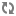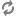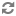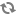A DispatchLogger is a LogListener that routes LogEvents to other LogListeners based on the types of those LogEvents. For example, you might wish to send ErrorLogEvents to an EmailLogger, while all other log event types are sent to a file.
A DispatchLogger is configured with the following properties:
logEvents
The class names of the different types of log events to be dispatched to various listeners. For example, to dispatch ErrorLogEvents and WarningLogEvents to different listeners, specify:
logEvents=\ atg.nucleus.logging.ErrorLogEvent,\ atg.nucleus.logging.WarningLogEvent
The next property, logDestinations, specifies where those two types of events are to be sent.
logDestinations
The names of the LogListeners that receive the log event types specified by the logEvents properties. For example:
logDestinations=\ SysadminPager,\ SysadminEmailer
This specifies that ErrorLogEvents are to be sent to the SysadminPager component, while WarningLogEvents are to be sent to the SysadminEmailer component. The LogEvent is sent to the first destination matching the given class, as either an exact class match, or a subclass. So any ErrorLogEvent or subclass of ErrorLogEvent is sent to SysadminPager.
defaultDestinations
The destinations of any log events that do not match any of the types in logEvents. For example:
defaultDestinations=\ FileLogger
This specifies that any LogEvents that are not errors or warnings are sent to the FileLogger component. You can specify multiple destinations; in that case, the event is sent to all specified destinations in order. If you do not specify the logEvents or logDestinations properties, events are always be distributed to the defaultDestinations. This is a useful way for you to send a single LogEvent to multiple destinations—for example, e-mail and a file.
However, unlike the defaultDestinations property, the logDestinations property cannot be used to send one type of LogEvent to two different destinations. If you set these properties:
logEvents=\ InfoLogEvent,\ InfoLogEvent logDestinations=\ /logging/infoListener1,\ /logging/infoListener2
then no InfoLogEvents reach infoListener2; all are sent to infoListener1. You can send a single LogEvent to multiple destinations either by using the defaultDestinations property, or by using two DispatchLoggers in sequence. The first DispatchLogger might have these properties:
logEvents=\ InfoLogEvent,\ FooLogEvent logDestinations=\ /logging/infoDispatchLogger2,\ /logging/fooListener
while the second, the /logging/infoDispatchLogger2 named in the logDestinations property, receives only InfoLogEvents and can use the defaultDestinations property to route the InfoLogEvents to both /logging/infoListener1 and /logging/infoListener2:
defaultDestinations=\ /logging/infoListener1,\ /logging/infoListener2