GIS Assets
This chapter covers the following topics:
- Overview of GIS Asset Management
- Defining GIS Asset Numbers
- Updating GIS Assets
- Updating Reference Methods
- Using Asset Icons
- Using Line Styles
- Using Asset Properties
- Using Element Types
- Using GIS Relationships
- Using Map Manager
- Using Map Actions
- Using the GIS Asset Workbench
- Using the Map Workbench
- Using the Indoor Map Workbench
Overview of GIS Asset Management
A geographic information system (GIS) enables you to track the location of assets such as plants, buildings, vehicles, equipment, offices, and so on.
You can use Oracle Enterprise Asset Management to maintain and track GIS assets. GIS assets include the following types of assets:
-
Linear
A linear asset is represented by its length and measure values to indicate its start point and end point, and has a geometric profile and shape. For example, oil and gas pipe lines, roads, highways and utility lines (water, sewage and power transmission).
-
Area
An area asset has a geometric shape that is non-linear, but is identified by the closed area or shape having multiple linear sections forming its geometry. Examples are bodies of water such as lakes and ponds, forest areas, playgrounds, and so on.
The EAM asset numbers that are defined as GIS assets can be mapped to the route and geometry of GIS systems such as ESRI and Oracle Spatial. You can then visualize assets on a map, and execute work with reference to the measure values of the asset. Various asset attributes such as Properties, Elements and Relationships are created in EAM, and are used to track GIS assets.
In addition, you can maintain GIS assets in EAM by capturing the measure values in work orders when the work orders are executed.
Asset routes and non-serial rebuildable items cannot be defined as GIS assets.
Defining GIS Asset Numbers
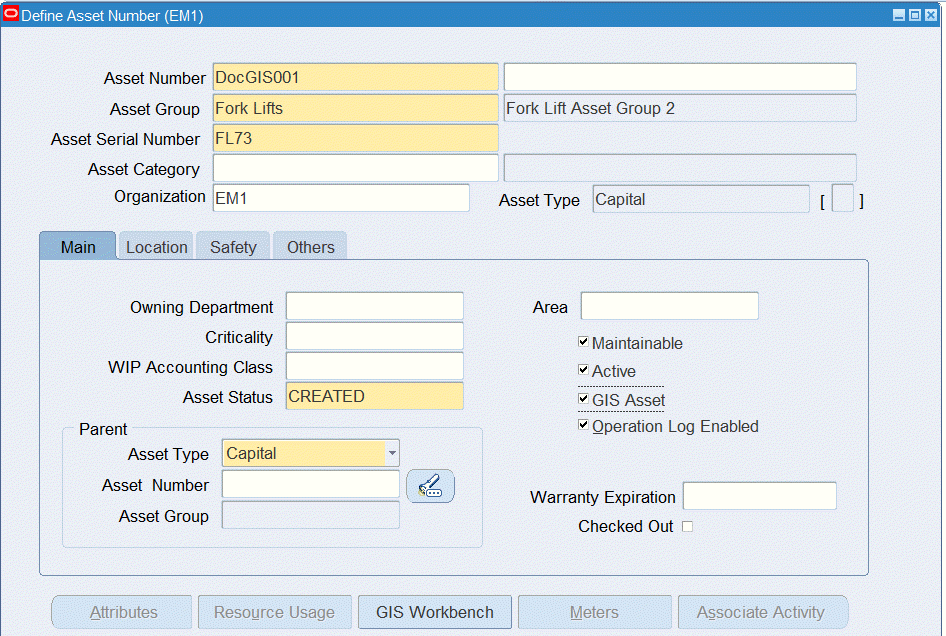
Use the Define Asset Number form to define GIS assets. GIS assets include linear and area assets. In addition, you can define rebuildable GIS assets.
-
Navigate to the Define Asset Number form (Enterprise Asset Management > Assets > Asset Numbers > Asset Numbers).
-
Select an Asset Status. This field represents the status associated with the GIS asset item instance.
-
Select the GIS Asset check box to define the asset as a linear or area asset.
-
When you select the GIS Asset check box, the GIS Workbench button becomes available.
Use the GIS Asset Workbench to enter details for GIS assets. See Using the GIS Asset Workbench for more information.
-
For more information regarding the fields on this page and other sub-tabs, see Defining Asset Numbers.
Updating GIS Assets
You can update GIS assets using one of the following pages:
-
Define Asset Number form (Enterprise Asset Management > Assets > Asset Number)
-
Asset Numbers (Maintenance Super User > Maintenance Home > Assets > Asset Numbers)
-
GIS Asset Workbench:
-
Assets > Update (Maintenance Super User > Maintenance Home > Assets > Capital or Rebuildable tabs)
-
Assets > View Assets (Maintenance Super User > Maintenance Home > Assets (Capital or Rebuildable tabs)
-
Asset Number form > Update (Enterprise Asset Management > Assets > Asset Numbers > Asset Numbers)
-
Updating Reference Methods
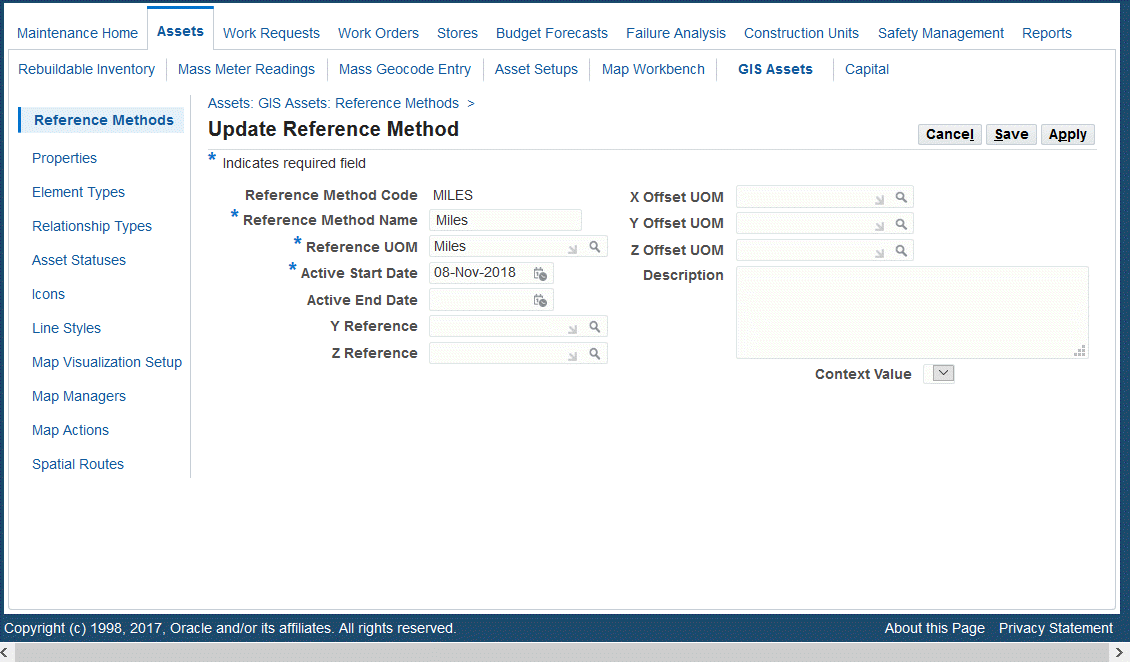
Use the Update Reference Methods page to update existing reference methods.
-
Navigate to the Update Reference Method page (Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > GIS Assets > Reference Methods > Search).
-
Search for a reference method and click the Update button.
-
Update information such as:
-
Reference Method Name (description)
-
Active Start Date
-
Active End Date
-
Y Reference
-
Z Reference
-
X Offset UOM
-
Y Offset UOM
-
Description
-
Context Value
Note: You cannot update the Reference Method Code value.
-
-
Click Save or Apply.
Using Asset Icons
Icons can be created for details such as element and properties, and these icons will be used in the Map Viewer.
