29 Work with Repetitive Manufacturing
This chapter contains these topics:
29.1 Working with Repetitive Manufacturing
Use repetitive manufacturing for highly repetitive production that relies on a production "rate." Repetitive manufacturing enables you to specify a rate schedule by effective date in daily, weekly, or monthly quantities.
Repetitive manufacturing reflects the following characteristics:
-
Production volume is stable and predictable.
-
Lead time is short.
-
Factory layout is product oriented and often characterized as cellular manufacturing: Dissimilar operations are physically grouped so that the product flows rapidly from one operation to the next.
-
Setups are short, so that switching between products does not impact the time available for production.
-
Group technology is often incorporated into the design engineering and manufacturing engineering to accommodate some variety with low impact on cost or production speed.
-
Unit of measure is often "each." However, it can also be volume- or weight-related when it is used in an environment that is similar to process manufacturing as opposed to discrete.
Some examples of repetitive products are:
-
Electronic goods
-
Automobiles
-
Durable consumer goods (washing machines, refrigerators, and so on)
To plan for repetitive items, you:
-
Identify the item as a rate scheduled item for a specific branch/plant
-
Create a routing for the item
-
Attach the rate scheduled item to a line
After you process the repetitive items, generate a master schedule and output that you can review. This output consists of time series and messages. You can then validate the load on lines or cells by viewing the effects of a rate schedule on a given work center and adjusting the priorities of the schedule.
Working with repetitive manufacturing consists of the following tasks:
-
Defining Order Policy for Repetitive Items
-
Creating Repetitive Routings
-
Creating Line/Item Relationships
-
Creating Rate Schedules
-
Generating MPS for Repetitive Items
-
Reviewing Repetitive Rate Scheduled Output from MPS Generation
-
Validating Load on Lines or Cells
29.2 Defining Order Policy for Repetitive Items
From Inventory Management (G41), choose Inventory Master/Transactions
From Inventory Master/Transactions (G4111), choose Item Branch/Plant Information
You must identify the item as a repetitive item for a specific branch/plant for the MPS/MRP/DRP system to process the item as repetitive.
To define order policy for repetitive items
On Item Branch/Plant Information
Figure 29-1 Item Branch/Plant Information screen
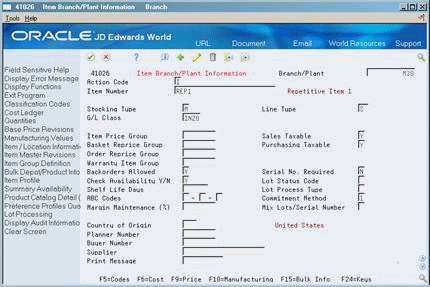
Description of ''Figure 29-1 Item Branch/Plant Information screen''
-
To locate the item record, complete the following fields:
-
Branch/Plant
-
Item Number
-
-
Choose Manufacturing Values (F10).
Figure 29-2 Plant Manufacturing Data screen
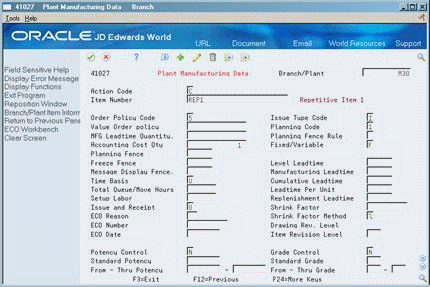
Description of ''Figure 29-2 Plant Manufacturing Data screen''
-
On Plant Manufacturing Data, identify the item as a rate scheduled item in the following field:
-
Order Policy Code
-
29.3 Creating Repetitive Routings
From Product Data Management (G30), choose Daily PDM Discrete
From Daily PDM Discrete (G3011), choose Enter/Change Routing
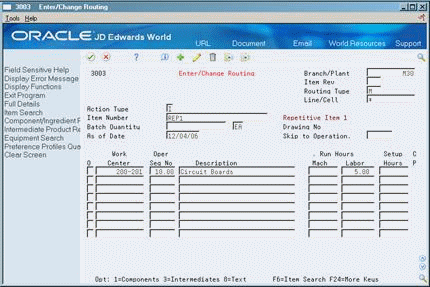
A routing is a list of the operations and resources that are required to complete a process. The repetitive routing includes line and cell information in the header as well for each operation.
