 Understanding Accounting Entry and Financial Processing
Understanding Accounting Entry and Financial ProcessingThis chapter provides an overview of accounting entry and financial processing and discusses how to:
Define accounting entries.
Define financial processing.
Define capitalization threshold processing.
Define fair value processing.
Define investment property.
Enable combination editing.
Define document sequencing.
 Understanding Accounting Entry and Financial Processing
Understanding Accounting Entry and Financial ProcessingPeopleSoft Asset Management provides the tools to create accounting entries and manage financial reporting for your enterprise. To enable these functions, you must first define the tables used to process accounting entries and financial processes.
You may be required to set up transaction processing with document sequencing. The document sequencing features in PeopleSoft help you to maintain established business practices by meeting these requirements.
 Defining Accounting Entries
Defining Accounting Entries
Use the following components to set up accounting entries:
Asset Book (BOOK_DEFN1).
Accounting Entry Template ID (AMAE_TMPL_ID_PNL).
Accounting Entry Template (DIST_TEMPLATE_DEFN).
Accounting Templates in Mass (RUN_AMAEMASS).
Accounting Entry Templates Report (RUN_AMAE1000)
Transfer Definition (IU_TRF_DEFN_TBL).
Transaction Codes (TRANSACTION_CODE).
Transaction Groups (TRANS_PNL_GRP).
Book Code (BOOK_CODE).
Acct (accounting) Template Book Code Reset (RUN_AM_BKC_RESET).
ChartField Mapping Templates (AM_CF_MAPPING).
This section provides an overview of accounting entry options, lists the pages used to set up accounting entries, and discusses how to:
Set up transaction codes.
Set up accounting entry template IDs.
Create accounting entry templates.
Create accounting entry templates in mass.
Set up InterUnit transfer definitions.

 Understanding Accounting Entry Options
Understanding Accounting Entry OptionsPeopleSoft uses tables to support accounting entries for PeopleSoft Asset Management. Some tables are required for accounting entry processing and are noted as such. All others are optional.
Accounting Books
Defining asset books is required for accounting entry processing. Asset books are used to store financial information about assets such as cost history, depreciation rules, and retirement information.
An unlimited number of asset books per business unit can be defined. The number of books that you use depends on your reporting needs. Using multiple books enables you to keep separate cost and depreciation rules for each asset. Typically, organizations use at least two books: corporate and tax, also known as financial and fiscal. Your organization may need additional books if it does business in more than one state or country or uses any of the United States-recognized special tax treatments of accelerated current earnings (ACE) and alternative minimum tax (AMT).
Note. The depreciation criteria for each book are specified when you add assets or create asset profiles.
Accounting Entry Templates
The Accounting Entry template is the central table used for creating accounting entries to general ledger journals. Each is defined by an accounting entry template ID. When you add an accounting entry template, PeopleSoft Asset Management populates it with standard accounting entry types, based on the asset category, cost type, and transaction type that you specify. It also identifies each entry as either a debit or credit.
To begin, create accounting entry template IDs and if applicable in your business, mark the cost types for impairment and revaluation. For the setID, create or select an existing accounting entry template to apply depreciation features and distribution methods. These features control what distribution types need to be set up in the accounting entry template.
PeopleSoft Asset Management enables you to create one or multiple accounting entry templates in a single operation. You may generate accounting entry templates for an asset category for all transaction types. You can generate templates for cost type, transaction code, and retirement disposal code.
Once you have defined the accounting entry template IDs, run the Create Accounting Templates in Mass Application Engine process (AMAEMASS) that generates accounting entry templates for all transaction types and user-defined cost type, transaction code, and disposal code.
Multiple GAAP and Book Codes
PeopleSoft delivers the ability to book accounting transactions according to different and often conflicting accounting principles for one Business Unit in one ledger and to maintain these entries in compliance with the rules of government and regulatory organizations. You can add book codes for PeopleSoft Asset Management to facilitate accounting entry processing.
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) as determined in one country or jurisdiction often vary from country to country or by self-governing accounting bodies and jurisdictions. Consequently, organizations record and report their operations according to local accounting requirements as well as by rules applicable to parent corporations that are often under the rules of another national jurisdiction. PeopleSoft has provided the ability to maintain separate ledgers and ledger groups for different accounting principles, record transactions under varying statutory rules using Alternate Account and using MultiBook in PeopleSoft General Ledger and its subsystems for its automatic synchronization capabilities. A sometimes much favored method, especially within financial organizations, is defining book codes. This method enables you to simultaneously generate in one business unit and ledger all the relevant accounting entries for a transaction that addresses different local and corporate accounting rules.
You can use book codes to simultaneously generate sets of entries to record related transactions according to multiple GAAP for the same business unit in the same ledger. For example, where local and corporate accounting principles are not compatible, you define a local (L) and a corporate (C) book code. For those situations where requirements are alike, you define a code for both (B). You can attach these book codes to accounts as attributes. This results in separate permutations of accounts and book codes in which you simultaneously record related transactions under local, corporate, or both rules. You can choose to associate a single book code with one account value. Using this method, a unique account value must be created for each book code.
See Managing Multiple GAAPs and Prior Period Adjustments.

 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesBefore you can define accounting entry processing, you must first complete the following task:
Define overall installation options to enable Book Code functionality. Use the Installation Options Overall (INSTALLATION_FS1) page.
Define ChartField accounts.
Define journals, ledgers and ledger groups.

 Pages Used to Define Accounting Entry for PeopleSoft Asset Management
Pages Used to Define Accounting Entry for PeopleSoft Asset Management|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
BOOK_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Asset Books, Asset Books |
Define asset books. See Establishing PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units. |
|
|
AMAE_TMPL_ID_PNL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Accounting Entry Template IDs, Accounting Entry Template IDs |
Create a template ID with options for depreciation features and distribution methods. |
|
|
DIST_TEMPLATE_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Accounting Entry Templates, Accounting Entry Templates |
Add or modify accounting entry templates. Note. When accessing the Accounting Entry Templates page, you can use a transaction code as a key to determine what accounting entries to create. |
|
|
RUN_AMAEMASS |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Accounting Templates in Mass, Accounting Templates in Mass |
Create one or multiple accounting entry templates for journal templates, cost types, transaction codes, and retirement disposal codes in a single process. |
|
|
RUN_AMAE1000 |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Reports, Accounting Entry Templates, Accounting Entry Templates |
Run a report showing a list of accounting entry templates. |
|
|
IU_TRF_DEFN_TBL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, InterUnit Transfer Definition, InterUnit Transfer Definition |
Set up an InterUnit transfer definition. |
|
|
TRANSACTION_CODE |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Transaction Codes, Transaction Codes |
Review or modify the transaction codes. |
|
|
TRANS_GROUP_PNL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Transaction Groups, Transaction Groups |
Set up transaction groups for purposes of allocating depreciation. For example, depreciation and prior period depreciation may be treated the same for allocations, so you can combine them into one transaction group. |
|
|
BOOK_CODE |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Design ChartFields, Define Values, ChartField Values, Book Code |
Add book codes in pairs to facilitate multiple GAAP within the same chart of accounts. |
|
|
RUN_AM_BKC_RESET |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Acct Template Book Code Update, Acct Template Book Code Update |
Reset accounting templates book codes in accounting templates. |
|
|
ChartField Mapping Template |
AM_CF_MAPPING |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, ChartField Mapping Template, ChartField Mapping Template |
Create a ChartField map template to map dissimilar charts of accounts when entities have different ChartField structures. |

