This section includes descriptions of the terms or concepts used throughout this manual to describe the installation and configuration of multiple ATG applications.
Agent-Facing Server
This is the server (or cluster of servers) on which you install the agent-facing pieces of your applications and services.
For more information about the agent-facing server and the applications that can run on it, see the architecture diagram and Agent-Facing Cluster in Architecture Overview.
Asset Management Server
This is the server (or cluster of servers) on which you install the applications and services used to manage and publish assets to the customer-facing server. Assets include applications and services.
This is also called the management server, the publishing server, or the ATG Content Administration server.
For more information about the asset management server and the applications that can run on it, see the architecture diagram and the Asset Management Cluster section in the Architecture Overview.
Cluster
In a multiple application configuration, you can have clusters (groups) of asset management servers, customer-facing servers, and agent servers. The servers in each cluster must be configured to correctly communicate with each other.
For more information about working with clusters, refer to the instructions on setting up clustering for your application server in the ATG Installation and Configuration Guide.
Customer-Facing Server
This is the server (or cluster of servers) on which you install the customer-facing pieces of your applications and services.
The customer-facing server is sometimes referred to as the production server.
For more information about the customer-facing server and the applications that can run on it, see the architecture diagram and Customer-Facing Cluster in Architecture Overview.
Data Warehouse Load Server
This is the server that supports the Data Warehouse reporting and analysis database for ATG applications
For a complete view of the Data Warehouse load servers and what they include, see the Architecture Overview.
Internal and External Users
An ATG environment includes two type of users: internal and external. Internal users are people in your company who use ATG applications to perform activities related to your customer-facing sites. For example, marketers who use the Business Control Center to create user segments or other targeting assets are internal users. Customer service representatives (agents) are also internal users. External users are your Web site customers (for Commerce or ATG Service installations) or site visitors (for non-commerce sites).
Both types of users have profiles that can be managed through the Business Control Center.
For more information about users and user profiles, see the following documentation:
Internal and External Scenarios
You can create scenarios for internal or external users. Scenarios are a series of choreographed interactions that are tailored to the user. For example, you can create an external user scenario that customizes the Web site content, promotions, and e-mail messages based on that user’s actions when visiting your Web sites. You can create an internal user scenario for use by customer service representatives to guide them through a suggested sequence of events when interacting with a customer.
For details about scenarios, creating them, and setting up your system to use them, see Creating Scenarios in the ATG Personalization Guide for Business Users and Scenarios Module Programming in the ATG Personalization Programming Guide.
Multisite Environment
A multisite environment is one in which a single instance of ATG products is used to support more than one Web site, and the Web sites are configured to share data such as user profiles or a shopping cart. For example, a clothing manufacturer could have two brands, one for luxury items and one for regularly priced items. Each brand could have its own Web site, but they would share certain data and could both be supported by the same ATG instance.
Scenario Servers
Scenario servers are servers that handle scenario events or actions. A scenario server can be individual or global. Scenario editor servers are instances of process editor servers.
For details about scenarios and the types of scenario editor servers, see Scenarios Module Programming in the ATG Personalization Programming Guide.
Shared Repositories
Shared repositories are repositories that run on dissimilar ATG instances but point at the same database table.
In the following example, the agent-facing and customer-facing clusters each have a repository named /atg/userprofiling/ProfileAdapterRepository that points to the same database schema. The schema contains external profiles that represent customers. The customer-facing cluster uses the external profiles to store information related to customer interactions with your Web site (e-mail address, preferences, gift list data, available discounts, and so on). The agent-facing cluster also needs access to external profiles so that agents (internal users) can view the profile information of customers visiting the Web site and use it to assist them.
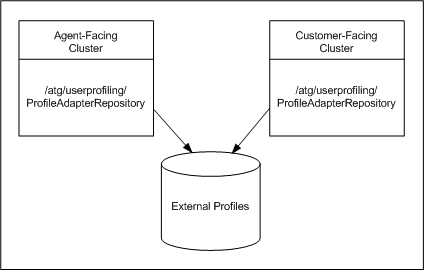
Shared Repository Example