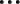
Process Tasks in Parallel with a Parallel Action
You can use a parallel action to process tasks in parallel to improve integration performance and response times. A parallel action allows the path of an integration to be split into multiple branches. Each branch is processed in parallel due to their independence from each other. Messages are sent to each service endpoint in parallel.
When all tasks are completed, all branches are automatically synchronized and merged at their termination points in the parallel action and the main path of the integration is resumed. Any variables created inside the parallel branches (for example, invoke responses) are available for use in the main path.
Want to see a video demo of the parallel action?
Use Cases
- An order processing integration contains individual tasks for checking inventory, customer credit, and legal constraints. These tasks are processed in parallel to ensure a better response time.
- An integration obtains the lowest price for an item from suppliers. The integration checks three suppliers for prices and takes the best offer. The three price checks are done in parallel because they are independent of each other. Once the three suppliers have responded, the branches are terminated. The three prices are compared to identify the lowest. The integration then continues its main path by placing the order with that supplier.
- An integration processes an incoming order from both an inventory and legal perspective (for example, can the product be shipped to the customer's country). Both checks are done in parallel.
Guidelines and Restrictions
- You can create a maximum of five branches
to a parallel action. If you attempt to create a sixth branch by selecting
Actions
 , and then Add on the parallel action, the
selection is disabled.
, and then Add on the parallel action, the
selection is disabled.
- There is no limit to the number of parallel actions you can include in an integration.
- Synchronous and asynchronous integrations are supported.
- You cannot add a parallel action inside another parallel action.
- Parallel actions can be used in application integrations and schedule integrations.
- Only map, scope, switch, logger, JavaScript, B2B, and notification actions and invoke connections are supported in a parallel action branch.
- You can add parallel actions to the branches of a pick action.
- You can add parallel actions inside scope and switch actions.
- Nesting of parallel actions in for-each actions, while actions, or stage file actions with chunking is not supported.
- No independent branch-specific fault handling is supported. You can catch faults at the integration level with a global fault handler.
- Synchronization of global variables is not supported.
- Branch-specific timeouts are not supported.
Design Time Behavior
The following example provides a high-level overview of how to design a specific parallel action. This is just one example of parallel action use.
- Add a parallel action to an integration in either of the following
ways:
- On the side of the canvas, click
Actions
 and drag the Parallel action to the
appropriate location.
and drag the Parallel action to the
appropriate location.
- Click
 at the location where you want to add the parallel action, then
select Parallel.
at the location where you want to add the parallel action, then
select Parallel.
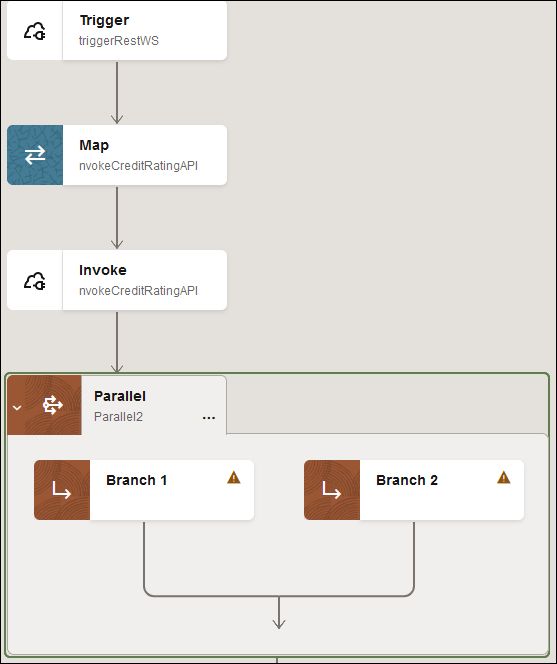
A parallel action with two branches is created.
- On the side of the canvas, click
Actions
- Select Actions
 to perform the following tasks.
to perform the following tasks.
- Edit: Change the name of the parallel action.
- Add: Add more branches. You can add a maximum of five branches.
- Delete: Delete the parallel action.
- Collapse/Expand: Collapse or expand the parallel action.
- Cut: Cut the parallel action and paste it elsewhere in the integration. You can also cut and paste existing maps/invokes into the new parallel branches to make them process in parallel. You cannot cut an individual branch of a parallel action and paste it into another parallel action.
For this example, a third branch is added.