 Setting Up Transaction Codes
Setting Up Transaction Codes
Access the Transaction Codes page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Transaction Codes, Transaction Codes).
|
Transaction Code |
Enter a transaction code that identifies special asset transactions and that are used in combination with actions to create accounting entries. You can modify these codes by changing the description and short description. The transaction code associated with revaluation displays revaluation related distribution types for additions. |
When you define accounting entry options for a book, you can choose to distribute by disposal code. If you choose this option, the disposal code appears by default as the transaction code. In this case, you must use the transaction codes from the delivered TableSet defined for the tubbiest that you are using. You must also define corresponding accounting entry templates.
Note. The standard transactions are predefined and delivered with PeopleSoft Asset Management. To modify the transaction types, use the Asset Management (INSTALLATION_AM) page of the Installation Options (INSTALLATION) component.
See Defining Asset Management Installation Options.

 Setting Up Accounting Entry Template IDs
Setting Up Accounting Entry Template IDs
Access the Accounting Entry Template IDs page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Accounting Entry Template IDs, Accounting Entry Template IDs).
|
Select to accumulate derogatory depreciation. Used in France, derogatory depreciation represents the difference between two methods of depreciation (usually straight-line versus declining balance) applied to the same asset, where one method best reflects the economic depreciation and the other is used for tax reporting purposes. |
|
|
Select to accumulate like kind exchange in support of the US 1031 Like-Kind Exchange guidelines issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Note. Selecting this check box results in unrecognized gain and loss. |
|
|
Select to accumulate differences derived from revaluation of tangible fixed assets and financial assets. This option not available if you have not selected the revaluation option on the Installation Options — Asset Management page. |
|
|
Book Code |
Select this check box to apply book code to this accounting entry template ID. If it is not applicable, all generated entries will be created with no Book Code and all entries will post to General Ledger. If it is applicable, the book code functionality will be applied either for every book or none of them in the same ledger group by default. This field appears only if the Book Code feature is enabled at the system level within overall Installation Options. |
|
Cap Threshold Processing (capitalization threshold processing) |
Select to enable capitalization threshold processing at the accounting entry template ID level. This option appears only when the Capitalization Threshold feature is enabled at the system level within Installation Options. See “Defining Capitalization Threshold Processing” |
|
Create Gain/Loss Lines |
Select this distribution method to distribute the accounting entries created by the template to gain and loss totals. There are two general methods of registering a fixed asset's sales. Create Gain/Loss Lines is used to reflect in only one account the gain or loss that the sale transaction represents for the company. |
|
Create Net Book Value lines |
Select this distribution method to distribute the accounting entries created by the template to net book value totals. There are two general methods of registering a fixed asset's sales. Create Net Book Value lines is used to reflect the proceeds of the sale in one account and the cost of sold asset in the other account. The PeopleSoft system provides the flexibility to generate entries for the wanted method. |
Note. When setting up a new template or changing a template ID on a template that previously used either Gain/Loss or Net Book Value distribution, you may see a warning that the previous templates will be deleted. You have the option to go back and update the template instead.
See Also
Using the Global Features of PeopleSoft Asset Management

 Creating Accounting Entry Templates
Creating Accounting Entry TemplatesAccess the Accounting Entry Templates page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Accounting Entry Templates, Accounting Entry Templates).
Set up an accounting entry template for each possible combination of:
Asset category.
Cost type.
Transaction type.
Transaction code.
Accounting entry template ID.
Note. If you enter an asset into your system by using a combination of these values for which no accounting entry template exists, your accounting entry process fails when you next attempt to run it.
For each accounting entry type, select:
|
Journal Template |
For recording actual transactions. |
|
Budget Journal Template |
For recording budget transactions. |
|
Accounting Entries |
Select the appropriate accounts and alternative accounts to be associated with each accounting entry type. If Book Code functionality is set up at Accounting Entry Template IDs level, the Accounting Entry Templates page displays the Book Code related to that account. |
|
|
Click the refresh button to update the display after you enter changes. |
Accounting entry types are set by the system. Each asset event has an associated set of accounting entry types.
For each possible combination of category, cost type, and transaction code, you must set up an accounting entry template for each of the following transaction types:
ADD: Additions.
ADJ: Adjustments.
TRF: Transfers.
RCT: Recategorizations.
DPR: Depreciation expenses.
PDP: Prior period depreciation.
Note. The DPR and PDP transaction types are used only on an accounting entry template with a blank transaction code.
RET: Retirements (also used for processing reinstatements).
LPY: Lease payments.
INF Inflation adjustment.
Book Code
Specify a book code for each account value.
The Allow Book Code Override option that is set on the Account (ACCOUNT) page determines whether this book code can be overridden on the transaction line. The Effective Date and Status fields on the Account page must match the settings for the account values to which the book code is attached. Assets take the most recent and active date to populate its templates. To avoid any situation where Book Code might generate unbalanced entries in General Ledger, a warning message is generated when the template is saved when there are paired distribution types with different Book Codes. Paired distribution types are those distribution types that play against other in order to balance the entry.

 Creating Accounting Entry Templates in Mass
Creating Accounting Entry Templates in Mass
Access the Accounting Templates in Mass page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Accounting Templates in Mass, Accounting Templates in Mass).
When you begin the process, the page displays your request ID and default process frequency. Select the setID, account entry template ID, and category. Three actions can be carried out:
|
Delete All Cost Types |
Select to erase all cost types displayed in the Cost Type group box. |
|
Delete All Trans Codes (delete all transaction codes) |
Select to erase all transaction codes displayed in the Transaction Codes group box. |
|
Delete All Disposal Codes |
Select to erase all disposal codes displayed in the Retirement Disposal Code group box. |
Distribution Options
The page displays a distribution type list and corresponding account and alternate account specific to the template ID or category selected. The list is refreshed when these values change.
If Book Code functionality is set up at Accounting Entry Template ID level, the book code related to the account displays. The Allow Book Code Override option set on the Account page determines whether the book code can be overridden for each distribution type. This process populates the book codes using the criteria defined for the Accounting Entry Template.
If the book code column does not display, it is not selected at Accounting Entry Template ID level. The template uses the book code based on the accounts effective date set in the Account definition page.
SetID Options
The page includes expandable subpages of options determined by setID.
|
Journal Template ID |
(AM_JRNL_TMPL_SBP, RUN_AMAEMASS_02) Select journal and budget journal templates for each type of transaction (add, adjust, and so forth). |
|
Cost Type |
(AM_COST_TYPE_SBP, RUN_AMAEMASS_03) Select cost types for which templates should be generated (cost, margin, revaluation, and so forth). If cost types are not used, leave this field blank. |
|
Transaction Codes |
(AM_TRANS_CODE_SBP, RUN_AMAEMASS_04) Select transaction codes for which templates should be generated (abandoned, inventory, donated, and so forth). |
|
Retirement Disposal Code |
(AM_RETDISP_CODE_SBP, RUN_AMAEMASS_05) Select retirement code for which templates should be generated (abandoned, inventory, donated, and so forth). |
See Also
Creating PeopleSoft Asset Management Accounting Entries

