Messaging Multiplexor is available as part of Netscape Messaging Server. You can install Multiplexor at the same time as you install Messaging Server, or you can install it later using the Server Setup program. Either way, you first need to prepare the system to support Multiplexor.
Before You Install (Unix)
Before you install Messaging Multiplexor on a Unix machine, perform the following tasks:
Choose the machine on which you will install Multiplexor. Netscape recommends against installing Multiplexor on a system that is also running Messaging Server or Directory Server. It is best to use a separate machine for Multiplexor.
Check that the system meets all the hardware and software requirements for using Netscape Messaging Server. For more information about installation requirements, see the Messaging Server Installation Guide.
On the machine that Messaging Multiplexor is to be installed on, create a new user to be used exclusively by Multiplexor. This new user must belong to a group. Suggested names for the user are nsmmp ("Netscape Messaging Multiplexor") or nsmail.
Set up the LDAP directory server and its host machine for use with Messaging Server, if they are not already set up. For more information, see the Directory Server documentation.
If you already have an older version of the Multiplexor installed and want to replace it, you must remove the old version of Multiplexor before you can install the new one. To remove Multiplexor, remove the mmp server root directory and the /etc/netscape.mmp.conf file.
HP-UX. If you're using Messaging Multiplexor on HP-UX, you must install the operating-system patches that are required to run Messaging Server 4.1. For more information, see the Messaging Server Installation Guide.
Also for HP-UX, you should increase the values of the configurable kernel parameters maxfiles, maxfiles_lim, and nfiles to a much larger number. For example, with the settings shown below, Multiplexor can support approximately 8,000 simultaneous sessions. (The more RAM you have in your machine, the higher these values can be.)
maxfiles 16384
maxfiles_lim 16384
nfiles 32768
See your platform documentation for information on how to set these parameters.
Multiplexor Files (Unix)
In Unix environments, Multiplexor executable files are stored in the Multiplexor installation directory (MMPRoot in this document), and two subdirectories of MMPRoot: MMPRoot/bin and MMPRoot/lib. At installation time you specify the directory that you want to use as MMPRoot. For example,
/usr/netscape/server4/bin/mmp.
When you install Multiplexor, you create one or more Multiplexor instances. Different instances can use different configuration variables. Each instance has its own directory that contains the configuration files for that instance. Instance directories are created as subdirectories of MMPRoot. For example,
MMPRoot/mplex1.
Table 13.6 lists the principal files that make up a Messaging Multiplexor installation in a Unix environment.
Multiplexor Installation (Unix)
In Unix environments, there are two ways to install Messaging Multiplexor on a machine:
Note: Netscape recommends that Multiplexor not be installed on a machine that is also running either Messaging Server or Directory Server.
Creating a Multiplexor Instance (Unix)
You must use the Server Setup program to create your first Multiplexor instance. This program sets up and then uses the Netscape Messaging Multiplexor Installer. (Note that Multiplexor installation is not the default; you must select it as part of the Messaging Server suite.) For subsequent installations of additional instances, you can call the Multiplexor Installer directly by running the mmp-setup script.
When the Multiplexor Installer starts (either from the Server Setup program or from running mmp-setup), follow these steps to install and configure the Multiplexor:
When prompted for the user name that Multiplexor should run as, enter the user name that you created for exclusive use of Multiplexor as explained in Before You Install (Unix).
The default value is nobody. Change this to the user name that you
created.
At the next prompt, enter the installation directory (called MMPRoot/ in this document), the directory path into which you want Multiplexor to be installed.
To accept the default (/usr/netscape/suitespot4/mmp), press Enter.
In this example the /mmp directory is the MMPRoot.
The installation program creates the directories for the Multiplexor
installation and installs the files. (If you are creating a second or subsequent
instance of Multiplexor on this machine, the installation program uses the
existing installed files.)
The installer program starts to create an instance of Multiplexor from those
files. (If there is a previously installed instance of Multiplexor, you can at
this point choose to either configure the existing instance or create a new
one.)
If you choose to configure a new instance of Multiplexor, enter the name you want to give it.
To accept the default name (the host name of the machine you are
installing Multiplexor onto) press Enter. The installation program finishes
creating the new instance, installing it into the subdirectory MMPRoot/
MMP-instanceName/ where instanceName is the name you specified.
Enter one of the following numbers to specify which kind of mail service you want this instance to support:
1 - Configure this instance for IMAP mail service
2 - Configure this instance for POP3 mail service
3 - Configure this instance for both IMAP4 and POP3 mail service
You are then stepped through a series of configuration prompts that allow you to specify environment variables that will control how this instance of Multiplexor operates. See Configuration Prompts (Unix) for a description of these prompts.
The installer shows you a summary of the information you have entered. If the information is correct, type y. If you need to make changes, type n, in which case the install program takes you back through the prompts again.
After you have approved the configuration parameters and the Multiplexor
Installer has implemented them, the program displays the following
information:
Creating Additional Instances (Unix)
Use the Multiplexor Installer to create a new instance after an initial installation.
