Connect to OCI GoldenGate using a public IP
When you create an OCI GoldenGate deployment, you can select whether it's accessible through a public or private endpoint. This quickstart walks you through the steps to create a deployment with a public endpoint.
Overview
Note:
For Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Federal Government Cloud customers in regions that don't support DNS Zone Management, to enable a public endpoint, Create a Sev 1 Service Request titled, "Create DNS Entry for Public OCI GG Deployment," and include the correct deployment OCID. The support team will ensure that the appropriate DNS record gets created for your deployment.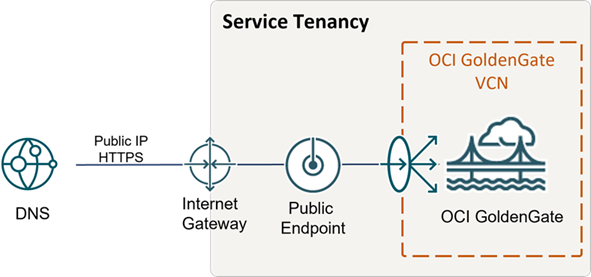
Description of the illustration publicendpoint.png
Before you begin
To successfully complete this quickstart, you need:
- An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure account
- Access to OCI GoldenGate
- The proper policies, quotas, and limits in place for OCI GoldenGate to create a load balancer in your tenancy VCN