 Setting Up InterUnit Transfer Definitions
Setting Up InterUnit Transfer Definitions
Access the InterUnit Transfer Definition page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, InterUnit Transfer Definition).
To begin, from the search dialog page, select the books used by the To Business Unit business unit.
|
From Book |
Enter the book whose information you want to enter into the To Book. Then select the action that you want to use: Transfer or Add book. Usually you use the transfer action. |
InterUnit transfer definitions act as templates to simplify performing InterUnit transfers.
InterUnit transfer definitions tell the system which books exist for the transfer from and transfer to business units, and what type of transactions the InterUnit transfer should generate for each book. If you are planning to perform many InterUnit transfers, it helps to first define all the possible InterUnit transfers.
For example, if you have three business units, US001, US002, and US003, and you expect to perform all possible InterUnit transfers, you would set up these six InterUnit transfer definitions:
|
Transfer From |
Transfer To |
|
US001 |
US002 |
|
US001 |
US003 |
|
US002 |
US001 |
|
US002 |
US003 |
|
US003 |
US001 |
|
US003 |
US002 |
When transferring from a business unit with two books to a business unit with three books, enter information into the extra To Book by using either the Add Book action or the Transfer Book action.
For example:
|
From Book |
To Book |
Action |
|
Corporate |
Local |
Transfer Book |
|
Federal |
Reporting |
Transfer Book |
|
Corporate |
Other |
Add Book |
The transactions generated to pass book information for InterUnit transfers differ depending on how many To Book entries a From Book is passing information to, and whether it is passing the information by using a transfer action or an add book action.
Note. Assets that are transferred to new business units
by using the add action will have a cost row of zero on the new business unit
until you run the Depreciation Calculation process (AM_DEPR_CALC). Running
this process updates the asset's cost row with its net book value from the
From Book.
When you use an asset profile, the book information
appears by default from the profile.
When a From Book is used once only, an add action generates a retirement for the From Book and an add to the To Book. A transfer action generates a transfer out for the From Book and a transfer in for the To Book.
The asset that is retired receives an asset status of Disposed.
Assets that are transferred between books by using the transfer action receive a status of Transferred:
|
From Book |
From Trans |
To Book |
To Trans |
Action |
|
CORPORATE |
Transfer Out |
CORPORATE |
Transfer In |
Transfer Book |
|
FEDERAL |
Transfer Out |
FEDERAL |
Transfer In |
Transfer Book |
|
From Book |
From Trans |
To Book |
To Trans |
Action |
|
CORPORATE |
Transfer Out |
CORPORATE |
Transfer In |
Transfer Book |
|
FEDERAL |
Retire |
FEDERAL |
Add |
Add Book |
|
From Book |
From Trans |
To Book |
To Trans |
Action |
|
CORPORATE |
Retire |
CORPORATE |
Add |
Add Book |
|
FEDERAL |
Retire |
FEDERAL |
Add |
Add Book |
Using a From Book for Two or More Transfers
When a From Book is used for two or more transfer book actions, only one transfer out transaction is generated. Because this takes care of the cost on the From Book, no additional transfer outs are generated for that book.
Assets that are transferred between books by using the transfer book action receive a status of Transferred:
|
From Book |
From Trans |
To Book |
To Trans |
Action |
|
CORPORATE |
Transfer Out |
CORPORATE |
Transfer In |
Transfer Book |
|
CORPORATE |
|
LOCAL |
Transfer In |
Transfer Book |
Using a From Book for Both Transfer and Add
When a From Book is used for both a transfer and an add action, a transfer out is generated for the Transfer Book. Because this takes care of the cost on the From Book, the add action does not generate a retirement for that book.
Assets that are transferred between books by using the transfer book action receive a status of Transferred:
|
From Book |
From Trans |
To Book |
To Trans |
Action |
|
CORPORATE |
Transfer Out |
CORPORATE |
Transfer In |
Transfer Book |
|
CORPORATE |
|
LOCAL |
Add |
Add Book |
Using a From Book for Two or More Adds
When a From Book is used for two or more add actions, a retirement is generated for the first add action. Because this takes care of the cost on the From Book, no further retirements are generated for it.
The asset that was retired receives a status of Disposed:
|
From Book |
From Trans |
To Book |
To Trans |
Action |
|
CORPORATE |
Retire |
CORPORATE |
Add |
Add Book |
|
CORPORATE |
|
LOCAL |
Add |
Add Book |
Note. When you transfer from a business unit with three books to a business unit with two books, the cost information on the extra From Book is automatically retired. You do not need to enter an action.
See Adjusting, Transferring, and Evaluating Assets.
Assets that are retired receive a status of Disposed:
|
From Book |
From Trans |
To Book |
To Trans |
Action |
|
CORPORATE |
Transfer Out |
CORPORATE |
Transfer In |
Transfer Book |
|
LOCAL |
Transfer Out |
LOCAL |
Transfer In |
Transfer Book |
|
FEDERAL |
Retire |
|
|
|
See Retiring Assets.
 Defining Financial Processing for PeopleSoft Asset Management
Defining Financial Processing for PeopleSoft Asset Management
Use the Asset Categories (CATEGORY_DEFN) component and the Capitalization Limits (DEPR_CAP_LIMIT) component to define financial processing in PeopleSoft Asset Management.
This section provides an overview of financial processing, lists the pages to define financial processing and describes how to:
Define asset categories.
Set up capitalization limits.
Set up capitalization threshold processing.
Set up fair value processing.

 Understanding Financial Processing in PeopleSoft Asset Management
Understanding Financial Processing in PeopleSoft Asset ManagementPeopleSoft Asset Management enables you to apply various attributes to assets for financial reporting purposes, such as categories, cost types, financing codes, and indexes. The purpose of defining these asset attributes is to help refine asset information into meaningful information blocks.
The combination of asset category and transaction code determines into which accounts an asset transaction is entered. Asset category is required.
To group assets by class for reporting or informational purposes only, use the asset class field.
Cost types represent different cost components of an asset, such as materials, labor, and overhead. For example, you can differentiate between the cost of building an asset and its market value by allocating the cost of production to one cost type and the margin of profit to another cost type. Cost type, in combination with asset category and transaction code, determines into which accounts the costs are entered in the general ledger.
Use indexes to remeasure assets according to set percentages. An index may consist of several subindexes, each of which has a separate index amount. You can set up a subindex for each asset category, with amounts that correspond to the inflation or valuation percentages for that year.
You also use indexes and subindexes to calculate replacement costs for assets. Tying an index, such as the consumer price index (CPI), to an asset profile enables replacement cost to be updated in adjustment, partial InterUnit transfer, partial retirement, and partial reinstatement transactions. Revaluation indexes are usually dictated by regulatory agencies, but you can also set up your own.
In compliance with Financial Accounting Standards (FAS) 157, which establishes U. S. guidelines for measuring the fair values of assets and liabilities, PeopleSoft Asset Management provides a framework by which to designate the appropriate valuation method for proper fair value valuation processing. Asset Management also supports fair value processing for international organizations.
PeopleSoft Asset Management validates capitalization limits when you add assets. At the business unit or book level, indicate whether validation should occur against a specific limit or against a table where you have stored step limit amounts and specified various messages for assets whose costs fall below these steps. You can also specify incremental valuation thresholds that identify the asset as a low value asset and how it should be treated during processing. The capitalization limit table accommodates the processing requirements of various countries. In some countries, a low value asset must be fully depreciated in the year of acquisition; in others, a low value asset may be added but must be taken as an expense.
PeopleSoft Asset Management can also determine capitalization status of an asset based on its cost according to capitalization thresholds that you define. When adding new assets, either online or batch, the system automatically classifies them according to their cost into capital assets, noncapital assets or expense assets. You create a Capitalization Threshold for each profile of asset that you want to evaluate and associate it with that asset profile. Processes are available to validate capitalization status and deal with adjustments to the original cost, reconcile any potential clearing account with feeder systems, and access reports and audit trails to facilitate control of these transactions.
See Also

