4.4 Styling a Map Layer
Spatial Studio allows you to explore different styling options for your map layers, in order to enhance visualization and analysis.
The styling options provided to you may vary depending on the type of data you are mapping.
The following sections describe a few styling techniques for the different data types:
- Applying a Render Style For a Point Layer
- Applying Style for a GeoRaster Layer
- Applying Data-Driven Style to a Map with H3 Aggregations
- Applying Predefined Colors to a Map Layer
- Applying Predefined Symbols to a Map Layer
- Applying Predefined Colors to Symbols
- Applying Custom Map Symbols to a Map Layer
- Applying an Animated Map Symbol to a Map Layer
- Applying Style to a CZML Cesium Map Layer
- Applying Style to a Map Layer Using a GeoJSON URL Dataset
- Setting Selection Tolerance on a Map Layer
- Adding a Pin on a Map
- Applying Map Backgrounds
- Using the Redline Map Tool
Parent topic: Visualization in Oracle Spatial Studio
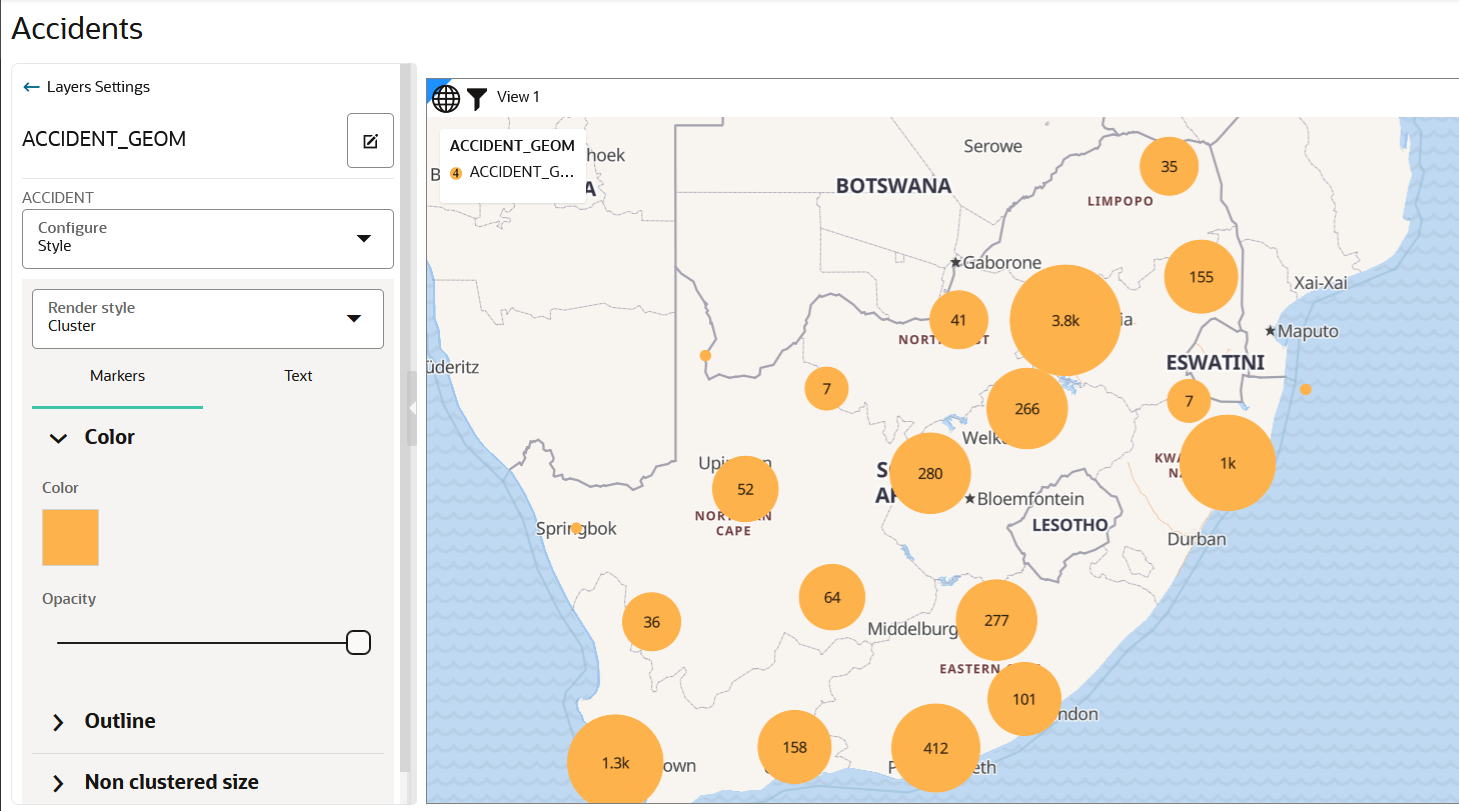
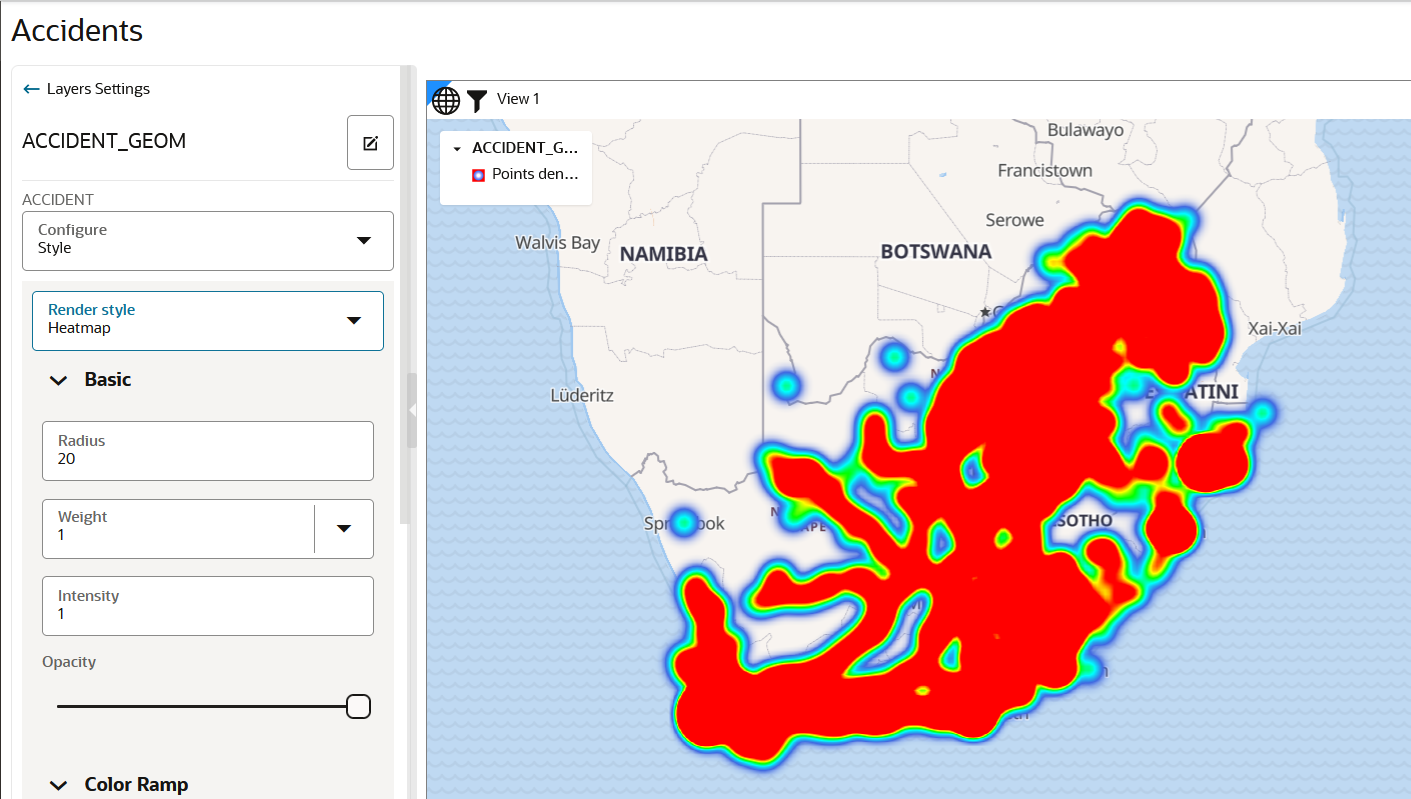
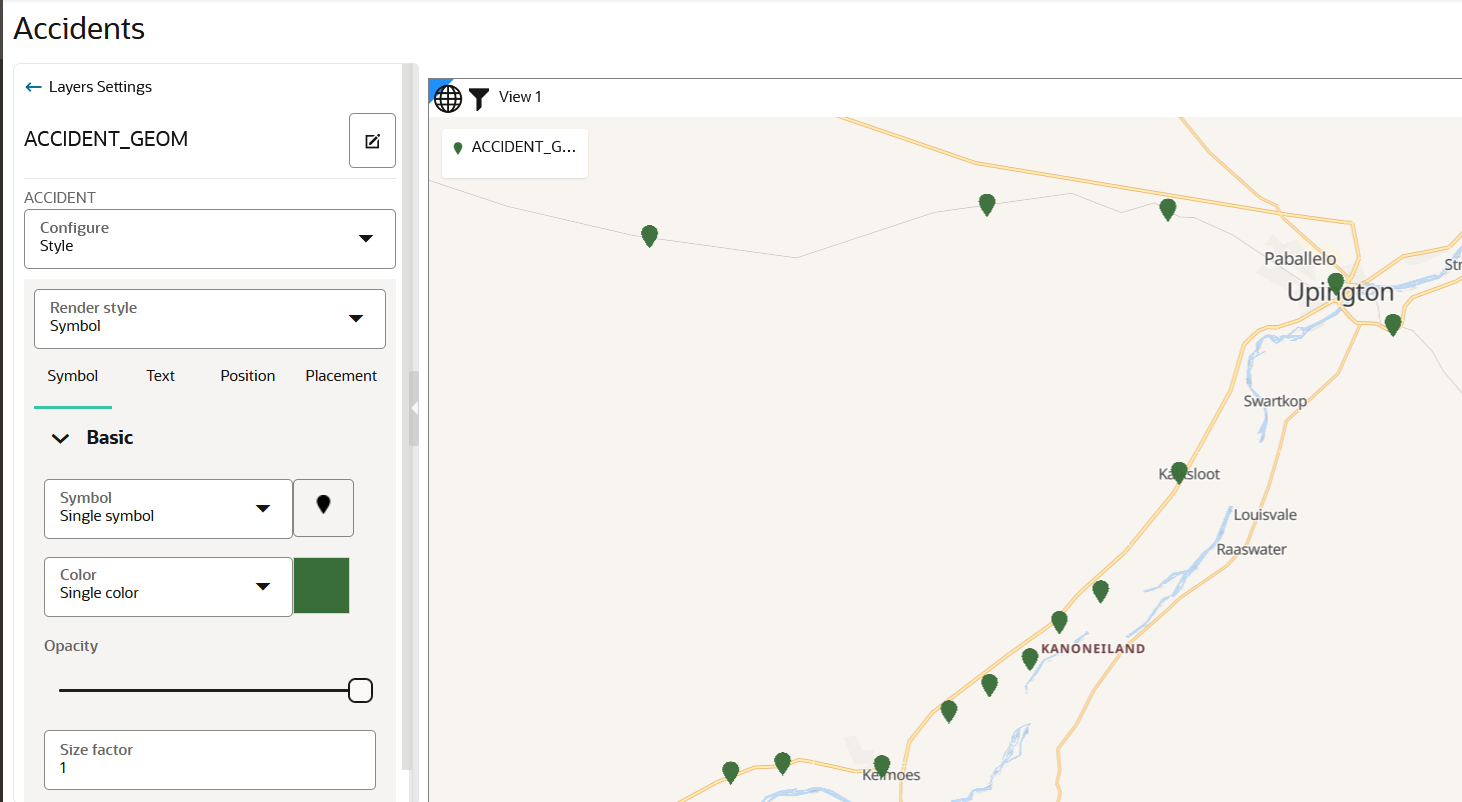
4.4.1 Applying a Render Style For a Point Layer
- Circle (default)
- Symbol
- Heatmap
- Cluster
The following steps enable you to apply your preferred render style option.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
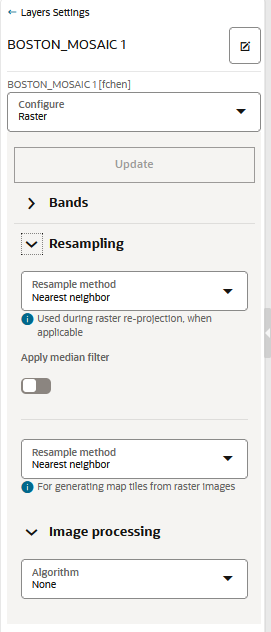
4.4.2 Applying Style for a GeoRaster Layer
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
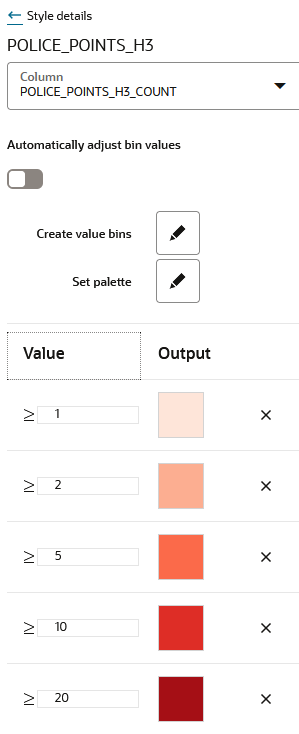
4.4.3 Applying Data-Driven Style to a Map with H3 Aggregations
