SuperCluster Networks Overview
Before deploying SuperCluster in your environment, review the networking information in this section, and ensure that your site provides the minimum network requirements listed in Network Connectivity Requirements.
Networking Interfaces
SuperCluster M8 and SuperCluster M7 include compute servers, storage servers, and the ZFS storage appliance, as well as equipment to connect the compute servers to your network. The network connections enable the servers to be administered remotely and enable clients to connect to the compute servers.
Each compute server consists of the following network components and interfaces:
-
Several 10GbE NICs for connection to the 10GbE client access network:
-
SuperCluster M8 – Oracle Quad Port 10GbE NIC (the Oracle Quad 10 Gb or Dual 40 Gb Ethernet Adapter is used in the 2x2x10GbE mode, where each port is split into two physical functions that operate at 10Gbps.)
-
SuperCluster M7 – Sun Dual Port 10GbE SFP+ NIC
-
-
Four 1GbE ports (NET 0, NET 1, NET 2, and NET 3) provided by 1GbE NICs for connections to the host management network
-
One Ethernet port (NET MGT) for Oracle ILOM remote management
-
Several dual-ported IB HCAs for connection to the IB private network
Each storage server consists of the following network components and interfaces:
-
One embedded Gigabit Ethernet port (NET 0) for connection to the host management network
-
One dual-ported Sun QDR IB PCIe Low Profile HCA for connection to the IB private network
-
One Ethernet port (NET MGT) for Oracle ILOM remote management
Each storage controller consists of the following network components and interfaces:
-
One embedded Gigabit Ethernet port for connection to the host management network:
-
NET 0 on the first storage controller (installed in slot 25 in the rack)
-
NET 1 on the second storage controller (installed in slot 26 in the rack)
-
-
One dual-port QDR IB HCA for connection to the IB private network
-
One Ethernet port (NET 0) for Oracle ILOM remote management using sideband management. The dedicate Oracle ILOM port is not used due to sideband.
The Ethernet management switch supplied with SuperCluster M8 and SuperCluster M7 is minimally configured during installation. The minimal configuration disables IP routing, and sets these parameters:
-
Host name
-
IP address
-
Subnet mask
-
Default gateway
-
Domain name
-
Domain Name Server
-
NTP server
-
Time
-
Time zone
Additional configuration, such as defining multiple virtual local area networks (VLANs) or enabling routing, might be required for the switch to operate properly in your environment and is beyond the scope of the installation service. If additional configuration is needed, your network administrator must perform the necessary configuration steps during installation of SuperCluster.
There are three networks for SuperCluster. Each network must be on a distinct and separate subnet from the others.
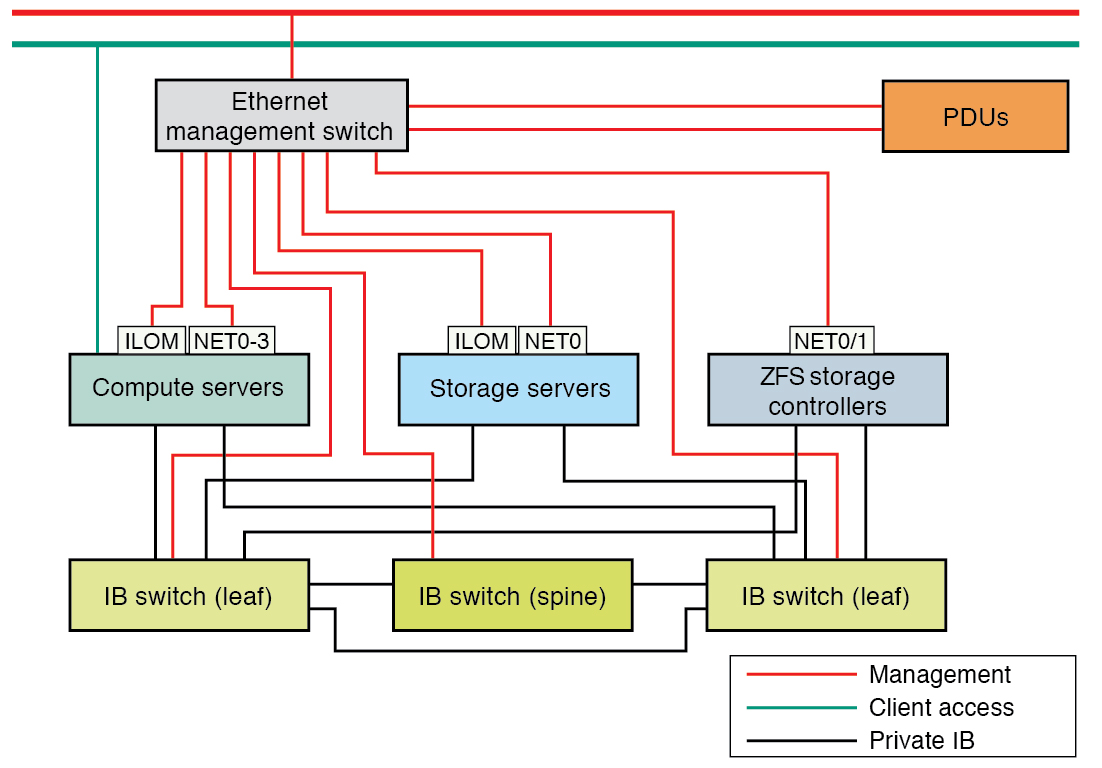
The network descriptions are as follows:
-
Client access network — This required 10GbE network connects the compute servers to your existing client network and is used for client access to the servers. Database applications access the database through this network using Single Client Access Name (SCAN) and Oracle RAC Virtual IP (VIP) addresses.