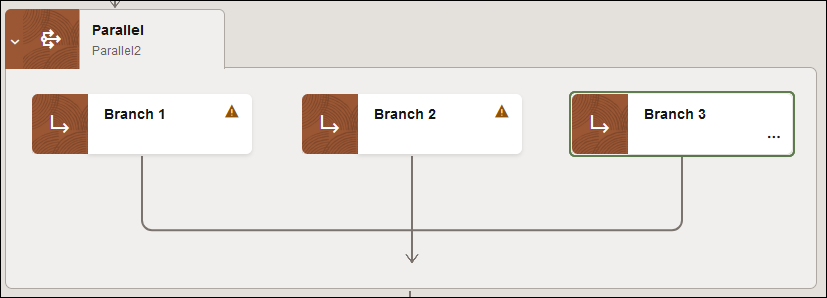
For this example, the three branches are designed to obtain loan offers from three service endpoints and then select the best one.
- Add and configure three REST Adapter connections to invoke the
following service endpoints. At runtime, all three loan service endpoints are
invoked in parallel to identify their specific loan offers.
- American Loan
- United Loan
- Star Loan
- In the mapper for each invoke action, map your SSN to the loan
application for that service endpoint.
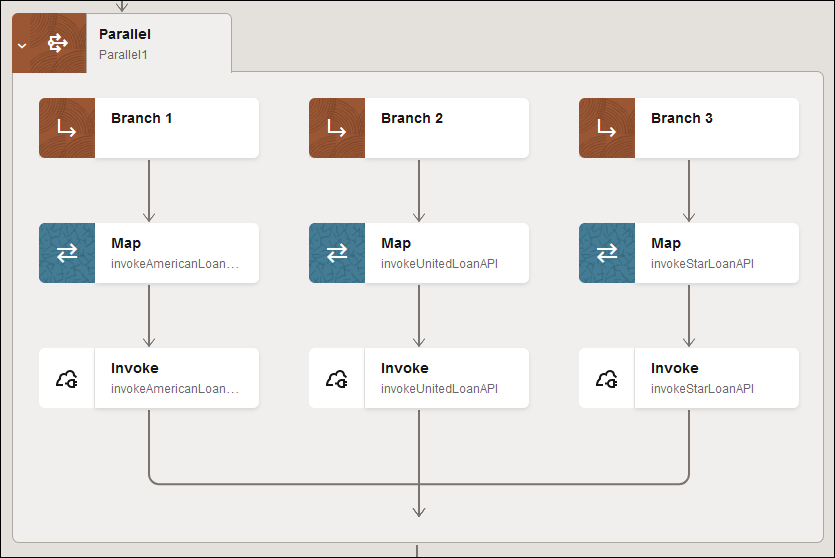
At the bottom, the three branches are synchronized at their termination points and the parallel action rejoins the main branch of the integration. The main integration does not continue until all branches are complete
- Add a switch action to define the routing rules to check for the
best offer returned from the loan service endpoints.

- Define the message in a log action for each switch branch.
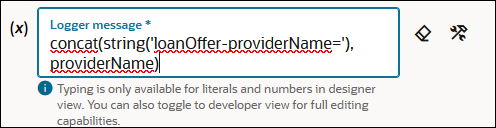
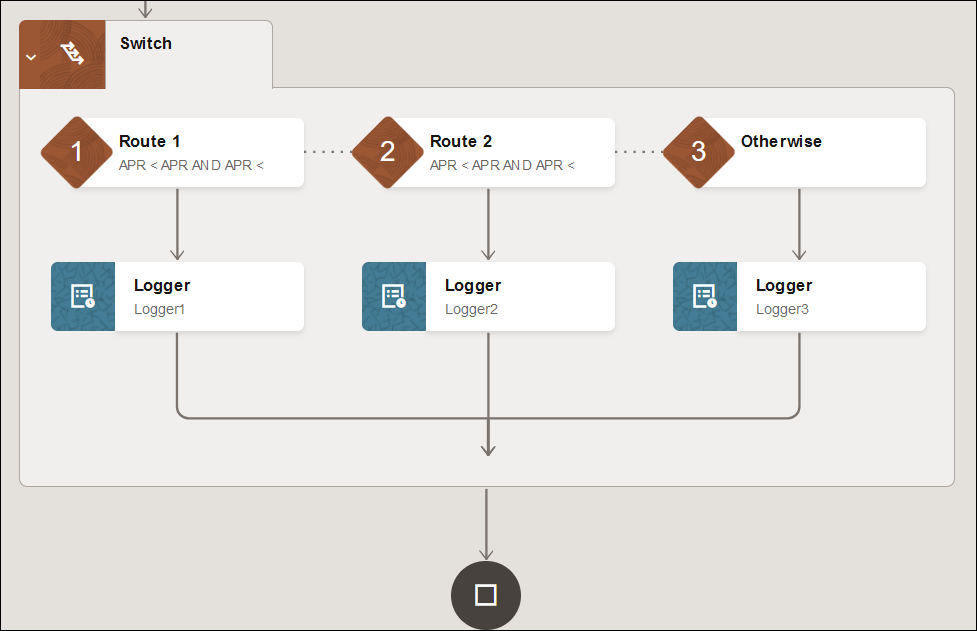
When complete, the integration looks as follows.

