176 Automatic Accounting Instructions (AAIs)
This chapter contains these topics:
The Automatic Accounting Instructions screen lets you view the AAIs that are set up for the JD Edwards World systems you use. AAIs make up a table of instructions about your accounting logic and rules. These instructions, which are stored in the Automatic Accounting Instructions Master file (F0012), are used primarily to enforce consistent accounting rules and minimize repetitive manual entry of account numbers. AAIs link the accounting information in the different JD Edwards World systems to the chart of accounts in the general ledger. Therefore, each system that has an interface with the General Accounting system uses AAIs.
Each AAI includes a description, company number, account number (business unit.object.subsidiary), and item. Depending on the AAI, one or more of the components in the account number may be optional or not used. The system uses the combination of an item and a company to determine the account number in the AAI table. You set up these specific item-company combinations on the Auto Accting Instr. Revisions screen.
For more information about AAIs and their setup screens, see the JD Edwards World General Accounting I Guide.
Caution:
Because AAIs are central to the process related to the general ledger, you should be thoroughly familiar with them before you change the AAI table.From any Real Estate Management menu, enter 29 in the Selection field.
From the Real Estate Management Setup menu (G1541), choose System Setup. From the System Setup menu (G1542), choose Automatic Accounting Instr.
Figure 176-1 Automatic Accounting Instructions screen
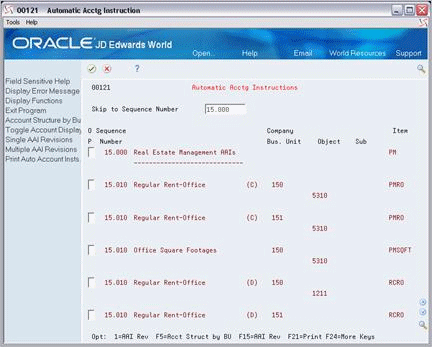
Description of "Figure 176-1 Automatic Accounting Instructions screen"
176.1 AAIs Related to Real Estate Management
Most AAIs in the Real Estate Management system are made up of one of the following prefixes and the appropriate bill code or adjustment reason:
For information about how the bill codes and AAIs relate to A/R invoices and A/P vouchers, see Chapter 22, "G/L Transaction Generation" in this guide.
In the Automatic Accounting Instructions Master file, the AAIs related to the Real Estate Management system have sequence numbers between 15.000 and 15.999. The following table shows some of the groups of AAIs that are already defined for the system:
| SEQUENCE NUMBER | DESCRIPTION | SAMPLE ITEMS |
|---|---|---|
| 15.010 | Regular rent - office | PMRO, RCRO |
| 15.020 | Regular rent - retail | PMRRTL, RCRRTL |
| 15.040 | Rent expense - payable lease | PCRENT, RMRENT |
| 15.050 | Expense participation | PMEXPA, RCEXPA |
| 15.060 15.065 | Sales overage Sales overage - payable and rent expense | PMSLSO, RCSLSO PCSALE, RMSALE |
| 15.070 | Escalation | PMESCA, RCESCA |
| 15.080 | Management fees | PMMGMT, RCMGMT |
| 15.090 | Miscellaneous receivable
FASB 13 - accruals FASB 13 - adjustments FASB 13 - catch-up adjustments FASB 13 - deferrals |
PMMISC, RCMISC
PMACCR, RCACCR PMAJST, RCAJST PMCACH, RCCAC PMDEFR, RCDEFR |
| 15.100 | Security deposit Security deposit interest | PMSECD, RCSECD RASI |
| 15.110 | Non-sufficient funds | PMNSF, RCNSF |
| 15.650 | Write-offs (such as bad debt) | RABD |
| 15.700 | Late fees | PMLATE, RCLATE |
| 15.800 | Sales taxes - payable | PCTXTX, RMTXTX |
| 15.850 | Range of accounts for revenue fees related to business units Beginning account Ending account | PM001B PM001E |
| 15.900 | Security deposit refunds - offset account Security deposit clearing account | PCREFD RARF |
For revenue fees and their account ranges (sequence number 15.850), you can define up to 999 different ranges, such as PM001B (beginning) and PM001E (ending), PM002B and PM002E, and so on to PM999B and PM999E. For more information, see Chapter 136, "Revenue Fee Tables" in this guide.