5.3 Services for the AppleTalk Realm
This section contains instructions for the following tasks:
5.3.1 Starting AppleTalk Services
Follow these steps to start the AppleTalk realm and set its services to accept client connection requests:
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Configuration and Control->Start all AppleTalk Services
The Confirmation screen appears.
-
Click OK.
The Start all AppleTalk Services screen appears.
-
Click OK.
5.3.2 Shutting Down AppleTalk Services
Follow these steps to shut down in the AppleTalk realm and set its services to reject client connection requests:
-
Follow these links:
-
AppleTalk Realm->Configuration and Control->Shutdown all AppleTalk Services
The Confirmation screen appears.
-
-
Click OK.
The Shutdown all AppleTalk Services screen appears.
-
Click OK.
5.3.3 Checking Realm Status
Follow these steps to check the status of the TAS system, transports, services, and client connections in the AppleTalk realm:
-
Follow these links:
-
AppleTalk Realm->Configuration and Control->AppleTalk Realm Status
The AppleTalk Realm Status screen appears:
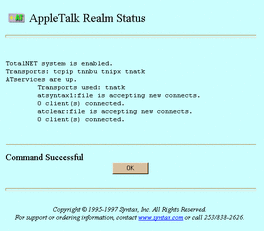
-
-
When finished, click OK.
To check realm status from the UNIX command line, use the tnstat command.
5.3.4 Creating and Modifying File Services
TAS allows AppleTalk-compatible clients to share file and print resources by connecting them through the AppleTalk realm.
Follow the steps below to create or modify a file service in the AppleTalk realm. You can also use the file service creation wizard at AppleTalk Realm->File Service Creation or System->File Service Creation->AppleTalk Realm File Service to create a file service.
-
Follow these links:
-
AppleTalk Realm->Manage File Services
The List of AppleTalk File Services screen appears.
-
-
From the list, select the file service you want to modify, or enter the name of a service you want to create in the text field. A file service name can contain up to 15 ASCII characters and no spaces, and it must not begin with an asterisk (*). The list contains nothing if no file services exist.
-
Click Create or Administer. The Administer button does not appear if no file services exist.
If you clicked Create, the Create New AppleTalk File Service screen below appears. Go to Step 4.
If you clicked Administer, the AppleTalk File Service servicename screen appears. Click Configuration, or click the appropriate link from the following, then click OK on the subsequent screen: Accept Service Connections, Reject Service Connections, Status, Start Service, Shutdown Service. If you click Configuration, the Update AppleTalk File Service servicename screen, same as the Create New AppleTalk File Service screen below, appears. Go to Step 4.

-
Enter or select values for the following attributes, as needed:
-
AppleTalk file service name -- The file service to which users connect, according to its appearance in their Chooser lists. The file service name conventionally appears in lower-case on clients and in upper-case on the network. If you clicked Administer and Configuration, this attribute does not appear.
-
Service description -- The description used within TAS for the service. It consists of an arbitrary line of text.
-
Volume references -- A list of the volumes this file service references and exports. You can configure the referenced volumes and their attributes via System->Volumes. Select the volumes you want to reference.
-
Umask -- The default file access permissions for TAS clients. This three-digit octal-number represents the UNIX file protection mask and works the same as the UNIX umask command. Refer to the UNIX umask(1) man page for more information on how the system interprets digits.
-
Client character set -- The character set that TAS assumes all of this service's clients use. It defaults to builtin-mac-roman. Select a different character set if necessary.
-
Freespace report method -- The method for calculating the amount of free disk space. Systems that do not support the UNIX statfs() system call or its equivalent do not support this option. If set to the default all, this attribute makes TAS report to clients the free space on all of the partitions. If set to root, this attribute makes TAS report only free disk space on the partition in which the virtual root of a client's connection resides.
-
Allow whitespace in file names -- The option to allow AppleTalk clients to use spaces in file names.
-
Use client specified file time stamps -- The option to stamp files created or modified on the server by clients with the clients' date and time rather than the server's date and time.
-
Log activity -- The option to enable activity logging. This directs this file service to record client activity in activity.tn in the TAS home directory. When a client disconnects, TAS appends a line of data about the client's session to the log file at activity.tn. This attribute defaults to no activity logging.
-
Tracing -- The option to direct this file service to write debugging traces to a file. Syntax Technical Support can use the trace file to help diagnose problems.
-
Start this file service? -- The option to start this file service when you click Submit. If you clicked Administer and Configuration, this attribute does not appear.
-
-
Click Submit.
The Create New AppleTalk File Service servicename screen or the Update AppleTalk File Service servicename screen appears.
