4 Auditing Stored Procedures and Roles
This chapter contains:
About Auditing Stored Procedures and Roles
You can audit and approve changes to stored procedures and user roles in the databases on a specified database server. Oracle Database Firewall connects to the database server at scheduled intervals and determines which changes or additions (if any) have been made to stored procedures. Stored procedure auditing and user role auditing are supported for Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, Sybase ASE, Sybase SQL Anywhere, and IBM DB2 SQL (Linux, UNIX, and Microsoft Windows) databases.
Before you can audit stored procedures and roles, you must configure the Database Firewall-protected database to enable stored procedure and role auditing. See Oracle Database Firewall Administration Guide for more information.
Viewing and Approving Changes to Stored Procedures
This section contains.
About Viewing and Approving Changes to Stored Procedures
After you have configured stored procedure auditing, you can begin to monitor changes to stored procedures being run on the protected database right away. You can run a manual audit on a stored procedure at any time, in addition generating reports that run automatically according to the schedule set up in the SPA enforcement point settings. After the audit process is complete, you can approve changes made to the stored procedure.
You can perform the following types of stored procedure auditing activities:
-
View all additions or changes made to the stored procedures
-
Determine which changes are pending approval
-
Approve changes
-
View all approvals made
-
Examine a history of previous approvals
Note:
For Oracle databases, privileges such as invoker's right or definer's rights do not affect stored procedure auditing.See Also:
-
Chapter 6, "Generating Oracle Database Firewall Reports," for information about running reports
-
Oracle Database Firewall Administration Guide for information about configuring stored procedure auditing
Running a Manual Stored Procedure Audit
To run a manual audit for stored procedures:
-
Log in to the standalone Database Firewall or Management Server Administration Console.
See "Logging in to the Administration Console" for more information.
-
Select the Monitoring tab.
-
Under Enforcement Points, click List.
The Enforcement Points page appears, and lists the available enforcement points.
-
For the enforcement point that is responsible for the stored procedure audit, click Manage.
-
In the Manage Enforcement Point page, scroll down to Stored Procedure Auditing Control.
-
Click the Run Now button.
Database Firewall displays a message letting you know that the audit has been started.
Approving Changes Made to a Stored Procedure
To approve or decline approval for changes made to a stored procedure:
-
If you are not already logged in, log in to the standalone Database Firewall or Management Server Administration Console.
See "Logging in to the Administration Console" for more information.
-
Select the Reporting tab.
-
Under Stored Procedure Auditing, select Pending.
See "Filtering Options for Approving Changes in Stored Procedures" for descriptions of all the options.
The Pending Approvals for Stored Procedures page appears, with a list of audited stored procedures.
-
Check each stored procedure by clicking the area just below the stored procedure link, as shown in the following screen.
