 Understanding Consolidation Processing
Understanding Consolidation ProcessingThis chapter provides an overview of consolidation processing and discusses how to:
Validate the consolidation setup.
Process eliminations.
Process equitization.
Lock scenarios.
Process closing rules.
Run tree flattener.
Review application engine messages.
Run related processes.
Note. This chapter assumes that you are already familiar with run controls, jobstreams, and PeopleSoft Enterprise Process Scheduler.
See Also
PeopleTools PeopleBook: PeopleSoft Process Scheduler
 Understanding Consolidation Processing
Understanding Consolidation ProcessingThis section lists prerequisites and discusses:
Consolidation processing.
Reconciliation for consolidation processes.
Delivered application engines and job streams.

 Prerequisites
PrerequisitesBefore processing consolidations, you must:
Prepare ledgers (including all related rules and processing).
Define consolidation models and include elimination, equitization, flows, and non-controlling interest groups.
See Also
Establishing Consolidation Models
Preparing Data for Consolidations

 Consolidation Processing
Consolidation ProcessingThere are three main consolidation application engines: eliminations, data flows, and equitization. Each application engine is launched by a separate run control page. You can initiate and monitor consolidation processing from the Consolidation Manager page.
See Managing Consolidation Processing.
As with all application engines within the PeopleSoft EPM environment, you specify the following run control parameters: unit, scenario, fiscal year, and accounting period for each application engine. The system uses these parameters to determine which consolidation model to use.
For PeopleSoft Global Consolidations processes, the specified unit must be the common consolidation business unit. Depending on the processing method that you specify for the consolidation ledger template, the system processes either a single period or all periods for that fiscal year that are less than or equal to the specified run control period.
Global Consolidations uses several record objects during processing: the consolidation ledger (CLED), the input log (ILOG), the output log (OLOG), the journal table, and related temporary tables. During processing, the general data flow is:
The system retrieves data that matches the run control parameter criteria from the consolidation ledger and stores it in the input log (ILOG).
Processing occurs, using the consolidation model rules that apply.
The system writes results to the output log (OLOG) and calculates any out-of-balance amounts.
The system writes the resulting journal lines to the journal table that you define in the ledger template for the consolidation ledger.
Depending on the processing options that you select, the system posts the journals to the consolidation ledger as the last processing step, or you can run the Ledger Post application engine at a later time.
The system does not update the consolidation ledger with the results until you run the ledger post process.
The following diagram illustrates this process flow:
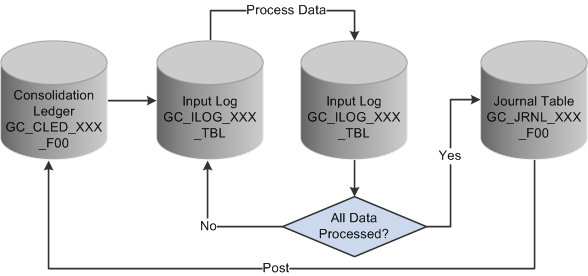
Overview of process flow
When you process eliminations and equitization, the system uses spawning to process multiple jobs, optimizing performance. The main application engines, or parent jobs, spawn the child jobs.
During elimination processing, the system assigns one record suite to the parent elimination manager (GC_ELIMMGR) engine, spawns one job for intercompany eliminations, and as many non-controlling interest jobs as the number of remaining available record suites. For example, if there are a total of three record suites available, one is used by the elimination manager, one is used by the intercompany elimination spawned job, and the third is used for an NCI spawned job. If there are five record suites available, three can be used for non-controlling interest-spawned jobs.
During equitization processing, the system equitizes subsidiaries based on the ownership level sequence. Spawning of equitization jobs depends on the total number of subsidiaries in the ownership level divided by the number of record suites available. This strategy enables parallel processing for subsidiaries, reducing the amount of time required to process them all. The more record suites that are available, the faster processing occurs. For example, if there are a total of three record suites available during equitization processing, the system assigns one record suite to the parent equitization manager (GC_EQ_MGR) engine, spawning two (child) equitization jobs for each ownership level. When both jobs for the lowest ownership level are complete, the system spawns two more jobs for the next ownership level, and so on.
If you need to cancel processing for eliminations or equitization jobs, you should cancel the spawned jobs first (the child jobs), then the parent job. If you are using the delivered jobstreams for processing, you can identify parent jobs by the process name PF_JOBSTREAM. The process names for spawned jobs are:
GC_ICUELIMS for intercompany eliminations.
GC_NCI_ELIM for non-controlling interest eliminations.
GC_EQTZ for equitization.
ILOG and OLOG Maintenance for Reruns
During a rerun, the system adds the prior run's batch ID to GC_DELBATCH_TBL. The Delete Batch engine (GC_DELB) deletes the ILOG and OLOG data for the prior run batch. You should either run this as the last job in the jobstream when processing eliminations or equitization, or run it as a separate jobstream that you can schedule to run during off-peak hours—for example, sometime overnight. The delivered jobstream is GC_DELB.
See Also
Streamlining Processing with Jobstreams
Defining System-Wide Security and Processing Options
Defining System-Wide Security and Processing Options