On Enter/Change Routing
-
To locate the routing for your item, complete the following fields:
-
Branch/Plant
-
Line/Cell
-
Item Number
-
-
Access the detail area (F4).
Figure 29-4 Enter/Change Routing (Detail) screen
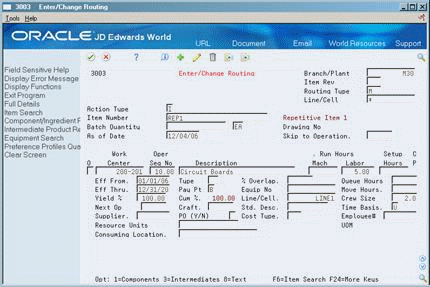
Description of ''Figure 29-4 Enter/Change Routing (Detail) screen''
-
Review the information for each operation sequence:
-
Line/Cell
-
Resource Units Consumed
-
Replenishment Location
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Line/Cell | Defines a production line or cell. Detailed work center operations can be defined inside the line or cell. For rate based manufacturing to use this value for reporting, this value must match the line cell in the header. |
| Resource Units Consumed | Indicates how many of the line's resource units are needed to produce one item. |
| Replenishment Location | A code that identifies inventory locations in a branch/plant. You define the format of the location identifier by branch/plant. |
29.4 Creating Line/Item Relationships
From Shop Floor Control (G31), choose Shop Floor Control Setup
From Shop Floor Control Setup (G3141), choose Line/Item Relationships
To define the schedule data for the rate, choose Line/Item Relationships. Line/Item Relationships defines on which production line the product will be assembled. It also defines shift and period information for that line.
To create a line/item relationship
On Line/Item Relationships
Figure 29-5 Line/Item Relationships screen
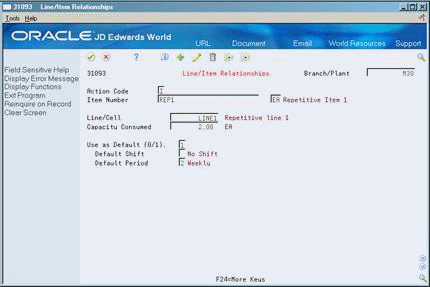
Description of ''Figure 29-5 Line/Item Relationships screen''
Complete the following fields:
-
Branch/Plant
-
Item Number
-
Line/Cell
-
Capacity Units
-
Shift
-
Period
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Capacity Units | Indicates how many of the line's resource units are needed to produce one item. |
| Shift | A user defined code (07/SH) that identifies daily work shifts. In payroll systems, you can use a shift code to add a percent or amount to the hourly rate on a timecard.
For payroll and time entry: If an employee always works a shift for which a shift rate differential is applicable, enter that shift code on the employee's master record. When you enter the shift on the employee's master record, you do not need to enter the code on the timecard when you enter time. If an employee occasionally works a different shift, you enter the shift code on each applicable timecard to override the default. |
| Period | A code that determines the frequency of the schedule. Valid codes are:
1 – Monthly 2 – Weekly 3 – Daily 4 – Per Shift |
29.5 Creating Rate Schedules
From Shop Floor Control (G31), choose Repetitive
From Repetitive Daily Processing (G3141), choose Enter/Change Rate Schedule
A rate schedule is a request to produce a certain quantity of items on a specified periodic basis for a given length of time. Rate schedules eliminate the need to create multiple work orders for items you want to produce monthly, weekly, or daily in regular quantities. You generally use rate schedules in repetitive manufacturing.
To create a rate schedule, you:
-
Specify engineering information, such as schedule types and effective dates.
-
Specify production information, such as the item and quantities on which the rate is based.
You can use processing options to define a default schedule type, schedule period, and spread value. You can also choose to display only active schedules. In addition, you can access associated screens by indicating the version of these screens in the processing options. You can use these screens to view and modify information for routing, work center, MPS/MRP/DRP time series, rate generation, and scheduling.
29.5.1 Before You Begin
-
Set up your line/item relationships. See Section 29.4, "Creating Line/Item Relationships."
