3 Completing Configuration and Starting Connections
This chapter explains how to create and start databases, configure Service Provider contact information, work with key lists, and configure and start NPAC components, EMS components, LSMS components.
Overview
This chapter explains how to create and start databases, configure Service Provider contact information, work with key lists, and configure and start NPAC components, EMS components, LSMS components.
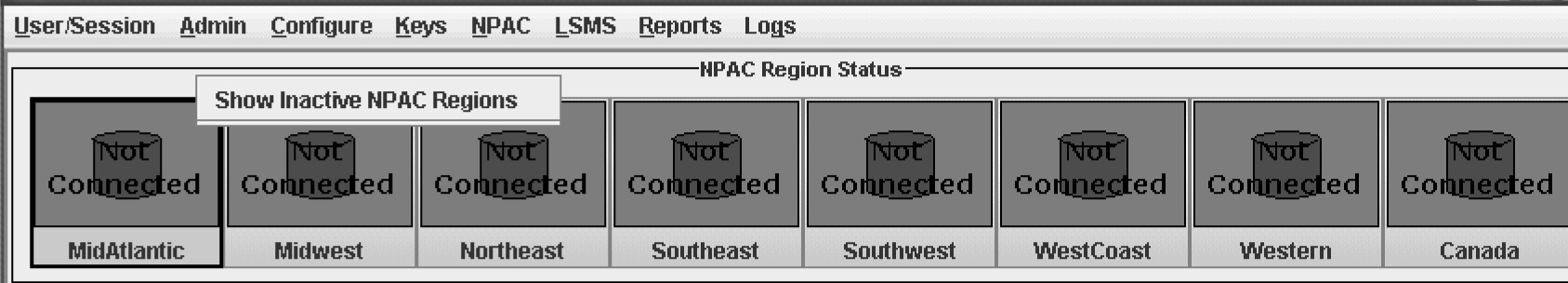
- Midwest
- MidAtlantic
- Northeast
- Southeast
- Southwest
- Western
- WestCoast
- Canada
LSMS can support all eight NPACs simultaneously. The LSMS acts as the interface between one or more NPACs and one or more network elements (NEs). Each NE is accessed through its Element Management System (EMS).
After you have installed the LSMS (for more information, refer to the LSMS Hardware Reference Manual) and integrated it into your network (see Integrating EAGLE Application B Card (E5-APP-B) into the LSMS Network), perform the remaining configuration procedures, as shown in Table 3-1 and Table 3-2.
Completing Configuration
Perform the procedures shown in Table 3-1 in the order shown, depending on whether you are installing LSMS for the first time or adding an NPAC region at a later time. In either case, the last step in Table 3-1 directs you to perform the steps in Table 3-2.
Table 3-1 Recommended Order of Configuration Procedures
| Recommended Order for Initial Installation | Recommended Order for Adding New Region After Installation | Procedures |
|---|---|---|
|
1 (Only if needed) |
1 |
|
|
2 |
(Not needed) |
Log into the LSMS GUI for the first time (see "Starting an LSMS GUI Session" in the Alarms and Maintenance Guide). |
|
3 |
(Not needed) |
Create a service provider entry for the LSMS owner in the LSMS database by performing the procedure “Adding Service Provider Contact Information”. |
|
4 |
(Not needed) |
Select and log in with the SPID you created in the previous step. |
|
5 |
2 (if needed) |
For each additional SPID that you desire to allow access to LSMS data, create a supported service provider entry in the LSMS database by performing the procedure “Adding Service Provider Contact Information”. |
|
6 |
(Not needed) |
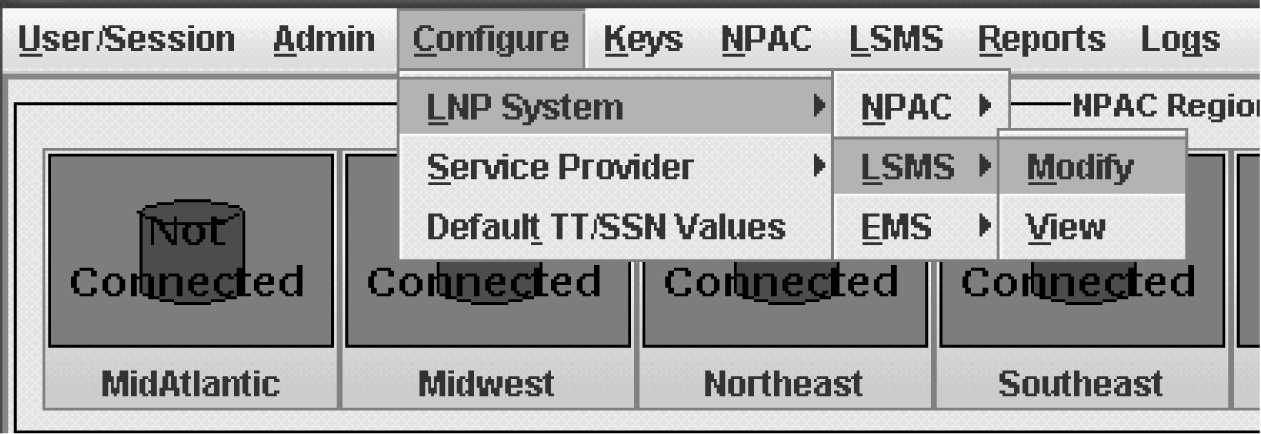
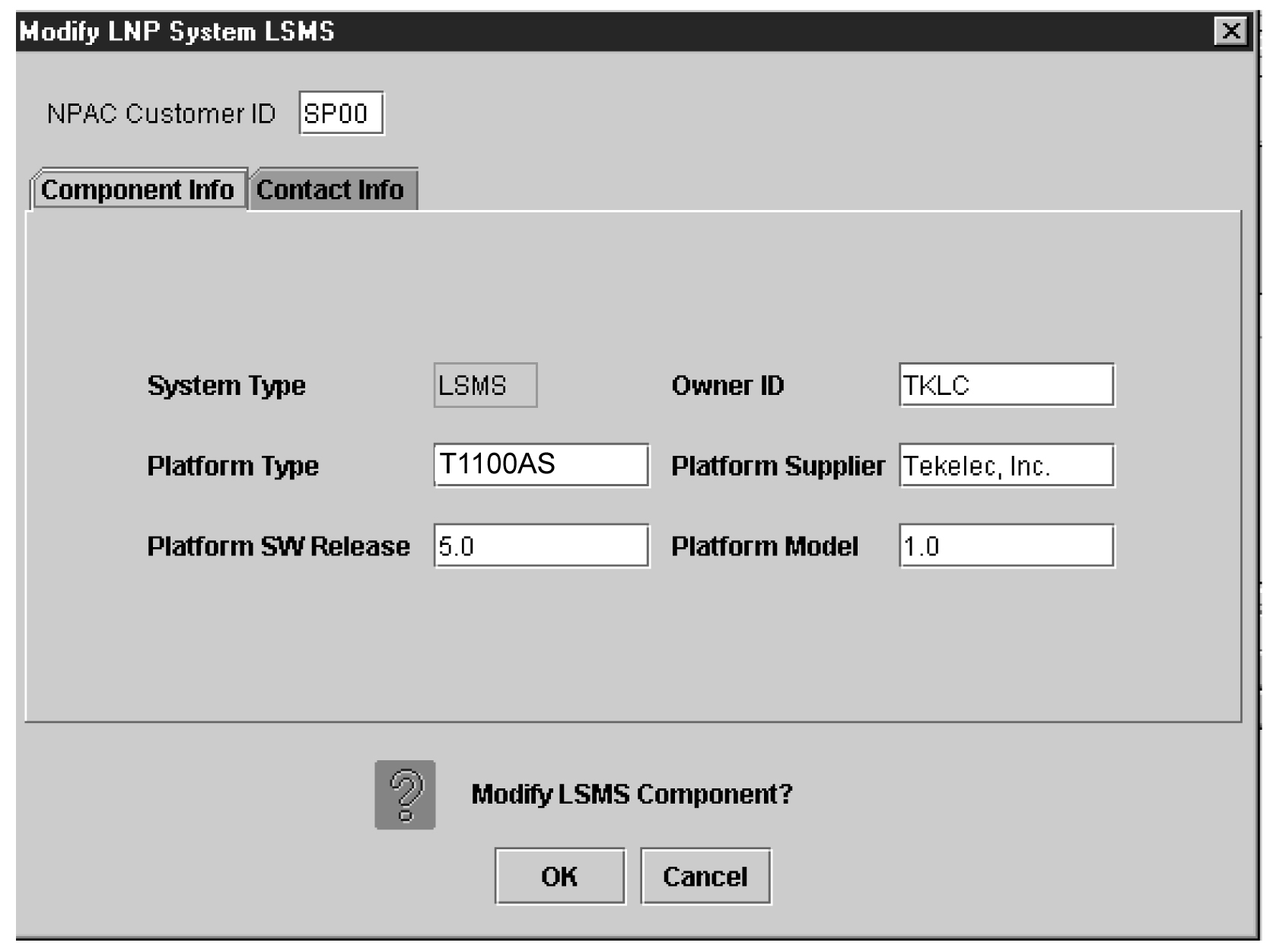