 Reconciliation for Ledger Preparation and Consolidation Processes
Reconciliation for Ledger Preparation and Consolidation Processes
As part of consolidation processing, reconciliation occurs at several stages. The reconciliation programs include balance rules that check the records used during ledger preparation and consolidation processing.
For ledger preparation, the system uses a filter-based query that returns the count of the number of records in the source and target tables during calendar mapping, account mapping, and currency mapping. The number of records in the source and target should be equivalent.
For consolidation processing, the system uses a filter-based query that verifies that debits equal credits in the output journal, based on the balancing rule associated with the consolidation model.
This table describes the individual jobs that are used to reconcile specific aspects of ledger preparation or consolidation processing:
|
Job ID |
Consolidation Phase |
Description |
Usage |
|
GCRECNCAL |
Ledger Preparation |
Reconciliation for calendar mapping. |
Counts the number of records in the source and target tables for each ledger business unit during the calendar mapping phase of ledger preparation processing. The counts should be the same. As illustrated in the diagram that follows this table, the reconciliation compares 1 and 2. |
|
GCRECNCLED |
Ledger Preparation |
Reconciliation for ChartField mapping. |
Counts the number of records in the source and target tables for each ledger business unit during the ChartField mapping phase of ledger preparation processing. The counts should be the same. As illustrated in the diagram that follows this table, the reconciliation compares 2 and 3. |
|
GCRECNCUR |
Ledger Preparation |
Reconciliation for currency mapping. |
Counts the number of records in the source and target tables for each ledger business unit during the currency mapping phase of ledger preparation processing. The counts should be the same. As illustrated in the diagram that follows this table, the reconciliation compares a and b for each ledger business unit that has a GC_SOURCE equal to 01 (the source staging ledger) and whose base currency field is not blank. |
|
GCRECNELIM |
Consolidation |
Reconciliation for intercompany elimination processing. |
Verifies that the output journal is balanced. |
|
GCRECNEQTZ |
Consolidation |
Reconciliation for equitization processing. |
Verifies that the output journal is balanced. |
|
GCRECNNCI |
Consolidation |
Reconciliation for NCI processing (within intercompany elimination processing). |
Verifies that the output journal is balanced. |
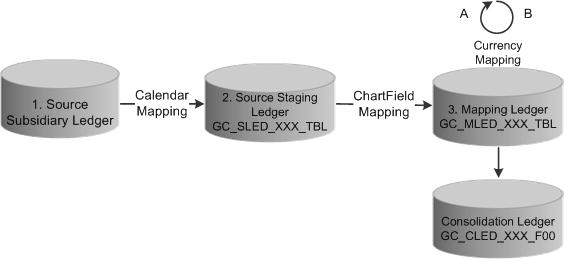
Ledger preparation reconciliation points
These jobs are run as part of ledger preparation or consolidation processing. The IDs for the balance rules, filters, and constraints used by these jobs all start with GCRECN, and are in the SHARE setID. For these jobs to work, you must not remove any rows from the delivered filter and constraint definitions. The delivered rules are intended primarily as examples; review them for applicability to your specific business requirements.
To set up the Consolidation Manager and Ledger Preparation Manager pages to view the status of the reconciliation jobs, use the Consolidation Processes page to add the job IDs to their related page, and then on the Status Details page, click the View Reconciliation Totals link to view the results.
See Also
Using Balancing and Reconciliation Features

