Install ETL Component
Note:
All the tasks below need to be followed in sequential order.Prerequisites
Before installing the OUAW ETL component, verify the following:
-
Use the same operating system user used to install the required software.
-
Ensure Oracle GoldenGate Microservices is installed on the target database server.
-
Ensure that Oracle GoldenGate Microservice Manager, Admin, and Receiver Services are running on the target database server.
-
Ensure that the ODI Repository schema is created on the target database server.
-
Ensure Java is installed on the application server.
-
Ensure Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure is installed on the target application server.
-
Ensure Oracle Data Integrator (ODI) is installed on the target application server.
See Perform Pre-Installation Steps for OUAW for more information.
Set Up the Target Database Server for Oracle GoldenGate Microservices
alter system set enable_goldengate_replication=TRUE scope=both;Install the ETL Component
-
Log in to application server.
-
Navigate to the temporary directory where OUAW installer is downloaded. Example: <TEMPDIR/application>.
-
Set the JAVA HOME and add PATH.
export JAVA_HOME=<JAVA HOME> export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH -
Launch the OUAW installer by running the command below. The OUAW installer Welcome page appears.
java -jar OUAW_2.9.0.0.0_ETL_generic.jar -logLevel finestNote:
For an AIX Operating System, set the following environment variable before starting the Oracle Utilities Analytics Warehouse installation:export IBM_JAVA_OPTIONS="-Xmx2g -XX:PermSize=64m - XX:MaxPermSize=3200m" -
Review the information before you begin the installation. Click Next to continue.
Note:
If you are installing Oracle software on the server for the first time, provide central inventory details such as the inventory directory location and operating system group. -
On the Installation Location page, define the installation location in the Oracle Home field and click Next.
Note:
The specified Oracle home directory must be an empty directory.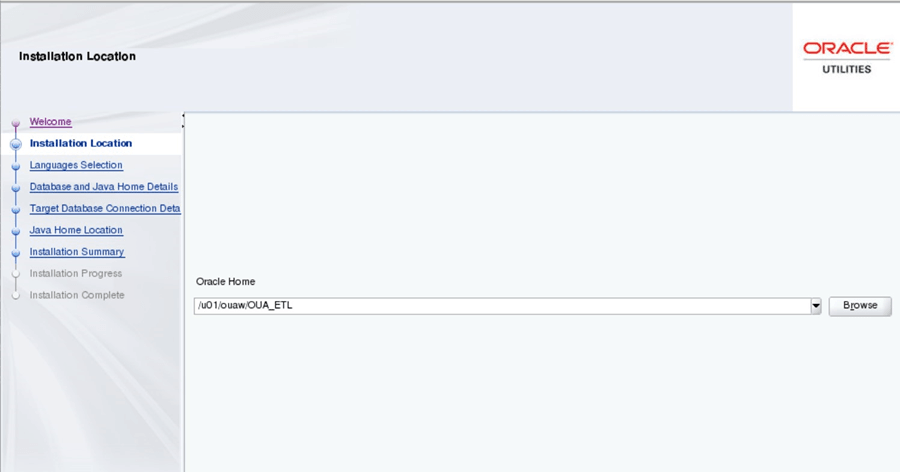
Field Name and Description Value Oracle Home: The directory where the Oracle Utilities Analytics Warehouse ETL is going to be installed.
Note:
This directory location is called the ETL Home. Keep track of it as it will be used during some deployment steps.Example: <OUA ETL Home>
</u01/ouaw/OUAW_ETL>
-
On the Languages Selection page, select English and click Next.
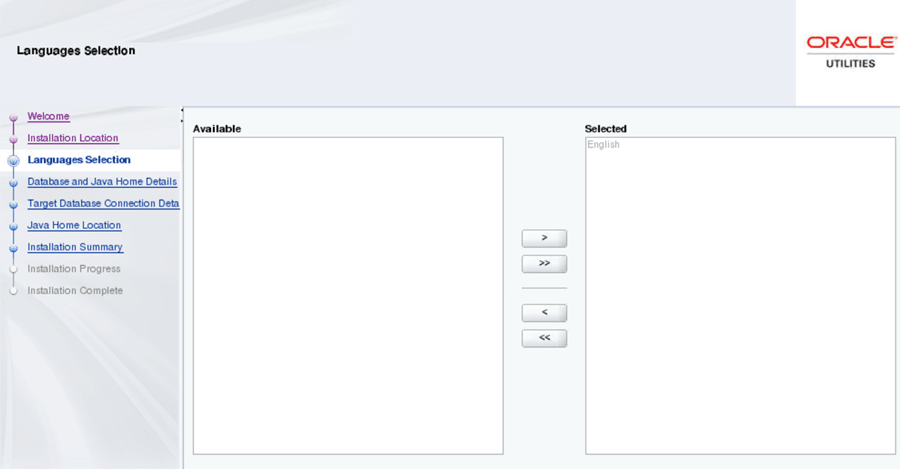
Field Name and Description Value Language Selection: The language for the installation process. English -
On the Database and Java Home Details page, enter the details as in the table below, and click Next.
