 Understanding PeopleSoft Asset Management in Global Settings
Understanding PeopleSoft Asset Management in Global SettingsPeopleSoft Asset Management provides enhanced enterprise-wide global support. This chapter provides an overview of Asset Management in global settings and discusses how to:
(AUS) Use PeopleSoft Asset Management options to meet Australian requirements.
(CAN) Use PeopleSoft Asset Management options to meet Canadian requirements.
(FRA) Use PeopleSoft Asset Management options to meet French requirements.
(DEU) Use PeopleSoft Asset Management options to meet German requirements.
(IND) Use PeopleSoft Asset Management options to meet Indian requirements.
(ITA) Use PeopleSoft Asset Management options to meet Italian requirements.
(JPN) Use PeopleSoft Asset Management options to meet Japanese requirements.
Note. You must have established the correct international options at implementation to display and use these pages.
See Also
Getting Started with PeopleSoft Asset Lifecycle Management Fundamentals
Getting Started With PeopleSoft Asset Management
Establishing PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units
 Understanding PeopleSoft Asset Management in Global Settings
Understanding PeopleSoft Asset Management in Global SettingsRequirements for asset tracking and the subsequent taxing and reporting on assets vary around the world. This chapter provides the information necessary to implement country-specific options to meet local tracking, taxation, and reporting requirements for Asset Management.
Using PeopleSoft Asset Management in Australia
PeopleSoft Asset Management provides the options to identify assets for and calculate deductions of expenditures on assets for research and development (R&D) based on aggregate values.
The system provides options to manage Australian tax credit allowances related to capital investment projects that include provisions for rebates (often referred to as credits).
The system provides the options to track and report on the usage of assets requiring changes in creditable purpose (CCP), assets that may be subject to goods and services tax (GST) or value-added tax (VAT), and capital gains taxes (CGT).
The system provides the functionality to perform "net-method" asset revaluation in accordance with Australian accounting standards (AASB1010 and AASB1041), which require crediting to related asset accounts the balance of accumulated depreciation at the date on which an asset is revalued.
Using PeopleSoft Asset Management in Canada
PeopleSoft Asset Management enables you to calculate depreciation for tax purposes in Canada under the terms of the Capital Cost Allowance (CCA) Reporting. In Canada, all depreciation is calculated on the pool or class of assets by using the rate that is prescribed by the Income Tax Act.
The CCA calculation consists of several components. To calculate CCA, the undepreciated capital cost (UCC) of assets at the beginning of the taxation year is determined, and acquisitions and dispositions during the year are added and subtracted to obtain the balance that can be depreciated. A percentage depreciation and CCA rate is applied to this UCC balance to determine the maximum amount that can be claimed. The CCA that is claimed is deducted from the beginning UCC to calculate the UCC at the end of the year. The final balance is used at the beginning of the following year.
Using PeopleSoft Asset Management in France
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports the specialized derogatory depreciation methods commonly used in France.
The system provides the reporting features necessary to track and report the French business tax at the asset book level and the asset profile level.
The system provides the functionality to perform asset revaluation as necessary.
Using PeopleSoft Asset Management in Germany
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports commonly used practices in Germany, including Staffel depreciation, a half-year prorate convention, geometric digressive depreciation, a parameter-driven automatic retirement process, and management of capitalization limits for low-value assets. In addition, PeopleSoft Asset Management provides reports to meet German statutory requirements.
Using PeopleSoft Asset Management in India
PeopleSoft Asset Management provides asset processing features that correspond to the tax reporting requirements established by the Indian Tax Depreciation Act of 1961. This local standard requires that assets are grouped within a defined tax block. Currently India identifies four asset tax blocks: buildings, furniture and fixtures, machinery and plant, and intangibles. Each block of assets is further assigned a tax groupor class, and each class maintains an individual tax rate. The Indian tax year is a fixed fiscal calendar starting April 1 and ending March 31. Tax depreciation is reported annually at the fiscal year to the tax authority per asset block.
The system takes into account the rules regarding the treatment of capital and operating leases by enabling you to designate them.
The system provides the Straight Line Percent depreciation method for India, which calculates depreciation based on rates, and useful life is calculated on cost, salvage value, and depreciation rate combined.
The system provides the India Asset Tax Register, which reports all booked transactions to show the cost, depreciation, and net book value of assets, as well as tax depreciation reporting options.
Using PeopleSoft Asset Management in Italy
PeopleSoft Asset Management enables you to produce a fixed-asset book, required by Italian regulations (article 16, D.P.R. 600/73), to record information regarding depreciable fixed assets. The fixed-asset book lists information that is relevant to fixed assets, including the date of purchase, original cost, accumulated depreciation (beginning of year balance), depreciation rate, year-to-date (YTD) depreciation (current year activity), retirement and disposal information, ending balance, and any revaluation and devaluation information in a particular fiscal year for either the economic or fiscal book. Most Italian business entities use an economic book to record depreciation that is not subject to fiscal constraints and a fiscal book to record specific rules and depreciation methods that are regulated by fiscal authorities.
Using PeopleSoft Asset Management in Japan
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports commonly used practices in Japan, including depreciation methods for fixed and leased assets, composite depreciation, and collateral assets. In addition, PeopleSoft Asset Management provides reports to satisfy tax reporting requirements.
 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesBefore you can perform some of the functions discussed in this chapter, you must have already performed some or all of the following country-specific tasks:
|
Country |
Task |
|
VAT countries |
Set up the appropriate value-added-tax (VAT) defaults and reporting options, and associate these defaults and options with business units or VAT-driven entities. See Working with VAT. |
|
Before processing asset revaluations, ensure that these conditions have been set up for Australia: |
|
|
Set up the following conditions to calculate CCA reporting for Canada: |
See (CAN, IND, and USA) Defining and Maintaining Tax Classes. |
|
Set up the following conditions for France: |
|
|
Set up the following tables to process tax and depreciation for Germany: |
|
|
Set up the following tables to process tax and depreciation for India: |
|
|
Set up the following tables to process tax and depreciation for Japan: |
Set up the overall options for user preferences (OPR_DEF_TABLE_FS1) in the Common Definitions component: Set the Localization Country value to JPN (Japan), which enables the JPN Info (Japan information) link in the Define Business Units component for Asset Management. See Establishing PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units. |
 (AUS) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet Australian
Requirements
(AUS) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet Australian
Requirements
This section discusses how to:
Define asset R&D categorization.
Use the Australian tax credit allowance.
Track changes in CCP.
Report changes in CCP.
Calculate CGT.
Generate asset revaluation (net method).

 Pages Used to Meet Australian Requirements
Pages Used to Meet Australian Requirements
 Defining Asset R&D Categorization
Defining Asset R&D Categorization
Enable R&D calculations and define assets as R&D eligible assets from the following pages:
Asset Unit Aggregate RD page.
Asset Profiles - Definition page.
Set R and D Info page.
Access the Asset Unit Aggregate RD - AUS page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Taxes, Asset Unit Aggregate RD - AUS, Asset Unit Aggregate RD - AUS).
To calculate the amount of deductions that it is possible to claim, enter the aggregate R&D amount for each fiscal year. Enter the fiscal year, expenditure, and description for the business unit.
Defining an Asset as R&D Eligible on the Asset Profile Page
Access the Asset Profile - Definition page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Profiles, Asset Profiles, Definition.) Asset profiles that are defined with R&D options that are selected indicate that all assets that are added to your system by using this profile are used for R&D and are entitled to R&D tax concessions.
|
R and D Plant Asset (research and development plant asset) |
Select if this asset is used for R&D and is entitled to R&D tax concessions. |
|
R and D Start Date (research and development start date) |
Enter the date on which the asset was first used exclusively for R&D. If you leave this field blank, the in-service date from the business unit's tax book is used as the start date. The start date determines the first year in which you can claim R&D concessions. |
|
Use NBV for R and D (use net book value for research and development) |
Select if you want to base the R&D concessions calculation on the net book value of the asset (at the R&D start date) instead of the book cost. This is useful when an asset previously being depreciated as a non-R&D asset subsequently becomes eligible for R&D concessions. |
Defining an Asset as R&D Eligible on the Set R&D Information Page
Assets that are added to your system through either the Basic Add- General Information page or the ExpressAdd-Cost/Asset Information page with R&D options selected identify that the asset is used for R&D and therefore entitled to R&D tax concessions.
Access the Asset R&D Information page (Asset Management, Asset Transactions, Owned Assets, Basic Add, General Information, Set R&D Info, Asset R&D Information page).
|
R and D Plant (research and development plant) |
Select if you want to identify the asset as specifically allocated for R&D. |
|
R and D Start Date (research and development start date) |
Enter the R&D start date for this asset. |
|
Use NBV (use net book value) |
Select if appropriate for your tax reporting purposes. Click the OK button to return to the Asset Information or Cost/Asset Information page. |
See Also
Setting Up Depreciation Processing
Setting Up Tax Processing and Tax Reporting