 Delivered Application Engines and Jobstreams
Delivered Application Engines and JobstreamsThe Global Consolidation batch processes use several PeopleSoft application engine programs. This section provides a complete list of the engines used and the jobstream definitions that are provided with the delivered sample database in the SHARE setID. This information is provided so that you can create your own jobstreams or modify the delivered ones to suit your implementation.
Delivered Application Engines
PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management applications use application engines to run each process. Engine metadata is delivered with the system; unless you are revising the application, you should not need to modify it. This metadata stores information about the various PeopleSoft application engine programs used within an engine. This table lists the delivered engines that are used by PeopleSoft Global Consolidations when processing consolidations by using the delivered jobstreams and their associated jobs:
|
Engine ID |
Description |
Usage |
|
GC_CLOSMGR |
Global Consolidations closing manager application engine. |
Runs the closing process. Uses the GC_CLOSE_MGR application engine. |
|
GC_DELB |
Audit log cleanup engine. |
Cleans up the ILOG and OLOG data for a prior run when you rerun any of the consolidation processes. Uses the GC_DELBATCH application engine. You should either run this as the last job in the jobstream when processing eliminations or equitization, or set it up as a separate jobstream that you can schedule to run during off-peak hours. |
|
GC_ELIM |
Spawned intercompany eliminations application engine. |
Processes intercompany eliminations. Uses the GC_ICUELIMS application engine. |
|
GC_ELIMMGR |
Main elimination manager application engine. Spawns processing of the Intercompany Eliminations engine (GC_ELIM) and the NCI engine (GC_NCI). |
Processes intercompany eliminations. Uses the GC_ELIM_MGR application engine. |
|
GC_EQ_MGR |
Main Equitization Manager application engine. Spawns processing of the equitization engine (GC_EQTZ). |
Processes equitization. Uses the GC_EQTZ_MGR application engine. |
|
GC_EQTZ |
Spawned equitization application engine. |
Processes equitization for each subsidiary entity. Uses the GC_EQTZ application engine. |
|
GC_FILEIMP |
File import application engine. |
Processes file import. Uses the GC_FILE_IMP application engine. |
|
GC_FLJRNL |
Journal flow update application engine. |
Processes journal flows. Updates the journal flow activity table based on the run criteria. Uses the GC_FLJRN_ENG application engine. |
|
GC_FLOWFLT |
Global Consolidations flow flattener application engine. |
Creates a flattened table based on the flow group and the flow template attached to the model. Uses the GC_FLOW_FLAT application engine. |
|
GC_FLSRC |
Source flow update application engine. |
Processes source flows. Updates the flow activity table based on the run criteria. Also calls the currency engine to perform translation of flow amounts. Uses the GC_FLSRC_ENG application engine. |
|
GC_FX_MGR |
Global Consolidations currency adjustment application engine |
Processes currency adjustments. Uses the GC_FX_MGR application engine. |
|
GC_JR_PUB |
Publishes selected journals that result from consolidation processing. Uses the GC_JRNL_PUBL application engine. Note. This application engine publishes the journals only; you must set up application messaging to subscribe to the published journals. See Publishing Journals. |
|
|
GC_JRNLEDT |
Manual journal edit application engine. |
Edits consolidation manual journals. Uses the GC_JRNLEDIT application engine. |
|
GC_JRNLRCR |
Consolidations create recurring journal application engine. |
Creates recurring journals. Uses the GC_JRNL_RCR application engine. |
|
GC_LEDVERF |
GC ledger verification application engine. |
Processes ledger verification rules. Uses the GC_LEDVERIFY application engine. |
|
GC_MATCH |
Matching report application engine. |
Processes matching. Uses the GC_MATCH application engine. |
|
GC_NCI |
Spawned NCI application engine. |
Processes NCI eliminations. Uses the GC_NCI_ELIM application engine. |
|
GC_OWN_FLT |
Ownership Inquiry Preparation engine. |
Prepares a flattened ownership table prior to running the ownership inquiry. The flattened ownership table is populated with keys such as business unit, scenario, and as of date. |
|
GC_PREP |
Spawned ledger preparation application engine. |
Processes ledger preparation. Uses the GC_PREP application engine. |
|
GC_PREPMGR |
Main ledger preparation process. Spawns processing of the ledger preparation engine (GC_PREP). |
Processes ledger preparation. Uses the GC_PREP_MGR application engine. |
|
GC_RECON |
Reconciliation application engine. |
Processes reconciliation rules defined for the ledger preparation and consolidation processes. Calls the PF_RECON application engine. |
|
GC_VALID |
Consolidation Validation application engine. |
Validates consolidation rules and objects. A validation process that validates consolidation setups (elimination, non-controlling interest, equitization, ownership rules) and data preparation setups (ChartField, calendar, currency mapping). Uses the GC_VALIDATE application engine. |
|
GCTREEFLAT |
Tree flattener application engine. |
Processes tree flattener. Uses the GC_TREE_FLAT application engine. |
|
RECN |
Reconciliation application engine. |
PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management engine; processes reconciliation. Uses the PF_RECON application engine. |
|
ALLOCATION |
Allocation application engine. |
PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management engine; processes allocations. Uses the PF_ALLOC_ENG application engine. |
|
EDIT |
PF Journal edit application engine. |
PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management engine; processes journal edit. Uses the PF_EDIT application engine. |
|
POST |
PF Ledger post application engine. |
PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management engine; processes ledger post. Uses the PF_POST application engine. |
|
UNPOST |
PF Ledger unpost application engine. |
PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management engine; processes ledger unpost. Uses the PF_UNP application engine. |
|
MERGE |
Merge application engine. |
PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management engine; merges temp tables to permanent tables. Uses the PF_MERGE application engine. |
Delivered Jobstreams
PeopleSoft Global Consolidations uses jobstreams for processing. Jobstreams enable different users to run a series of application engines at the same time by using temporary tables. Instead of using fact tables in the Peoplesoft EPM database, temporary tables, using record suites, use only the relevant data from the main fact tables to run the application engines and process the data. This strategy enables the application engines in the jobstream to run faster (because the entire fact table is not being used) while keeping the fact tables open and accessible to other users so that they can run the same engines simultaneously. The record suites are assigned when the first application engine runs, then released when the last application engine is finished.
You associate each main application engine with a job ID on the Job Metadata page. You associate jobs with a jobstream on the Jobstream setup page. You must also define record suites for the jobstream on the Jobstream Record Suites page. A job must be unique across all jobstreams, so if you require additional jobstreams, you first need to create new jobs to use in each jobstream. This table lists each batch process, the delivered jobstream, and the engines and job IDs used in that jobstream:
|
Process |
Delivered Jobstream ID |
Application Engines Used (Engine ID) |
Job IDs in Jobstream |
Description |
|
Closing |
GC_CLOSMGR |
GC_CLOSMGR MERGE |
GC_CLOSMGR GC_MERGE |
Global Consolidations closing process for year end closing and period roll forward. |
|
Audit Log cleanup utility |
GC_DELB |
GC_DELB |
GC_DELB |
Cleans up ILOG and OLOG for prior run when you rerun eliminations or equitization. |
|
Elimination |
GC_ELIM |
GC_ELIM |
GC_ELIM |
Processes intercompany eliminations. Uses the GC_ICUELIMS Application Engine program. |
|
Elimination Manager |
GC_ELIMMGR |
GC_ELIMMGR MERGE |
GC_ELIMMGR GC_ELIMMRG |
Processes intercompany and non-controlling interest eliminations. |
|
Equitization |
GC_EQ_MGR |
GC_EQ_MGR MERGE |
GC_EQ_MGR GC_EQ_MRG |
Processes equitization and NCI for current income. |
|
Equitization |
GC_EQTZ |
GC_EQTZ |
GC_EQTZ |
Processes equitization. |
|
GC file import |
GC_FILEIMP |
GC_FILEIMP |
GC_FILEIMP |
Import files. |
|
Journal flow update |
GC_FLJRNL |
GC_FLJRNL MERGE |
GC_FLJRNL GC_FLMERGE |
Processes journal flow updates. |
|
Flow flattener |
GC_FLOWFLT |
GC_FLOWFLT MERGE |
GC_FLOWFLT GC_FLOWMRG |
Creates a flattened table based on flow group and flow templates attached to the model. |
|
Source flow update |
GC_FLSRC |
GC_FLSRC MERGE |
GC_FLSRC GC_FLMERGE |
Processes source flow updates. |
|
Currency adjustment |
GC_FX_MGR |
GC_FX_MGR MERGE |
GC_FX_MGR GC_MERGE |
Processes currency adjustments. |
|
Journal publish |
GC_JR_PUB |
GC_JR_PUB |
GC_JR_PUB |
Publishes journals. |
|
Manual Journal Edit |
GC_JRNLEDT |
GC_JRNLEDT |
GC_JRNLEDT |
Processes manual journal edits. |
|
Create Recurring Journals |
GC_JRNLRCR |
GC_JRNLRCR |
GC_JRNLRCR |
Processes recurring journal creation. |
|
Ledger verification |
GC_LEDVERF |
GC_LEDVERF |
GC_LEDVERF |
Processes ledger verification. |
|
Consolidation Match |
GC_MATCH |
GC_MATCH |
GC_MATCH |
Processes consolidation match report. |
|
NCI Elimination |
GC_NCI |
GC_NCI |
GC_NCI |
Processes NCI eliminations. |
|
Ownership Inquiry Preparation |
GC_OWN_FLT |
GC_OWN_FLT |
GC_OWN_FLT |
Moves data to flattened ownership table prior to running Ownership Inquiry. |
|
Ledger Preparation |
GC_PREP |
GC_PREP |
GC_PREP |
Processes ledger preparation. |
|
Ledger Preparation Manager |
GC_PREPMGR |
GC_PREPMGR MERGE |
GC_PREPMGR GCPREPMRG |
Processes ledger preparation. |
|
Tree Flattener |
GC_TREEFLT |
GCTREEFLAT MERGE |
GC_TREE GCTREEMRG |
Processes tree flattener as a standalone job. |
|
Validation |
GC_VALID |
GC_VALID |
GC_VALID |
Validates the consolidation setups (for example, elimination, non-controlling interest, equitization, ownership rules) and data preparation setups (for example, ChartField, calendar, and currency mapping). |
Note. When running these jobs and jobstreams, do not select the As Of Dated Jobstream option on the run control page. This option is not supported for PeopleSoft Global Consolidations application engines. If you select this option, your results will be incorrect.
 Validating the Consolidation Setup
Validating the Consolidation SetupThis section provides an overview of the Consolidation Validation application engine and describes how to run the Validation application engine.