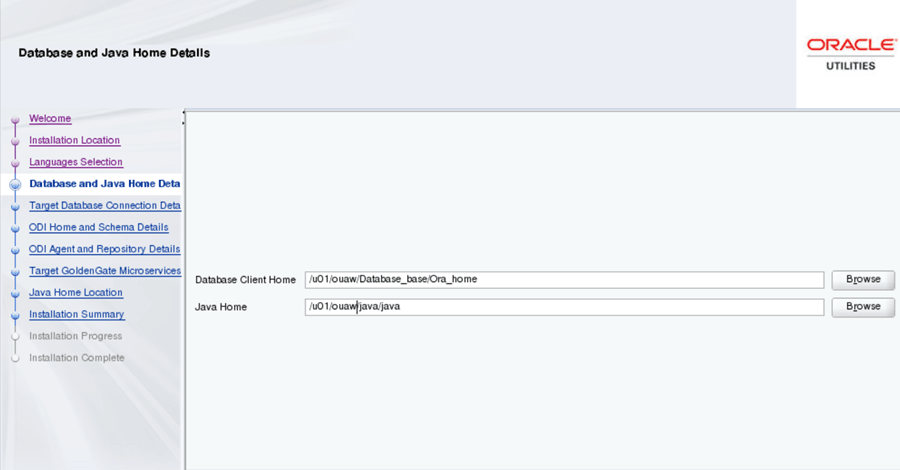
Field Name and Description Value Database Client Home: Enter the Oracle Database Client installed location or Database Home location in the case where the same server is being used for both the application and database server. Example: <Database Client> or <ORACLE_HOME>
</u01/ouaw/dbclient> or </u01/ouawcicd/Database_base/Ora_home>
Java Home: Enter the Java installed location. Example: <JAVA HOME>
</u01/ouaw/java/java>
-
On the Target Database Connection Details page, enter the following and click Next.
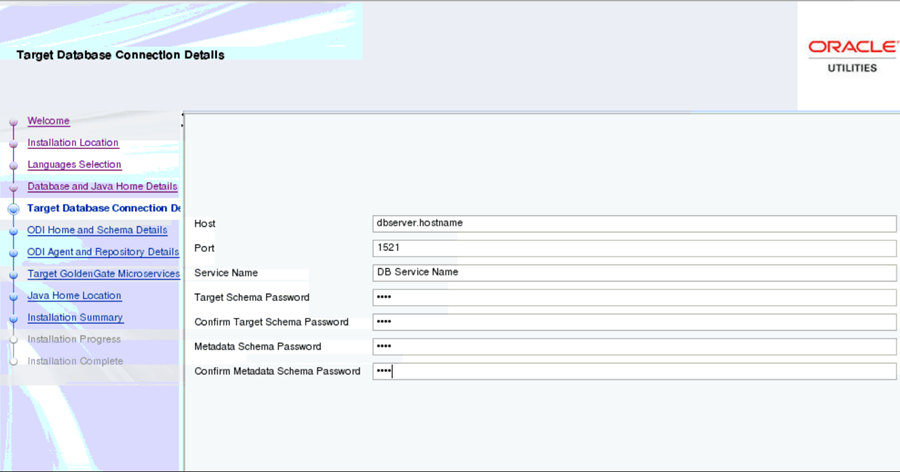
Field Name and Description Value Host: The target database server where database resides. Target Database server host name.
Example: dbserver.hostname
Port: The target database server port number. Target Database port.
Example: <1521>
Service Name: The target database service name. <Database service name> Target Schema Password: Password for the target schema (DWADM). <DWADM user password> Confirm Target Schema Password: Confirm password for the target schema (DWADM). <DWADM user password> Target Schema Password: Password for the metadata schema (MDADM). <MDADM user password> Confirm Target Schema Password: Confirm password for the metadata (MDADM) schema. <MDADM user password> -
On the ODI Home and Schema Details page, enter the following and click Next.
