| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Solaris Cluster 4.1 Hardware Administration Manual Oracle Solaris Cluster 4.1 |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
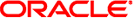
|
Oracle Solaris Cluster 4.1 Hardware Administration Manual Oracle Solaris Cluster 4.1 |
1. Introduction to Oracle Solaris Cluster Hardware
2. Installing and Configuring the Terminal Concentrator
3. Installing Cluster Interconnect Hardware and Configuring VLANs
Interconnect Requirements and Restrictions
Cluster Interconnect and Routing
Cluster Interconnect Speed Requirements
Ethernet Switch Configuration When in the Cluster Interconnect
Requirements When Using Jumbo Frames
Requirements and Restrictions When Using Sun InfiniBand from Oracle in the Cluster Interconnect
Requirements for Socket Direct Protocol Over an Oracle Solaris Cluster Interconnect
Installing Ethernet or InfiniBand Cluster Interconnect Hardware
How to Install Ethernet or InfiniBand Transport Cables and Transport Junctions
4. Maintaining Cluster Interconnect Hardware
5. Installing and Maintaining Public Network Hardware
6. Maintaining Platform Hardware
7. Campus Clustering With Oracle Solaris Cluster Software
Oracle Solaris Cluster software supports the use of private interconnect networks over switch-based virtual local area networks (VLANs). In a switch-based VLAN environment, Oracle Solaris Cluster software enables multiple clusters and nonclustered systems to share an Ethernet transport junction (switch) in two different configurations.
Note - Even if clusters share the same switch, create a separate VLAN for each cluster.
By default, Oracle Solaris Cluster uses the same set of IP addresses on the private interconnect. Creating a separate VLAN for each cluster ensures that IP traffic from one cluster does not interfere with IP traffic from another cluster. Unless you have customized the default IP address for the private interconnect, as described in How to Change the Private Network Address or Address Range of an Existing Cluster in Oracle Solaris Cluster System Administration Guide, create a separate VLAN for each cluster.
The implementation of switch-based VLAN environments is vendor-specific. Because each switch manufacturer implements VLAN differently, the following guidelines address Oracle Solaris Cluster software requirements with regard to configuring VLANs with cluster interconnects.
You must understand your capacity needs before you set up a VLAN configuration. You must know the minimum bandwidth necessary for your interconnect and application traffic.
For the best results, set the Quality of Service (QOS) level for each VLAN to accommodate basic cluster traffic and the desired application traffic. Ensure that the bandwidth that is allocated to each VLAN extends from node to node.
To determine the basic cluster traffic requirements, use the following equation. In this equation, n equals the number of nodes in the configuration, and s equals the number of switches per VLAN.
n (s-1) x 10Mb
Interconnect traffic must be placed in the highest-priority queue.
All ports must be equally serviced, similar to a round robin or first-in, first-out model.
You must verify that you have correctly configured your VLANs to prevent path timeouts.
The first VLAN configuration enables nodes from multiple clusters to send interconnect traffic across one pair of Ethernet transport junctions. Oracle Solaris Cluster software requires a minimum of one transport junction, and each transport junction must be part of a VLAN that is located on a different switch. The following figure is an example of the first VLAN configuration in a two-node cluster. VLAN configurations are not limited to two-node clusters.
Figure 3-3 First VLAN Configuration
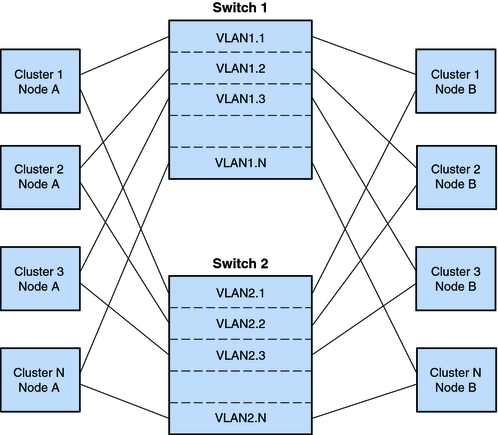
The second VLAN configuration uses the same transport junctions for the interconnect traffic of multiple clusters. However, the second VLAN configuration has two pairs of transport junctions that are connected by links. This configuration enables VLANs to be supported in a campus cluster configuration with the same restrictions as other campus cluster configurations. The following figure illustrates the second VLAN configuration.
Figure 3-4 Second VLAN Configuration