Custom CRM Fields as XML Definitions
You can create XML definitions for custom CRM fields as SDF custom objects using SuiteCloud Development Framework (SDF). You can either create a crmcustomfield object in a SuiteCloud project or import a custom CRM field from a NetSuite account into a SuiteCloud project. For information about creating a custom CRM field in a NetSuite account, see the following:
Add custom CRM fields to your CRM records to gather information specific to your business needs.
These CRM records include:
-
task records
-
phone call records
-
campaign records
-
case records
-
solution records
-
event records
After a crmcustomfield object is deployed to an account, a custom CRM field is created. The field appears on the CRM records that you applied the object to.
Setting Values on the crmcustomfield SDF Custom Object
Provide a readable script ID attribute by using the underscore followed by a meaningful name for the SDF custom object. NetSuite automatically adds a custevent prefix that indicates the type of field, for example, custevent_mynewfield.
The following fields are required for crmcustomfield objects:
-
label- Specifies the label for the custom field. Thelabelis the text that your users see as the name of the custom field when it is displayed on the record. -
fieldtype- Specifies the type of custom field. For more information about the possible values offieldtype, see generic_customfield_fieldtype. -
selectrecordtype (conditional)- Specifies the list or record that contains the items for the custom field. This field is required only when thefieldtypevalue is equal toSELECTorMULTISELECT.
The following XML definition example is a basic crmcustomfield object with the required fields.
<crmcustomfield scriptid="custevent_mynewfield">
...
<fieldtype>SELECT</fieldtype>
<label>SAMPLE CRMFIELD</label>
<selectrecordtype>-103</selectrecordtype>
...
</crmcustomfield>
For more information about possible fields for crmcustomfield objects, see crmcustomfield.
If you include any SDF custom objects, files, or scripts in your fields, you must define the dependencies for them in your SuiteCloud project's manifest. For more information, see SDF Custom Object Dependencies in SuiteApps.
To index a custom field to be included in global search, set the globalsearch field value to T. The globalsearch field can equal to T only if the following field conditions are met:
-
storevalueequals toT -
fieldtypeequals to one of the following:-
CURRENCY -
FLOAT -
EMAIL -
TEXT -
HELP -
URL -
INLINEHTML -
INTEGER -
PERCENT -
PHONE -
TEXTAREA
-
You cannot index a custom field for global search if any of your searchlevel field values equal to 0.
Embedding Structured Fields Within a crmcustomfield SDF Custom Object
You can create custom filters for your custom field by embedding customfieldfilter structured fields within the crmcustomfield SDF custom object. You can also customize the default access that a role has to the custom field by embedding roleaccess structured fields within the object.
For more information about the possible fields to define for these structured fields, see the following:
To view a full XML definition example for a crmcustomfield object, see Example of a crmcustomfield SDF Custom Object.
Custom Field Filters
You can add custom field filters to a list/record or multiple select custom field to filter the choices available in that custom field on records and transactions. In SDF, you can use custom field filters by embedding customfieldfilter structured fields within a custom field object.
Filtering can apply only when the fieldtype value of your custom field object is equal to SELECT or MULTISELECT. It does not apply to custom lists, meaning if you include customfieldfilter structured fields, your selectrecordtype value cannot equal a custom list scriptid.
customfieldfilters is the parent element and customfieldfilter is the child element. You can include multiple customfieldfilter child elements within the parent.
The fldfilter subfield specifies a standard field on the list/record that you entered for the selectrecordtype field. The fldfilter subfield is required. For more information about the supported fields and values for customfieldfilter structured fields, see customfieldfilter.
When an object with a customfieldfilter structured field is deployed to a target account, the Sourcing & Filtering subtab of the custom field record is populated with the field values specified by the structured field. The choices available to users in a record or transaction for that custom field are tailored by the filter settings from the structured field.