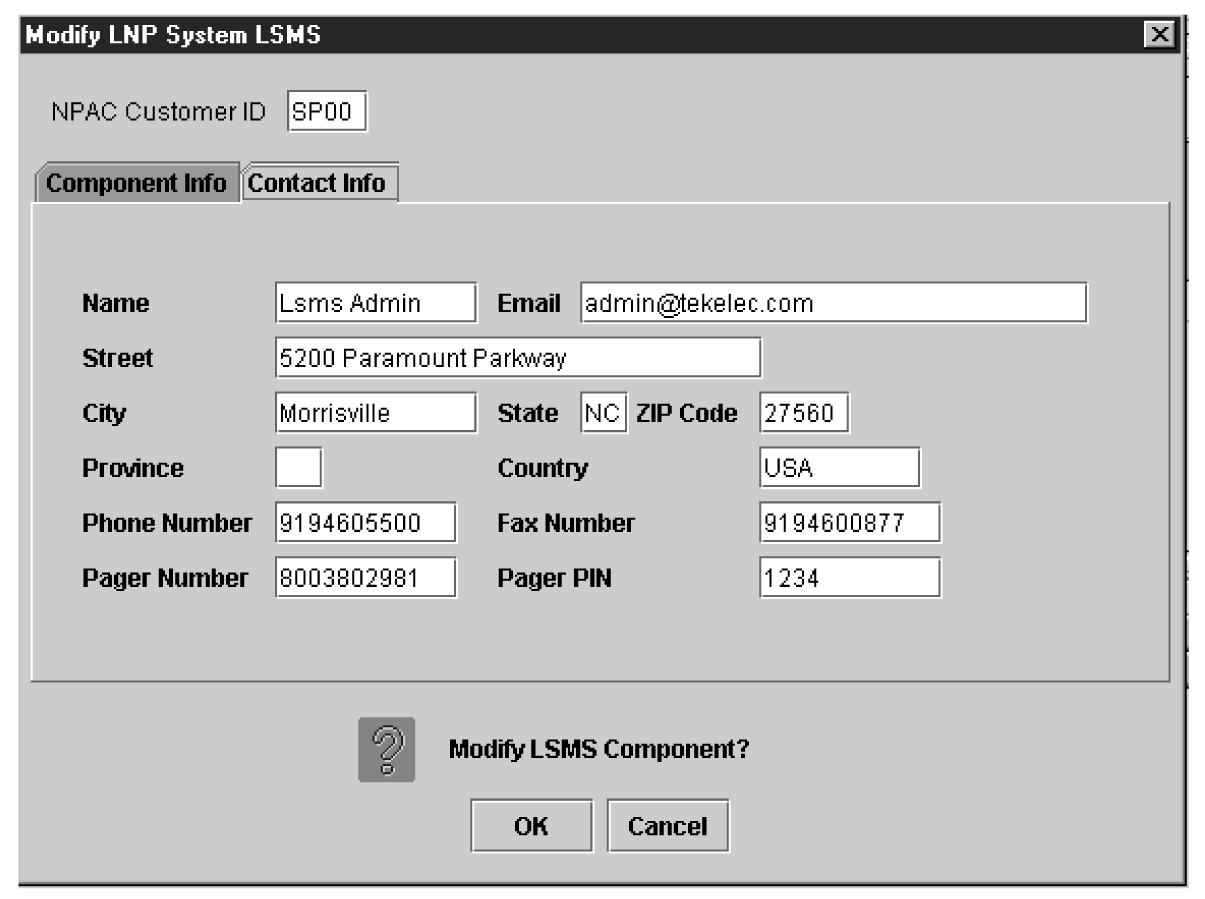
Modify the LSMS component by performing the procedure Modifying LSMS Configuration Components. |
|
7 |
(Not needed) |
For each EMS to be supported, create an EMS component by performing the procedure Creating an EMS Configuration Component. |
|
8 |
3 |
For each NPAC, perform the list of procedures described in Table 3-2. |
|
9 |
4 |
If desired, change the default TT/SSN values by performing the procedure “Modifying Default TT/SSN Values”. |
Completing Configuration and Associating with Each NPAC Region
Either as part of initial installation or to add an additional region after the initial installation, perform the procedures in the order shown below once for each NPAC region you need to support.
Table 3-2 Configuring and Associating Each NPAC Region
| Step | Procedure to Perform |
|---|---|
|
1 |
Perform the procedure “Generating a Key List”. |
|
2 |
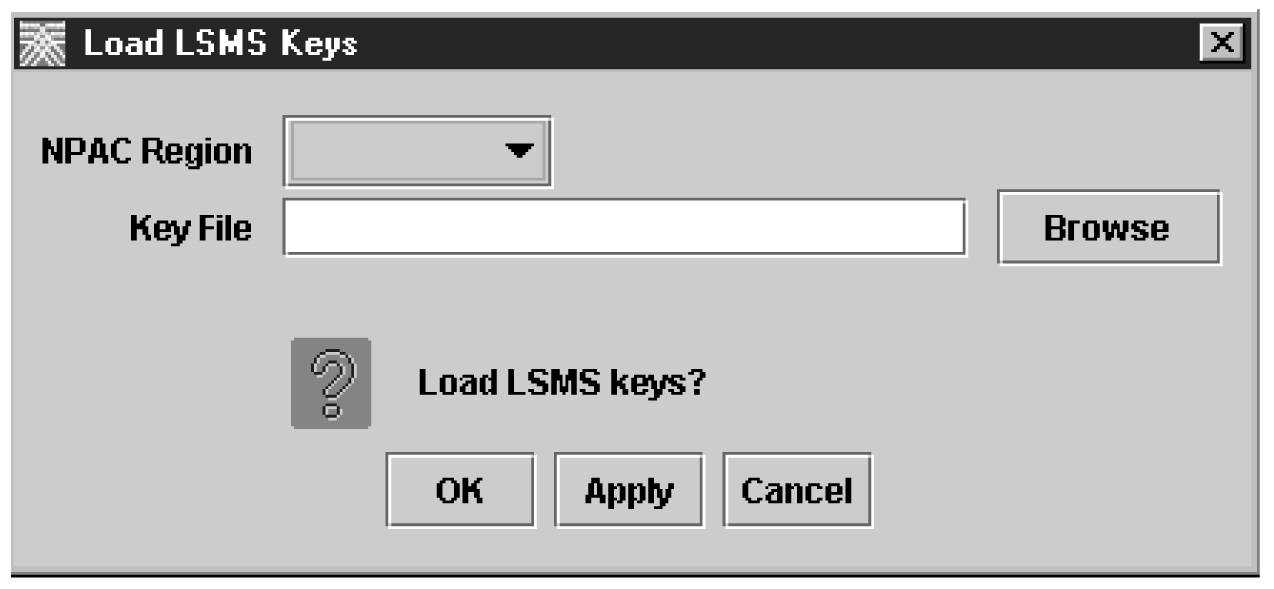
Select to load the NPAC public key list into the LSMS database by performing the procedure Loading an NPAC Key List. For the Key File field, type the following value in the Key List File field, where
|
|
3 |
Select to load the LSMS private key list into the LSMS database by performing the procedure Loading an LSMS Key List. For the Key File field, type the following value in the Key List File field, where
|
|
4 |
Select to create a secondary NPAC component and enter the information described in “Modifying an NPAC Component”. Ensure that the Activate Region checkbox is empty. For the Component ID field, a value that is one greater than the value entered in the procedure in row 5 is suggested. |
|
5 |
Click the icon that corresponds to this region so that the icon is highlighted, and select to create a primary NPAC component. Enter the information described in “Modifying an NPAC Component”. Ensure that the Activate Region checkbox is filled in. When you click the OK button, the sentry utility will automatically attempt to associate with the NPAC. |
Creating Databases
If you are adding a region to be supported, use the following procedure to create the database for the new region:
Service Provider Contact Information
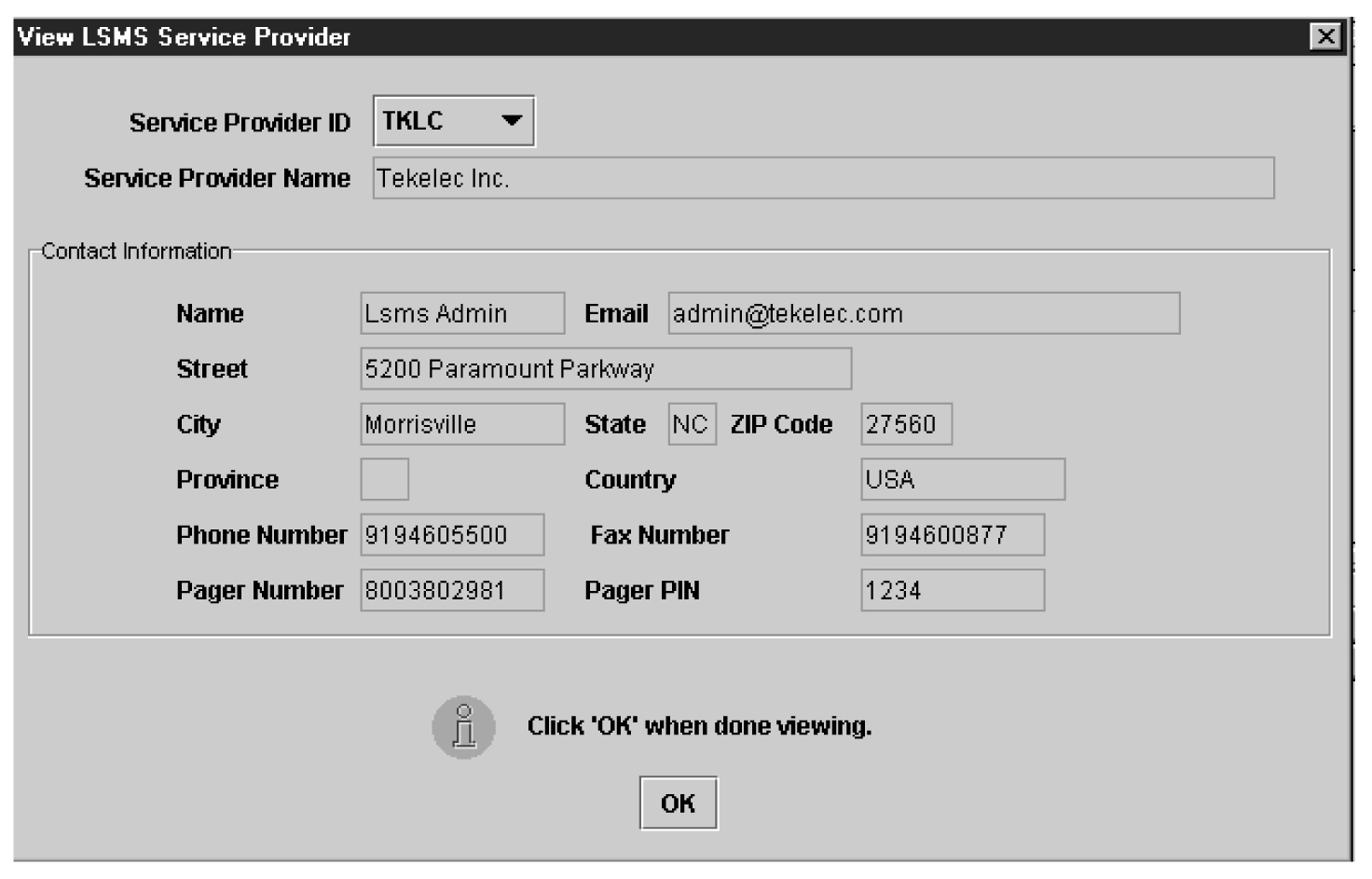
Use the following procedures to add, modify, view, and delete service provider contact information.