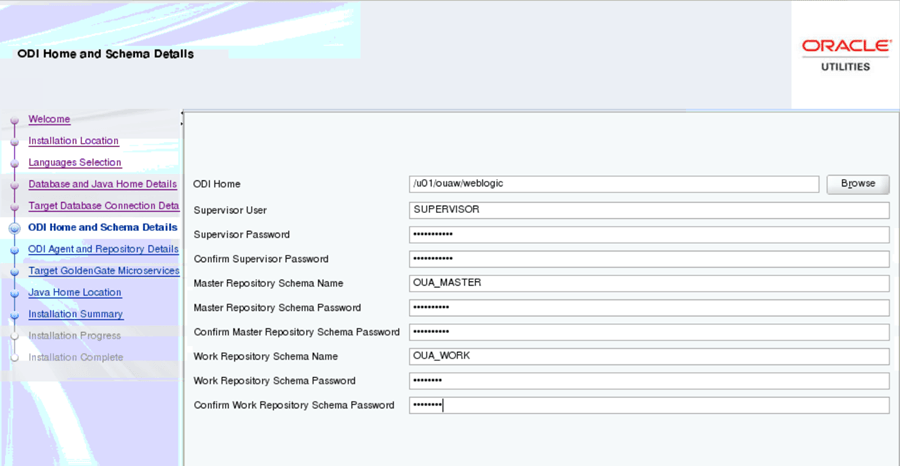
Field Name and Description Value ODI Home: The directory where Oracle Data Integrator (ODI) is installed. Location of FMW Home
Example: </u01/ouaw/weblogic>
Supervisor User: Name of the Oracle Data Integrator Supervisor. SUPERVISOR Supervisor Password: Enter the Supervisor Password and store it for future reference. <Supervisor user password > Confirm Supervisor Password: Enter same as Supervisor Password. <Supervisor user password > Master Repository Schema Name: Oracle Data Integrator master repository schema name. OUA_MASTER Master Repository Schema Password: Master Repository schema password. <OUA_MASTER user password> Confirm Master Repository Schema Password: Confirm password of the Oracle Data Integrator master repository schema. <OUA_MASTER user password> Work Repository Schema Name: Oracle Data Integrator work repository schema name. OUA_WORK Work Repository Schema Password: Work Repository schema password. <OUA_WORK user password> Confirm Work Repository Schema Password: Confirm password of Oracle Data Integrator work repository schema. <OUA_WORK user password> -
On the Oracle Data Integrator Agent and Repository Details page, enter the details as in the table below and click Next.
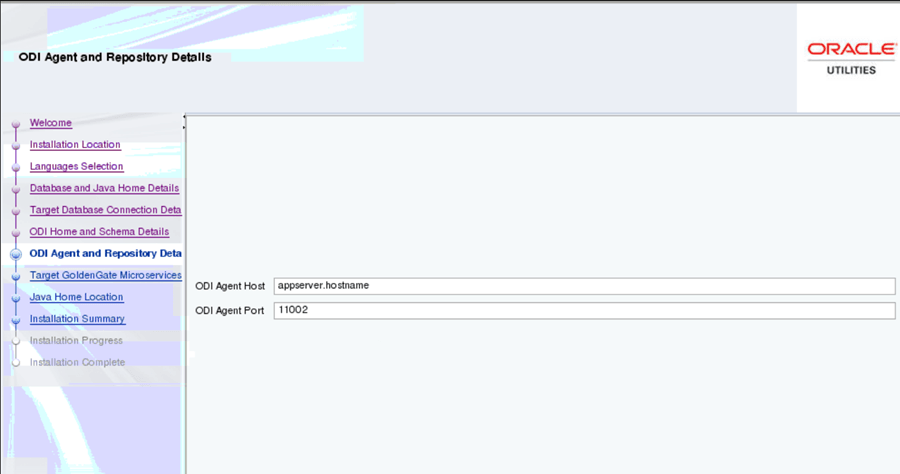
Field Name and Description Value ODI Agent Host: The application server hostname where the ODI application server is installed. Target APP Server Host
Example:
<appserver.hostname>
ODI Agent Port: Enter the port which is the Oracle Data Integrator WebLogic Managed Server port. Make sure that you use the same port while creating Oracle Data Integrator managed server. Example: <11002> -
On the Target GoldenGate Microservices Details page, enter the details as in the table below, and click Next.
