10g (9.0.4)
Part Number B10188-01
Home |
Solution Area |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle Application Server Wireless Administrator's Guide 10g (9.0.4) Part Number B10188-01 |
|
This chapter includes the following sections:
Oracle Application Server Wireless supports multi-locale and multi-encoding. The Wireless server dynamically determines locale and request and response encoding based on the runtime context.
The Wireless Server dynamically determines the appropriate locale of a user by using such locale information as PALocale, the user's preferred locale, the Accept Language header, and the site locale.
PAlocale is a HTTP parameter that specifies the preferred value before login. The possible value for the PAlocale parameter follows the http accept-language header format. For example, PAlocale = en-US. This format is distinct from the java locale format (en_US).
The user's preferred locale is the language preference of a Wireless user, which is set with the User Manager. For more information, see Section 4.5 in Chapter 4, "Managing Users".
The Accept Language header is an HTTP protocol parameter that user agents (Web browsers) send with HTTP requests.
|
Note: For information on the HTTP accept-language header format, see the HTTP specification of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). |
The Site Locale is an instance-wide default locale of the Wireless Server. For more information, see Section 15.2.4.
After login, the Wireless Server respects the user's preferred locale.
Before login, the Wireless Web Server (ptg/rm), Async Listener, the Wireless Tools and the Customization Portal each determine the appropriate locale of a user's device.
Table 15-1 illustrates how the Async Listener, the WirelessWeb Server, the Wireless Tools and the Customization Portal determine the locale of a user. The numeric value indicates the preference for the detection methods in descending order.
The Wireless Web Server (ptg/rm) determines the locale of a user in the following order:
PAlocale (if present).
The Wireless Tools and Customization Portal determine the location of a user in the following order:
The Async Listner determines the location of a user in the following order:
You can set a preferred location for a user when you create a user or edit a user profile. If the preferred location is not specified, then the default site locale is used. For more information, see Section 4.5.1.1 in Chapter 4, "Managing Users".
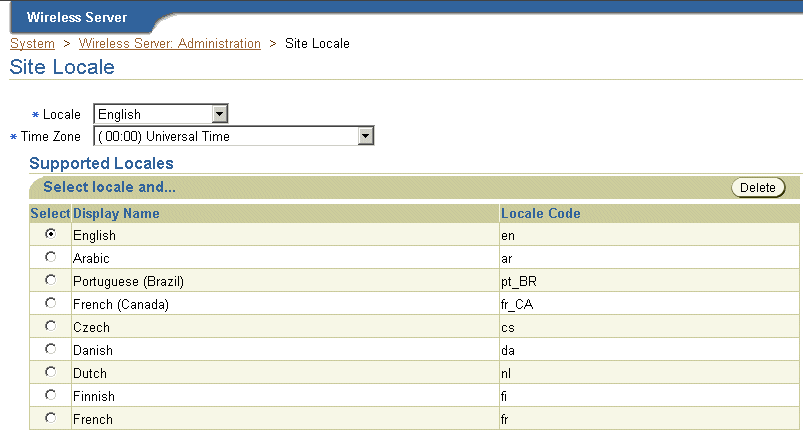
From the Site Administration screen of the System Manager (accessed through the Oracle Enterprise Manager Application Server Control), you can specify the default site locale and add to the list of locales that the site can support. Use a java locale (such as en_US) when adding to the list of supported locales (depicted in Figure 15-1). For more information, see Section 3.6.1.4 in Chapter 3, "Managing the Wireless Server".
|
Note: You can also set the site locale using the Basic Site Configuration wizard, accessed from the Home page of the System Manager. For more information, see Section 3.3.1 in Chapter 3, "Managing the Wireless Server". |
The content encoding of a logical device is used to transport of the result of the device type. The default encoding for all of the devices that ship with Wireless is set to UTF-8. The encoding format of a device is that of the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
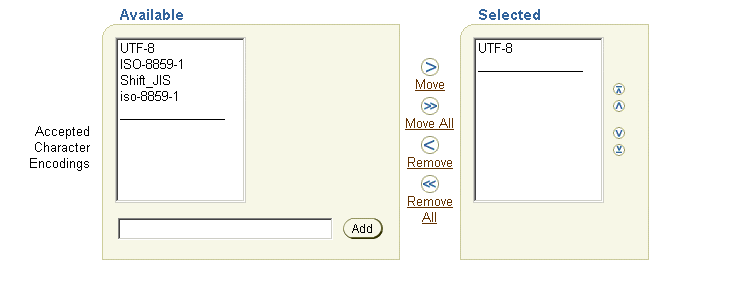
Using the Foundation Manager, you can edit the browser capabilities of a device in the Wireless repository to update it to the encoding appropriate to a given country or locale (Figure 15-2). For more information on creating, cloning, or editing a device, see Section 7.3.2, Section 7.3.3, and Section 7.3.2.1, respectively, in Chapter 7, "Managing Foundation Services".
The following table illustrates how the encoding is determined.
This section describes the encoding for the request and response of a HTTPAdapter-based application
When sending the HTTP request to the remote content provider, only the parameters of the HTTPAdapter application are encoded using the input_encoding of the application (if it is specified). Use the encoding format of the IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority) when specifying the value for input_encoding.
Wireless determines the encoding of the response of an HTTPAdapter-based application in the following order:
Users can view the online help for the Wireless Tool and the Customization Portal in 29 languages. The site locale, configured through the System Manager, determines the display language. For more information, see Section 3.6.1.4 in Chapter 3, "Managing the Wireless Server".
In this release, the built-in labels and on-line help for the Wireless Tools and System Manager display in nine languages.
The Multi-Channel Server (ptg/rm) can display the built-in labels in 29 different languages.
Each driver handles encoding individually .
|
|
 Copyright © 2003 Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|