To run the Multiplexor Installer, follow these steps:
Go to the directory that contains the Multiplexor Installer.
The program is installed at the top of the installation directory, under
MMPRoot/.
From the command line, type mmp-setup.
The Multiplexor Installer asks whether you want to change an existing instance or create a new one. If you choose to create a new instance, the installer takes you through the installation process, as described in Creating a Multiplexor Instance (Unix).
Modifying an Instance (Unix)
Use the Multiplexor Installer to modify the configuration of a previously installed instance of the Multiplexor.
To run the Multiplexor Installer, follow these steps:
Go to the directory that contains the Multiplexor Installer. The program is installed at the top of the installation directory, under MMPRoot/.
From the command line, type mmp-setup.
The Multiplexor Installer asks whether you want to change an existing instance or create a new one. To change an existing instance, select the name of that instance. The installer takes you back through the prompts for configuring the Multiplexor so you can make the changes you want. For information about each parameter, see Multiplexor Configuration.
Multiplexor Configuration (Unix)
Multiplexor is controlled by setting the configuration parameters that are described in Table 13.3. See Table 13.2 for different methods you can use to set configuration parameters.
This section describes how to set Multiplexor configuration variables by:
You can also set Multiplexor configuration variables by running the PopProxy and ImapProxy commands with the install option as described in Command-Line Configuration Options, then copying the screen output into the configuration files.
Listing Options (Unix)
To display a list of the current configuration parameters, you can execute Multiplexor for either POP or IMAP by running either PopProxy or ImapProxy from the command line, using the -h option with no attributes:
PopProxy -h
ImapProxy -h
Choosing a Port Number (Unix)
Keep the following in mind when entering a port number:
Configuration Prompts (Unix)
Table 13.7 lists the Multiplexor configuration prompts and associated environment variables in Unix environments. See Table 13.3 for environment variable descriptions.
Table 13.7 Multiplexor configuration prompts (Unix)
Installer prompt
| Environment variable
|
|---|
LDAP Host:
|
LDAPHost
|
Base DN:
|
BaseDN
|
[IMAP4/POP3] MMP LogDir:
|
LogDir
|
Log Level:
|
LogLevel
|
Should the MMP bind to LDAP as someone in particular (y/n):
If you answer yes, the following two questions are asked:
What user should the MMP
authenticate as:
What's the password for "BindDN":
|
LDAPAuth
LDAPAuth
BindPassword
|
Number of Threads:
|
NumThreads
|
Should the MMP listen on a non-default port (y/n):
(See Choosing a Port Number (Unix) for additional information about choosing a port.)
If you answer yes, the following question is asked:
Which port:
|
ListenPort
|
Do your main [IMAP4/POP3] servers listen on non-default ports (y/n):
If you answer yes, the following question is asked:
Which port:
|
BacksidePort
|
Would you like to override the IMAP4 MMP's CAPABILITY response (y/n):
If you answer yes, the following question is asked:
Please type in the new CAPABILITY,
and hit return.
|
Capability
|
Would you like to override the MMP's banner (y/n):
If you answer yes, the following prompt is displayed:
Please type in the new banner,
and hit return.
|
Banner
|
Would you like to override the MMP's LDAP search string (y/n):
If you answer yes, the following prompt is displayed:
Please type in the new search
string, and hit return.
|
UidSearch
|
Would you like MMP to use a particular attribute for auth replay (y/n):
If you answer yes, the following prompt is displayed:
Please type in attribute, and hit
return.
|
UidAttr
|
Would you like the MMP to use a non-default attribute for the mailhost?
(y/n):
If you answer yes, the following prompt is displayed:
Please type in the list of
attributes, and hit return.
(Comma-delimited list.)
|
MailHostAttrs
|
Should this MMP do virtual domain mapping(y/n):
If you answer yes, the following prompt is displayed:
Please type the location of the
mapping file, and hit return:
|
VirtualDomainFile
|
Do you want to specify a list of virtual
domain delimiters? (y/n)
If you answer yes, the following prompts are displayed:
Please type in the new delimiter and
hit return:
Do you want to specify a canonical
virtual domain delimiter? (y/n)
Please type in the new delimiter and
hit return:
|
VirtualDomainDelim
VirtualDomainDelim
CanonicalVirtual
DomainDelim
CanonicalVirtual
DomainDelim
|
Would you like to provide a "spoof" message for POP3 (y/n):
This prompt is only displayed for POP Multiplexors.
If you answer yes, the following prompt is displayed:
Please type in the location of the
file to be used, and hit return:
|
SpoofMessageFile
|
Would you like to override the Server Down Alert for the MMP? (y/n)
If you answer yes, the following prompt is displayed:
Please type in the alert string and
hit return:
|
ServerDownAlert
|
Should the IMAP4 MMP do SSL (y/n):
(This prompt is only displayed for IMAP Multiplexors.)
