Payroll Statutory Deductions and Reporting
Payroll Statutory Deductions and Reporting Overview
Oracle Payroll enables you to ccalculate an employer's tax liability and deduct the appropriate sums from employee earnings. You can calculate employer and employee tax liabilities for all the taxes and statutory deductions that are applicable to your country. For example, this includes employer liability for state taxes such as State Unemployment Insurance and employee liability for federal, state and local taxes in the US, PAYE and NIC in the UK, PAYE and PRSI in Ireland, Social Security, Unemployment and Complementary Pension in France, Standard and Special tax and Social Insurance in the Netherlands, and so on.
In each instance, Oracle Payroll enables you to enter details of the tax liability and process it at regular intervals.
Reporting on Payroll Statutory Deductions
See: Reports and Processes in Oracle HRMS, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
Payroll Statutory Deductions and Reporting
Oracle Payroll allows you to process tax and insurance deductions for employers and employees, and helps you comply with the legislative requirements applying to your organization.
Is Oracle Payroll flexible enough to calculate different legislative taxes?
Yes. Oracle Payroll supports many country specific models of taxation, including the local, federal and state tax requirements of organizations operating in the US.
Is the entry of tax details flexible enough to meet my organizational needs?
Yes. You can calculate taxes for different types of employer to represent the diversity of your organization. You can also make retrospective adjustments to allow for overpayments and underpayments.
Is Oracle Payroll capable of processing the latest taxation updates?
Yes. The details of taxation policy and social security entitlements are constantly changing, but Oracle Payroll is always promptly updated so that your processing includes the most recent updates.
Can Oracle Payroll transmit PAYE information electronically? (UK only)
Yes. EDI allows two-way electronic transmission of documents between the Inland Revenue and employers. Oracle UK Payroll has developed a specified formatted file that, if used in conjunction with third party software, can be transmitted electronically to the Inland Revenue.
Can you record P11D details and submit an annual return? (UK Only)
You can use Oracle HR to update your records throughout the year to show all the Class 1A National Insurance contributions for which your organization is liable. You can make this information available to employees so that they can preview their NI liabilities. You can then generate a report to view the final details and you can submit the complete and validated records to the Inland Revenue to comply with all reporting requirements.
Payroll Statutory Deductions and Reporting
Dutch Tax and Social Insurance
Oracle Payroll for the Netherlands calculates statutory deductions, such as taxes and social insurance, as part of the payroll run. Through the use of FastFormula and employee assignments, you can determine how these processing rules apply to individual employees.
Tax
Oracle Payroll supports the following types of tax in the Netherlands:
-
Standard (Normal) Tax - Calculated using annual figures and can incorporate both tax reductions and exemptions.
-
Special Rate Tax - Annual or semi-annual bonuses are taxed according to a special rate.
-
Flat Rate Tax - A tax paid by employers on payments to or deductions from employees, an example being the saving scheme deductions. The periodic tax report displays the total tax amount.
Several tax reductions can apply to the employee, depending on indicators set for the employee assignment. Oracle Payroll supports the following reductions:
-
Labour Tax Reduction
-
Senior Tax Reduction
-
Additional Senior Tax Reduction
-
Young Handicapped Employees Reduction
-
Student Taxation- A student working throughout the summer can have their tax calculated at a more beneficial rate. Applying to standard tax only, the calculation assumes the standard taxable income is based on a quarter of the year, even if the employee is on a monthly or weekly payroll.
-
The 30% Rule for Foreign Employees- For a stipulated period, certain foreign employees can be taxed at a more beneficial rate, with taxable income reduced by 30%. If this rate applies, their social insurance income and social insurance gross salary will also be reduced by 30%.
-
The Beneficial Rule (Special Rate Tax) - The beneficial rule is automatically applied to calculate an employee's tax at a more beneficial rate, unless stated otherwise, via an indicator at assignment level.
To process the tax deductions, you must define your earnings elements and predefined taxation secondary classifications. You then link your earnings elements and tax information elements to your payroll. The Taxation initialization element triggers a formula which determines if an assignment is subject to standard or special rate tax.
Social Insurance
You set up social insurance providers and the social insurance they provide for your organization. You then select the social insurance that applies to each employee.
The application calculates deductions using the following methods:
-
Average days- derived from the average number of days for each payroll period.
-
Average days with work schedules- derived from the average days an employee worked according to their work pattern.
-
Real Social Insurance days- derived from the number of days an employee actually worked during a payroll period.
Note: If you enable Law Walvis, these methods for calculating deductions no longer apply.
You use the Social Insurance days calculation to determine your employee's and employer's Social Insurance contributions. You do not calculate for amounts over the maximum day salary or below the salary threshold. However, when you enable Law Walvis, the application uses period amounts for SI thresholds and maximum wages instead of social insurance days for calculating the social insurance contributions.
To calculate the social insurance salary, you select one of the following calculation methods:
-
Normal cumulative method. This includes values accumulated in previous payrolls in the current year.
-
Normal periodical calculation. This only calculates contributions based on figures in the current payroll period.
Note: If you enable Law Walvis, the application uses either Normal Cumulative Re-calculation method or Increasing SI Base method to calculate the social insurance contributions. Therefore, the remaining methods, such as Normal Periodical Calculation and Pseudo Calculation methods no longer apply.
To process the social insurance deductions you must define your elements, and select the predefined tax and social insurance classifications. You then link your earnings elements and social insurance information elements to your payroll. The Social Insurance initialization element triggers a formula which checks your employee's eligibility for each social insurance type, and then makes the calculations for each eligible type.
The Social Insurance calculation uses a single generic SI base for all SI types and calculates the total SI days at person level instead of assignment level. The ZVWS Health Insurance - ZVW Standard and ZVWL Health Insurance - ZVW Low SI Types replace the ZVW Social Insurance effective after 31 December 2012. Additionally, the following SI Types are not valid after 31-DEC-2012 and are not part of the Social Insurance calculations:
-
ZVW Social Insurance
-
IVA Social Insurance
-
WGA Social Insurance
-
E4 Social Insurance
-
E5 Social Insurance
-
E6 Social Insurance
-
E7 Social Insurance
-
E8 Social Insurance
-
E9 Social Insurance
-
E9 Social Insurance
However, you can use WAOD to record the WGA employer and employee contributions. Effective from 2013, the application does not generate both employer and employee run results for all the SI types. The run results for the SI Types are as follows:
| SI Type | Run Results |
|---|---|
| ZVWL | Only Employee |
| WAOD, E1, E2 and E3 | Both Employee and Employer |
| Rest of the SI types | Only Employer |
Defining an Earnings Element
You must assign a secondary classification to each of your Earnings elements to identify how they are taxed, or a default of non-taxable will be assigned to the elements. When adding secondary classifications to an Earnings element, make sure you do not assign different tax categories, for example Special Rate tax and Standard tax, to the same element, otherwise the tax calculation will return incorrect values. To rectify this you must delete the invalid element entry, create a new element with the correct classifications, re-link the element to the employee assignment and re-run your payroll.
See: Payroll Runs and Processes Overview
Multiple Assignment Processing for Social Insurance and Taxation
Oracle Payroll for the Netherlands enables you to carry out multiple assignment processing for both Social Insurance and Taxation, enabling processing to take place for employees who have more than one assignment within a payroll.