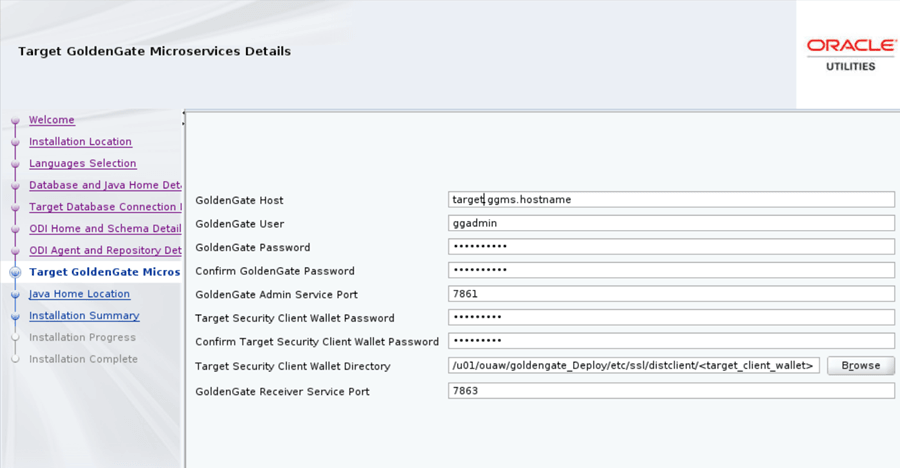
Field Name and Description Value GoldenGate Host: Target Oracle GoldenGate Microservice Host.
Enter the Target database hostname where GoldenGate Microservices is installed.
Target database server host/Target GoldenGate Microservice Server Host
Example: <target.ggms.hostname> or <dbserver.hostname>
GoldenGate User: Enter the GoldenGate Microservices Admin user. Example: <ggadmin> GoldenGate Password: Enter the GoldenGate Microservices Admin user password. Example: <ggadmin user password> Confirm GoldenGate Password: Re-enter the GoldenGate Microservices Admin user password. Example: <ggadmin user password> GoldenGate Admin Service Port: The Target Oracle GoldenGate Microservices Admin Service port which is running on the target database server host. Example: <7861> GoldenGate Target Security Client Wallet Password: Enter the Client Wallet Password on the target database server host. <Client Wallet Password> Confirm GoldenGate Target Security Client Wallet Password: Re-enter the Client Wallet Password on the target database server host. <Client Wallet Password> Target Security Client Wallet Directory: Enter the Client Wallet directory path on the target database server host.Note:
OGG client wallet location is under "<OGG Deploy Home>/etc/ssl/" after OGG MS deployment.Note:
You can find the exact Target GoldenGate Microservices client wallet location from <Target GoldenGate Microservices Deployment Home>/etc/conf/deploymentConfiguration.dat> file and search for the outbound section, you can find the client wallet location under the file: tag.Example:"outbound": { "authMode": "client_server", "wrl": "file:/u01/ouaw/goldengate_Deploy/etc/ssl/distclient/target_client_wallet",Here, the Target Security Client Wallet Directory is <u01/ouaw/goldengate_Deploy/etc/ssl/distclient/<target_client_wallet>>
GoldenGate Receiver Service Port: The Target Oracle GoldenGate Microservices Receiver Service port which is running on the target database server host. Example: <7863> -
