Configuring Load Balancers
Configuring the Load Balancer
The Load Balancer element has the following ports:
-
One management port for each primary port on the device
-
16 Virtual IPs (VIPs) for each primary port
There is no restriction on the number of subnets that you may use for VIPs. Subnets may reside on any VLAN. Similarly, the management interfaces may be connected to any subnet on any VLAN. Servers attached to the management subnets on either or both management ports are balanced. Allocate IPs on a subnet by connecting the VIP to the Subnet element. Set the number of IPs by adding VIPs in the Configure Load Balancer dialog box.
Note –
If you are balancing servers that run a Linux operating system that does not support VLANs, all subnets must reside on the same VLAN.
This section describes the following types of Load Balancer configurations.
-
Path Failover, see How To Configure a Load Balancer in Path Failover Mode
-
Device Failover or High Availability (HA), see How To Configure the Load Balancer
-
Single Device (non-HA), see How To Configure the Load Balancer
Single load balancer device configuration (non-HA) is provided by the standard replacefaileddevice request mechanism. See Troubleshooting Farm Device Failure in N1 Provisioning Server 3.1, Blades Edition, System Administration Guide and Responding to Farm Device Failure in N1 Provisioning Server 3.1, Blades Edition, System Administration Guide for a description of replacefaileddevice request.
The following graphic illustrates a single device load balancer configuration.
Figure 4–1 Farm with Single Load Balancer Device
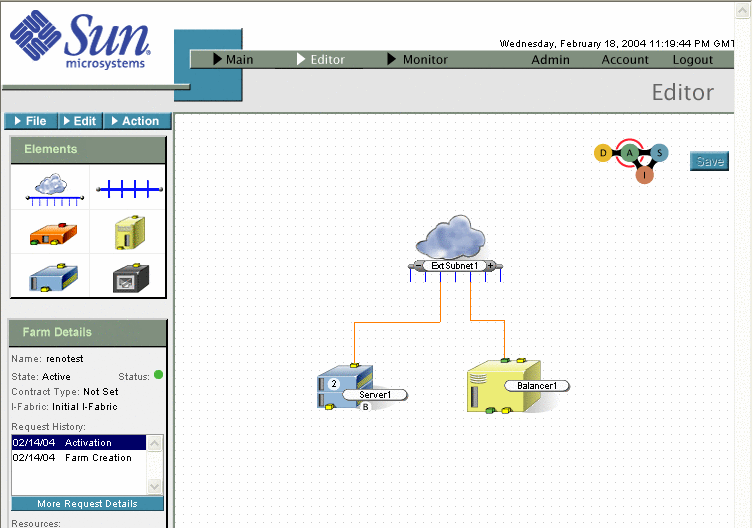
To enable path failover, connect both management interfaces (green ports) to the same subnet. If one interface fails, paths on the failed interface will be restored on the live interface. The following graphic illustrates a server farm configured for path-failover load balancing.
Figure 4–2 Farm with Path-Failover Load Balancing
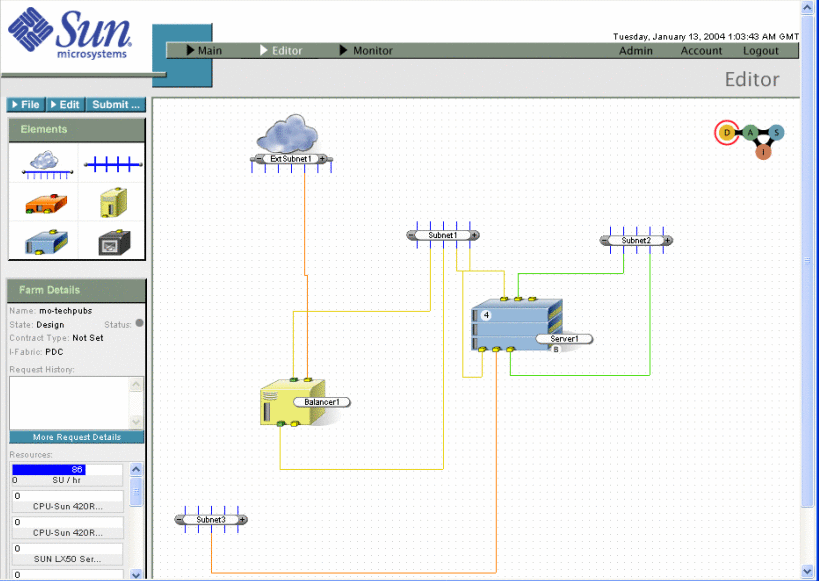
By default, the Server element has one interface for each primary port, corresponding to the primary interface for that port. The primary interfaces have DNS names. To set the native VLAN of the physical interfaces, place the primary interfaces on the same VLAN. Primary interfaces cannot be removed, and their primary port cannot be changed. DNS names appear only for primary interfaces. IP addresses appear for all interfaces when they are assigned.
