| Solstice Enterprise Manager 4.1 Customizing Guide |
Managing Devices Using RPC Agents
Solstice Enterprise Manager (Solstice EM) is shipped with a suite of agents developed for the Site/SunNet/Domain Manager (SNM) network management system. These agents communicate with a network manager, such as Solstice EM, using Remote Procedure Call (RPC) protocol within an Internet (TCP/IP) network environment. When deployed on systems in your network, these RPC agents and proxy agents can be used by Solstice EM as part of your strategy for managing network resources. The resource may be a machine, a component in a machine (such as a router interface card), or some other resource. The RPC agent may be local to or remote from that resource.
This chapter describes the following topics:
- Section 6.1 Types of RPC Agent Management
- Section 6.2 Preparing for Device Management with RPC Agents
- Section 6.3 RPC Management Protocol Adapter
- Section 6.4 RPC MPA Configuration Parameters
6.1 Types of RPC Agent Management
There are two types of SunNet Manager RPC agents: those that directly access managed resources and those that indirectly access managed resources. Most of the RPC agents provided with Solstice EM manage resources on the Sun workstations (or PCs running Solaris for x86) where they are installed. For example, the diskinfo agent provides file system usage data.
The second type of agent provides the ability to manage resources that reside in other Sun workstations or in other vendors' devices. Such agents are called proxy agents. Proxy agents run on machines running Solaris, called proxy systems, and use protocol translation mechanisms to provide the necessary access to the managed resources. The proxy system can also be a workstation in a different subnet or domain from where the Solstice EM MIS is running.
As illustrated in the following figure, SNM agents and proxies use Remote Procedure Call (RPC) protocol to communicate with the Solstice EM MIS (via the RPC Management Protocol Adapter). However, an SNM proxy agent may use a different management protocol in gathering information from other agents.
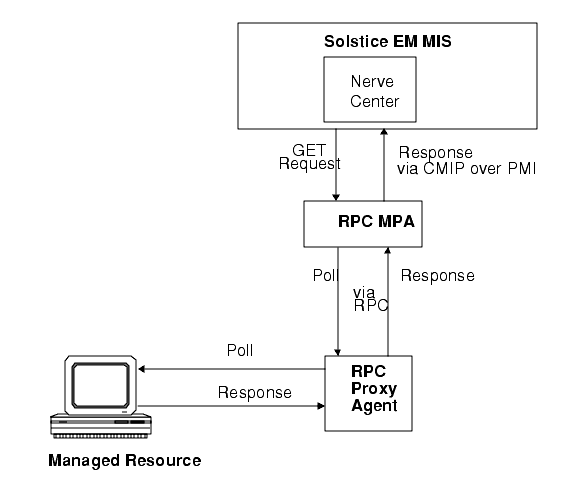
FIGURE 6-1 Communication With RPC Agents in Direct Polling RequestsSolstice EM Nerve Center requests can obtain information from RPC agents in two ways:
- Direct polling by the Nerve Center--A request running in the Nerve Center can directly poll the agent, at intervals specified in the request template. The goal of such a request is to obtain the values of the specified attributes directly from the agent. Building request templates that do direct polling of RPC agents is described in Chapter 15. Communication between manager and managed resource in a direct polling request is illustrated in FIGURE 6-1.
- Offload polling activity to the RPC proxy agent--A Nerve Center request can send a one-shot message, called an SNM event request, to a RPC proxy agent. The event request causes the RPC proxy agent to begin polling for a threshold specified in the event request. The event request also specifies the polling interval. Polling of the managed resource is thus handled by the RPC agent rather than the Nerve Center. This minimizes the polling work required by the MIS and allows the polling to be distributed to a site closer to the resource being polled. If the event defined in the event request occurs, the RPC agent sends event information to the SNM Event Dispatcher (na.event) running on a specified management station (by default, this is the station that initiated the request). When a SNM event notification arrives at an MIS machine, this information is forwarded to the Solstice EM MIS by Solstice EM's SNM Event Forwarder (em_snmfwd). Communication between manager and agents in SNM event requests is illustrated in the following figure.
- Building templates that use the Nerve Center's SNM event request capability is described in Chapter 17.
Note – If you are using SNM Consoles to manage segments of your network, these SNM Consoles will be initiating SNM event requests and tracking network view changes. Event and network view information received by these SNM management stations can be forwarded to an Solstice EM MIS using Cooperative Consoles. This type of distributed management scenario is described in Chapter 7.