 Using the Australian Tax Credit Allowance
Using the Australian Tax Credit Allowance
Australia tax law provides certain tax credit allowances related to capital investment projects that include provisions for rebates (often referred to as credits). Unlike allowable deductions, the tax credits are not part of the calculation of taxable income.
The tax credit allowance is calculated in this way:
Tax credit cost basis = book cost x basis reduction rate (%)
Tax credit = tax credit cost basis x tax credit (%)
To use this feature:
Set up your own credit tables or modify the existing tables on the Tax Credits page.
Assign a status to the defined tax credits.
The status enables you to classify assets when reporting credits. Use the Tax Credit Status page to enter or modify a tax credit status.
Enter tax credits against assets.
Use the Asset Profiles, Asset Book Definition, or Asset ExpressAdd component.
See Defining Tax Credits.
Entering Tax Credits Against an Asset
Tax credits are entered against an asset in the Asset Book Definition or Asset ExpressAdd component, or at the asset profile level by using the Asset Profile Tax Credits page. You can enter tax credits against leased assets by using the Asset Book Definition page after the asset has been entered through Leased Asset Entry.
See Creating PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units.
See Working With Leased Assets.
Entering Tax Credits in the Asset Book Definition Component
The Tax Credit Options region on the Tax page (PROFILE_BK_03) of the Asset Profiles component provides you with the options to identify which investment credits are taken for a selected asset. You must specify the tax criteria before you can enter tax credits.
After you enter the tax credit code, PeopleSoft Asset Management retrieves the percentage figures that are specified for the tax credit and calculates the computation amount using the following formula:
Book cost x basis reduction percentage = amount qualifying for the tax credit
Amount qualifyingx tax credit percentage = amount of tax credit
The sum of all tax credits that are defined in the current book appears in the Tax Credit field. The total tax credit amount is updated each time that you change tax credit information.
See Setting Up Asset Profiles.
Entering Tax Credits in the Asset ExpressAdd Component
The Asset ExpressAdd component enables you to identify which investment credits are taken for a selected asset from the Tax Credit Options region on the Tax Information page (ASSET_ENTRY_02). You must specify the tax criteria before you can enter tax credits.
Access the Tax Credit Options group box on the Tax Information page.
Enter the tax credit code. You can optionally enter a tax credit status.
After you enter the tax credit code, PeopleSoft Asset Management retrieves the percentage figures that are specified for the tax credit and calculates the computation amount by using the following formula:
Book costx basis reduction percentage = amount qualifying for the tax credit
Amount qualifying x tax credit percentage = amount of tax credit
The sum of all tax credits that are defined in the current book appears in the Tax Credit field. The total tax credit amount is updated each time that you change tax credit information.
If you change the cost information on the Cost/Asset Information page of the Asset ExpressAdd component after you have entered tax credits, click the Calculate Credit button to recalculate the amount of the credits. This reloads the percentage figures from the Tax Credit table and then recalculates the amounts for all tax credits that are defined for the current asset.
See Adding Assets with the Asset ExpressAdd Component.

 Tracking Changes in CCP
Tracking Changes in CCP
Australian financial services organizations are required to track the usage of fixed assets that are used in making input tax supply. Input tax that is not creditable is capitalized in the value of the asset and depreciated accordingly. Creditable tax is eligible for refund and is not included in the value of the asset. Because a single asset can be used by a business entity in multiple activities, some of which may be taxable or GST-free and some of which may be input taxed, the full amount of GST that is paid must be recorded and apportioned creditable and noncreditable based upon usage. Over the life of an asset, this apportionment must be reviewed annually and adjusted to reflect the asset's current usage. The time period during which an asset is subject to this review is determined by the cost of the asset. Review periods are maintained in the Asset Threshold-VAT table referenced when assigning the last date of mandatory review.
Recording GST in Payables and Passing GST on to Asset Management
To track the apportionment of GST that is relevant to an asset, four fields are passed to Asset Management from Payables using the Run Load Assets process (INTFAPAM):
Asset ID
Merchandise Amount
Non Recoverable VAT
Total VAT
Payables validates the information that you entered on the invoice before passing it to Asset Management.
Note. The invoice information must be validated in PeopleSoft Payables before it is passed to PeopleSoft Asset Management. Invoice information cannot be rejected once it has reached PeopleSoft Asset Management.
This diagram illustrates the interface process:
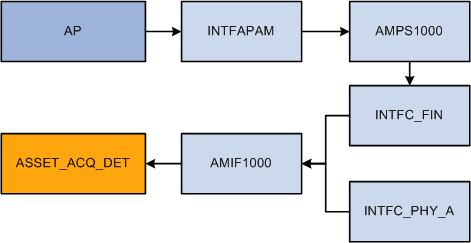
PeopleSoft Payables to PeopleSoft Asset Management GST process
See Processing Value Added Tax (VAT) in PeopleSoft Payables.
Adding GST Online in Asset Management
You can enter GST information directly into Asset Management when entering an asset online through the Asset Basic Information component. Use the Tax link on the Asset Acquisition Detail page to enter tax amounts that are charged to the asset.
Changes in CCP are recorded on the same page that you use to enter an asset's GST amounts manually and to designate recoverable and nonrecoverable amounts. When changing the usage percentage of an existing asset, select the transaction type Adjustment rather than Addition; otherwise, the entry process is the same.
When working in a business unit that is identified for Australia, the Calculate Last Date of Review button appears on the Asset Information page. Select a schedule type code, and click the Calculate Last Date of Review button to generate the last date of mandatory review for the asset. The last date of mandatory review is stored on the Asset Basic Information page.
See Also
Adding and Maintaining Asset Information

 Reporting Changes in CCP
Reporting Changes in CCP
Some organizations must track fixed assets that are used in making input tax supply. You can track the change in the extent to which a fixed asset is used to make taxable supply from reporting period to reporting period, and you can make adjustments for any change. For instance, in Australia, Australian financial services organizations require a solution to record the apportionment of recoverable versus nonrecoverable VAT on invoices. This information is then sent to PeopleSoft Asset Management for capital assets.
Access the Australia CCP Report page (RUN_AMTX30AU) to generate the report.

 Calculating CGT
Calculating CGT
CGT legislation in Australia requires payment of tax on certain capital gains that are realized at the time of an asset's sale, net of inflation, of all components of the cost basis. Tax deductions can also be realized in certain circumstances for losses. PeopleSoft Asset Management provides pages on which you designate the applicability of a gain or loss calculation for specific assets or for all of the assets in a book. When an asset on which gain or loss has been designated as applicable is retired, the system calculates the gain or loss and stores the results for later reporting. The gain or loss calculation is split into an assessable gain or loss and a capital gain or loss amount.
Specifying Capital Gain or Loss Options for an Asset
There are multiple components where you can indicate that an asset is CGT-applicable if you want the capital gain or loss calculated for an asset upon retirement:
Asset Book Definition - Book Tax page (if the CGT calculation is applicable for assets on a book level).
Asset Profile.
ExpressAdd.
To be prompted to identify an asset as CGT-applicable, you must associate the book for the asset with the country (Australia) on the Asset Book Definition page.
If CGT is applicable for this asset, select the CGT Applicable check box on any of these pages.
Run the Australian Retirements reports to view the results of CGT-applicable assets. Use these calculations:
Capital gain or loss = asset proceeds – indexed revalued amount or original price – removal amount
Assessable gain/loss = asset proceeds or original price – net book value – removal amount
These calculations use existing indexing tables containing local consumer price indexes (CPI). A logical extension of this calculation is to determine the actual amount of tax to be paid, or in the case of a loss, the tax credit that you can later net against a future capital gain.
See Also

 Calculation of CGT
Calculation of CGT
Here are the elements that are used in the calculation of a capital gain or capital loss on the disposal of an asset:
The cost base of the asset, which is used to determine the amount of a capital gain if the disposal of the asset occurs within 12 months of the taxpayer's acquisition of the asset.
The indexed cost base of the asset, which is used to calculate the amount of a capital gain if the taxpayer disposes of the asset 12 months or more after the date of its acquisition.
The reduced cost base of the asset, which is used to calculate the amount of a capital loss that arises on the disposal of the asset.
Using the Asset Retirements page, you can view the CGT that is calculated upon retirement for each asset by book.
The Retirement reports also contain CGT information.

