A Search engine is a piece of software that performs the work of either indexing content or answering queries. Engines are managed through Search Administration and are started and shut down automatically through a service running on the engine location.
Note: A given partition on a given host should only have one Search engine associated with it. In order to add engines to support that partition, additional hardware is required.
The process of adding engines is most easily understood through an example.
Say that you have installed Search and used the Search Administration’s estimation tool to determine the size of your index. It is going to be large, with four physical partitions. You have two options:
Run Search Administration on hardware robust enough to support four engines for answering queries in addition to performing indexing tasks.
Add hardware resources that will be dedicated to answering queries.
The first option does not require any additional installation work to add the engines. In Search Administration, you create an indexing environment and specify the machine on which you are running Search Administration as the host. Engines will be created as needed on this machine, up to the number specified in the environment configuration. This is not a recommended solution, however, since indexing and answer serving functions could compete for resources.
Instead, you add two machines to your Search installation. Each has four cores, providing for a robust answering configuration. The machine on which you are running Search Administration will continue to handle indexing. You run the ATG Search installer once on each machine, following the steps described below. In Search Administration, you create a new environment, give it the type “production” and associate your two new machines with that environment (see the ATG Search Administration Guide for detailed information on environment configuration). When your site is up and answering user queries, engine instances will be started as needed, up to the limit configured on each machine.
The following diagram summarizes the procedures involved. This diagram uses indexing engines as an example; to add engines dedicated to server query answers instead, you would create a new environment in Search Administration (see Step 2 in the diagram).
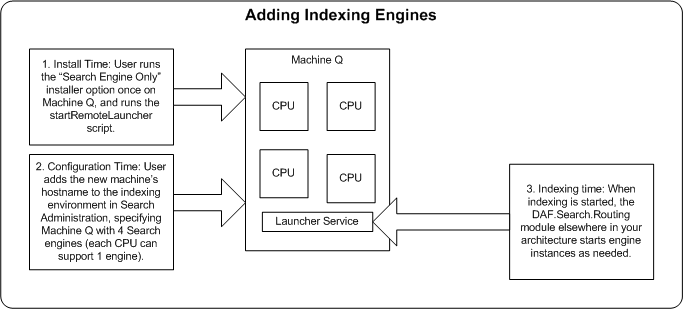
Note: All Search engines in your installation, including the indexing engine, must run on the same operating system with the same bit size.
The Search Administration installation includes the Search engine and a default environment, which can be used for indexing. For anything other than a basic evaluation environment with a very small index, you will need additional, standalone Search engines on separate hardware. If you have multiple physical partitions in your index, you need one Search engine per partition. See the Estimating Index Size section of the ATG Search Administration Guide for information on sizing your index.
These standalone Search engines run on dedicated hardware; you must add hardware and install the Search engine on them. Engines are in turn associated with Search environments. The environments are configured in Search administration.
Standalone Search engines run without an ATG installation or application server. To add a standalone Search engine to your installation:
Download the ATG Search installation executable.
Double-click the installer icon to start installing.
On the start page, click Next to begin the installation.
Read the license agreement. Select “I accept the terms of the license agreement” and click Next.
Select Search Engine Only for the installation type.
Select an installation location.
Review your selections, and click Install to begin the installation.
On the machine where you have installed the standalone engine, navigate to the Search engine installation and execute the
<SearchEngineDir>/SearchAdmin/bin/startRemoteLauncher.shor.batscript. ThestartRemoteLauncherscript starts up a launcher service, which is then used by the routing component to start Search engines on that machine. Under normal use, you do not need to manually start or stop Search engines.Note: This step is required only for stand-alone Search engines. Engines running local to your Search Administration installation do not need this script.
The
startRemoteLauncherscript includes two optional parameters–pand–o, which allow you to specify the ports used for remote method invocation (RMI). For example:startRemoteLauncher.bat -p 8860 -o 8861If you do not specify a port, the second port is chosen randomly. The default for the first port is always 8860.
If you are adding engines for indexing purposes, see the Configuring Remote Indexing Engines section of this guide for additional steps.
In Search Administration, you can now create an environment that includes this machine. When Search indexes content (if an indexing environment) or serves answers (if a staging or production environment), the Routing module starts engine instances on that machine as needed. See the Managing Search Environments section of the ATG Search Administration Guide for information on creating Search environments.
When you deploy a new index, the Search engines serving the old index continue to answer query requests until new engines are started for the new index. Once the new engines are started, queries are directed to them by the Routing module, and the old ones are shut down.