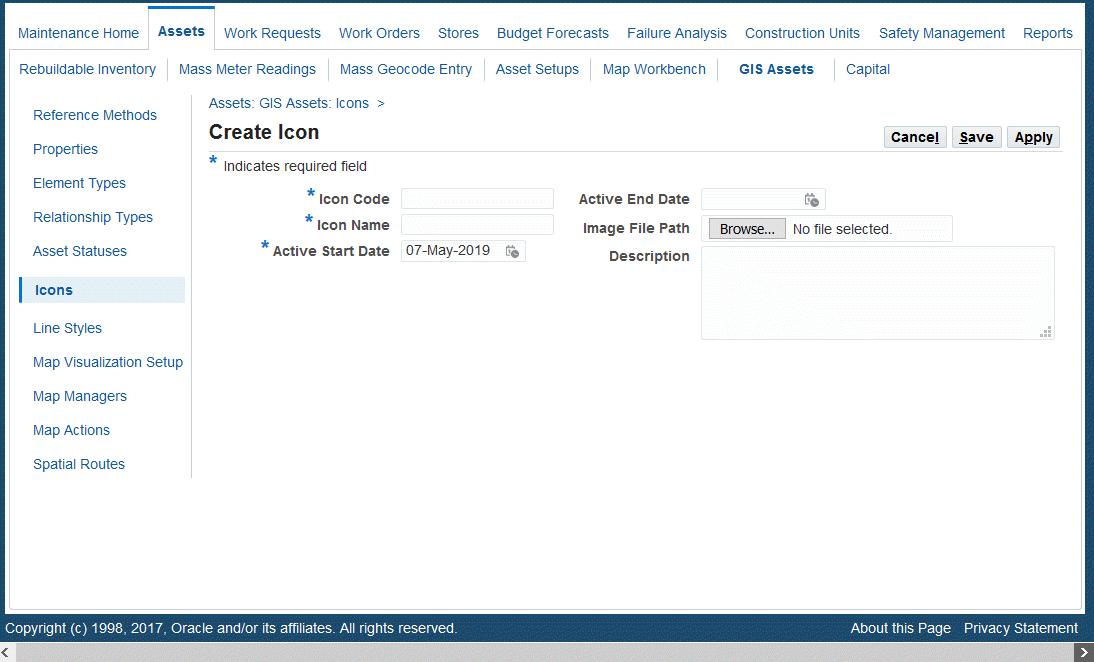
Creating Icons
-
Navigate to the Create Icon page (Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > GIS Assets > Icons).
-
Enter values in the following fields:
-
Icon Code (required)
-
Icon Name (required)
-
Active Start Date (required)
-
Active End Date (optional)
-
Image File Path - Click Browse to locate image to upload
-
Description (optional)
-
-
Click Save or Apply.
Updating Asset Icons
-
Navigate to the Update Icon page (Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > GIS Assets > Icons).
-
Search for an icon and click the Update button.
-
Update the fields on this page.
Note: You cannot update the Icon Code value.
-
Click Save or Apply.
Using Line Styles
Line styles are used details such as elements and properties, and will be used in the Map Viewer.
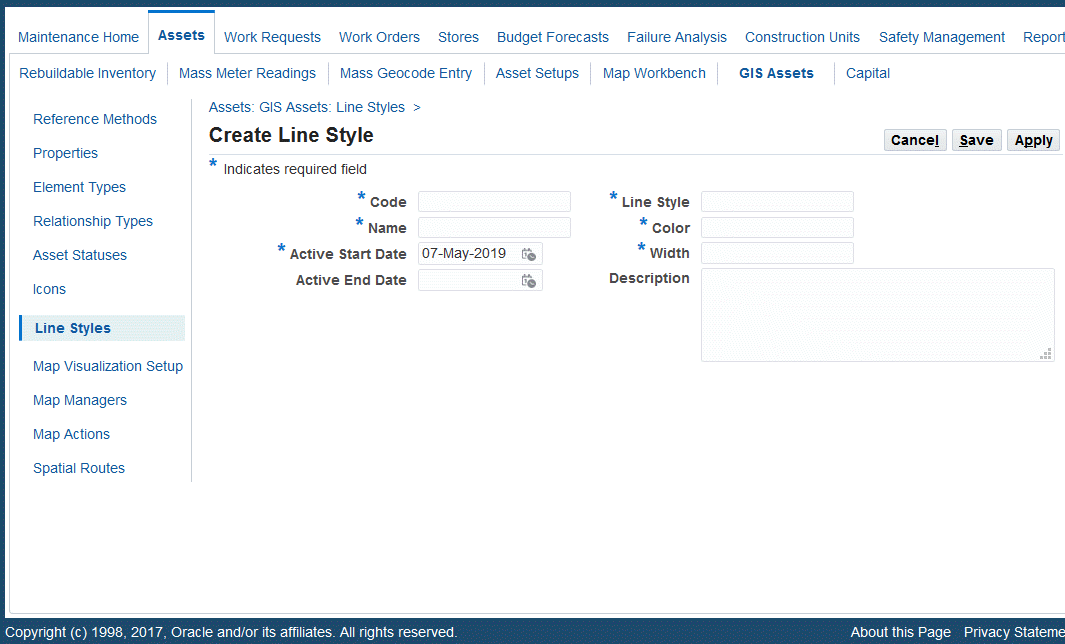
Creating Line Styles
-
Navigate to the Create Line Style page (Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > GIS Assets > Line Styles).
-
Enter a line style Code (required).
-
Enter a Name for the line style (required).
-
Enter the Active Start Date (required).
-
Optionally enter the Active End Date.
-
Enter the Line Style (required). The values for this field are defined in the Lookups page.
-
Enter the line Color and Width (required).
-
Optionally enter a Description.
-
Save your work.
Updating Line Styles
-
Navigate to the Line Styles page (Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > GIS Assets > Line Styles).
-
Optionally enter search criteria to narrow the results, and click the Go button.
-
Click the Update button and the Update Line Style page appears.
-
Update the fields as necessary.
You cannot update the Code field.
-
Save your work.
Using Asset Properties
Properties are the attributes of GIS assets that are tracked along its length with reference of measure values or for a point on the GIS asset. For example:
-
Diameter and Material (MOC) of the pipeline.
-
Speed Limit and Surface Condition of the road.
-
Line Voltage of the transmission line.
-
Fluid Pressure of the pipeline.
Creating Asset Properties
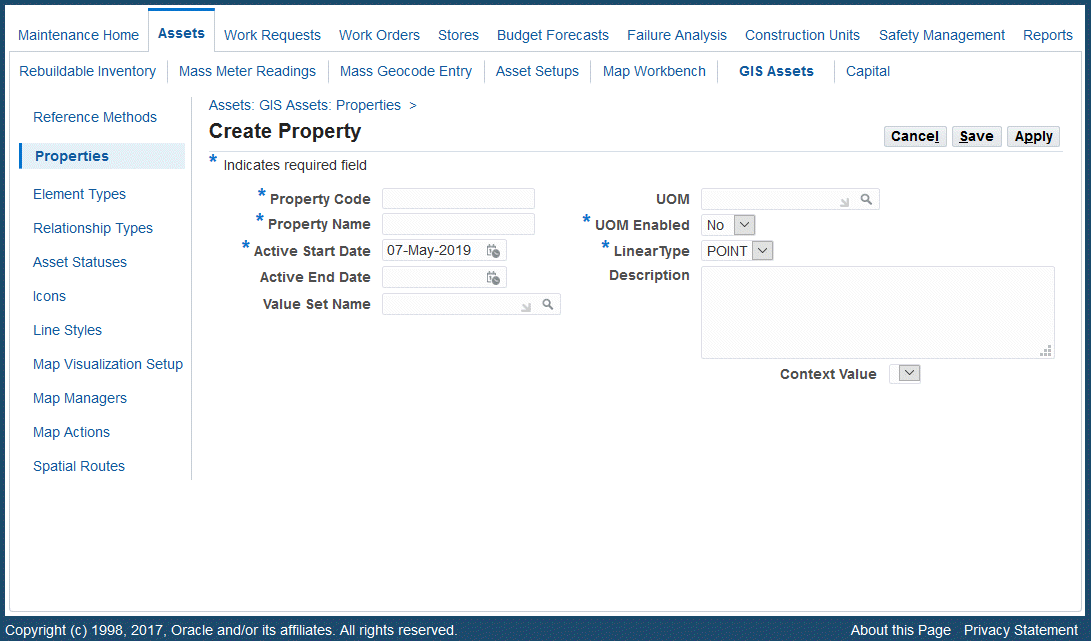
Define properties for assets by using the Create Property page.
-
Navigate to the Create Property page (Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > GIS Assets > Properties > Create Property).
-
Enter values for the following fields:
-
Property Code (required)
-
Property Name (required)
-
Active Start Date (required)
-
Active End Date (optional)
-
Value Set Name (optional)
-
UOM (optional)
-
UOM Enabled (required) - Yes or No
-
Icon (optional)
-
Line Style (optional)
-
LinearType (required): Values are Point or Line.
-
Description (optional)
-
Context Value (optional)
-
Updating Asset Properties
You can update asset properties by using the Update Property page or the GIS Asset Workbench. Use these pages to associate properties to GIS assets. See Using the GIS Asset Workbench for more information.
-
Navigate to the Update Property page (Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > GIS Assets > Properties > Properties > Search).
-
Search for a property code, and click Go.
-
Click the Update button for the property code, and the Update Property page appears.
-
Update fields on this page.
Note: You cannot update the Property Code value.
-
Click Save or Apply.
Associating Properties to GIS Assets
Use the GIS Asset Workbench to associate properties to GIS assets.
See Using the GIS Asset Workbench for more information.
Using Element Types
Elements are significant pieces of installations located on the GIS asset network and are integral parts of the network. You can define and track the elements of the GIS assets for ease of maintenance, reference, and identification.
Elements can be both Linear and Point types.