Multiple Assignment Processing with Social Insurance
-
You aggregate multiple assignments for assignments on the same payroll and, in the case of social insurance, only for those who also have the same social-insurance type.
-
If an employee has multiple assignments across different employers, you must assign a separate payroll for each assignment with a different employer.
-
If an employee has multiple assignments, the selected maximum SI days method must be the same across all assignments. This rule is not enforced, but ignoring it could lead to inconsistent payroll results.
-
Do not perform a supplementary run for social insurance calculations where an employee has multiple assignments, as it could lead to inconsistent payroll results.
-
Set the method for deriving Maximum SI Days to Payroll Period for any secondary assignments.
Note: If you enable Law Walvis, the application does not use the existing methods for deriving maximum SI days. Instead, the calculations use the period amounts for SI thresholds and maximum wages.
Social Insurance Aggregation
Oracle Payroll aggregates Social Insurance in the order of Primary Assignment, followed by Secondary Assignments in order of Assignment ID. If the payroll is the same, the application ensures the total SI days used for the assignments processed so far does not exceed the maximum SI days for the current assignment being processed. Assignments process in sequence, with the SI days totalled as each assignment is processed. This system determines the number of SI days available for the next assignment. The Threshold and Max SI Salary are also calculated, with the values not used carried over to subsequent assignments.
Examples of Multiple Assignment Processing in Social Insurance
Processing the first assignment.
Using Oracle Payroll to process multiple assignments enables you to carry over the Threshold and the Max SI Salary values not used in the first assignment, over to the next one. In this example in the table below, the SI Income (1000) is subtracted from the Total Threshold (1500) and the Max SI Salary (3000). This results in values not used - Threshold (500) and Max SI Salary (2000). These values carry over to Assignment 2, and are added to the Total Threshold and Max SI Salary, where the same deductions as in Assignment 1 take place.
| Values | Amount |
|---|---|
| SI Income | 1000 |
| SI Days | 15 |
| Threshold/day | 100 |
| Max Day Salary | 200 |
| Total Threshold (Threshold/day*SI Days) | 100 * 15 = 1500 |
| Max SI Salary (Max Day Salary * SI Days) | 200 * 15 = 3000 |
| SI Base (minimum of SI Income and Max SI Salary) | 1000 |
| Actual SI Base (SI Base - Threshold) | 0 |
| Threshold not used | 500 |
| Max SI Salary not used | 2000 |
Subtract the SI days used for the first assignment from the maximum SI days derived for the second assignment. This provides the available SI days for the second assignment. Carry any remaining threshold or maximum SI salary from previous assignments to the next assignment. See the table below.
| Values | Amount |
|---|---|
| SI Income | 1500 |
| SI Days | 5 |
| Threshold/day | 100 |
| Max Day Salary | 200 |
| Total Threshold (plus the amount not used in assignment 1) | (100 * 5) + 500 = 1000 |
| Max SI Salary (plus the amount not used in assignment 1) | (200 * 5) + 2000 = 3000 |
| SI Base (minimum of SI Income and Max SI Salary) | 1500 |
| Actual SI Base (SI Base - Threshold) | 500 |
| Threshold not used | 0 |
| Max SI Salary not used | 1500 |
Continue the same process from Assignment 2, until there are no more SI days available. See the table below.
| Values | Amount |
|---|---|
| SI Income | 2000 |
| SI Days | 0 |
| Threshold/day | 100 |
| Max Day Salary | 200 |
| Total Threshold (plus the amount not used in assignment 2) | (100 * 0) + 0 = 0 |
| Max SI Salary (plus the amount not used in assignment 2) | (200 * 0) + 1500 = 1500 |
| SI Base (minimum of SI Income and Max SI Salary) | 1500 |
| Actual SI Base (SI Base - Threshold) | 1500 |
| Threshold not used | 0 |
| Max SI Salary not used | 0 |
Multiple Assignment Processing with Taxation
-
You aggregate multiple assignments if an employee has assignments on the same payroll.
-
If an employee has multiple assignments across different divisions, assign a separate payroll for each assignment with a different division.
-
Do not perform supplementary runs for tax calculations where multiple assignments exist, as it can lead to inconsistent payroll results.
Note: If an employee has multiple assignments with differing tax codes it is likely that aggregation of those assignments will return incorrect values. Multiple assignments affect the automatic calculation for previous years taxable income, meaning you must enter manual override values in such situations.
Taxation Aggregation
-
Oracle Payroll aggregates tax in order of assignment number, for assignments on the same payroll. Calculating tax deductions for the first assignment is carried out normally, but when processing the next assignment, taxable income from the previous assignment is added to the taxable income of the current assignment. Deductions are calculated on these combined totals. Once calculated, the deductions from the previous assignment are subtracted. This process is repeated for all subsequent assignments.
Processing Student Taxation
-
When processing student taxation, the application uses the taxable income for the quarter to date, to determine the annual salary. If multiple assignments exist and student taxation applies, the quarterly taxable income for any previous assignments is added to the quarterly taxable income for the assignment being processed. You need a total taxable income before calculating the tax. Once the tax is calculated, the quarterly deductions for all previous assignments is subtracted from the total deduction, along with the quarterly deduction for the current assignment.
Processing the Beneficial Rule
-
Processing the beneficial rule involves adding the standard taxable income to the special taxable income. The standard tax deduction is calculated from this combined amount to determine if the tax payable is less than the total if the standard and special rate deductions were calculated separately.
-
If the beneficial rule applies, and your employee has multiple assignments, the standard taxable income for any previous assignments is added to the standard taxable for the current assignment being processed. The same calculation is performed if an employee with multiple assignments has special taxable income.
-
Once the tax deductions are calculated, subtract the standard and special rate tax deductions for any previous assignments from the total deduction. Compare the result to the individual deductions, in order to determine whether the beneficial rule should apply.
-
Both the beneficial rule and student taxation can apply to an employee. In this case the standard taxable income for the quarter, including all the previous assignments is added to the special taxable income for the period, for all previous assignments to derive the taxable amount. Once the tax deduction is calculated , subtract the quarterly standard deductions for any previous assignments from the total deductions, along with the period to date special rate deductions for any previous assignments.
IZA Private Health Insurance Multiple Assignment Processing
Ensuring Reporting Information is Correct When You Adjust Multiple Assignments with the Same Employer.
This table explains what happens when:
-
A part time adjustment to the income of an assignment is made because the working hours are deemed to be less than 50% of the full time hours.
-
It is discovered, when processing a subsequent assignment, that an adjustment should not have been made to the income of the first assignment, as the total working hours for both assignments is greater than 50% of the full time hours.
| Corrective Action | Effect on First Assignment | Effect on Second Assignment | Effect at Person Level |
| Correct the second assignment to counter the adjustment made to the first. | The income and contribution of the first assignment higher than it should be. | The income and contribution of the second assignment lower than it should be. | The total income and contributions will be correct for both assignments at the person level, therefore correct for IZA reporting. |
Note: For multiple assignments with different employers, it is the users responsibility to add the income from the 'non paying' assignment to the income balances of the assignment, where the IZA contribution is to be calculated.