 Generating Asset Revaluation (Net Method)
Generating Asset Revaluation (Net Method)
Asset Management supports asset revaluations in accordance with Australian accounting standards (AASB1010 and AASB1041), which require crediting to related asset accounts a balance of accumulated depreciation at the date on which an asset is revalued.
The net method of revaluation cannot be run from the Revaluation worksheet. You must use the process described here.
To process asset revaluations:
Run the Australian Revaluation process (AMAUSCAL) from Asset Management, Asset Transactions, Financial Transactions, Revaluation in Mass
Select the net method as the revaluation method, define the run control parameters and click the Run button on the Process request page.
If you select the Include Current Period Depr (include current period depreciation) option, the process includes the depreciation in the revaluation accounting entries.
Note. Not all of the parameters that are normally available from the run control page are available for this revaluation method.
Select the Australian Revaluation check box.
The process updates the Financial Loader table (PS_INTFC_FIN) with four rows for each asset included in the process request: one for retirement (RET) with the total cost, one for reinstatement (REI) with the total cost, one for an adjustment (ADJ) reflecting the difference between the original cost and the cost calculated with revaluation parameters, and one for book change (BKS).
(Optional) Preview the data in the Financial Loader table by using an online page.
Run the Transaction Loader process (AMIF1000) to load the retirement transactions that are created by revaluation.
Use the load type RET to find the load ID to process.
Run the Depreciation Calculation process (AM_DEPR_CALC) to account for the retirement transactions.
Run Transaction Loader (AMIF1000) to load the reinstatement transactions that are created by the revaluation.
Use the load type REI.
Run the Revaluation Australia process (AMAUSUPD) to update depreciation and distribution status for retirement and reinstatement transactions.
Run Transaction Loader (AMIF1000) to load the adjustment transactions that are created by the revaluation.
Use the load type ADJ.
Run Depreciation Calculation (AM_DEPR_CALC) to account for the adjustment transactions.
Run Transaction Loader (AMIF1000) to load the adjustment transactions created by the revaluation.
Use the load type BKS.
Run the Depreciation Calculation process (AM_DEPR_CALC) to account for the book change transactions.
Run the Accounting Entry Creation process (AM_AMAEDIST) to generate accounting entries.
Run the Detail Net Book Value Report by Category (AMDP2110).
See Also
Previewing Data in the Loader Tables
Running the Transaction Loader
Creating PeopleSoft Asset Management Accounting Entries
 (CAN) Using Asset Management Options to Meet Canadian Requirements
(CAN) Using Asset Management Options to Meet Canadian Requirements
This section discusses how to:
Calculate CCA reporting.
Run the CCA Year-End Update process.

 Pages Used to Meet Canadian Requirements
Pages Used to Meet Canadian Requirements
 Calculating CCA Reporting
Calculating CCA Reporting
Asset Management enables you to calculate and report CCA amounts as required by Schedule 8 of Revenue Canada.
To calculate the CCA:
Set up or modify CCA tax classes on the Tax Class page, and specify the CCA percentage rate.
Asset pools or classes and CCA rates are set by governmental regulations. In the year that assets are acquired, 50 percent of the normal rate should be used. The value that you enter for an asset tax class for the CCA rate percent is used later when you run a process to calculate the CCA rate.
On the Asset Book Definition - Book Tax page, select the tax guideline class that reflects the CCA tax class to which the asset belongs.
For each reporting fiscal year, associate a CCA UCC beginning year value with a CCA tax class.
Run the CCA Year End Update process that extracts the data that is necessary for CCA calculation, populates the CCA_YR_END_TBL table, and calculates all amounts that are required by the CCA report.
Run the CCA Year End reports.
See Also
(CAN, IND, and USA) Defining and Maintaining Tax Classes

 Running the CCA Year-End Update Process
Running the CCA Year-End Update Process
Access the CCA Year End Updates Request page.
Enter the business unit, CCA book name, and applicable fiscal year. Select a process frequency. This process is iterative. Run it as many times as necessary to complete CCA reporting. To run the process for multiple business units, leave the Unit field blank.
The CCA Year End Update process populates the CCA_YEAR_END_TBL table with these values:
|
Business Unit |
Acquisitions |
|
Book |
Adjustments |
|
Fiscal Year |
Transfers |
|
CCA Tax Class |
Net Proceeds |
|
Currency Code |
Capital Gains |
The process calculates CCA amounts according to the following formula:
UCC = UCC beginning of year + additions +/–adjustments – retirements
CCA = UCC –(50% * addition) * CCA rate
UCC end of year = UCC –CCA
 (FRA) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet French Requirements
(FRA) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet French Requirements
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports asset management practices that are commonly used in France. This section discusses how to:
Report business tax.
Depreciate assets by using the derogatory method.
Revalue assets.
Generate French statutory reports.

 Pages Used to Meet French Requirements
Pages Used to Meet French Requirements|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RUN_AMBT1000 |
Asset Management, Taxes, Reports, Business Tax |
Run the Business Tax report or the Business Tax by Alternate Account report. |
|
|
EU_AM_RUNCNTRL |
Asset Management, Taxes, Reports, Statutory Report 2054/2055 |
Obtain information on the asset, its cost and net book value, and all transactions that occurred in the specified reporting year, including depreciation and yearly depreciation. |

 Reporting Business Tax
Reporting Business Tax
To calculate and report a business tax that is assessed on the gross value of fixed assets:
Define the business tax rates by country, year, and location.
Define asset profiles as business tax applicable by selecting the Business Tax check box in the Asset Profile component.
Define asset books as business tax applicable by selecting the Business Tax check box in the Asset Book Definition component.
Run the Business Tax reports: Business Tax by Account or Business Tax by Alternate Account.
See Also
Maintaining Asset Book Information

 Depreciating Assets by Using the Derogatory Method
Depreciating Assets by Using the Derogatory Method
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports derogatory depreciation and enables you to generate appropriate accounting entries.
To use the derogatory method:
Set up rates for use with the derogatory method by using the Depreciation Rate - User Defined page in the Establishing Asset Processing component.
Define appropriate reporting books for France.
In the statutory book, select France Derogatory Balance as the depreciation method.
Creating Accounting Entries for Derogatory Depreciation
By setting up the appropriate accounting entry information using an accounting entry template, you can generate accounting entries and see the difference between depreciation that is reflected in the economic book and the statutory book.
To set up appropriate accounting entries:
Define the economic and statutory books at the business unit level.
Select the Derogatory Depreciation check box on the Business Unit/Book Definition page for the statutory book.
Add assets.
Identification of derogatory depreciation processing is defined at the business unit or book level.
Select the Derogatory Accounting entries check box when setting the accounting entry template ID Derogatory to define the accounting treatment for derogatory depreciation.
Run the Depreciation Calculation process (AM_DEPR_CALC) for both books.
Run the Accounting Entry Creation process (AM_AMAEDIST).
Review depreciation entries on the Asset Depreciation - Period Depreciation page.
Review accounting entries for each book in the Asset Accounting Entries component.
The pages in this component provide the accounting date, transaction type, account, and amount of each entry.
Run the French Net Book Value by Account report (AMFR2120) on the Report - Asset Net Book Value page.
After you specify parameters for the report and click the Run button, select the French Net Book Value by Account check box from the process list that appears.
Run the French Net Book Value by Alternate Account report (AMFR2121) on the Report - Alt Acct Activity Detail page.
After you specify parameters for the report and click the Run button, select the French Net Book Value by Alternate Account check box from the process list that appears.
See Also
Establishing PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units