Elements can also be defined with a type of Labeled or Non-Labeled. Labeled elements will have an element instance (Name); however, non-labeled elements will not have an element instance. If the elements themselves require maintenance activities to be performed on them, they should be defined as assets in EAM and related to the GIS assets using the Relationships functionality.
For example, Point Type, Labeled Elements could be inspection points of pipelines, mile markers on roads, and transmission towers. Examples of Linear Type, Non-Labeled Elements are guard rails, medians, and fencing.
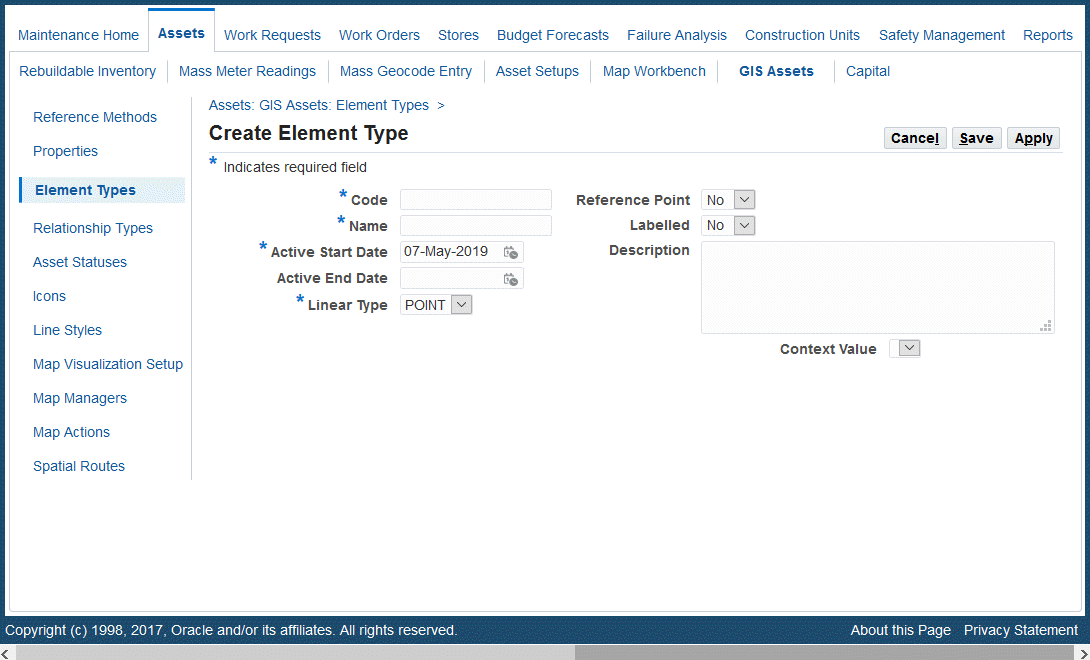
Use the Create Element Type page to define element types. Use the GIS Asset Workbench to associate element types to GIS assets.
Creating Element Types
-
Navigate to the Create Element Type page (Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > GIS Assets > Element Types > Element Types > Create Element Type).
-
Enter values for the following fields:
-
Code (required)
-
Name (required)
-
Active Start Date (required)
-
Active End Date (optional)
-
Linear Type (required): Values are Point or Line.
-
Reference Point (optional): Values are Yes or No. A reference point is used as an identification entity located on the GIS asset network. For example, inspection points on a pipeline, mile markers on roads, and transmission towers.
-
Labelled (optional): Values are Yes or No. This field indicates if the element will be labelled or non-labelled.
-
Icon (required)
-
Line Style (optional)
-
Description (optional)
-
Context Value (optional)
-
-
Click Save or Apply.
Updating Element Types
-
Navigate to the Update Element Type page (Maintenance Super User > Assets > GIS Assets > Element Types > Element Types).
-
Enter search criteria to retrieve the element code that you want to update.
-
Click the Update button.
-
Update the following fields:
-
Name (required)
-
Active Start Date (required)
-
Active End Date (optional)
-
Linear Type (required): Values are Point or Line.
-
Reference Point - Yes or No (optional)
-
Labelled - Yes or No (optional)
-
Icon (required)
-
Line Style (optional)
-
Description (optional)
-
Context Value (optional)
Note: You cannot update the element Code value.
-
-
Click Save or Apply.
Associating Elements to GIS Assets
Use the GIS Asset Workbench to associate elements to linear assets.
See Using the GIS Asset Workbench for more information.
Using GIS Relationships
A relationship describes the connection between two GIS assets, such as a linear and a point asset, or a linear asset and a location. Assets and elements in the GIS asset network can share a relationship in terms of deployment, geometry, location or any other such need. User-defined relationship types provide the ability to capture the various relationships that exist between different components of the network. Relationships can also be a Linear or Point type. For example: Parallel (Linear type) and Intersection (Point type).
Use the Create Relationship Type page to define relationship types. Then, associate GIS assets with relationship types using the GIS Asset Workbench.
Creating Relationship Types
-
Navigate to the Create Relationship Type page (Maintenance Super User > Assets > GIS Assets > Relationship Types > Create Relationship Type).
-
Add values for the following fields:
-
Code (required)
-
Name (required)
-
Active Start Date (required)
-
Active End Date (optional)
-
Reference Point (required): Values are Yes or No.
-
Direction (optional)
-
Linear Type (required): Values are Point or Line.
-
Description (optional)
-
Context Value (optional)
-
-
Click Save or Apply.
Updating Relationship Types
-
Navigate to the Relationship Type page (Maintenance Super User > Assets > GIS Assets > Relationship Types).
-
Search for a relationship type and click the Update button.
-
Update values for the following fields:
-
Name (required)
-
Active Start Date (required)
-
Active End Date (optional)
-
Reference Point (required): Values are Yes or No.
-
Direction (optional)
-
Linear Type (required): Values are Point or Line.
-
Description (optional)
-
Context Value (optional)
Note: You cannot update the relationship Code value.
-
-
Click Save or Apply.
Associating Relationships to GIS Assets
Use the GIS Asset Workbench to associate relationships to GIS assets.
See Using the GIS Asset Workbench for more information.
Using Map Manager
The Map Manager enables you to set up the parameters required for map integration. This is a mandatory EAM setup which captures various parameters necessary to display map layers and also to communicate with the GIS system (ESRI/Oracle Spatial).
Important: You can have only one active map manager record defined in the system. Currently, the association level supported is Site.
Note: This setup is mandatory for any map integration, even if you are not using the GIS Asset Management functionality. This setup enables you to use the Map Visualization for discrete assets.
Creating Map Manager
-
Navigate to Map Managers (Maintenance Super User > Assets > GIS Assets > Map Managers).
-
Click the Create button.
-
Enter Map Manager values in the Create page.
-
Review Map Manager values section.
-
Save your work.
Modifying Map Manager
-
Navigate to Map Managers (Maintenance Super User > Assets > GIS Assets > Map Managers).
-
Click the Go button.
-
Click the Update icon to make changes to the Map Manager values.
-
Enter new values in the Update page.
-
Review changes.
-
Save your work.
The Map Manager values are based on map integration you have selected in profile CSI: Map Viewer Name. The Create or Update page automatically displays the ESRI related or Oracle Spatial related parameters based on selected map integration.
If the ESRI integration option is selected, the ESRI setup will display. If the Oracle Spatial or Custom GIS with Oracle Spatial integration is selected, the respective set up will display.
Oracle Spatial Map Manager Setup
-
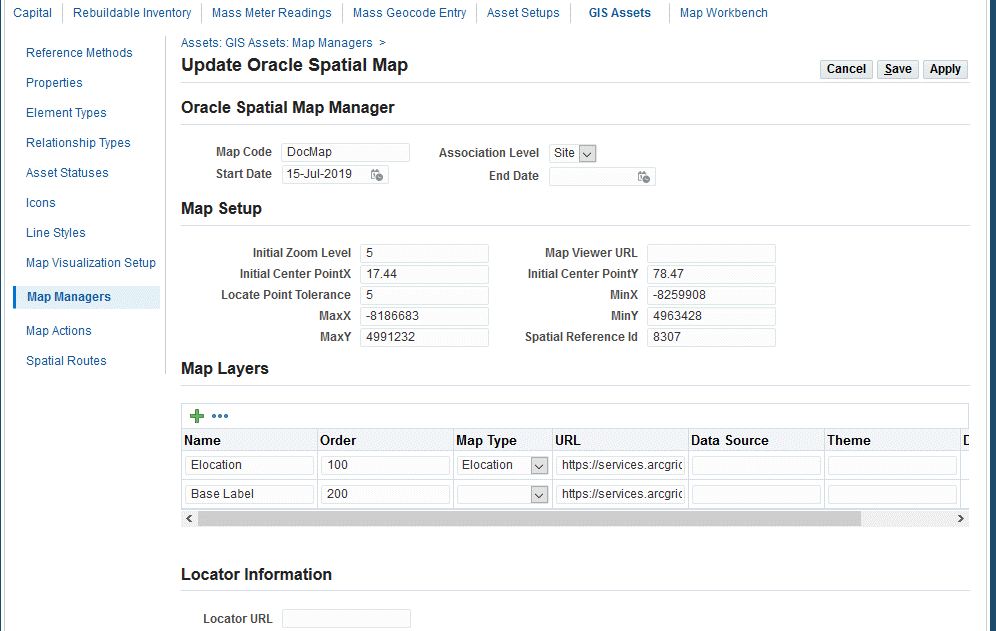
Navigate to Create Map Manager page (Maintenance Super User > Assets > GIS Assets > Map Managers > Create).