On the Java Home Location page, enter the details as in the table below, and click Next.
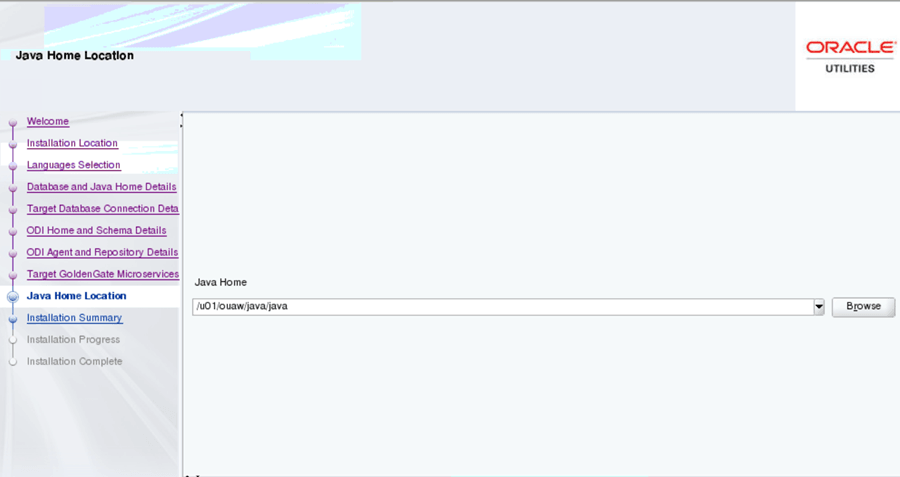
Field Name and Description Value Java Home: Enter the Java installed location (on the Application server). Example: </u01/ouaw/java> -
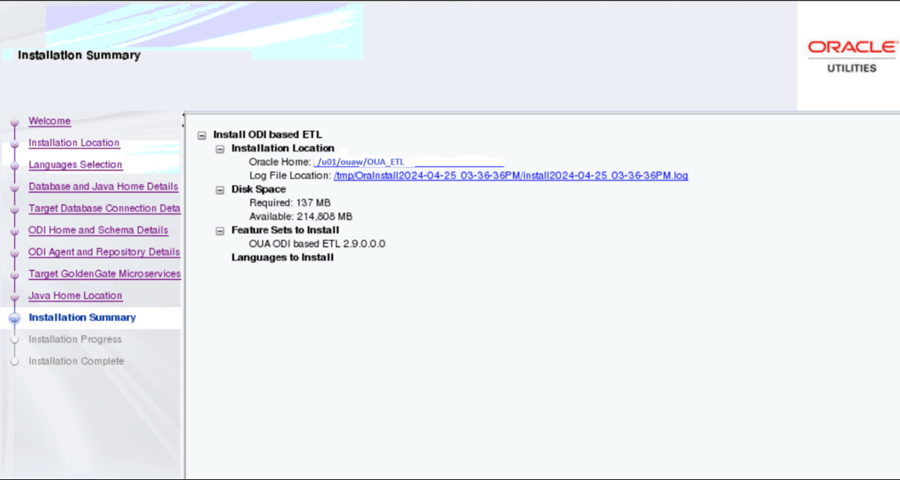
On the Installation Summary page, a summary is displayed. Click the Install button to proceed.
-
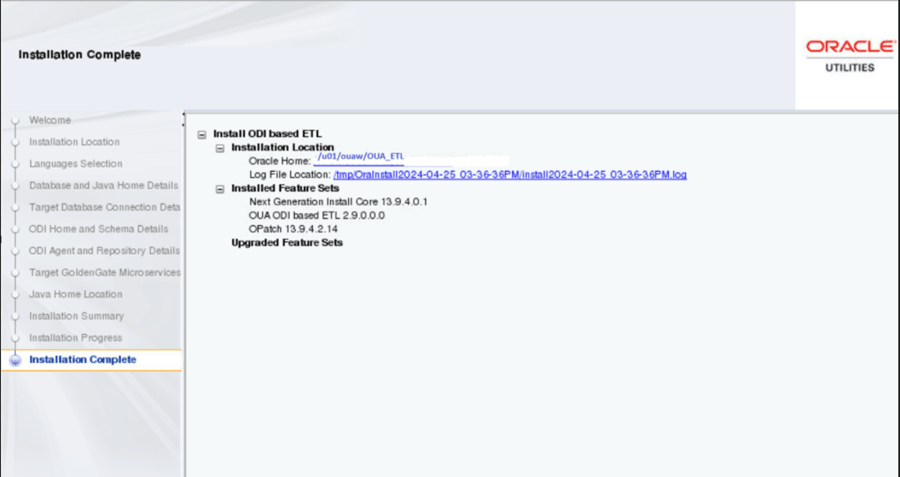
On the Installation Complete page, note the displayed details and click Finish to close the installer wizard. The ETL is now installed.
Verify the OUAW ETL Installation
cd <ETL HOME>;
tree -d <OUA_ETL> -L 1This will confirm that the ETL component installation was successful.
Create a Database Directory
CREATE DIRECTORY B1_DATA_DUMP_DIR AS '</u01/file_data>';Create the WebLogic Domain for Oracle Data Integrator Agent
Create the WebLogic Domain to bring up the WebLogic Agent (ODI Agent) to complete the steps in this section. The ODI Domain creation utility is an automated script that lets you create a non-clustered domain or a clustered domain. Choose which type of domain you want to create and follow the steps below. There are also steps for adding another ODI managed server and editing .sh files for ODI agent connectivity.
-
Create a Non-Clustered ODI Domain
-
Create a Clustered ODI Domain
-
Add Another ODI Managed server.
-
Edit setDomain.sh and startWeblogic.sh files for ODI Agent Connectivity
Create a Non-Clustered ODI Domain
Note:
The password fields values (RCUSCHEMAPWD,WEBLOGIC_PASSWORD) will be cleared from ODI_CONFIG.properties after executing createDomain.sh or createMachine.sh. Ensure these fields are updated for each invocation of createDomain.sh or createMachine.sh.-
Navigate to the <ETL Home>/etc directory and provide the following properties in the ODI_CONFIG.properties file.
Property Description DOMAIN_PATH The directory where odi_domain will be created.