IZA Upload and Reporting Overview
The IZA upload and reporting process consists of the following tasks:
-
Uploading the monthly IZA file to Oracle HRMS
-
Generating a report detailing the employee records processed, rejected, or missing from the IZA file
-
Removing obsolete information about processed, rejected, and missing records from the application database, when required
You can upload the monthly IZA file, which IZA sends to your organization, to Oracle HRMS to include the nominal employee IZA contributions in your regular payroll runs.
Note: For the upload process to read the IZA file on the file system, you must set the UTL_FILE_DIR parameter in the INIT.ORA file. In addition, you must set the system profile PER_DATA_EXCHANGE_DIR to the directory where the IZA file is located. This directory must be in the file system specified in the INIT.ORA file.
The information in the application must meet the following conditions for the successful upload of the IZA file:
-
All employee numbers are numeric and are 9 digits in length.
-
All the client and subemployer numbers are valid, three-digit numbers.
Caution: Note that even if the report contains a single invalid client number and/or sub employer number, the entire IZA upload process can fail and the entire IZA input file will not be processed.
See: Running the Dutch IZA Upload Process
Once you complete the IZA file upload process, you can generate a report detailing the employee records processed, rejected, or missing from the IZA file. For each processed record, the application creates a Batch Element Entry (BEE) for each employee contribution and attaches the contribution to a nonrecurring element for the payroll run. In addition, the application creates a new BEE header for the whole upload process.
See: Running the IZA Upload Process Status Report
Some reasons for the rejection of employee records from the IZA file are as follows:
| Reason | Description |
| Employee no longer employed | A mismatch between the effective date of the employee's nominal IZA contribution record and the entire period of the payroll run |
| Employee not insured for IZA | Employee not insured for IZA on the primary assignment during the entire period of the payroll run to which the effective date of the employee's nominal IZA contribution relates |
| Employee on contract with another enterprise | Employee on contract with another organization for at least one day in the payroll period to which the effective date of the nominal IZA contribution record relates |
| Employee on unpaid leave | Employee absence covers the entire payroll period where the flag Non-SI Days is set on the absence indicating that all days in the absence period are considered as non-SI days |
| Unknown exchange number | The application fails to recognize an exchange number, a combination of the employer number and the employee number, during the entire payroll period to which the effective date of the nominal IZA contribution record relates |
| Employee gross salary insufficient for the IZA deduction | An employee has less net pay than the nominal IZA contribution, after the remaining deductions from the employee's gross salary
Caution: Note that this condition is not checked automatically and can result in negative net pay for the primary assignment. In such cases, you should correct the payroll run results manually. |
Finally, you can use a purge process on a regular basis to remove obsolete information about processed, rejected, and missing records stored from the application database.
See: Running the Dutch IZA Upload Process Status Purge report
Dutch Wage Reporting
Wage reporting is a multistep process that employers follow to submit the wage report to the tax authorities for every payroll period. The wage report contains information about the employer, the personal and assignment information of all employees, and corresponding payroll-related information. Oracle HRMS enables you to process the wage report as shown here:
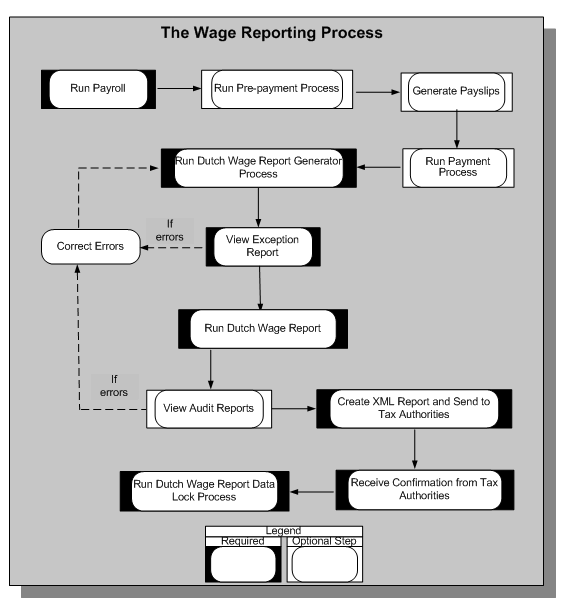
Dutch Wage Report Generator Process
Oracle HRMS uses this process to validate the social insurance and tax information available for wage reporting so that the report information complies with the legislative requirements. When you run the generator process, the application archives the relevant report information required for the wage report.
The Dutch Wage Report Generator process validates the wage report information and, if information is incorrect or missing, generates an exception report. After correcting any errors, you run the generator process again until you have no errors.
See: Running the Wage Report Generator Process
Dutch Wage Report
Once the generator process has run without error, you can run the Dutch Wage Report process, which generates two types of reports:
-
Audit reports, which are in PDF format so that you can easily verify the report contents
-
XML Report, which you send to the tax authorities
See: Running the Dutch Wage Report
Dutch Wage Report Data Lock Process
You run the Dutch Wage Report Data Lock Process after the tax authorities have confirmed that your wage report is valid. This process prevents you from accidentally rolling back the generator process, which is the source of the wage report you submit to the tax authorities.
See: Running the Dutch Wage Report Data Lock process
Setting up Tax and Social Insurance Deductions
Before you can set up your tax and social insurance deductions, you must create your social insurance and tax office information at the organization level, and link it to your employer. You then need to record the information that applies to each employee at the assignment level.
See: Setting up Tax and Social Insurance Organizations
To set up tax and social insurance deductions for your employees
-
Define your Earnings elements and select the predefined tax and social insurance secondary classifications.
Important: When creating an Earnings element, make sure you assign a secondary classification to indicate whether it is taxable or not. Failure to do so will result in the earnings element having a default classification of non-taxable.
You must therefore assign one of the following secondary classifications to each of your Earnings elements:
-
Non-taxable: Earnings
-
Subject to standard tax: Earnings
-
Subject to special tax: Earnings
When adding secondary classifications to an Earnings element, make sure you do not add the secondary classifications for different tax categories to the same element. For example, if an element has the classification Subject to Standard Tax, it should not also have the classification SI Income Subject to Special Tax.
Similarly, if the element is non-taxable, you should not assign an SI Income or SI Gross Salary secondary classification that is taxable. If you choose different types of taxes for the same element, the tax may calculate incorrectly.
See: Defining an Element, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
See: Predefined Elements for a list of the taxation and social insurance elements provided with Oracle HRMS for the Netherlands.
For information about the predefined primary and secondary element classifications (and their processing priorities), see: Survey of the Classifications
-
-
Link the Earnings elements, and the Taxation and Social Insurance Information elements to your payrolls.
The information elements trigger the eligibility formulas. The tax formula enables you to determine if an assignment is subject to standard or special rate tax. Checking the taxable income balances for each tax type, it initiates the calculation formula for each one. The social insurance formula determines the social insurance types assigned to an employee, and initiates the contribution calculation formula for each eligible type.
See: Defining Element Links, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
-
In the Element Entries window select the elements you have created to complete the information for the employee.
See: Making Manual Element Entries, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
-
For the Social Insurance element, you can enter an override figure for SI days for each type of social insurance and a figure to override the real SI days derived value. The figures you enter here override any figures manually entered or derived at the organization and assignment levels. Use the SI days overrides to ensure the correct payroll results for your employees. Choose the Entry Values button to enter any override figures for the SI days.