-
Enter the Map Code (required).
-
Select the Association Level of Site (required).
-
Enter the Active Start Date.
-
Enter the Initial Zoom Level (required). This is default zoom level is used when the Map Workbench is launched.
-
Optionally enter a Map Viewer URL if you have the Map Viewer Server set up to maintain Oracle Spatial.
-
Enter values for the Initial CenterX point and Initial CenterY point. These default X and Y values (latitude and longitude) are used as a center for the map when the Map Workbench is launched.
-
Enter a value for the Locate Point Tolerance. This tolerance will be applied when capturing points between two points.
-
Enter the Spatial Reference ID which is the spatial reference that the asset geometry needs to use.
-
Enter the Map Layers to be used on the maps to extend the map visualization by adding user-defined layers on the base map. Examples: Customer Names, Zone Divisions, Engineering layout.
-
Enter Map Name.
-
Enter Order. This is the sequence in which the layer should be added.
-
Choose the Map Type:
-
Elocation: Select to display Oracle Maps.
-
Google: Select to display Google Maps.
-
Data Source: Select to display maps from Oracle Spatial map viewer data source.
You must select Elocation or Google. You cannot have both layers.
If Elocation or Google Layer is chosen as one of the map layers, it should have an Order value minimum of all layers (for example, 1), so that the first layer is added to the display.
Additionally, if Google is the selected map layer, then the Google Maps license key must be entered in profile, CSI:Google Maps Client ID.
You add more data sources as needed for additional map layers.
-
-
Enter the URL from which the data source is available. This field is available only if the selected map type is Data Source.
-
Enter the Theme name as configured in the Map Viewer data source. This field is available only if the selected map type is Data Source.
-
-
Enter the Locator URL: This field is used by the Search by address feature. This is the map viewer URL through which the location address can be converted to latitude and longitude.
-
Save your work.
-
Navigate to Create Map Manager page (Maintenance Super User > Assets > GIS Assets > Map Managers > Create).
If ESRI is the chosen map viewer, then the ESRI fields will appear.
-
Enter the Map Code (required).
-
Select the Association Level of Site (required).
-
Enter the Active Start Date.
-
Enter values for MinX, MinY, MaxX and MaxY points. These points form the rectangular area that needs to be initially zoomed to when the Map Manager is launched.
-
Enter the value for the WikiID (well known ID) which is the Spatial Reference of the map. This component of the coordinate system is used by the Map Manager to display the map and assets on the map.
-
Enter the Map Layers to be used on the maps to extend the map visualization to extend the map visualization by adding user-defined layers on the base map. Examples: Customer Names, Zone Divisions, Engineering layout.
Enter values for the following:
-
Name
-
Order: The sequence in which the layer needs to be added.
-
URL: The ARCGIS map layer URL.
-
Transparency: The transparency that the map layer needs to use.
-
Display by Default: Select the check box so that the map layer appears automatically.
-
-
Enter the Locator URL. This geocoding field is used by the Find My Place feature in the Map Workbench.
This is the URL through which the location address can be sent and equivalent coordinates could be derived to zoom to a location.
-
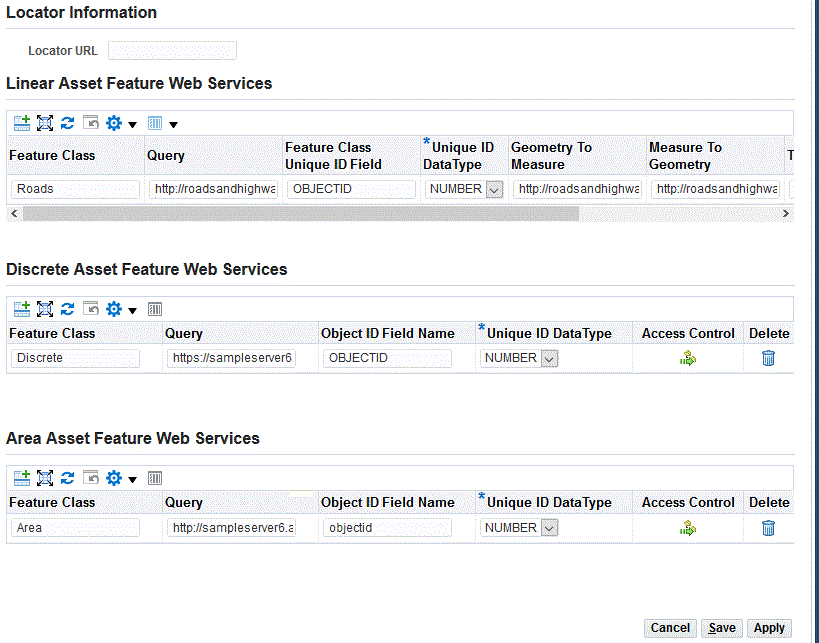
Enter values for the Linear Assets Web Services feature.
These are Web Services generated from ESRI. The Feature Class/Table contains the Polyline shape and is published to the ESRI server to expose as webservices. A 'query' operation for the published webservices should be enabled so that EAM can query the Feature Class data.
Further, if the shape has measure dimensions, the webservice should also include the Linear Referencing operation. This Linear Referencing Publishing would generate additional webservices geometrytomeasure and measuretogeometry which is required by EAM to perform dynamic segmentation.
Please refer to ESRI Roads and Highways Extension for more details on how to publish Feature Route with Linear Referencing capability.
-
Feature Class: Enter a name which represents an ESRI Feature Class. The Feature Class can be selected when you define asset segments in the GIS Asset Workbench to map the segment to ESRI geometry.
Note: You can create and associate multiple ESRI Feature Classes.
-
Query: The REST URL through which geometry can be queried by passing the Object ID or any unique ID in the Feature Class.
-
Feature Class Unique ID Field: The identifier of the Feature Class table in the ESRI system.
You can publish and define multiple ESRI Feature Classes, and map them to various asset segments to associate the ESRI shape and geometry.
For example, the Electrical and the Water and Sewage departments could have their respective functional assets in the ESRI system, each residing in the respective Feature Class tables.
-
The Electrical Department will have transmission lines in the Transmission Feature Class table. This table would be defined and published with a Feature Class name with respective URLs in Map Manager. When defining the transmission line asset, the segments would choose the Transmission Line Feature class to associate to its ESRI shape/geometry.
-
Similarly, the Water and Sewage Department will have its own Feature Class tables which would be published and defined in the Map Manager. When defining water and sewage assets, the respective Feature Class would be chosen to map the shape and geometry in ESRI.
-
-
Unique ID Data Type: Type of data in the unique column name on the ESRI Feature Class Table. Can be Number or Varchar.
-
The following URLs are required for the linear referencing capability only if the published ESRI Feature class has measure dimensions.
If the shape has measure dimensions, then the Feature table is a route and is eligible for dynamic segmentation. The URLs would be used by EAM to dynamically segment the route. The Linear Referencing option is provided by ESRI while publishing to generate additional URLs. Please refer to ESRI Map Integration for more details on REST services publishing.
Geometry To Measure: The URL through which a geometry point is passed so that the equivalent measure value on the asset geometry is returned.
Important: This URL can be generated only if you have Roads and Highways Extension for ARCGIS desktop and Server installed.
-
Measure To Geometry: The REST URL through which a measure is passed so that the equivalent geometry point value on the asset geometry is returned.
Important: This URL can be generated only if you have Roads and Highways Extension for ARCGIS desktop and Server installed.
-
Tolerance: Tolerance: Enter a tolerance offset value. You can click the asset geometry in the Map Workbench; however, it is not always possible to click the asset. This value considers the mouse click as an asset click if it is within the tolerance limit.
Important: Use the GIS Asset Workbench to associate Feature Classes to asset segments. See Using the GIS Asset Workbench for more information.
-
-
Click the icon in the Responsibility and User columns to restrict access control to feature classes based on the responsibility and user. This control restricts users to access specific feature class data in the Map Workbench.
Note: All users associated with the specific responsibility will have the same access to the feature classes. This is applicable only when no user entry is made in the 'Users' column.
-
Enter values for the Discrete Asset Feature Web Services to publish point shape Feature Classes and map to discrete assets for the following fields.
These are web services generated from the ESRI System. The Feature Class and table that contain the Point shape is published to the ESRI server to get exposed as webservices. A query operation for the published webservices should be enabled so that EAM can query the Feature Class data.
