the cost center. The list of people consists of all active employees from your business group. If the HR: Cross Business Group profile option is set to yes, then it includes employees from all your business groups.
Note: If you are using management reporting in DBI, then you must enter a manager.
-
Enter a start date for the relationship, and an end date if required.
HR Organizations: Entering Parent Organizations
After you set up organization hierarchies, use the Parent Organization window to place a subordinate organization in hierarchies by naming its immediate parent in each hierarchy.
To enter a parent organization
-
In the Organization window, query the HR Organization if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select HR Organization, choose Others, and select Parent Organization to open the Parent Organization window.
-
Select the hierarchy name.
-
Select the name of the parent organization to which the HR Organization is subordinate in this hierarchy.
-
To enter the HR Organization in another hierarchy, repeat steps 2 and 3.
HR Organization: Entering Social Insurance Provider Information
You can assign multiple SI (Social Insurance) classifications and SI providers to your HR Organization. Oracle recommends that you select at least one SI classification and provider at the highest level in your named hierarchy to ensure that the information is inherited by any subordinate organizations.
You enter SI provider information for your HR organization in the Organization window.
To enter social insurance provider information
-
Query the organization if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classification region, select HR Organization, the Others button and Dutch SI Provider.
-
Enter the dates for the period of time the social insurance is valid for the organization.
Important: When you select the dates for an SI provider, ensure that they cover the entire tax year period. This is to ensure that when a payroll is run for an employee's assignment, the correct SI information is used and avoids inconsistent payroll calculations. If you end date this information part way through a tax year, the payroll calculations will search up your organization hierarchy for another SI provider that offers the relevant SI type. This SI type may have different SI contribution percentages, thresholds and calculation methods set up, therefore resulting in incorrect SI calculations for the assignment.
-
Select the SI classification. Ensure you choose an SI classification for the SI type you defined previously.
For example, if you have defined an SI type of WAO basis for the SI provider, select the SI classification of WAO for your HR Organization.
Warning: The application will not prevent you from choosing an SI classification that is different from the SI type you have defined previously. It is important that you set up this information correctly in order for the application to find the relevant social insurance information for your employees.
If you select All Mandatory Insurances as the SI classification, effective from 2013, then the SI type ZVWS are included. The SI types, ZVW Social Insurance, IVA Social Insurance, and WGA Social Insurance are not included. Ensure that each SI provider you select has all mandatory social insurance types assigned correctly to that provider. This means that you would only have to record this information once for your internal organization and it will prevent inconsistencies in your payroll results.
-
Select the SI provider that you defined previously.
-
Select whether you want this SI provider to be the primary SI provider in the Primary Provider field. This field determines the default SI provider.
Important: If you select Yes in the Primary Provider field and also select the SI classification: All Mandatory Insurances, then all of the insurances apply to the employees you assign to this internal organization. If you have a different individual social insurance type, you can set up a separate record for that particular type of insurance, and assign it to the internal organization using the same SI classification as the SI type.
See: Examples of Assigning Social Insurance Types and Providers to Employees for more information.
-
Enter the branch registration number and select a transfer indicator.
-
Enter the sender's and employer's reporting names and registration numbers. The UWV social security agencies use this information to identify the sender and employer of the Notification Social Insurance (NSI) file.
You receive a reporting name and registration number when you register with the UWV social security agency.
-
Save your work.
HR Organization: Entering Dutch ABP Provider Information
You enter ABP provider information for your HR organization in the Organization window. The ABP Notification report uses this information.
To enter ABP provider information
-
Query the organization if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classification region, select HR Organization, choose the Others button, and select Dutch ABP Provider.
-
Click in the field to open the Dutch ABP Provider window.
-
Select an ABP Provider name.
-
Enter the registration number supplied by ABP.
-
Optionally, enter Submitter Identification. If you enter a name, it appears in the header of the ABP Notification report. If you leave this field blank, the organization name appears in the header instead.
-
Enter the period type belonging to the organization. Currently, only Calendar Month and Lunar are supported. This is a mandatory field.
-
Enter any information as free text for your reference.
-
Choose OK and save your work.
HR Organization: Entering ABP Pensions General Information
You enter ABP pensions general information for your HR organization in the Organization window. The ABP report uses this information.
To enter ABP pensions general information
-
In the Organization window, query the HR Organization if it does not already appear there.
-
In the Organization Classifications region, select HR Organizations, choose Others, and select ABP Sender Details.
-
Click in the field to open the ABP Pensions General Information window.
-
Select average of the previous year or first of January or hire date as the part time percent calculation for non recurring bonus.
-
Specify whether to apply OHT correction or not.
-
Enter the end of year bonus percentage.
-
Enter the employee number override, a number that replaces specific positions of the employee number.