Example : </u01/ouaw/domains/odi_domain>
RCUPREFIX Repository prefix created in the Perform Pre-Installation Steps for OUAW - Prerequisites for Application Server - Configure Repository . Example: ODI RCUSCHEMAPWD Enter the RCU SCHEMA PASSWORD. WEBLOGIC_USERNAME WebLogic user name for <odi_domain>. WEBLOGIC_PASSWORD WebLogic password for <odi_domain>. CLUSTER_NAME(OPTIONAL) -- ODI_DBSERVER ODI database server name (target.databaseserver). ODI_DBPORT ODI database port (target database port). Example: 1521 ODI_DBNAME ODI database service name (target database service name). ADMIN_PORT ODI WebLogic domain AdminServer port. Example: 11000 MANAGED_SERVER_PORT ODI WebLogic domain ManagedServer port. Example: 1001
If not specified, default port 15101 will be assigned.
NONSSL_PORT ODI WebLogic NONSSL_PORT. Example: 11000
If not specified, default port 7001 will be assigned.
ODI_DOMAIN_HOSTNAME Host name(application server) on which the odi_domain is to be created. MACHINE_NAME (OPTIONAL) -- MACHINE_PORT (OPTIONAL) -- MANAGED_SERVER_NAME Example: <ODI_Server1> -
Navigate to the <ETL Home>/bin directory and invoke the createDomain.sh script. After creating the ODI Domain, see Edit setDomain and startWeblogic files for ODI Agent Connectivity and Start the ODI Domain below to start the admin server and managed server.
Create a Clustered ODI Domain
Note:
The scope of the domain creation scripts for clustered domain is limited to creation of a 2 node cluster with managed servers running on the same machine but on different ports. In case your cluster needs more than two managed servers or if the managed servers will be running on different machines, the clustered domain should be created manually using ODI documentation as reference.Note:
The password fields values (RCUSCHEMAPWD,WEBLOGIC_PASSWORD) will be cleared from ODI_CONFIG.properties after executing createDomain.sh or createMachine.sh. Ensure these fields are updated for each invocation of createDomain.sh or createMachine.sh.-
Navigate to the <ETL Home>/etc directory and provide the following properties in the ODI_CONFIG.properties file
Property Description DOMAIN_PATH The directory where <odi_domain> will be created.
Example: </u01/ouaw/domains/odi_domain>
RCUPREFIX Repository prefix created in the LINK TO ODI RCU. Example: ODI RCUSCHEMAPWD Enter the RCU SCHEMA PASSWORD. WEBLOGIC_USERNAME WebLogic user name for <odi_domain>. WEBLOGIC_PASSWORD WebLogic password for <odi_domain>. CLUSTER_NAME Additional mandatory property ODI Cluster name <odi_cluster>. ODI_DBSERVER ODI database server name (target database server). ODI_DBPORT ODI database port (target database port). Example: <1521> ODI_DBNAME ODI database name (target database name). ADMIN_PORT ODI WebLogic domain AdminServer port. Example: <11000> MANAGED_SERVER_NAME The managed server name can be used as <ODI_Server1> and can be added to CLUSTER_NAME. MANAGED_SERVER_PORT ODI WebLogic domain Managed Server port. Example: <11001>
If not specified, default port 15101 will be assigned.
NONSSL_PORT ODI WebLogic NONSSL_PORT. Example: 11000
If not specified, default port 7001 will be assigned.
ODI_DOMAIN_HOSTNAME Host name(application server) on which the <odi_domain> is to be created. -
Navigate to the <ETL Home>/bin directory and invoke the createDomain.sh script. This creates an ODI domain with an admin server and a managed server (called <ODI_server1>) assigned to the cluster.
Add Another ODI Managed Server
-
Navigate to the <ETL Home>/etc directory and provide the following mandatory properties in the ODI_CONFIG.properties file:
• MANAGED_SERVER_NAME
• MANAGED_SERVER_PORT
-
Provide the following optional properties in the ODI_CONFIG.properties file:
• MACHINE_NAME
• MACHINE_PORT
-
Navigate to <ETL Home>/bin and invoke createMachine.sh. A new managed server is created with the specified name and assigned to the cluster.
Edit setDomain and startWeblogic files for ODI Agent Connectivity
-
In the command shell, change the directory to ODI Domain Home. Example: cd <odi_domain>/bin
-
Add the -Dweblogic.oif.serialFilterScope=weblogic argument to setDomainEnv.sh immediately below an existing JAVA_OPTIONS command. Example:
JAVA_OPTIONS="${JAVA_OPTIONS} -Dweblogic.oif.serialFilterScope=weblogic"

-
Create a backup of the startweblogic.sh script.