-
Feature Class: This value is selected during asset creation to map the asset to the ESRI Point geometry.
-
Use the Define Asset Number form to associate Point Feature Classes to discrete assets. See Defining Asset Numbers.
-
Use the GIS Asset Workbench to associate Point Feature Classes for assets. See Using the GIS Asset Workbench for more information.
-
-
-
Enter values for the Area Asset Feature Web Services. Area assets have a geometric shape that is non-linear, but is identified by the closed area or shape having multiple linear sections forming its geometry. Examples are bodies of water such as lakes and ponds, forest areas, playgrounds, and so on.
Feature Class: This value is selected during asset creation to map the asset to the ESRI geometry.
-
Use the Define Asset Number form to associate area Feature Classes to discrete assets. See Defining Asset Numbers.
-
Use the GIS Asset Workbench to associate area Feature Classes for area assets. See Using the GIS Asset Workbench for more information.
These are web services generated from the ESRI System. The Feature Class and table that contain the area shape is published to the ESRI server to get exposed as webservices. A query operation for the published webservices should be enabled so that EAM can query the Feature Class data.
-
-
Save your work.
Setting up the Create Map Manager for the Indoor Map Workbench
You can set up the Map Manager to define the fields to be included on the Indoor Map Workbench.
-
Navigate to Map Managers (Maintenance Super User > Assets > GIS Assets > Map Managers).
-
Click the Create button.
-
Enter Map Manager values in the Create ESRI Map Manager page.
Header Region Field Mandatory? Default Value Map Code Yes NA Association Level Yes Site Start Date Yes Sysdate End Date No NA ESRI Map Type Yes Null
Values are Indoor, Outdoor
For this feature, select Indoor.Map Setup Region Field Mandatory? Initial Zoom Yes Initial Center Point X Yes Initial Center Point Y Yes Map Layers Region Field Mandatory? Default Value Name Yes NA Order Yes NA URL Yes NA Transparency Yes NA Display By Default Yes Selected Delete NA NA Feature Layers Region Field Mandatory? Default Value Type Yes Null Feature Class Yes Null Query Yes Null Object ID Field Name Yes Null Object ID Data Type No Null Delete NA NA -
Save your work.
See Using the Indoor GIS Workbench for more information.
Using Map Actions
GIS asset toolbar actions are used with the Map Workbench. The toolbar actions that you create appear in the Map Actions fields in the Map Workbench.
Creating Map Tool Bar Actions
-
Navigate to the Create Map Toolbar page (Maintenance Super User > Assets > GIS Assets > Map Actions > Create Tool Bar Actions).
-
Enter a Toolbar Code (required).
-
Enter a Toolbar Name (required).
-
Enter an Active Start Date (required).
-
Select a Toolbar Type (required).
-
Optionally enter an Active Start Date.
-
Optionally enter the name of the API to be used with this map toolbar.
-
Save your work.
Updating Asset Map Toolbars
-
Navigate to the Create Map Toolbar page (Maintenance Super User > Assets > GIS Assets > Map Actions > Create Tool Bar Actions).
-
Edit the values on the page. You cannot update the Toolbar Code.
-
Save your changes.
Using the GIS Asset Workbench
Use the GIS Asset Workbench to enter and view GIS and area asset details for a specific asset. Use this workbench to associate the following:
-
Linear Reference Method
-
Segments, including ESRI Feature Classes
-
Properties
-
Elements
-
Relationships
You can access the GIS Asset Workbench using any of the following:
-
Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > Capital > Asset Numbers > Search > Go > View action drop-down > GIS Asset Workbench
-
Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > Rebuildable Inventory > Serialized Numbers > Search > View action drop-down> GIS Asset Workbench
-
Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > Capital > Asset Numbers > Search > View action drop-down> > Details > Go > GIS Asset Workbench
-
Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > Rebuildable Inventory > Serialized Numbers > Search > View action drop-down> > Details > Go > GIS Asset Workbench
-
Enterprise Asset Management > Assets > Asset Numbers > Find Asset Numbers > Search > GIS Asset Workbench
-
Enterprise Asset Management > Assets > Asset Numbers > Find Rebuildable Serial Number > Search > GIS Asset Workbench
To add asset details using the GIS Asset Workbench
-
Navigate to the Asset Numbers page (Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets).
-
Search for a GIS asset by using one of these search methods:
-
Select a GIS asset in the Asset Numbers field.
-
Click the Advanced Search button, and select Yes in the GIS Assets field. The results will include GIS assets only.
-
-
Click the Go button.
-
Select the row for the asset.
-
Choose the GIS Asset Workbench value from the View drop-down.
-
Click the Go button, and the GIS Asset Workbench appears.
-
Select a Linear Reference Method (required).
-
Optionally select the Direction of the asset.
-
Select if this is an Area Asset. Area assets have a geometric shape that is non-linear, but is identified by the closed area or shape having multiple linear sections forming its geometry. Examples are bodies of water such as lakes and ponds, forest areas, playgrounds, and so on.
Values are Yes and No; the default value is No. If you select Yes, the Segmented option will be No. You cannot have an area asset that is segmented.
-
Optionally indicate if the linear asset is Segmented and will contain a single segment or multiple segments. Values are Yes or No.
If you select Yes, the Segments region becomes available to add multiple rows.
A segment is a section of the linear asset identified by its start and end measure. A linear asset can have one or more segments within its length. Creating segments enables you the ability to analyze and work on specific sections of the linear asset. Example: Gathering and Transmission Pipeline Segments, Freeway Road Segments, Main and Feeder Segment Pipelines.
You can enter an end date for the linear asset segment, and update the segment details with new measure values. This enables the same segment name to be retained in the system with updated measure values.
-
Select Yes to enable the Add 3 Rows icon in the Segment Details region to add multiple segments. Add Segment Details such as:
-
Segment Name
-
Segment Description
-
Feature Class: Available with the ESRI integration only. These values are defined on the ESRI Map Manager page, and is a reference to a published Feature table from ESRI System which has a Polyline shape.
-
ESRI Route ID: Available with the ESRI integration only. The ESRI reference identifier from the eSRI Feature table which contains the corresponding Polyline geometry.
-
Spatial Route: Available for Oracle Spatial integration option only. The Spatial route can be associated during the GIS assets setup.
-
Custom Route ID: Available for Custom integration option only. The identifier must be passed to a custom API to derive SDO geometry.
-
From Measure: Optional if ESRI Feature class shape does not have measure dimension.
-
To Measure: Optional if ESRI Feature class shape does not have measure dimension.
-
Length: Optional if ESRI Feature class shape does not have measure dimension.
-
Start Date
-
End Date
You can have more than one segment with the same segment name with a different segment description as long as the dates are not overlapping. This enables you to have version control of geometry changes based on time. Versioning the segments with the same name would keep the properties, elements and relationships intact as they continue to point to the same segment name.
Important: Based upon the map integration that you use, the segment row may also include additional columns such as ESRI Route ID, Spatial Route ID or Custom Spatial Route ID. This provides the ability to associate the geometry shape to the linear asset.
See GIS Asset Maps Integration for more information.
Select No to enter segment details for one row. Enter Segment Details such as:
-
Feature Class: Available with the ESRI integration only. These values are defined on the ESRI Map Manager page, and is a reference to a published Feature table from ESRI System which has a Polyline shape.
-
ESRI Route ID: Available with the ESRI integration only. The ESRI reference identifier from the ESRI Feature table which contains the corresponding Polyline geometry.
-
Custom Route ID: Available for Custom integration option only. The identifier must be passed to a custom API to derive SDO geometry.
-
From Measure: Optional if ESRI Feature class shape does not have measure dimension.
-
To Measure: Optional if ESRI Feature class shape does not have measure dimension.
-
Length: Optional if ESRI Feature class shape does not have measure dimension.
-
Start Date
-
End Date
Note: The Measure UOM defaults to the UOM associated with the Linear Reference Method.