On Enter/Change Rate Schedule
Figure 29-6 Enter/Change Rate Schedule screen
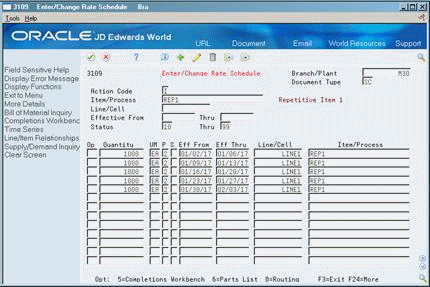
Description of ''Figure 29-6 Enter/Change Rate Schedule screen''
-
Complete the following fields:
-
Branch/Plant
-
Schedule Type
-
Item Number
-
Line/Cell
-
Effective From
-
Effective To
-
Quantity
-
Unit of Measure
-
-
Access the detail area (F4).
Figure 29-7 Enter/Change Rate Schedule (Detail) screen
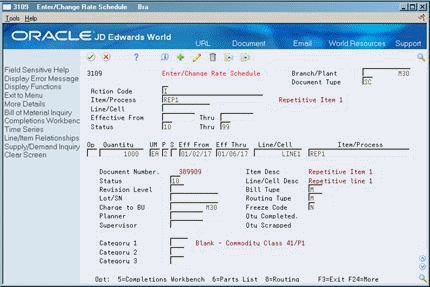
Description of ''Figure 29-7 Enter/Change Rate Schedule (Detail) screen''
-
Review the following default information:
-
Period
-
Shift
-
Category 1
-
Category 2
-
Category 3
-
Quantity Completed
-
Quantity Scrapped
-
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Schedule Type | A user defined code (system 31, type ST) that identifies the type of schedule, for example, AC for actual schedule and PL for planned schedule. |
| Quantity | The quantity of units affected by this transaction. |
| Category 1 | A user defined code (00/W1) that indicates the current stage or phase of development for a work order. You can assign a work order to only one phase code at a time.
Note: Certain screens contain a processing option that allows you to enter a default value for this field. If you enter a default value on a screen for which you have set this processing option, the system displays the value in the appropriate fields on any work orders that you create. The system also displays the value on the Project Setup screen. You can either accept or override the default value. |
| Category 2 | User defined code system 00, type W2, which indicates the type or category of a work order.
Note: A processing option for some screens lets you enter a default value for this field. The value then displays automatically in the appropriate fields on any work orders you create on those screens and on the Project Setup screen. (You can either accept or override the default value.) |
| Category 3 | User defined code system 00, type W3, which indicates the type or category of a work order.
Note: A processing option for some screens lets you enter a default value for this field. The value then displays automatically in the appropriate fields on any work orders you create on those screens and on the Project Setup screen. (You can either accept or override the default value.) |
| Qty Scrapped | The number of units canceled in Sales Order or Work Order Processing, using either the entered or the primary unit of measure defined for this item.
In manufacturing, this can also be the number of units scrapped to date. |
| Qty Completed | The number of units committed for shipment in Sales Order Entry, using either the entered or the primary unit of measure defined for this item.
In the Manufacturing system and Work Order Time Entry, this field can indicate completed or scrapped quantities. The quantity type is determined by the type code entered. |
29.5.2 What You Should Know About
29.6 Generating MPS for Repetitive Items
From Material Planning Operations (G34), choose Single Site Planning
From Single Site Periodic Planning Operations (G3422), choose MPS Regeneration
When you run the MPS Net Change or Regeneration program, the system:
-
Evaluates selected information
-
Performs calculations
-
Generates a time series and messages for the selected items
29.6.1 What You Should Know About
|
See Also:
|
29.7 Reviewing Repetitive Rate Scheduled Output from MPS Generation
From Material Planning Operations (G34), choose MPS
From MPS Daily Operations (G3412), choose MPS Time Series Inquiry or MPS Detail Message Review
After you generate a master production schedule, use MPS Time Series Inquiry and MPS Detail Message Review to review the time series and messages that the system has generated.
The time series is a record of time-phased supply and demand netting for selected items. The system links the planned order releases for the parent item to the gross requirements of component items.
If a component does not have its own rate schedule, the system applies the demand from the parent item. The demand from the rate scheduled parent follows the same logic as regular work orders. When a rate schedule is added for a component of a rate based parent, the calculation includes the information for the component in both the rate schedule (+RS) and unadjusted rate schedule (-RS) lines of data. The component is processed as supply, and regular MRP logic applies.