 Revaluing Assets
Revaluing Assets
PeopleSoft Asset Management enables you to revalue assets as a whole by using an Application Engine process. You can also revalue one or more assets at one time using the Revaluation Worksheet page. The system enables you to track and report on the revalued amount separately.
Distribution types to support accounting entries for asset revaluation are available. When setting up accounting entry templates, you can use the Derogatory accounting entry template ID and select Asset Adjustments and Transfers. In the Accounting Entries column, Asset Management provides two entries: Provision for Revaluation and Reversal of Depreciation.
See Also

 Generating French Statutory Reports
Generating French Statutory Reports
French statutory reports EU_2054 and EU_2055 are attachments to the annual balance sheet and provide information about the history and activity of assets during the specified fiscal year. Asset categories on both reports are based on the French statutory chart of accounts. The system provides a reporting option to generate both of these statutory reports for France.
Access the 2054 2055 Reports page.
 (DEU) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet German Requirements
(DEU) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet German Requirements
This section provides an overview of commonly used German depreciation methods and discusses how to:
Use a half-year prorate convention.
Use geometric digressive depreciation.
Process low-value assets.

 Pages Used to Meet German Requirements
Pages Used to Meet German Requirements|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
User-Defined Method |
UD_METHOD_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Depreciation, User Defined Methods |
Create a user-defined Staffel depreciation method. |
|
Auto-Retire Fully Depreciated Assets |
RUN_AMRETFDA |
Asset Management, Send/Receive Information, Financial Transactions, Auto-Retire Fully Depr Assets |
Identify run control parameters to automatically retire fully depreciated assets. |
|
Capitalization Limit CD |
DEPR_CAP_LIMIT |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Capitalization Limits |
Specify asset value minimums and associate warning or error actions with assets whose values fall below those limits. |
|
Depreciation Terms |
DEPR_TERMS_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Depreciation, Terms Definition |
Define special depreciation terms for accelerated depreciation and associate the terms at the asset or book level. |
|
Load History Report Table |
LOAD_AM_HIST_TBL |
Asset Management, Reports, Load Reporting Tables, Load Asset History Table |
Run one of two SQR processes that load asset data into tables where it can be used for reports.
Note. Before running this process, you must run a process to load the depreciation report table. |
|
Asset History Reports |
RUN_AMDE1000 |
Asset Management, Reports, Owned Assets, Asset History Sheet |
Run the Asset History Sheet reports that are attached to annual balance sheets and provide information about the history of an asset and its transactions. |
|
Reconciliation AP/AM (reconciliation accounts payable/asset management) |
RUN_AMDE5000 |
Asset Management, Reports, Cost and Depreciation, Reconciliation AP/AM |
Run a report to help you reconcile accounts payable asset vouchers with Asset Management asset transaction information. |

 Staffel Depreciation Method
Staffel Depreciation Method
The Staffel depreciation method is used for depreciating buildings in Germany and other countries. The Staffel depreciation method can be characterized as a "step straight line." For example, for a building with an acquisition cost of $100,000 and a life of 25 years, the depreciation calculation is 10 percent ($10,000) per year for years one through four, 5 percent ($5,000) per year for years five through seven, and 2.5 percent ($2,500) per year for years eight through twenty-five. These percentages vary due to legislation and the acquisition date of the building.
Three Staffel Depreciation Methods
There are three common Staffel depreciation methods.
The first Staffel method is for domestic buildings that are used by an organization for non-habitational purposes (for example, production buildings within Germany) and where the request to build was submitted to the local construction authorities after March 31, 1985, but before February 28, 1989:
|
Year |
Percentage |
|
Years 1–4 |
10% each year |
|
Years 5–7 |
5% each year |
|
Years 8–25 |
2.5% each year |
Non-habitational buildings that do not fulfill the preceding criteria are depreciated according to this criteria:
|
Year |
Percentage |
|
Years 1–8 |
5% each year |
|
Years 9–14 |
2.5% each year |
|
Years 15–50 |
1.25% each year |
Exceptions (all buildings that are used for habitational use and where the request to build was submitted to local construction authorities after February 28, 1989) are depreciated according to this criteria:
|
Year |
Percentage |
|
Years 1–4 |
7% each year |
|
Years 5–10 |
5% each year |
|
Years 11–16 |
2% each year |
|
Years 17–40 |
1.25% each year |
Depreciation periods in Germany are based on calendar years (January 1 – December 31). Because not all buildings are completed or purchased on January 1, if you activate an asset in a different month, you must prorate the depreciation for the first year, including the month of asset addition. For example, the depreciation amount for the first year is 36,000 EU if activated on January 1. But if the asset was activated on August 12, the depreciation amount for the first year is 15,000 EU, reflecting the months August through December.
Also, you must prorate the depreciation in the year of asset retirement (or sale) excluding the month in which it is retired. For example, the depreciation for the last year is 60,000 EU if the asset is retired at the end of the year. But if the asset was retired or sold on August 12, then the depreciation amount must be adjusted to 35,000 EU, reflecting the months January through July.
Creating a User-Defined Staffel Depreciation Method
To calculate depreciation by using the Staffel method, you can create a user-defined depreciation method for this formula. For example, in this case:
The asset basis of the building is $100,000 (EU).
The asset life is 25 years (300 periods).
The depreciation convention is AM (actual month).
The user-defined depreciation method name is Staffel.
To create a Staffel user-defined depreciation method, use the User-Defined Method page. Enter a description for the method ID.
You must define the following four variables to create a Staffel user-defined depreciation method:
Result A= ALLOC_LIFE – Total Periods Depr
This calculation results in the number of remaining periods in weeks:
Result D=Result A/52
This is the number of remaining periods in years.
Result C=No Periods to Depr/Alloc Total
This provides the number of periods for the year to be depreciated / total periods for the year, for example, 6 / 12 for the first year.
Result B=Asset basis x Percentage
This result is:
Asset basis – Salvage value x Appropriate Staffel Percentage
Finally, to calculate the depreciation proration for the first year and the year of retirement, specify the following in the formula:
Depreciation=Result B x Result C
See Also
Using User-Defined Asset Depreciation

 Using a Half-Year Prorate Convention
Using a Half-Year Prorate Convention
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports the German half-year convention. The German half-year convention differs from the U.S. half-year convention in that an asset takes a full year's depreciation if it was acquired in the first half of the year. This convention is delivered in the tables shipped, but you can modify it as necessary to suit a specific requirement.
See Also
Setting Up Depreciation Conventions

 Using Geometric Digressive Depreciation
Using Geometric Digressive Depreciation
Geometric digressive depreciation calculates depreciation up to three times the annual straight-line depreciation with a maximum of 30 percent of the asset cost per year. Asset Management supports this depreciation method by providing the declining balance with a Switch to Straight Line depreciation method option. To depreciate assets by using this method, select DB w/SL By Limit% on the Book-Tax page in the Asset Book Definition component, the Depreciation page in the Asset Profiles component, or the Depreciation Information page in the Asset ExpressAdd component. Specify 300 as the declining balance percent and 30 as the limit percent.
See Also
Declining Balance with Depreciation Limit

 Processing Low-Value Assets
Processing Low-Value Assets
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports low-value asset processing by providing a capitalization limit table where you can specify asset value minimums and associate warning or error actions with assets whose values fall below those limits. Additionally, you can set the limit at which an asset is marked as a low-value asset.
Access the Capitalization Limit Cd page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Financials, Capitalization Limits, Capitalization Limits).
After you have set up the necessary capitalization limits, select Table Lim (table limit) and the correct code as the capitalization limit method on the Business Unit/Book Definition page in the Establish Business Units - Asset Management Definition component.
When you add assets to that business unit and book combination, Asset Management checks the capitalization limits against the amounts that are stored by code in the capitalization limit table.
In Germany, assets marked as low value should be depreciated in one year.
PeopleSoft Asset Management provides the PROGWG asset profile that is defined with depreciation attributes that are appropriate for German low-value asset processing. These include depreciation using the straight-line method and a useful life of 12 periods. Also, Asset Management provides the German First Day Last Period depreciation convention that you can use to generate one accounting entry for the annual depreciation for a low-value asset.
Low-value assets can be retired in mass using the Auto-Retire feature to satisfy the requirement that low-value assets be fully depreciated and retired after the first year of service.
See Also
Creating PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units
Setting Up Capitalization Limits
Setting Up Depreciation Conventions

 Special Depreciation Terms and Methods
Special Depreciation Terms and Methods
Access the Terms Definition page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Depreciation, Terms Definition, Terms Definition).
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports special depreciation methods that are used in Germany, such as accelerated depreciation, by enabling you to define special terms and associate them at the asset and book level.
After you have defined special terms, associate them with an asset or book by selecting the Special Depreciation check box on the Depreciation Information page in the Asset ExpressAdd component.
See Also
Setting Up Depreciation Processing
 (IND) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet Indian Requirements
(IND) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet Indian Requirements
PeopleSoft Asset Management addresses issues related to fixed-asset accounting in India. This section provides an overview of asset depreciation processing for India and discusses how to process tax depreciation.