GIS Asset Workbench
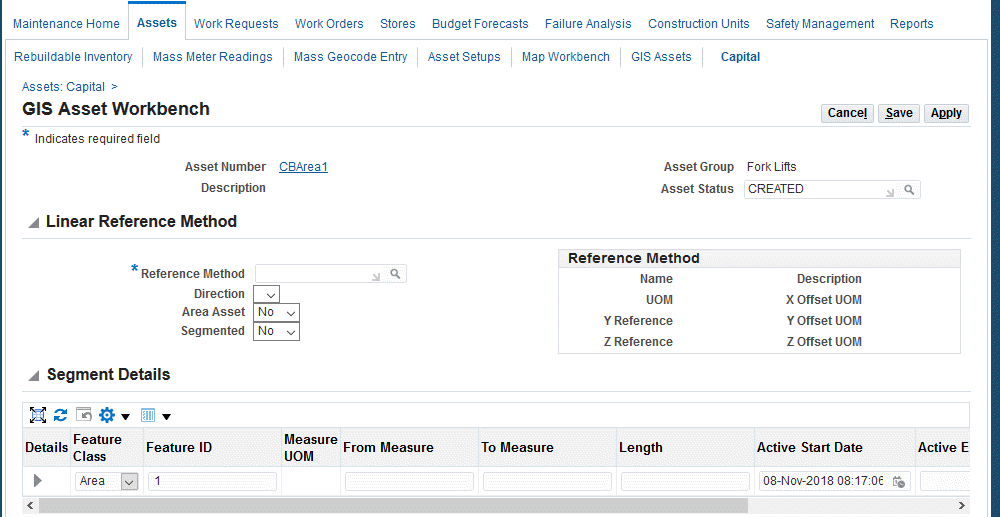
-
-
Optionally click the following to add Properties and associated details:
-
Add 3 Rows icon
-
Copy Property: Copy the property details for the selected row
-
Copy Segment Details: Copy the segment details for the selected row
-
Copy Row: Copy the entire selected row
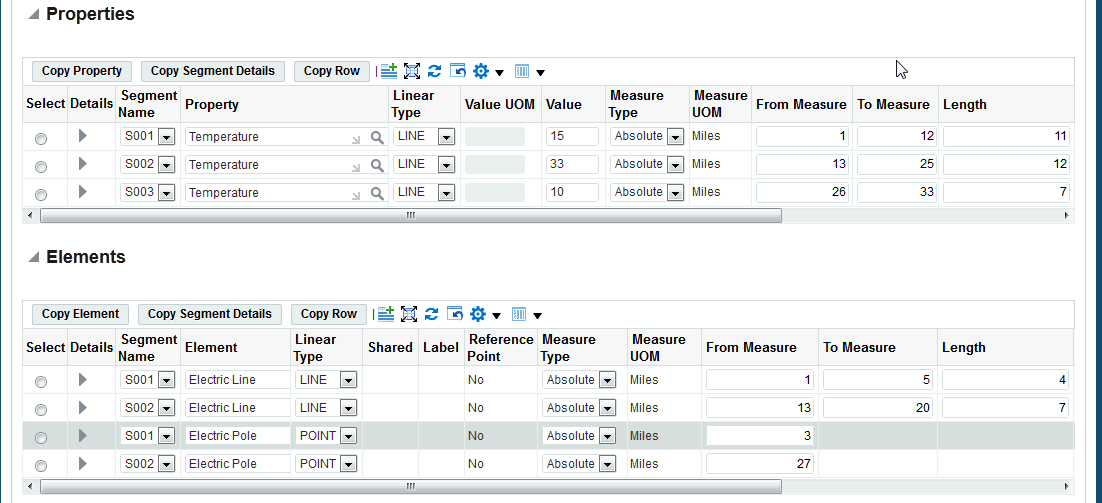
-
-
Optionally add Elements details. Elements can be Labelled or Non_labelled, Point or Line. You can add elements by clicking one of the following:
-
Add 3 Rows icon
-
Copy Element: Copy segment name
-
Copy Segment Details: Copy the segment details for the selected row
-
Copy Row: Copy the entire selected row
If you click the Add 3 Rows icon, enter information such as:
-
Segment Code
-
Element
-
Shared
-
Label
-
Measure Type
-
Active Start Date
-
Active End Date
-
-
Click one of the following buttons to add Relationships to the GIS asset:
-
Add Relationship: Enter relationship information.
-
Copy Relationship: Copy a specific relationship row.
-
Copy Segment Details: Copy the segment details for the selected row.
-
Copy Row: Copy the entire selected row.
-
-
Click the Manage Relationships icon to access the Manage Relationships page.
Use this region to edit relationship details such as Assets and Related Assets.
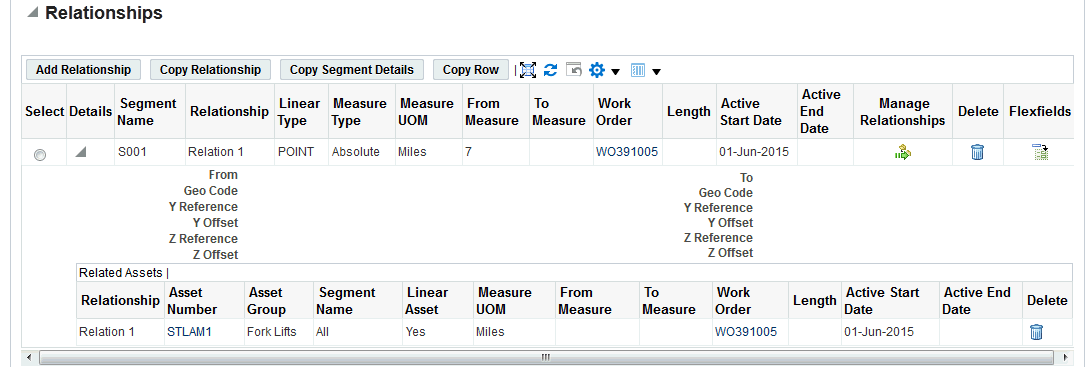
-
Click the Save button to return to the GIS Assets Workbench.
-
Click the Apply button.
To view assets using the GIS Assets Workbench
-
Navigate to the Asset Numbers page.
-
Enter search criteria for a asset, and then click Go.
-
Click the link for the asset and the Asset Details page appears.
-
Click the GIS Asset Workbench link.
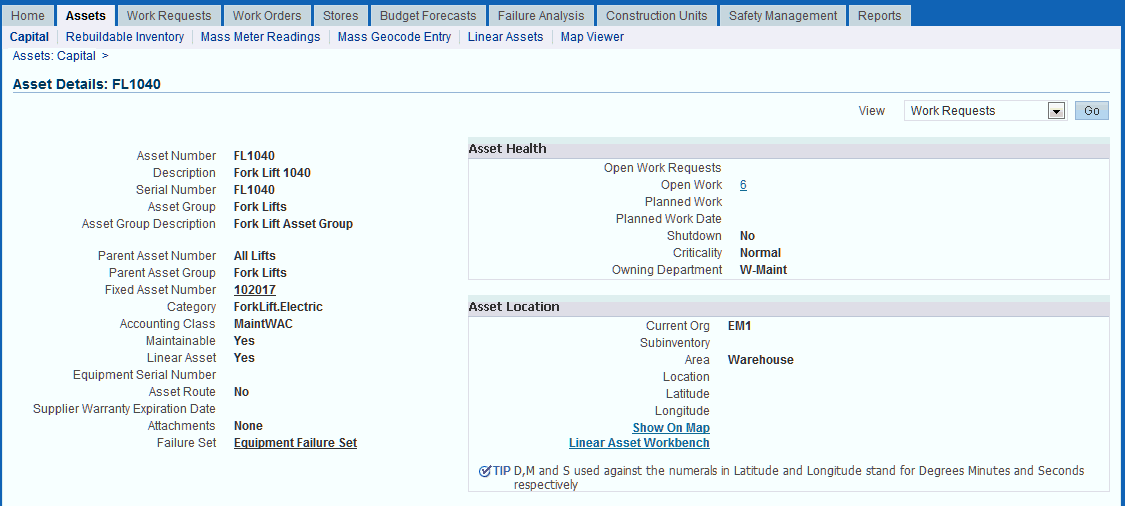
-
View the associated asset details such as the measure values associated for the current active segment.
Using the Map Workbench
Use the Map Workbench to view GIS, discrete, and area assets. You can also view and create work requests and work orders, including express work orders for the located assets.
Important: Discrete assets must have geocoded information or an associated ESRI Point Feature Class defined to be displayed on the Map Workbench.
Segments must have an association to a Spatial Route or ESRI polyline Feature Class to be displayed on the Map Workbench.
You can perform the following using the Map Workbench:
-
Search for assets by asset numbers, asset status and asset relationships.
-
Search for assets using the Asset Search, GIS Attributes Search, Work Order Search, Locate Segments, and Work Request Search tabs.
-
Locate assets in a circle or polygon area on a map.
-
Locate assets using segments.
-
Search for GIS asset attributes, Elements and Properties.
-
Search for work orders by number or status.
-
Search for work requests based on number or status.
-
Create Dynamic Segments of assets by entering measure values or using reference points.
-
Create Dynamic Segments of assets by clicking an asset displayed on a map.
-
Create work orders including express work orders on Located Assets.
-
Create work orders including express work orders for located assets with Located Measures.
Note: Dynamic segmentation is the process of clipping the asset geometry for the given measure values without disturbing the underlying asset geometry. Refer to Oracle Spatial and ESRI materials for more information on dynamic segmentation.
Navigating the Map Workbench
-
Navigate to the Map Workbench page (Maintenance Super User > Home > Assets > Map Workbench).
The Map Workbench can also be accessed using the Map All action from the Asset Search and Work Order Search. In addition, you can navigate to the Map Workbench by clicking the Show on Map link in asset and work order details.