Adding Service Provider Contact Information
To add service provider contact information into the LSMS database, use the following procedure.
Modifying Service Provider Contact Information
To modify service provider contact information, use the following procedure.
LSMS Configuration Components
Use the following procedures to manage LSMS configuration components:
EMS Configuration Component
Use the following procedures to manage TekPath or ELAP EMS configuration components:
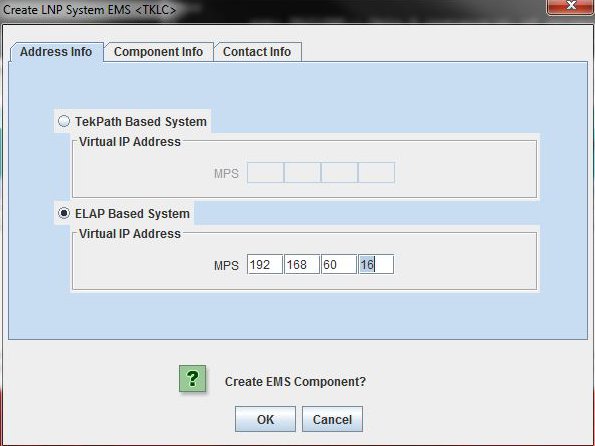
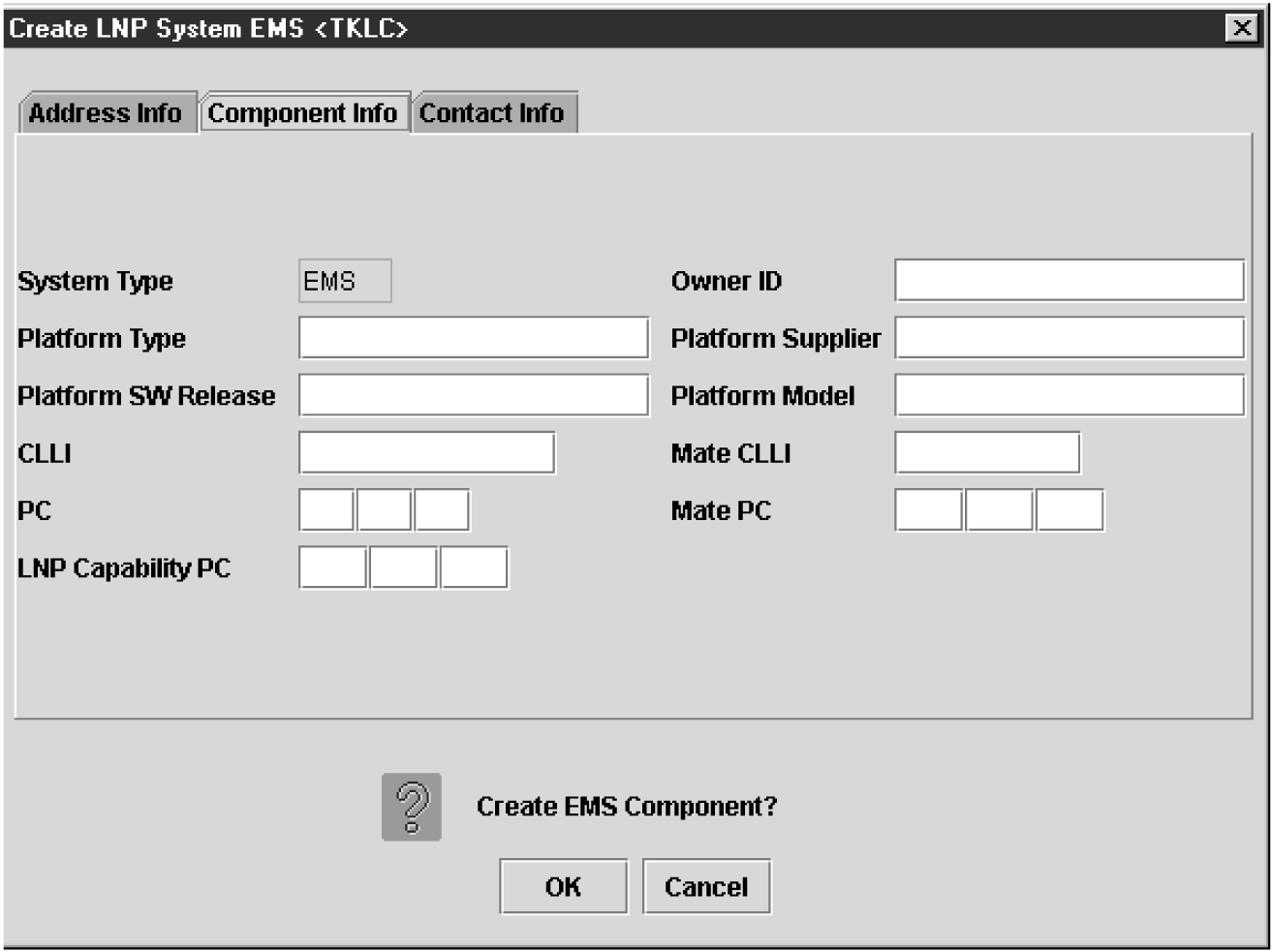
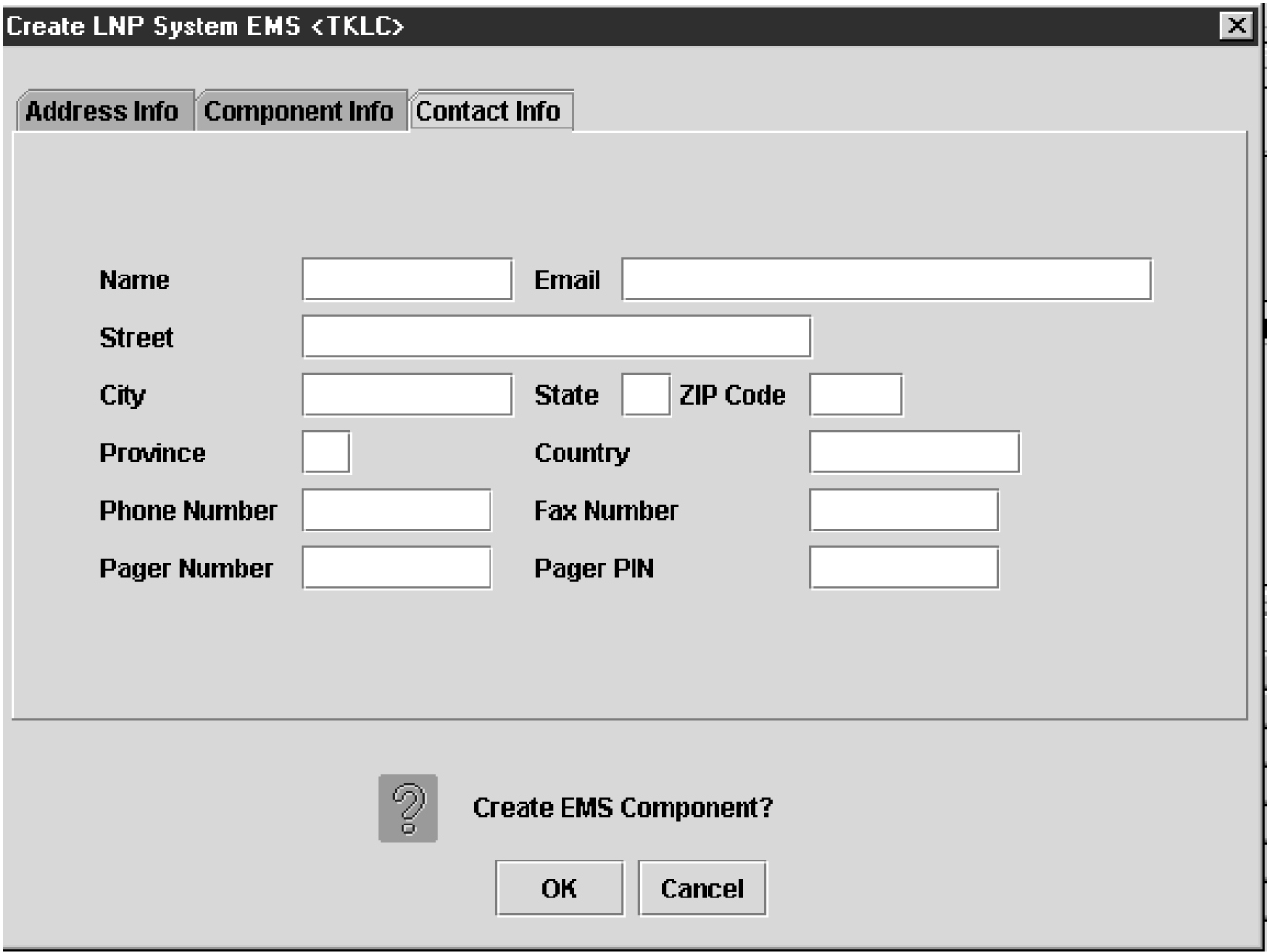
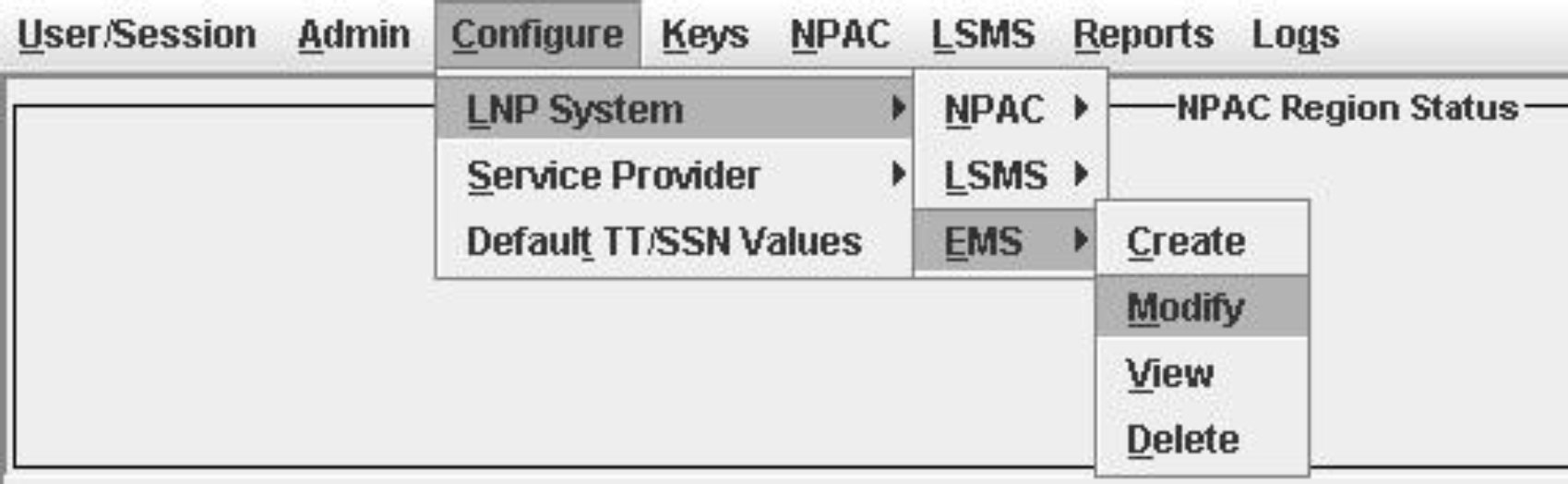