-
Edit the startweblogic.sh script in the editor.
-
Add the following code after the pattern # START WEBLOGIC.
export CONFIG_JVM_ARGS="-Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -Dweblogic.security.SSL.enableJSSE=true -Dweblogic.security.SSL.ignoreHostnameVerification=true -Dweblogic.security.TrustKeyStore=DemoTrust -Dweblogic.security.CustomTrustKeyStoreType=JKS" -
Insert the following code after the pattern Djava.security.policy=${WLS_POLICY_FILE }:
-Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -Dweblogic.security.SSL.enableJSSE=true -Dweblogic.security.SSL.ignoreHostnameVerification=true -Dweblogic.security.TrustKeyStore=DemoTrust -Dweblogic.security.CustomTrustKeyStoreType=JKSNote:
Insert the code in all three places where the pattern occurs. As an example, here is how the code looks before inserting the new code lines above.${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java ${JAVA_VM} ${MEM_ARGS} ${LAUNCH_ARGS} -Dweblogic.Name=${SERVER_NAME} -Djava.security.policy=${WLS_POLICY_FILE} ${JAVA_OPTIONS} ${PROXY_SETTINGS} ${SERVER_CLASS}Here is how the code looks after inserting the new code lines above.${JAVA_HOME}/bin/java ${JAVA_VM} ${MEM_ARGS} ${LAUNCH_ARGS} -Dweblogic.Name=${SERVER_NAME} -Djava.security.policy=${WLS_POLICY_FILE} -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -Dweblogic.security.SSL.enableJSSE=true -Dweblogic.security.SSL.ignoreHostnameVerification=true -Dweblogic.security.TrustKeyStore=DemoTrust -Dweblogic.security.CustomTrustKeyStoreType=JKS ${JAVA_OPTIONS} ${PROXY_SETTINGS} ${SERVER_CLASS}
Start the ODI Domain
Starting the ODI Domain involves two steps: starting the AdminServer and starting the ODI_server1 managed server.
Start the AdminServer
-
In the command shell, change the directory to <ODI DOMAIN>/servers/AdminServer/security.
-
Create a boot.properties file with <username and password>. Example:
-
username=<weblogic username>
-
password=<weblogic password>
-
-
Change the directory to <ODI DOMAIN>/bin and execute the following command:
nohup ./startWebLogic.sh > startWebLogic.log 2>&1 &
Start the Managed Server <ODI_server1>
-
In the command shell, change directory to <ODI DOMAIN>/servers/<Managed server name>/security.
Example: </u01/ouaw/domains/odi_domain>/servers/<ODI_server1>/security/
If the ODI_server1/security directory does not exist under <ODI DOMAIN>/servers, then create it manually using the following command:mkdir -p ODI_server1/security -
Create a boot.properties file with <username and password>. Example:
-
username=<weblogic username>
-
password=<weblogic password>
-
-
Change the directory to <ODI DOMAIN>/bin and execute the following command:
nohup ./startManagedWebLogic.sh <ODI_server1> > StartManagedWeblogic.log 2>&1 &
Perform Initial Setup for Star Schema
-
Change the directory to <FMW HOME>/odi/studio/bin.
-
Set the JAVA HOME.
export JAVA_HOME=<JAVA_HOME> export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH -
Run the ODI executable file ./odi. This opens Oracle Data Integrator Studio.
Note:
Oracle Data Integrator (ODI) Studio 12.2.1.4 is not supported in AIX and Solaris operating systems. Install ODI in either Linux or Windows machines to connect to the target database. -
Log in to Oracle Data Integrator Studio and navigate to Designer > Load Plans and Scenarios > Framework > scheduler.
-
Navigate to the Load Plans and Scenario folder in the Designer tab.
