Chapter 6 Installing the Open Telecommunications Platform Using an Existing OTP System
This chapter provides the procedures for using an existing production standalone OTP host or the first OTP host in a clustered OTP system to install and configure the Open Telecommunications Platform software to a new OTP System.
In the following sections and procedures, the OTP host used as the installation source is called the OTP master server. The new standalone OTP host and each new clustered OTP host is called a new OTP host.
The following topics are discussed:
-
Preparing the OTP System Management Service to Provision the OS
-
Installing OTP on New OTP Hosts Using the Production OTP Host
Tip –
Before you begin, review the OTP Plan settings described in OTP System Plan Settings Descriptions, and then print out the worksheet and fill in the values based on the host or hosts to which you will install OTP:
Preparing the OTP System Management Service to Provision the OS
This section provides the procedures for preparing the OTP system management service to provision the Solaris 10 Update 2 to a new standalone OTP host or to clustered OTP hosts.
Before you can use an existing OTP system to install the Open Telecommunications Platform to one or more OTP hosts, you must first perform the following tasks.
-
Create the OS image on the source OTP master server as described in To Create the OS Image
-
If you are going to provision the OS to bare metal OTP hosts, in other words, hosts on which an OS has not been installed, create the XML discovery file which the OTP discovery process uses to discover and manage the bare metal new OTP hosts as described in To Create the XML Discovery File
-
If you are going to install OTP to new OTP hosts on a different subnet, create a DHCP relay as described in To Create the DHCP Relay for Deploying to New OTP Hosts on Different Subnets
 To Create the OS Image
To Create the OS Image
-
Log in as root to the production OTP host.
-
Type /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/n1sh to open the OTP command shell. For example:
# /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/n1sh N1-ok>
-
Create the Solaris 10 Update 2 OS image.
In the OTP command shell, type create os os name file path to iso image where os name is the name of the image to create, and path to iso image is the path to the Solaris 10 Update 2 ISO image you created and NFS-mounted in To Download and Uncompress the OTP and Solaris OS Installation Zip Files.
For example, if:
-
The name of the OS image to be created is to be sol10u2
-
The name of the server on which you created the ISO image is otpsource
-
The ISO image sol10u2-ga-sp-dvd.iso was created in the NFS-mounted directory /otp-download
you would then type:
N1-ok> create os sol10u2 file /net/otpsource/otp-download/sol10u2-ga-sp-dvd.iso
Note –A job is submitted to create the OS image, and a job ID is displayed. The create os command can take up to 60 minutes to complete.
To check for job completion, type show job job ID. When the job has completed, type show os to list the OS images.
-
Next Steps
Create the XML discovery file as described in the next section.
 To Create the XML Discovery File
To Create the XML Discovery File
To discover, manage, and provision an OS to bare metal (no operating system installed) OTP hosts, you must create an XML discovery file that lists the server name, model number, and MAC address of each OTP host.
-
Log in as root to the production OTP host.
-
Create the XML discovery file.
For example, vi /tmp/discovery-mac-addresses.
-
Add the system name, model number, Ethernet port address, and MAC address for each host to be discovered.
The file format is:
<!xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <servers> <server name="otpclient1" model="model name"> <ethernetPort name="GB_0" mac="mac address"/> </server> <server name="otpclient2" model="model name"> <ethernetPort name="GB_0" mac="mac address"/> </server> </servers>Where otpclient1 is the name to be assigned to the host, model name is the model name listed in the following table, and mac address is the MAC address of the host.
Host Type
Model Type for Bare Metal Discovery
Sun Netra 240
NETRA-240
Sun Netra 440
NETRA-250
Sun Fire V240
SF-V240
Sun Fire V440
SF-V440
Sun Fire V890
SF-V890
Sun Fire E2900
SF-E2900
Sun Fire T1000
SF-T1000
For example:
<!xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?> <servers> <server name="otpclient1" model="NETRA-240"> <ethernetPort name="GB_0" mac="0:3:ba:19:c5:b"/> </server> <server name="otpclient2" model="SF-V20"> <ethernetPort name="GB_0" mac="0:7:3c:12:b6:a"/> </server> <server name="otpclient3" model="SF-T1000"> <ethernetPort name="GB_0" mac="0:14:4f:25:5e:78"/> </server></servers> -
Save and close the file.
Next Steps
-
If you are deploying the OS to new OTP hosts in the same subnet, prepare and deploy the OS as described in Preparing and Deploying the OS to the New OTP Hosts.