-
Specify the starting position from where the employee number needs to be replaced. For example, to replace position 1 to 4 with 1015 in employee number, the fields should be populated with Employee Number Override - 1015 and Starting Position - 1.
HR Organizations: Entering ABP Sender Details
Oracle HRMS enables you to enter details about the ABP file and sender. You enter ABP sender details for your HR organization in the Organization window. The ABP report uses this information.
To enter ABP sender details
-
In the Organization window, query the HR Organization if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select HR Organizations, choose Others, and select ABP Sender Details.
-
Click in the field to open the ABP Sender Details window.
-
Specify whether the file is generated for Test or Production environment. This is a mandatory field.
-
Enter the ABP registration number of the sender. This is a mandatory field.
-
Enter the name of the organization acting as the sender.
HR Organization: Entering Dutch Organization Information
Use the Dutch Organization information type to enter additional information for the Daily Sick and Recovery Report, tax office information, an average social insurance days figure, and a regular working hours figure for your internal organizations.
See: Running the Daily Sick and Recovery Report
See: Setting Up Social Insurance Days
Enter Dutch Organization information from the Additional Organization Information window.
To enter additional information for a Dutch organization
-
Query the Organization if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select HR Organization, choose Others and select Dutch Organization to open the Dutch Organization window.
-
Select the region and organization number.
-
Select the tax office. You can only select a tax office that you defined previously as an external organization with the classification of Dutch Tax Office.
-
Enter the tax registration number.
-
In the Tax Reporting Name field, enter the name of your company, for tax reporting purposes.
-
Enter a value for the average number of days in a month. The figure you enter here is used in the social insurance days calculations for average SI days with work schedules for monthly and quarterly payrolls.
-
Enter a value for the regular working hours in a week. Ensure that the figure you enter is correct, as it defaults to each employee's assignment in this organization. If, at a later date, you need to change the regular working hours, for example, you entered an incorrect figure, the new value only effects new assignment records.
Note: This figure does not override any values that you previously entered for the employee's regular working hours in the employee's assignment.
-
Select Contract or Real Working Hours in the Part Time Percentage Method field. The method you select defines the type of hours used in the part-time percentage calculation for wage tax subsidies.
-
If you have a 53-week year with a 4-week payroll and a 5-week final month, then select the Yearly or Weekly Factor from the Lunar 5 Week Month Wage Method. The lunar method calculates the wages, wage limits, and wage tax subsidy for the period.
-
Select which tax table to use to enable proration of standard tax for this organization. This means that you can calculate daily tax for newly hired employees and employees that are leaving your enterprise part way through a payroll period. For example, select Daily Table using Calendar Days to convert the employee's standard taxable income to a day value, based on the number of calender days that the employee worked during the period, multiplied by 365.
-
Select the WAO contribution insurance type that applies to your employees. Record this information for the ABP pensions report.
-
Enter the percentage of the employee's gross salary that you pay as a Parental Leave Wage Percentage.
-
In the Customer Number field, optionally enter the company assigned by the service or accountancy agency.
-
If the employer is based in the public sector, select Yes in the Public Sector Organization field.
-
In the Full Sickness Wage Paid field, select Yes if the employer pays 100% of the employee's wage during sickness.
-
In the IZA Weekly Full Time Hours field, enter the number of full time weekly hours to use in the adjustments for part time and incidental employees.
Note: This field only applies if your employee is eligible for IZA private health insurance.
-
In the IZA Monthly Full Time Hours field, enter the number of full time monthly hours to use in the adjustments for part time and incidental employees.
Note: This field only applies if your employee is eligible for IZA private health insurance.
-
When you set the LHD Proration Override field to 'Yes', the application does not use the proration values given in the user-defined formula 'NL_OVERRIDE_SOCIAL_INSURANCE_DAYS' for Labour Handicap Discount calculation. When you set this field to 'No', the application uses the proration values for Labour Handicap Discount calculation. If the value is not set, the value defaults to 'No'. Note: This field is used only in case of Labour Handicap Discount calculations and has no impact on other tax calculations where proration values defined in the formula 'NL_OVERRIDE_SOCIAL_INSURANCE_DAYS' are used. It enables you to keep the proration details of 'NL_OVERRIDE_SOCIAL_INSURANCE_DAYS' as applicable to achieve the desired calculations for Labour Handicap Discount.
-
Use the Beneficial Rule in Process Separate Run field to skip processing Beneficial Rule along with Net to Gross in Process Separate Run to avoid a Special Tax Deduction for the second assignment without any special taxable income. When this field is not set, it defaults to 'Yes'. When this field is set for a Parent organization, it is applicable for all its child organizations unless you override it. If you choose 'No' for an Organization, then the Beneficial Rule is not applied for applicable assignments of the Organization during the Process Separate Run.
