Dedicated Domains
Dedicated domains have dedicated CPU and memory resources for each domain, and one or more dedicated InfiniBand host channel adapters (HCAs), 10 GbE NICs, and optionally fibre channel HBAs. Because the key CPU, memory, and I/O resources are not shared, these domains are referred to as dedicated domains.
Two types of dedicated domains are available to run workloads:
-
Application Domains – Run the Oracle Solaris 11 OS. and any applications that are supported on Oracle’s SPARC/Oracle Solaris platforms. You can have Oracle Solaris 10 branded zones installed in Oracle Solaris 11 domains..
-
Database Domains – Run the Oracle Database software, and directly leverage the Oracle Exadata Storage Servers. A Database Domain can also include Database zones.
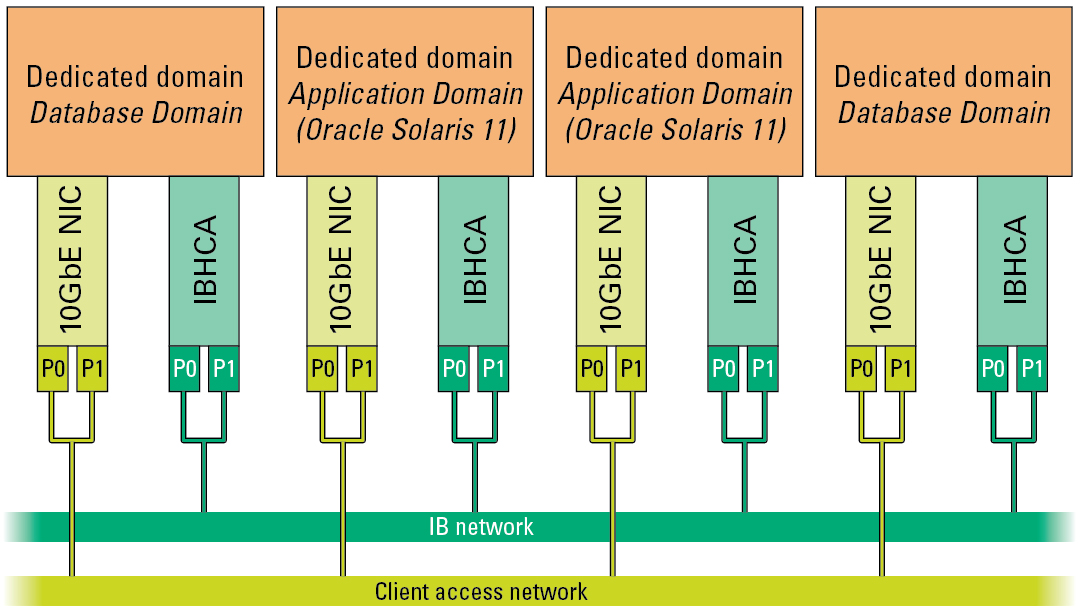
Each domain has access to the 10GbE NICs and IB HCAs, with connections to those networks occurring in the following manner:
-
To the 10GbE client access network through the physical ports on each 10GbE NIC
-
To the IB network through the physical ports on each IB HCA
This diagram shows this concept on a SuperCluster with four domains.
In addition, the first domain (the control domain) in each PDomain has direct access to the management network through the physical port on 1GbE NICs, and the other domains in each PDomain connect to the management network through VNETs. See Understanding PDomain PCIe Card Configurations and SuperCluster Networks Overview.
For dedicated domains, the domain configuration (the number of domains and the SuperCluster-specific types assigned to each) are set at the time of the initial installation, and can only be changed by an Oracle representative.