Query Database (Aggregate Storage)
Click here for non-aggregate storage version
Get advanced information about the current state of the database.
Minimum permission required: Read. This statement requires the database to be started.
Syntax
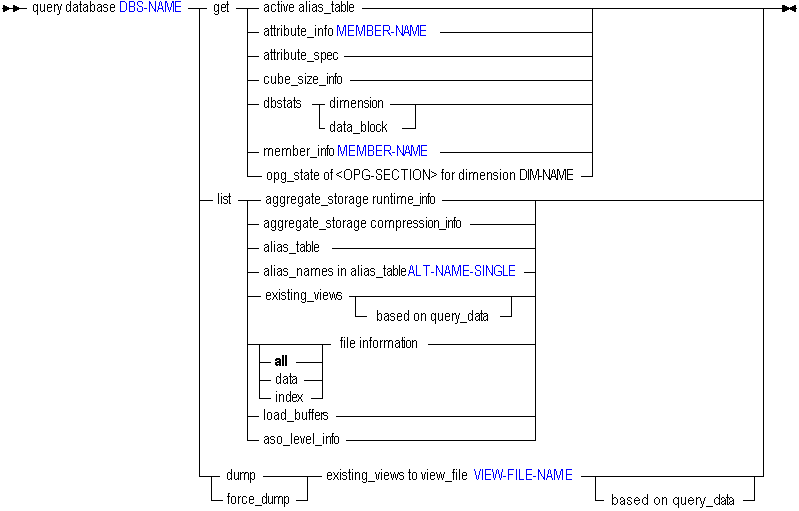
You can query for database information in the following ways using query database:
| Keyword | Description | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
get active alias_table | Display the active alias table for the user issuing the statement. | ||||||||||||||||
get attribute_info | Get attribute member, dimension, and name information for the specified attribute member. | ||||||||||||||||
get attribute_spec | Display the current attribute specifications for the database. These specifications include attribute member name format, Attribute Calculation dimension member names, Boolean and date member names, and numeric range specifications. These settings are defined in Outline Editor. | ||||||||||||||||
get cube_size_info | Display information about input data size, aggregated data size, and number of queries tracked (when query tracking is enabled). This statement returns the output listed in the following table:
| ||||||||||||||||
get dbstats dimension | Get information about dimensions. The index_type field values are numeric, and translate as follows: 0 Dense 1 Sparse 3 None (database is aggregate storage) | ||||||||||||||||
get dbstats data_block | Get information about data blocks. The information returned has little relevance to aggregate storage databases. | ||||||||||||||||
get member_info <MEMBER-NAME> | Get information on a specific member. Output The unary_type field values are numeric, and translate as follows: 0 Add 1 Subtract 2 Multiply 3 Divide 4 Percent 5 NoRollUp The member_tag_type field values translate as follows: 0 SkipNone 16384 SkipMissing 32768 SkipZero 49152 SkipBoth 1 BalFirst 2 BalLast 4 TwoPass 8 Average 64 Expense Variations are possible. The field value consists of one of the first four "skip" values plus any/all/none of the last five values. Some examples: 0 SkipNone 77 SkipNone, BalFirst, TwoPass, Average, Expense 16385 SkipMissing and BalFirst The first four "skip" values are base values, and added to them are combinations of 1, 2, 4, 8, and 64. The status field values are hexadecimal, and translate as follows: 0 Normal 1 Never Share 2 Label 4 Refer Share 8 Refer Share (with different name) 16 Implicit share 32 Virtual Member (stored) 64 Virtual Member (not stored) 2048 Attribute 32768 Referred | ||||||||||||||||
get opg_state of member_data | Display outline navigational information (for example, parent, child, or sibling), fixed-length information (for example, the line aggregation symbol or the number of children), and text strings (for example, member names or aliases). See Outline Paging Dimension Statistics for a description of the output. | ||||||||||||||||
get opg_state of member_name_namespace | Display information that matches member names to internal member identifiers (one section per database, thus the information for all dimensions is the same). See Outline Paging Dimension Statistics for a description of the output. | ||||||||||||||||
get opg_state of member_formula | Display all formulas for the dimension. See Outline Paging Dimension Statistics for a description of the output. | ||||||||||||||||
get opg_state of member_UDA | Display all user defined attributes (UDAs) for the dimension. See Outline Paging Dimension Statistics for a description of the output. | ||||||||||||||||
get opg_state of member_UDA_namespace | Display information that matches UDAs to internal member identifiers. See Outline Paging Dimension Statistics for a description of the output. | ||||||||||||||||
get opg_state of attribute_to_base_member_association | Display information that identifies the attribute member associated with each base member of the dimension. See Outline Paging Dimension Statistics for a description of the output. | ||||||||||||||||
