Use Case: Configuring a Layer 3 VRRP Router on an IPMP Interface
The following example shows the configuration of L3 VRRP router on IPMP interface. The configuration is based on the following scenario:
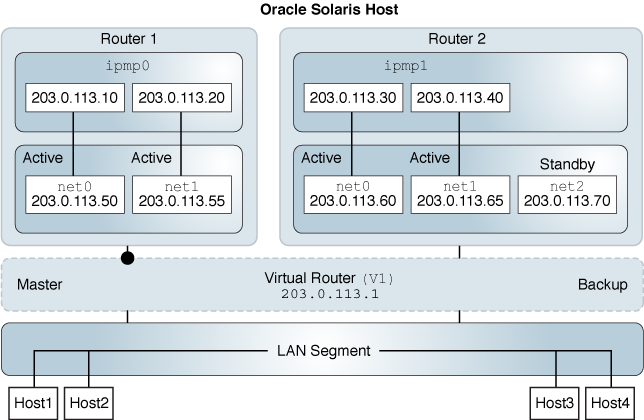
Figure 3 Layer 3 VRRP Router on an IPMP Interface
-
There is a virtual router V1.
-
In the virtual router V1, Router1 is the master router and Router2 is the backup.
-
In Router1, the underlying interfaces net0 and net1 are configured into an IPMP group and all the underlying interfaces are assigned the test addresses.
-
Master router is configured on the active-active IPMP interface, which is Router1.
-
In Router2, the underlying interfaces net0, net1, and net2 are configured into an IPMP group. The interface net2 is configured as a standby interface.
-
Backup router is configured on the active-standby IPMP interface.
On Router1:
$ pkg install vrrp Router1$ ipadm create-ipmp ipmp0 Router1$ ipadm create-ip net0 Router1$ ipadm create-ip net1 Router1$ ipadm add-ipmp -i net0 -i net1 ipmp0 Router1$ ipadm create-addr -a 203.0.113.10/24 ipmp0 ipadm: ipmp0/v4 Router1$ ipadm create-addr -a 203.0.113.20/24 ipmp0 ipadm: ipmp0/v4a Router1$ ipadm create-addr -a 203.0.113.50/24 net0 ipadm: net0/v4 Router1$ ipadm create-addr -a 203.0.113.55/24 net1 ipadm: net1/v4 Router1$ vrrpadm create-router -T L3 -V 1 -A inet -I ipmp0 -P 203.0.113.10 \ -a 203.0.113.1 -p 150 vrrp1 Router1$ vrrpadm show-router -x vrrp1 NAME VRID TYPE IFNAME AF PRIO ADV_INTV MODE STATE VNIC vrrp1 1 L3 ipmp0 IPv4 150 1000 e-pa- MASTER --
On Router2:
Router2$ ipadm create-ipmp ipmp1 Router2$ ipadm create-ip net0 Router2$ ipadm create-ip net1 Router2$ ipadm create-ip net2 Router2$ ipadm add-ipmp -i net0 -i net1 -i net2 ipmp1 Router2$ ipadm create-addr -a 203.0.113.30/24 ipmp1 ipadm: ipmp1/v4 Router2$ ipadm create-addr -a 203.0.113.40/24 ipmp1 ipadm: ipmp1/v4a Router2$ ipadm create-addr -a 203.0.113.60/24 net0 ipadm: net0/v4 Router2$ ipadm create-addr -a 203.0.113.65/24 net1 ipadm: net1/v4 Router2$ ipadm create-addr -a 203.0.113.70/24 net2 ipadm: net2/v4 Router2$ ipadm set-ifprop -p standby=on net2 Router2$ vrrpadm create-router -T L3 -V 1 -A inet -I ipmp1 -P 203.0.113.30 \ -a 203.0.113.1 -p 100 vrrp2 Router2$ vrrpadm show-router -x NAME VRID TYPE IFNAME AF PRIO ADV_INTV MODE STATE VNIC vrrp2 1 L3 ipmp1 IPv4 100 1000 e-pa- BACKUP --
The following commands show you how specifying a higher priority number can promote a router to become the master router. The priority of vrrp2 is raised to 200, which is over vrrp1's priority of 150.
Router2$ vrrpadm disable-router vrrp2 Router2$ vrrpadm modify-router -p 200 vrrp2 Router2$ vrrpadm enable-router vrrp2 Router2$ vrrpadm show-router -x vrrp1 NAME VRID TYPE IFNAME AF PRIO ADV_INTV MODE STATE VNIC vrrp1 1 L3 ipmp0 IPv4 150 1000 e-pa- BACKUP -- Router2$ vrrpadm show-router -x vrrp2 NAME VRID TYPE IFNAME AF PRIO ADV_INTV MODE STATE VNIC vrrp2 1 L3 ipmp1 IPv4 200 1000 e-pa- MASTER --