 Pages Used to Define Financial Processing
Pages Used to Define Financial Processing|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
CATEGORY_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Categories, Categories |
Establish asset categories, which classify assets by type for accounting entry purposes. Typically, these categories reflect how assets are reported on balance sheets. Examples of commonly used asset categories are Furniture and Fixtures, Machinery and Equipment Office Equipment, Leasehold Improvements, and so forth. |
|
|
Inflation Information |
CATEGORY_SEC |
Click the Inflation Information link from the Category page. |
Establish an inflation adjustment factor by selecting the market index and rate to apply. |
|
RUN_AMAS1100 |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Reports, Asset Categories, Asset Categories |
Run a report on asset categories. |
|
|
COST_TYPE_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Cost Types, Cost Types |
Define cost types. |
|
|
FINANCING_CD |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Financing Codes |
Define financing codes to help you analyze your debit and credit relationships for capital-intensive and government projects. For example, you could set up codes to identify bonds, such as IRBs, IDBs, and TEBs. |
|
|
AM_INDEX_TBL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Indexes |
Set up an index, which is used to remeasure assets according to set percentages. Gain and loss on retirement is then calculated by using the resulting net book value. Indexes are usually maintained by regulatory agencies, but you can set up your own as well. You can set up rates to associate with indexes on the Defining Market Rates page. |
|
|
CAP_TYPE |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Profiles, Capital Acquisition Plan Types |
Set up C.A.P. types. If you are using Asset Budgeting, you set up codes to be used with the C.A.P. function. You can also use C.A.P. type codes to track assets acquired as part of a C.A.P. |
|
|
DEPR_CAP_LIMIT |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Capitalization Limit |
Set up capitalization limit codes by business unit by book, as necessary, especially Germany. |
|
|
CAP_THR_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Capitalization Thresholds, Capitalization Thresholds |
Establish capitalization thresholds by asset profile to be used in automatic classification of capital asset, noncapital asset or expense asset. |
|
|
AM_CAPVAL_RQST |
Asset Management, Financials, Capitalization Thresholds, Capitalization Thresholds |
Run the process to validate whether an asset still meets conditions to remain in the capitalization status that it was originally catalogued upon asset addition based on the capitalization threshold process. |
|
|
AM_CLEREC_RQST |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Clearing Reconciliation |
Run the process to reconcile the clearing account that is created by trackable assets from feeder systems against the expense account. |
|
|
ASSET_NF_DIST |
Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Review Expense Entries |
Run a report to show the capitalization status of assets based upon criteria selection. |
|
|
AM_CAPSUM_RQST |
Asset Management, Financial Reports, Capitalization Summary Report |
Run a report to show the capitalization status of assets based upon criteria selection. |

 (Required) Defining Asset Categories
(Required) Defining Asset Categories
Access the Categories page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Categories).
Complete the appropriate fields for each asset category. Identify the depreciable status as Depreciable or Non Depreciable.You can optionally associate inflation processing information with the category.
See Setting Up Asset Profiles.
Options
These options drive the accounting entries to display in the accounting entry template. When possible, assign these options at the asset category level to alleviate this identification at the individual asset level. Identification at the category or profile level is also necessary for handling batch transactions where there is no use intervention.
|
Intangible |
Select if the asset category applies to intangible assets. |
|
Leased Assets |
Select if the asset category applies to leased assets. |
|
Investment Property |
Select if the asset category applies to assets that are considered investment property as defined by International Accounting Standards (IAS) 40. This selection can be used in conjunction with the Leased Assets check box if the category applies to leased assets that are also investment property. However, you cannot select the Intangible check box and the Investment Property check box in combination. A warning message appears in the event that you select this invalid combination. |
|
Property Interest |
Select if the asset category applies to an operating lease that meets the conditions for investment property as defined by IAS 40. Operating leases that fall under this category are not treated as operating leases according to Financial Accounting Standards (FAS) 13, which are normally expensed, but rather as capital leases for accounting purposes (capitalized and amortized over the lease term). The Leased Asset check box must also be selected when selecting this option. A message alert appears upon saving the page if the Property Interest check box is selected without the selection of the Leased Assets check box. |

 Defining Cost Types
Defining Cost Types
Access the Cost Types page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Cost Types, Cost Types).
|
Impairment Process |
Select to use this cost type for impairment. Selecting this check box displays impairment related accounts at the accounting entry template level. This field is not displayed if impairment options are not selected on the Installation Options - Asset Management page. Note. This option cannot be selected with the Revaluation Process option for a single cost type. |
|
Revaluation Process |
Select to use this cost type for revaluation. Selecting this check box displays revaluation related accounts at the accounting entry template level. This field is not displayed if revaluation options are not selected on the Installation Options - Asset Management page. Note. This option cannot be selected with the Impairment Process option for a single cost type. |
Note. When selecting a cost type for impairment or revaluation, you should update the accounting entry templates because new accounting entries need to be set up for these transactions.

 Setting Up Capitalization Limits
Setting Up Capitalization Limits
Access the Capitalization Limits page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Capitalization Limits, Capitalization Limits).
Create a cost limit code, complete the applicable fields, and select the Low Value Switch check box to identify which limit amount triggers low value asset reporting. This is used only in certain countries.
For example, you might set up capitalization limits for Germany. Using the Cap Limit table, you can set up your system so that assets with a cost less than 800.00 EUR could be added, but the system would generate a warning that the cost was below the capitalization limit; likewise, assets with a cost less than 100.00 EUR could not be added and would generate an error message.
See Also

