
HOME | SITE MAP | SEARCH | CONTACT | GLOSSARY | PDF FILES | WHAT'S NEW
GETTING STARTED | TABLE OF CONTENTS | PREVIOUS TOPIC | NEXT TOPIC | INDEX

|
BEA WebLogic Enterprise 4.2 Developer Center | |
|
HOME | SITE MAP | SEARCH | CONTACT | GLOSSARY | PDF FILES | WHAT'S NEW |
||
|
GETTING STARTED | TABLE OF CONTENTS | PREVIOUS TOPIC | NEXT TOPIC | INDEX |
||
This chapter discusses the following topics:
The WLE product offers a security model based on the CORBAservices Security Service. The WLE security model implements the authentication portion of the CORBAservices Security Service.
Security information is defined on a domain basis. The security level for the domain is defined in the configuration file. Client applications use the SecurityCurrent object to provide the necessary authentication information to log on to the WLE domain.
The following levels of authentication are provided:
Overview of the Security Service
No authentication is needed; however, the client application may still authenticate itself, and may specify a user name and a client application name, but no password.
The client application must authenticate itself to the WLE domain and must specify a user name, client application name, and application password.
In addition to the TOBJ_SYSAUTH information, the client application must provide application-specific information. If the default WLE authentication service is used in the application configuration, the client application must provide a user password; otherwise, the client application provides authentication data that is interpreted by the custom authentication service in the application.
Note:
If a client application is not authenticated and the security level is TOBJ_NOAUTH, the IIOP Listener/Handler of the WLE domain registers the client application with the user name and client application name sent to the IIOP Listener/Handler.
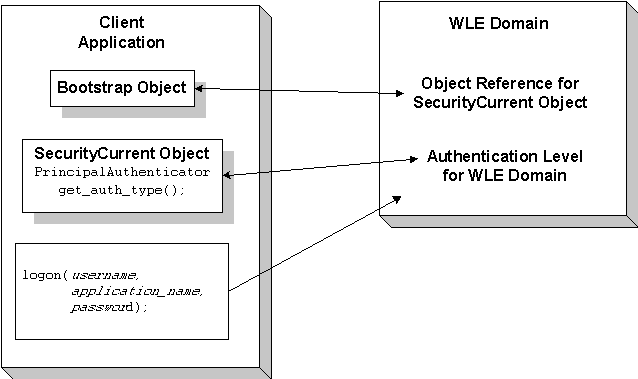
In the WLE software, only the PrincipalAuthenticator and Credentials properties on the SecurityCurrent object are supported. For a description of the Figure 3-1 illustrates how security works in a WLE domain.
The steps are as follows:
SecurityLevel1::Current and SecurityLevel2::Current interfaces, see the C++ Programming Reference or the Java Programming Reference on the Online Documentation CD.
How Security Works
Figure 3-1 How Security Works in a WLE Domain
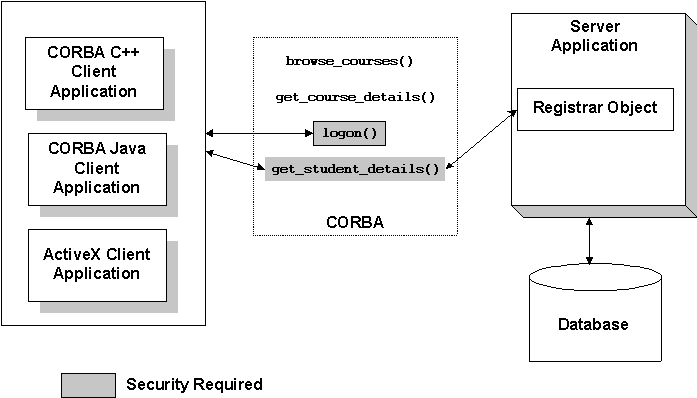
The Security sample application demonstrates application-level security. The Security sample application requires each student using the application to have an ID and a password. The Security sample application works in the following manner:
Figure 3-2 illustrates the Security sample application.
The source files for the Security sample application are located in the Table 3-1 lists the development steps for writing a WLE application that has security.
1
Define the security level in the configuration file.
2
Write the client application.
The security level for a WLE domain is defined by setting the
In the Security sample application, the Write client application code that does the following:
Figure 3-2 Security Sample Application
\samples\corba\university directory in the WLE software. For information about building and running the Security sample application, see the Guide to the University Sample Applications on the Online Documentation CD.
Development Steps
Table 3-1 Development Steps for WLE Applications That Have Security
Step
Description
Step 1: Defining the Security Level in the Configuration File
SECURITY parameter RESOURSES section of the configuration file to the desired security level. Table 3-2 lists the options for the SECURITY parameter.
Table 3-2 Options for the
SECURITY ParameterSECURITY parameter is set to APP_PW for application-level security. For information about adding security to a WLE domain, see the Administration Guide on the Online Documentation CD.
Step 2: Writing the Client Application
Listing 3-1 and Listing 3-2 include the portions of the CORBA C++ and CORBA Java client applications in the Security sample application that illustrate the development steps for security. To see an example of the code for ActiveX client applications, see the Guide to the University Sample Applications on the Online Documentation CD.
Listing 3-1 Example of Security in a CORBA C++ Client Application
CORBA::Object_var var_security_current_oref =
bootstrap.resolve_initial_references("SecurityCurrent");
SecurityLevel2::Current_var var_security_current_ref =
SecurityLevel2::Current::_narrow(var_security_current_oref.in());
//Get the PrincipalAuthenticator
SecurityLevel2::PrincipalAuthenticator_var var_principal_authenticator_oref =
var_security_current_oref->principal_authenticator();
//Narrow the PrincipalAuthenticator
Tobj::PrincipalAuthenticator_var var_bea_principal_authenticator =
Tobj::PrincipalAuthenticator::_narrow
var_principal_authenticator_oref.in());
//Determine the security level
Tobj::AuthType auth_type = var_bea_principal_authenticator->get_auth_type();
Security::AuthenticationStatus status = var_bea_principalauthenticator->logon(
user_name,
client_name,
system_password,
user_password,
0);
Listing 3-2 Example of Security in a CORBA Java Client Application
org.omg.CORBA.Object SecurityCurrentObj =
gBootstrapObjRef.resolve_initial_references("SecurityCurrent");
org.omg.SecurityLevel2.Current secCur =
org.omg.SecurityLevel2.CurrentHelper.narrow(secCurObj);
//Get the PrincipalAuthenticator
org.omg.SecurityLevel2.PrincipalAuthenticator authlevel2 =
secCur.principal_authenticator();
//Narrow the PrincipalAuthenticator
com.beasys.Tobj.PrincipalAuthenticatorObjRef gPrinAuthObjRef =
(com.beasys.Tobj.PrincipalAuthenticator)
org.omg.SecurityLevel2.PrincipalAuthenticatorHelper.narrow(authlevel2);
//Determine the security level
com.beasys.Tobj.Authtype authType = gPrinAuthObjRef.get_auth_type();
org.omg.Security.AuthenticationStatus status = gPrinAuthObjRef.logon
(gUserName, ClientName, gSystemPassword, gUserPassword,0);