Opening Image Files and Documents
There are several ways to open (or display) an image for viewing, depending on your starting point:
Open an image by selecting File -> Open.
See Chapter 1, Introduction to the Solaris User Environment, for standard information on opening a file.
In Mail Tool, open an attached image file or multiple page document.
Drag and drop a file from another application to the Image Tool View window.
In Snapshot, after an image has been snapped, choose the View option.
Once Image Tool is launched from Mail Tool or Snapshot you don't have to open Image Tool again to view other images.
Viewing Single Page Images and Multiple Page Documents
If the image you opened is a single page image, the View window resizes to the size of the image (unless the image extends beyond the size of the screen.)
You can now save your image as described in "Saving an Image", print your image as described in "Printing Images", or use the palette with your image as described in "Using the Image Tool Palette".
If your document is a multiple page document, refer to "Viewing Multiple Page Documents".
Formats that Image Tool Can Open
Table 13-1 lists the file formats that Image Tool can open along with recommended file name extensions. These extensions may help you recognize file formats.
Note -
PostScript file formats are for PostScript and Encapsulated PostScript File (EPSF) documents. For simplicity, in the rest of this chapter the term PostScript includes EPSF.
Table 13-1 Image Tool File Formats and Extensions
|
File Format |
File Name Extension |
|---|---|
|
Encapsulated PostScript File |
.ps, .eps, .epsf |
|
PostScript |
.ps |
|
3 Portable Graymap |
.rgb3 |
|
Abekas YUV |
.yuv |
|
Andrew Toolkit |
.atk |
|
Atari Compressed |
.spc |
|
Atari Uncompressed Spectrum |
.spu |
|
Atari Degas 1 |
.pi1 |
|
Atari Degas 3 |
.pi3 |
|
AutoCAD Slide |
.sld |
|
Benet Yee Face File |
.ybm |
|
CMU Window Manager |
.cmu |
|
FITS |
.fits |
|
GEM |
.img |
|
GIF |
.gif, .GIF |
|
Gould Scanner |
.gould |
|
Group 3 Fax |
.g3 |
|
HIPS |
.hips |
|
IFF ILBM |
.ilbm |
|
HP PaintJet |
.pj |
|
JFIF (JPEG) |
.jpg, .jpeg, .JPG, .JPEG |
|
Lisp Machine Bit-Array |
.lispm |
|
MGR |
.mgr |
|
MTV/PRT Ray-Tracer |
.mtv |
|
MacPaint |
.mac |
|
PBM |
.pbm |
|
PC Paintbrush |
.pcx |
|
PGM |
.pgm |
|
PICT |
.pict |
|
PPM |
.ppm |
|
QRT Ray-Tracer |
.qrt |
|
Raw Grayscale |
.rawg |
|
Raw RGB |
.raw |
|
Sun Icon |
.icon |
|
Sun Raster |
.im1 (monochrome) .im8 (8-bit color) .im24 (24-bit color) .im32 (32-bit color) .rs |
|
TIFF |
.tif, .tiff, .TIF, .TIFF |
|
TrueVision Targa |
.tga |
|
Usenix FaceSaver |
.fs |
|
X Bitmap |
.xbm |
|
X11 Window Dump |
.xwd |
|
XPM |
.xpm |
|
Xerox Doodle Brush |
.brush |
|
Xim |
.xim |
Opening Your File in a Specific Format
If Image Tool cannot recognize the file format you want to open, you may need to specify the format, as described in the following section. To do so:
-
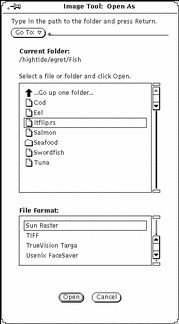
Choose File -> Open As.
The Open As window displays, as shown in Figure 13-3, with the current folder location and document file type.
Figure 13-3 The Open As Window
-
Select a file type from File Format.
Table 13-1 shows the possible file extensions and list of file formats Image Tool can open.
-
Select a file from the scrolling list.
-
Click Open.
Your file or document is opened in the View Window. The palette is automatically displayed when your file is opened. If you do not want to automatically display the palette, refer to "Setting Image Tool Properties".
Getting Information About Your Image
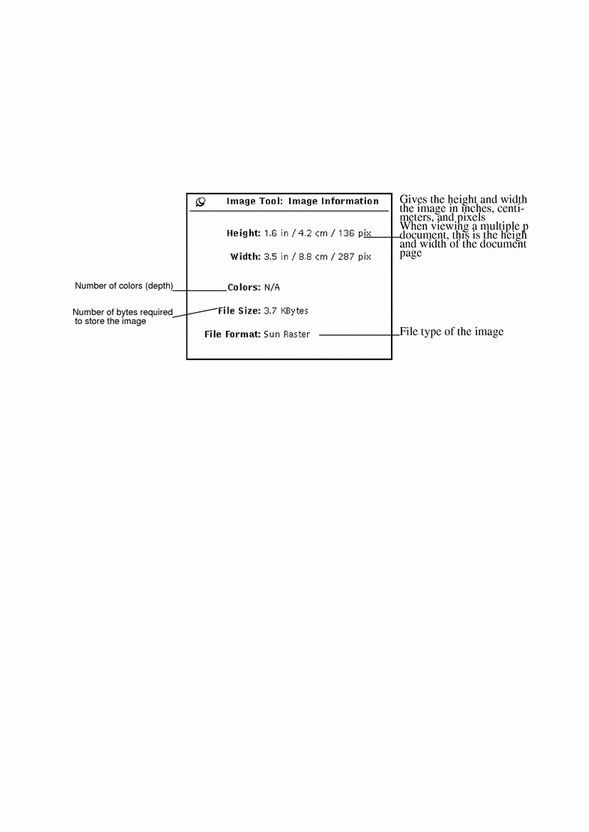
Image Tool provides the following information about the currently opened file: height, width, colors, or size. To view this information:
Select View -> Image Info.
The Image Information window displays as shown in Figure 13-4.
Figure 13-4 Image Information Window
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