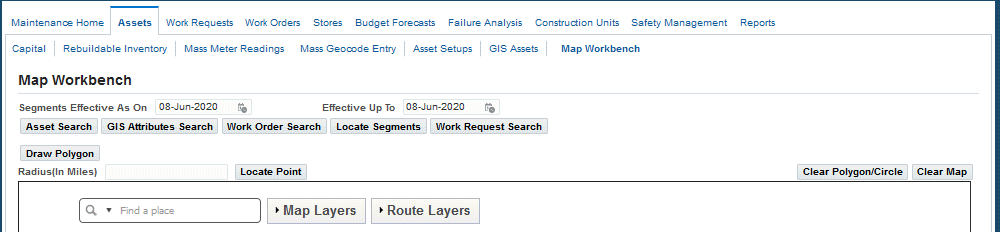
The Map Workbench page appears and displays the following to enable you to search for discrete or GIS assets, GIS asset attributes, work orders on maps and perform2 dynamic segmentation for measured GIS assets. Work orders and work requests can be initiated on the selected assets and asset segments.
-
Segments Effective From and Effective To: Enter the effective dates of the segments and to perform an asset search based on the effective date.
-
Search Options:
-
Asset Search
-
GIS Attribute Search
-
Work Order Search: You can search for multiple work orders.
-
Locate Segments
-
Work Request Search: You can search for multiple work requests.
-
-
Search Results Tab: Initiate work based on the following:
-
Located Assets
-
Located Attributes
-
Located Work Orders
-
Located Measures
-
Located Work Requests
-
-
-
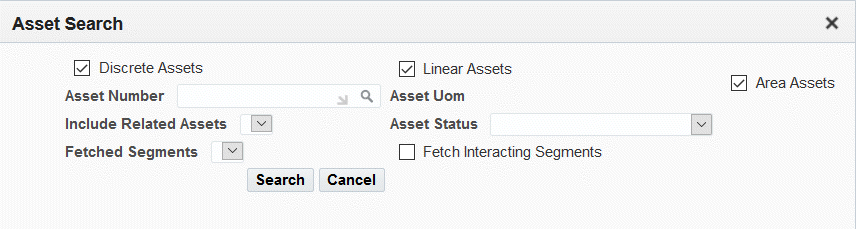
Click the Asset Search button to search for discrete, linear, or area assets on a map.
You can perform an asset search using one of these options:
-
Select the check box for Discrete Assets, Linear Assets, or Area Assets.
-
Select the Asset Number.
-
Select Include Related Assets and Fetched Segments to further narrow your search.
-
Optionally select the Asset Status.
-
Click the Search button.
-
-
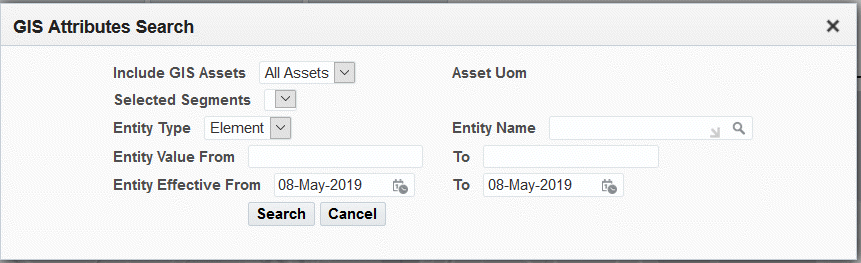
Click the GIS Attributes Search button to search for asset attributes:
-
Select a value in the Include GIS Assets drop-down list: All Assets or All Selected Assets.
-
Search by Entity Type of Element or Property (required).
-
Select a value in the Selected Segments field:
-
Enter an Entity Name.
-
Optionally enter an Entity Value From and To value to narrow your search.
-
Enter Effective From and To dates.
-
Click the Search button.
-
-
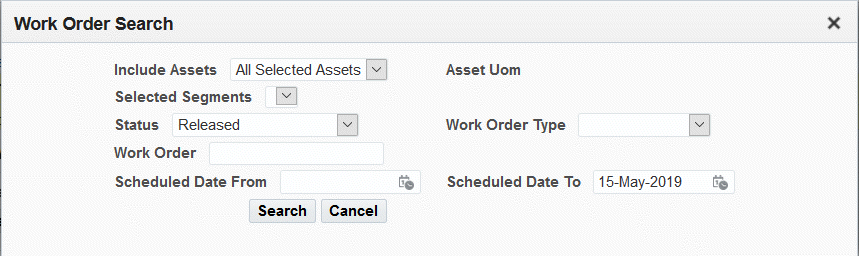
Click the Work Order Search subtab to enter selection criteria such as:
-
Include Assets: Enter a specific retrieved asset, All Selected Assets, or All Assets.
-
Selected Segments
-
Status
-
Work Order Type
-
Work Order
-
Effective From and To dates
-
Click the Search button.
-
-
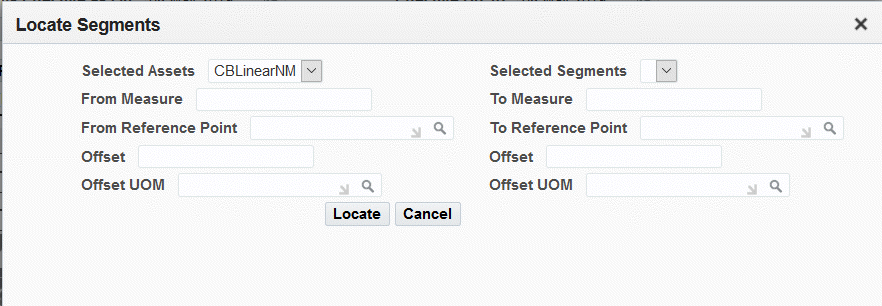
Click the Locate Segments button to search for assets with segments.
Enter values for any of the following fields:
-
Select a value from the Selected Assets drop-down list.
-
Select a value from the Selected Segments drop-down list.
-
Optionally enter a value in the From Measure and To Measure fields to narrow your search.
-
Optionally enter a value in the From Reference Point, Offset and Offset UOM fields to narrow your search.
-
Optionally enter a value in the To Reference Point fields, Offset, and Offset UOM fields to narrow your search.
-
Click the Locate button.
-
-
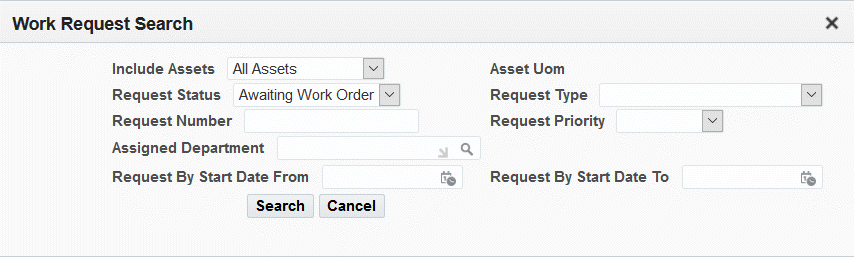
Click the Work Request Search button to search for work requests associated with the assets. Enter values for any of the following fields to narrow your search:
-
Include Assets: All Assets or All Specific Assets
-
Asset UOM
-
Request Status
-
Request Type
-
Request Number
-
Request Priority
-
Request By Start Date From
-
Request By Start Date To
-
-
Click the Draw Polygon button to draw a polygon to restrict the search on the map to the drawn polygon area only.
-
Enter a Radius and Click point to draw circle area covering the radius distance. Search on the map would be restricted only to the radius distance.
-
Optionally enter a numerical value in the Radius (In Miles) field, and click the Locate Point button to locate assets located within a specific mile radius.
-
Optionally enter the Zoom to Location (Address, City, State, Zip), and then click the Locate button.
-
Optionally click the Clear Polygon button or the Clear Map button.
-
Optionally right-click the map to select the Map Layers.
Route Layers in Map Workbench
Optionally right-click the map to select the Route Layers.