 Understanding the Consolidation Validation Application Engine
Understanding the Consolidation Validation Application EnginePeopleSoft recommends that you run the Consolidation Validation application engine to verify that the consolidation setup is correct. The delivered job and jobstream are both named GC_VALID. You may opt to run the Consolidation Validation application engine in its own jobstream by using the delivered run control page, or consider adding it to other jobstreams, depending on your organization's requirements. Optimally, you should check the validation errors before running the Ledger Preparation application engine or processing consolidations business rules.
The Consolidation Validation application engine checks that these objects and rules are valid, writing the results to the message log:
Consolidation model definition.
Mapping rules (calendar mapping, currency mapping, data mapping for ChartFields).
Consolidation tree.
Equitization rules.
Elimination rules.
Non-controlling interest rules.
Data flow rules.
Closing rules.
Ownership rules, including circular references or ownership validation.
If you make any changes to consolidation rules, it is import to run the validation engine again and carefully review the output.
Note. Circular references in ownership rules are checked only when the consolidation dimension is ledger business unit.

 Page Used to Validate the Consolidation Setup
Page Used to Validate the Consolidation Setup|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RUN_GC_VALIDATE |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Validation |
Run the Validation application engine. |

 Running the Validation Application Engine
Running the Validation Application EngineAccess the Validation run control page (Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Validation).
|
Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Period |
Specify the common consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period to process. |
|
Jobstream ID |
Accept the default value, GC_VALID, to use the delivered jobstream ID. |
Review the application engine message log for the process instance after processing is complete to see the results.
See Reviewing Application Engine Messages.
 Processing Eliminations
Processing EliminationsThis section provides an overview of elimination processing and discusses how to run the Elimination application engine.