Creating an EMS Configuration Component
For each network element to be supported by the LSMS, create an EMS configuration component using the following procedure.
Note:
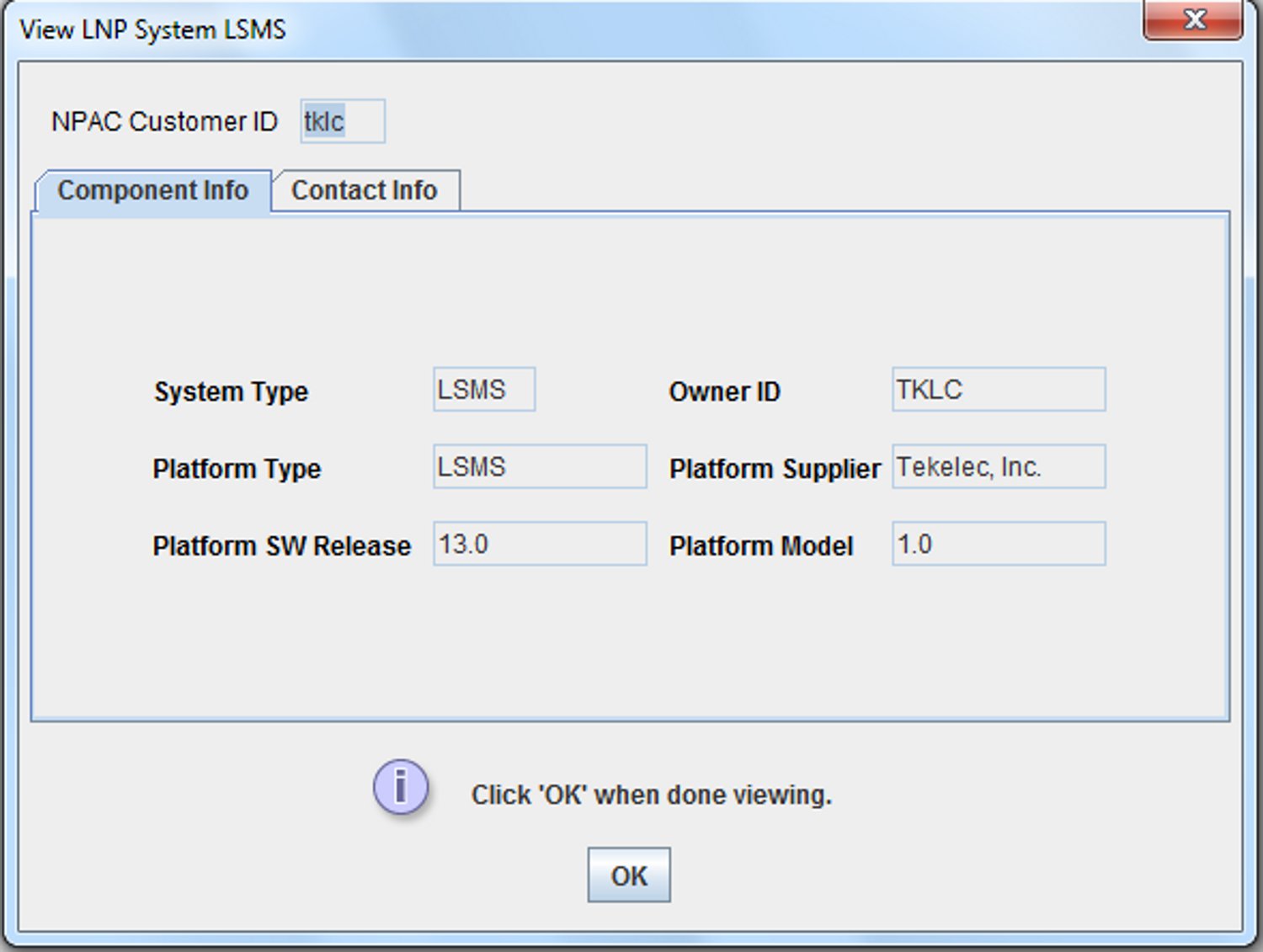
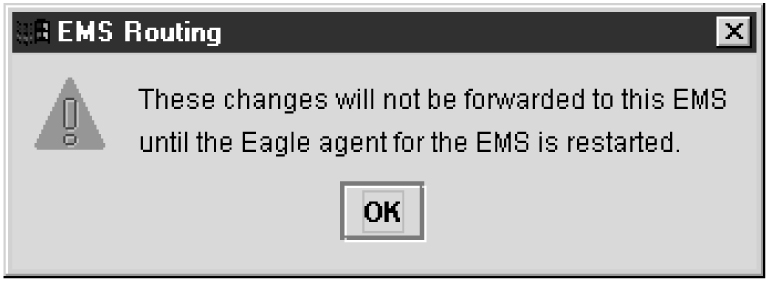
For each EMS configuration created, you must perform a bulk download to the associated EMS/network element. Refer to the LNP Database Synchronization User's Guide for bulk loading procedures.Modifying an EMS Configuration Component
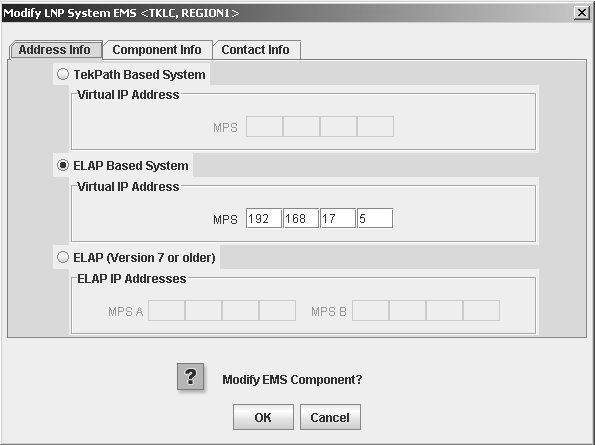
To modify an existing EMS configuration component, use the following procedure.