-
Click OK.
To administer a file service from the UNIX command line, use the tnservice command.
5.3.5 Shutting Down File Services
Follow these steps to shut down a file service:
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Manage File Services
The List of AppleTalk File Services screen appears.
-
From the list, select the file service you want to shut down.
-
Click Administer.
The AppleTalk File Service servicename screen appears.
-
Click Shutdown Service.
The Confirmation screen appears.
-
Click OK.
The Shutdown servicename Service on AppleTalk Compatible Realm screen appears.
-
Click OK.
5.3.6 Deleting File Services
Follow the steps below to delete file services in the AppleTalk realm. These steps include instructions for shutting down the file services you want to delete, because you must shut down a file service to delete it.
-
Follow these links:
-
AppleTalk Realm->Manage File Services
The List of AppleTalk File Services screen appears.
-
-
From the list, select the file service you want to delete.
-
Click Administer.
The AppleTalk File Service servicename screen appears.
-
Click Shutdown Service.
The Confirmation screen appears.
-
Click OK.
The Shutdown servicename Service on AppleTalk Compatible Realm screen appears.
-
Click OK.
-
Repeat Steps 1-5 for each service you want to delete.
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Manage File Services
The List of AppleTalk File Services screen reappears.
-
From the list, select the file services you want to delete.
-
Click Delete.
The Confirmation screen appears.
-
Click OK.
The Delete AppleTalk File Service screen appears.
-
Click OK.
5.3.7 Accepting Services
AppleTalk file services accept connection requests unless you set them to reject connection requests. Starting TAS also sets its services to accept connection requests.
Follow these steps to make AppleTalk file services accept client connection requests:
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Configuration and Control->Accept Service Connections
The Confirmation screen appears.
-
Click OK.
The Accept all AppleTalk Service Connections screen appears.
-
Click OK.
To accept services from the UNIX command line, use the tnaccept command.
5.3.8 Rejecting Services
AppleTalk file services accept connection requests unless you set them to reject connection requests. Shutting down TAS also sets its services to reject connection requests.
Follow these steps to make AppleTalk file services reject client connection requests:
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Configuration and Control->Reject Service Connections
The Confirmation screen appears.
-
Click OK.
The Reject all AppleTalk Service Connections screen appears.
-
Click OK.
To reject services from the UNIX command line, use the tnreject command.
5.3.9 Administering Attach Points
Follow these steps to create, modify, or delete attach points--points on directory paths at which clients must provide credentials--in the AppleTalk realm:
-
Follow these links:
-
AppleTalk Realm->Manage File Services
The List of AppleTalk File Services screen appears.
-
-
From the list, select the file service in which you want to administer an attach point.
-
Click Administer.
The AppleTalk File Service servicename screen appears.
-
Click Attach Points.
The List of Defined Attach Points screen appears.
-
From the list, select the attach point you want to modify or delete, or enter the name of an attach point you want to create in the text field. If deleting, you may select more than one attach point. The list contains nothing if no attach points exist.
-
Click Create, Modify, or Delete. The Modify and Delete buttons do not appear if no attach points exist.
If you clicked Create, the Create New Attach Point screen below appears. Go to Step 7.
If you clicked Modify, the Update Attach Point attachpoint screen, same as the Create New Attach Point screen below, appears. Go to Step 7.
If you clicked Delete, the Confirmation screen appears. Click OK. The Delete Attach Points screen appears. Click OK. Do not go to Step 7.
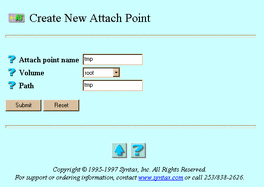
-
Enter or select values for the following attributes:
-
Attach point name -- The attach point. If you clicked Modify, this attribute does not appear.
-
Volume -- The list of volumes exported by the service. TAS defines volumes at the system level. File services can reference defined volumes; such references export the volumes.
-
Path -- The directory below the selected volume, used as the virtual root by clients who connect to this attach point.
-
-
Click Submit.
The Create New Attach Point attachpoint screen or the Update Attach Point attachpoint screen appears.
-
Click OK.
To administer attach points from the UNIX command line, use the tnattach command.
5.3.10 Creating and Modifying Print Services
Follow these steps to create or modify an AppleTalk print service:
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Manage AppleTalk Print Services
The List of AppleTalk Print Services screen appears.
-
From the list, select the print service you want to delete, or enter the name of a service you want to create in the text field. The list contains nothing if no print services exist.
-
Click Create or Administer. The Administer button does not appear if no print services exist.
If you clicked Create, the Create New AppleTalk Print Service screen below appears. Go to Step 4.