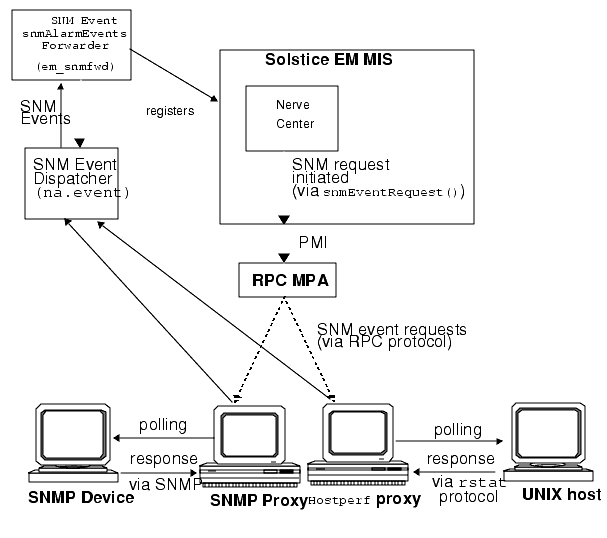
FIGURE 6-2 Using SNM Event Requests with Solstice EM6.2 Preparing for Device Management with RPC Agents
The first thing you must do is prepare your device management with RPC agents.
To Prepare the Device Management with RPC Agents
1. Install and configure the RPC agents.
- Proxy agents may be installed on either the machine to be managed or on a remote system, called a proxy system. RPC agents can be installed on three types of machine:
- SPARC machines running Solaris 1.x (SunOS 4.x)
- SPARC machines running Solaris 2.x (SunOS 5.x)
- PCs running Solaris 2.x for x86
- SUNWsnmag is installed by default during installation of Solstice EM 4.1. Use pkgadd on other machines to install the RPC agents package (machines to be managed or proxy systems).
- To install agents on a machine running Solaris 1.x, use the getagents script.
- For information on installation of RPC agents on the three types of system listed above, refer to Chapter 6 in Installation Guide.
- If you have written your own SNM agent or have a third-party SNM agent, copy the file for that agent, with its accompanying configuration files, to the target machine. (You will also need to load a GDMO translation of the SNM schema file into the MIS; this is discussed in Step2 below.)
- For information on configuring the SNMP proxy agent (na.snmp), or the SNMP Version 2 proxy agent (na.snmpv2), see Chapter 10.
2. Add Object Classes to the MIS based on SNM Schemas. If you are using only those SNM agents shipped with Solstice EM, you can skip to Step4.
The definition language used internally in the Solstice EM MIS to describe object classes is the Guidelines for the Definition of Managed Objects (GDMO), outlined in the ISO/IEC 10165-4 standard. An object class defines the structure of the management information of a managed resource.
Schema files are the corresponding method for object type definition native to SNM. Schema files are used for loading information about the management capabilities of RPC agents into the SunNet Manager Console. Solstice EM includes a schema-to-GDMO compiler for translating native SNM schema files into GDMO documents. If you want Solstice EM to acquire knowledge of the capabilities of an SNM-compatible RPC agent that you have written, or which you have acquired from a product vender, you must convert the agent's schema file to pertinent GDMO and ASN.1 files, and these must be loaded into the MIS. The procedure for accomplishing these tasks is described in Chapter 8 of Management Information Server (MIS) Guide.
However, you will only need to do a schema-to-GDMO conversion if you have SNM schemas not provided with Solstice EM. For all SNM schemas shipped with Solstice EM, corresponding GDMO documents are already provided with the product, and these are loaded into the MIS at startup.
Note – If you are using an RPC-based SNMP proxy agent (na.snmp or na.snmpv2), SNM schema files must also be provided on the proxy system to enable the proxy agent to map Management Information Bases (MIBs) for SNMP devices that are to be managed. For more information, see Chapter 10.
3. Install and configure the RPC MPA.
- The RPC Management Protocol Adapter (MPA) is a protocol translator that enables communications between the MIS SunNet Manager proxy agents using Remote Procedure Call (RPC) protocol. By default, the RPC MPA is installed on the same machine as the MIS. However, to improve performance you may want to distribute the RPC MPA to another machine. For information on installation of the RPC MPA, refer to Chapter 6 in Installation Guide. For more information on the RPC MPA, refer to Section 6.3 RPC Management Protocol Adapter.
4. Configure the managed object in the MIS.
Note – This is applicable only for proxy agents.
- The object in the MIS that represents the target managed resource must be configured to indicate support for appropriate SNM agents. There are two ways to accomplish this task:
- If you use Network Discovery to populate your MIS, you can configure Network Discovery to query hosts for RPC agents and automatically configure objects to indicate RPC agent support when it adds them to the database. The RPC agent selection sheet in the Network Discovery Properties window is shown in FIGURE 6-3. You can also select the host that will be configured as the proxy system for RPC-manageable devices that are added to the MIS by Network Discovery. When SNM event requests are targeted at these devices, the RPC proxy agents on the "default proxy" are used to conduct the threshold-checking of the target device. If localhost (the default) was selected during discovery, the RPC proxy agents on the MIS machine are used to carry out threshold-checking. In the example in the following figure, the machine localhost is selected to be the proxy host for all devices added to the MIS through this use of Network Discovery. For more information on using the Network Discovery tool, refer to Chapter 3 in Managing Your Network.