You can apply different resolutions to your H3 map layer to enhance your visualization.
In case of an H3 aggregation dataset, the hexagonal cells and the distribution of points in these hexagons automatically change at each resolution level, as you zoom in and out of the map. This implies that the color bins for one level might not be the same as for another level.
Spatial Studio provides an option to automatically calculate color bins as you alter your resolutions. You can also turn this option off if you want to test against a set of specific thresholds.
The following steps enable you to apply a data-driven styling option for your H3 map layer.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
4.4.4 Applying Predefined Colors to a Map Layer
Using a column with predefined color codes or values, you can create accurate and consistent choropleth map layers.
You can store a color-coded value in a column of your dataset and then use this column property to color code your map.
The following steps enable you to color code your map layer.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
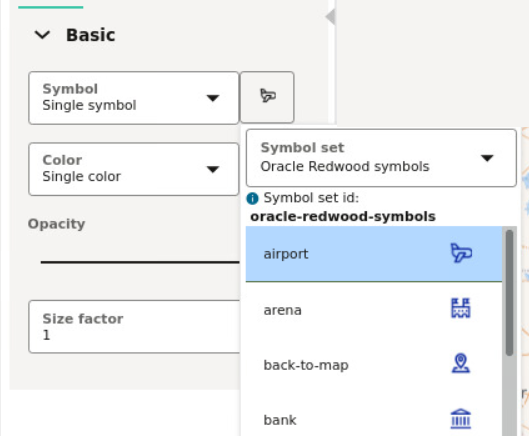
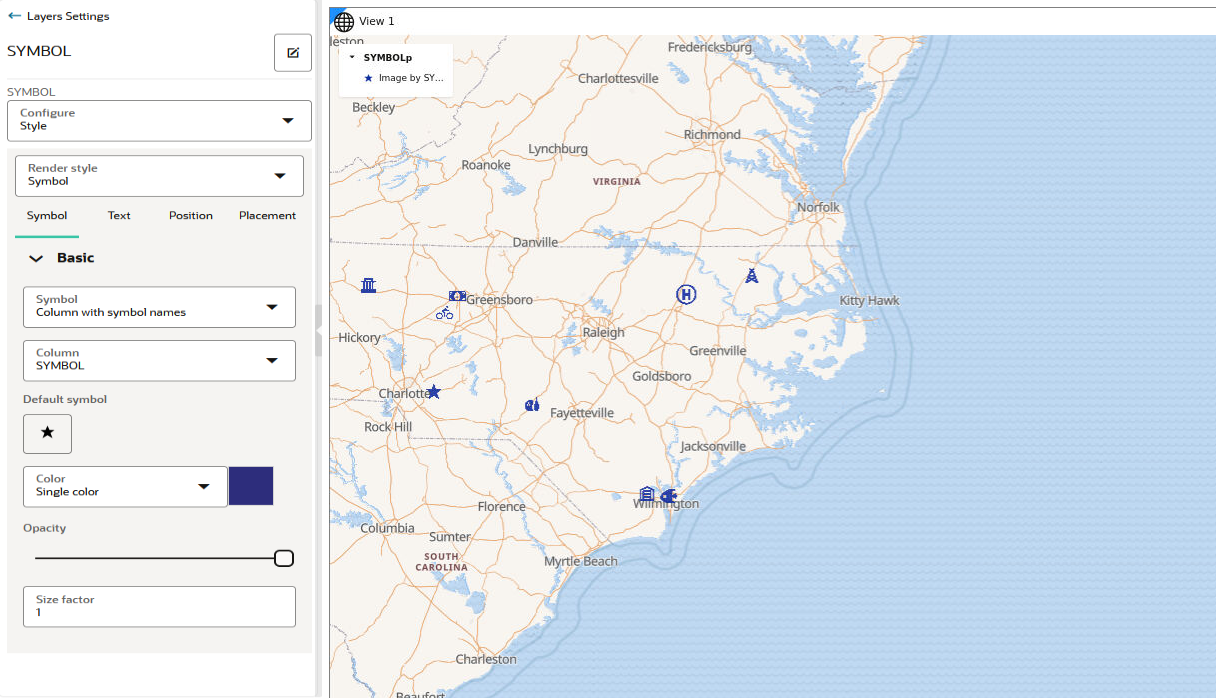
4.4.5 Applying Predefined Symbols to a Map Layer
Using a column with predefined symbol values, you can apply data-driven symbol styling to your map layer.
Symbol set id as
described in the following table:
Table 4-1 Symbol Set
| Symbol Set | Symbol set id |
|---|---|
| Spatial Studio default | studio |
| Oracle Redwood symbols | oracle-redwood-symbols |
| Airfields | airfields |
You can store a symbol name and the symbol set to which it belongs in a column of your dataset and then use this column property to assign symbols to your map.
airport icon as
shown in the following figure:
You must then use oracle-redwood-symbols/airport as the
symbol name in your dataset column. In this case:
oracle-redwood-symbols: is the symbol set idairport: is the name for the icon to be used on the map layer
The following steps enable you to apply data driven symbol styling for your map layer.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
4.4.6 Applying Predefined Colors to Symbols
You can color the symbols on a map layer by using an attribute column of the dataset that contains predefined color codes.