Note: If you enable Law Walvis, the application does not use SI days. Instead, calculations are based on the period amounts for SI thresholds and maximum wages.
For more information on social insurance days see: Methods for Deriving Social Insurance Days and Setting Up Social Insurance Days
-
To make manual corrections to the tax deductions Oracle Payroll calculates and report them along with the deduction values in reports, such as payslip, wage report, remuneration statement, and annual tax statement, you can use the Standard Tax Correction and Special Tax Correction predefined balances. You must set up elements for these balances in accordance with your tax-correction requirements.
Setting Up ZW, WW, WAO/IVA/WGA, ZVW (standard en low) and UFO Contributions
To set up ZW, WW, WAO/IVA/WGA, ZVW (standard en low) and UFO contributions, perform the following steps:
-
Link the following predefined elements to initiate the contribution-calculation FastFormulas for specific social insurance contributions:
-
ZVW Social Insurance
-
WGA Social Insurance
-
IVA Social Insurance
Note: You need not attach these elements to assignments eligible for the respective SI contributions. The application checks for eligibility during SI processing, and the relevant elements initiate the contribution calculation accordingly. Ensure you link the elements for costing purposes.
-
-
Set up social insurance types corresponding to the ZVW, WGA, IVA, and UFO social insurance contributions for the SI providers.
-
Modify the social insurance classifications for HR organizations to include the ZVW, WGA, IVA, and UFO social insurance types.
-
Add social insurance information for all assignments subject to the ZVW, WGA, IVA, and UFO contributions.
Setting Up Flat Rate Taxation
To enable flat rate taxation in Oracle HRMS, you must set up the relevant balances and elements, corresponding RetroPay components, and appropriate feeds.
To set up flat rate tax deductions for your employees
-
Ensure that you set up the relevant balances related to flat rate taxation.
See: Netherlands Balancesfor a list of balances provided with Oracle HRMS for the Netherlands.
-
Set up the feeds for the following balances:
-
Pre Pension Taxable Amount
-
National Holiday Gift Taxable Amount
-
Single Rate Taxable Amount
-
Gross Up Rate Taxable Amount
-
-
The period-to-date value for the relevant taxable amount balance must be greater than zero. Therefore, create elements that contribute to the taxable-amount balances listed in Step 2, and set up the related element entries.
See: Predefined Elements for a list of elements provided with Oracle HRMS for the Netherlands.
-
Ensure that corresponding element links are set up for all the predefined RetroPay elements related to flat rate taxation.
See: Predefined RetroPay Elements for a list of elements provided with Oracle HRMS for the Netherlands.
-
Derive deductions relating to flat rate taxation that are specific to handling major issues, and feed the balance Major Issue Flat Rate Tax Deduction with appropriate elements.
See: Netherlands Balancesfor a list of deduction balances provided with Oracle HRMS for the Netherlands.
-
Ensure that all relevant elements that contribute to the Major Issues Flat Rate Tax Deduction have corresponding RetroPay elements, Retro Component Usages, and Element Span Usages set up for RetroPay.
See: RetroPay Component Usagesfor predefined RetroPay component usages provided with Oracle HRMS for the Netherlands.
See: Element Span Usagesfor predefined element span usages provided with Oracle HRMS for the Netherlands.
-
To handle retrospective changes, set up the appropriate feeds to the balance Retro Major Issue Flat Rate Tax Deduction.
Running the Payment Output File (Dutch)
You use this report to initiate the creation of the EFT Payment file from within Oracle Payroll. The file is produced in the standard format required by the official body Interpay, in the Netherlands. The EFT Payment file enables you to send employee payment details to your bank on magnetic tape.
You can prevent the payee address information from appearing in the EFT Payment file. Select Yes in the Suppress Payee Address field of the Dutch Further Payment Method Info flexfield to achieve this.
Oracle enables you to override the contents of the Description field in the Transaction Description Record 160 of the EFT Payment file and enter your own information. To differentiate postal bank account numbers from other bank account numbers in the EFT Payment File, select Yes in the Identify Post Bank Numbers field of the Dutch Further Payment Method flexfield. This value ensures that the application sets the Transaction Type field to 003 on record 0100 of the EFT Payment File. The value 008 identifies other types of bank accounts.
To enable the transfer of the payment file to postal banks, select Desired in the NAW Code field of the Dutch Further Payment Method flexfield.
See: Netherlands EFT Payment Override Formula
You run the Payment Output File from the Submit Requests window.
To run the Payment Output File (Dutch)
-
Query the Payment Output File (Dutch) in the Name field.
-
In the Parameters window, optionally enter the payroll name.
Note: You can restrict the processing of assignments to the specified payroll on the effective date.
-
Select the consolidation set.
-
Enter a start date. The date you enter here determines the start date of the prepayments.
-
Enter the effective date.
-
Select a payment method. This is a mandatory field.
-
Enter the process date or date of transfer.
-
In the batch description field, optionally enter a value.
-
Select the employee name or employee number for the sort sequence and choose OK.
-
Select Yes in the Account Number Consolidation field to consolidate multiple third party payments made to a single account on the employee's behalf. Otherwise, select No for separate entries for each third party payment..
-
Choose the Submit button.
Running the Dutch Annual Tax Statement Archive
In the Netherlands, you run the Annual Tax Statement Archive prior to the Dutch Annual Tax Statement for the Employee Report, enabling employee data to be archived before it is processed by the Annual Tax reports.
To run the Dutch Annual Tax Statement for the Employee.
See: Running the Dutch Annual Tax Statement for the Employee
You run the Dutch Annual Tax Statement Archive from the Submit Requests window.
To run the Dutch Annual Tax Statement Archive
-
Select Dutch Annual Tax Statement Archiver in the Name field.
-
In the Parameters window, the Year defaults to the year prior to the effective date.
-
Select the Organization Hierarchy.
-
Select an employer from the HR Organizations in the list of values.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
Running the Dutch Annual Tax Statement for the Employee
In the Netherlands, employers must produce an annual tax statement for each employee in their organization detailing the employee's taxes paid during that period.
Note: You must run the Dutch Tax Statement Archive before running this report.
See: Running the Dutch Annual Tax Statement Archive
You run the Dutch Annual Tax Statement for the Employee Report from the Submit Requests window.
To run the Dutch Annual Tax Statement for the Employee Report
-
Select Dutch Annual Tax Statement for the Employee Report in the Name field.
-
In the Parameters window, the Year defaults to the year prior to the effective date.
-
Select the Organization Hierarchy.
-
Select an employer from the HR Organizations in the list of values.
Note: A separate page is printed for each employee assignment directly assigned to the employer. If there are employers below the selected employer in the hierarchy, employees of those employers are not included in the report. It is your responsibility to run this report for all your employers.
-
Select an employee. The list includes the names of all employees in the selected organization hierarchy.
-
In the Template field, enter the location and name of the PDF template to use with the XML Data Source. The predefined template is used by default.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
Setting up the Dutch Remuneration State Report
You print the Dutch remuneration state report for a specific employer within an organization hierarchy.