 Understanding Elimination Processing
Understanding Elimination ProcessingUse the Elimination run control page to process eliminations, which eliminates or cancels out the effects of intercompany transactions and non-controlling interests. When you process eliminations, you can opt to process intercompany eliminations, non-controlling interest eliminations, or both.
When running the intercompany elimination process, the system:
Resolves data from the consolidation ledger (CLED) into the ILOG, based on the elimination rules for the consolidation model, the fiscal year, and period that you specify in the run control, and adds a sequence number key to each row.
Processes eliminations on the resolved ILOG data by creating entries in the OLOG to the specified elimination target ChartFields with a reversed sign, booking the entries to the elimination entity for that node.
After populating the OLOG with the elimination entries, calculates the out-of-balance amount from the OLOG lines and creates the out-of-balance entries to the OLOG.
Creates reversal entries for eliminations, if necessary.
This step depends on the processing method, which is established on the Ledger Template page for the consolidation ledger. The system creates reversal entries only if you are using a trial balance format and processing year-to-date, except when you are processing the last accounting period of the year.
Note. Steps one through four use temporary (work) tables.
Merges the temporary ILOG and OLOG tables into their permanent tables, GC_ILOG_XXX_TBL and GC_OLOG_XXX_TBL, respectively.
Creates the journal lines in the journal table with a GC_SOURCE of 04 (elimination entry).
Posts the journals to the consolidation ledger (CLED), if you choose to automatically post them.
If you are processing a rerun, during the initial stages of processing, the system unposts any posted journals from the prior run that affect the same data, or the system deletes them if they weren't posted. If you rerun using a different consolidation tree node, the system only unposts (or deletes) journals from the prior run that were recorded against nodes within the tree node now being processed.
When you run the non-controlling interest eliminations process, the system:
Resolves the data for the subsidiary equity accounts from the CLED into the ILOG, and adds a sequence number key to each row.
Resolves the data for the parent investment accounts from the CLED into the ILOG.
Eliminates the subsidiary equity data by creating the entries in the OLOG to the specified elimination target ChartFields with a reversed sign, booking the entries to the elimination entity.
Similarly, eliminates the parent investment data, generates non-controlling interest adjustments, and creates out-of-balance amounts in the OLOG, if applicable.
Creates reversal entries for the non-controlling interest eliminations, if necessary.
This step depends on the processing method, which is established on the Ledger Template page. The system creates reversal entries only if you are using a trial balance format and processing year-to-date, except when you are processing the last accounting period of the year.
Note. Steps one through five use temporary (work) tables.
Merges the temporary ILOG and OLOG tables into their permanent tables, GC_ILOG_XXX_TBL and GC_OLOG_XXX_TBL, respectively.
Creates the journal lines in the journal table with one of these GC_SOURCE values:
|
6A |
The parent investment elimination and the elimination of the portion of the subsidiary equity that is from that parent, as well as any out-of-balance entries. |
|
6B |
The non-controlling interest liability elimination, and the elimination of the portion of the subsidiary equity due to the non-controlling interest. |
Posts the journals to the consolidation ledger (CLED), if you choose to automatically post them.
Note. If you are using the financial statement consolidation ledger format, you must run the non-controlling interest eliminations after the equitization process. In this way, the system properly eliminates the additional investment from the equitization process.
See Also
Defining Non-Controlling Interest Rules

 Pages Used to Process Eliminations
Pages Used to Process Eliminations|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RUN_GC_CONSL |
Global Consolidations, Process Consolidations, Run Consolidations Processes, Eliminations |
Run the Elimination application engine. |
|
|
RUN_GC_JRNL |
Click the Select Journals link on the Eliminations run control page. |
Select which journals to include when using the proforma option. |

 Running the Elimination Application Engine
Running the Elimination Application EngineAccess the Eliminations run control page (Global Consolidations, Process Consolidations, Run Consolidations Processes, Eliminations).
|
Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Period |
Specify the common consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period to process. |
|
Jobstream ID |
Accept the default value, GC_ELIMMGR, to use the delivered jobstream ID. |
Select any of these processing options:
|
Override Scenario's Tree Node |
Select to use a different tree node than the one that is specified on the consolidation model. If you use this option, then in the Tree Node field, select the applicable tree node. The tree node that you specify must be at a lower hierarchical level of the tree than the node specified on the consolidation model. If the consolidation model is configured for tiered consolidations, you can select only the tree nodes specified on Tiered Consolidation page. |
|
Process Inter-Company Eliminations |
Select to run the inter-company elimination engine. |
|
Process Non-Controlling Interest Eliminations |
Select to eliminate subsidiary equity and parent investment amounts, and generate adjustments attributed to non-controlling owners. |
|
Select to use proforma journals (journals that have not been posted) as source data, rather than the consolidation ledger. When you select this option, the Post Journal Created option is disabled, because the system does not post proforma journals for consolidation processing. Use the ledger post process to post proforma journals. |
|
|
Select to automatically post the resulting journals to the consolidation ledger by calling the ledger post process. This option is not available when the Proforma option is selected. |
|
|
Select to send email notifications when out-of-balance amounts exceed their tolerance level. |
|
|
Get Prior Run Differences |
Select to compare results of the current run with that of the previous run and store the differences in the consolidation change log, which you can view by using the Run Difference Analysis page. This field is available if you select it on the General Options page. |
|
Update Flow Amounts |
Select to update flow amounts when processing eliminations. Updates any flow amounts after the consolidation process has been run. This option is available only if the Post Journal Created option is selected. The Update Flow Amounts option appears only if flow processing has been turned on for the consolidation ledger template. |
 Processing Equitization
Processing EquitizationThis section provides an overview of equitization processing and discusses how to run the Equitization application engine.