-
Management network — This required network connects to your existing management network, and is used for administrative work for all SuperCluster components. This network connects the servers and IB switches to the Ethernet switch. There is one uplink from the Ethernet management switch to your existing management network.
Note - Management network connectivity to the PDUs is optional, and only needed if the PDU power will be monitored remotely.Each compute server and storage server use two network interfaces for management. One provides management access to the operating system through the 1GbE host management interfaces, and the other provides access to the Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager through the NET MGT Ethernet interfaces.
The method used to connect the storage controllers to the management network varies depending on the controller:
-
Storage controller 1 — NET 0 is used to provide access to the Oracle ILOM network using sideband management, as well as access to the 1GbE host management network.
-
Storage controller 2 — NET 0 is used to provide access to the Oracle ILOM network using sideband management, and NET1 is used to provide access to the 1GbE host management network.
The 1GbE host management interfaces on the compute servers should not be used for client or application network traffic. Cabling or configuration changes to these interfaces is not permitted.
-
-
IB private network — This network connects the compute servers, ZFS storage appliance, and storage servers using the IB switches. This nonroutable network is fully contained in SuperCluster, and does not connect to your existing network. This network is automatically configured during installation.
For systems with Database Domains, Oracle Database uses this network for Oracle RAC cluster interconnect traffic and for accessing data on storage servers and the ZFS storage appliance.
For systems with Application Domains, Oracle Solaris Cluster uses this network for cluster interconnect traffic and to access data on the ZFS storage appliance.
Note - All networks must be on distinct and separate subnets from each other.
Supported IPMP Network Features
SuperCluster network interfaces use link-based IP network multipathing (IPMP) for the IB switches, the 10GbE Client Access network, and the GbE management network. Datalink multipathing (DLMP) and probe-based IPMP (including transitive IPMP) are not supported.
IPMP ports are always configured active-standby, with the exception of IB HCA ports in the global zone of Database Dedicated Domains, where ports are configured active-active for the database pkey 0xFFFF partition (and therefore consume two IP addresses per HCA rather than one). All other IB ports are configured active-standby, including for non-global Database Zones in Database Dedicated Domains, and for both global zones and non-global zones in Database I/O domains.
VLAN tagging and trunking are supported on SuperCluster both in domains and zones.
Aggregation (LACP) is supported in Dedicated Domains (some manual configuration is required), but it is not supported in I/O Domains.