-
Save your work.
HR Organization: Entering General PGGM Information
Use the PGGM General Info window to specify employer's PGGM information, such as the holiday allowance and yearly-bonus percentages for all employees in your HR organization. The application uses these values for calculating the PGGM pension salary.
To Enter General PGGM Information
-
In the Organization window, query the HR organization. In the Organization Classifications region, select HR Organization, click Others, and select PGGM General Info.
-
Click in the field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the PGGM General Info window.
-
In the Date From field, enter the first day on which the holiday allowance and yearly bonus percentages become valid for this organization. Optionally, enter an end date.
-
To provide default values for employees assigned to this organization or its child organizations, enter or change the holiday allowance and yearly-bonus percentages.
-
Enter the PGGM employer number and CAO Code, which identifies the collective agreement reference of the employer. Oracle HRMS uses this information for reporting purposes.
-
Click OK, and save your work.
HR Organization: Entering Wage Report Information
Use the Wage Report Information window to specify the sender ID and contact details for the wage report that you send to the tax authorities.
To enter wage report information
-
In the Organization window, query the HR organization identified as the employer.
-
In the Organization Classifications region, select HR Organization, click Others, and select Wage Report Information.
-
Click in the field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Wage Report Information window.
-
Enter sender ID, contact name, and contact number.
-
In the Paid Assignments Only field, specify whether to include only assignments processed in the payroll run during the period specified in the wage-report-generator process.
-
Specify whether you have insurance cover other than WAO.
-
Click OK, and save your work.
HR Organization: Entering Flat Rate Taxation Information
Use the Wage Report Information window to specify flat rate taxation information.
To enter flat rate taxation Information
-
In the Organization window, query the HR organization identified as the employer.
-
In the Organization window, select HR Organization in the Organization Classifications region, and click Others.
-
Select Flat Rate Taxation in the Additional Organization Information window.
-
In the Additional Organization window that displays, click in the Flat Rate Taxation EIT. Enter the following values in the Flat Rate Taxation window and click OK in both the windows:
-
Date From and Date To
-
Taxation Type – Choose from the following:
-
Alternative use of Company Car
-
Flat Rate Tax Deduction for Gifts
-
Flat Rate Taxation for Early Retirement/Pre-Pension
-
Labour Cost Arrangement
-
Major Issue Flat Rate Tax Deduction
-
Single Rate Exceptional Payment Tax Deduction
-
Wage Tax Subsidy for Research and Development
-
-
Amount
-
Period Type
-
Payroll Frequency
-
Correction - Yes or No
-
-
To update amount information, correct the Amount and select the Correction value as Yes.
-
Save the record.
Once you have entered flat rate tax information you can run the Dutch Wage Report to view the corrected flat rate taxation information.
Adding Sickness Information
Use the Organization window to enter details of sickness information for the classification you selected.
To add sickness information
-
Select Yes or No in the Test Message field.
-
Enter the Sector. This is a mandatory field.
-
Enter the Risk Group. This is a mandatory field.
-
Enter the Role of Sender. This is a mandatory field.
-
Enter the Sender Tax Registration Number. This is a mandatory field.
-
Enter the Contact Person or Department.
-
Enter the Establishment Name.
-
Select the Gender of Contact Person from the list.
-
Enter the Phone Number of Contact Person.
-
Click OK.
Adding Labor Cost Arrangement Information
Use the Organization Additional Information EIT to enter additional details about your labor cost arrangement.
To add Labor Cost Arrangement Information
-
Enter a value in the Year field. By default, this displays the current session date
-
Enter a Calculation Method.
-
The Previous Year Taxable Income field displays automatically based on the value of the Year.
-
Save your work.
Entering GL Company Cost Center Information for a Company Cost Center
Use the GL Company Cost Center window to enter information about the company or cost center in Oracle General Ledger that the organization represents. Liaise with your Financials implementation team to get this information.
Oracle HRMS may default this information automatically if it is set up to generate organizations in HRMS whenever a cost center is defined in GL.
Once your company cost center information has been set up then you must not change it.
To define GL Company Cost Center Information:
-
Query the company cost center in the Organization window, if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Company Cost Center, choose the Others button, and select GL Company Cost Center Information.
-
Click in the field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the GL Company Cost Center Information window.
-
Select the company value set that validates the company segment in your GL flexfield and the GL company name for the organization.
Note: If you are defining an organization that represents a company in GL do not complete any further fields and save your work.
-
Select the cost center value set that validates the cost center segment in your GL flexfield and the GL cost center name for the organization.
-
Save your work.
Entering Representative Body Information
You use the Representative Body Information window to record details about organizations classified as a representative body; for example, jurisdiction and duration of mandate.