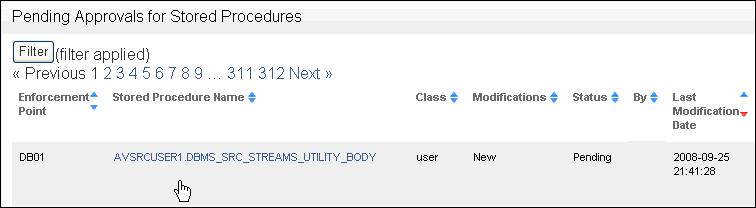
Description of the illustration sp-audit1.gif
The area expands to show a modification history and notes for the stored procedure:
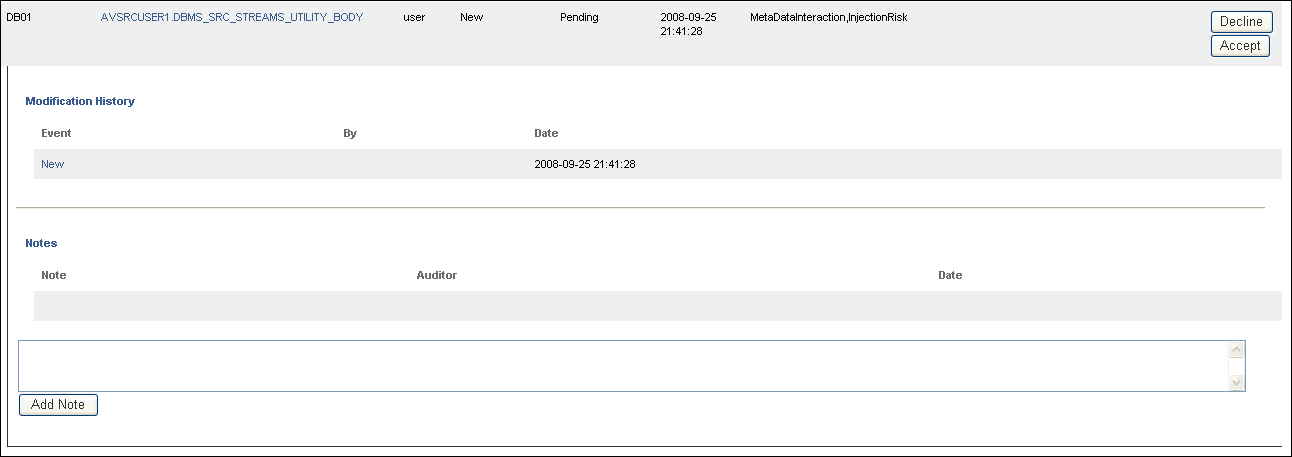
Description of the illustration sp-audit2.gif
-
Check the modification history of the stored procedure.
The Event column provides a history of all changed events for the stored procedure. (If there are no changed events, only the New link is shown under Event.) To find how the stored procedure changed, click the Show Differences link, which appears after the listed events for the stored procedure. A separate window appears, showing how the SQL for the stored procedure was modified.
Note:
The Show Differences link appears only after a stored procedure has been approved.If you want to see the original SQL text that was used to create the stored procedure, then click on the link for the stored procedure itself.
The following example, shows how an original stored procedure appears. The red text indicates keywords.
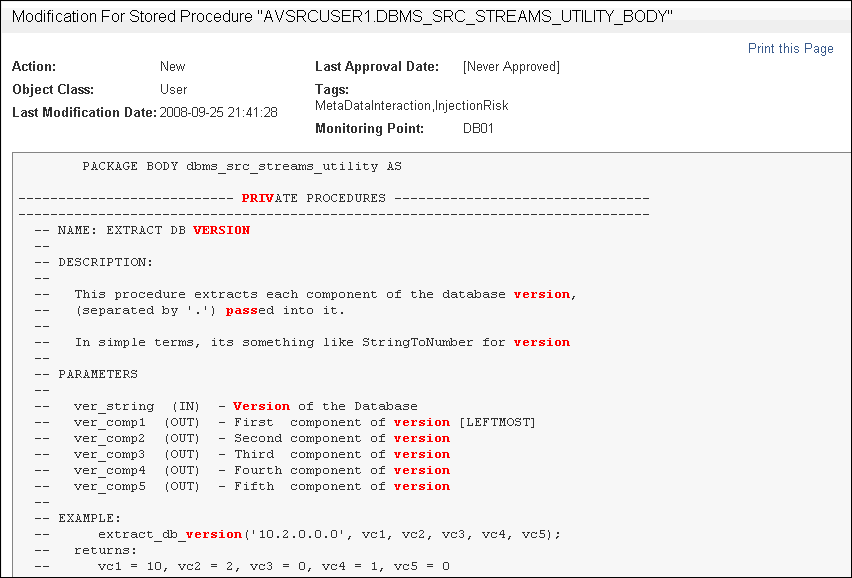
Description of the illustration sp-audit3.gif
-
In the Notes area of the Modification History area for the stored procedure, optionally add a note and then click the Add Note button.
