17 セパレータ
この章では、セパレータを使用してJavaFXアプリケーションのUIコンポーネントを編成する方法について説明します。
JavaFX APIで使用可能なSeparatorクラスは水平および垂直のセパレータの線を表します。 これはアプリケーション・ユーザー・インタフェースの要素を分割しますが、アクションは何も生成しません。 ただし、これにはスタイルの設定、視覚効果の適用、またはアニメーション化を行うこともできます。 デフォルトでは、セパレータは水平です。 この方向はsetOrientationメソッドを使用して変更できます。
セパレータの作成
例17-1のコード・フラグメントでは、1つの水平セパレータと1つの垂直セパレータを作成します。
例17-1 垂直および水平セパレータ
//Horizontal separator Separator separator1 = new Separator(); //Vertical separator Separator separator2 = new Separator(); separator2.setOrientation(Orientation.VERTICAL);
SeparatorクラスはNodeクラスの拡張です。 このため、このセパレータはNodeクラスのインスタンス変数をすべて継承します。
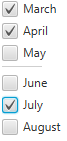
通常、セパレータはUIコントロールのグループの分割に使用されます。 例17-2に示すコード・フラグメントを調べます。 ここでは、春季の月のチェック・ボックスと夏季の月のチェック・ボックスを分けています。
例17-2 チェック・ボックス・カテゴリ間でのセパレータの使用
final String[] names = new String[]{"March", "April", "May",
"June", "July", "August"};
final CheckBox[] cbs = new CheckBox[names.length];
final Separator separator = new Separator();
final VBox vbox = new VBox();
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
cbs[i] = new CheckBox(names[i]);
}
separator.setMaxWidth(40);
separator.setHalignment(HPos.LEFT);
vbox.getChildren().addAll(cbs);
vbox.setSpacing(5);
vbox.getChildren().add(3, separator);
このコード・フラグメントをアプリケーションに適用すると、図17-1に示すコントロールが作成されます。
セパレータは割り当てられている水平または垂直スペース全体を使用します。 setMaxWidthメソッドが適用され、特定の幅を定義します。 setValignmentメソッドは、割り当てられたレイアウト・スペース内のセパレータの垂直位置を指定します。 同様に、setHalignmentメソッドを適用すると、セパレータの線の水平位置を設定できます。
例17-2では、専用のメソッドadd(index, node)を使用してセパレータが垂直ボックスに追加されています。 このアプローチをアプリケーションで使用すると、UIを作成した後、またはUIを動的に変更する場合にセパレータを組み込むことができます。
アプリケーションのUIへのセパレータの追加
前述のとおり、セパレータはUIコントロール・グループの分割に使用できます。 また、ユーザー・インタフェースの構成にも使用できます。 図17-2に示す天気予報データを表示するタスクについて考えてみます。
図17-2に示すアプリケーションでは、LabelオブジェクトとImageViewオブジェクトの分割にセパレータを使用しています。 例17-3に示すこのアプリケーションのソース・コードを調べます。
例17-3 天気予報アプリケーションでのセパレータの使用
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.geometry.Orientation;
import javafx.geometry.VPos;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.*;
import javafx.scene.image.Image;
import javafx.scene.image.ImageView;
import javafx.scene.layout.GridPane;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class SeparatorSample extends Application {
Label caption = new Label("Weather Forecast");
Label friday = new Label("Friday");
Label saturday = new Label("Saturday");
Label sunday = new Label("Sunday");
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Group root = new Group();
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 350, 150);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.setTitle("Separator Sample");
GridPane grid = new GridPane();
grid.setPadding(new Insets(10, 10, 10, 10));
grid.setVgap(2);
grid.setHgap(5);
scene.setRoot(grid);
Image cloudImage = new Image(getClass().getResourceAsStream("cloud.jpg"));
Image sunImage = new Image(getClass().getResourceAsStream("sun.jpg"));