 Understanding Asset Depreciation Processing for India
Understanding Asset Depreciation Processing for India
PeopleSoft Asset Management provides asset processing features that correspond to the tax reporting requirements established by Indian tax legislation. Indian tax law does not recognize depreciation on individual assets. Instead, it groups similar pools of assets under a prescribed tax block. There are only four tax blocks of assets provided for under the tax act: buildings, furniture and fixtures, machinery and plant, and intangibles. Further, each tax block of assets comprises tax groups, and each tax group has its own individual tax rate. The Indian tax year is fixed on a fiscal year calendar that runs from April 1 through March 31. Annual tax depreciation is reported to the tax authority per tax block per fiscal year .
To meet these requirements, PeopleSoft Asset Management allows for the grouping of assets by asset blocks for accumulating and reporting depreciation and taxes. Each asset block can have as many depreciation rates associated with it as necessary to delineate Indian tax groups. To meet reporting requirements, a tax entity is defined, associated with a specific book, and has as many business units and asset books associated with it as necessary.
The Straight Line Percent method of depreciation in PeopleSoft Asset Management uses the asset useful life to calculate the depreciation rate. India calculates useful life based on the depreciation rate guidelines published by the governmental finance authority. The rates established depreciate 95 percent of the cost over the useful life of the asset, at minimum: accelerated depreciation is allowed. India calculates depreciation based on the rates rather than useful life. In addition, these rates also consider the residual or salvage value at the end of the asset useful life. To determine useful life of an asset in India, the straight line percent method multiplies the depreciation rate by cost and this results in the useful life. Further, there are two different ways to calculate depreciation adjustments under the Indian Straight Line Percent method: remaining value and life-to-date. All transactions use an actual day (AD) convention for calculating depreciation. Assets are depreciated when they are placed in service. Processing for leased assets is included.
During the end-of-year processing of depreciation and taxes for India, assets are grouped into blocks based on the tax entity and asset profile definition in place for the asset. The opening written down value (WDV) is retrieved from the prior year WDV for the corresponding tax entity, asset block, and rate.
Asset Management provides these reporting processes to manage Indian tax and depreciation requirements:
Produce the Asset Register - India: Reports an historical record of assets over the fiscal year period.
Produce the Depreciation Balance - IND report: Displays the calculated opening WDV balance and reports depreciation during the year.
Calculate and Update Depreciation Balance - IND processes: Calculates depreciation balances for India and provides an online update of balances (depending on your setup options).
The system provides functionality to process operating and capital leases when manually specified.

 Pages Used to Meet Indian Requirements
Pages Used to Meet Indian Requirements|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
AM_DEPR_TAX |
Asset Management, Taxes, Depreciation, Calculate Balances IND, Calculate Balances IND |
Calculate tax depreciation balances for India. |
|
|
TAX_DEPR_BAL |
Asset Management, Taxes, Depreciation, Update Balances IND |
Displays tax depreciation balance for India that you can update. |
|
|
RUN_AMDP2510 |
Asset Management, Financial Reports, Cost and Depreciation, Assets Register - IND |
Reports historical depreciation for the fiscal year. |
|
|
TAX_DEPR_RQST |
Asset Management, Taxes, Reports, Depreciation Balance IND |
Generate tax depreciation balance report for the tax period. |

 Processing India Tax Depreciation
Processing India Tax Depreciation
When you accumulate assets subject to India's depreciation and tax guidelines, you must first assign an asset block, a guideline (tax) class, and a tax entity to each asset. Also, you should set up each asset to depreciate when in service. These attributes are defined in the Book Definition component and the Book - Depreciation (ASSET_BOOK_01) and Book - Tax (ASSET_BOOK_02) pages. When depreciation and tax processing commences, the system retrieves these designated assets for processing.
See Adding and Maintaining Assets.
To process and report on depreciation and tax for India:
To process depreciation for India, request the depreciation calculation process (AM_DEPR_CALC).
To calculate depreciation balances for India for the tax period, request the process to calculate balances for India (AMTX2000).
To update depreciation balances for India for the tax period, request the process to update balances for India (TAX_DEPR_BAL).
To review the asset register for India, request the assets register for India (AMDP2510).
Calculating Tax Depreciation Balances for India
Access the Calculate Balances IND page (Asset Management, Taxes, Depreciation, Calculate Balances IND, Calculate Balances IND).
|
Tax/Reporting Entity |
Select the tax and reporting entity for this process. The available tax entities are defined by the asset blocks, tax class tax rates, setID calendar, and business unit/books that are associated with it. |
|
Entity Book |
Select the entity book for this process. The entity book defines how to group the tax or reporting information. |
See (IND) Defining Tax Entities and Tax Options.
Updating Depreciation Balances for India
Access the Tax Depr Bal page (Asset Management, Taxes, Depreciation, Update Balances IND).
If your setup options have enabled manual adjustments to depreciation balances, you can access calculated balances and enter adjustments in the Manual Adjustment column. No recalculations are processed on the basis of any manual adjustment entered, but the values are added to the WDV.
Generating the Asset Register India
Access the Assets Register - IND page (Asset Management, Financial Reports, Cost and Depreciation, Assets Register - IND, Assets Register - IND).
|
Selection Request Parameters |
Define the parameters for the asset register to report by business unit or report entity. Complete these fields as dictated by your needs:
|
Processing Rules
When calculating the annual tax depreciation balances, the following rules apply:
Tax depreciation is calculated for each tax group per the tax group tax rate.
Opening balance (WDV) is required for each tax group each year.
The opening balance in the conversion year is entered; in subsequent years, the opening balance is processed by Asset Management and is equal to the ending balance of the previous year.
Additions and adjustments for the fiscal year are lumped together.
However, these are subgrouped separately to include assets that have been in use for more than 180 days and those that have been in use for less than 180 days. For assets in use for less than 180 days, only 50 percent of the normal depreciation rate is allowed (per Section 32).
To determine the assets that fall in the category of Additions/Adjustments more than 180 days, the system calculates the difference between the fiscal year end date (March 31) and the in-service date for ADD and ADJ transaction types. For additions less than 180 days, the system calculates the difference between the year end (March 31) and the in-service date for ADD and ADJ transaction types. If the in-service date is in the current year but the acquisition date is in prior years, the asset is depreciated at the regular rate rather than at 50 percent of the prescribed rate.
Proceeds for the assets sold during the year are calculated.
Use the formula for calculating WDV depreciation, where:
A = Opening WDV/Balance.
B= Proceeds from sale of an asset.
C= Additions/Adjustments > 180 days.
D= Additions/Adjustments < 180 days.
E= Rate of Depreciation, Depr Value.
(A-B+C)xE +(DxE/2)= Depreciation Value (F)
Closing WDV=A-B+C+D-F
In case the entire tax block of assets ceases to exist (for example, all of the assets are sold or transferred), the net income is taxed as short term capital gain. In this case, the opening WDV of all the tax groups in this block becomes zero for the subsequent year.
See Also
Setting Up Tax Processing and Tax Reporting
 (ITA) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet Italian Requirements
(ITA) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet Italian Requirements
This section discusses how to generate the fixed-asset register for Italy.