-
If you approve the modifications to the stored procedure, then click Accept; if you disapprove, click Decline.
If you click Decline, then the stored procedure changes are declined immediately.
-
If you click Accept, the Accept Changes for
namearea appears; enter a note in the Approval Comment field.For example:
Changes to stored procedure AVSRCUSER1.DBMS_SRC_STREAMS_UTILITY_BODY approved by LBouligny, 8/17/10
Click Accept. The list of audited stored procedures re-appears.
You can add notes from this main list by clicking on any of the stored procedure settings, such as
userorauthorization. The screen expands to display an Add Note field. To remove the display of this field, click it again.If you click the stored procedure name, which is a link, it displays the text of the stored procedure.
Filtering Options for Approving Changes in Stored Procedures
You can use any of the following filtering options to view the stored procedure audit report.
-
Summary: Lists each enforcement point that has Stored Procedure Auditing enabled in the enforcement point settings. For each enforcement point, the page lists the number of stored procedures that have been fully approved, the number that are pending at least one approval, and the total number of records in the audit history.
-
Approved: Lists each stored procedure that has at least one approval. A Filter button is available to filter the results (see "Searching for Traffic Logs" for details of how to set up filter search conditions). Clicking the name of a stored procedure shows the modification detail, including when it was first approved, and any approvals that have been granted for subsequent modifications. The text shown in the Tags column is highlighted in red in the detail. The tags are generated by Oracle Database Firewall itself, based on preset rules.
-
Pending: Lists each stored procedure that matches the Filter settings and is awaiting at least one approval. The type of change, such as New or Modify, is displayed in the Modifications column. Clicking the name of the stored procedure shows the content of the procedure after the change. Clicking anywhere along the green bar displays the modification detail and a box to enter notes, such as details of the actions that need to be investigated before approval can be granted. If the change is Modify, also displayed is a Show Difference link, which you can use to identify the changes made. The text shown in the Tags column is highlighted in red in the detail.
On the right side of the page, you will see Decline and Accept buttons for each stored procedure. Clicking the Accept button approves all changes that are pending approval for the stored procedure. Clicking Decline prevents the changes from being approved when Approve All is selected.
Clicking Approve All near the top of the page approves all changes made to all stored procedures that match the currently-selected Filter and have not been declined.
-
Audit History: Lists all previous approvals and all pending approvals that match the Filter settings. Each time a procedure is approved, the transaction is recorded in the audit history. Click anywhere along the green bar to see more detail.
Viewing and Approving Changes to User Roles
This section contains:
About Viewing and Approving Changes to User Roles
After you have configured user role auditing, you can begin to monitor changes to user roles being used on the protected database right away. You can run a manual audit on a user role at any time, in addition to generating reports that run automatically according to the schedule set up in the URA enforcement point settings. After the audit process is complete, you can approve the changes made to the user role.
You can perform the following types of user role auditing activities:
-
View all additions or changes made to the user roles.
-
Approve the changes.
-
Determine which changes are pending approval.
-
View all approvals made.
-
Examine a history of previous approvals.
See Also:
-
Chapter 6, "Generating Oracle Database Firewall Reports," for information about running reports
-
Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for information about configuring user role auditing
Running a Manual User Role Audit
To run a manual audit for user roles:
-
Log in to the standalone Database Firewall or Management Server Administration Console.
See "Logging in to the Administration Console" for more information.
-
Select the Monitoring tab. the Monitoring tab.
-
Under Enforcement Points, click List.
The Enforcement Points page appears, and lists the available enforcement points.
-
For the enforcement point that is responsible for the user role audit, click Manage.
-
In the Manage Enforcement Point page, scroll down to User Auditing Control.
-
Click the Run Now button.
Database Firewall displays a message letting you know that the audit has been started. The audit process should last a couple of minutes.