-
If you are deploying the OS to new OTP hosts in a different subnet, create the DHCP relay as described in the next procedure.
 To Create the DHCP Relay for Deploying to New OTP Hosts
on Different Subnets
To Create the DHCP Relay for Deploying to New OTP Hosts
on Different Subnets
If you are going to deploy the Solaris 10 Update 2 to new OTP hosts on a different subnet, you must set up a DHCP relay on each subnet as described in this procedure before you can discover and subsequently deploy the OS to the hosts.
The examples in the following substeps assume:
-
The production OTP host that is to be used to provision the OS is on subnet 10.1.15
-
The new OTP host or hosts are on subnet 10.1.30
-
Log in as root to a Solaris OS SPARC server on the 10.1.30 subnet.
The server must not be a standalone OTP host or a clustered OTP host.
-
Type the ps -ef | grep dhcp to verify that the DHCP service has started.
# ps -ef | grep dhcp oot 24992 1 0 18:20:53 ? 0:00 /usr/lib/inet/in.dhcpd
-
Type dhcpconfig -R production OTP hostIP address,otpclient1 IP address ..., otpclientn IP address.
For example:
# dhcpconfig -R 10.1.15.1,10.1.30.5, 10.1.30.6,10.1.30.7,10.1.30.8,\ 10.1.30.9,10.1.30.10,10.1.30.11,10.1.30.12
-
Log in as root to the production OTP host.
-
Type /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/n1sh to open the OTP command shell.
# /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/n1sh N1-OK>
-
Set up the OTP DHCP service.
In the OTP command shell, type create dhcpconfig DHCP configuration name network IP address of base network netmask netmask value defaultgw gateway IP address domain domain name where:
-
DHCP configuration name is the name you assign to the OTP DHCP configuration
-
IP address of base network is the base address of the target subnet
-
netmask value is the netmask value of the target subnet
-
gateway IP address is the IP address of the target subnet gateway
-
domain name is your corporate domain name
For example:
N1-ok> create dhcpconfig test network 10.11.55.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 defaultgw 10.11.55.1 domain mycompany.com
Note –The above example was split into two lines to fit on the page. When typing the create dhcpconfig command, type the full command as a single line.
-
Next Steps
Prepare and deploy the OS as described in the next section.
Preparing and Deploying the OS to the New OTP Hosts
This section provides the procedures for using either the graphical user interface or the command line to create an OS profile, discover the new OTP hosts, and deploy the OS to the new OTP hosts.
The following topics are discussed:
-
Preparing and Deploying the OS to the New OTP Hosts Using the Graphical User Interface
-
Preparing and Deploying the OS to the New OTP Hosts Using the Command Line
Tip –
If you are unfamiliar with the OTP system, use the graphical user interface to prepare and deploy the OS to the new OTP hosts. The graphical user interface provides setup wizards to help you create the OS profile.
Preparing and Deploying the OS to the New OTP Hosts Using the Graphical User Interface
This section provides the graphical user interface procedures for creating the OS profile, discovering the new OTP hosts, and deploying the OS to the new OTP hosts.
 To Create the OS Profile
To Create the OS Profile
-
Open a Web browser and log in to the production OTP host system management service.
Go to URL https://production OTP host:6789 where production OTP host is either the IP address or the fully qualified name of the production OTP host.
The Java Web console log in page is appears. Type your OTP account name and password to log in.
The system management page appears.
-
Click Sun N1 System manager.
The System Manager page appears.
-
Click New... beneath OS Profiles in the Task Shortcuts panel on the right side of the page.
The Create Operating System Profile wizard appears. Step 1, Specify Initial OS Profile Information is displayed.
Tip –Click Help on this panel and subsequent panels for a description of each panel.
-
Specify the initial OS profile information.
-
Type a name for the OS profile in the Name field.
-
(Optional) Type a description of the OS profile in the Description field.
-
Choose the OS distribution from the drop-down list in the Distribution field.
-
Type the root password to be used for the new OS distribution in the Root Password field.
-
Type the root password again in the Confirm Password field.
Click Next. Step 2, Specify Preferences is displayed.
-
-
Specify the language and time zone preferences.
-
Choose the language locale from the Language drop down list.
-
Choose the time zone from the Time Zone drop down list.
Click Next. Step 2.1, Specify Solaris Flash archive is displayed.