HA Configuration
If the load balancer you selected is in a high availability (HA) configuration, the element in the farm view area displays an HA.
To enable device failover or high availability, configure a standby-active pair of load balancer devices. You may add and remove virtual interfaces from within the Configure Server dialog box. See How To Configure the Load Balancer and How To Configure Virtual Interfaces for procedural information.
Load Balancer Best Practices
Multiple subnets are used for data, service, and management VLANs.
-
The data VLAN is where the VIPs will reside.
-
The service VLAN is the VLAN on which traffic flows from the Load Balancer to the server.
-
The management VLAN is one on which servers are load balanced.
To support the path failover configuration, the Control Center allocates Virtual IPs (VIP) on multiple subnets. The Control Center displays connections between the ports and multiple subnets. This functionality enables you to use both load balancer ports and show separation between the data VLAN and the management VLAN.
The Load Balancer management interface must be on a subnet on which one of the server interfaces resides (the management subnet). This subnet should be on a separate VLAN than the Data VLAN or the Service VLAN.
You can perform more extensive configurations directly on the device. After you perform these manual configurations, you can use the snapshot mechanism to capture the configuration. Refer to the section Creating an Account Image By Using Snapshot and How To Snapshot Load Balancer for more details.
Multiple load balancers are needed only when the load balancers are connected to multiple subnets. A common use of multiple load balancers would be to balance web traffic to web server and then balance database traffic to database servers. Each VLAN is indicated by a different wire color.
Note –
A load balancer can only balance the server. A load balancer cannot balance a subnet, external subnet, or ethernet port.
 How To Configure the Load Balancer
How To Configure the Load Balancer
Load balancing evenly distributes data and processing across selected resources. Specify the type of load balancing and identify a load balancing group according to your business requirements. IP addresses are assigned after the farm is activated. The following procedure describes how to use the Editor screen to configure a Load Balancer device.
Steps
-
Double-click the Load Balancer element on the Editor screen.
The Configure Load Balancer dialog box appears.
-
Type the name in the Name field.
-
Select the device from the Type drop-down list, use HA device for high availability.
Note –You may modify this type only when the device is in the Design state.
-
Select the load-balancing policy from the Policy drop-down list.
The following choices appear.
-
Round Robin (default)—New connections are routed sequentially to servers in the Load Balancer group, thereby spreading new sessions equally across all servers.
-
Least Connected—New connections are sent to the server with the least number of active sessions.
-
Weighted—New connections are sent to servers according to weight assignments. Servers with a higher weight value receive a larger percentage of connections. You can assign a weight to each real server, and that weight determines the percentage of the current connections given to each server. The default weight is 1. You must set the load balancer weights manually.
Note –You may modify the Load Balancer policy in the Design and Active states.
-
-
Type notes or comments in the Notes field.
-
Click Add Binding and specify the IP port used to balance incoming traffic.
Each virtual interface has a set of bindings that consist of the virtual port, the real interface, and the real port. Traffic is balanced across the bindings for the interface that shares the same port.
Note –You may change this port only in Design and Active states.
-
Select the device from the Real Interface drop-down list.
The traffic coming into the virtual port on the virtual interface is balanced to the real interfaces according to the load balancing policy specified. For example, if an interface on a server group is specified as the real interface, then the binding applies to all the servers in the group.
-
Select the port used by the server(s) to balance traffic from the Real Port drop-down list.
The Real Port should be the same as the virtual port.
Note –If you use a non-standard port, you are required to set the port.
-
Click OK.
The Configure Load Balancer dialog box is closed.
-
Configure Servers. See How To Configure Servers for Load Balancing.
See Also
 How To Configure a
Load Balancer in Path Failover Mode
How To Configure a
Load Balancer in Path Failover Mode
This procedure describes configuration of three separate VLAN subnets to enable Path Failover. These subnets are used for data, service, and management path failover.
Before You Begin
Servers running the Solaris Operating System require that the clbmod package is installed to enable load balancing. During the farm activation process, the interface will be plumbed for the clbmod module. If the module is not present the activation will fail.
Path Failover mode requires that the Load Balancer be able to change the interface on which traffic flows from the VIP to the Load Balancer. This is accomplished by placing both management interfaces on the same subnet. When the Load Balancer determines that it no longer has a path to the target IP via the interface on which it was configured, it will then restore those paths on the other, live, interface. See Load Balancer Best Practices for additional information and illustrations.