The following steps enable you to color code the symbols on a map layer.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
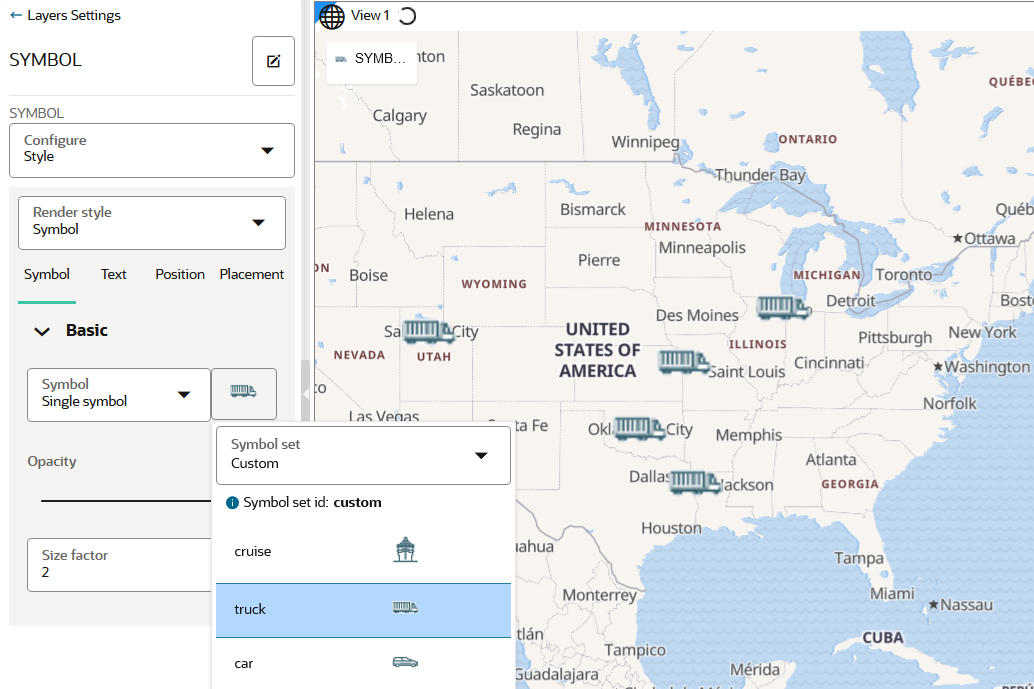
4.4.7 Applying Custom Map Symbols to a Map Layer
You can apply custom map symbols for styling your map layer.
However, note that if a point dataset is being styled by custom symbols, then it can no longer use any of the built-in symbols. Essentially, you cannot mix both custom and built-in symbols on a map layer in the map visualization.
Perform the following steps to style your map layer using custom map symbols.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
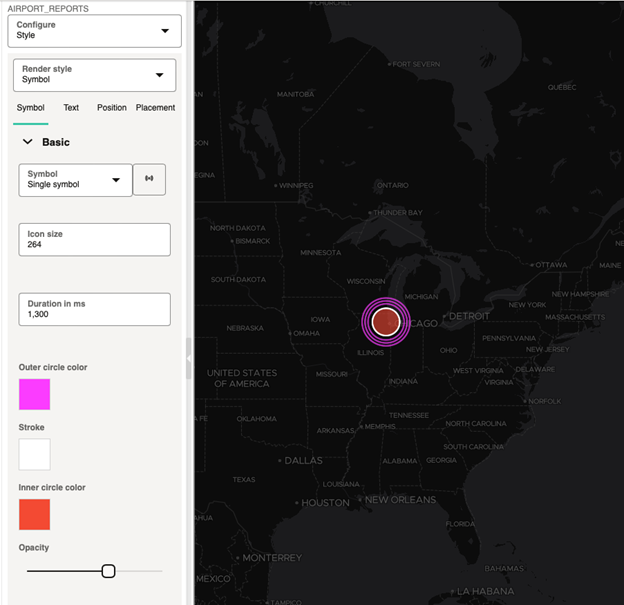
4.4.8 Applying an Animated Map Symbol to a Map Layer
You can apply a circular animating (pulsing) symbol for styling point-type map layers.
Perform the following steps to apply an animating symbol to a map layer.