To Set Up the Dutch Remuneration Report
-
The report derives information for each employee from specific details.
Ensure that the following Employee Details information are correct:
-
Name and Initials
-
Social Insurance Number
-
Date of Birth
-
Address
-
Postal Code
-
Residence
All information is up to date at the date paid of the period being printed or for 31st December if the report is for the year.
Note: You can maintain running totals for an employee or for the whole report, and print out the totals as required.
See: Entering a New Person, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
See: Entering Addresses, Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
-
Ensure that the following employer details are correct:
-
Name
-
Address
-
Residence of the company
-
Tax Registration Number
See: HR Organizations: Entering Social Insurance Provider Information
See: HR Organizations: Entering Dutch Organization Information
All information is as at the date paid of the period being printed or for 31st December if the report is for the year.
-
-
Ensure that the following assignment details are correct:
-
Assignment Number
-
Service Start Date and End Date
See: Entering an Assignment (Assignment Window), Oracle HRMS Workforce Sourcing, Deployment, and Talent Management Guide
-
-
Ensure that the following tax table details are correct:
-
Colour Table
-
Effective From
-
Wage Tax Discount
-
Effective From
-
Student Arrangement (this is special indicator 28)
See: Entering Additional Assignment Details (Assignment Window)
-
-
Ensure that the following special rate table details are correct:
-
Annual Salary Taxable
-
Inspectors Approved Lower %
-
Commencing From
-
Date Approved
See 'Income Details' and 'Special Rate Taxation' in: Entering Additional Assignment Details (Assignment Window)
All information is as at the date paid of the period being printed or for 31st December if the report is for the year.
-
-
Ensure that the following special indicators are correct. Set the values for these indicators to true if the employee is eligible for them at any time in the period/year:
-
Company car or van placed at the employee disposal (special indicator 01)
-
Agreement private use of company car or van (special indicator 02)
-
Transportation on the account of employer (special indicator 03)
-
Travel allowance (special indicator 04)
See: Entering Additional Assignment Details (Assignment Window)
-
-
Check the secondary classification of your earnings or imputed earnings elements (including RetroPay elements) currently set up with secondary classifications for Wage in Money, Wage in Kind or Tips and Fund Payments. These elements are now treated as related to standard taxation. If these elements are related to special rate tax then you must assign them with the relevant secondary classification. For example, use the secondary classification 'Wage in Money Special Tax SI:Earnings' instead of Wage in Money Standard Tax SI:Earnings'.
Important: This step only applies to existing users prior to Family Pack H.
Note: To ensure the application deducts parental-leave amount from the Wage In Money amount in the third column of the Dutch Remuneration State Report, you must attach one or more of the following secondary classifications in addition to the regular secondary classifications:
-
Deduction Standard Tax SI : Pre-SI and Pre-Tax Deductions
-
Deduction Special Tax SI : Pre-SI and Pre-Tax Deductions
-
Deduction Standard Tax SI : Retro Pre SI Pre Tax Deductions
-
Deduction Special Tax SI : Retro Pre SI Pre Tax Deductions
See: Element Classifications and Processing Sequence, Oracle HRMS Compensation and Benefits Management Guide
-
See: Running the Dutch Remuneration State Report
Running the Dutch Remuneration State Report
The report contains separate pages for each employee assignment that is assigned to the employer either directly, or indirectly through organizations below it in the hierarchy. The report retrieves all non employer organizations (these are HR organizations without tax details) below the employer specified in the parameters in the organization hierarchy, including the employer itself.
Information regarding payroll run result information is broken down by each period in the year for each employee assignment.
Additional Information: This report now displays the net employee ZVW contributions under columns 9 and 16, irrespective of the tax category the original social income base relates to.
You run the Dutch Remuneration State Report from the Submit Request window.
To run the Dutch Remuneration State Report
-
Query the Dutch Remuneration State Report in the Name field.
-
In the Payroll Period field, enter the date relating to the period that you want to run the report for. For example, 1st March 2004 would relate to the March 2004 period for monthly payrolls.
-
In the Year field, enter the year that you want to run the report for. This option is unavailable if you enter a payroll period.
-
The Organization Hierarchy is defaulted to the named hierarchy from the business group. If this is not correct, then choose the correct one from the list of values.
-
If required, chose an Employer from the list of values which contains all the HR Organizations that have Tax Registration Number and Tax Office details.
-
The Include Subordinate Employers option is only enabled if you have chosen an employer. Choose 'Yes' or 'No'.
Note: If this option is set to 'Yes', then all the employer organizations below the employer specified in the parameters are also retrieved. If the option is set to 'No', then only the employer and all non employer organizations below the employer in the hierarchy are retrieved. If the employer is not specified, then both employer and non employer organizations in the hierarchy are retrieved.
-
In the Employee field, choose from the list of values that includes the full names of all the employees in the selected organization hierarchy and also the employer, if applicable.
Related Topics
See: Setting Up the Dutch Remuneration State Report
Setting Up the Dutch Wage Report
Before you run the Dutch Wage Report:
-
Set up tax and social insurance deductions.
-
If required, use the Legal Employer classification to record additional reporting employers for the wage report. You can record information, such as tax reference number, reporting name, and the HR organization. This task enables you to have multiple wage reports per employer.
-
Record additional organization information as follows:
-
Use the Wage Report Information window to record the wage report information.
-
Record the risk group and sector information using the Dutch UWV Organization window.
See: Dutch UWV Organization: Entering Dutch SI Provider Information
-
-
Record additional assignment information using the Assignment window:
-
Use the Dutch Temp Labour Information window to record the Temp Labour Code.
-
Use the Dutch Influence Information window to record Influence Code.
-
Use the Dutch Labour Relation Information window to record Labour Relation Code.
-
-
Use the Further Collective Agreement Details descriptive flexfield in the Collective Agreements window to record the collective agreement code.
Note: The application reports this collective agreement code only if you use the global collective agreement functionality.
-
Link the legal employer to a payroll using the Further Payroll Information window. This task enables you easily to identify all employees and assignments belonging to a specific employer for the wage report.
-
Link predefined elements, such as Holiday Coupons, Incidental Income Decrease, Additional Allowance, and New Wage Report Override. These element entries indicate whether an employee is eligible for employee benefits, such as holiday coupons and additional allowance over the UWV payments.
To report a RetroPay calculation as a correction in the wage report, you must create an element entry for the New Wage Report Override element. The application then reports the entry under the Correction section in the wage report. This is only applicable using the old retropay. Using the adjustment retropay, all adjustments will be reported in the current period and all corrections will be reported in the correction section of the wage report.
-
You can use the element-link criteria to control eligibility for these elements based on your business requirements.
-
When you process retropay for the previous year, ensure that you run it as an adjustment.
-
-
Set up appropriate feeds for the following balances:
-
Wage Tax Subsidy Arbo Non Profit
-
Wage Tax Subsidy Ses Going EES
-
Wage Tax Subsidy Research
-
Reservation Holiday Allowance
-
Additional Period Wage
-
Reservation Additional Period Wage
-
Overtime
-
WWB Allowance Paid Alimony
-
Directly Paid Alimony
-
Hours Worked
Note: You need to feed these balances manually using user-defined elements, as the application does not feed these balances using a classification or a sub classification.