-
-
(Optional) Type the full path to the Solaris flash archive.
-
If you have not created a Solaris flash archive, click Next.
-
If you have created a Solaris flash archive, type the full path to the location of the flash archive, and then click Next.
Step 3, Add Distribution Groups is displayed.
-
-
Choose Entire Distribution plus OEM.
Click Entire Distribution plus OEM in the Available column and then click Add to add it to the Selected column.
Note –If your browser displays only a portion of the distributions, choose the second Entire Distribution in the list.
Click Next. Step 4, Define Partitions is displayed.
-
Define the partitions.
Refer to Disk Drive Partitioning Requirements for disk drive partitioning requirements when allocating the root /, swap, and /globaldevices partitions.
For each partition:
-
Type the partition name in the Mount Point field.
-
Type the file system type in the File System field.
-
Type the partition size in Mbytes in the Size (MB) field.
-
Click add.
The partition is added beneath the entry fields.
 Caution –
Caution – When specifying the disk partitions, ensure that you allocate the /globaldevices directory with at least 512 Mbytes of free space.
The Partitions panel should be similar to the following:
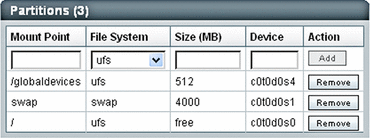
When you have completed defining the partitions, click Next. Step 4, Specify NIS and LDAP Preferences is displayed.
-
-
(Optional) Specify NIS and LDAP Preferences.
-
If you do not want to specify NIS and LDAP preferences, click Next.
Step 6, Review Selections is displayed.
-
To specify NIS and LDAP preferences, check the items you want to specify and then click Next.
Additional substeps labeled 5.1 up to 5.4 are displayed for each item you have checked. Click the Help tab within each step to display information about that step.
When you have completed specifying the information for all of your selections, click Next. Step 6, Review Selections is displayed.
Check the items that you want to specify and then click next. Depending on your choices
-
-
Review your selections.
 Caution –
Caution – Make certain that Entire Distribution plus OEM has been selected.
If the selections are correct, click Finish. Otherwise, click the appropriate Step to correct the selections.
When you click Finish, a job ID is displayed in the Command Pane. To view the job status, click the Jobs tab or type show job job ID in the Command Pane. When the job completes, the OS profile name is listed beneath OS Profiles in the Task Shortcuts panel.
Next Steps
Discover the new OTP hosts as described in the next procedure.
 To Discover the New OTP Host
To Discover the New OTP Host
-
Open a Web browser and log in to the production OTP host system management service.
Go to URL https://production OTP host:6789 where production OTP host is either the IP address or the fully qualified name of the production OTP host.
The Java Web console log in page is appears. Type your OTP account name and password to log in.
The system management page appears.
-
Click Discover.
The Discovery wizard appears. Step 1, Specify Discovery Method is displayed.
Tip –Click Help on this panel and subsequent panels for a description of each panel.
-
Specify the discovery method.
Select Use MAC address From a File and type the name of the file you created in To Create the XML Discovery File. For example, /tmp/discovery-mac-addresses
Step 2, Specify Security Credentials is displayed.
-
Specify the security credentials.
-
If you have not changed the ALOM settings, select Use Default Credentials and then click next.
-
If you have changed the settings, type the user name and password in the fields provided, and then click next.
Refer to the server hardware documentation for information about ALOM credentials.
Step 3, Specify the Server Group is displayed.
-
-
Specify the server group into which the discovered new OTP host or hosts are to be placed and then click next.
Tip –Place all of the new OTP hosts of a clustered OTP system in a single server group.
Step 4, Review Selections is displayed.
-
Review your selections.
If the selections are correct, click Finish. Otherwise, click the appropriate step to correct the selections.
When you click Finish, a job ID is displayed in the Command Pane. To view the job status, click the Jobs tab or type show job job ID in the Command Pane. Wait for discovery to complete. When the new OTP host or hosts are discovered, discovered hosts are listed on the System Dashboard tab.
Next Steps
Deploy the OS to the Clustered OTP Hosts as described in the next procedure.
 To Deploy the OS to the New OTP Hosts
To Deploy the OS to the New OTP Hosts
-
If you have closed the Web browser, open a Web browser and log in to the OTP master server system management service as described in the previous procedure.
When you have logged on, click Sun N1 System manager to display the System Manager page.