- You can also manually configure RPC agent support for objects in the MIS using the Network Views Object Properties/Create Object. It is invoked from the Solstice EM Network Views. For more information, refer to Chapter 3 in Managing Your Network.
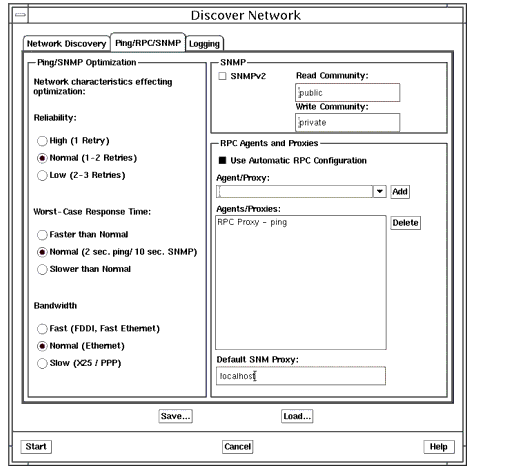
FIGURE 6-3 Selecting RPC Agents to be Configured During Network Discovery5. Build request templates for RPC agents.
- The Nerve Center module in the MIS contains the request-handling capabilities of Solstice EM. Nerve Center requests are based on request templates, which are built using the Design Advanced Requests tool. A key building block in request templates are request conditions--sets of instructions defined using the Solstice EM Request Condition Language (RCL). RCL supports both direct polling of RPC agents as well as setting thresholds for polling by proxy agents. A number of predefined request templates for use with RPC agents are shipped with Solstice EM; these are described in the following table. If you wish to build additional request templates for RPC agents, you may want to consult the following sources of information:
- For guidance on building direct polling request templates, consult Chapter 15.
- For information on the Design Advanced Requests, see Chapter 18.
- For information on Request Condition Language, see Chapter 20.
- RCL provides two built-in functions, snmEventRequest() and snmKillRequest(), for starting and stopping SNM event requests. Building templates for SNM event requests is described in Chapter 17.
- For additional information on RCL functions that can be used in building request templates, see Chapter 22.
6.3 RPC Management Protocol Adapter
The Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Management Protocol Adapter (MPA) provides the mechanism to get data and set attribute values for devices that are managed via RPC-based agents. The RPC MPA works as a proxy agent between the Solstice EM MIS and any device on the network having RPC agents installed.
The RPC MPA serves a major role in providing compatibility with SunNet Manager 2.2 or later products. Agents that were written for SNM 2.2 or later can be registered with the Solstice EM MIS, so that when a request is made, the RPC MPA will be called by the MIS to route the request via RPC calls to the appropriate SNM 2.2 or later agent on the appropriate host.
Note – SNM 2.2 or later schema files get compiled by the Schema compiler (em_snm2gdmo) into GDMO descriptions which then get loaded into the Solstice EM MIS. This is described in the Management Information Server (MIS) Guide.
When an RPC request is received by the Solstice EM MIS, the MIS will route the request to the RPC MPA. When the new request arrives from an MIS, the RPC MPA translates the CMIS-like message it received into a corresponding RPC request. It then sends the request to the specified SNM agent on the specified device and waits for a response. Upon receiving a response from the SNM agent, the RPC MPA translates the RPC message into a CMIS-like message, and sends it on to the MIS.
All communication between the MIS and the RPC MPA are CMIS-like. All communication between the RPC MPA and the manageable SNM agents are via RPC.
6.4 RPC MPA Configuration Parameters
The following configuration parameters for the RPC MPA are set during installation:
- Default MIS host--The name of the machine running the MIS that the MPA is to connect to.
- Default MIS port--The port used in communicating with the MIS (by default this is port 5555).
- Default RPC MPA port--The port on which the RPC MPA listens for incoming messages (by default this is port 5577).
- RPC request timeout--The length of time the RPC MPA waits for a response to a request sent to an RPC agent (by default, this is 15 seconds).
- RPC retries--The number of times the RPC MPA retries a request to an RPC agent if there is no response (by default this is zero).
The request and retry parameters determine when the RPC MPA determines that an RPC agent is unavailable.
|
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Copyright information. All rights reserved. |
Doc Set | Contents | Previous | Next | Index |