 Page Used to Meet Italian Requirements
Page Used to Meet Italian Requirements|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Fixed Asset Register |
RUN_AMDP2500 |
Asset Management, Financial Reports, Cost and Depreciation, Assets Register - ITA |
Specify report request parameters to generate the Assets Register - ITA report. |

 Generating the Fixed-Asset Register for Italy
Generating the Fixed-Asset Register for Italy
Access the Assets Register - ITA page (Asset Management, Financial Reports, Cost and Depreciation, Assets Register - ITA, Assets Register - ITA).
Define the parameters to generate the register.
 (JPN) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet Japanese Requirements
(JPN) Using PeopleSoft Asset Management Options to Meet Japanese Requirements
This section lists prerequisites and discusses how to:
Use Japanese depreciation methods.
Use special depreciation and increased depreciation.
Use advanced depreciation.
Use composite depreciation.
Identify collateral assets.
Use currency rounding options.
Process local tax reports.
Enter consumption tax.

 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesMany of the features for processing assets for Japan are dependent on the business unit information definitions established at the business unit level. You must establish these business unit definitions in order to complete processing for Japanese requirements.
Access the Business Unit Info for Japan page from the AM Business Unit Definition component (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Business Unit Related, Assets, Asset Management Definition, AM Business Unit Definition), Click the JPN Info link.
Note. To enable the JPN Info link, you must set up the overall options for user preferences in the Common Definitions component: Set the Localization Country value to JPN (Japan).Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Common Definitions, User Preferences, Define User Preferences, Overall Preferences.
|
Corporate Book for Japan |
Select the corporate book for Japan. |
|
Tax Book for Japan |
Select the tax book for Japan. |
|
Memorandum Amount and Currency |
Enter the memorandum amount at the end of the useful life of the asset as required by the Japanese tax regulation. This value can be updated, as the law requires. This value is used in conjunction with the following depreciation methods: J6 - Tangible Declining Balance, J7 - Tangible Straight Line, and Japan Extended Straight Line. The memorandum amount reflects the currency of the tax book for Japan as the default. For books that use one of the aforementioned depreciation methods in a currency other than JPY, the memorandum amount is translated to the respective book's currency. The memorandum value is established for each asset business unit. |
|
Advanced Depreciation |
Select if advanced depreciation is used. |
|
Japan Composite |
Select if composite assets are used. |
|
Use JPN Local Tax (use Japan local tax) |
Select if local tax reporting is enabled. |
See (JPN) Defining Business Unit Information for Japan.
The following steps are recommended when implementing Japanese tax reform changes:
Establish the memorandum amount on the Business Unit Info for Japan page.
Verify that the proper and most current depreciation rates, guaranteed rates, and revised rates are represented on the Life and Rate information secondary page [MR_AM_LIFERATE].
Select the appropriate depreciation methods at the asset profile level or override them at the asset level.
Use the Extended Depreciation Worksheet to select the eligible assets for extended depreciation. As an alternative to the Extended Depreciation Worksheet, you can extend depreciation manually, asset by asset, from the Define Tax/Depr Book page.
Run the Transaction Loader process prior to calculating depreciation and closing. However, this step is not necessary if you have manually extended depreciation from the Define Tax/Depr Book page.

 Pages Used to Meet Japanese Requirements
Pages Used to Meet Japanese Requirements|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
Advanced Depreciation |
RUN_AMAD1000 |
Asset Management, Financial Reports, Cost and Depreciation, Advanced Depreciation |
Specify report request parameters to generate the advanced Depreciation Amount or Advanced Depreciation Reversal Schedule report. |
|
Owner Information |
OWNER_INFO_DEFN |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Owner Information Definition |
Enter owner information that is printed on the Depreciable Asset Tax Return (Tax Roll) report. |
|
Depreciation Rate-User Defined |
UD_DEPR_RATE_TBL |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Depreciation, Rate-User Defined |
Set up useful life and depreciation rate tables. |
|
Life and Rate Information |
MR_AM_LIFERATE |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Depreciation, Rate-User Defined, Life and Rate Information |
Set up useful life and depreciation rate tables. |
|
Extended Depreciation Worksheet |
AM_EXTENDED_DEPR |
Asset Management, Depreciation, Processing, Extended Depreciation, Extended Depreciation |
Search for candidate assets according to desired parameters. Select to extend or not extend the depreciation period, remove from the list and enter the dates to resume depreciation. |
|
Return Information |
RETURN_INFO_DEFN1 |
Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Return Information Definition |
Enter information that is required for the Depreciable Asset Tax Return (Tax Roll) report. |
|
Local Tax Return |
LTAX_ADD_INFO_SEC |
Asset Management, Asset Transactions, Owned Assets, Asset ExpressAdd Asset Management, Asset Transactions, Owned Assets, Asset Basic Add |
Enter local tax information when you acquire depreciable fixed assets. |
|
Criteria and Defaults |
MC_DEFN_01 |
Asset Management, Mass Change, Define Criteria, Criteria and Defaults |
Use the Mass Change component to process composite depreciation for Japan. |
|
NBV - Assessment Calculation |
AMLTPROC_RQST |
Asset Management, Taxes, Calculate Local Taxes, Calculate Amounts JPN |
Run an SQR process to load asset data and calculate the theoretical net book value and assessment value for each asset. (Theoretical NBV is not needed since 2009, but still available for historical reporting). |
|
Local Tax Information - Adjustment |
LTAX_ADJ_01 |
Asset Management, Taxes, Calculate Local Taxes, Adjust Amounts JPN |
Change the theoretical net book value and assessment value. (Theoretical NBV is not needed since 2009, but still available for historical reporting). |
|
Local Tax Report |
RUN_LTAXPROCESS |
Asset Management, Taxes, Reports, Local Tax Returns |
Run local tax reports for Japan. |
|
Local Tax Information |
LTAX_COST_01 |
Asset Management, Taxes, Calculate Local Taxes, Change Local Tax JPN |
Change the local tax office where the return is filed and the asset return type. |
|
Extended Depreciation Report |
RUN_AMED1000 |
Asset Management, Taxes, Reports, Extended Depreciation |
Run the Extended Depreciation report to analyze the J1, J2, J6 and J7 asset depreciation in compliance with Japanese tax law as reformed. |
|
National Tax |
RUN_AMNT1000 |
Asset Management, Taxes, Reports, National Tax |
Run a report of the depreciation calculation details to be reported to the Japanese Tax Office. The report includes all required information for the National Depreciable Asset Tax Return Beppyo 16(1), (2) in Japan. |