-
-
You can use the global Payroll Event Model functionality to monitor and report the HR data changes to the tax authorities through the wage report. To be able to monitor and report HR data, you must enable the Incident Register for your business group from the time you want to start monitoring changes to avoid getting invalid record in the Wage report you generate first. Use the Functional Area Maintenance window to enable the Incident Register.
For monitoring and reporting payroll changes, use the RetroPay functionality to process retrospective calculations and then use the predefined element New Wage Report Override to manually indicate which retrospective calculation is a changed event either as an adjustment or correction.
You can exclude a complete period previously reported for an employee by selecting Withdrawals as the value for the New Wage Report Override element.
To avoid displaying correction amounts from the previous period in the wage report, use the Adjustment component as the RetroPay type.
-
Use the Application Utilities Lookups window to add sector codes to the NL_SECTOR lookup.
-
Use the shared type NL_NATIONALITY in the User Types and Statuses window to map the nationality codes to NEN1888 Norm.
See: Creating User Types and Statuses, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting, and System Administration Guide
-
Use the NL_EMPLOYMENT_CATEGORY shared type in the User Types and Statuses window to map employment category to code contract.
-
You are now ready to run the Dutch Wage Report Process.
See: Dutch Wage Reporting
Running the Dutch Wage Report Generator
You run the Dutch Wage Report Generator before running the Dutch Wage Report. The Dutch Wage Report generator validates and archives the required reporting information for the Dutch Wage Report.
Use the Submit Requests window to run the Dutch Wage Report Generator.
To run the Dutch Wage Report Generator
-
In the Name field, select Dutch Wage Report Generator. The Parameters window opens
-
Enter the effective start and end dates.
-
Select the legal employer.
-
Select the payroll type, such as calendar month or weekly.
-
Enter the sequence number.
-
Correction Report – Select Yes if this is a correction.
-
Employer Only – Select Yes or No.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
Running the Dutch Wage Report
The Dutch Wage Report includes the total wages paid to employees, social insurance and tax contribution details, and various tax amounts to be paid to the tax authorities.
Use the Submit Requests window to run the Dutch Wage Report.
To run the Dutch Wage Report
-
In the Name field, select Dutch Wage Report. The Parameters window opens.
-
Select the wage-report-generator request ID you want to report on. The application generates this ID when you run the Dutch Wage Report Generator process.
-
Select the report type.
-
Audit Reports, which you can run for some or all wage-report information, enable you to identify and correct errors before generating the XML report.
-
XML Report generates the complete report you send to the tax authorities.
-
-
To include information for specific employees only, select an assignment set.
-
Specify the order of the report information.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
Running the Dutch Wage Report Data Lock Process
You run the data lock process to ensure you do not accidentally roll back the Dutch Wage Report Generator process after submitting the wage report to the tax authorities. The data lock process locks all the actions performed on employee assignments since you run the wage report generator process. You use the Submit Requests window to run the data lock process.
To run the Dutch Wage Report Data Lock Process
-
In the Name field, select Dutch Wage Report : Data Lock Process.
-
Select the report-generator request ID associated with the wage report. The application generates this ID when you run the Dutch Wage Report Generator process.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
Setting Up the Labor Cost Arrangement Report
The Labor Cost Arrangement implies that the employer can pay tax free amounts for labor costs to the employees, without having to administer why these payments are made. However, when the total of payments for an employer increases the threshold the employer has to pay Labor Cost Arrangement flat rate tax over the amount that is above the threshold.
There are three methods available to determine the amount of Labor Cost Arrangement flat rate tax:
-
· Method 1 - Periodic tax based on current period threshold value.
-
· Method 2 - Periodic tax based on pre-defined periodic threshold value.
-
· Method 3 - Cumulative tax based on pre-defined annual threshold value.
Set up the Labor Cost Agreement report as follows:
-
Record additional organization information to define Labor Cost Arrangement Information details.
See: Adding Labor Cost Arrangement Information
Note: If you do not enter details in the Labor Cost Arrangement Information window, then , the existing Flat Rate Taxation will be used. Flat rate taxation if mentioned for Labour Cost Agreement will override the Labor Cost Arrangement Information.
-
Feed the Labor Cost Arrangement Payments balance with the element you require.
See: Balances in Oracle Payroll, Oracle HRMS Implementation Guide
Running the Dutch Labour Cost Agreement Audit Report
You run the Dutch Labour Cost Agreement Audit Report to view the calculated amounts of Labor Cost Arrangement tax and the threshold required.
Labour Cost Agreement Audit Report will report values only after running the Wage Report Data Lock Process for the period.
Note: Ensure that for a period, Wage Report Data Lock Process is run only once.
You run this report from the Submit Requests window.
To run the Dutch Labour Cost Agreement Audit Report
-
Select Dutch Labour Cost Agreement Audit Report in the Name field.
-
Select the Employer from the list.
-
Enter the Year for which you want to run the report.
-
Select the Payroll Type from the list.
-
Click OK and submit your request.
Setting Up the First Day Report
Follow these steps to set up the first day report for employees in your organization.
To Set Up the First Day Report
-
Ensure that you attach the First Day Report Information EIT to the responsibility of your choice.
See: Setting Up Extra Information Types For a Responsibility, Oracle HRMS Configuring, Reporting and System Administration Guide
-
Ensure that the following employee information is correct:
-
Tax registration number of the employer
-
Hire date
-
BSN/SOFI number or employee number, if BSN/SOFI number is unavailable
-
Initials
-
Prefix
-
Last Name
-
Date of Birth
-
Generating the First Day Report
The First Day Report is an electronic file in the XML format and contains new employees' information, such as employee number, name, and BSN/SOFI number. You send this report to tax authorities for new employees and rehires.
To Run the First Day Report
-
In the Name field, select Dutch First Day Notification Report. The Parameters window opens.
-
Enter the report date.
-
Select the organization hierarchy, employer, and employee.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
Running the Dutch Element RetroPay Setup Report
Use the new Dutch Element RetroPay Setup Report to view the retropay setup of user elements. Run the report either to display all the elements or the elements with retropay setup only.
To run the Dutch Element RetroPay Setup Report
-
In the Name field, select Dutch Element Retropay Setup Report.
-
In the Effective Date field, select a date to display all the elements that are effective from that date.
-
Select the default template in the Template Name field, or, to change the look and feel of the report select a customized template. The Element Retropay Setup Report template is the default template.
-
Select All Elements to display all the elements irrespective of their retropay setup. Alternatively, select Elements with Retropay Setup to display only elements that have retropay setup.
-
Click Ok.
-
Click Submit.
Running the Dutch ABP Report Archiver
The Dutch ABP Report Archiver concurrent program archives the data that needs to be reported for the given period. An Exception Report similar to the Dutch Wage Report Generator is generated to inform user-related exceptions. Dutch ABP Report concurrent program reports the archived data in the desired output format.
Use the Submit Request window to run this program.
To run the Dutch ABP report archiver
-
In the Name field, select Dutch ABP Report Archiver.
-
As all the parameters are mandatory, enter the following:
-
Start Date - Start Date of the period for which the ABP Pension details must be reported. Start Date cannot be earlier than 01-JAN-2013.