 Setting Up Capitalization Thresholds
Setting Up Capitalization Thresholds
PeopleSoft Asset Management can determine capitalization status of an asset based on its cost or quantity according to limits that you define. This can be accomplished by enabling the optional Capitalization Threshold feature. Once you enable this feature and complete the required setup, the system automatically classifies assets using the defined thresholds when adding new assets, either online or in batch: Assets are classified within one of the following categories:
Capital Assets - The system generates an asset ID and stores physical and financial information. Financial information is stored in the cost table (COST). The system also stores acquisition details. Therefore, these assets are trackable from both a physical and financial standpoint. This term is interchangeable with Financial Assets.
Noncapital Assets - The system generates an asset ID and stores only physical information. The cost information is stored in the noncapitalized cost table, (COST_NON_CAP). The system also stores acquisition details. Therefore, these assets are trackable from a physical standpoint only. This term is synonymous with Trackable Assets or Nonfinancial Assets.
Expense Assets - The system does not generate an asset ID. If an asset is entered online that does not meet the capitalization threshold, an error message appears saying that the asset has been catalogued as an expense due to its cost amount and could not be considered as an asset. If the asset is entered in batch, the system stores a message in an audit table that explains why that interface line was not processed. Because of their low cost, these assets are considered an expense when acquired and there is no interest in tracking them within the Asset Repository.
To begin using the Capitalization Threshold feature, complete the following setup steps:
Enable the Cap Threshold Processing option at the system level within Installation Options - Asset Management.
Enable the Capitalization Threshold option at the business unit level.
See BU Set Up Options.
Define Capitalization Thresholds and associate them to the appropriate asset profiles.
Access the Capitalization Thresholds page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Capitalization Thresholds).
|
Threshold ID |
Supply a meaningful threshold ID when creating capitalization thresholds to assign them to asset profiles or assets. |
|
Basis |
Select the basis to be used for calculating the appropriate capitalization action to take. Select from the following options:
|
|
Currency Code |
Enter the currency code of the amounts reflected in the Amount fields. |
|
Effective Date |
Enter the date when the threshold becomes applicable. |
|
Active |
Activate each threshold bracket. When deselected, the amount becomes unavailable. |
|
Action |
Select to activate and set thresholds for the following brackets:
|
|
Amount |
Enter the ceiling amount for each bracket. Amounts that are less than or equal to the amount entered are included in that bracket. |
Running the Capitalization Threshold Validation Process
The Capitalization Threshold Validation process validates whether assets still belong to the capitalization brackets to which they were initially catalogued after adjustments are made to the original cost. If an asset is in the same bracket as originally classified, then this process takes no further action; however, if it is not, the asset is moved to its respective capitalization bracket.
The following graphic represents the process flow for the capitalization threshold validation process:
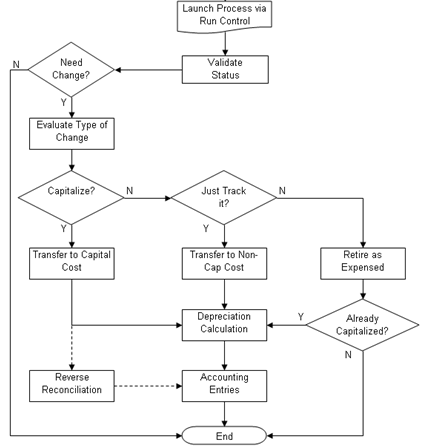
Capitalization Validation process flow
Access the Capitalization Threshold Validation page (Asset Management, Asset Transactions, Financial Transactions, Cap Threshold Validation)
Supply the selection criteria for assets to be evaluated for capitalization threshold validation.
|
Chartfield Search Criteria link |
Access the Chartfield Search Criteria page to supply ChartField filter information for those assets that have particular ChartFields active. |
|
Trans Code (transaction code) |
Select this criteria, which is useful for assets that are converted from trackable to capitalized. If you want to identify them or perform a different accounting entry, you can define and utilize a transaction code for that purpose. |
|
Validation Basis |
Select the criteria to use in order to evaluate the total cost of the asset against the threshold. The following options are available:
|
Running the Clearing Reconciliation Process
When an asset is deemed trackable by the capitalization threshold process, the asset ID is generated but in fact no accounting activities take place. Additionally, when assets are added through feeder sources, it is likely to debit the Fixed Account and credit a Clearing account that was previously debited at the source accounting. The Clearing Reconciliation process provides a way to balance out (credit) the clearing account that was previously debited at the source product accounting and debit the expense account. This is not applicable to the trackable assets that are entered directly into Asset Management with no clearing account at all. In this instance, the expense account is most likely debited when the asset is added.
This process checks the noncapital cost lines, determines the expense and clearing accounts from the accounting entry templates and inserts rows into the staging table (DIST_LN) to be loaded as journal entries into general ledger for posting.
Access the Clearing Reconciliation page (Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Clearing Reconciliation)
This process creates the clearing accounting entries from the noncapitalized assets that have the selected system source. For each noncapital row that matches the criteria, an entry is generated in the DIST_LN table that credit the clearing account and debit the expense account according to the accounting entry template for the EX distribution type. This distribution type is available for the ADD and ADJ accounting entry templates for those template IDs that have the capitalization threshold enabled.
See Accounting Entry Types (Distribution Types).
Reviewing Assets that are Categorized Using Capitalization Threshold Processing
Access the Review Expense Entries page (Asset Management, Accounting Entries, Review Expense Entries)
This online inquiry page enables you to enter search criteria and view the expense entries that were created by running the Clearing Reconciliation process.
Access the Capitalization Threshold Summary Report page (Asset Management, Financial Reports, Capitalization Summary Report, Capitalization Threshold Summary Report.)
Select criteria to report assets as they are classified according to the Capitalization Threshold process. The report displays the acquisition date, asset ID, description, quantity, tag number, serial ID, capitalized cost and noncapitalized cost.
|
Report Type |
Select to report only the assets that are candidates for recategorization or select to report all assets. |
|
Validation Basis |
Select to report assets that are capitalized (from the cost table) or select to report both capital and noncapital assets. |
 Defining Fair Value Processing
Defining Fair Value Processing
This section provides an overview of fair value processing and lists the pages used to define fair value processing for PeopleSoft Asset Management.

 Understanding Fair Value Processing in Asset Management
Understanding Fair Value Processing in Asset ManagementFinancial Accounting Standards (FAS) 157 establishes a framework for measuring the fair values of assets and liabilities and how to disclose them for the financial statements. It is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007. Asset Management supports fair value processing for international customers as well as providing the following solution in compliance with FAS 157 for U.S. companies:
Standardized parameters when loading and capturing fair values in accordance with FAS 157.
Appropriate fair value processing for revaluation, impairment and leases.
Corresponding fields and prompts on the Fair Value page.
Reports for disclosure of fair values: Fair Value Activity Report and Fair Value Detail Report.
Setup pages for fair value valuation methods, fair value groups and fair value templates.

 Pages Used to Define Fair Value Processing
Pages Used to Define Fair Value Processing|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
AM_FV_METHOD |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Fair Value Valuation Methods, Fair Value Valuation Methods |
Define the fair value valuation methods to be used in fair value processing in accordance with FAS 157. |
|
|
AM_FV_GROUP |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Fair Value Groups, Fair Value Groups |
Define fair value groups by business unit to be used in fair value processing in accordance with FAS 157. |
|
|
AM_FV_TEMPLATE |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Fair Value Templates, Fair Value Templates |
Define fair value templates by business unit by selecting the fair value valuation method, valuation premise, input level and fair value group ID. |

 Defining Fair Value Valuation Methods
Defining Fair Value Valuation Methods
Access the Fair Value Valuation Methods page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Fair Value Valuation Methods, Fair Value Valuation Methods).
Use this page to establish various valuation methods that are used to capture the most representative fair values for an organization, whether they be valuation techniques as defined by FAS 157 or any global techniques.
|
Approach |
Select from the following fair value approach values to be used for the valuation method:
|
|
Input Type |
Select from the following input types for the valuation method:
|

 Defining Fair Value Groups
Defining Fair Value Groups
Access the Fair Value Groups page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Fair Value Groups, Fair Value Groups).
Use this page to establish groups of assets for valuation processing when their valuation premise is In Use.