Here is an example of a custom item field configuration page in NetSuite with filters set for the field:
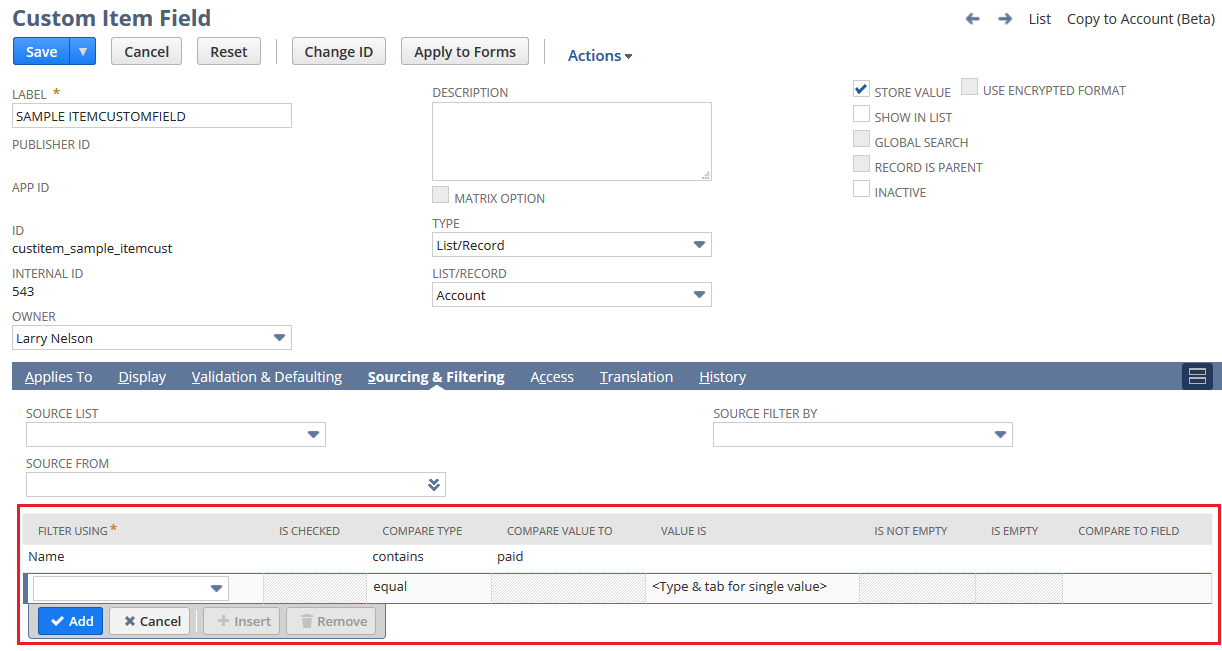
If you change the field type or the list/record for a field that is used for sourcing or filtering on other custom fields, all sourcing and filtering based on the field is removed.
Additionally, you can define custom field filters in NetSuite. For more information, see Setting Filtering Criteria.
Example of a customfieldfilter Structured Field
The following XML definition example is a customfieldfilter structured field embedded within an itemcustomfield object whose fieldtype equals SELECT. After this object is deployed to the target account, a custom item field labeled SAMPLE ITEMCUSTOMFIELD appears on the Main tab of all Inventory item records. The fldfiltercomparetype equals LIKE and fildfilterval equals paid. Therefore, the field's dropdown list is filtered to display only accounts that contain 'paid' in the account name.
<itemcustomfield scriptid="custitem_sample_itemcust">
<appliestoinventory>T</appliestoinventory>
<fieldtype>SELECT</fieldtype>
<label>SAMPLE ITEMCUSTOMFIELD</label>
<selectrecordtype>-112</selectrecordtype>
...
<customfieldfilters>
<customfieldfilter>
<fldcomparefield></fldcomparefield>
<fldfilter>STDRECORDACCOUNTACCTNAME</fldfilter>
<fldfilterchecked></fldfilterchecked>
<fldfiltercomparetype>LIKE</fldfiltercomparetype>
<fldfilternotnull>F</fldfilternotnull>
<fldfilternull>F</fldfilternull>
<fldfiltersel></fldfiltersel>
<fldfilterval>paid>
</customfieldfilter>
</customfieldfilters>
...