Approving Changes Made to a User Role
To approve or decline approval for changes made to stored procedures:
-
If you are not already logged in, log in to the standalone Database Firewall or Management Server Administration Console.
See "Logging in to the Administration Console" for more information.
-
Select the Reporting tab.
-
Under User Role Auditing, select the filtering option Pending.
See "Filtering Options for Approving Changes in User Roles" for descriptions of all the options.
The Pending Approvals for User Roles page appears, with a list of audited user roles.
-
Check each user role by clicking the area just below the user role link, as shown in the following screen.
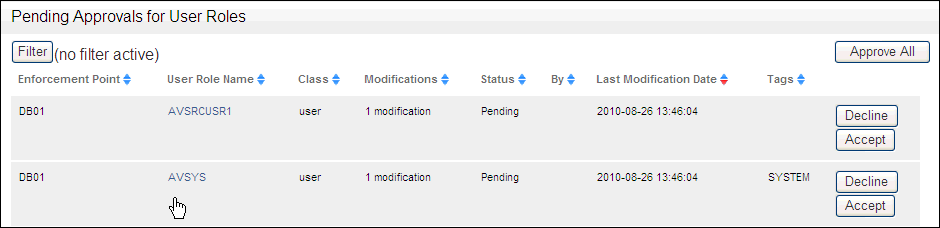
Description of the illustration ur_audit1.gif
The area expands to show a modification history and notes for the user role.
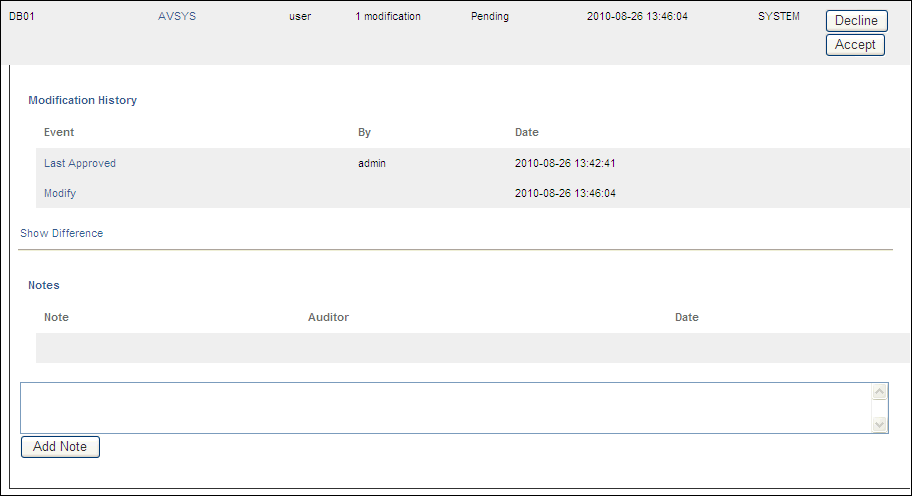
Description of the illustration ur_audit2.gif
-
Check the modification history of the user role.
The Event column provides a history of all changed events for the user role. (If there are no changed events, only the New link is shown under Event.) To find how the user role changed, click the Show Differences link, which appears following the events for that user role. A separate window appears, showing how the SQL for the user role was modified.
If you want to see the original SQL text that was used to create the user role, then click the link for the user role itself.