Note:
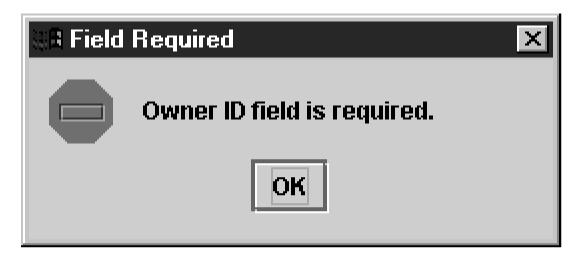
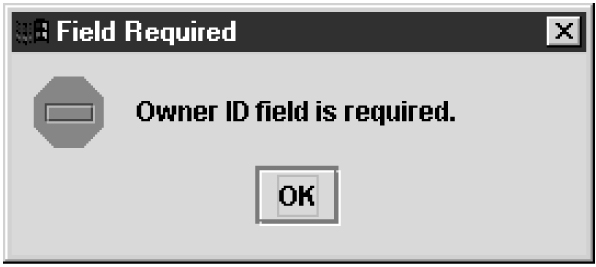
For each EMS configuration created, you must perform a bulk download to the associated EMS/network element. Refer to the LNP Database Synchronization User's Guide for bulk loading procedures.Figure 3-26 More Fields Needed Dialog

Click OK and correct the appropriate field.
Repeat this step until you receive an Update Successful notification.
Note:
Changes do not take effect until theeagleagent is restarted (refer to "Manually Verifying and Restarting the Eagle Agents" in the Alarms and Maintenance Guide).
Using Key Lists
LSMS maintains a list of keys for each NPAC Service Management System. You use a key list to secure encrypted communications between the LSMS and its associated NPACs.
Key lists are loaded whenever one of the following occurs:
-
LSMS is initially configured
-
The system administrator issues the appropriate key list commands
The LSMS system administrator can view any key list in his system. Key lists can be exchanged off-line to ensure security. Each key list has an assigned expiration date.
During an LSMS GUI session configuration, you load these lists as directed by the LSMS system administrator. You must fully configure one GUI session (including loading key lists) for each NPAC associated with the LSMS.
Use the following procedures to generate a key list, load an NPAC key list, and load an LSMS key list.