 Defining Fair Value Templates
Defining Fair Value Templates
Access the Fair Value Templates page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Fair Value Templates, Fair Value Templates).
Use this page to establish default values when you add fair values from a page other than the online Fair Value page.
See Capturing and Maintaining Asset Fair Value.
|
Valuation Method |
Select a valuation method defined from the Fair Value Valuation Method page. The valuation method allocates valuation techniques. This can be a valuation method according to FAS 157 or a combination of valuation techniques. |
|
Valuation Premise |
Select from the following valuation premise values:
|
|
Input Level |
Select from the following input levels:
|
|
Group By |
This field is available only when the valuation premise is In Use. Select to group the fair value of assets by the following:
|
|
FV Group ID (fair value group ID) |
Select the applicable FV Group ID value, which is required when selecting to group by FV Group ID, Group Asset ID or Parent ID. The prompt values differ depending on your selection in the Group By field. For example, if you select to group fair values by Parent ID, you are prompted with the available Parent IDs from which to select. If you select Cash Generating Unit for the Group By field value, the FV Group ID becomes unavailable. |
 Defining Investment Property
Defining Investment Property
This section provides an overview of investment property and lists the pages used to identify investment property for proper accounting entry processing in PeopleSoft Asset Management.

 Understanding Investment Property in Asset Management
Understanding Investment Property in Asset ManagementIn accordance with International Accounting Standards (IAS) 40, PeopleSoft Asset Management facilitates the administration of investment properties that are stored in the Asset Repository. To help organizations more easily comply with IAS 40, PeopleSoft provides:
Ease of identification of investment property as distinguished from other assets.
Accounting entry templates for investment property - accounting entry template and distribution type, IX, is used for investment property accumulated adjustments for nondepreciable categories.
Reporting capabilities - investment property fields appear on the Asset Management Units/Books report (AMBU1000) and Asset Categories report (AMAS1100). Information for required disclosure of investment property fair values is provided within the Fair Value Activity Report and Fair Value Detail Report.
During the addition of property or later, you can identify the asset as investment property. This attribute can be applied at the asset level or at the asset profile or category. Identification at the category level is necessary for handling batch transactions where there is no human intervention. Investment property can be owned assets and capital leases. Property interest is an operating lease that meets the conditions to be deemed as an Investment Property. Operating leases that fall under this category are not ruled by the ordinary lease accounting rules but are treated as capital leases for accounting purposes. In other words, they are considered capital leases even if they are technically considered operating leases per FAS 13.
The following diagram summarizes the classification process and treatment of investment property for International Accounting Standards (IAS):

Summarization of Investment Property Classification and Treatment

 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesBefore you can begin identifying investment property and make use of the delivered functionality for proper accounting treatment of investment property, you must:
Review IAS 40 to determine the assets that must be accounted for and reported as investment property or property interest. Determine whether they are leased assets as well and whether they require revaluation.
Establish categories as Investment Property or Property Interest as necessary on the Categories page.
Enable the Revaluation Process feature on the Installation Options - Asset Management page.
Once you enable the revaluation process at the installation level, the Investment Property option appears on the Business Unit/Book Feature page within the Impairment/Revaluation Options group box. The distribution type for investment property also appears on the Accounting Entry Template.
Select the investment property options within the Impairment/Revaluation Options group box (if applicable) on the Business Unit/Book Feature page. These include options for the revaluation method and the investment property transaction code.

 Pages Used to Define Investment Property in Asset Management
Pages Used to Define Investment Property in Asset Management|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
CATEGORY_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Categories, Categories |
Establish categories as Investment Property or Property Interest, as necessary. |
|
|
INSTALLATION_AM |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Install, Installation Options, Asset Management |
Enable the Revaluation Process feature to be able to select investment property options on the Business Unit/Book Feature page and the Accounting Entry Template. |
|
|
BU_BOOK_FEATURE |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Business Unit Related, Asset Management, Asset Management Definition, Business Unit/Book Feature |
Select the investment property options within the Impairment/Revaluation Options group box (if applicable), as well as the revaluation method and the investment property transaction code. |
|
|
DIST_TEMPLATE_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Accounting Entry Templates, Accounting Entry Templates |
Select an investment property asset category in order to display the proper investment property accounting entries. |
|
|
AM_REVALUATION |
Asset Management, Asset Transactions, Financial Transactions, Revaluation Worksheet, Revaluation Worksheet |
Select the investment property revaluation method to retrieve the assets that should receive investment property accounting treatment. |
|
|
AMREVAL_RQST |
Asset Management, Asset Transactions, Financial Transactions, Revaluation in Mass, Revaluation in Mass |
Select the investment property revaluation method to process the assets that should receive investment property accounting treatment. |

 Establishing Asset Categories for Investment Property
Establishing Asset Categories for Investment Property
Access the Categories page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Categories, Categories).
The Categories page provides investment property indicators that enable proper accounting treatment and generate investment property reporting detail for required disclosure.
Selection of the depreciable status and investment property options on this page dictates which accounting entries to display in the accounting entry template.
See Defining Combination Editing for Batch Transactions.

 Creating Accounting Entries for Investment Property
Creating Accounting Entries for Investment Property
The Asset Management accounting entry templates accommodate accounting entries that are required for investment property. When selecting an asset category (for the accounting entry template) that has investment property options selected, the Investment Property distribution type (IP) directs related accounting entries for all processes to the investment property account. This is applicable for all of the templates where a fixed asset account appears.
See Creating Accounting Entry Templates.
See Creating PeopleSoft Asset Management Accounting Entries.

 Enabling the Revaluation Process for Investment Property
Enabling the Revaluation Process for Investment Property
If you decide to measure investment properties using the fair value model, PeopleSoft Asset Management provides a calculation to reflect the gain or loss that is generated by the fair value fluctuation over time. To enable revaluation for investment properties, the following setup is required:
Enable the Revaluation Process feature within the Installation Options - Asset Management page.
Enable the specific investment property options for Impairment and Revaluation processes on the Business Unit/Book Feature page.
Enable Revaluation Installation Option
Access the Installation Options - Asset Management page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Install, Installation Options, Asset Management).
Select the Revaluation Process check box. The selection of this check box makes investment property options visible on the Business Unit/Book Feature page for impairment and revaluation processing.
See Defining Asset Management Installation Options.
Enable Investment Property Impairment and Revaluation Options
Access the Business Unit/Book Feature page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Business Unit Related, Asset Management, Asset Management Definition, Business Unit/Book Feature).
Enable the Impairment/Revaluation Options that deal with the investment property treatment: The enhancement here consists in two new fields, the first to check if the book will enable the Investment Property revaluation and the second to assign the corresponding Transaction Code associated to that kind of transaction
Investment Property - select to enable investment property revaluation for a book within the business unit.
Revaluation Method - select the Inv Prop (investment property) field.
Inv. Property Trans. Code - select the investment property transaction code.
See Establishing PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units.
Enable Revaluation Worksheet for Investment Property
As with other assets, use the Revaluation Worksheet to revalue investment properties. Select the Inv Prop revaluation method on the Revaluation Worksheet to retrieve all of the investment property assets. When making this selection, these assets are retrieved even if the Asset Category field is left blank.
See Revaluing Assets Using the Revaluation Worksheet.
 Enabling Combination Editing
Enabling Combination Editing
This section provides an overview of combination editing and lists the pages used to define combination edit processing for PeopleSoft Asset Management.

