How to Create ZFS File Systems for Audit Files
The following procedure shows how to create a ZFS pool for audit files, as well as the corresponding file systems and mount point. By default, the /var/audit file system holds audit files for the audit_binfile plugin.
Before You Begin
You must become an administrator who is assigned the ZFS File System Management and ZFS Storage Management rights profiles. The latter profile enables you to create storage pools. For more information, see Using Your Assigned Administrative Rights in Securing Users and Processes in Oracle Solaris 11.2.
-
Determine the amount of disk space that is required.
Assign at least 200 MB of disk space per host. However, how much auditing you require dictates the disk space requirements. Your disk space requirements might be far greater than this figure.
Note - The default class preselection creates files in /var/audit that grow by about 80 bytes for every recorded instance of an event in the lo class, such as a login, logout, or role assumption. -
Create a mirrored ZFS storage pool.
The zpool create command creates a storage pool, that is, a container for the ZFS file systems. For more information, see Chapter 1, Oracle Solaris ZFS File System (Introduction), in Managing ZFS File Systems in Oracle Solaris 11.2 .
# zpool create audit-pool mirror disk1 disk2
For example, create the auditp pool from two disks, c3t1d0 and c3t2d0, and mirror them.
# zpool create auditp mirror c3t1d0 c3t2d0
-
Create a ZFS file system and mount point for the audit files.
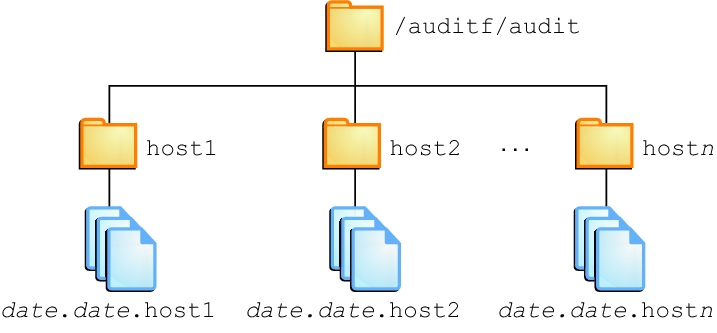
You create the file system and mount point with one command. At creation, the file system is mounted. For example, the following illustration shows audit trail storage that is stored by host name.
Note - If you plan to encrypt the file system, you must encrypt the file system at creation. For an example, see Example 4–1.Encryption requires management. For example, a passphrase is required at mount time. For more information, see Encrypting ZFS File Systems in Managing ZFS File Systems in Oracle Solaris 11.2 .
# zfs create -o mountpoint=/mountpoint audit-pool/mountpoint
For example, create the /audit mount point for the auditf file system.
# zfs create -o mountpoint=/audit auditp/auditf
-
Create a ZFS file system for the audit files.
# zfs create -p auditp/auditf/system
For example, create an unencrypted ZFS file system for the sys1 system.
# zfs create -p auditp/auditf/sys1
- (Optional)
Create additional file systems for audit files.
One reason to create additional file systems is to prevent audit overflow. You can set a ZFS quota per file system, as shown in Step 8. The audit_warn email alias notifies you when each quota is reached. To free space, you can move the closed audit files to a remote server.
# zfs create -p auditp/auditf/sys1.1 # zfs create -p auditp/auditf/sys1.2
-
Protect the parent audit file system.
The following ZFS properties are set to off for all file systems in the pool:
# zfs set devices=off auditp/auditf # zfs set exec=off auditp/auditf # zfs set setuid=off auditp/auditf
-
Compress the audit files in the pool.
Typically, compression is set in ZFS at the file system level. However, because all the file systems in this pool contain audit files, compression is set at the top-level dataset for the pool.
# zfs set compression=on auditp
-
Set quotas.
You can set quotas at the parent file system, the descendant file systems, or both. If you set a quota on the parent audit file system, quotas on the descendant file systems impose an additional limit.
-
Set a quota on the parent audit file system.
In the following example, when both disks in the auditp pool reach the quota, the audit_warn script notifies the audit administrator.
# zfs set quota=510G auditp/auditf
-
Set a quota on the descendant audit file systems.
In the following example, when the quota for the auditp/auditf/system file system is reached, the audit_warn script notifies the audit administrator.
# zfs set quota=170G auditp/auditf/sys1 # zfs set quota=170G auditp/auditf/sys1.1 # zfs set quota=165G auditp/auditf/sys1.2
-
Set a quota on the parent audit file system.
-
For a large pool, limit the size of the audit files.
By default, an audit file can grow to the size of the pool. For manageability, limit the size of the audit files. See Example 4–3.
To comply with site security requirements, the administrator performs the following steps:
-
Creates, if necessary, a new ZFS pool to store the encrypted audit logs.
-
Generates an encryption key.
-
Creates the audit file system with encryption turned on to store the audit logs, as well as sets the mount point.
-
Configures auditing to use the encrypted directory.
-
Refreshes the audit service to apply the new configuration settings.
# zpool create auditp mirror disk1 disk2 # pktool genkey keystore=file outkey=/filename keytype=aes keylen=256 # zfs create -o encryption=aes-256-ccm \ -o keysource=raw,file:///filename \ -o compression=on -o mountpoint=/audit auditp/auditf # auditconfig -setplugin audit_binfile p_dir=/audit/ # audit -s
You must back up and protect the file where the key is stored, such as filename in the example.
When the administrator creates additional file systems under the auditf file system, these descendant file systems are also encrypted.
Example 4-2 Setting a Quota on the /var/audit DirectoryIn this example, the administrator sets a quota on the default audit file system. When this quota is reached, the audit_warn script warns the audit administrator.
# zfs set quota=252G rpool/var/audit