To enter Representative Body Information:
-
Select the Job Group associated with the representative body.
Note: You cannot associate a representative body with the default HR Job Group.
-
Select the body's jurisdiction; for example, fire wardens or health and safety issues. This list is maintained using the JURISDICTION lookup type
-
Enter the duration of the body's mandate and select the units (for example, years).
-
Select the body's method of funding; for example, employer funded, employee funded, or joint funded. This list is maintained using the FUNDING_METHOD lookup type.
-
Enter the maximum number of seats.
Note: The maximum number of seats for a constituency must not exceed the total number of seats available for the representative body.
-
Save your work.
Warning: Once you have attached roles to a representative body, you must not change the Job Group associated with the representative body, as this may lead to errors in the operating of the system.
Entering Constituency Information for a Representative Body
You can assign constituencies to a representative body in the Constituency window.
To enter constituency information for a representative body:
-
Select a constituency.
-
Enter the number of seats.
Note: The number of seats allocated to a constituency must not exceed the maximum number of seats for its representative body.
-
Select a voting method.
-
Save your work.
Entering Location Information for Constituencies
Enter a location for the constituency from the Organization window.
To enter a location
-
Select Location from the Others window.
-
Select a valid location.
-
Include or exclude the location from the constituency in the selection field.
-
Save your work.
Entering Organization Hierarchy Information for Constituencies
Enter organization hierarchy information for the constituency in the Organization window. You can control which people to include or exclude in the constituency by indicating a starting node.
To enter organization hierarchy information:
-
Select organization hierarchy from the Others window.
-
Select the organization hierarchy.
-
Enter the hierarchy starting node.
-
Include or exclude the organization hierarchy from the constituency in the selection field.
-
Save your work
Entering Organization Information for Constituencies
Enter an organization for the constituency from the Organization window.
To enter an organization
-
Select organization from the Others window.
-
Select the organization.
-
Include or exclude the organization from the constituency in the selection field.
-
Save your work.
Entering Grade Information for Constituencies
Enter a grade for the constituency in the Organization window.
To enter additional grade information
-
Select grade from the Others window.
-
Select the grade.
-
Include or exclude the grade from the constituency in the selection field.
-
Save your work.
Entering Bargaining Unit Information for Constituencies
Enter a bargaining unit for the constituency from the Organization window.
To enter additional bargaining unit information
-
Select bargaining unit from the Others window.
-
Select the bargaining unit.
-
Include or exclude the bargaining unit from the constituency in the selection field.
-
Save your work.
Entering Job Information for Constituencies
Enter job information for the constituency from the Organization window.
To enter additional job information
-
Select job from the Others window.
-
Select the job.
-
Include or exclude the job from the constituency in the selection field.
-
Save your work.
Entering Collective Agreement Grade Information for Constituencies
Enter a collective agreement grade for the constituency from the Organization window.
To enter additional collective agreement grade information
-
Select collective agreement grades from the Others window.
-
Select the grade.
-
Include or exclude the grade from the constituency in the selection field.
-
Save your work.
Entering Trade Union Information for a Bargaining Association
Use the Trade Union Information window to record further information about your bargaining association if it is a trade union.
To enter trade union information for a bargaining association
-
Query the bargaining association in the organizations window if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Bargaining Association, choose the Others button.
-
Click in a field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Trade Union Information window.
-
Enter an employer reference and a trade union reference. These could be numbers to be used in an Electronic Data Interchange.
-
Save your work
Entering Additional Information for a Professional Body
Use the Professional Body Info window to define details for a professional body.
To define professional body information
-
Query the professional body in the Organization window, if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Professional Body Information and choose the Others button.
-
Click in the field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Professional Body Info. window.
-
Select the user defined table that should be used when calculating subscription rates for this professional body.
-
Enter the date upon which subscriptions to this body are to be reviewed.
-
Save your work.
Setting up Tax, Social Insurance, and Private Health Insurance Organizations
Before you set up your external tax and SI (Social Insurance) organizations and link them to your internal organizations, it is essential to set up an organization hierarchy for your business group. You can then assign your external organizations to at least the top-level HR Organization in your hierarchy. This ensures that the information you set up for your internal organizations is inherited by any child organizations in the hierarchy.
See: Creating Organization Hierarchies, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide
See: Dutch Organizations and Additional Information
For more information on selecting the organization hierarchy for your business group see: Business Groups: Entering Dutch Business Group Information
To set up your tax and social insurance organizations
-
Define the location for each of your external organizations. Ensure you enter additional postal address and contact details in the Location EIT.
See: Setting Up Locations
-
Create one or more external organizations for your tax office, SI providers and private health insurance providers using the Dutch Tax Office, the Dutch UWV Organization (for the SI provider), the Dutch Private Health Insurance Organization and the Dutch IZA Provider Information classifications respectively.