</itemcustomfield>
Role Accesses
In SDF, you can control how roles access the information in custom fields by embedding roleaccess structured fields within a custom field object. The accesses that you specify determines how the custom field can be accessed on the record or through search results and reports. This helps you to maintain the security of your business information.
roleaccesses is the parent element and roleaccess is the child element. You can include multiple roleaccess child elements within the parent.
After an object with a roleaccess structured field is deployed to a NetSuite account, the Role section under the Access subtab of the custom field record is populated with the access level values of the fields specified by the structured field.
Here is an example of a custom item field configuration page in NetSuite with access levels set for a role:
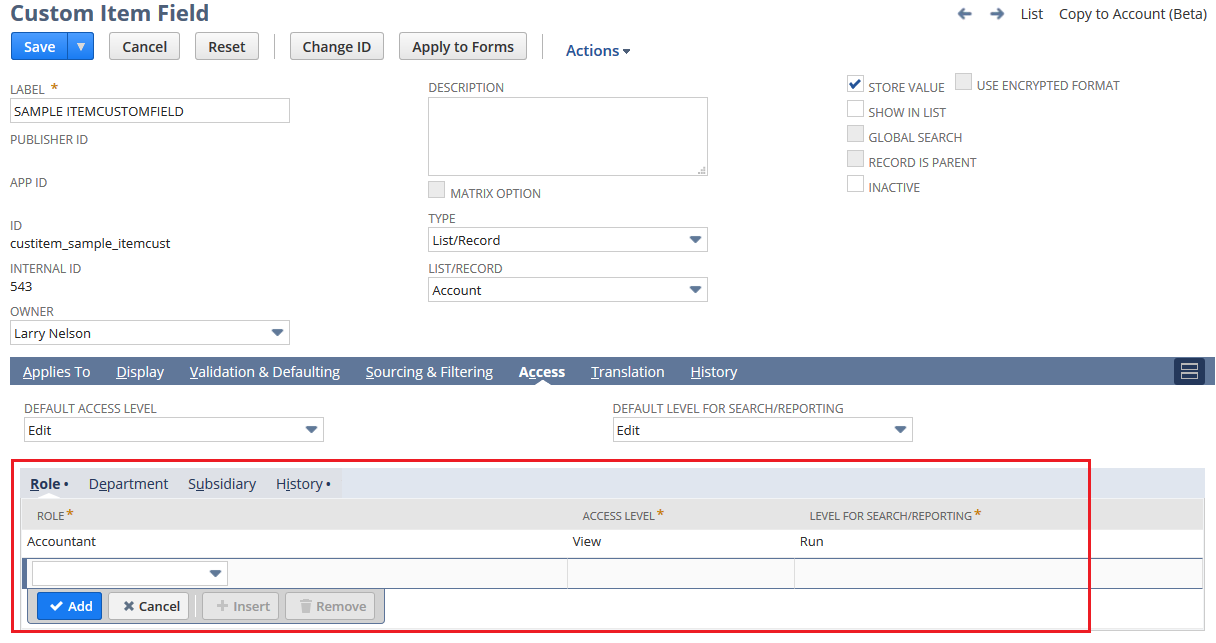
The following subfields are required for roleaccess structured fields:
-
role- Specifies the role. -
accesslevel- Specifies the access level granted to the role for the custom field object.Possible access level values:
-
0 - None
-
1 - View
-
2 - Edit
-
-
searchlevel- Specifies the access level granted to the role for the custom field object through search results and reports.Possible access level values:
-
0 - None
-
1 - Run
-
2 - Edit
-
For more information about the supported fields and values for roleaccess, see roleaccess.
Additionally, you can define role accesses to custom fields from a NetSuite account. For more information, see Restricting Access to Custom Fields.
Example of a roleaccess Structured Field
The following XML definition example is a roleaccess structured field embedded within a itemcustomfield object. In this example, the accesslevel for the Accountant role equals 1 and the searchlevel equals 1. Therefore, the role's access to the field is set to View and the access level through searching and reporting is set to Run.
<itemcustomfield scriptid="custitem_sample_itemcust">
<appliestoinventory>T</appliestoinventory>
<fieldtype>SELECT</fieldtype>
<label>SAMPLE ITEMCUSTOMFIELD</label>
<selectrecordtype>-112</selectrecordtype>
...