The following example shows how the
AVUSRrole was changed: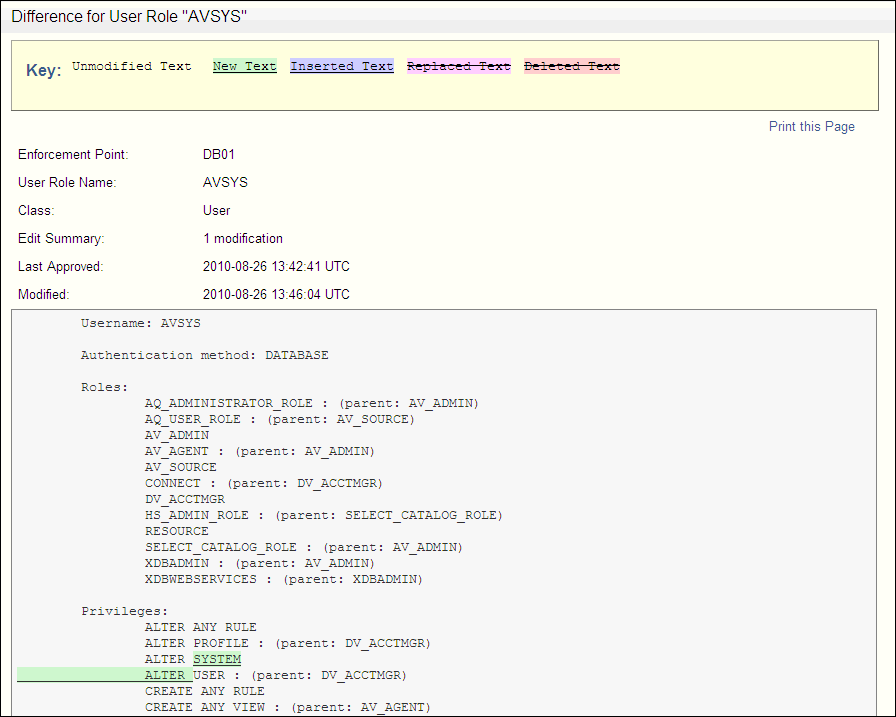
Description of the illustration ur_audit3.gif
-
In the Notes area of the Modification History area for the user role, optionally add a note and then click the Add Note button.
-
If you approve the modifications to the user role, then click Accept; if you disapprove, click Decline.
-
If you click Accept, the Accept Changes for
namearea appears; enter a note in the Approval Comment field.For example:
Changes to user role AVUSER approved by LBouligny, 8/17/10
Click Accept. The list of audited user roles re-appears.
You can add notes from this main list by clicking on any of the stored procedure settings, such as
userorauthorization. The screen expands to display an Add Note field. To remove the display of this field, click it again.If you click the stored procedure name, which is a link, it displays the text of the stored procedure.
Filtering Options for Approving Changes in User Roles
You can use any of the following filtering options to view the stored procedure audit report
-
Summary: Lists each enforcement point that has User Role Auditing enabled in the enforcement point settings. For each enforcement point, the page lists the number of user roles that have been fully approved, the number that are pending at least one approval, and the total number of records in the audit history.
-
Approved: Lists each user role that has at least one approval. A Filter button is available to filter the results (see "Searching for Traffic Logs" for details of how to set up filter search conditions). Clicking the name of a user role shows the modification detail, including when it was first approved, and any approvals that have been granted for subsequent modifications. The text shown in the Tags column is highlighted in red in the detail. The tags are generated by Oracle Database Firewall itself, based on preset rules.
-
Pending: Lists each user role that matches the Filter settings and is awaiting at least one approval. The type of change, such as New or Modify, is displayed in the Modifications column. Clicking the name of the user role shows the content of the user role after the change. Clicking anywhere along the green bar displays the modification detail and a box to enter notes, such as details of the actions that need to be investigated before approval can be granted. If the change is Modify, also displayed is a Show Difference link, which you can use to identify the changes made. The text shown in the Tags column is highlighted in red in the detail.
On the right side of the page, you will see Decline and Accept buttons for each user role. Clicking the Accept button approves all changes that are pending approval for that user role. Clicking Decline prevents the changes from being approved when Approve All is selected.
Clicking Approve All near the top of the page approves all changes made to all user roles that match the currently-selected Filter and have not been declined.
-
Audit History: Lists all previous approvals and all pending approvals that match the Filter settings. Each time a user role is approved, the transaction is recorded in the audit history. Click anywhere along the green bar to see more detail.