The Dutch Private Health Organization classification has the mandatory field Provider Type attached to it. Within this field, select one of the following types of private health insurance:
-
Collective
-
GVP
-
IZA
-
IZR
-
IZZ
-
Other
Note: No additional organization information for the Dutch Tax Office classification is required. You enter further private health insurance information for your employees at the assignment level.
The Dutch IZA Provider Information classification requires you to enter the dates, contribution percentages and the maximum annual income fields.
See: Dutch Private Health Organization: Entering IZA Provider Information
-
Set Up Information for Dutch UWV Organizations
-
For each Dutch UWV Organization you set up, enter additional information on the SI provider and the SI type. You can set up multiple SI types for each SI provider you create.
See: Dutch UWV Organization: Entering Social Insurance Type Information
-
Select a method of calculating the number of SI days in a payroll period for each SI type.
Set Up Information for the Employer
-
Assign your external tax office organization to your internal organizations.
See: HR: Organizations: Entering Dutch Organization Information
-
Assign your SI provider organizations to your internal organizations and enter any additional information.
If you create a record for each mandatory SI type for an individual SI provider, you can use this one SI provider for your internal organization to ensure that all of the mandatory insurances apply to your employees.
Note: You select the private health insurance organization at the employee level, you do not link it to an internal organization.
See: HR: Organizations: Entering Dutch SI Provider Information
-
Enter the sender's reporting name and registration number for the SI provider. As there can be multiple SI providers within your internal organization, the sender's reporting name and registration number help the UWV social security agencies to identify the sender of the NSI file.
-
Enter the employer's reporting name and registration number for the SI provider. The UWV social security agencies use this information to identify the employer of the NSI file.
Set Up Information for your Employees
-
You can now record the social insurance, private health insurance and tax information that you require for your employees:
-
Social insurance and private health insurance information, see: Assignment Extra Information Types
-
Tax information see: Entering Additional Assignment Details
-
Dutch Private Health Insurance Organization: Entering IZA Provider Information
To calculate the IZA contributions of employees eligible for IZA private health insurance, information must be entered at the private insurance provider level.
You enter the Dutch IZA Provider Information from the Additional Organization Information window.
To enter Dutch IZA Provider Information
-
In the Organization Classifications region, select Dutch Private Health Insurance Organization.
-
Choose the Others button and select Dutch IZA Provider Information.
-
Click in the highlighted field of the Additional Organization window to open the Dutch IZA Provider Information window.
-
Enter the start date, and optionally enter the end date.
-
Enter the percentage of the Employee Contribution.
-
Enter the percentage of the Employer Contribution.
-
Enter the Maximum Annual Income Base.
-
Save your work.
Setting up Social Insurance Days
Use the following steps to derive social insurance (SI) days correctly for your employees.
See: Methods for Deriving Social Insurance Days for more information.
-
Set up your SI organizations and SI types and assign them to an internal organization. Select the SI derivation method for the SI type in the Dutch SI Type window.
See: Setting up Dutch Organizations and Entering Social Insurance Type Information
Specify the same method of calculation for all of the mandatory social insurance types (ZVW, WW, WAO and ZW).
See: Entering Dutch SI Type Information
Note: This rule does not apply to the additional SI types.
-
If want to override the SI days method of calculation for a specific assignment, you can choose an alternative method in the Day Method field at the assignment level.
-
Enter the average days in a month for the internal organization. This figure is used by the formula to calculate the Average SI days with work schedules, if the payroll period is monthly or quarterly.
-
To correctly derive the number of regular working days for an employee, you must attach a work pattern to their assignment. Oracle HRMS recommend that you create a default work pattern that you can easily assign to your employees, as all employees must have a work pattern attached to their assignment.
-
Choose the method for determining the maximum number of SI days to be used in the calculation. You can also override the real SI days derived value in the Override Real SI Days field.
See: Entering Social Insurance Information in Entering Additional Assignment Details
-
If you need to perform an end of year adjustment, you can adjust the SI days to the real SI days figure and you can adjust the calculation method for the contribution calculations to the normal cumulative recalculation method. Select Yes in the Day Adjustment and Contribution Adjustment fields for the SI type at organization level.
-
You can override the day and contribution adjustments for a specific employee at the assignment level. Indicate whether you want to override the day adjustment to the real SI days value in the Day Adjustment field. In the Contribution Adjustment field indicate whether you want to adjust the contribution calculations to the normal cumulative recalculation method.
-
You can manually enter a figure or percentage of SI days at the assignment level to override the SI days figure derived from the day method. You can choose Manual Entry, Percentage of Average Days, or Percentage of Maximum SI Days in the Overriding Day Method field. If you choose Manual entry, you enter the number of SI days in the Overriding Day Value field. If you choose a percentage option, you enter the percentage in this field. Ensure that the override figure does not exceed the maximum number of SI days in a calendar year.