The integration is now ready to be activated and invoked.
Runtime Behavior
- One parallel action with two branches
- A second parallel action with three branches
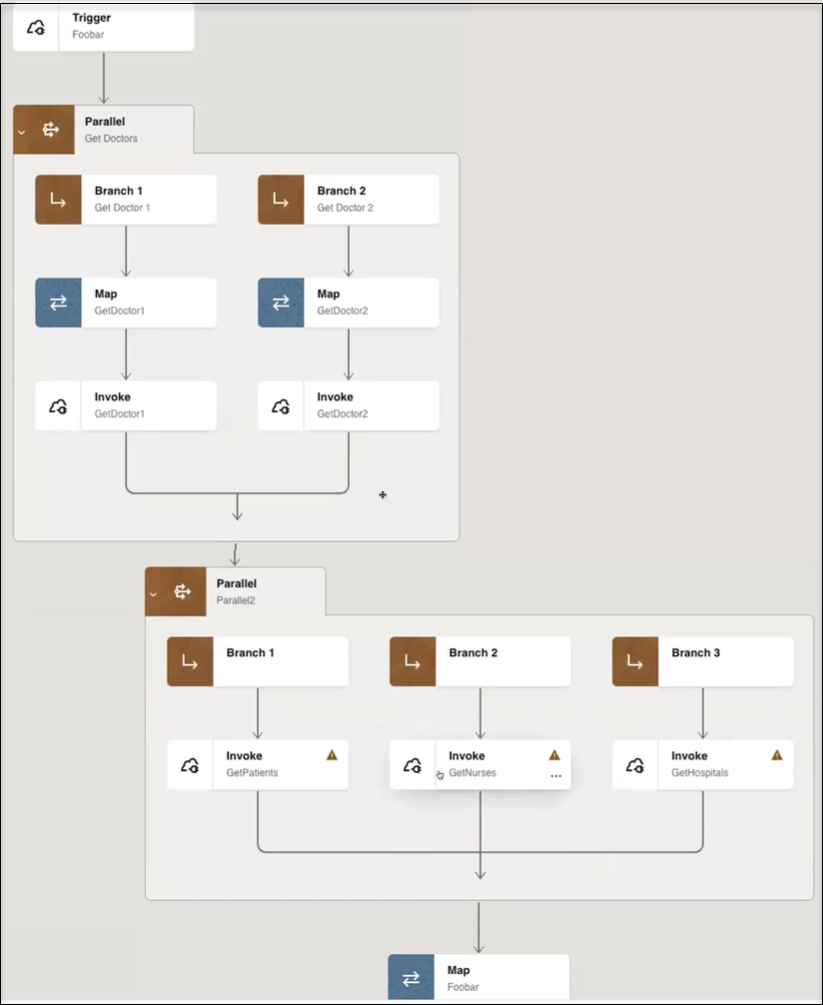
- Invoke an instance of your integration and go to the Instances
page.
During runtime, the activity stream shows both parallel actions and their number of branches. For this example, both parallel actions processed successfully.
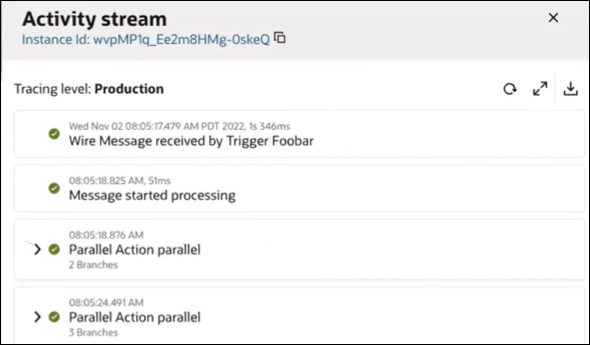
- Expand each branch to view more specific details.