The new animating symbol is found in the Symbol render style or symbol picker.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
4.4.9 Applying Style to a CZML Cesium Map Layer
When using a CZML dataset in a Cesium map visualization, you can filter on a specific entity value or control the visibility (show or hide) for the displayed entities. Also, you can add an info window to enhance your map interaction.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
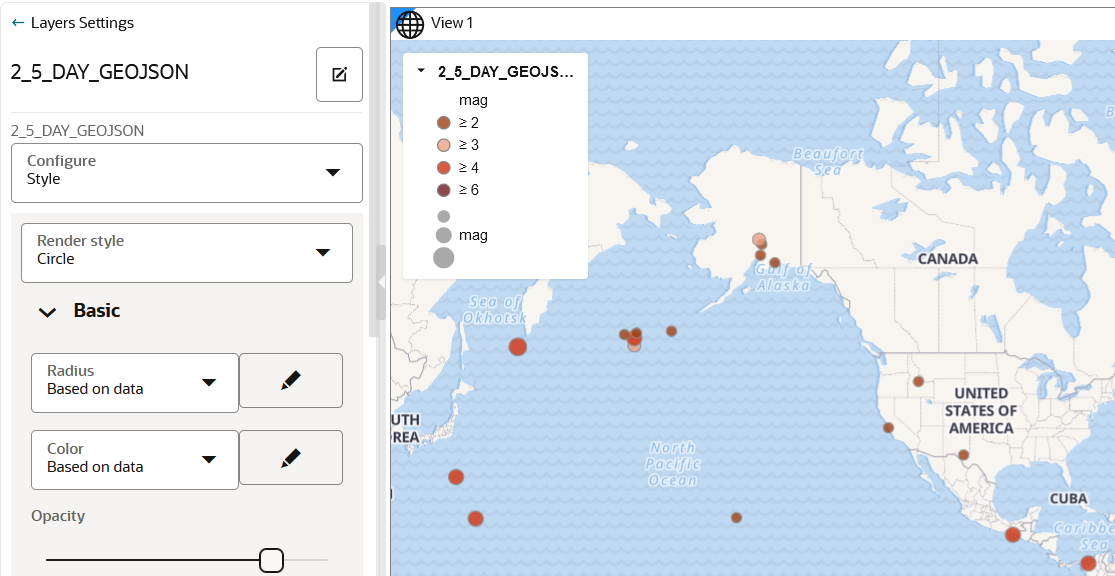
4.4.10 Applying Style to a Map Layer Using a GeoJSON URL Dataset
Spatial Studio supports data-driven styling for your GeoJSON URL dataset map layer. You can access the dataset columns that are sourced from the source URL and apply the desired styling for the map layer.
See Also:
Creating a GeoJSON URL DatasetParent topic: Styling a Map Layer
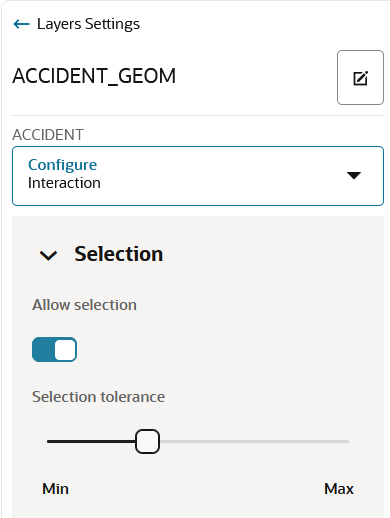
4.4.11 Setting Selection Tolerance on a Map Layer
Spatial Studio allows you to increase or decrease the selection tolerance on a map layer, so that selecting small and linear geometry features is easier.
The following steps enable you to adjust and set the selection tolerance on a map.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
4.4.12 Adding a Pin on a Map
The following steps enable you to inspect the current mouse pointer's latitude and longitude coordinates and pin a location on the map layer.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
4.4.13 Applying Map Backgrounds
Spatial Studio provides ready-to-use map backgrounds to enhance your visualization.
You can select one of the following map backgrounds for your project visualization:
- MapTiler Vector Basemaps
- Oracle Raster Basemaps
- Blank Basemaps
- User-defined Basemaps
As an administrator, you can also register custom basemaps and use them in map visualizations. They may be raster or vector tiles that are typically hosted on third party servers, or they be created using a WMS OGC web service. See Spatial Studio Administration Page for more information on adding basemaps.
The default language for the MapTiler Vector Basemaps is English. However, you can change the language for these vector basemaps. See Configuring a Map Visualization for more information.
The following section describes how to apply a specific map background for your project:
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer
4.4.13.1 Changing Map Backgrounds
The following steps enable you to apply different map backgrounds in your project visualization.
Parent topic: Applying Map Backgrounds
4.4.14 Using the Redline Map Tool
Spatial Studio provides the Redline map tool for drawing and annotating different geometry shapes on your map.
In addition, you can edit, delete, or share these redline drawing sets by exporting it to a GeoJSON file.
Parent topic: Styling a Map Layer