 Understanding Equitization Processing
Understanding Equitization ProcessingIf you have set up equitization groups for your consolidation model, use the Equitization run control page to equitize the current period changes in equity (for example, net income) of subsidiaries.
When processing equitization, the system completes these steps for each ChartField value in the equitization rule group:
Resolves data from the consolidation ledger (CLED) into the ILOG, based on the equitization rule group for the consolidation model, the fiscal year, and the period that you specify in the run control, and adds a sequence number key to each row.
Debits the ownership percentage amount for the account of the subsidiary against the parent investment account of the parent (if the control percentage is greater than the threshold), and credits the ownership percentage amount for the account of the subsidiary against the investment offset of the parent, and then moves the data to the OLOG.
These entries, which increase the parent investment account and increase parent earnings, are booked directly against the parent. Optionally, the system eliminates the amount equitized against the elimination entity (if you define the eliminate equitizations fields for the rule). For financial statement format ledgers, the system creates offset balance entries for the income statement side, similar to the investment offset entries.
Offsets the total equitized source amount to the equitization summary account specified in the rule by debiting the equitization offset account for the subsidiary and crediting the equitization summary, and then moves the data to the OLOG.
These entries are booked against the subsidiary. (This is an optional step, completed only if defined on the Equitization - Subsidiary Offset page.)
Generates non-controlling interest adjustments for claims on the subsidiary's net income for the period.
For trial balance format ledgers, the system debits the non-controlling interest expense account and credits the non-controlling interest liability account. For financial statement format ledgers, only the expense entries are created. The entries are booked to the elimination entity.
For financial statement format ledgers, creates elimination entries at the controlling parent to eliminate 100 percent of the source amounts identified if the equitization rule's processing option is Source Elimination.
Optionally, the system creates non-controlling interest entries and the corresponding elimination entries.
Creates dividend reclassification entries to the equitizing parent for the dividend amounts of a subsidiary, distributed to the direct parents of the subsidiary if the equitization rule's processing option is Dividend Reclassification.
Optionally, the system creates additional reclassification entries for the dividend amount to the elimination unit that is common to both the equitizing parent and the direct parent.
Creates reversal entries for the equitization, if necessary.
This step depends on the processing method, which is established on the Ledger Template page for the consolidation ledger. The system creates reversal entries only if you are using a trial balance format ledger and processing year-to-date, except when you are processing the last accounting period of the year.
Merges the temporary ILOG and OLOG tables into their permanent tables, GC_ILOG_XXX_TBL and GC_OLOG_XXX_TBL, respectively.
Creates journal lines in the journal table with one of these GC_SOURCE values:
|
5A |
Equitization. |
|
5B |
Equitization - elimination entry. |
|
5C |
Non-controlling interest for current earnings. |
|
5D |
Equitization - subsidiary offset entry. |
|
5E |
Equitization - elimination of NCI. |
|
5F |
Equitization - elimination of source. |
|
5G |
Equitization - dividend reclassification. |
Posts the journals to the CLED, if you choose to automatically post the journals.
If you are processing a rerun, then during the initial stages of processing, any journals that were posted during the prior run affecting the same data are unposted, or are deleted if they weren't posted. If you rerun using a different consolidation tree node, the system only unposts (or deletes) journals from the prior run that were recorded against nodes within the tree node now being processed.
If you make any changes to consolidation rules, it is import to rerun the validation engine again and carefully review the output.
See Also
Validating the Consolidation Setup

 Pages Used to Process Equitization
Pages Used to Process Equitization|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RUN_GC_EQTZ |
Global Consolidations, Process Consolidations, Equitization |
Run the Equitization application engine. |
|
|
RUN_GC_JRNL |
Click the Select Journals link on the Equitization run control page. |
Select which journals to include when using the Proforma option. |

 Running the Equitization Application Engine
Running the Equitization Application EngineAccess the Equitization run control page (Global Consolidations, Process Consolidations, Equitization).
|
Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Period |
Specify the common consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period to process. |
|
Jobstream ID |
Accept the default value, GC_EQ_MGR, to use the delivered jobstream ID. |
Select any of these processing options to use:
|
Override Scenario's Tree Node |
Select to use a different tree node than that specified on the consolidation model. In the Tree Node field select a tree node if you use this option. The tree node that you specify must be at a lower hierarchical level of the tree than the node specified on the consolidation model. If the consolidation model is configured for tiered consolidations, the user can select only the tree nodes specified on the Tiered Consolidation page. Note. Use this option carefully. When processing by nodes, if you run equitization for a node that includes only the parent, the system does not equitize from the child to the parent. If you run the process for a node that includes only the child, the system does not create the equitization entries on the parent or to the elimination unit. You must pick a node that includes both the child and the parent to create the equitization entries; the entries are booked to the appropriate parent and elimination unit. |
|
Select to use proforma journals (journals that have not been posted) as source data, rather than the consolidation ledger. When you select this option, the Post Journal Created option is disabled, as the system does not post the proforma journals as part of consolidation processing. Use the ledger post process to post proforma journals. |
|
|
Select to automatically post the resulting journals to the consolidation ledger by calling the ledger post process. This option is not available when the Proforma option is selected. |
|
|
Get Prior Run Differences |
Select to compare results of the current run with that of the previous run and store the differences in the consolidation change log, which can be viewed on the Run Difference Analysis page. This field is available only if it is selected on the General Options page. |
|
Update Flow Amounts |
Select to update flow amounts when processing equitizations. Updates any flow amounts after the consolidation process has been run. This option is available only if flow processing has been turned on at the ledger template level. and the Post Journal Created option has been selected on the Equitzation run control page. |
 Locking Scenarios
Locking ScenariosThis section provides an overview of scenario locking and discusses how to lock scenarios.

