9 Understanding CNAO Version 2 Audit Files in China
This chapter contains these topics:
9.1 CNAO Version 2 Audit Files
You use the GB/T 24589-2010 Financial Information Technology- Data Interface of Accounting Software to submit CNAO audit files. The China National Audit Office (CNAO) refers to the reporting standards as CNAO Version 2 (CNAO-V2)
If your organization is affected by the new standards, you must submit XML files to report on your financial transactions. Among the transactions that you must report are those for:
-
Accounts payable
-
Accounts receivable
-
General ledger
-
Fixed assets
-
Payroll
You also submit an XML file that includes information about the reporting organization, customers, suppliers, and employees for which transactions are reported. This XML file is referred to as the Shared Information XML file.
|
Note: You might also need to report information according to the version 1 standards. |
9.1.1 Process Overview
Much of the data that you need to report is available in the base and China-specific software tables. However, you will need to set up some additional information to include in the XML files that you generate to report your transactions.
|
Note: Some of the setup data is used by multiple XML output programs. Be sure to verify that you have completed all of the setup described in the chapter for each output file, including any steps noted in the prerequisites and the checklist provided in each chapter. |
You can generate the XML files in any order you choose. However, because some setup is used by multiple programs, Oracle recommends that you:
-
Set up the primary functionality that is used across all modules.
This functionality includes the document titles that you want to print in the XML file, alternative UDC descriptions, currency code information, and so on.
See Setting Up Your System to Generate CNAO Version 2 Audit Files
-
Set up and generate the Shared Information XML file.
The CNAO Shared Information XML file includes data about the reporting organization as well as metadata about records in the other CNAO XML files. Some of the data exists in the tables provided for the electronic accounting books for China. Other data includes customer and supplier master records; address book records for employees, customers and suppliers; and data that you enter in new programs for CNAO version 2 audit files.
Because some of the data that you enter in the new setup programs for the shared information XML file is used by the programs for other XML files, you must complete some of the setup described in the Setting Up and Generating the CNAO Shared Information XML File chapter before generating the XML files for other XML files
See Setting Up and Generating the CNAO Shared Information XML File
-
Process your payroll, and then set up and generate the Payroll XML file.
Because China-specific payroll processing is not available in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne system, you must add data about your employees, payroll periods, payroll categories, and the payroll amounts that you paid to employees in new programs provided in this ESU. You must process your payroll before setting up and generating the payroll XML file because you must enter up-to-date information about payroll transactions before you generate the XML file.
Setting Up and Generating Payroll Information for CNAO Audit Files for China
-
Process and post your general ledger records, and then set up and generate the general ledger XML file. The process for generating the general ledger XML file includes two sub-processes. After you set up subsidiary information, you must run several programs to update the subsidiary information for general ledger; accounts receivable and accounts payable; purchase orders; and, sales orders. You must also run several programs to update financial statement data such as cash flow, income statements, and balance sheets. The subprocesses each populate a table that is used by the XML generation program to produce the final output file.
See Setting Up and Generating GL Information for CNAO Audit Files
-
Process and post your accounts payable and accounts receivable records, and then generate the AP/AR XML file.
See Setting Up and Generating AP and AR Information for CNAO Audit Files
-
Set up and generate the fixed asset XML file.
See Setting Up and Generating Fixed Assets Information for CNAO Audit Files
Detailed process flows for each XML file are available in the chapters that describe how to generate each XML file.
This illustration shows the high-level process flow for the primary setup, the shared information XML file, and the payroll XML file.
Figure 9-1 High-Level Process Flow for Primary Setup, Shared Information, and Payroll

Description of ''Figure 9-1 High-Level Process Flow for Primary Setup, Shared Information, and Payroll''
This illustration shows the high-level process flow for the general ledger XML file.
Figure 9-2 High-Level Process Flow for the General Ledger XML File
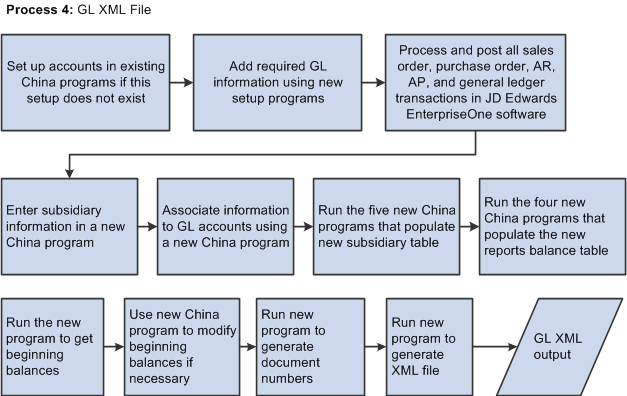
Description of ''Figure 9-2 High-Level Process Flow for the General Ledger XML File''
This illustration shows the high-level process flow for the accounts receivable and accounts payable, and the fixed asset XML files:
Figure 9-3 High-Level Process Flow for the AR/AP and Fixed Assets XML Files
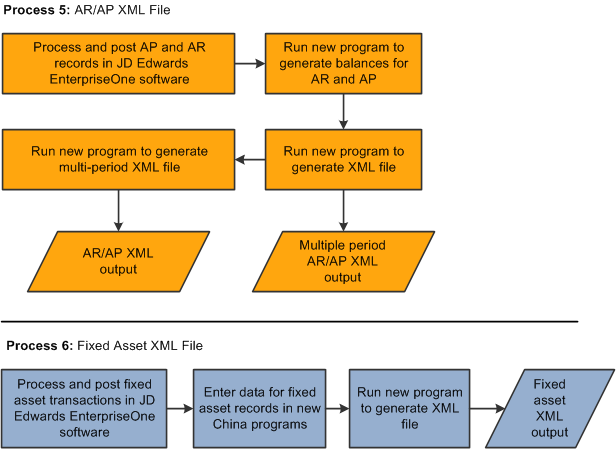
Description of ''Figure 9-3 High-Level Process Flow for the AR/AP and Fixed Assets XML Files''
9.2 Using the XML Encoding Converter Utility
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne software creates all XML files for CNAO version 2 in the UTF 8 format. However, if required, you can convert the XML files to the GB18030 format. To convert the files, you need to run the XML Encoding Converter utility. Before you run this utility, you must ensure that you have Java Virtual Machine version 1.6 installed on your computer.
You must perform these steps to run the converter utility:
-
Create a folder in the C directory. This is the input folder for the conversion.
-
Copy the XML files that you need to convert to this input folder on the C drive.
-
Create a folder on the C drive for the output files. This is the output directory.
-
Access the DOS command line and enter this command: type this command cd C:\b9\system\Classes, where C:\b9\system is the default folder for the EnterpriseOne package.
If you have installed the EnterpriseOne package in some other location, type that instead of C:\b9\system in the above command. The XMLEncodingConverter_JAR.jar file exists in the Classes folder of the folder where you install the EnterpriseOne package.
-
On the command prompt, type this command java -jar XMLEncodingConverter_JAR.jar InputDir UTF-8 OutputDir GB18030, where InputDir and OutputDir refer to the input and output directories created in the above-mentioned steps. Output
For example, if you created folders with names Input and on your C drive, you must enter this command java -jar XMLEncodingConverter_JAR.jar c:\input UTF-8 c:\output GB18030.
-
Press the Enter key on your keyboard.
The system generates text that mentions what files are being converted and the directory locations. When all files are converted, the system generates the FinishedEncoding message. This indicates that all files have been converted to the desired format. You can review the files from the output directory.