 Understanding Combination Editing in Asset Management
Understanding Combination Editing in Asset ManagementAsset Management leverages the existing common setup for valid and invalid ChartField combinations and is consistently applied to all transactions that generate accounting entries for General Ledger.
See Editing ChartField Combinations.
ChartField combination editing is applicable for books that are associated to a GL ledger. Set ChartField combination editing options at the business unit/book level. These settings are applied upon saving certain online components, at which time the Combo Edit processor is invoked (FS_COMBO_EDIT). If the ChartField combination fails validation, an additional Combo Edit page appears within the online component that displays the error message. Depending upon the combo edit options settings, the page may be saved with errors, rejected, or bypass combination editing.
Note. As account values are not entered in the asset transactions themselves, it is the fixed asset (FA) accounts that are defined for the transaction type, cost type, category and accounting entry template that are used in validating ChartField combinations.
For batch Asset Management transactions, the process invokes the Combination Editing Options setup. Specify the system sources that are to be excluded from ChartField combination editing validation (generally includes sources wherein ChartField combinations may have already been validated).
This table presents the Asset Management components for which combination editing is available:
|
Event |
Type of Processing |
Components/ Pages/ Processes |
|
Add assets. |
Online Batch |
Express Add (ASSET_ENTRY_00) page. Transaction Loader process (AMIF1000). Asset Basic Add (ASSET_GENERAL_01) page. |
|
Adjust, revalue, recategorize, or transfer assets and costs. |
Online Batch |
Cost Adjust/Transfer Asset (COST_BAL) page. Transaction Loader process (AMIF1000). |
|
Retirements and reinstatements. |
Online Batch |
Retire/Reinstate Asset (RETIRE) component. Transaction Loader process (AMIF1000) |
|
Leased assets. |
Online |
Leased Assets, Express Add (LEASE_ENTRY) page. Update Lease Information (LEASE_ENTRY) page. Transfer Operating Lease (LEASE_OPR_TFR) page. |
|
Consolidate and unitize assets. |
Online |
Consolidate Assets (ASSET_CONSOL) page. Unitize Assets (ASSET_UNIT) page. |
|
Copy an asset. |
Online |
Copy Existing Asset (COPY_ASSET) page. |
|
Review financial entries. |
Online |
Review Financial Entries (ASSET_DIST). |
|
Review operating leases. |
Online |
Review Operating Leases (NF_DIST_LN). |
|
Review expense entries. |
Online |
Review Expense Entries (ASSET_NF_DIST). |
|
Impairment, Revaluation, Disposal |
Batch |
Transaction Loader process (AMIF1000) |
|
Update noncapitalized costs. |
Batch |
Update Non-capitalized Costs (NON_CAP_COSTS) page. |

 Pages Used to Enable Combination Editing in Asset Management
Pages Used to Enable Combination Editing in Asset Management|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
BU_BOOK_DEFN_01 |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Business Unit Related, Asset Management, Asset Management Definition, Business Unit/Book Definition |
If the Create Accounting Entries check box is selected, the ChartField Edit Options group box appears. Select to receive a warning message, to reject the transaction or to perform no ChartField combination edits for the business unit and book. |
|
|
AM_CEDT_SSRC |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Combination Editing Options, Combination Editing Options |
Select the system source or sources of the processes for which you want to enable ChartField combination editing. |

 Enabling Combination Editing for Asset Management
Enabling Combination Editing for Asset Management
Access the Business Unit/Book Definition page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Business Unit Related, Asset Management, Asset Management Definition, Business Unit/Book Definition).
See Defining Business Unit Processing Options.
Warning! Changes to the original ChartField combination editing rules may result in invalid ChartField combinations for subsequent Asset Management processes, such as depreciation. Some transactions such as retirements cannot be done at all (if the Combination Edit option is set to Reject) if you invalidated previously accepted combinations. A similar situation occurs when you deactivate a ChartField that is assigned to an asset. In this case, you would have to reactivate the ChartField and include those combinations again, or set the Combination Edit Option to Warning or No Edits.

 Defining Combination Editing for Batch Transactions
Defining Combination Editing for Batch Transactions
Combination Editing Options page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Combination Editing Options, Combination Editing Options).
|
Template |
The combination editing process uses the record template for structural information to perform ChartField combination edits. The record templates have a unique name that is applicable to a particular PeopleSoft application. |
Exceptions
|
System Source |
Enter the trusted sources that do not need ChartField combination validation. Select the system source code as it appears in the interface tables. |
 Defining Document Sequencing
Defining Document Sequencing
Use the Document Type Template (AM_DOCTYPE_TMPL) component to define document sequencing.
This section provides an overview of document sequencing for PeopleSoft Asset Management, lists pages used to set up document sequencing, and describes how to define Document Sequence Type Templates.