 Understanding Scenario Locking
Understanding Scenario LockingYou can lock a consolidation scenario to ledger preparation, ledger posting, and ledger unposting, by specifying a period for which the scenario is locked. You can also specify individual nodes on the consolidation tree to lock. You can lock:
An entire scenario to journal activity for a specific period.
A specific node (dimension) on the consolidation tree for a specific period.
You identify the common consolidation business unit, scenario, fiscal year, and period. From this information, the system derives the consolidation ledger, the consolidation dimension ChartField, and the consolidation tree. The locking information is stored in the Locked Scenario Header (GC_LEDLOCK_DEFN), Locked Scenario Details (GC_LEDLOCK_DTL), and the Locked Scenario Detail History (GC_LEDLOCK_DHIS) tables.
Locking an Entire Scenario
If you lock an entire scenario through a specified fiscal year and period, the system allows neither manual or system-generated journal activity to post or unpost, nor ledger preparation to run for that fiscal year and period. Essentially, nothing can be run to change the scenario, including ledger preparation, consolidation, currency adjustment, and, if the target period is locked, period-end closing.
Locking a Dimension Node
Optionally, instead of locking an entire scenario, you can lock a node on the scenario consolidation tree for the specified fiscal year and period. Journals whose lines include a locked node cannot be posted or unposted. Journals whose lines do not include a locked node can still be posted or unposted to the ledger. Additionally, ledger preparation cannot be run for the business units in the locked node.
Note. When a dimension node is locked, all child nodes and detail dimension values of that dimension node are also locked.
Impact on Journal Posting and Unposting
If you lock an entire scenario for a specified fiscal year and period, no further journal activity is allowed to the consolidation ledger through that period; the Ledger Post and Unpost application engines skip any journals that would be booked to the locked periods.
The locking functionality can also be based on consolidation tree nodes. If a node is locked, all of the business units under that node are locked and you cannot run ledger preparation for the locked nodes. This is also true for manual journals. You cannot post a manual journal if a node is locked
The Ledger Post and Unpost application engines check whether there are nodes that are locked. If any journal line contains a locked node, the entire journal (batch ID) is not posted. Other system-generated journal entries are allowed to post.

 Page Used to Lock Scenarios
Page Used to Lock Scenarios|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GC_LEDLOCK_DEFN |
Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Common Definitions, Lock Scenario, Scenario Locking |
Lock and unlock scenarios and nodes on the consolidation tree for specified business unit, scenario, fiscal year and period. |

 Locking Scenarios
Locking ScenariosAccess the Scenario Locking page (Global Consolidations, Define Consolidations, Common Definitions, Lock Scenario, Scenario Locking).
Specify the common consolidation business unit, scenario, fiscal year, and period when accessing the Scenario Locking page.
Lock Entire Scenario
In the Lock Entire Scenario group box, select Lock Scenario to lock the entire scenario for the specified fiscal year and period. Select Unlock Scenario to unlock a previously locked scenario. When you select either of these buttons, you will also need to enter a reason in the Reason window.
Lock Dimension Node
To lock a node, first select the node from the Consolidation Tree group box, and then, in the Lock Dimension Node group box, select either Lock Node to lock the tree node, or, if the node has already been locked, select Unlock Node. When you select either of these buttons, you will also need to enter a reason in the Reason window.
 Processing Close
Processing CloseThis section provides an overview of the close process and discusses how to run the close process (GC_CLOSMGR).

 Understanding the Closing Process
Understanding the Closing Process
Use the Close Process run control to page to close the income statement account balances to retained earnings and roll forward balance sheet account balances. In order to use this feature, you must set up closing rules and rule sets, roll forward rules and rule sets, a close process group, and associate the close process group with the consolidation model.
See Understanding Close Process Rules.
When running the close process, you either run year-end or period-end processing. Trial balance-based consolidations use year-end processing, and financial statement-based consolidations use period-end processing.
When you enter the business unit and scenario on the run control page, an edit checks the consolidation model, consolidation ledger, and the ledger template to determine whether the business unit and scenario combination is a trial balance or financial statement based consolidation.
If the consolidation method is trial balance, the period input field is display-only, and the system selects a close process type of Year End Processing. In addition, the request type options are limited to Close/Roll Forward or Delete. The Delete request type enables you to clear out the previous run data and reset the close and roll forward amounts to zero.
If the consolidation method is Financial Statement, enter the fiscal year and period in which you want to perform the close processing. If the period selected is not the last period of the fiscal year (typically, period 12), then you may only select Roll Forward Only or Delete. If the period selected is the last period, then you may select Close/Roll Forward or Delete.
The closing process does not update flow amounts. You will have to enter the closing amounts on a manual flow template.
See The Global Consolidations red papers on My Oracle Support.
Here is an overview of the steps performed for each Consolidation Dimension value/Tree Node in the Close Process group when the closing process is run:
Resolves data from the consolidation CLED, based on the Close Process group for the consolidation model, the fiscal year, and the period that you specify in the run control, and Ledger Template associated with the consolidation Model.
If processing the Close Option, the system creates a target entry in the next fiscal year/accounting period based on the ChartField value sets andxource input option specified on the close rule.
For elimination entities in Financial Statement-based ledger, only non-system-generated entries are closed.
If processing the Roll Forward Option, the system rolls forward balances in the next accounting period based on the ChartField value sets and source input option specified on the roll forward rule.
For elimination entities in Financial Statement-based ledgers, only non-system generated entries are rolled forward.
The closing process creates ledger entries with following Global Consolidations source values:
|
9A |
Closing Entry |
|
9B |
RollForward Entry |
|
9C |
Elimination Reversal — Closing Represents the reversal amounts booked to period one for elimination entity amounts closed during year-end close process. These entries are only created for the trial balance ledger format system-generated entries. Manual journal entries are not reversed. |
|
9D |
Elimination Reversal — RollForward Represents the reversal amounts booked to period one for elimination entity amounts rolled forward during the year-end close process. These entries are only created for the trial balance ledger format. Reversals are only performed for system-generated journals. Manual journal entries are not reversed. |
After the close process has run, you can review the results on the Ledger Inquiry page.
To view the amounts closed to retained earnings or balances rolled forward for trial balance-based consolidations, specify the period of zero for the next fiscal year.
For financial statement-based consolidations, select the fiscal year and period in which the balances were rolled forward.
View this inquiry after the roll forward process has been run but before the next period is processed. You can also view these entries through the consolidation audit, and filter by the source process on the roll forward processing entries.
See Reviewing Ledger Balances.
See Auditing Consolidation Data.
Closing Processing and Elimination Business Units
If you want to roll forward manual journal entries that are recorded to elimination entities, be sure that the Include Elimination Entities check box is selected for each applicable close rule set.
For trial balance-format ledgers, both system-generated and manual journal entries will be rolled forward.
The trial balance roll forward engine closes and rolls forward the entries to the elimination entity to period zero with an auto reversal in period one for system-generated entries. Manual journal entries to the elimination entity are not reversed.
For financial statement-format ledgers, only manual journal entries booked to the elimination entity are rolled forward. System-generated entries are not rolled forward.
Manual journal entries are not reversed.