If you answer yes, the following five prompts are displayed:
|
SSLEnable
|
1 - Should the MMP listen for SSL on a
non-default port (y/n)
If you answer yes, you are asked:
Which port?
|
ListenPort
|
2 - Do your main servers listen on non-default SSL ports? (y/n):
If you answer yes, you are asked:
Which port?
|
SSLBacksidePort
|
3 - Do you have a secmod database (y/n):
If you answer yes, you are asked:
Please type the location of the
secmod database:
Please type the location of the
certificate database:
Please type the location of the key
database:
|
SSLSecmodFile
SSLSecmodFile
SSLCertFile
SSLKeyFile
|
4 - Is the key file password protected
(y/n)
If you answer yes, you are asked:
Please type the key file password:
Please type the names of the desired
cipher specs, separated by colons,
or the word "all":
Please type the name of the
certificate in the database:
|
SSLKeyPasswd
SSLKeyPasswd
SSLCipherSpecs
SSLCertNicknname
|
5 - Do you have a certmap.conf (Should MMP do client-cert auth) (y/n):
If you answer yes, the following prompts are displayed:
Please type in the location of the certmap.conf file:
Who should the MMP authenticate as for the proxy-auth?
What's the password for StoreAdmin?
|
CertMapFile
CertMapFile
StoreAdmin
StoreAdminPass
|
Should the MMP pre-authenticate clients? (y/n)
|
PreAuth
|
Directly Setting Configuration Variables (Unix)
On Unix, Multiplexor configuration parameters are stored in the configuration files ImapMMP.config and PopMMP.config. These files are stored in the directory MMPRoot/MMP_instanceName. You can set configuration parameters by directly modifying the parameter specifications in these files.
For example, on Unix you can specify the Capability configuration parameter by adding it as an environment variable to the ImapMMP.config file. For example, you would add this line:
Capability="IMAP IMAP4rev1 AUTH=LOGIN AUTH=PLAIN X-NETSCAPE"
Example Messaging Topology
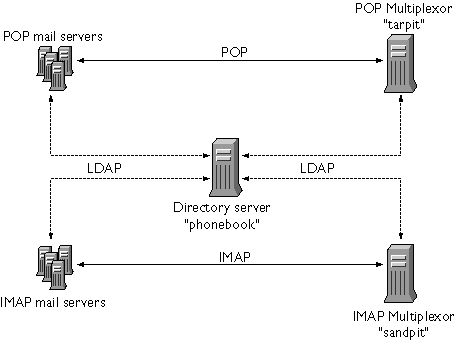
In the example shown in Figure 13.3, the fictional Airius Corporation has two Multiplexors (on separate machines), each supporting several Netscape Messaging Servers. POP and IMAP user mailboxes are split across the Messaging Server machines, with each server dedicated exclusively to POP or exclusively to IMAP. (You can restrict client access to POP services alone by removing the IMAP-server binary; likewise, you can restrict client access to IMAP services alone by removing the POP-server binary.) Each Multiplexor also supports only POP or only IMAP. The LDAP directory service is on a separate, dedicated machine.
Figure 13.3 Example Multiplexor Topology
IMAP Configuration Example
The IMAP Multiplexor in Figure 13.3 is installed on sandpit, a machine with 2 processors. This Multiplexor is listening to the standard port for IMAP connections (143). Multiplexor communicates with the LDAP server on the host phonebook for user mailbox information, and it routes the connection to the appropriate IMAP server. It overrides the IMAP capability string, provides a virtual domain file, and supports SSL communications.
This is its ImapMMP.config configuration file:
LDAPHost=phonebook
BaseDN="o=Airius.com"
LogDir="/usr/netscape/suitespot/mmp/MMP_sandpit/log"
LogLevel=5
BindDN="cn=Directory Manager"
BindPassword="password"
NumThreads=2
ListenPort=143
BacksidePort=143
Capability="IMAP4 IMAP4rev1 AUTH=LOGIN AUTH=PLAIN X-NETSCAPE"
VirtualDomainFile="/usr/netscape/suitespot/mmp/vdfile.txt"
SSLEnable=y
SSLListenPort=993
SSLSecmodFile="/usr/netscape/suitespot/mmp/secmod.db"
SSLCertFile="/usr/netscape/suitespot/mmp/cert7.db"
SSLKeyFile="/usr/netscape/suitespot/mmp/key3.db"
SSLKeyPasswd=""
SSLCipherSpecs="all"
SSLCertNickname="Airius.com Server Cert"
POP Configuration Example
The POP Multiplexor example in Figure 13.3 is installed on tarpit, a machine with 4 processors. This Multiplexor is listening to the standard port for POP connections (110). Multiplexor communicates with the LDAP server on the host phonebook for user mailbox information, and it routes the connection to the appropriate POP server. It also provides a spoof message file.
This is its PopMMP.config configuration file:
LDAPHost=phonebook
BaseDN="o=Airius.com"
LogDir="/usr/netscape/suitespot/mmp/MMP_tarpit/log"
LogLevel=10
BindDN="cn=Directory Manager"
BindPassword="password"
NumThreads=4
ListenPort=
BacksidePort=
SpoofMessageFile="/usr/netscape/suitespot/mmp/pop3spoof.txt"
SSLEnable=n