 Using Japanese Depreciation Methods
Using Japanese Depreciation Methods
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports depreciation methods that are used in Japan for both fixed assets and leased assets.
Fixed Assets
This table shows depreciation methods, the calculations used by the methods, and the types of assets to which these methods are applied:
|
Asset Depreciation Methods |
Depreciation Calculation Method |
|
(J3) - Intangible/Straight Line |
Acquisition cost * straight line depreciation rate based on useful life (years) |
|
(J1) - Tangible/Straight Line (assets placed in service prior to April 1, 2007) (J7) - Tangible/Straight Line (assets placed in service April 1, 2007 and beyond) |
For assets placed in service prior to April 1, 2007: (Acquisition cost − 10% of acquisition cost) * straight line depreciation rate based on useful life (years). For assets placed in service on or after April 1, 2007: Cost basis * straight line rate effective on or after April 1, 2007. Note. The straight line rates are derived from the Life and Rate Information page for the J7 depreciation method. The final year's depreciation is the annual depreciation amount less the memorandum value (no salvage value). |
|
(J2) - Tangible/Declining Balance (assets placed in service prior to April 1, 2007) (J6) - Tangible/Declining Balance (assets placed in service April 1, 2007 and beyond) |
For assets placed in service prior to April 1, 2007: Beginning net book value * declining balance depreciation rate based on useful life (years) For assets placed in service on or after April 1, 2007: If (beginning net book value * declining balance depreciation rate of 250 percent) < (beginning net book value * guaranteed rate per Japanese law) then, switch to straight line method using the revised rate. Note. Guarantee rates and revised rates are derived from the Life and Rate Information page for the J6 depreciation method. The final year's depreciation is the annual depreciation amount less the memorandum value (no salvage value). |
|
(J5) - Change Declining Balance to Straight Line |
(Beginning net book value at method change – 10% of acquisition cost) * straight line depreciation rate based on useful life (years) The only method to adapt the depreciation rate based on useful life (years), this method is determined by regulations instead of the rate based on useful life for salvage year. |
|
(J4) - Lease Depreciation |
Declining balance depreciation calculation result * 10/9. |
|
Extended Straight Line Depreciation |
This depreciation method is used for fully depreciated assets under J1 and J2 methods that are subject to an extended depreciation useful life of five years using a Straight Line depreciation method starting from the first period of the following fiscal year. The basis for this extended depreciation is the original 5 percent salvage value. There is no salvage value for the new round of depreciation but the memorandum value is taken from the business unit definition. |
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports useful life in years as specified for Japan. This is applied from the Rate-User Defined table (UD_DEPR_RATE_TBL, MR_AM_LIFERATE) in the Depreciation Rate-User Defined component. To apply the appropriate depreciation rates, use the delivered depreciation methods for Japan or add new ones as needed.
Access the Depreciation Rate-User Defined page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Depreciation, Rate-User Defined).
Select a setID and a depreciation method code matching the depreciation method to be used. Enter the effective date, and click the Life and Rate Information button. The Life and Rate Information page displays.
Enter the useful life and corresponding rates as determined by regulations issued from the Ministry of Finance. The Guarantee Rate and Revised Rate fields are only used in the J6 depreciation method.
Note. Useful Life rates also use the Residual Rate Definition.
See Setting Up Depreciation Processing.
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports the Declining Balance Depreciation Method - Finance Lease (excluding transfer of ownership) 10/9 method, which is calculated in this way:
Declining balance depreciation calculation result x10/9
Use the Depreciation Rate-User Defined - Life and Rate Information page to modify rates for the lease depreciation method.
Example Values
This table shows the values used in an example using the Declining Balance Depreciation Method - Finance Lease (excluding transfer of ownership) 10/9 method:
|
Acquisition Cost |
1,000,000 |
|
Useful Life |
5 years |
|
Depreciation Rate |
0.369 |
Calculation Results for Example Values
Using the values from the previous table and applying the Declining Balance Depreciation Method (J6) - Finance Lease (excluding transfer of ownership) 10/9 method, the results are:
|
Year |
Depreciation Amount by Declining Balance Method |
Depreciation Amount by 10/9 Method |
|
1 |
369,000 |
410,000 |
|
2 |
232,839 |
258,710 |
|
3 |
146,921 |
163,245 |
|
4 |
92,707 |
103,007 |
|
5 |
58,588 |
65,038 |
|
Total |
900,000 |
1,000,000 |
Select the example depreciation methods on the Book-Tax page in the Asset Book Definition component, the Depreciation page in the Asset Profiles component, or the Depreciation Information page in the Asset ExpressAdd component.

 Using the Extended Depreciation Worksheet
Using the Extended Depreciation WorksheetThe 2007 Japanese Tax Reform affects not only assets that are placed in service after March 31, 2007 but also increases the depreciation basis and expands the depreciation period for those fully depreciated assets that are using the J1 and J2 depreciation methods. As a result, those depreciable assets acquired before April 1, 2007 are allowed, after having depreciated to the final depreciable limit, to depreciate the existing salvage value to the memorandum value of 1 JPY in five years using the Straight Line method.
Use the Extended Depreciation Worksheet to apply the extended depreciation calculation to assets after they have reached the depreciation limit under the J1 and J2 depreciation methods. You can also identify assets that qualify for the extended depreciation using the Extended Depreciation Worksheet.
Access the Extended Depreciation page (Asset Management, Depreciation, Processing, Extended Depreciation).
Enter the required fields Business Unit, Book Name, and Method to retrieve assets that are candidates for extended depreciation (those assets depreciated using the J1 and J2 methods and are fully depreciated up to 95% of asset cost). You can also search by ChartField by clicking the ChartField Search Criteria link or use a date range to retrieve assets whose original transaction dates fall within the given period.
The Transaction Information section relates to the information needed to perform the extension of the asset useful life. It is applicable to the assets in the Results section. The Transaction Date should match the date that depreciation resumes for extended depreciation. The Life End Date field shows the calculated date in which the depreciation activity stops, including the additional period due to rounding down the remaining depreciation.
Note. It is important to run the Depreciation Reporting Table load process (AMDPREPT) as a prerequisite to retrieve fully depreciated assets from the Extended Depreciation page.
See Setting Up Depreciation Processing.

 Using Special Depreciation and Increased Depreciation
Using Special Depreciation and Increased Depreciation
PeopleSoft Asset Management supports special depreciation (initial and accelerated) and increased depreciation used in Japan. This table shows the types of special depreciations and their associated accounting methods, depreciation calculations, and additional notes as appropriate:
|
Depreciation Method |
Type |
Accounting Method |
Depreciation Calculation |
Notes |
|
Special |
Initial |
Expense |
Acquisition cost * special depreciation rate |
Book the initial special depreciation amount as the depreciation amount, and add it to the standard depreciation amount. |
|
Special |
Initial |
Reserve/Allowance |
Acquisition cost * special depreciation rate |
Do not add the initial special depreciation amount to the standard depreciation amount. |
|
Special |
Accelerated |
Expense |
Standard depreciation amount * accelerated depreciation rate |
Book the accelerated depreciation amount as the depreciation amount, and add it to the standard depreciation amount. |
|
Special |
Accelerated |
Reserve/Allowance |
Standard depreciation amount * accelerated depreciation rate |
Do not add the accelerated depreciation amount to the standard depreciation amount. |
|
Increased |
NA |
NA |
Standard depreciation amount * increased depreciation rate |
For the initial special depreciation and accelerated depreciation rate, specify the useful life in years and the depreciation rate on the Depreciation Terms Definition page.
For the increased depreciation rate, enter the specific rate on the Depreciation Details page.
See Processing Asset Depreciation.
See Understanding Depreciation Calculations.

 Using Advanced Depreciation
Using Advanced Depreciation
You can also use advanced depreciation for Japan. This table shows the accounting methods that you can use with advanced depreciation:
|
Accounting Method |
Action |
|
Expense |
Adds a cost line to the Corporate and Tax book for the advanced depreciation amount and enters a negative (–) cost as a compressed amount on the Asset/Cost Adjust Transfer page. |
|
Allowance |
Adds a cost line to the Corporate and Tax book for the advanced depreciation amount and enters a negative (–) cost as a compressed amount on the Asset Cost/Adjust Transfer page. You must select A (allowance) as the cost type. |
|
Reserve |
Adds a cost line to the Corporate and Tax book for the advanced depreciation amount and enters a negative (–) cost as a compressed amount on the Asset Cost Adjust/Transfer page. You must selectR (reserve) as the reserve method. |
When you adopt the advanced depreciation method by using the Allowance or Reserve method, you can verify the allowance or reserve amount for the compressed amount by using the Advanced Depreciation Amount of Advanced Depreciation Reversal Schedule report.

 Using Composite Depreciation
Using Composite Depreciation
Composite depreciation, as practiced in Japan, is supported by calculating the useful life in years or by using the 5 percent retirement method.
Use the Mass Change component to process composite depreciation.
Note. To use the Composite Depreciation method for Japan, you must specify the Corporate and Tax book for Japan and select Japan Composite when you establish asset management business units.
You can add composite depreciable assets and individual assets by using the Asset Basic Information page. When you add composite depreciable assets, you must enter a profile ID, transaction date, and accounting date, and then click the Capitalize button on the Asset Acquisition Details page. When you add individual assets, you must enter the Reporting Lifein periods on the Asset Information page.
After adding composite depreciable assets and individual assets for composite assets, you must capitalize by using the Mass Change template CC-JPN Capitalize Composite.
Calculating the Automatic Useful Life in Years for Composite Depreciable Assets
The total acquisition cost includes the acquisition cost of each composite member asset divided by its respective useful life, calculating the depreciation amount for each composite member asset.
The acquisition costs of each composite member asset are then summed, and the total is divided by the summed depreciation amounts for each composite member asset.
This table displays the depreciation values calculated to find the total depreciation for 20,000,000 of asset costs:
|
Assets |
Acquisition Cost (A) |
Useful Life (B) |
Depreciation Amount (A)/(B) |
|
Asset1 |
1,000,000 |
4 years |
250,000 |
|
Asset2 |
3,000,000 |
5 years |
600,000 |
|
Asset3 |
4,000,000 |
4 years |
1,000,000 |
|
Asset4 |
7,000,000 |
10 years |
700,000 |
|
Asset5 |
5,000,000 |
8 years |
625,000 |
|
Totals |
20,000,000 |
NA |
3,175,000 |
The calculation of composite depreciation useful life is then:
20,000,000 / 3,175,000 = 6.29 or 6 years (composite depreciation useful life)
Using the 5 Percent Retirement Method
When using this method, depreciable composite member assets are retired, and the book value is 5 percent of the acquisition cost of each member asset retired.
Access the Mass Change page, and add the Mass Change Definition JPN Composite Retirement. Composite member assets can be retired by using the mass change template CR-JPN Composite Retirement.
Enter the composite asset ID to be retired in theField Value field. Specify Retire as Fully Depreciated in the Mass Change Field Value field. Generate the SQL, and run the mass change.
See Processing Asset Mass Changes.