Note: Any end of year adjustments or multi assignment processing for SI days will not apply if an override has been entered.
-
Indicate whether or not to deduct an absence from the number of SI days in the Absence window. These absences reduce the number of SI days in a payroll period.
See: Entering Absences, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
-
You can use the Payroll Run window to override any of the above steps for deriving a real SI days figure and the SI days used in the calculation. You can enter the overrides using input values on the Social Insurance element. This override option ensures the correct payroll results for your employee.
Dutch UWV Organization: Entering Dutch SI Provider Information
You set up social insurance providers using the Dutch UWV Organization information type. You can enter SI (Social Insurance) provider information such as the provider type, contract number, branch number and branch name.
You can enter social insurance provider information from the Additional Organization Information window.
To enter additional information for a Dutch UWV organization
-
Query the social insurance provider if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Dutch UWV Organization.
-
Choose the Others button and select Dutch UWV Organization.
-
Click in a field of the Additional Organization Information window to open the Dutch UWV Organization window.
-
Enter the contract number.
-
Select the provider type.
-
Select the sector for the SI provider type. The sector determines the type of NSI file that applies to the SI provider.
-
Enter the risk group code associated with the UWV organization.
Note: If the same SI provider covers multiple sector and risk group combinations, then you need to set up multiple UWV organizations, one for each sector and risk group combination.
-
Enter the branch name and number of the SI provider.
-
Save your changes.
Dutch UWV Organization: Entering Social Insurance Type Information
You can set up many different SI (Social Insurance) types for the SI provider depending on the different types of employment in your enterprise. The information you set up here is used in the process of social insurance calculations.
Tip: You can set up information for each mandatory social insurance type for the same SI provider and assign it to your internal organization. Then you can select the SI provider as the primary provider for your internal organization with the SI classification of All Mandatory Insurances. This setup ensures that all employees assigned to the internal organization inherit the mandatory social insurance information.
You enter social insurance type information using the Organization window.
To enter Dutch SI type information
-
Query the organization if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select Dutch UWV Organization, choose Others and select Dutch SI Type.
-
Select the dates for the period of time the SI type is valid for the SI provider organization.
Note: When you select the start and end dates for an SI type, ensure that for the same SI type, the information does not overlap for any period of time. For example, if you set up information for the SI type of ZW for the period 01-Jan-2001 to 31-Dec-2001, you must not set up SI information using the same SI type within this period of time. Otherwise this could lead to inconsistent payroll calculations for an employee's assignment during a payroll run.
-
Enter the name for the SI type.
-
Select the type of social insurance.
-
Select the basis calculation rule. Social Insurance Income and Total Gross are the only valid basis calculation rules. Hence you must choose either of these two basis calculation rules. The basis calculation you select here determines the type of SI income to be used in the calculation of the SI contributions.
-
Enter the employee and employer contribution percentages as the standard SI contribution rates for the SI calculations.
-
Effective after 31-Dec-2012, the employee and employer contribution percentages for senior SI contribution rates do not impact SI calculations and hence are non-mandatory.
-
Effective after 31-Dec-2012, the employee and employer thresholds do not impact SI calculations and hence are non-mandatory.
-
Effective after 31-Dec-2012, the maximum salary figure as a daily amount does not impact SI calculations and hence is non-mandatory.
If you enable Law Walvis, as of 2013, you need to create a user table with periodic amounts for the maximum salary for SI. See: Additional Implementation Steps for Netherlands, Oracle HRMS for Netherlands Supplement. The created period must be the same as the payroll period. Ensure that daily amounts are stored for calculation of SI during hire and termination within the payroll period. In specific cases, the application calculates as follows:
-
For new hires and terminations within the payroll period, the application adjusts the maximum SI wages to meet the legislative requirements. For these calculations, the application uses the total number of days in the period on which employee belongs to the payroll rather than the number of days the employee actually worked. For example, if an employee starts working on 20th February 2006 (Monday) for three days a week (Monday, Wednesday, Friday), then the employee will be paid for 4 days (Monday, Wednesday, Friday, Monday) in February. However, as the employee is on the payroll for a total of 7 week days in February, the application uses 7 days for calculation of maximum wages.
-
For employees with the tax code for anonymous employees (tax code 940), the application sets the maximum salary to SI income. However, when an employee's status changes, the application calculates maximum salary retrospectively up to the employee's hire date (but not further back than the start of the current year). In addition, the application adjusts social insurance contributions retrospectively.
-
-
Select the calculation code. This code indicates the calculation method for the contribution calculation. Increasing SI Base Calculation and Adjusted Increasing SI Base Calculation are the only valid calculation methods. Hence you must choose either of these two calculation code.