caption.setFont(Font.font("Verdana", 20));
GridPane.setConstraints(caption, 0, 0);
GridPane.setColumnSpan(caption, 8);
grid.getChildren().add(caption);
final Separator sepHor = new Separator();
sepHor.setValignment(VPos.CENTER);
GridPane.setConstraints(sepHor, 0, 1);
GridPane.setColumnSpan(sepHor, 7);
grid.getChildren().add(sepHor);
friday.setFont(Font.font("Verdana", 18));
GridPane.setConstraints(friday, 0, 2);
GridPane.setColumnSpan(friday, 2);
grid.getChildren().add(friday);
final Separator sepVert1 = new Separator();
sepVert1.setOrientation(Orientation.VERTICAL);
sepVert1.setValignment(VPos.CENTER);
sepVert1.setPrefHeight(80);
GridPane.setConstraints(sepVert1, 2, 2);
GridPane.setRowSpan(sepVert1, 2);
grid.getChildren().add(sepVert1);
saturday.setFont(Font.font("Verdana", 18));
GridPane.setConstraints(saturday, 3, 2);
GridPane.setColumnSpan(saturday, 2);
grid.getChildren().add(saturday);
final Separator sepVert2 = new Separator();
sepVert2.setOrientation(Orientation.VERTICAL);
sepVert2.setValignment(VPos.CENTER);
sepVert2.setPrefHeight(80);
GridPane.setConstraints(sepVert2, 5, 2);
GridPane.setRowSpan(sepVert2, 2);
grid.getChildren().add(sepVert2);
sunday.setFont(Font.font("Verdana", 18));
GridPane.setConstraints(sunday, 6, 2);
GridPane.setColumnSpan(sunday, 2);
grid.getChildren().add(sunday);
final ImageView cloud = new ImageView(cloudImage);
GridPane.setConstraints(cloud, 0, 3);
grid.getChildren().add(cloud);
final Label t1 = new Label("16");
t1.setFont(Font.font("Verdana", 20));
GridPane.setConstraints(t1, 1, 3);
grid.getChildren().add(t1);
final ImageView sun1 = new ImageView(sunImage);
GridPane.setConstraints(sun1, 3, 3);
grid.getChildren().add(sun1);
final Label t2 = new Label("18");
t2.setFont(Font.font("Verdana", 20));
GridPane.setConstraints(t2, 4, 3);
grid.getChildren().add(t2);
final ImageView sun2 = new ImageView(sunImage);
GridPane.setConstraints(sun2, 6, 3);
grid.getChildren().add(sun2);
final Label t3 = new Label("20");
t3.setFont(Font.font("Verdana", 20));
GridPane.setConstraints(t3, 7, 3);
grid.getChildren().add(t3);
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
このアプリケーションでは、水平セパレータと垂直セパレータの両方を使用して、GridPaneコンテナ内で行と列を分割するセパレータを作成します。 実際のアプリケーションでは、セパレータの望ましい長さ(水平セパレータの幅と垂直セパレータの高さ)を設定し、ユーザー・インタフェースのサイズが変更されたときに動的に変化するようにもできます。 また、Separatorオブジェクトに使用できるCSSクラスを適用すると、セパレータの視覚的な外観を変更できます。
セパレータのスタイル設定
例17-3に示すすべてのセパレータに同じスタイルを適用するには、CSSファイル(controlStyle.cssなど)を作成し、このファイルをアプリケーションのメイン・クラスと同じパッケージに保存します。 例17-4は、controlStyleファイルに追加できるCSSクラスを示しています。
例17-4 CSSクラスを使用したセパレータのスタイル設定
/*controlStyle.css */
.separator .line {
-fx-border-color: #e79423;
-fx-border-width: 2;
}
例17-5に示すように、SceneクラスのgetStylesheetsメソッドを使用すると、アプリケーションでのセパレータのスタイルを有効にできます。
図17-3では、アプリケーションをコンパイルして実行したときに、天気予報のセパレータがどのように表示されるかを示します。
関連APIドキュメント