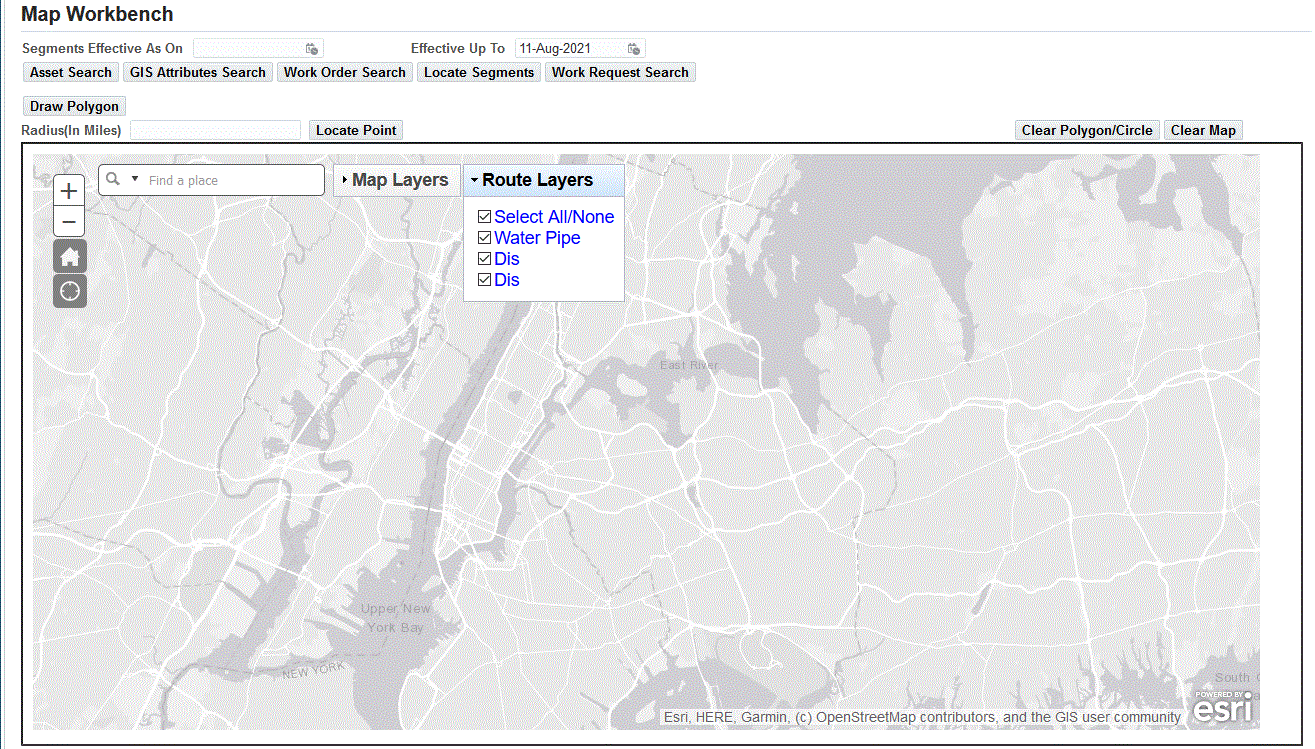
The following are rules related to the Route Layers functionality in Map Workbench:
-
All the feature classes of Linear, Discrete, and Area Asset types appear in the Map Workbench Route Layers list.
-
The Route Layers list of values is not limited based on the access control provided for the responsibility or user.
-
The Route Layers list values are available for selection.
The default value for all the selected layers is Yes.
[psx
-
When a particular route layer is unselected and the asset search is performed, the asset geometries belonging to that feature class will not be retrieved in the search results.
bbb
This is applicable for asset search by entering search parameters or during searches by polygon/circle area.
-
The route layers selection is considered before the asset search is executed.
If the selection is modified with existing search results displayed on the Map Workbench, then it will not modify the retrieved asset geometries.
-
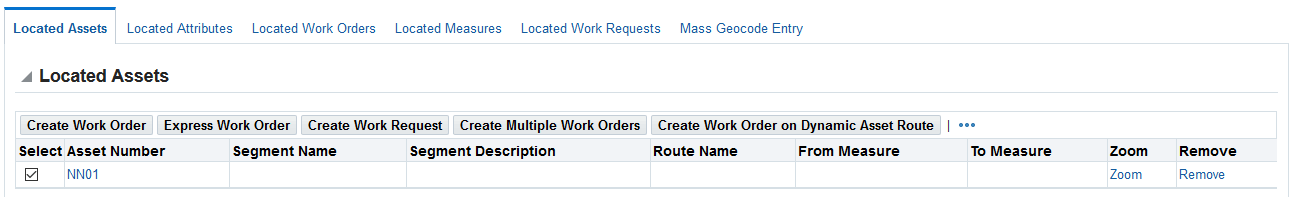
Click the Located Assets subtab to view GIS asset information such as:
-
Asset Number
-
Segment Name
-
Segment Description
-
Route Name
-
From Measure and To Measure
-
Zoom to display the asset location on the map
-
Remove to delete the asset number row from the results
Note: The Zoom and Remove buttons are available for discrete, linear, and area assets.
-
-
Click the Create Work Order button to access the Create Work Order page for the selected assets.
You can select the work order status for a specific organization.
See Creating Work Orders for more information.
-
Select an asset number.
Select an asset number, and then click the Express Work Order subtab to create an express work order. See Creating Express Work Orders for more information.
-
Click the Create Work Request button to access the Create Work Request page for selected assets. See Creating and Updating Work Requests, Oracle Enterprise Asset Management User's Guide for more information.
-
Click the Create Multiple Work Orders button to create one work order for each selected asset number.
For linear assets, if the segments are selected, then the work order will be created on the selected segments only. If no segments are selected from the search results, but only the asset is selected, then the work order will be created with all the segments.
The Create Multiple Work Orders window appears in which work order default values can be applied to all the work orders to be created. The Number of Assets Selected is a read-only field that displays the number of assets selected for the work order creation process.
-
Optionally select values for these fields:
-
Asset Activity
-
Department
-
Work Order Type
-
Priority
-
Status
-
Scheduled Start Date
-
Scheduled Completion Date
Note: If no values are selected in the fields, then all the work orders will be created based on the standard default values for the work order.
-
-
Click the Create Work Order button to create a work order. User-defined work order statuses available for your organization are available for selection.
-
Click the Submit button.
-
A confirmation message appears on the Map Workbench page that displays the request ID for the EAM Create Multiple Work Orders concurrent program that was successfully called. View the concurrent program log for the list of work orders that were created or failed.
-
-
Click the Create Work Order on Dynamic Asset Route button. A pop-up window appears enabling the creation of work order route for each of the selected assets.
-
The following information displays:
-
Number of Assets Selected
-
Assign to Asset Route: Select an asset route.
-
Work Order (required): Accept the auto-generated work order number if work order numbers are automatically generated, or a different work order number.
-
Description: Optionally enter text.
-
-
Click the Proceed to Create Work Order button.
The Update Work Order page appears with the work order created on the dynamic asset route available for edit. The work order is created with a status of Draft. However, the Route Details pop-up window appears where work order details such as the status can be modified.
-
-
Click the Located Attributes subtab to view:
-
Asset Number
-
Segment Name
-
Entity Type
-
Entity Name
-
Value
-
Zoom to display the asset location on the map
-
Remove to delete the asset number row from the results
-
-
Click the Located Work Orders subtab on the lower region of the page to view associated work order information such as:
-
Asset Number
-
Segment Name
-
Segment Description
-
Status
-
Work Order Number
-
Zoom to display the asset location on the map
-
Remove to delete the asset number row from the results
-
-
Click the Located Measures subtab to view:
-
Asset Number
-
Segment Name
-
From Measure and To Measure
User-defined work order statuses available for your organization are available for selection.
Click the Create Multiple Work Orders button to create a work order for each selected asset number.
For linear assets, all segments from one asset are grouped into the details of one work order.
-
-
Select the row for the asset number.
Click the Mass Geocode Entry subtab to add, view, and update geocode information for the located asset. See Entering Geocodes for EAM Assets for more information.
Using the Indoor Map Workbench
Use the Indoor Map Workbench to visualize assets indoors on a GIS map.
Important: The Indoor Map Workbench menu must be enabled before you can use this feature. See Enabling the Indoor Map Workbench Menu.
To use the Indoor Map Workbench
-
Navigate to the Indoor Map Workbench (Maintenance Super User > Assets > Indoor Map Workbench).
-
Use these options to perform the following searches:
-
Asset Search - Only GIS assets will be available for selection.
-
Asset Number
-
Asset Status
-
-
Work Order Search
-
Status
-
Work Order Type
-
Work Order
-
Scheduled Date from
-
Scheduled Date to
-
-
Work Request Search
-
Request Status
-
Request Type
-
Request Number
-
Request Priority
-
Assigned Department
-
Request By Start Date From
-
Request By Start Date To
-
Results Region
Click the following subtabs to perform additional actions the selected row:
-
Located Assets: Create work orders, express work orders, work requests, and multiple work orders for the asset.
-
Located Work Orders - Click one of the following:
-
Create Work Order - to create a work order. See Creating Work Orders.
-
Express Work Order - to create an express work order. See Creating Express Work Orders.
-
Create Work Requests - to add work requests to the asset. See Creating and Updating Work Requests.
-
Create Multiple Work Orders - to add a work order for several selected work orders. You must select more than one row to click this button. See Using the Map Workbench.
-
Asset Number link - to view asset details. See Defining Asset Numbers.
-
Work Order Number link - to view work order details. See Viewing Work Orders.
-
Zoom - to display the asset location on the map.
-
Remove - delete the row from the results.
-
-
Located Work Requests
-
-
Place the cursor over the map area where the asset is located to access the following actions:

-
Create Work Order - To create a work order. See Creating Work Orders.
-
View Work Order - To navigate to an existing work order for the asset. See Viewing Work Orders.
-
Create Work Request - To add a work request for the asset. See Creating and Updating Work Requests.
-
View Work Request - To navigate to an existing work request. See Obtaining Work Request Information.
-