get opg_state of member_comment | Display all member comments for the dimension. See Outline Paging Dimension Statistics for a description of the output. | ||||||||||||||||
get opg_state of member_alias_namespace | Display information that matches member alias names to internal member identifiers (one section per alias table, thus the information for all dimensions is the same). See Outline Paging Dimension Statistics for a description of the output. | ||||||||||||||||
list aggregate_storage runtime_info | Display runtime statistics about the aggregate storage database. For a description of the output returned by this statement, see Aggregate Storage Runtime Statistics. | ||||||||||||||||
list aggregate_storage compression_info | Display estimated compression for aggregate storage databases when different dimensions are hypothetically used as the accounts dimension. These estimates can help you choose the best dimension to use as the accounts dimension. In aggregate storage databases, the accounts dimension enables database compression. A good candidate for an accounts dimension is one that optimizes data compression and maintains retrieval performance. This statement returns the following output:
| ||||||||||||||||
list alias_table | Get a list of alias tables that are defined for the database. | ||||||||||||||||
list alias_names in alias_table | List the alias names defined in an alias table. Alias tables contain sets of aliases for member names and are stored in the database outline. Use this grammar to see a list of alias names defined in the specified table. | ||||||||||||||||
list existing_views | Display information about all aggregate views. An aggregate view is a collection of aggregate cells based on the levels of the members within each dimension. The optional based on query_data clause causes the returned query cost information to be based on the collected cost of actual user queries. If this clause is not used, the default assumption is that all possible queries happen with the same probability. To use the based on query_data clause, query tracking must first be enabled. To enable query tracking, use alter database <dbs-name> enable query tracking. For more information about aggregate views, see the Oracle Essbase Database Administrator's Guide. | ||||||||||||||||
list ... file information | Get accurate index and data file information. Provides index and data file names, counts, sizes, and totals, and indicates whether or not each file is presently opened by Essbase. The file size information is accurate. Note that the file size information provided by the Windows operating system for index and data files that reside on NTFS volumes may not be accurate. | ||||||||||||||||
list load_buffers | Display a list and description of the data load buffers that exist on an aggregate storage database. See Using Aggregate Storage Data Load Buffers. | ||||||||||||||||
list aso_level_info | Display the aggregation level count for each real dimension in the outline. Aggregation level count is the total number of aggregation levels in a real dimension (including associated attribute dimensions) that exist on an aggregate storage database. | ||||||||||||||||
dump|force_dump existing views... | Saves existing views of this database to an aggregation script. This action requires a minimum permission of execute (Execute). If the specified script name already exists, you can use the force_dump keyword to overwrite it; otherwise, an error is returned if the file name already exists. If the based on query_data phrase is used, the view selection that is saved will be based on previously collected query-tracking data. You must have enabled query tracking to use this option. For more information about query tracking, see the based on query_data description in execute aggregate selection. See also the Oracle Essbase Database Administrator's Guide. |
Example
query database Asosamp.Sample list load_buffers;
Display a list and description of the data load buffers that exist on Asosamp.Sample.