Note: If you enable Law Walvis, then only the Increasing SI Base Calculation method applies.
-
Use the Adjusted Increasing SI Base Calculation method, which is based on the Increasing SI Base Calculation, if you have employees who, either simultaneously or successively, work in different Sector and Risk Group combinations within the same payroll period.
-
If you choose Increasing SI Base Calculation as the method, the application includes the values accumulated in previous payrolls in the current year. However, for calculating the maximum salary, this method uses the cumulative year-to-date values of the existing balances.
Note: Any non-SI absences, for example, absences without leave or explanation, reduce the maximum SI salary.
-
-
Select the calculation method for calculating the number of SI days in a payroll period. Select Law Walvis to enable Law Walvis calculations in the application.
Note: The method you select here determines the calculation method for deriving SI days for employees within this organization. Ensure you use the Law Walvis method for all the mandatory SI types from January 2006 to meet the legislative requirements.
For more information on the different calculation methods see: Methods for Deriving Social Insurance Days and for information on setting up SI days see: Setting up Social Insurance Days
-
Effective after 31-Dec-2012, the employer contribution taxable income does not impact SI calculations and hence is non-mandatory.
-
Effective after 31-Dec-2012, the employee contribution gross or net does not impact SI calculations and hence is non-mandatory.
-
Choose whether the application adjusts the SI days as part of an end of year adjustment in the Day Adjustment field. Select Yes to adjust the SI days to the real SI days value, and select No to keep the average SI days value.
Warning: This adjustment can be overridden at the employee assignment level for the SI classification.
-
Choose whether the application adjusts the SI contributions as part of an end of year adjustment in the Contribution Adjustment field. Select Yes to use the normal cumulative recalculation method, and select No to use whatever method has been chosen.
Warning: This adjustment can be overridden at the employee assignment level for the SI classification.
-
Save your work.
Entering Statement of Earnings Information
The Statement of Earnings (SOE) displays details of earnings, deductions and other payroll related information for an employee assignment. You must enter the required elements and balances in the SOE Information flexfield for the business group you are using, to enable the information to feature on the Statement of Earnings.
For further information about the required elements and balances, see: Configuring the Netherlands Statement of Earnings
For further information about defining your element or balance display names, see: Entering Statement of Earnings Detail Information
You enter Statement of Earnings information from the Organization window.
To enter Statement of Earnings information
-
In the Organization Classifications region, select your business group and click the Others button.
-
Select SOE Information, from the Additional Organization Information list.
-
Choose the resulting SOE Information entry to open the SOE Information flexfield.
-
In the Elements 1 field, select Dutch SOE Earnings.
-
In the Elements 2 field, select Dutch SOE Deductions.
-
In the Elements 3 field, select Dutch SOE Imputed Earnings.
-
In the Balances 1 field, select the Period to Date balance attribute.
-
In the Balances 2 field, select the Year to Date balance attribute.
-
Choose OK.
Entering Statement of Earnings Detail Information
The Statement of Earnings (SOE) displays details of earnings, deductions and other payroll-related information for an employee assignment. You can define the display name and the order your elements and balances appear on the statement of earnings, if required.
For further information about the required elements and balances, see: Configuring the Netherlands Statement of Earnings
For further information about entering SOE information, see: Entering Statement of Earnings Information
You enter Statement of Earnings Detail Information from the Organization window.
To enter Statement of Earnings Detail Information
-
In the Organization Classifications region, select your business group and click the Others button.
-
Select SOE Detail Information, from the Additional Organization Information list of values.
-
Click on the highlighted field to open up the SOE Detail Information flexfield.
-
In the Type field, select Element or Balance as required.
Note: You will have to complete different fields, depending on your choice of element or balance.
-
If you opted for Balance, select the balance from the Balance Name field.
-
Select a Dimension.
-
If you opted for Element, select the element from the Element Name field.
-
Select an Input Value.
-
For both element and balance, enter the name you want to appear on the statement of earnings, in the Display Name field.
-
For both element and balance, enter a number to signify the order they will appear in, on the statement of earnings.
-
Click Ok
Entering Related Organizations Information for an HR Organization
Use the Related Organizations information type to associate an operating unit to an HR organization. If you use a multi-org application, then the operating unit you select here becomes the operating unit for workers assigned to the HR organization.
Tip: If you use the Multi-Org Access Control (MOAC) feature for a product that integrates with Oracle HRMS, then you can associate an operating unit to every HR organization in your enterprise using Web ADI. MOAC is a key feature in Oracle Applications that enables you to access multiple operating units from a single application responsibility. For more information on MOAC, see: Multiple Organizations Overview, Oracle HRMS Implementation Guide
See: Data Download and Upload Using Web ADI Overview, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
To enter related organizations information
-
Query the HR Organization in the Organization window if it does not already appear there. In the Organization Classifications region, select HR Organizations, choose Others, and select Related Organizations.