If you clicked Administer, the AppleTalk Print Service servicename screen appears. Click Configuration, or click the appropriate link from the following, then click OK on the subsequent screen: Accept Service Connections, Reject Service Connections, Status, Start Service, Shutdown Service. If you click Configuration, the Update AppleTalk Print Service screen, same as the Create New AppleTalk Print Service screen below, appears. Go to Step 4.
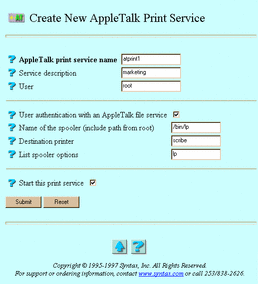
-
Enter or select values for the following attributes, as needed:
-
AppleTalk print service name -- The print service to which users connect. If you clicked Administer and Configuration, this attribute does not appear.
-
Service description -- The description used within TAS for the service. It consists of an arbitrary line of text.
-
User -- The UNIX user identity you want to execute the UNIX command line given in the command directive for the service. The server process inherits the appropriate group list for the user name. This attribute defaults to root.
-
User authentication with an AppleTalk file service -- The option to allow the user to log on to an AppleTalk-compatible file service to print. The user name can appear on the title page of the print job.
-
Name of the spooler (include path from root) -- The name of the UNIX print spooler that the server can execute, needed by the server when printing clients' spooled jobs. Provide the full path of the spooler; for example, /bin/lp or /bin/lpr.
-
Destination printer -- The UNIX printer this print server should use.
-
List Spooler options -- Command line arguments for the print spooler.
-
Start this print service -- The option to start this print service when you click Submit. If you clicked Administer and Configuration, this attribute does not appear.
-
-
Click Submit.
The Create New AppleTalk Print Service servicename screen or the Update AppleTalk Print Service servicename screen appears.
-
Click OK.
To administer AppleTalk print services from the UNIX command line, use the tnservice command.
5.3.11 Shutting Down Print Services
Follow these steps to shut down a print service:
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Manage AppleTalk Print Services
The List of AppleTalk Print Services screen appears.
-
From the list, select the print service you want to shut down.
-
Click Administer.
The AppleTalk Print Service servicename screen appears.
-
Click Shutdown Service.
The Confirmation screen appears.
-
Click OK.
The Shutdown servicename Service on AppleTalk Realm screen appears.
-
Click OK.
5.3.12 Deleting Print Services
Follow the steps below to delete print services in the AppleTalk realm. These steps include instructions for shutting down the print services you want to delete, because you must shut down a print service to delete it.
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Manage AppleTalk Print Services
The List of AppleTalk Print Services screen appears.
-
From the list, select the print service you want to delete.
-
Click Administer.
The AppleTalk Print Service servicename screen appears.
-
Click Shutdown Service.
The Confirmation screen appears.
-
Click OK.
The Shutdown servicename Service on AppleTalk Realm screen appears.
-
Click OK.
-
Repeat Steps 1-5 for each service you want to delete.
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Manage Print Services
The List of AppleTalk Print Services screen reappears.
-
From the list, select the file services you want to delete.
-
Click Delete.
The Confirmation screen appears.
-
Click OK.
The Delete AppleTalk Print Services screen appears.
-
Click OK.
5.3.13 Administering Suffixes for AppleTalk Maps
An AppleTalk map associates file suffixes with Macintosh applications. The client operating system uses these associations to determine which application it should invoke when it accesses a file.
Follow these steps to create, modify, or delete suffixes for AppleTalk maps:
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Suffixes for AppleTalk Map
The List of Suffixes for AppleTalk Map screen appears.
-
From the list, select the suffix you want to modify or delete, or enter a suffix you want to create in the text field. If deleting, you may select more than one map. The list contains nothing if no maps exist.
-
Click Create, Modify, or Delete. The Modify and Delete buttons do not appear if no maps exist.
If you clicked Create, the Create New Suffix for AppleTalk Map screen below appears. Go to Step 4.
If you clicked Modify, the Update Suffix suffixname for AppleTalk Map screen, same as the Create New Suffix for AppleTalk Map screen below, appears. Go to Step 4.
If you clicked Delete, the Confirmation screen appears. Click OK. The Delete Suffix for AppleTalk Map screen appears. Click OK. Do not go to Step 4.
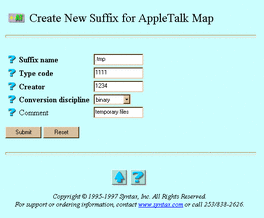
-
Enter or select values for the following attributes:
-
Suffix name -- The name of the suffix to associate with the AppleTalk map. If you clicked Modify, this attribute does not appear.