-
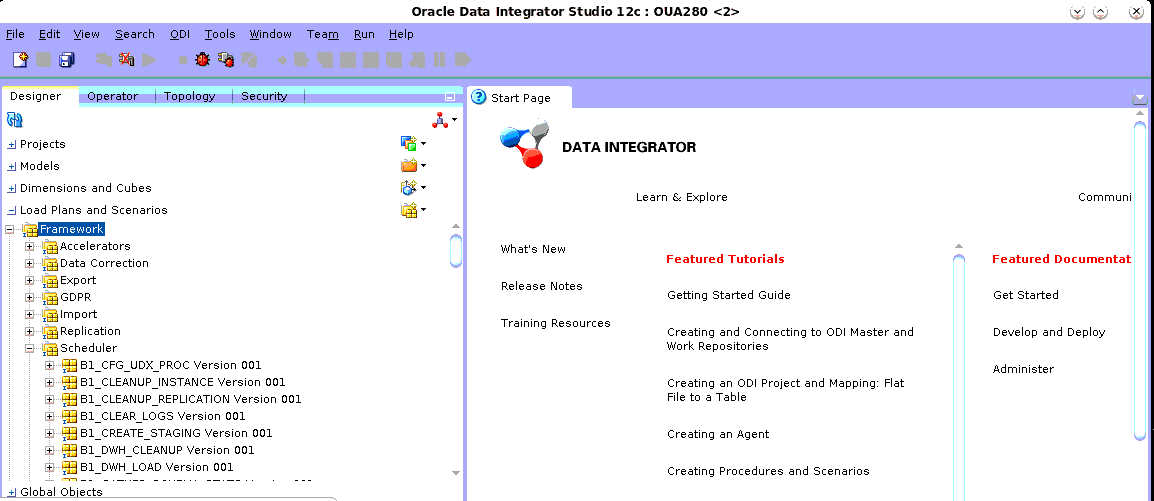
Expand the Framework folder.
-
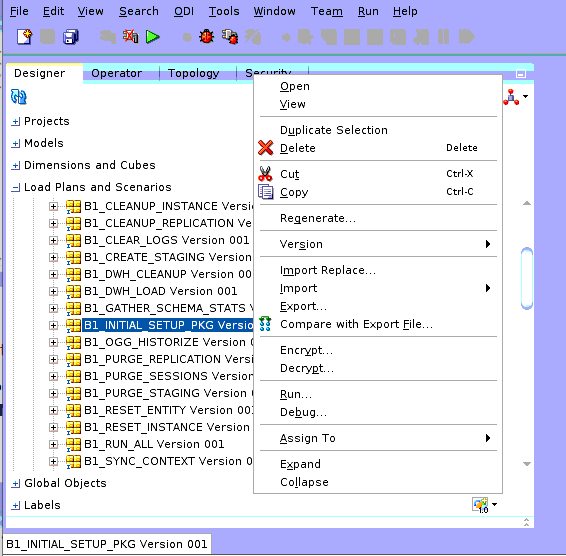
Right-click on B1_INITIAL_SETUP_PKG Version 001 and click Run. A popup windows opens.
-
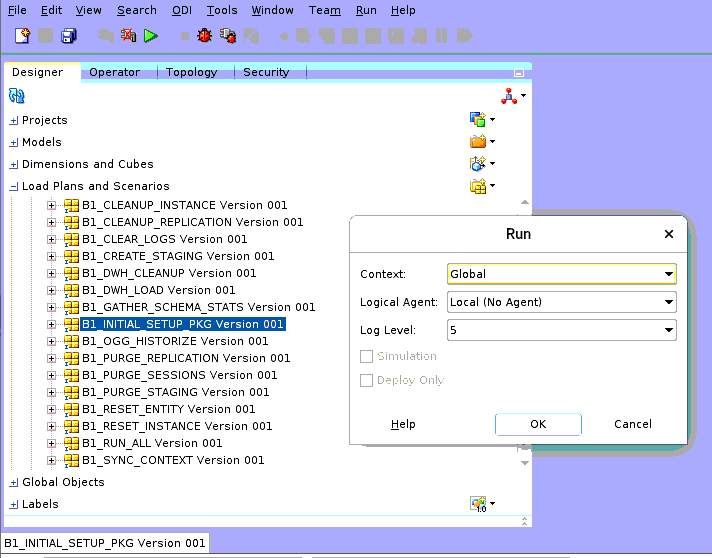
In the Context field, select GLOBAL. In the Logical Agent field, select Local (No Agent). Click OK.
Enable ODI scheduler
-
In Oracle Data Integrator Studio, navigate to Designer > Load Plans and Scenarios > Framework > B1_RUN_ALL Version 001 > Scheduling.
-
Right-click scheduling and select the New Scheduling option.
-
Select the source context as global, agent as WLS_AGENT, and the log level as 1.
-
To specify how often the scheduler should run, navigate to the Execution Cycle tab of the Scheduler and select the Many Times option. Set the interval between repetitions.
-
Navigate to Topology > Agents > OracleDIAgent.
-
Right-click on OracleDIAgent and click Update Schedule.
Modify Maximum Table Name Length Parameter
-
In ODI studio, navigate to Topology > Physical Architecture > Technologies.
-
Right click on Oracle and select Open.
-
Navigate to the Advanced tab and set the value of the Maximum Table Name Length parameter to 128.
-
Click Save.