-
Click in the Additional Information window to open the Related Organizations Information window.
-
Select an operating unit to associate to the HR organization.
Locations
Locations
In Oracle HRMS, you set up each physical site where your employees work as a separate location. If you use the Configuration Workbench to configure your basic enterprise structure, then you only need to create locations for the additional organizations you require.
See: Key Concepts for Representing Enterprises
You can set up:
-
Global locations: These are available in all Business Groups.
-
Business Group locations: These can only be used in one Business Group.
-
Business Place locations (Korea only): These can only be used in one Business Place.
Similarly, you enter the addresses of external organizations that you want to maintain in your system, such as employment agencies, tax authorities, and insurance or benefits carriers. When setting up internal or external organizations, you select from a list of these locations.
This approach has these advantages:
-
You enter information about each location only once, thereby saving data entry time.
-
Central maintenance of locations ensures consistency of address standards.
-
Your work sites exist as separate structures identifiable for reporting purposes, and for use in the rules that determine employee eligibility for various types of compensation and benefits.
Mexico Only
Oracle HRMS uses the location associated with an assignment to determine its social security affiliation. It is recommended that you associate all locations with one or more appropriate GRE using the Mexico HRMS Statutory Reporting Hierarchy. Oracle HRMS determines the GRE of an assignment based on the hierarchy you have associated the location with.
See: Government Reporting Entities (GREs), Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (Mexico)
See: Mexico HRMS Statutory Reporting Generic Hierarchy Type, Oracle HRMS Enterprise and Workforce Management Guide (Mexico)
See: Entering an Assignment (Assignment Window)
Location Extra Information Types
You can define as many Extra Information Types as you require to hold information about locations. There is also one predefined location EIT.
-
Postal Address and Contact Details - this EIT enables you to enter a postal address and contact details for external organizations such as the tax office, social insurance providers and pension providers.
If you create multiple postal addresses for a location, the application only uses the most recently entered or updated address it finds.
Note: You must enter the postal code in the following format NNNNAA, for example, 1234AB.
To be able to access the predefined EITs, you must link the EIT to your responsibility, see: Setting Up Extra Information Types Against a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Setting Up Locations
You can enter addresses in the Location window.
Locations are shared across Business Groups in HRMS and with two other Oracle applications: Inventory and Purchasing. HRMS does not use some of the fields in the Location window. These fields are disabled for HRMS users. For example, the Legal Address check box is read-only and supports future functionality in Oracle Financials.
For information about Oracle Purchasing locations, see: Defining Locations, Oracle Purchasing User's Guide.
To enter a work location and its address
-
Enter the name of the location, and a description if required.
-
Uncheck the Global check box if you want the location to only be available within the default Business Group of your current responsibility. Accept the default if you want the location to be a global location and therefore available to all Business Groups.
If you are setting up a global location, the location name must be unique across all Business Groups.
If you are setting up a location for one Business Group, the location name must be unique within that Business Group and all global locations, but does not have to be unique across all Business Groups.
Note: You cannot amend the Global check box once you have set up your location.
-
Select a national address style from the list. If a local address style exists for your country, it is displayed as the default. Otherwise, the international style is displayed.
US and Canadian users: The local style is only displayed if you have Vertex geocode data installed.
Note: You can change existing address styles or create new ones if required.
See: Changing Default National Address Styles, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
Enter address information in this window.
US Payroll users: If you change a location address, you need to update the location in the State Tax Rules window for each assignment at that location.
US Users: In the EEO Exception Report, location addresses are truncated to 115 characters if the combined length of the location code and address lines 1,2, and 3 is greater than 115 characters.
Canadian Payroll users: You enter Census Metropolitan Area codes here in the Location Address flexfield.
Irish users: You enter the employer's address here and attach it to the legal employer.
-
If the mailing address of the location differs from the payroll taxation address, you need to enter an overriding address into the Payroll Tax fields.
-
Select a time zone if you want to associate a time zone with the location.
Note: When you select a time zone, ensure that it corresponds to the location's address.
-
Choose OK, and then choose the Extra Information button to enter any additional information required by your enterprise.
See: Entering Extra Information, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
Save your location.
Making a location inactive prevents users from selecting it.
To remove an address from the Location list
-
Enter an inactive date when the location is no longer in use in your enterprise, and save your changes.
You can delete locations that have not been used.
Note: If a location is still in use, but you do not want it to be selected today or in the future, enter an inactive date.
-
Query the location you want to delete.
-
Delete the location.
-
Save the changes.