Generating a Key List
Each NPAC and LSMS generates a key list for use by the other side. That is, each NPAC generates a key list to be transferred to LSMS for decrypting the message signature sent from NPAC. The LSMS generates key lists that are transferred to the NPAC for decrypting LSMS message signatures sent from LSMS.
The keys in a key list are actually the public key component of a private/public key pair. The originating side keeps the private key component for encrypting the signature when transferred to the receiving side.
A key list contains exactly 1000 keys. Before an originating side can communicate with a receiving side, the receiving side must acknowledge the keys within a key list. For example, if LSMS sends a set of keys to the NPAC, the NPAC creates a file with a checksum for each of the 1000 keys in the list. This newly created file can then be used to acknowledge the keys in the list that were sent to the NPAC.
The following procedure explains how to generate a key list for the NPAC. An overview of the key list creation process is shown below.
Figure 3-30 Flowchart for Generating a Key List

Loading an NPAC Key List
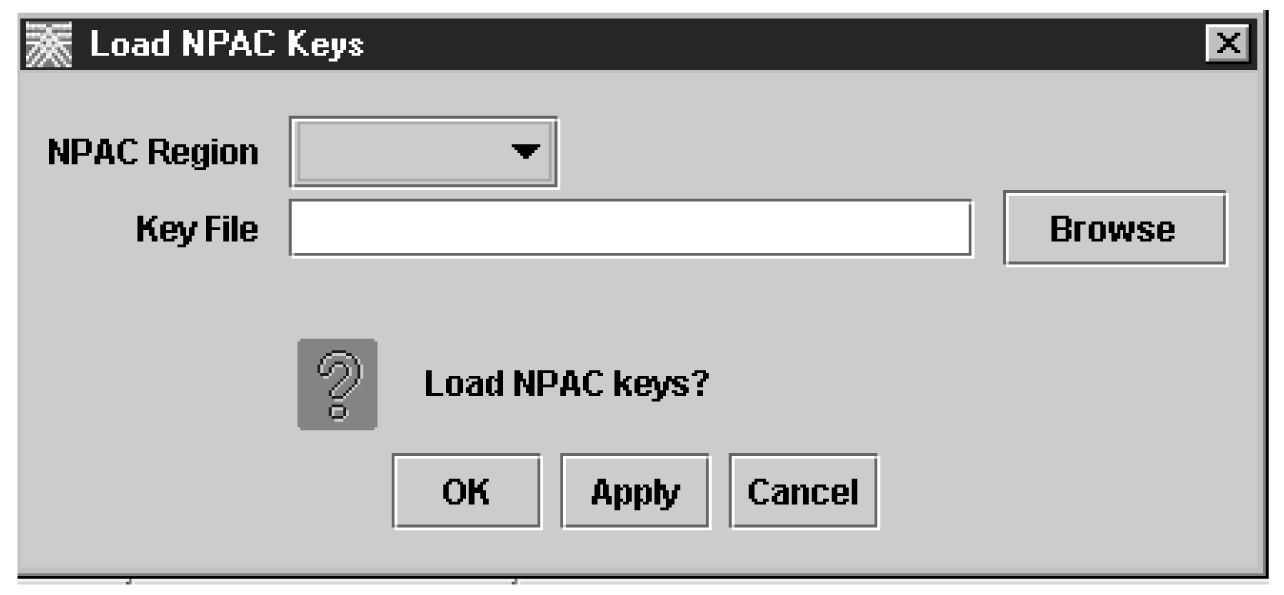
To load an NPAC public key list into the LSMS database, use either of the procedures described in the following sections:
Loading an LSMS Key List
To load an LSMS public key list into the LSMS database, use either of the procedures described in the following sections:
NPAC Component Configuration
Use the following procedures to manage NPAC component configuration:
Configuring iconectiv NPAC
The iconectiv NPAC compatibility feature makes the LSMS compatible with the iconectiv NPAC. Configurable options allow the user to specify if a region is connected to Neustar or iconectiv NPAC. The default value of the new configuration option is "N" to signify Neustar NPAC. The end user is able to set the value of the new configuration option per region to Y (for iconectiv).
The format is as follows: <Region Name>_ICONECTIV (for example, MIDWEST_ICONECTIV). To enable a region to connect to iconectiv NPAC, complete the following steps:
There is an audit script to identify the number of NPACs that are connected to iconectiv and Neustar. See Database Administrator's Guide for the NPAC Audit Report.
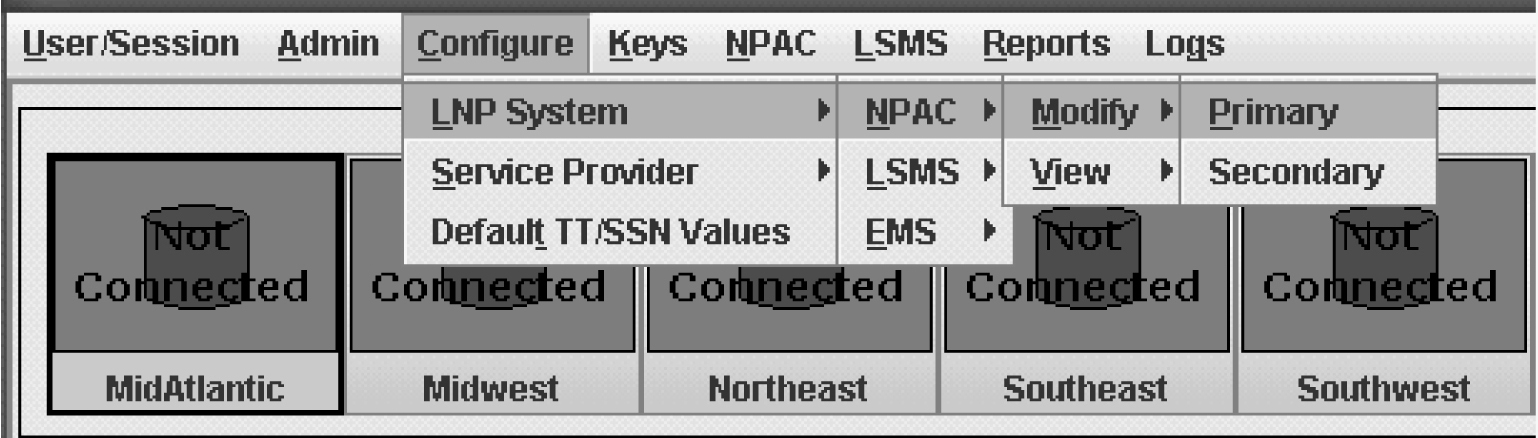
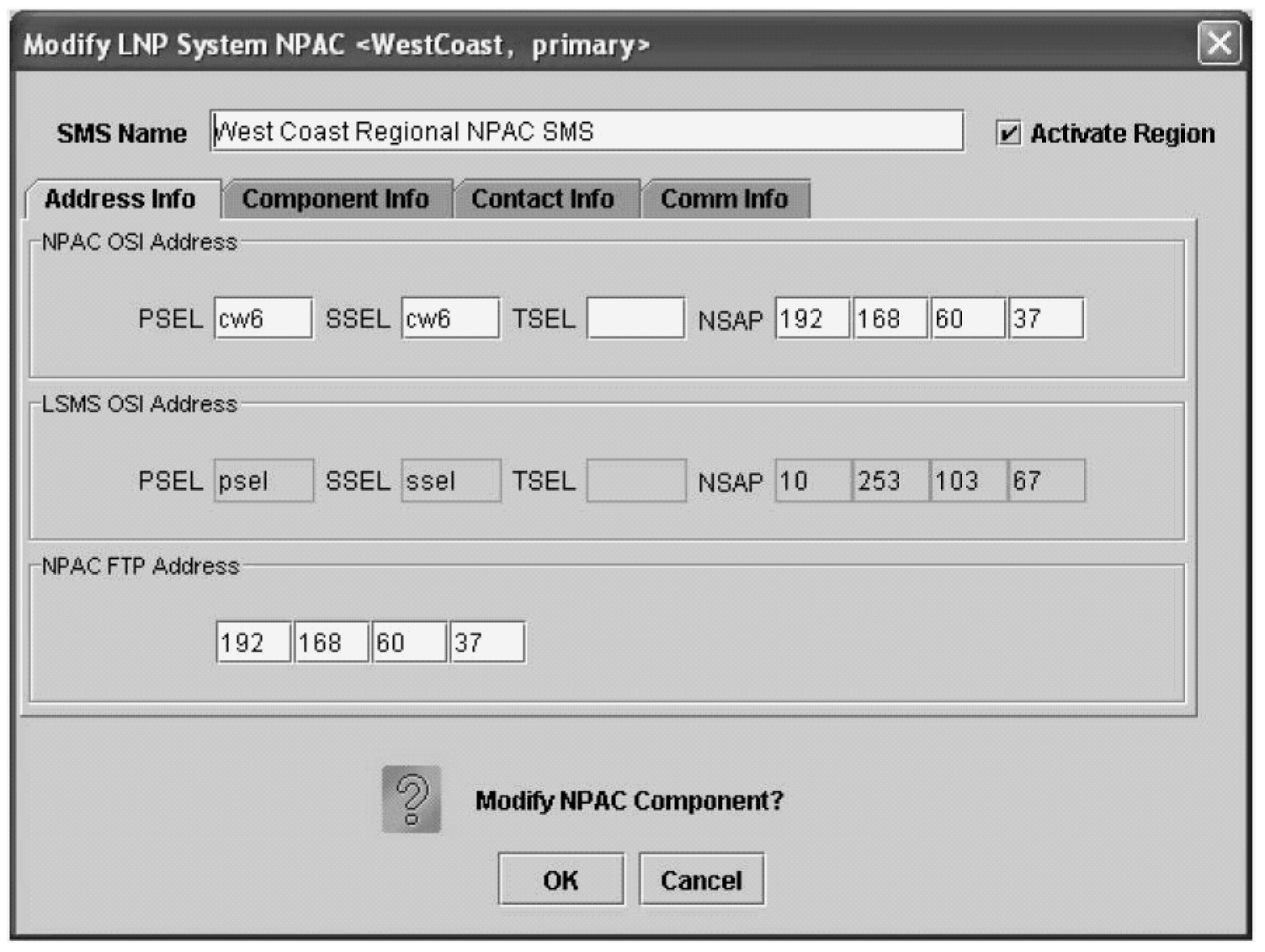
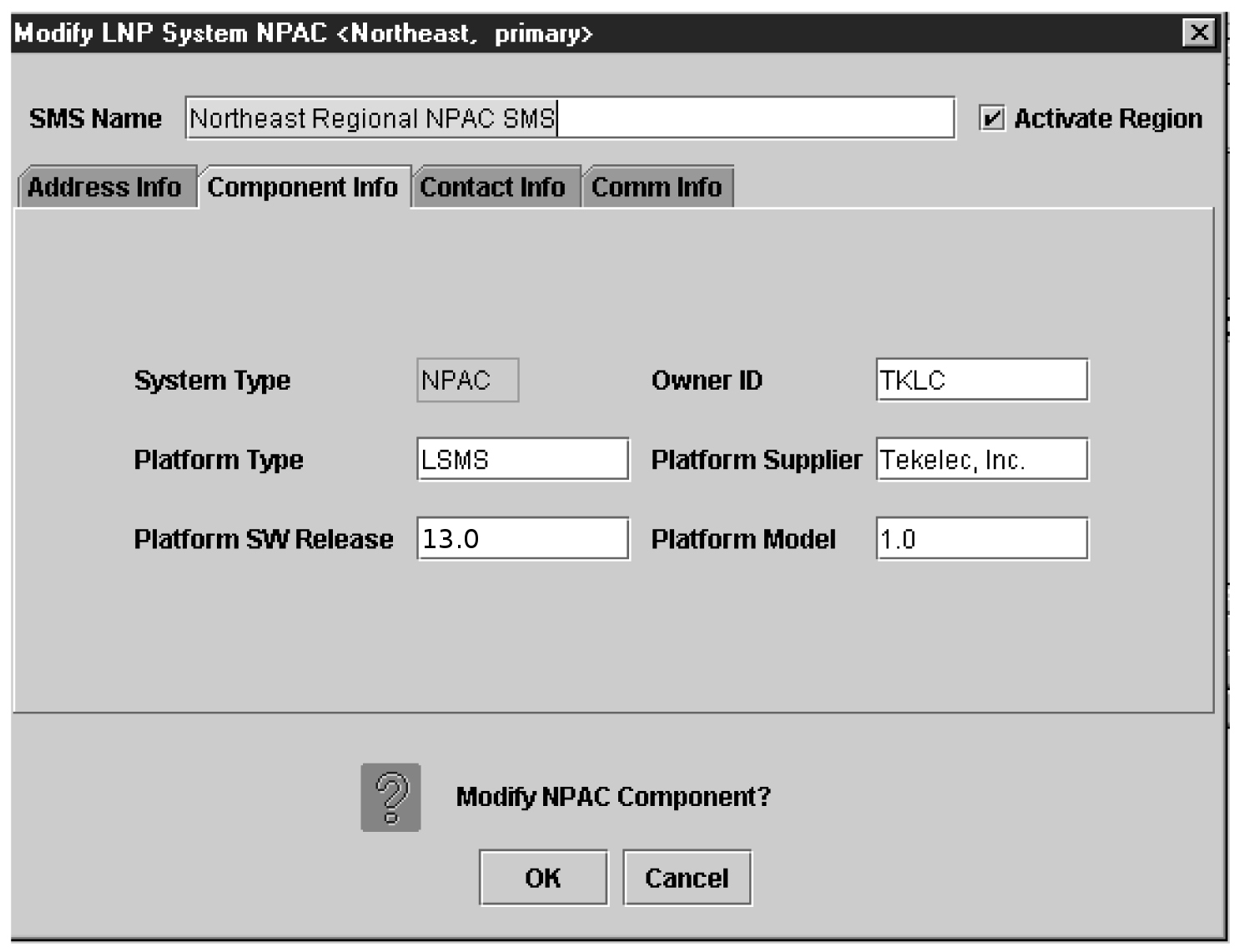
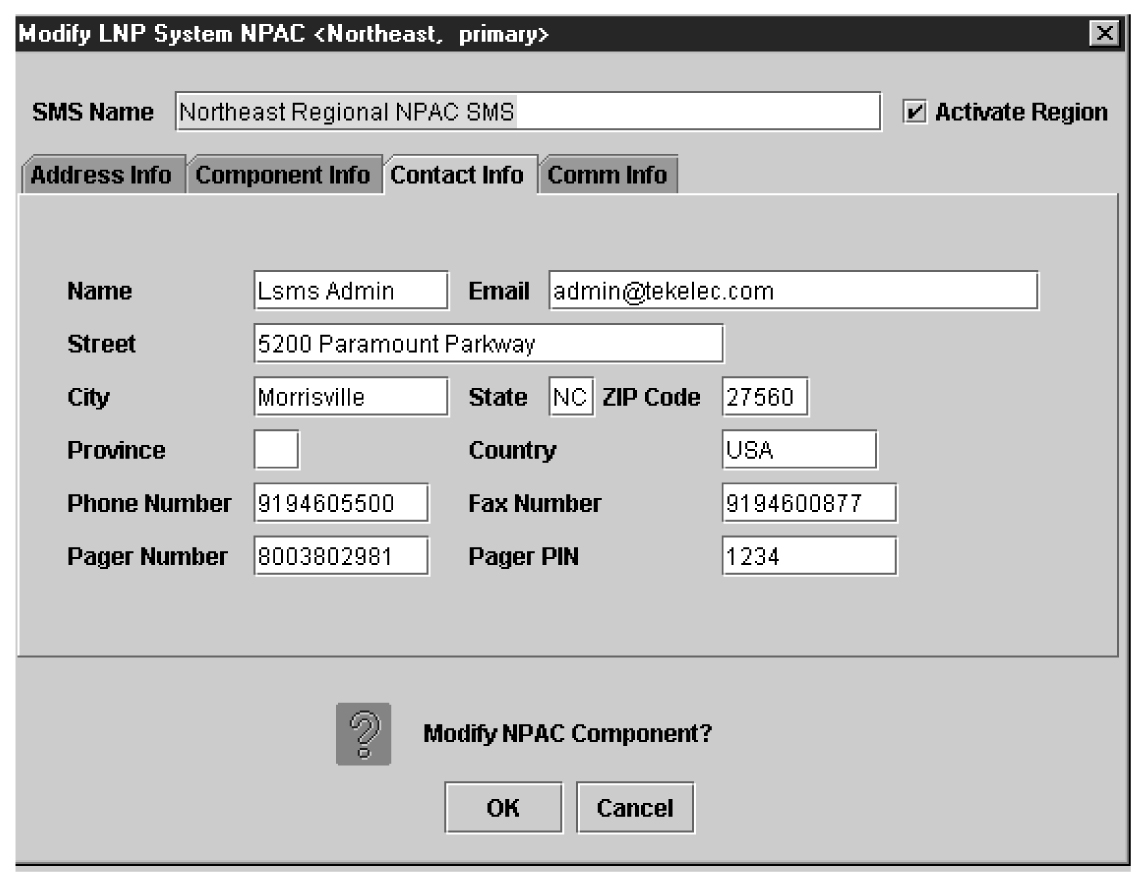
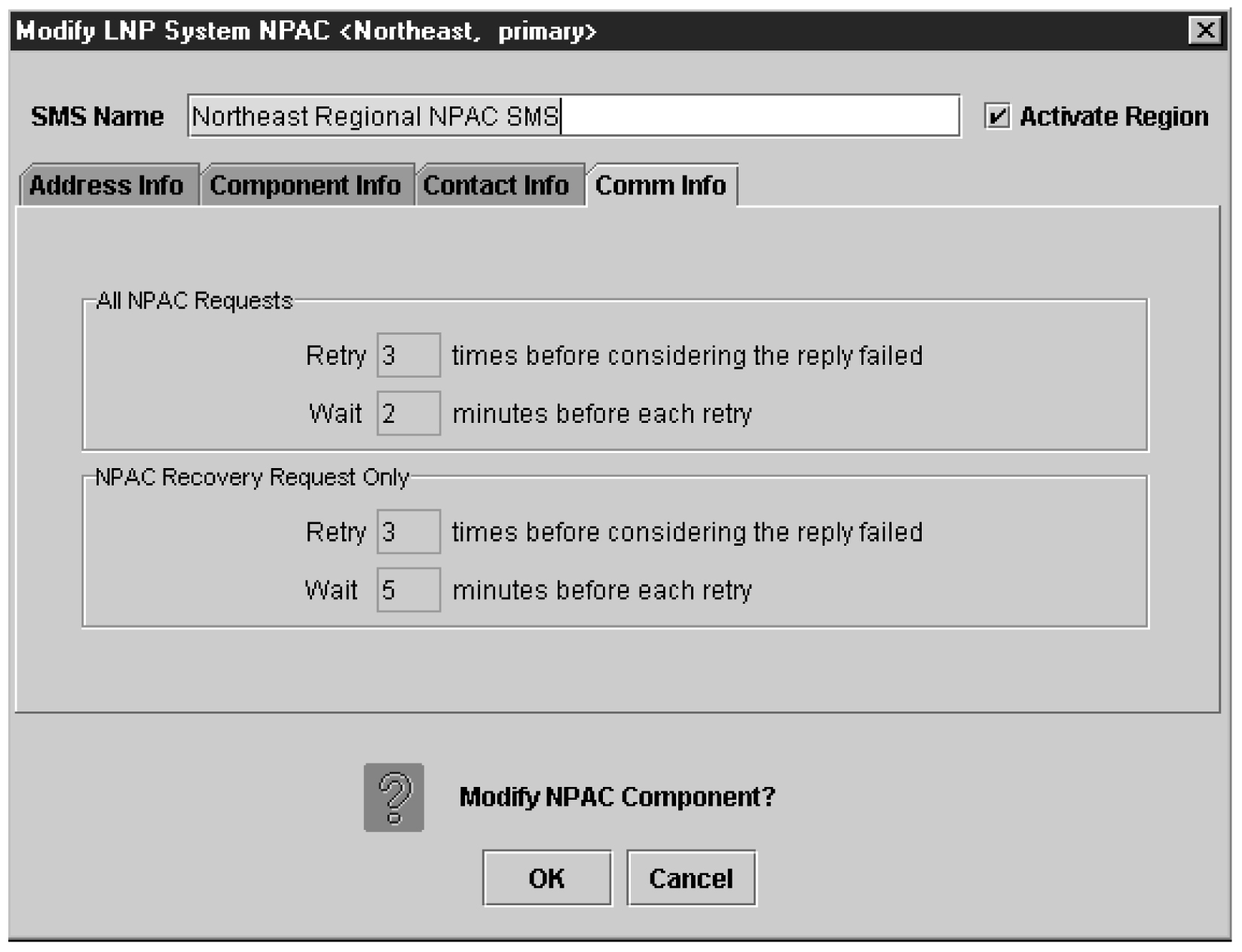
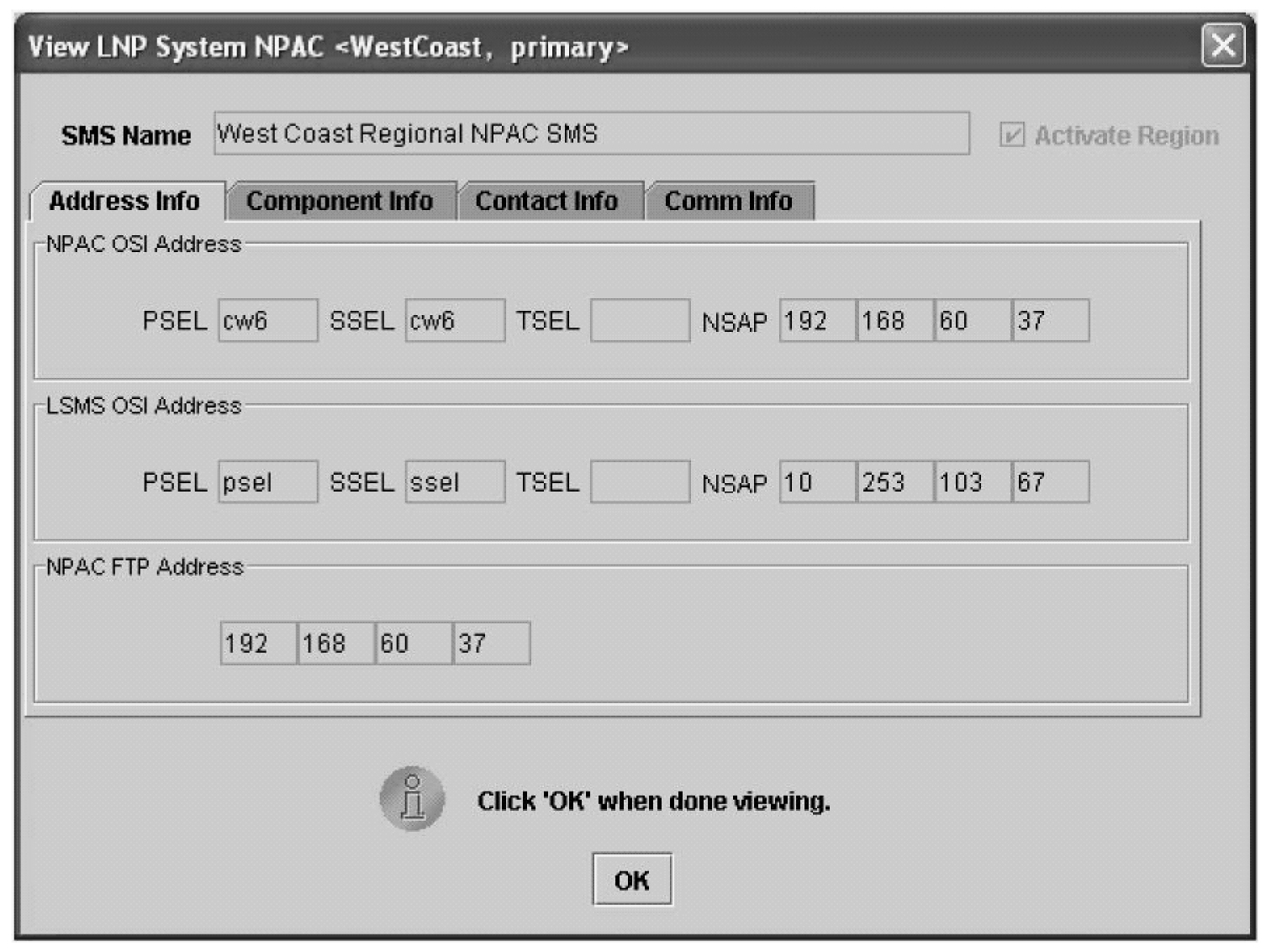
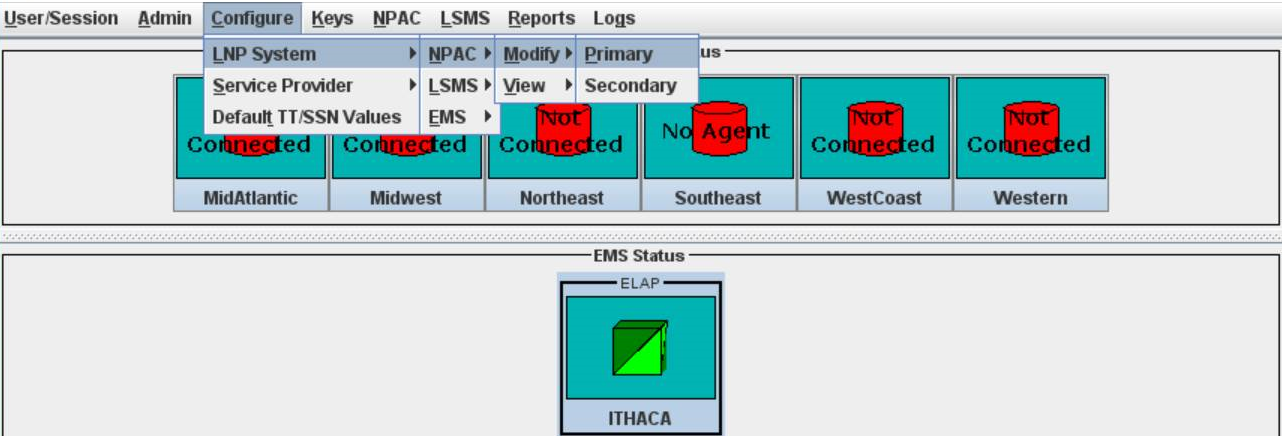
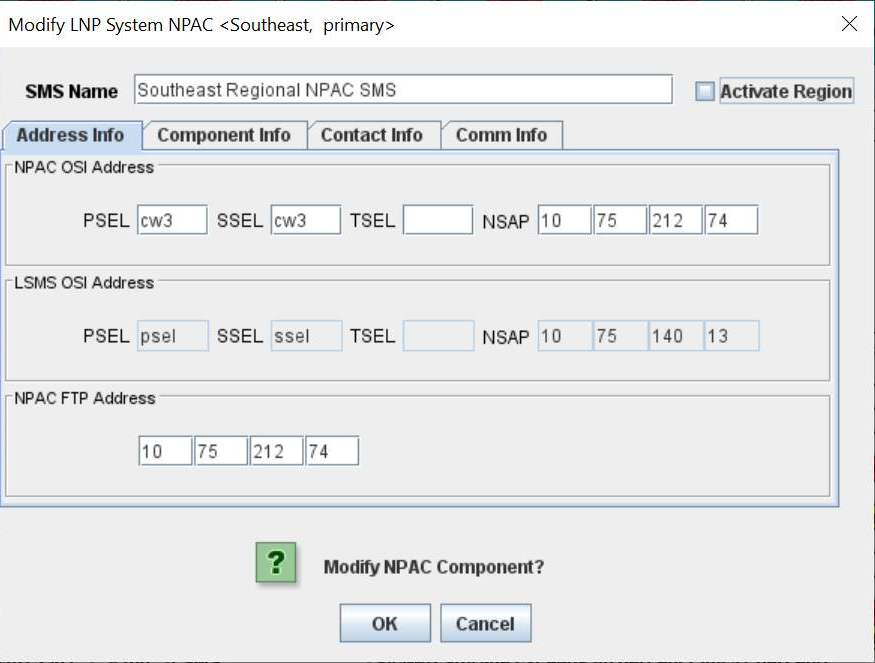
Modifying an NPAC Component
Use the following procedure to create or modify component configuration for an NPAC. Create components for both the primary NPAC SMS and the secondary NPAC SMS of the regional NPAC.