 Identifying Collateral Assets
Identifying Collateral Assets
Japanese accounting principles require that assets that are offered as collateral be treated according to financial reporting regulations under commercial law. Collateral assets are identified on the Cost/Asset Information page in the Asset ExpressAdd component as one of these types in compliance with Japanese reporting requirements:
Factory Foundation Mortgage.
Fixed Mortgage.
Mortgage.
Other.
See Adding Assets with the Asset ExpressAdd Component.

 Using Currency Rounding Options
Using Currency Rounding Options
Rounding options are applied to depreciation calculations and asset salvage values. You can select rounding options to be used for depreciation calculations on the Business Unit/Book Definition page in the Establish Business Units - Asset Management Definition component, and for salvage value calculations on the Depreciation page in the Asset Profiles component.
Select a rounding rule, which determines the type of rounding that is performed. Select the Currency rounding type.
Select the rounding precision, rounding factor, and truncation. Round precision is the number of places to the right or left of the decimal point to which the amount or number is rounded. Rounding factor is the number to which the amount is rounded.
See Creating PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units.
See Setting Up Asset Profiles.

 Processing Local Tax Reports
Processing Local Tax Reports
Asset Management supports reporting requirements defined by Japanese local tax laws. The system provides these reports, including all required information for the local depreciable asset tax return:
Depreciable Asset Tax Return (Tax Roll or Depreciable Assets) report (AMLT1000).
Asset Detail (Increased Assets/All Assets) report (AMLT1100).
Asset Detail (Decreased Assets) report (AMLT1200).
To set up local tax reporting:
Define the localization country as Japan.
This enables the business unit information link for Japan. The link appears in the Establish Business Units component. Use the User Preferences component, and set the overall preferences localization country to JPN.
Define business unit information for Japan.
This defines the corporate and tax default books for Japan, as well as enables advanced depreciation, composite asset functionality, and local tax usage. Specify the corporate and tax book that you use for Japan when you establish asset management business units, and select the Use JPN Local Tax check box.
Define owner information definition for Japanese assets.
This defines the information needed to process your local tax return.
Define local tax information in the Asset Information component.
Define the local tax return processing information.
To run the reports:
Process the theoretical net book value and assessment value calculation. (Theoretical NBV is not needed since 2009, but still available for historical reporting).
Process local tax reports.
Defining Local Tax Return Information
Access the Return Information page (Set Up Financials/Supply Chain, Product Related, Asset Management, Taxes, Return Information Defn. - JPN, Return Information Defn. - JPN).
Select an owner ID. Enter an owner code, capital amount (in millions of yen), recipient name of the taxation office where the return is filed, business category, and the year and month that the company commenced business.
Enter address information for up to three branch offices within the same city, district, or town (place of tax payment).
Note. If a branch office is located at the same address that is defined on the Owner Information page, you can leave these fields blank.
|
Tax Exception |
Select if you have assets to apply to the special treatment of the taxation standard. |
|
Special/Advanced Depreciation |
Select if you have assets to be applied to special depreciation under the Special Taxation Measures Law, or to be applied to advanced depreciation under Articles 42 to 50 and Article 142 of the Corporation Tax Law, or from Article 42 to 44 and Article 165, or Article 58 of the Tax on Income Law. |
|
Tax Free Asset |
Select if you have assets without taxation. |
|
Life Reduction |
Select if you have assets that have been applied a shorter useful life approved by the Director or the District Tax Office under the Corporate Tax Law − Govt. Order 57-1 and Tax on Income − Govt. Order 130-1. |
|
Increase Depreciation Notice |
Select if you have assets that have been submitted on a detailed statement for increased depreciation to the tax office under the Corporation Tax Law − Govt. Order 60 and Tax on Income Law − Govt. Order 133. |
|
Blue Returns |
Select if you file a blue return under the Corporation Tax Law, Article 122. |
|
Tax Acct Depr (tax account depreciation) |
Select a depreciation method in tax accounting. |
|
Building Category |
Select the possession classification of the building for the business place. |
|
Reply Person |
Enter the name and telephone number of the accounting representative. |
|
Licensed Tax Accountant |
Enter the name and telephone number of the licensed tax accountant. |
|
Rental Asset |
Select if you have rental assets. |
|
Lessor Name and Telephone |
Enter the name and telephone number of the lessor. |
Use the Notes region to add any relevant descriptions, such as appendixes or remarks, or to identify any attachments.
Entering Asset Local Tax Return Information
Access the Local Tax Return Information page (Asset Management, Asset Transactions, Owned Assets, Basic Add. Click the Local Tax Information Link).
Define the asset as New or Used, and select a local tax office.
Select one of these asset return type options:
Structure
Machinery
Ship
Airplane
Vehicle
Tool
Specify a numerator and denominator for the exception rate.
Specify a theoretical net book value and an assessment value for your information. (Theoretical NBV is not needed since 2009, but still available for historical reporting).
Note. The Theoretical Net Book Value and the Assessment Value fields are not required when you add a newly acquired asset in the current year, but you must enter the asset's assessment value reported in the previous year if you acquired assets in the previous year but added them to Asset Management for the first time.
Calculating Theoretical Net Book Value and Assessment Value
Access the Theoretical NBV and Assessment Value page (Asset Management, Taxes, Calculate Local Taxes, Calculate Amounts JPN).
Note. Theoretical NBV is not needed since 2009, but still available for historical reporting.
Note. Enter the same local tax office code in both fields when you are reporting to a single tax office.
The results of this process populate the LTAX_INFO1_TBL.
Select a range of local tax office codes to be declared for the theoretical net book value and assessment value.
Note. Enter the same local tax office code in both fields when you are reporting to a single tax office.
Specify a return year.
Select one of the Request Local Tax Return options:
|
All |
Include all assets. |
|
Increase |
Include assets added and received by transfer in this fiscal year. |
Changing the Local Tax Office and Asset Return Type
Enter the transaction date on which to change the local tax office and asset return type. Enter the new local tax office code for filing the return.
Select one of these new asset return types:
Structure
Machinery
Ship
Airplane
Vehicle
Tool
Changing the Local Tax Office and Asset Return Type While Transferring Assets
When you transfer assets, the operation process varies according to the transfer scenario. This table displays the various operation processes:
|
Transfer Scenario |
Operation Process |
|
Asset is partially transferred to another local tax office, or the asset return type is changed, or both. |
Use InterUnit Transfer to change the local tax office, or the asset return type, or both. |
|
Asset is fully transferred to another department ID and the local tax office where the return is filed, and the asset return type has changed. |
Use Transfer to change the local tax office or asset return type. |
|
Asset is partially transferred to another department ID and the local tax office where the return is filed, and the asset return type has changed. |
Use InterUnit Transfer to change the local tax office and asset return type. |

 Entering Consumption Tax
Entering Consumption Tax
Asset Management supports Japanese consumption tax on asset sales by using VAT functionality on the asset Retirement page. In addition to entering VAT information, you can enter customer information for asset sales.
See Specifying How VAT Is Calculated for Asset Retirement.
See Establishing PeopleSoft Asset Management Business Units.