-
If the OS profile you created is not displayed beneath OS Profiles in the Task Shortcuts panel, click Edit List to display the list of available OS profiles.
In the OS profile list, click the checkbox to the left of the OS profile you created, and then click OK.
The OS profile list closes, and the OS profile name is displayed beneath OS Profiles in the Task Shortcuts panel.
-
Click and drag OS profile over the name of the new OTP host that is to be provisioned, and release the mouse button.
The Load OS wizard appears. Step 1, Specify OS Profile Loading Options is displayed.
-
Specify OS profile loading operations.
Note –If the OS profile name you chose in the previous step is not displayed in the OS Profile field, choose the OS profile from the drop-down menu.
-
Select Static IP, and then enter the IP address that is to be assigned to the new OTP host when OS provisioning is completed.
-
Clear the Use Default Settings checkbox.
Click Next. Step 1.1, Specify Boot Parameters appears.
-
-
Specify the boot parameters.
Select Enable Manual Net Boot.
Note –Do not specify any other values for this section. For more information, click the Help tab.
Click Next. Step 1.2, Specify Boot Parameters appears.
-
(Optional) Specify the boot parameters.
-
Type ttya in the Console field.
-
Type the baud rate in the Console Baud field. The default is 9600 baud.
Click Next. Step 1.3, Specify Network Configuration is displayed.
-
-
(Optional) Specify the network configuration.
-
Type the gateway IP address in the Gateway field.
-
Type the IP address of the DNS server in the Name Server field.
-
Type the domain name in the Domain Name field.
Click Next. Step 1.4, Specify Hostname is displayed.
-
-
Specify the host name.
Type the host name in the Hostname field and then click Next. Step 2, Select OS Management Features is displayed.
-
Select OS management features.
Choose the OS management feature from the Features drop-down list.
-
If you choose Base management, only the SSH credentials are required, and the remaining fields are disabled.
-
If you choose Base management and OS monitoring, all credentials are required.
Type the required credentials in each field. Click the Help tab for information about each field.
Click Next when you have completed typing the required information.
-
-
Review your selections.
 Caution –
Caution – Make certain that Entire Distribution plus OEM has been selected. If Entire Distribution plus OEM, you must create a new OS Profile in which Entire Distribution plus OEM has been specified as described in To Create the OS Profile.
If the selections are correct, click Finish. Otherwise, click the appropriate Step to correct the selections.
When you click Finish, the Load OS wizard closes, and a job is submitted to load the OS profile to the new OTP host. A job ID is displayed in the Command Line pane.
-
Click the Jobs tab to view the job status, or type show job job ID in the Command Pane, where job ID is the ID that was displayed when you clicked Finish.
Note –The new OTP host status on the System Dashboard tab will not update until the host has rebooted and the Load OS job has completed.
-
When the new OTP host has rebooted, set up NIS on the host according to your network requirements.
Next Steps
Repeat the above steps for each new OTP host that is to be provisioned.
When you have completed provisioning the OS to all new OTP hosts, install OTP to the hosts as described in Installing OTP on New OTP Hosts Using the Production OTP Host
Preparing and Deploying the OS to the New OTP Hosts Using the Command Line
This section provides the command-line procedures for creating the OS profile, discovering the new OTP hosts, and deploying the OS to the new OTP hosts.
 To Create the OS Profile
To Create the OS Profile
-
Log in as root to the production OTP host.
-
Type /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/n1sh to open the OTP command shell. For example:
# /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/n1sh N1-ok>
-
In the OTP command shell, type create osprofile os profile name os OS image name rootpassword root password where:
-
os profile name is the name of the OS profile to be created
-
OS image name is the name of the OS image you created in To Create the OS Image
-
root password is the root password of the production OTP host
For example:
N1-ok> create osprofile s10u2-profile os sol10u2 rootpassword otpadmin
-
-
Set the OS profile language and time zone.
Type set osprofile os profile name language locale timezone time zone where:
-
os profile name is the name of the OS profile you created in the previous step
-
language is your locale code
-
time zone is your time zone
For example:
N1-ok> set osprofile s10u2-profile language en_US.ISO8859-15 timezone GMT
-
-
Set the OS installation type in the OS profile.
Type add osprofile os profile name distributiongroup "Entire Distribution plus OEM support" where os profile name is the name of the OS profile you created .
For example:
N1-ok> add osprofile s10u2-profile distributiongroup "Entire Distribution plus OEM support"
-
Set the root partition allocation in the OS profile.