The messages reflect how the system used rate scheduled items to generate quantities for net requirements for each time period. The MPS/MRP program produces three main action messages that pertain to repetitive items:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| I = Increase rate to | Updates an existing rate to the increased quantity. |
| H = Decrease rate to | Updates an existing rate to the decreased quantity. |
| N = Create rate | Treats messages as a group from the MPS/MRP Detail Message Review screen. You may answer more than one message at a time. The system creates one rate that averages the total of all Create Rate messages processed. |
When the system processes messages to create and update rates, it does not check the validity of the dates received. The MPS/MRP regeneration produces messages with valid dates. However, you can change these dates before processing the message. To avoid creating invalid rates, ensure the validity of the dates you enter whenever you change message dates before processing.
Reviewing repetitive rate scheduled output consists of the following tasks:
-
Reviewing the time series for rate scheduled output
-
Reviewing action messages for rate scheduled output
To review the time series for rate scheduled output
Figure 29-8 MPS Time Series Inquiry screen
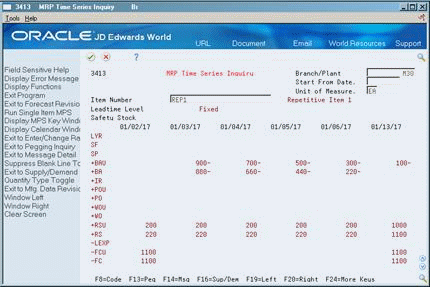
Description of ''Figure 29-8 MPS Time Series Inquiry screen''
To locate the time series for your item, complete the following fields:
-
Branch/Plant
-
Item Number
29.7.1 What You Should Know About
To review action messages for rate scheduled output
Figure 29-9 MPS Detail Message Review screen
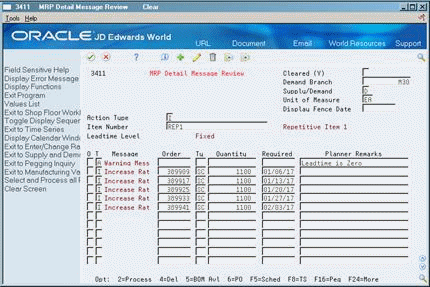
Description of ''Figure 29-9 MPS Detail Message Review screen''
-
To locate the messages for your item, complete the following fields:
-
Demand Branch
-
Item Number
-
-
To view additional message information, access the detail area (F4).
Figure 29-10 MRP Detail Message Review (Detail) screen
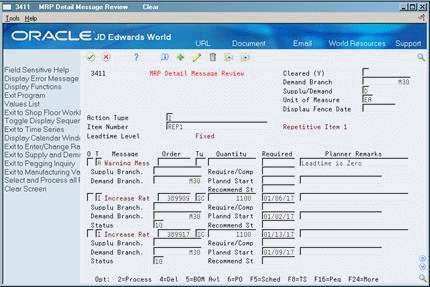
Description of ''Figure 29-10 MRP Detail Message Review (Detail) screen''
29.7.2 What You Should Know About
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Creating Rates | Instead of creating a single rate for a given schedule period type over a date range, the system creates a series of rates to cover the entire period. For instance, instead of having one weekly rate in effect for four weeks, the system creates four weekly rates, each in effect for a week.
When you process a Create Rate message, the system can attach the parts list and routing automatically. |
29.8 Validating Load on Lines or Cells
From Shop Floor Control (G31), choose Repetitive
From Repetitive Daily Processing (G3115), choose Schedule Review
Use Schedule Review to validate the load on lines or cells. You can view the effects of a rate schedule on a given work center and adjust the priorities of the schedule.
You can also:
-
View rate schedule load for:
-
A specific work center by day, week, or month
-
A specific date range
-
-
Revise rate schedules
-
Revise resource units
-
Review rate based load only, or rate based load and work order load together
To validate load on lines or cells
On Schedule Review
Figure 29-11 Line Schedule Review screen
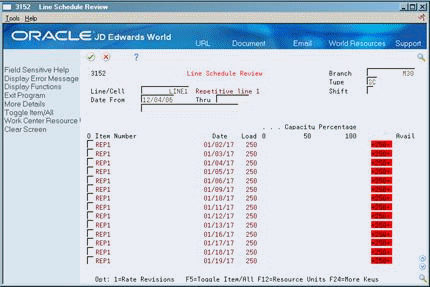
Description of ''Figure 29-11 Line Schedule Review screen''
To locate the schedule, complete the following fields:
-
Branch/Plant
-
Line/Cell or Work Center
-
Effective From
-
Effective To
29.8.1 Processing Options
See Section 55.3, "Schedule Review (P3152)."
|
See Also:
|