<roleaccesses>
<roleaccess>
<accesslevel>1</accesslevel>
<role>ACCOUNTANT</role>
<searchlevel>1</searchlevel>
</roleaccess>
</roleaccesses>
...
</itemcustomfield>
Example of a crmcustomfield SDF Custom Object
The following XML definition example is for a crmcustomfield object. After this SDF custom object is deployed to the target account, a custom item field labeled SAMPLE CRMFIELD appears on the System Information subtab of all CRM records that the object is applied to. In this example, the object applies to phone call records. The fieldtype equals SELECT. Therefore, a value for selectrecordtype is required.
<crmcustomfield scriptid="custevent_sample_crm">
<accesslevel>2</accesslevel>
<appliesperkeyword>F</appliesperkeyword>
<appliestocampaign>F</appliestocampaign>
<appliestocase>F</appliestocase>
<appliestoevent>F</appliestoevent>
<appliestophonecall>T</appliestophonecall>
<appliestoprojecttask>F</appliestoprojecttask>
<appliestoresourceallocation>F</appliestoresourceallocation>
<appliestotask>F</appliestotask>
<applyformatting>F</applyformatting>
<availableexternally>F</availableexternally>
<checkspelling>F</checkspelling>
<defaultchecked>F</defaultchecked>
<defaultselection></defaultselection>
<defaultvalue></defaultvalue>
<description>Enter a description of this field.</description>
<displayheight></displayheight>
<displaytype>NORMAL</displaytype>
<displaywidth></displaywidth>
<dynamicdefault></dynamicdefault>
<encryptatrest>F</encryptatrest>
<fieldtype>SELECT</fieldtype>
<globalsearch>F</globalsearch>
<help>Enter a brief explanation of the kind of information you want entered in this field.</help>
<isformula>F</isformula>
<ismandatory>F</ismandatory>
<isparent>F</isparent>
<label>SAMPLE CRMFIELD</label>
<linktext></linktext>
<maxlength></maxlength>
<maxvalue></maxvalue>
<minvalue></minvalue>
<onparentdelete>NO_ACTION</onparentdelete>
<parentsubtab></parentsubtab>
<searchcomparefield></searchcomparefield>
<searchdefault></searchdefault>
<searchlevel>2</searchlevel>
<selectrecordtype>-103</selectrecordtype>
<showhierarchy>T</showhierarchy>
<showinlist>F</showinlist>
<sourcefilterby></sourcefilterby>
<sourcefrom></sourcefrom>
<sourcelist></sourcelist>
<storevalue>T</storevalue>
<subtab>CRMSYSTEMINFORMATION</subtab>
<customfieldfilters>
<customfieldfilter>
<fldcomparefield></fldcomparefield>
<fldfilter>STDRECORDLOCATIONNAME</fldfilter>
<fldfilterchecked></fldfilterchecked>
<fldfiltercomparetype>LIKE</fldfiltercomparetype>
<fldfilternotnull>F</fldfilternotnull>
<fldfilternull>F</fldfilternull>
<fldfiltersel></fldfiltersel>
<fldfilterval>warehouse</fldfilterval>
</customfieldfilter>
</customfieldfilters>
<roleaccesses>
<roleaccess>
<accesslevel>0</accesslevel>
<role>ACCOUNTANT</role>
<searchlevel>0</searchlevel>
</roleaccess>
</roleaccesses>
</crmcustomfield>
Related Topics
- Lists, Records, and Fields
- Custom Lists as XML Definitions
- Custom Other Record Fields as XML Definitions
- Custom Item Fields as XML Definitions
- Custom Entity Fields as XML Definitions
- Custom Item Number Fields as XML Definitions
- Custom Transaction Body Fields as XML Definitions
- Custom Transaction Line Fields as XML Definitions
- Custom Transaction Item Option Fields as XML Definitions
- Custom Record Types as XML Definitions
- Custom Segments as XML Definitions
- Custom Transaction Record Types as XML Definitions