Type add osprofile os profile name partition / device disk slice type ufs sizeoption free.
For example:
N1-ok> add osprofile s10u2-profile partition / c0t0d0s0 type ufs sizeoption free
-
Set the swap space allocation in the OS profile.
Type add osprofile os profile name partition swap device disk slice type swap sizeoption fixed size size in Mbytes.
For example:
N1-ok> add osprofile s10u2-profile partition swap device c0t0d0s1 type swap sizeoption fixed size 4000
-
Set the /globaldevices file system allocation in the OS profile.
Type add osprofile os profile name partition /globaldevices device disk slice type ufs sizeoption fixed size size in Mbytes.
For example:
N1-ok> add osprofile s10u2-profile partition /globaldevices device c0t0d0s3 type ufs sizeoption fixed size 4000
Note –The above example was split into two lines to fit on the page. When typing the add osprofile command, type the full command as a single line.
Next Steps
Run discovery to identify the new OTP hosts to which the Solaris 10 Update 2 OS is to be deployed as described in the next procedure.
 To Discover the New OTP Hosts
To Discover the New OTP Hosts
-
Log in as root to the OTP master server.
-
Type /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/n1sh to open the OTP N1TM command shell. For example:
# /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/n1sh N1-ok>
-
Discover the new OTP host or hosts.
Type the command discover XML discovery file name format=file where XML discovery file name is the name of the XML discovery file you created in To Create the XML Discovery File.
An OTP job is submitted to discover the servers, and a job ID is displayed.
Type show job to display the job status. When the job has completed, type show servers all to display a list of the new OTP hosts that have been discovered. To view details about a specific server, type show server server id where server id is a server ID listed by the show servers all.
Next Steps
Repeat the above steps for each new OTP host. When you have completed discovering the hosts, deploy the OS to the discovered hosts as described in the next procedure.
 To Deploy the OS to the New OTP Host
To Deploy the OS to the New OTP Host
-
Log in as root to the production OTP host.
-
Type /opt/sun/n1gc/bin/n1sh to open the OTP command shell.
-
Deploy the OS to the new OTP hosts
In the OTP command shell, type load server ALOM IP address osprofile OS profile name networktype static IP Provisioning IP address hostname hostname manualnetboot=true where:
-
ALOM IP address is the IP address of the new OTP host's ALOM management port
-
OS profile name is the name of the OS profile
-
Provisioning IP address is the IP address of the new OTP host's provisioning interface
-
hostname is the name that will be assigned to the new OTP host
For example:
N1-ok> load server 10.1.15.1 osprofile sol10u2-profile networktype static IP 10.1.15.5 otpclient1 manualnetboot=true
Note –The above example has been split into two lines to fit on the page. When typing the load server command, type the entire command as one continuous line.
-
Next Steps
Repeat the above steps for each new OTP host that is to be provisioned.
When you have completed provisioning the OS to all new OTP hosts, install OTP to the hosts as described in Installing OTP on New OTP Hosts Using the Production OTP Host
Preparing the New OTP Hosts for OTP Installation
Before you can install OTP to the new OTP hosts, you must set up the OTP provisioning service remote agent on each host, and then add the host to the production OTP host as described in the following procedures.
The following topics are discussed:
 To Install the Service Provisioning Remote Agent on a New OTP Host
To Install the Service Provisioning Remote Agent on a New OTP Host
The following steps must be performed on each new OTP host.
-
Log in as root (su - root) to the new OTP host.
-
Install the OTP CLI package.
Type pkgadd -d /net/OTP install directory/Products/packages -R / SUNWotpcli where OTP install directory is the installation source directory you created in Step 8 of the procedure To Download and Uncompress the OTP and Solaris OS Installation Zip Files.
For example, if the installation server name is otpinstall, and the NFS-mounted installation directory is /otpinstall/otp1.0, you would then type:
# pkgadd -d /net/otpinstall/otp1.0/Products/packages -R / SUNWotpcli
The directory /opt/SUNWotp10/CLI is created.
-
Install the service provisioning remote agent.
Type/opt/SUNWotp10/CLI/setupRemoteAgent install directory where install directory is the Open Telecommunications Platform installation source directory. For example:
# /opt/SUNWotp10/CLI/setupRemoteAgent /net/otpinstall/otp1.0
The setupRemoteAgent script creates the service provisioning account, installs the patches needed by the remote agent, and installs the remote agent.