-
End Date - End Date of the period for which the ABP Pension details must be reported. End Date must be within 31 days from the Start Date as only Monthly and Lunar payrolls are supported.
-
Organization Hierarchy - The Organization Hierarchy selects all the available organization hierarchies in the business group. The existing value set HR_NL_ORG_STRUCT is used to list the available organization hierarchies.
-
Employer - The Employer parameter displays all the organizations in the selected hierarchy. You can choose the desired organization.
-
Report Type - Regular or Correction Report. Currently, only Regular report is generated.
-
Sequence Number - Sequence number of the file sent for an employer for a period. By default, the sequence number is populated. You can change it, if required.
-
Running the Dutch ABP Report
Run the Dutch ABP report after the archiver program. Use the Submit Request window.
To run the Dutch ABP report
-
In the name field, select Dutch ABP Report.
-
Enter the following mandatory parameters:
-
Archiver Request Id – Select the applicable archiver request ID from the list of request Ids of the Dutch ABP Report Archiver actions.
-
Output Type - You can choose the either the XML Report or the Audit Reports as the output type.
-
Running the Dutch ABP Retro Pension Salary Calculation
Use the Dutch ABP Retro Salary Calculation to calculate the retro difference in the ABP Pension Salary for the processing year and populates an assignment level EIT Dutch ABP Retro Pension Salary.
You run the Dutch ABP Retro Salary Calculation from the Submit Request window.
To run the Dutch ABP Retro Pension Salary Calculation
-
In the Name field, select Dutch Remuneration Statement.
-
Enter the following parameters:
-
Reporting Year - the year for which the retro has to be calculated.
-
Processing Year - the year for which the report is run.
-
Legal Employer - the tax unit for which the report is to be run. The process will run for all the employees in the tax unit.
-
Assignment Start Date - the assignment start date, assignments with assignment start date later than this date are not picked up for recalculation of ABP Pension Salary.
-
Override Salary - the indicator to Include or Exclude the Override Salary mentioned in the ABP Participation and Salary Information EIT. If this field is set as Include, then the Override Salary will be considered, otherwise not.
The program checks for the balances defined in the new EIT Dutch ABP Retro Pension Salary Balance Setup. For each balance, the program checks for the element configured using the Balance – Element Setup.
After the list of elements which impact the Pension Salary change has been derived, the application performs the following step for each element for each assignment.
-
Checks if the element is present in the run results for the first valid month of the year for the assignment. The first valid month refers to the first payroll period of the year or the period in which the assignment starts. The process takes all the employees for the legal employer and creates action for all employees.
-
The application then checks if the corresponding retro element (for the run result id) is present in the element entries in any period after that period till the current year.
-
Based on the Element Balance Setup, the application calculates the new balance values considering the original values and the Retro values as on the processing year and then recalculates the ABP Pension Salary for the original processing year using the same business logic used in normal payroll run.
-
If the application finds any difference in the existing value and the new value, then the assignment level EIT Dutch ABP Retro Pension Salary is populated with the list of values:
-
Reporting Year – The retro processing year for which the concurrent program has been run
-
Processing year – the current year in which the concurrent program has been run
-
Original Pension Salary
-
Revised Pension Salary
-
Pension Salary Variance
-
Change Reason
-
-
-
Click OK and Submit.
Running the Dutch Remuneration Statement
Use the Dutch Remuneration Statement for reporting from year 2013 instead of the Dutch Remuneration State Report. You can continue to use existing Dutch Remuneration State Report for the previous tax years.
You run the Dutch Remuneration Statement from the Submit Request window.
To run the Dutch remuneration statement
-
In the Name field, select Dutch Remuneration Statement.
-
Enter the following parameters:
-
In the Payroll Period field, enter the date relating to the period that you want to run the report for. For example, 1st March 2004 would relate to the March 2004 period for monthly payrolls.
-
In the Year field, enter the year that you want to run the report for. This option is unavailable if you enter a payroll period.
-
The Organization Hierarchy is defaulted to the named hierarchy from the business group. If this is not correct, then choose the correct one from the list of values.
-
If required, chose an Employer from the list of values which contains all the HR Organizations that have Tax Registration Number and Tax Office details.
-
The Include Subordinate Employers option is only enabled if you have chosen an employer. Choose 'Yes' or 'No'. Note: If this option is set to 'Yes', then all the employer organizations below the employer specified in the parameters are also retrieved. If the option is set to 'No', then only the employer and all non employer organizations below the employer in the hierarchy are retrieved. If the employer is not specified, then both employer and non employer organizations in the hierarchy are retrieved.
-
In the Employee field, choose from the list of values that includes the full names of all the employees in the selected organization hierarchy and also the employer, if applicable.
-
Dutch Wage Tax Subsidy Low Wages
Setting Up Wage Tax Subsidies
Employers can claim several wage tax subsidies to reduce their tax bill:
-
Wage Tax Subsidy for Low Wages. This subsidy applies to each employee who is 23 or over and earns no more than a specified wage. Oracle Payroll enables you to calculate the wage tax subsidy for low wages for both full-time and part-time staff. You can produce a report showing the subsidy amount for specific employees, along with the information used to calculate the subsidy amount.
See: Generating the Dutch Wage Tax Subsidy Report
-
Wage Tax Subsidy for Long-Term UnemploymentEmployees are eligible for the subsidy if they were receiving it prior to the 1st January 2003 and:
-
Their income is less than or equal to 125% of the minimum wage, if they are under 50.
-
Their income is less than or equal to 145% of the minimum wage, if they are 50 or over.
The subsidy is available for up to 48 months.
-
-
Wage Tax Subsidy for Parental Leave. You can claim for eligible employees who earn at least the Dutch minimum wage for their age. These values are Dutch legislation defined. The subsidy is 50% of the taxable income used in the calculation, with a maximum value dependent on the employee's age.
-
Wage Tax Subsidy for Education. You can claim the subsidy for employees whose taxable income is no more than 110% of the minimum wage. Employees under 23 must have been unemployed to be eligible. The subsidy amount depends on whether your employee is deemed to be participating in training.
Warning: In the wage tax subsidy for low wages calculation, the application checks that the combined subsidy amount for education and low wages does not exceed a specific maximum amount. If it does, the application reduces the low wages subsidy value accordingly. However, in the case of multiple assignments, the application does this check only if the first assignment has an associated education subsidy and the second has the low wages subsidy, and not vice versa. The application performs this check in the low wages calculation only after the education subsidy is known, which is not possible if the second assignment has an education subsidy.
To enable a wage tax subsidy for an assignment
You enable the various wage tax subsidies available by selecting the Wage Tax Subsidy element in the Element Entries window, for all applicable employee assignments. You must also set the appropriate indicators to yes in the Miscellaneous Tax Details, for the applicable wage tax subsidies.
-
In the People window select your employee.
-
Choose the Assignment button.
-
Choose the Entries button on the Assignment window.
-
In the Element Entries window, select the Wage Tax Subsidy element from the list of values.
-
Save your work and close the Element Entries window.
-
In the Assignment window, select the Miscellaneous Tax Details tab.
-
Select the required tax indicators and set to yes.
-
Save your work.