 Understanding Document Sequencing for PeopleSoft Asset Management
Understanding Document Sequencing for PeopleSoft Asset ManagementStatutory requirements in some countries require that all financial transactions (documents) be classified into different transaction types, and that within each transaction type, all documents entered be numbered sequentially. The document sequencing feature helps you maintain established business practices by meeting both of these requirements.
Document sequencing is available for transactions that you create either online or through background (batch) processing. When you activate document sequencing, the system automatically assigns a sequence number to each document (invoice, voucher, journal, and so on) that you create. You can also enter sequence numbers manually. When you delete, change, or unpost a document, the system may generate additional document sequence numbers, as appropriate.
PeopleSoft Asset Management uses the Document Type Template (AM_DOCTYPE_TMPL) page to add and maintain document types relevant to specific asset categories or transactions. Before you can establish a document type template, you must first establish the following:
The Document Sequence Range (SEQ_RANGE) page maintains the sequence number range; the range is user-defined, and often based on an annual (AN) or monthly (MN) counter.
Use the Journal Code (JRNL_CODE) page to define journal codes, specify sequence ranges, and determine how document sequence numbers are assigned for each journal code.
The Document Type (DOC_TYPE) page establishes document sequencing options for PeopleSoft Asset Management business processes that generate financial transactions. This is the equivalent of the Journal Type used by General Ledger.
Document sequencing occurs at either the journal code level or the document type level within a journal code. If sequencing occurs at the journal code level, all document types within a journal code share the same sequence numbers. If sequencing occurs at the document type level, each document type has its own sequence numbers. This is determined by the Sequence By field on the Journal Code table. In PeopleSoft Asset Management, this is defined on the Document Type Template (AM_DOCTYPE_TMPL) page.
Document sequencing can either be set to manual or automatic. In the case where the document sequence allows for manual entry, the system validates the number to ensure that the number falls within the appropriate range and is unique. If the option has been set to automatic, the system selects the next available number in the sequence. If the option is set to manual without entering a value, an error is generated. In cases where the option is set to manual, and a batch process inserts the sequence number, the batch process generates the numbers sequentially and the numbers can not be altered.
As transactions with document sequencing occur through online processing and from batch processes such as the transaction loader process (AMIF1000), the PeopleSoft Asset Management document sequencing table (AM_DOC_SEQ) stores the transaction data by row. This table joins with the PS_DIST_LN table so that the entries are created in General Ledger. If journals are created through the Journal Generator process from subsystem accounting entries, document sequence numbers are already assigned when the option to retain detail is selected. Assigned document sequence numbers are carried forward to the journal lines. When the summarization option is selected, document sequencing field values are left blank
The document sequence page (AM_DOC_SEQ) is used throughout the PeopleSoft Asset Management application where a financial transaction occurs: Express Add, Basic Add, Cost Transfer/Adjust, Leases, Copy Assets, Adjust Accumulated Depreciation, Update/Delete Pending Transactions, Impairment, and Retirement. Each page displays a document sequencing tab for the entry and allows you to view, enter or override document sequence information.
When using multiple ledger groups with multiple ledger assigned, the following rules apply: If the Keep Ledgers in Sync (KLS) option is enabled, the ledger group will maintain the same sequencing number across ledgers. Only the primary ledger group/ledger combination will have a unique sequencing number. If KLS is not enabled, then both ledgers assigned to the ledger group have different sequence numbers. If multiple ledger groups are assigned to a business unit, even with KLS on, the ledger groups would have different sequence numbers. They can independently have KLS enabled or not.
This table shows the details associated with each component, page or process where access to document sequencing is available.
|
Event |
Type of Processing |
Components/ Pages/ Processes |
|
Add assets. |
Online Batch |
Express Add (ASSET_ENTRY_00) page. Transaction Loader process (AMIF1000). Asset Basic Add (ASSET_GENERAL_01) page. |
|
Adjust, revalue, recategorize, or transfer assets and costs. |
Online Batch |
Cost Adjust/Transfer Asset (COST_BAL) page. Transaction Loader process (AMIF1000). |
|
Retirements and reinstatements. |
Online Batch |
Retire/Reinstate Asset (RETIRE) component. Transaction Loader process (AMIF1000) |
|
Lease assets. |
Online |
Leased Assets, Express Add (LEASE_ENTRY) page. |
|
Copy an asset. |
Online |
Copy Existing Asset (COPY_ASSET) page. |
|
Change or delete a pending transaction. |
Online Batch |
Change/Delete Pending Transactions (PEND_TRANS_UPD_DEL) page. |
|
Adjust accumulated depreciation. |
Online |
Adjust Accumulated Depr (DEPR_ACCUM_ADJ). |
|
Depreciation, reverse depreciation, prior depreciation. |
Batch |
Depreciation close application engine process (AM_DPCLOSE). |
|
Allocate depreciation. |
Batch |
Depreciation Allocation process (AMALLOC). |
|
Define tax and depreciation criteria (only when transaction involves accounting). |
Online |
Define Tax/Depr Criteria (BOOK_DEFN). |
|
Review financial entries. |
Online |
Review Financial Entries (ASSET_DIST). |
|
Adjust for inflation. |
Batch |
Adjust for inflation (AMDPINFL) process. |
|
Reverse depreciation adjustment. |
Batch |
Depreciation close application engine process (AM_DPCLOSE). |
|
Lease payment, reverse lease payments. |
Batch |
Depreciation close application engine process (AM_DPCLOSE). |
|
Impairment, Revaluation |
Batch |
Transaction Loader process (AMIF1000) |
A Parent asset that disposes, transfers or makes recategorizations to its children can have a different document type from its defaulted one. You can manually override it but the child assets inherit the parent asset document type. In such a case, the document type needs to be defined as automatically generated.
Group assets are treated as one entity for the purpose of depreciation, but as multiple entities for all other purposes. Therefore, these assets do not generate a different sequence number at asset level. For any other transactions, they are treated as ordinary assets. AMDPCGRP defines the sequence to be given to that transaction based on the accounting entry template selected. For transfers by Group ID, the system generates sequenced numbers for the transfer out transaction. The transfer in transaction is handled by GL in the same manner as a regular InterUnit transaction.
No transaction detail is carried by individual composite members. All transaction detail, including any gain or loss accrued upon retirement, is rolled up to the composite asset level. Once this roll up occurs, no transaction detail is retained by composite members. Composite assets will be treated as ordinary assets but not their members. These do not generate sequenced numbers.
Joint Ventures are not supported for participant business units.

 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesBefore you can begin using the Document Sequencing feature in PeopleSoft Asset Management, you must:
Enable document sequencing at the installation level.
The system does not perform any document sequencing functions unless you select the Document Sequencing option on the Installation Options - Overall page.
Enable document sequencing at the PeopleSoft General Ledger business unit level.
Once you enable document sequencing at the installation level, activate it for designated General Ledger business units on the General Ledger Definition page.
Specify a document sequence range.
Define the journal types and journal codes.
Define the document types.
Document sequencing uses the following components:
Journal Type (JRNL_TYPE)
Journal Code (JRNL_CODE)
Document Types (DOC_TYPE)
Sequence Range (SEQ_RANGE)
See Setting Installation Options for PeopleSoft Applications.
See Defining Document Sequencing.
See Defining General Ledger Business Units.
See Establishing PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units.

 Pages Used to Define Document Sequencing for PeopleSoft Asset Management
Pages Used to Define Document Sequencing for PeopleSoft Asset Management|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Document Type |
DOC_TYPE |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, Document Sequencing, Document Type |
Define asset management document types using this page. |
|
Journal Generator Template - Defaults |
JRNL_GEN_DEFAULTS |
General Ledger, Journals, Subsystem Journals, Journal Generator Template, Defaults |
Assign a document type to the accounting entries that PeopleSoft Asset Management generates. The Journal Generator Application Engine process (FS_JGEN) uses this information to assign a document sequence number when you create journals through the Journal Generator process. |
|
Journal Generator Template - Summarization |
JRNL_GEN_SUM |
General Ledger, Journals, Subsystem Journals, Journal Generator Template, Summarization |
SelectRetain Detail in the How Specified Option group box to retain and pass the document sequence numbers to General Ledger. |
|
Document Type Template |
AM_DOCTYPE_TMPL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Document Type Template, Document Type Template |
Assign document types to each accounting entry type in Asset Management. |

 Defining Document Type Templates
Defining Document Type TemplatesAccess the Document Type Template page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Accounting, Document Type Template, Document Type Template).
Assign document types to be used by default by document sequencing for asset categories and asset transaction codes.
Note. If you are using revaluation, you need to define a template for the revaluation transaction code.