Note –
Path failover is automatically configured when both management interfaces are placed on a single subnet. In this configuration, the VIPs will be configured on the primary port that the user selects, but when that primary port fails, they will be failed over to the other port.
This procedure assumes the following connections and naming conventions for farm components.
-
External Subnet is connected to Load Balancer (data VLAN)
-
Load Balancer is connected to the Management Subnet (management VLAN)
-
Management Subnet is connected to Server1 (management VLAN)
-
Server1 is connected to the Service Subnet (service VLAN)
-
Management Subnet is connected to Server2 (management VLAN)
-
Server2 is connected to Data Subnet (data VLAN)
Steps
-
Configure the management VLAN.
Servers are load balanced on the management VLAN.
-
Drag a Load Balancer, two Servers, an External Subnet and a Internal Subnet onto the Editor screen.
-
Connect the Load Balancer management interfaces to the Internal Management Subnet.
This automatically configures the Load Balancer in Path failover mode.
-
Connect a VIP from the Load Balancer to Internal Management Subnet.
-
Connect both primary interfaces on both physical ports of the Server to the Management Subnet.
-
Connect Server1 service interfaces to Service Subnet.
-
Place the data interface from the Server on the Data Subnet that will have the same VLAN as the VIPs.
-
-
Choose Save from the File menu.
The farm configuration is saved.
-
Double click the Load Balancer element.
The Configure Load Balancer dialog box appears.
-
Select the type of Load Balancer from the Type drop-down list.
-
Select the Policy type for the Load Balancer from the Policy drop-down list.
The following choices appear.
-
Round Robin (default)—New connections are routed sequentially to servers in the Load Balancer group, thereby spreading new sessions equally across all servers.
-
Least Connected—New connections are sent to the server with the least number of active sessions.
-
Weighted—New connections are sent to servers according to weight assignments. Servers with a higher weight value receive a larger percentage of connections. You can assign a weight to each real server, and that weight determines the percentage of the current connections given to each server. The default weight is one. You must set the load balancer weights manually.
Note –You may modify the Load Balancer policy in the Design and Active states.
-
-
Click the + button to add a binding to the eth0:vip0 interface.
The eth0:1 interface binding appears.
-
Type the appropriate port number in the virtual and real port edit fields, for example 50.
-
Select Server1-eth0:1 as the Real interface from the Real Interface drop-down list.
-
Click the + button under virtual interface to add an interface.
The eth0:2 interface appears.
-
Type the appropriate port number in the virtual and real port edit fields, for example 50.
-
Select Server2-eth0:2 as the Real interface from the Real Interface drop-down list.
-
Click the OK button to close the Configure Load Balancer dialog box.
-
Configure Servers. See How To Configure Servers for Load Balancing.
You must configure Servers to enable load balancing.
-
Connect the service and management VLANs.
-
Configure VLANs. See How To Modify a VLAN Configuration for Load Balancing.
-
Choose Save from the File menu.
The farm configuration is saved.
See Also
 How To Configure
Servers for Load Balancing
How To Configure
Servers for Load Balancing
Steps
-
Drag a Server and two Internal Subnet elements onto the Editor screen.
-
Name the elements Server2, Service Subnet and Data Subnet.
-
Double-click the Server element.
The Configure Server dialog box appears.
-
Click the + button twice to add two virtual interfaces to the available primary port.
These virtual interfaces will be used for the service and data VLANs.
-
To add an image to the new disk, click the Select button.
-
Select load balancer from the Def. Gateway drop-down list.
-
Click the OK button.
The Configure Server dialog box is closed.
Note –In order to submit the farm, all servers must have an eth0 connected. That is, each server must have an IP allocated on a subnet). Additionally, if any virtual interface on any other primary port is allocated, the primary interface on the port must also be connected.
 How
To Modify a VLAN Configuration for Load Balancing
How
To Modify a VLAN Configuration for Load Balancing
Steps
-
In the Editor screen, choose Configure VLANs from the Edit menu.
A message describing automatic VLAN configuration appears.
-
Select Manually from the Configure VLANs drop-down list.
The Configure VLANs dialog box appears.
-
Select a VLAN from the Current VLANs list.
The name, wire color, and included subnets display in the right pane.
-
Change the subnet on which the data IP resides to be in the data VLAN by double-clicking the Subnet element and selecting the appropriate VLAN.
-
Click OK.
The new VLAN information is applied and the Configure VLANs dialog box is closed.
Note –If you add or delete a VLAN, you must update the appropriate subnet configuration to associate the subnet with the correct VLAN. If you delete a VLAN and do not associate the subnet configuration with another VLAN, an error message is printed.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