Next Steps
Add each new OTP host to the production OTP host as described in the following procedure.
 To Add New OTP Hosts to the Production OTP Host
To Add New OTP Hosts to the Production OTP Host
-
Open a Web browser and log in to the production OTP host service provisioning service.
Go to URL http://production OTP host:9090 where production OTP host is either the IP address or the fully qualified name of the production OTP host.
-
Click Host Setup in the left menu to display the Host Setup page.
-
Click hosts in the central menu to display the hosts page.
-
In the host field, type the name of the new OTP host.
-
(Optional) In the description field, type a description of the host.
-
Click create.
The host details edit page is displayed.
-
-
Specify the new OTP host values on the details edit page.
-
Click include remote agent on this physical host.
-
Click the arrow to the right of the connection type field to display the drop-down list.
Choose TCP/IP (unencrypted).
-
In the ip address or name field, type either the IP address of the host or the host name.
-
In the port field, type 7000.
-
Scroll to the bottom of the host edit details page and click save.
-
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click save.
The host is added to the hosts list on the production OTP host. The hosts list page is displayed.
-
Check the box to the left of the host name, and then click prepare host...
The host is prepared for provisioning.
-
Next Steps
Repeat this procedure for every new OTP host. When you have finished adding all hosts to the production OTP host hosts list:
-
If you are installing the Open Telecommunications Platform to a standalone OTP host, install the Open Telecommunications Platform as described in Installing the Open Telecommunications Platform On A Standalone OTP Host.
-
If you are installing Open Telecommunications Platform to a clustered OTP system, install the Open Telecommunications Platform as described in Installing the Open Telecommunications Platform On A Clustered OTP System.
Installing OTP on New OTP Hosts Using the Production OTP Host
With the exception that you use the production OTP host instead of an external OTP installation server to install OTP to a new standalone OTP host or to new clustered OTP hosts, the procedures are otherwise identical.
Make certain that you use the production OTP host when performing the following tasks. When directed to log in to the OTP provisioning service, use URL http://production OTP host logical host name:9090 in each procedure where production OTP host logical host name of the production OTP host. Refer to the worksheet you prepared for the production OTP host logical host name.
The following topics are discussed:
 To Install OTP on a Standalone OTP Host
To Install OTP on a Standalone OTP Host
Make certain that you use the production OTP host as noted above when performing the following tasks. When directed to log in to the OTP provisioning service, use URL http://production OTP host logical host name:9090 in each procedure.
Before You Begin
-
The service provisioning remote agent must be installed on the standalone OTP host as described in To Install the Service Provisioning Remote Agent on a New OTP Host.
-
The standalone OTP host must be added to the OTP master server as described in To Add New OTP Hosts to the Production OTP Host.
-
Set up the OTP high availability framework as described in To Set Up the OTP High Availability Framework.
-
Set up the OTP System Management and Provisioning Services as described inTo Set Up OTP System Management and Provisioning Services.
-
Enable the OTP high availability framework as described inTo Enable High Availability For the OTP Provisioning Service
 To Install OTP on a Clustered OTP System
To Install OTP on a Clustered OTP System
Make certain that you use the production OTP host as noted above when performing the following tasks. When directed to log in to the OTP provisioning service, use URL http://production OTP host logical host name:9090 in each procedure.
Before You Begin
-
The service provisioning remote agent must be installed on all hosts in the new clustered OTP system as described in To Install the Service Provisioning Remote Agent on a New OTP Host.
-
Each new clustered OTP host must be added to the OTP master server as described in To Add New OTP Hosts to the Production OTP Host.
-
Set up the OTP high availability framework on the first OTP host as described in To Set Up the OTP High Availability Framework on the First OTP Host
-
Set up the OTP high availability framework on the additional OTP hosts as described in To Set Up the OTP High Availability Framework on the Additional OTP Hosts
-
Set up the OTP shared storage as described in To Create Shared Storage on the Clustered OTP System
-
Set up the OTP system management and application provisioning services on the first OTP host as described in To Set Up OTP System Management and Provisioning Services on the First OTP Host.
-
Set up the OTP system management and application provisioning services on the additional OTP hosts as described in To Set Up OTP System Management and Provisioning Services on the Additional OTP Hosts.
-
Enable the OTP high availability framework on the first OTP host as described in To Enable High Availability for the OTP Provisioning Service on the First OTP Host
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