 Page Used to Process Closing Rules
Page Used to Process Closing Rules|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
RUN_GC_CLOSE |
Global Consolidations, Process Consolidations, Run Other Processes, Close Processing, Close Process |
Run the closing process. |

 Running the Closing Process
Running the Closing Process
Access the Close Processing page (Global Consolidations, Process Consolidations, Run Other Processes, Close Processing, Close Process).
|
Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Period |
Specify the common consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period to process. |
|
Scenario Locking |
Click to access the Scenario Locking page, on which you can prevent journals from being posted to the selected scenario or tree node. |
|
Override Scenario's Tree Node |
Select to use a different tree node than that specified on the consolidation model. In the Tree Node field, select a tree node if you use this option. The tree node that you specify must be at a lower hierarchical level of the tree than the node specified on the consolidation model. |
|
Jobstream ID |
Accept the default value, GC_CLOSMGR, to use the delivered jobstream ID. |
|
Close Process Type |
Select the close process type. If the consolidation method is trial balance, the period input field is inactive and the system selects the close process type as Year End Processing. This field cannot be updated. If the consolidation method is financial statement based, the period input field is active and the system selects the close process type Period End Processing. This field cannot be updated. The parameter options are the same as year-end processing with two exceptions.
Note. Financial statement consolidations do not have a period zero. When selecting period end processing with a period set to the last period, the system runs the close process to period one of the next fiscal year. |
|
Close Request Type |
Select the close request type. When the request type option is Close/Roll Forward, the application engine posts the close amounts to the target account as a one-sided entry as well as posts the carry-forward balances to period zero of the next fiscal year. |
If you need to undo the year-end or period-end process, the system provides you with two options. First, if you incorrectly ran the close process and need to reset the posted amounts to zero, then set the close request type to Delete. If you want to replace the amounts that have been posted, then rerun the run control. The application engine deletes the entries from the previous run and replaces the amounts to retained earnings and roll forward balances with the current posting.
 Running Tree Flattener
Running Tree FlattenerThis section provides an overview of tree flattener and discusses how to run the Tree Flattener application engine (GC_TREEFLT).

 Understanding the Tree Flattener
Understanding the Tree FlattenerTo improve performance on the inquiry and analysis pages, run tree flattener on any trees that you use for inquiries—for example, an account tree. This process creates a database table of the tree structure, which the inquiry and analysis pages use to navigate through the tree nodes.
To use the Trial Balance page prior to processing eliminations or equitizations, you must run tree flattener on your consolidation tree. This step is not a requirement if you have already run eliminations or equitization, as the consolidation tree is automatically flattened during those processes.
See Also
Setting Up and Flattening Tree Metadata

 Page Used to Run Tree Flattener
Page Used to Run Tree Flattener|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
GC_RUN_TREE |
Global Consolidations, Request Processing, Tree Flattener |
Flatten trees. |

 Running Tree Flattener
Running Tree FlattenerAccess the Run Tree Flattener page (Global Consolidations, Request Processing, Tree Flattener).
|
Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Period |
Specify the common consolidation business unit, scenario ID, fiscal year, and accounting period to process. |
|
Jobstream ID |
Accept the default value, GC_TREEFLT, to use the delivered jobstream ID. |
|
Trees to Flatten |
Select the trees to process. |
 Reviewing Application Engine Messages
Reviewing Application Engine MessagesUse the Engine Message component to review any messages generated during a specific process instance.

 Pages Used to Review Engine Messages
Pages Used to Review Engine Messages|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
PF_ENGMSG_HEAD |
Global Consolidations, Process Consolidations, Review Messages, Message Header |
View application engine messages for a specific process instance. |
|
|
PF_ENGMSG_LOG |
Global Consolidations, Process Consolidations, Review Messages, Message Detail |
View application engine message details for a specific process instance. |
 Running Related Processes
Running Related ProcessesThere are several additional processes that you may run in the course of using PeopleSoft Global Consolidations:
Ledger Post and Ledger Unpost.
Allocations.
ETL to the Multidimensional Warehouse for Reporting.
Reconciliation.
These application engines are delivered as part of PeopleSoft EPM and are covered in detail in the PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management Fundamentals 9.1 PeopleBook.
See Setting Up the Operational Warehouse - Enriched for EPM Analytical Applications.