Important: Customers who have previously set up the wage tax subsidy, using the Wage Tax Subsidy Low Wages element, must remove any element entries set up for this element. For employee assignments affected by this subsidy, add an element entry for the element Wage Tax Subsidy. The default value of the Low Wages indicator at assignment level is Yes.
To override the age check for the wage tax subsidies for low wages and education
You can override the age check mechanism for this process if you do not require it.
-
In the People window enter your employee.
-
Choose the Assignment button.
-
Choose the Entries button on the Assignment window.
-
In the Element Entries window select the Wage Tax Subsidy element.
-
Choose the Entry Values button.
-
If you do not want to check that the employee meets the age criteria, then select Override Age Check, and enter Yes.
-
In the Training Type field select the type of Other or Starter Level from the list of values, if required.
-
Save your work.
-
Choose OK.
Required balances for the wage tax subsidies
The required balances are:
-
Wage Tax Subsidy Base Salary - holds the salary for use in the wage tax calculation.
-
Wage Tax Subsidy Parental Leave Hours - holds the parental leave hours for use in the wage tax subsidy calculation.
-
Wage Tax Subsidy Working Hours - holds the working hours for use in wage tax calculation.
Note: You need to set up the feeds for the above balances as they are not predefined. For starters and leavers, it is assumed that any value for parental leave hours has not been prorated.
You use the Wage Tax Subsidy Base Salary for comparing to the wage limit, to determine the wage tax subsidy. The same secondary element classifications as the existing standard and special rate taxable income balances can feed the subsidy salary. You, however, must set up the element classifications you require to feed the balance. The Wage Tax Subsidy Working Hours is sued to calculate the part time percentage, and adjusts the wage limit and resulting subsidy value. You must define the element feeds for the Wage Tax Subsidy Working Hours balance and Wage Tax Subsidy Base Salary.
-
In the Balance window, query the Wage Tax Subsidy Working Hours balance.
-
Choose the Feeds button.
-
Select the elements you have created to feed the working hours balance, in the Balance Feeds window.
-
Save your work.
Generating the Dutch Wage Tax Subsidy Report
In the Netherlands, employers must send a report to the tax office at least every quarter, detailing taxes paid, including the wage tax subsidies. On this report the subsidies section shows the overall figures for the subsidy low wages. The Dutch Wage Tax Subsidy Report provides greater detail, showing the subsidy amount for specific employees, along with information used to calculate the subsidy amount. The report displays person-level subsidies for a specified period for each subsidy type.
You run the Dutch Wage Tax Subsidy Report from the Submit Request window.
To run the Dutch Wage Tax Subsidy Report
-
Select the Dutch Wage Tax Subsidy Report in the Name field.
-
In the Parameters region, enter the month from which you want to generate the report.
-
Enter the end date in the Month From field. The date must be the same or later than the date in the Month From field.
-
Select your organization hierarchy in the Organization Hierarchy field. The default entry is the named hierarchy from the business group.
-
Select your organization from the Top HR Organization field. If left blank, then the report runs for all the employers in the hierarchy.
-
Specify whether to include all subordinate employers in the top HR organization.
-
Select your employee from the Employee Name field. If left blank, the report retrieves records for all the employees within the employer organization, along with the subsidy information for the payroll period defined in the month start and end fields.
-
Select the report template. For example, select PAY_NL_WTS_NLTMP.rtf to run the report in Dutch.
-
Choose the Submit button.
Running the Dutch IZA Upload Process
Each month, IZA sends an ASCII-format file to employers detailing nominal employee IZA contributions. This file contains information grouped by each employer that is identified by a unique client number and a sub employer number, if appropriate.
You upload the IZA file to the application using the Dutch IZA upload process. You can then run the batch element entries created by the application. The application processes the IZA contributions as net deductions in the payroll for each employee. You run the Dutch IZA Upload Process from the Submit Request window.
To run the Dutch IZA Upload Process
-
Query Dutch IZA Upload Process in the Name field.
-
In the Parameters window, enter the name of the IZA input file that contains the details of the employee IZA nominal contributions. The batch Name defaults to IZA Upload with the application date and time displayed.
-
Specify whether to create a new entry, reject existing entries, or update existing element entries. The application uses this information in the BEE process during the payroll run.
-
Specify whether to update, correct, or override date-effective changes to the records.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
Running the Dutch IZA Upload Process Status Report
This report identifies processed, rejected, and missing records in the IZA file uploaded to the application. The report also includes the reason for any rejection. You run the Dutch IZA Upload Process Status Report from the Submit Request window.
To run the Dutch IZA Upload Process Status Report
-
Query Dutch IZA Upload Process Status Report in the Name field.
-
In the Parameters window, select the unique combination of month and year that you want to process the IZA file for.
-
Select the organization hierarchy containing the employer with which the contributions are associated.
-
If the business group has multiple employers, select the employer. The processing month and year, organization hierarchy, and the employer name are part of the report that you send back to IZA for further processing.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
Running the IZA Upload Process Status Purge Process
This purge process enables you to delete the history of processed, rejected, and missing records from the application database. You run the Dutch IZA Upload Process Status Purge process from the Submit Request window.
To run the Dutch IZA Upload Process Status Purge process
-
Query Dutch IZA Upload Process Status Purge in the Name field.
-
In the Parameters window, specify the upload period of the processed IZA records that you want to purge using the Month From and Month To fields.
-
Select the organization hierarchy containing the employer with which the contributions are associated.
-
Select the employer in the business group.
-
Click OK.
-
Click Submit.
Re-generating the IZA Upload Process Report
The application can reject certain records during the IZA upload process, if you have incorrect information, such as invalid client number and sub employer numbers, set up in the application. This incorrect information can cause the upload process to fail without creating any new BEE lines or recording the details of processed, rejected, and missing records. In such cases, you can rerun the upload process after correcting any invalid information.
To rerun the IZA Upload Process
-
Run the Dutch IZA Upload Process Status Purge process to delete the history of the processed, rejected, and missing records from the previous upload. Ensure that you run the purge process for the relevant employer and that the specified time period matches the dates of the IZA file to be rerun.
-
Delete the BEE header and lines created during the previous IZA upload.
-
Run the Dutch IZA Upload Process for the file to be reprocessed. However, ensure that you set the parameter Action If Exists to Reject Entry. This setting will reject any BEE line with an existing element entry and create element entries for newly created BEE lines.
-
Run the newly created BEE header and lines.
-
Run the Dutch IZA Upload Process Status Report.
Running the Dutch AOW HR Report
Use this report to display the AOW HR date for employees of a legal employer, who are retiring during the specified period.
Run the Dutch AOW HR Report from the Submit Request window
To run the Dutch AOW HR Report
-
Query Dutch AOW HR Report in the Name field.
-
Enter the following parameters:
-
Employer: This is a mandatory parameter. Enter the legal employer name to include the employees of the organization.
-
Retire From: This is an optional parameter. Enter the Start Date to run the report. All the employees who have the AOW date after this date are included in the report. If you leave this field blank, then the application considers 01-01-0001 as the Start Date.
-
Retire To: This is an optional parameter. Enter the End Date to run the report. All the employees who have AOW date between the start date and the end date are included and reported in the report. If you leave this field blank, then the application uses the last day of the current year as the End Date.
-