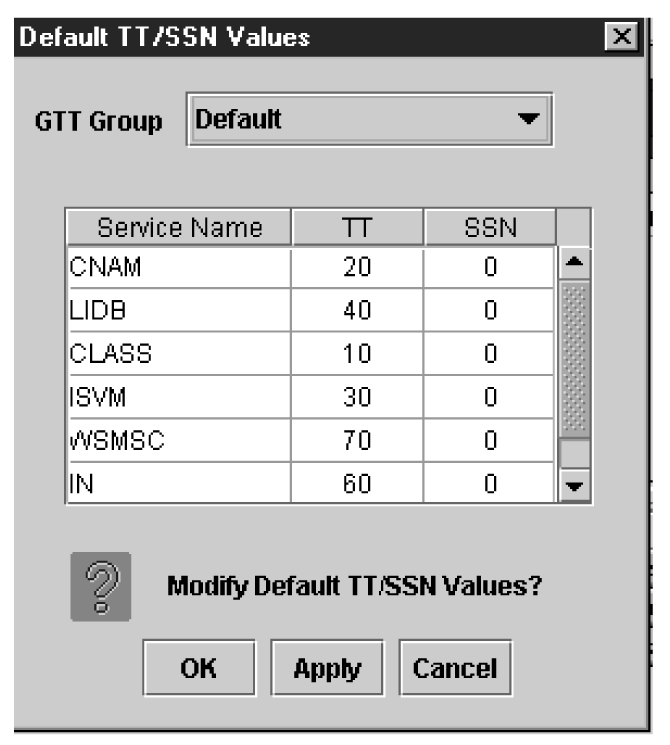
Modifying Default TT/SSN Values
If desired, use the following procedure to modify the default Translation Type (TT) and SS7 Subsystem Number (SSN) values for a given GTT group. Using default settings can simplify the amount of data entry required when creating Default GTTs and Override GTTs (for information about managing Default GTTs and Override GTTs, refer to the Database Administrator's Guide).
Working with NPAC Associations
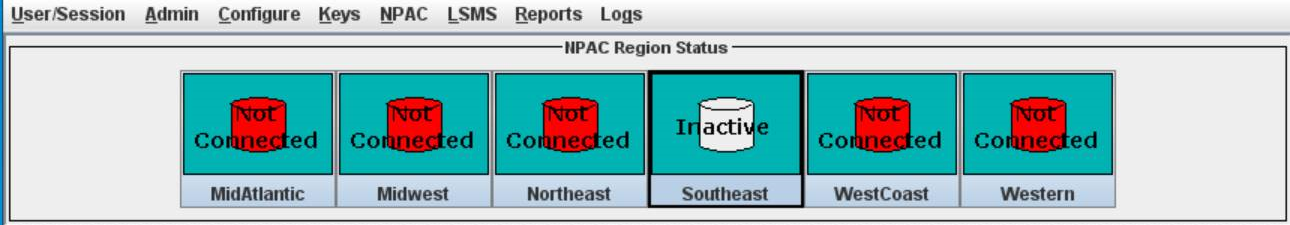
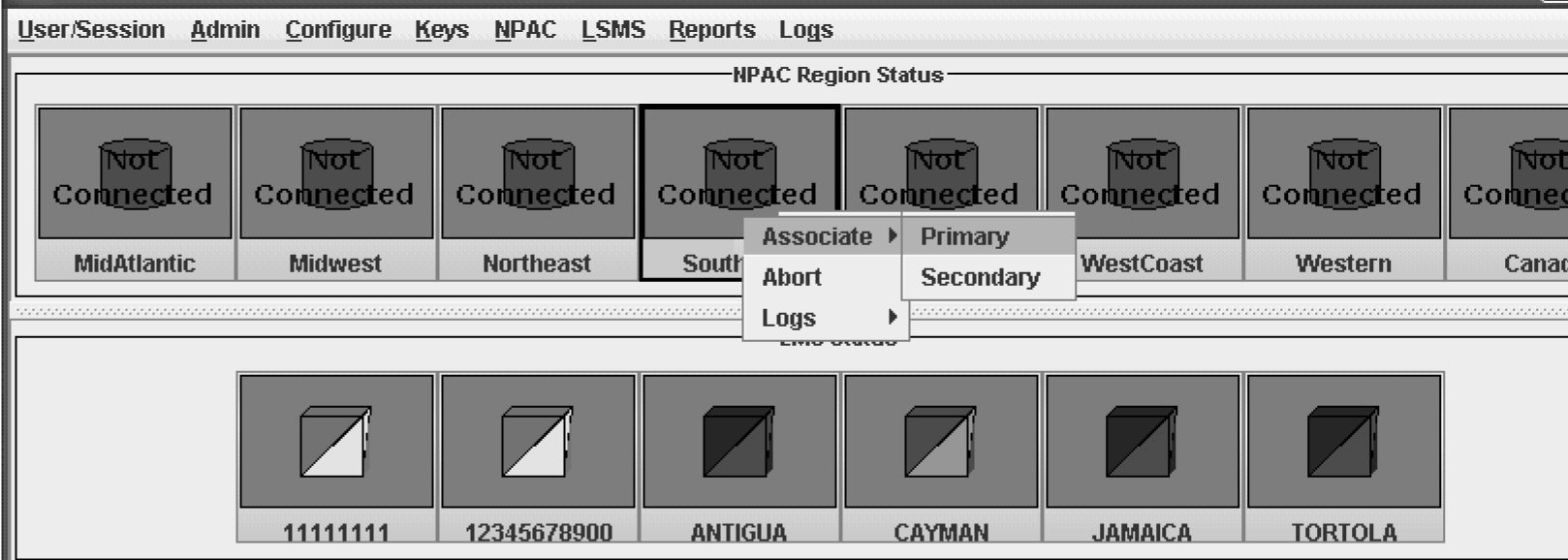
Ordinarily, NPAC associations are managed automatically by the sentry utility, according to the setting of the Activate Region checkbox in the Modify LNP System NPAC window (see Figure 3-39). This section explains how to manually create or abort NPAC associations. You can use the LSMS GUI interface to perform both of these procedures. You can also use the command line utility, lsmsclaa, to create and abort NPAC associations.
The following topics are covered in this discussion of the NPAC associations:
Creating an NPAC Association
Aborting an NPAC Association
The abort function breaks the association attempt between the LSMS and the NPAC by transmitting the abort command to the NPAC.
- “Aborting an NPAC Association Using GUI”
- “Aborting an NPAC Association Using Command-Line Interface”
lsmsadm or lsmsall user.
Aborting an NPAC Association Using GUI
To abort an NPAC association with the LSMS using the GUI, perform the following procedure:
- Log in to LSMS as a member of the permission group that is authorized to perform this operation.
- Click the icon that represents the NPAC whose association you wish to abort; then right-click and select Abort.
- When the LSMS has finished aborting the association with the NPAC, the NPAC status icon displays the text “Not Connected.”
Postfix
Postfix is an alternative mail program to the Sendmail program.
Note:
The Postfix daemon must be restarted manually after any operation that causes the host to reboot. Postfix is disabled by default.The normal configuration of Postfix requires DNS (Domain Name System). Postfix uses fully qualified hostnames for source and destination resolution.
Note:
The Postfix configuration affects only the local server.The following topics are covered in this discussion of Postfix.
Configuring Postfix
Modifications to the Postfix configuration files or aliases database require the Postfix utility to be restarted. To configure Postfix, perform the following procedure:
Caution:
Loss of data can result if you do not properly configure Postfix. For technical assistance, call the Customer Care Center.Starting and Stopping Postfix
To start Postfix, use this command:
# /usr/sbin/postfix start
To stop Postfix, use this command:
# /usr/sbin/postfix stop
Note:
The user must be root to start and stop Postfix.