-
Type code -- The four-character Macintosh type code to associate with TAS files for the suffix.
-
Creator -- The Macintosh creator code--a four-byte sequence of characters that uniquely identifies a Macintosh program.
-
Conversion discipline -- The discipline for file conversions between client and server. Macintosh text files use carriage returns for new lines, whereas UNIX files use linefeeds.
-
Comment -- Information you would like to associate with the suffix type.
-
-
Click Submit.
The Create New Suffix suffixname for AppleTalk Map screen or the Update Suffix suffixname for AppleTalk Map screen appears.
-
Click OK.
To administer suffixes for AppleTalk maps from the UNIX command line, use the tnsuffix command.
5.3.14 Configuring Security
Follow these steps to configure AppleTalk file authentication:
-
Follow these links:
AppleTalk Realm->Manage File Services
The List of AppleTalk File Services screen appears.
-
From the list, select a file service for which you want to configure authentication.
-
Click Administer.
The AppleTalk File Service servicename screen appears.
-
Click Authentication and Service Mode Options.
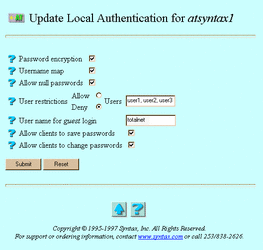
The Update Local Authentication for servicename screen appears:
-
Select or enter values for the following attributes, as needed:
-
Password encryption -- The option to keep passwords from transmitting across the network. Without password encryption, any UNIX user can potentially connect to the server. In this open authentication environment, client and server exchange clear-text passwords. Password encryption, the secure authentication method, provides improved security, but you must maintain a separate user-password database for it. When you enable password encryption and secure authentication, only users added via Passwords can connect. With secure authentication, client and server exchange a series of messages that allows the server to verify that the client knows the correct password, without transmitting the password or any representation of it. Most AppleTalk-compatible clients support password encryption.
-
Username map -- The option to allow file services to validate clients by mapping them to valid UNIX users. You must define username maps before selecting this option (see "4.2 Administering Username Maps").
-
Allow null passwords -- The option to allow UNIX users without passwords to access the server. By default, TAS denies such users access to the server, for better security. This option has no effect if you enable Password encryption.
-
User restrictions -- The option to restrict the users who can connect to this service. Select it by selecting either Allow or Deny and the names of the users in the adjacent Users field. If you enter no user names, TAS ignores this attribute. Separate user names with commas.
-
User name for guest login -- The name assigned to LM-NT-OS/2 share-mode clients for accessing the AppleTalk realm.
-
Allow clients to save passwords -- The option to allow clients to save their passwords on the server.
-
Allow clients to change passwords -- The option to allow clients to change their server passwords.
-
-
Click Submit.
The Update Local Authentication for servicename screen appears.
-
Click OK.
To configure security from the UNIX command line, use the tnservice command.
5.3.15 Disconnecting Users
Follow these steps to disconnect connected users:
-
Follow one of these sets of links:
AppleTalk Realm->AppleTalk Connected Users->Disconnect Users
AppleTalk Realm->Manage File Services->[select a service] ->Administer->Disconnect Users
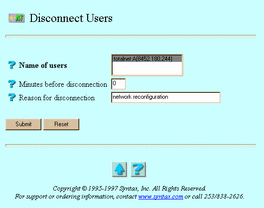
The Disconnect Users screen appears:
-
Select or enter values for the following attributes, as needed:
-
Name of users -- The users to disconnect
-
Minutes before disconnection -- The time, in minutes, before you want to disconnect the users.
-
Reason for disconnection -- A brief message to the users to disconnect. Users must have message reception enabled to see this message.
-
-
Click Submit.
The Disconnect Users screen reappears, this time containing the statement "Command Successful".
-
Click OK.
To disconnect a user from the UNIX command line, use the tnkill command.
5.3.16 Viewing Realm Connections
Follow these steps to list AppleTalk realm connections:
-
Follow one of these sets of links:
AppleTalk Realm->AppleTalk Connected Users->Connection Information
AppleTalk Realm->Manage File Services->[select a service] ->Administer->Connection Information
The Connection Information screen appears.
-
From the list, select a user whose information you want to view.
-
Click Submit.
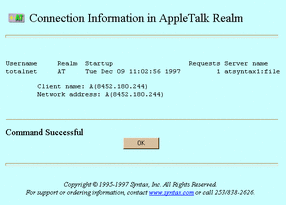
The Connection Information in AppleTalk Realm screen appears:
-
When finished, click OK.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
